Multivariate Urban Air Quality Assessment of Indoor and Outdoor Environments at Chennai Metropolis in South India
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
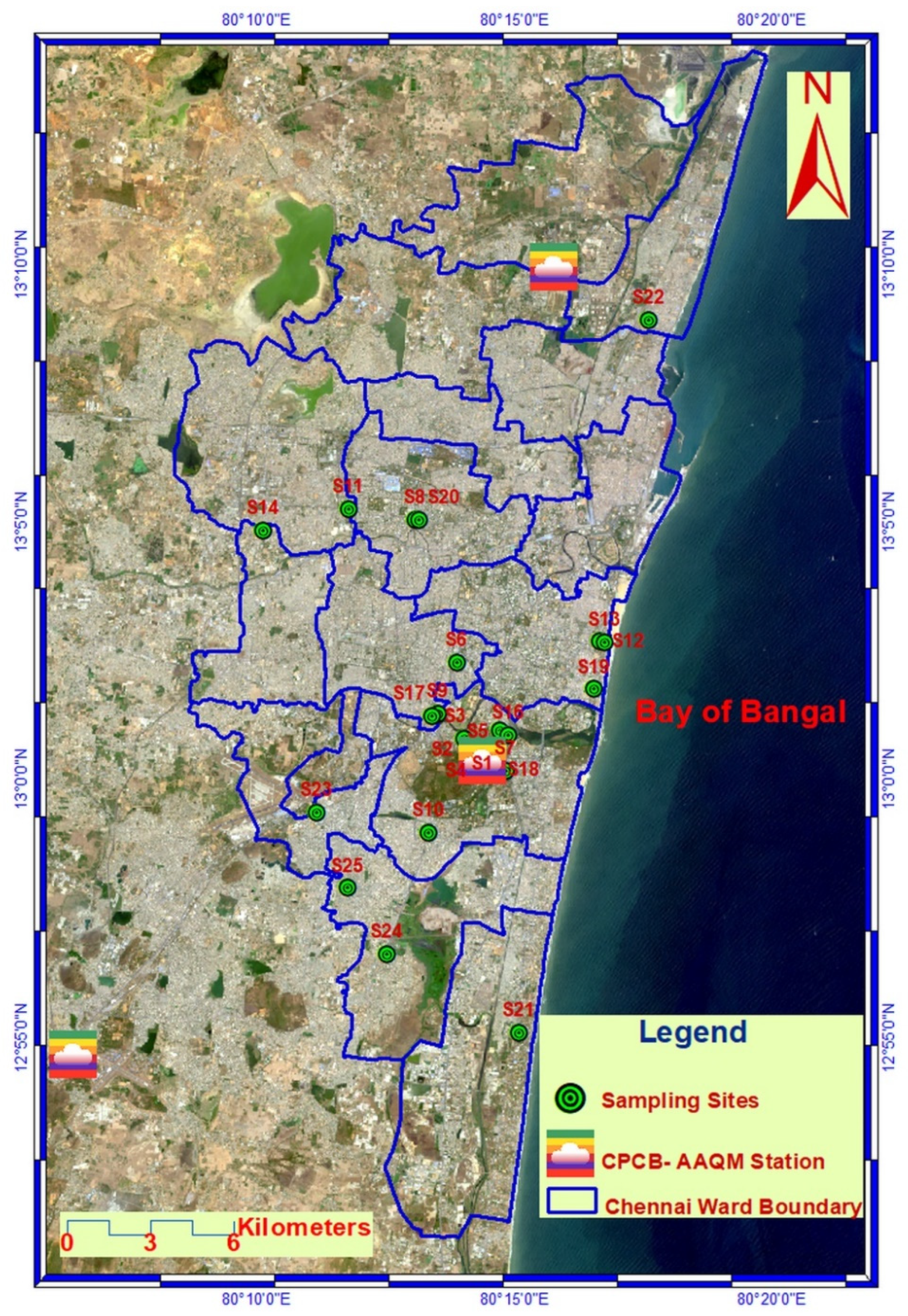
2.1. Location of the Study Area
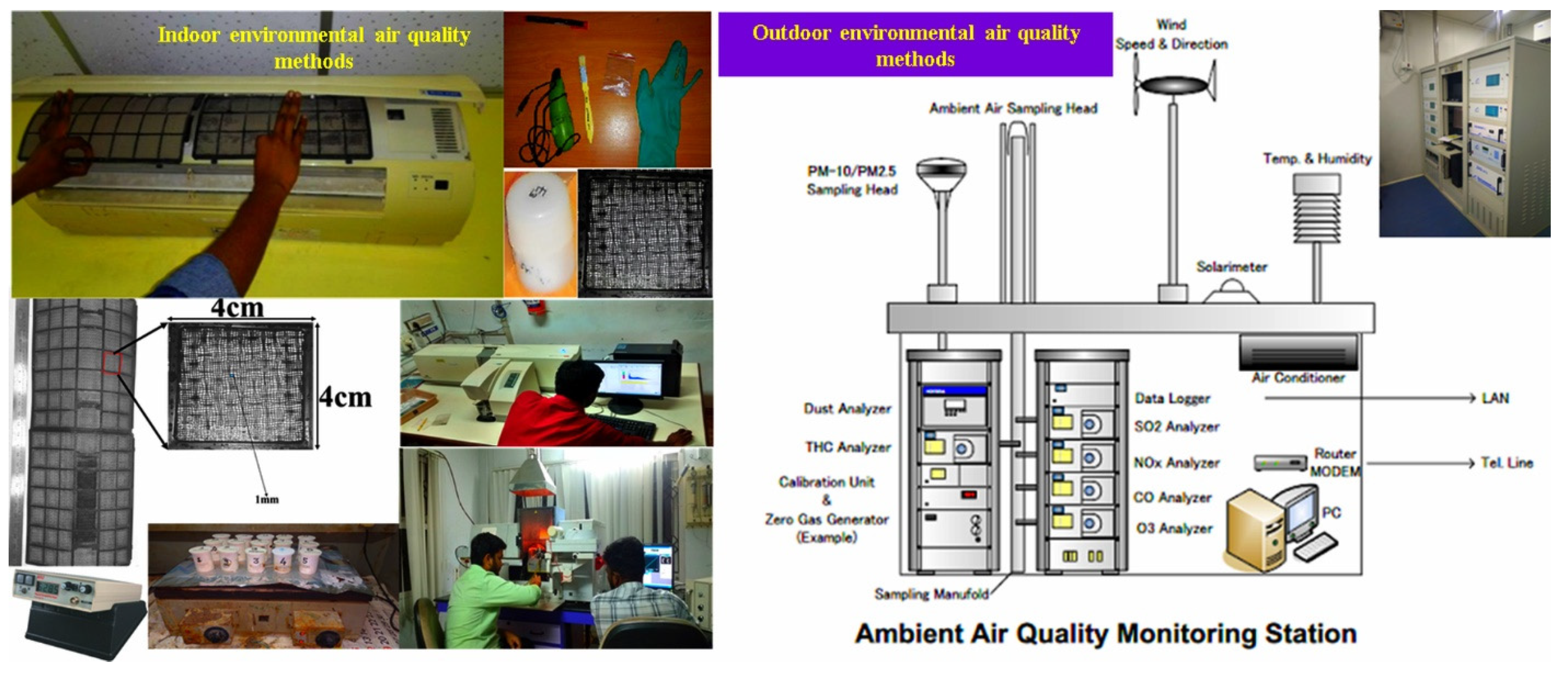
2.2. Sampling and Laboratory Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
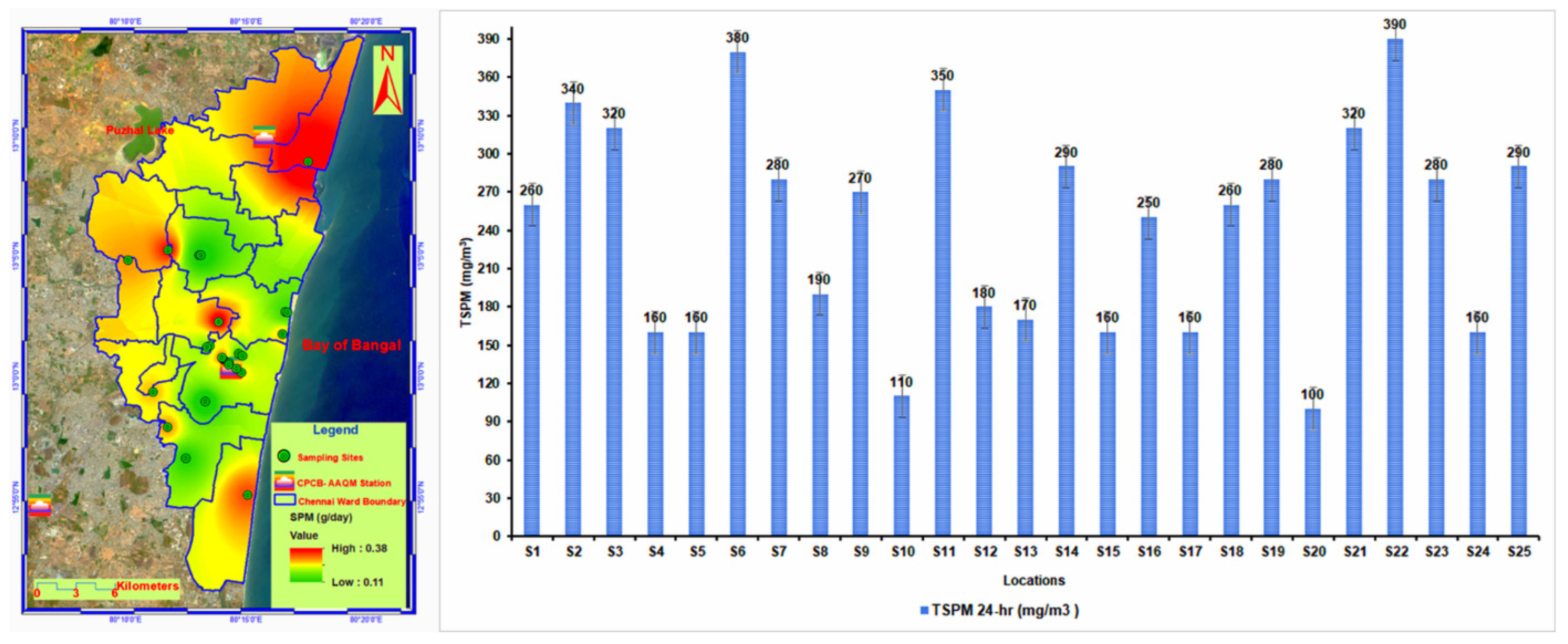
3.1. Indoor Environmental Suspended Particulate Matter (SPM) Characterization
3.1.1. Particle Size of the Atmospheric Particulate in Indoor Environments
3.1.2. Environmental Magnetism of Indoor AC Filter Particulate
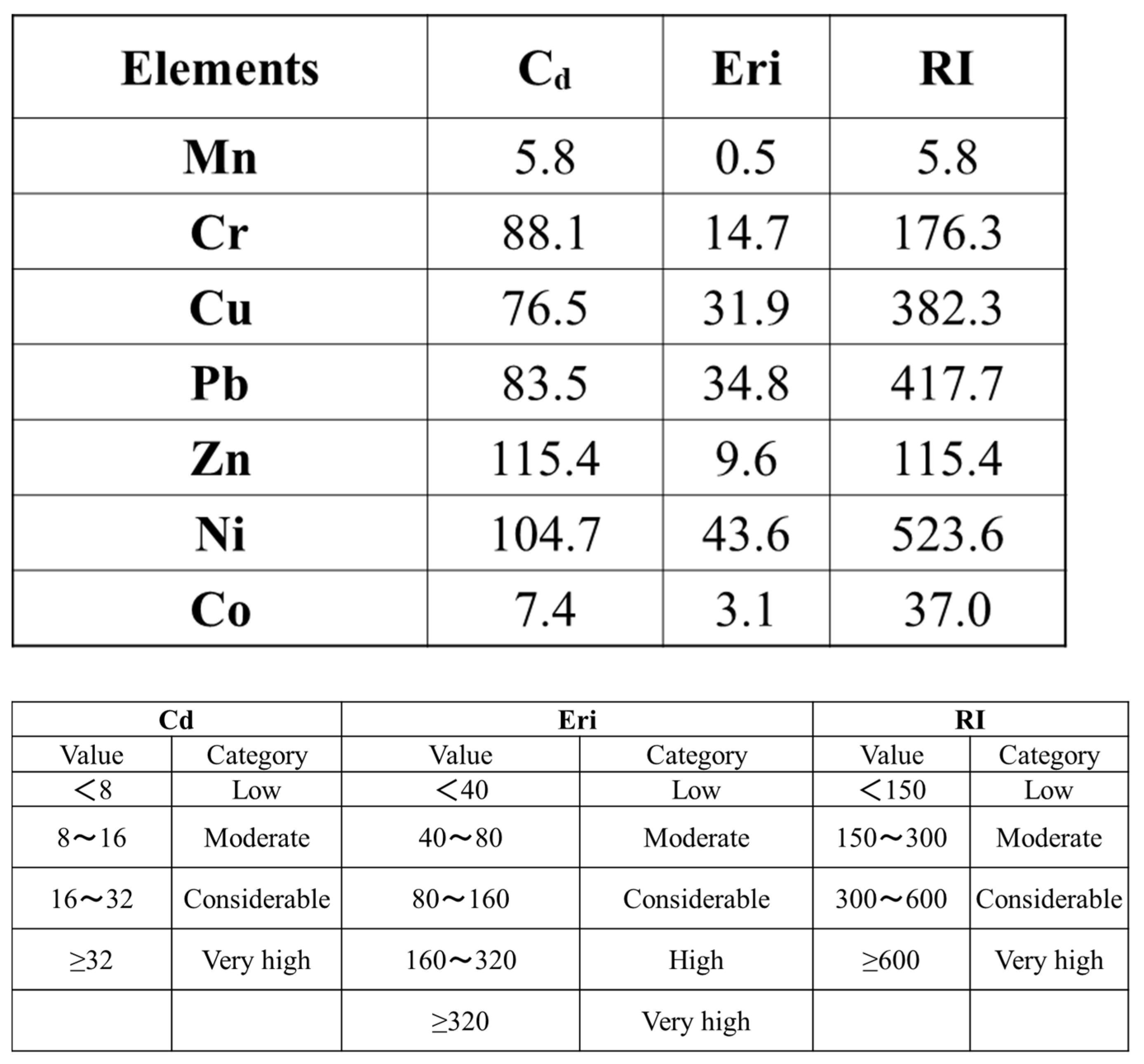
3.1.3. Chemical Composition and Pollution Indices of the Air Conditioner Filter Particulate
3.1.4. Air Quality Index of Indoor Particulate of SPM
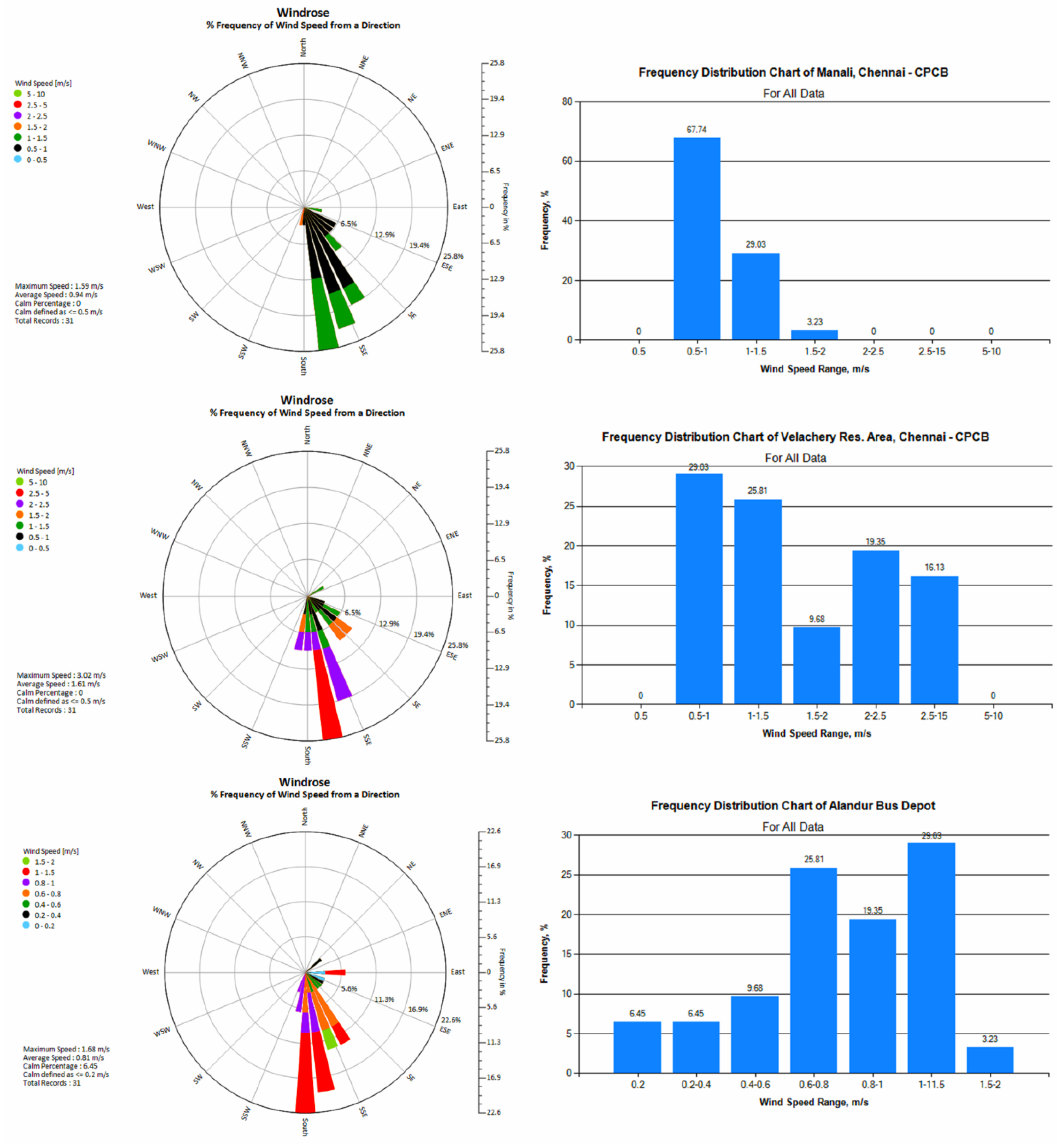
3.2. Outdoor Environmental Air Quality
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balamadeswaran, P.; Karthik, J.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Manikanda Bharath, K. Impact of COVID-19 outbreak on tropospheric NO2 pollution assessed using Satellite-ground perspectives observations in India. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 1645–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, S.; Singh, G. Pollution evaluation, human health effect and tracing source of trace elements on road dust of Dhanbad, a highly polluted industrial coal belt of India. Env. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 2081–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwela, D.H.; Haq, G. Strengths and Weaknesses of the WHO Urban Air Pollutant Database. Aerosol. Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 1026–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Lu, S.; Zhao, H.; Kai, X.; Jiaxian, P.; Win, M.S.; Yu, S.; Yonemochi, S.; Wang, Q. Magnetic, geochemical characterization and health risk assessment of road dust in Xuanwei and Fuyuan, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 1541–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichu, B.C.; Opara, A.I.; Ejike, E.N.; Nkwoada, A.U.; Ibe, F.C.; Dioha, E.C. Multivariate analysis and spatial distribution of suspended particulate metals of Abakaliki and Enugu in Southeastern Nigeria. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2021, 45, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharath, K.M.; Narasimhan, C.L.; Srinivasalu, S.; Arumugam, K.; Venkateshwarlu, M. Potentially toxic element (PTEs) related health risk assessment from air conditioner filter dust in and around Chennai metropolitan. IJMS 2020, 49, 1078–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Gaude, G.S.; Hattiholi, J.; Chaudhury, A. Role of health education and self-action plan in improving the drug compliance in bronchial asthma. J. Family Med. Prim. Care 2014, 3, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, K.; Good, N.; Wilson, A.; Mölter, A.; Moore, B.F.; Carpenter, T.; Peel, J.L.; Volckens, J. The Fort Collins commuter study: Variability in personal exposure to air pollutants by microenvironment. Indoor Air 2019, 29, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, T.; Karanasiou, A.; Amato, F.; Lucarelli, F.; Nava, S.; Calzolai, G.; Chiari, M.; Coz, E.; Artíñano, B.; Lumbreras, J.; et al. Daily and hourly sourcing of metallic and mineral dust in urban air contaminated by traffic and coal-burning emissions. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 68, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppasamy, M.B.; Seshachalam, S.; Natesan, U.; Ayyamperumal, R.; Karuppannan, S.; Gopalakrishnan, G.; Nazir, N. Air pollution improvement and mortality rate during COVID-19 pandemic in India: Global intersectional study. Air Qual. Atmosphere Health 2020, 13, 1375–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfouz, M.M.; Yigiterhan, O.; Elnaiem, A.E.; Hassan, H.M.; Alfoldy, B. Elemental compositions of particulate matter retained on air condition unit’s filters at Greater Doha, Qatar. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 2533–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Yan, T.; Birch, G.; Zhu, Y. Pollution and health risk of potentially toxic metals in urban road dust in Nanjing, a mega-city of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 36, 476–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.K.M. Metal concentrations and distribution in the household, stairs and entryway dust of some Egyptian homes. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 54, 207–215. Available online: http://www.afdevinfo.com/htmlreports/lor/lor_ni_10_15.html (accessed on 28 August 2022).
- Massey, D.D.; Habil, M.; Taneja, A. Particles in different indoor microenvironments-its implications on occupants. Build. Environ. 2016, 106, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, D.; Verma, P.K.; Kumari, K.M.; Lakhani, A. Chemical fractionation of heavy metals in fine particulate matter and their health risk assessment through inhalation exposure pathway. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 41, 1445–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzola, L.C.; Muttoni, G.; Merlini, M.; Rotiroti, N.; Pagliardini, L.; Hirt, A.; Pelfini, M. Investigating distribution patterns of airborne magnetic grains trapped in tree barks in Milan, Italy: Insights for pollution mitigation strategies. Geophys. J. Int. 2017, 210, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bourliva, A.; Papadopoulou, L.; Aidona, E. Study of road dust magnetic phases as the main carrier of potentially harmful trace elements. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 553, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spassov, S.; Egli, R.; Heller, F.; Nourgaliev, D.; Hannam, J. Magnetic quantification of urban pollution sources in atmospheric particulate matter. Geophys. J. Int. 2004, 159, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, G.; Shen, M.; Hu, R.; Liu, Y. Source identification of heavy metals and stable carbon isotope in indoor dust from different functional areas in Hefei, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 710, 135599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Dong, C.; Hutchinson, S.M.; Ge, C.; Wang, F.; Feng, H. Recent Applications of Mineral Magnetic Methods in Sediment Pollution Studies: A Review. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2018, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, A.S.; A Mendonça, C.; A Moraes, P.L.; Ustra, A.T. A procedure for quantitative characterization of superparamagnetic minerals in environmental magnetism. Geophys. J. Int. 2018, 215, 1974–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Ambient Air Quality Standards. Central Pollution Control Board Notification. 2009. Available online: http://www.cpcb.nic.in/upload/Latest/Latest_48_FINAL_AIR_STANDARD.pdf (accessed on 18 November 2009).
- Zhou, L.; Liu, G.; Shen, M.; Hu, R.; Sun, M.; Liu, Y. Characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in indoor dust from different functional areas in Hefei, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 251, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayan, V.; Paramesh, H.; Salvi, S.; Dalal, A.K. Enhancing indoor air quality –The air filter advantage. Lung India 2015, 32, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Liu, Q.; Li, H.; Zeng, Q.; Chan, L. Anthropogenic magnetic particles and heavy metals in the road dust: Magnetic identification and its implications. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klepeis, N.E.; Nelson, W.C.; Ott, W.R.; Robinson, J.P.; Tsang, A.M.; Switzer, P.; Behar, J.V.; Hern, S.C.; Engelmann, W.H. The National Human Activity Pattern Survey (NHAPS): A resource for assessing exposure to environmental pollutants. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 2001, 11, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heider, F.; Zitzelsberger, A.; Fabian, K. Magnetic susceptibility and remanent coercive force in grown magnetite crystals from 0.1 μm to 6 mm. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1996, 93, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuoco, F.C.; Stabile, L.; Buonanno, G.; Trassiera, C.V.; Massimo, A.; Russi, A.; Mazaheri, M.; Morawska, L.; Andrade, A. Indoor Air Quality in Naturally Ventilated Italian Classrooms. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1652–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnov, H.; Katra, I.; Friger, M.D. Insights into Indoor/Outdoor PM Concentration Ratios due to Dust Storms in an Arid Region. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution: An Examination of the Geochemical Record Preserved in Sedimentary Rocks; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 1985; p. 312. [Google Scholar]
- Dearing, J. Environmental Magnetic Susceptibility: Using the Bartington MS2 System; Chi Publishing: Keniloworth, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Dearing, J.A.; Bird, P.M.; Dann, R.J.L.; Benjamin, S.F. Secondary ferrimagnetic minerals in Welsh soils: A comparison of min-eral magnetic detection methods and implications for mineral formation. Geophys. J. Int. 1997, 130, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearing, J.A.; Hannam, J.A.; Anderson, A.S.; Wellington, E.M.H. Magnetic, geochemical and DNA properties of highly magnetic soils in England. Geophys J. Int. 2001, 144, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, B.; Thompson, R. Quaternary Climates, Environments and Magnetism; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, B.A. Rain and Dust: Magnetic Records of Climate and Pollution. Elements 2009, 5, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Sun, G.; Bi, X.; Li, Z.; Yu, G. Identification of trace metal pollution in urban dust from kindergartens using magnetic, geochemical and lead isotopic analyses. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harb, M.K.; Ebqa’Ai, M.; AlRashdi, A.; Alaziqi, B.H.; Al Rashdi, M.S.; Ibrahim, B. Investigation of selected heavy metals in street and house dust from Al-Qunfudah, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 1755–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engineering ToolBox. Particle Sizes. 2005. Available online: https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/particle-sizes-d_934.html (accessed on 28 August 2022).
- Abt, E.; Suh, H.; Allen, G.; Koutrakis, P. Characterization of indoor particle sources: A study conducted in the metropolitan Boston area. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.G.; Bai, S.Q.; Xue, Q.F. Magnetic properties as indicators of heavy metals pollution in urban topsoils: A case study from the city of Luoyang, China. Geophys. J. Int. 2007, 171, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, B. Magnetic properties of some synthetic sub-micron magnetites. Geophys. J. Int. 1988, 94, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.E.; Heller, F. Environmental Magnetism: Principles and Applications of Enviromagnetics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Proposed Amendments to the Guidelines for the Health Assessment of Suspect Developmental Toxicants; 54 Federal Register, 9386; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1989.
- Ibe, F.C.; Opara, A.; Duru, C.E.; Obinna, I.B.; Enedoh, M.C. Statistical analysis of atmospheric pollutant concentrations in parts of Imo State, Southeastern Nigeria. Sci. Afr. 2020, 7, e00237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


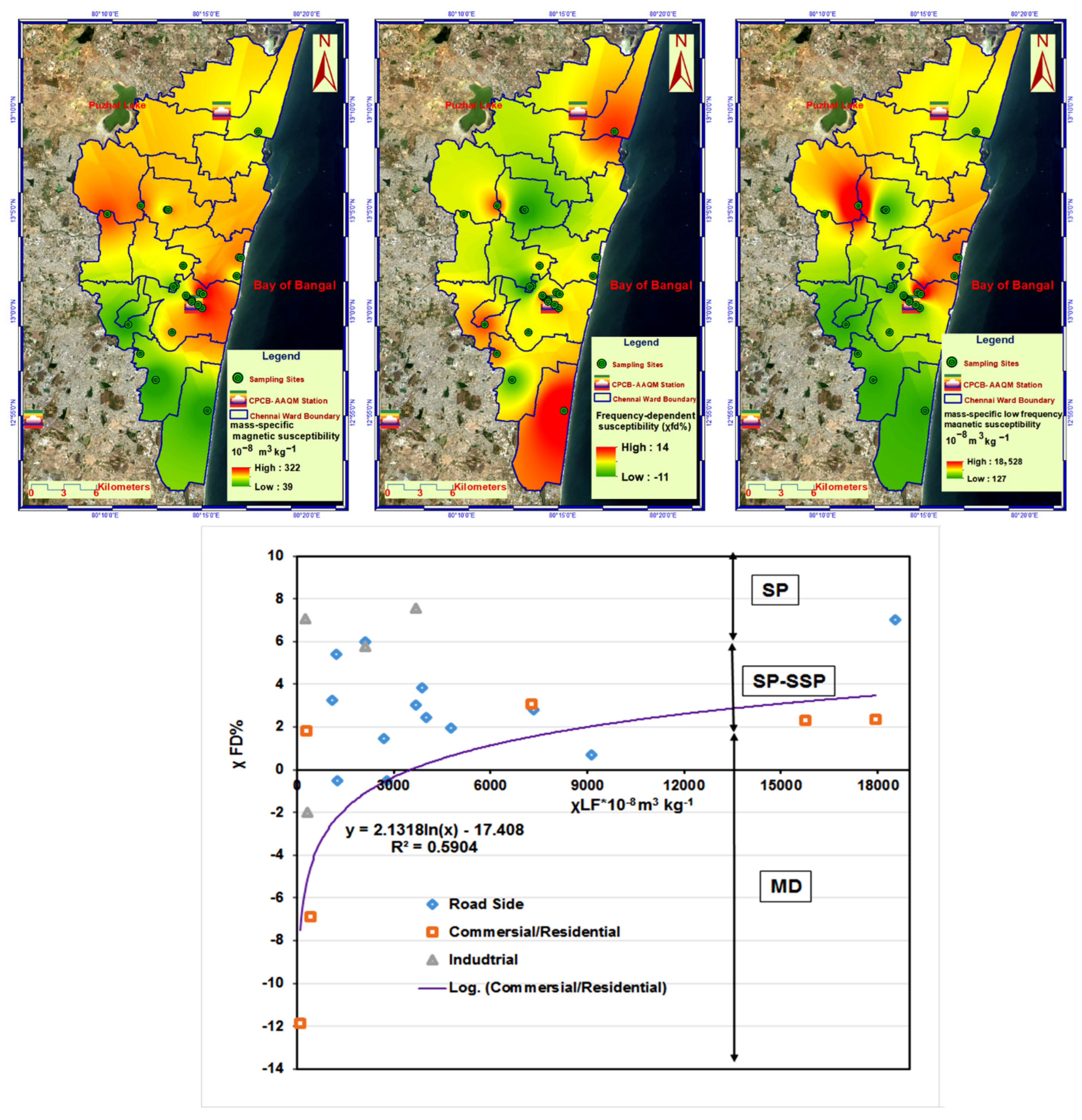


| χfd% | Category/Nature of Grains | Sample % from Sites |
|---|---|---|
| <2 | Coarse MD grain | 36% |
| 2–5 | Frequently independent grain | 32% |
| 5–15 | SP/SD grain admixture of the multi-domain and single-domain magnetic materials | 32% |
| Comparison of χlf and χfd% | Pollution Index | Sample % from sites |
| Low χfd% and high χlf | Anthropogenic input | 68% |
| High χfd% and low χlf | Pedogenesis | 18% |
| Same χfd% and χlf | High heavy metal pollution | 14% |
| Low χfd% and χlf | Normal | 0% |
| Parameter Statistics | Minimum | Maximum | Average | Median | Kurtosis | Geomean | Skewness | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 (µg/m3) | 18.0 | 214.5 | 51.0 | 46.6 | 13.5 | 45.6 | 2.9 | 28.0 |
| NO (µg/m3) | 0.3 | 30.1 | 9.8 | 7.5 | 1.0 | 8.0 | 1.0 | 5.9 |
| NO2(µg/m3) | 3.4 | 44.0 | 16.5 | 13.5 | 0.3 | 14.2 | 1.0 | 9.2 |
| NOx (ppb) | 3.4 | 32.8 | 13.6 | 13.1 | 0.1 | 12.1 | 0.6 | 6.3 |
| CO (mg/m3) | 0.3 | 1.9 | 0.9 | 1.0 | -0.5 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| SO2 (µg/m3) | 1.2 | 39.1 | 8.2 | 5.4 | 7.7 | 6.7 | 2.5 | 6.2 |
| WS (m/s) | 0.2 | 3.0 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 2.2 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 0.6 |
| WD (deg) | 54.6 | 200.2 | 155.3 | 161.7 | 3.0 | 152.2 | −1.5 | 26.9 |
| Temperature (°C) | 26.1 | 29.5 | 27.9 | 27.9 | -1.0 | 27.9 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| SR (W/mt2) | 98.6 | 915.9 | 290.3 | 224.2 | 4.8 | 248.5 | 2.5 | 217.0 |
| RH (%) | 53.5 | 82.9 | 67.5 | 66.9 | 0.9 | 67.2 | 0.1 | 6.0 |
| Ozone (µg/m3) | 8.5 | 56.3 | 26.9 | 23.3 | 0.1 | 24.0 | 0.8 | 12.8 |
| Benzene (µg/m3) | 0.1 | 3.9 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 4.7 | 0.9 | 1.6 | 0.8 |
| Toluene (µg/m3) | 0.0 | 9.5 | 2.5 | 1.6 | 3.1 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 2.1 |
| O-Xylene (µg/m3) | 0.0 | 3.0 | 1.7 | 1.7 | −1.9 | 1.1 | −0.1 | 1.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karuppasamy, M.B.; Natesan, U.; Karuppannan, S.; Chandrasekaran, L.N.; Hussain, S.; Almohamad, H.; Dughairi, A.A.A.; Al-Mutiry, M.; Alkayyadi, I.; Abdo, H.G. Multivariate Urban Air Quality Assessment of Indoor and Outdoor Environments at Chennai Metropolis in South India. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101627
Karuppasamy MB, Natesan U, Karuppannan S, Chandrasekaran LN, Hussain S, Almohamad H, Dughairi AAA, Al-Mutiry M, Alkayyadi I, Abdo HG. Multivariate Urban Air Quality Assessment of Indoor and Outdoor Environments at Chennai Metropolis in South India. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(10):1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101627
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaruppasamy, Manikanda Bharath, Usha Natesan, Shankar Karuppannan, Lakshmi Narasimhan Chandrasekaran, Sajjad Hussain, Hussein Almohamad, Ahmed Abdullah Al Dughairi, Motrih Al-Mutiry, Ibrahim Alkayyadi, and Hazem Ghassan Abdo. 2022. "Multivariate Urban Air Quality Assessment of Indoor and Outdoor Environments at Chennai Metropolis in South India" Atmosphere 13, no. 10: 1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101627
APA StyleKaruppasamy, M. B., Natesan, U., Karuppannan, S., Chandrasekaran, L. N., Hussain, S., Almohamad, H., Dughairi, A. A. A., Al-Mutiry, M., Alkayyadi, I., & Abdo, H. G. (2022). Multivariate Urban Air Quality Assessment of Indoor and Outdoor Environments at Chennai Metropolis in South India. Atmosphere, 13(10), 1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101627











