Relationships between Mass Level of Allergenic Platanus acerifolia Protein 3 (Pla a3) and Redox Trace Elements in the Size-Resolved Particles in Shanghai Atmosphere
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
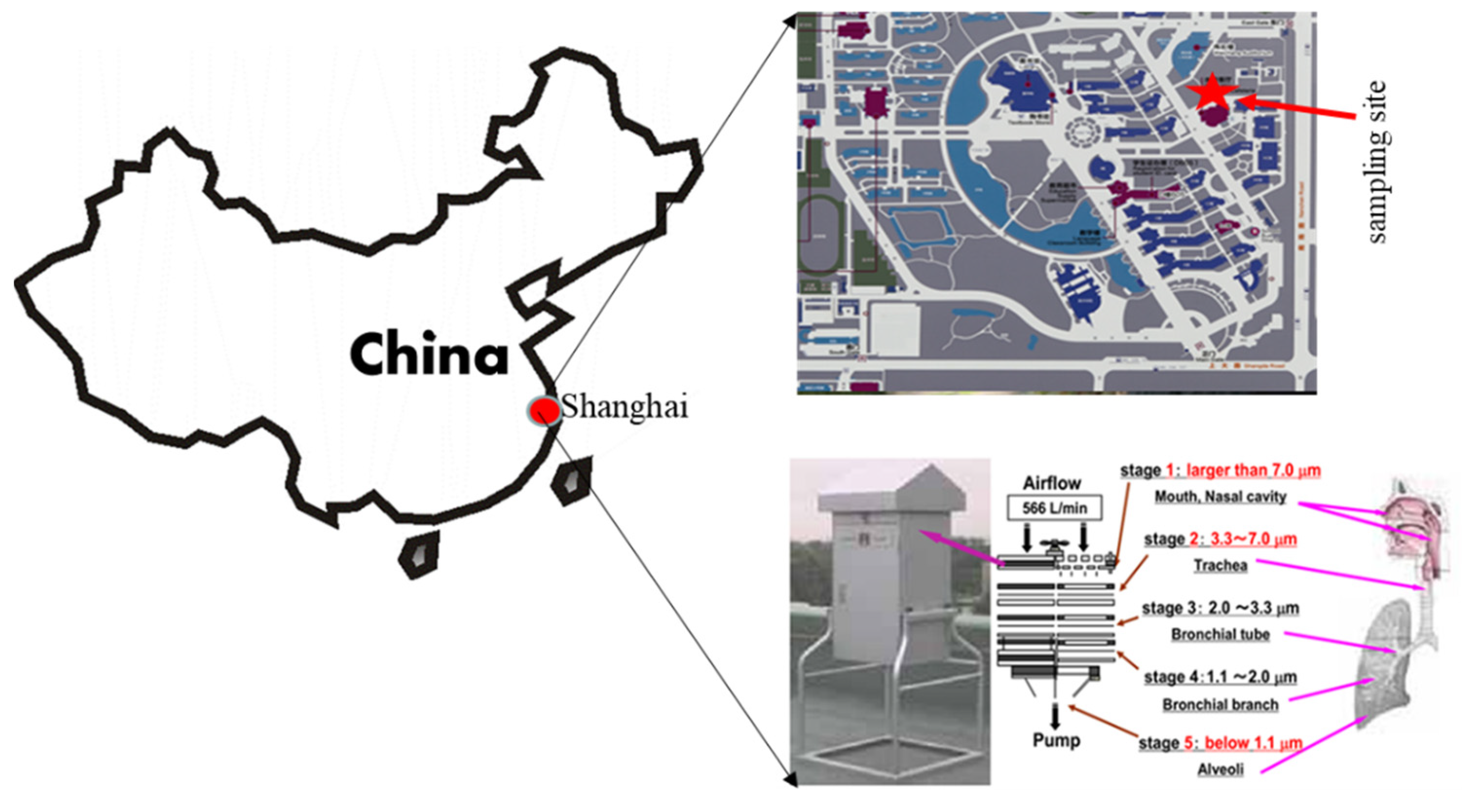
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Total Protein Detection in the Ambient Particles
2.3. Specific Antibody Preparation for the Pla a3 Detection
2.4. Detection of Pla a3 Distribution in the Ambient Particles
2.5. Chemical Elements in the Size-Resolved Particles Were Measured by ICP-MS
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
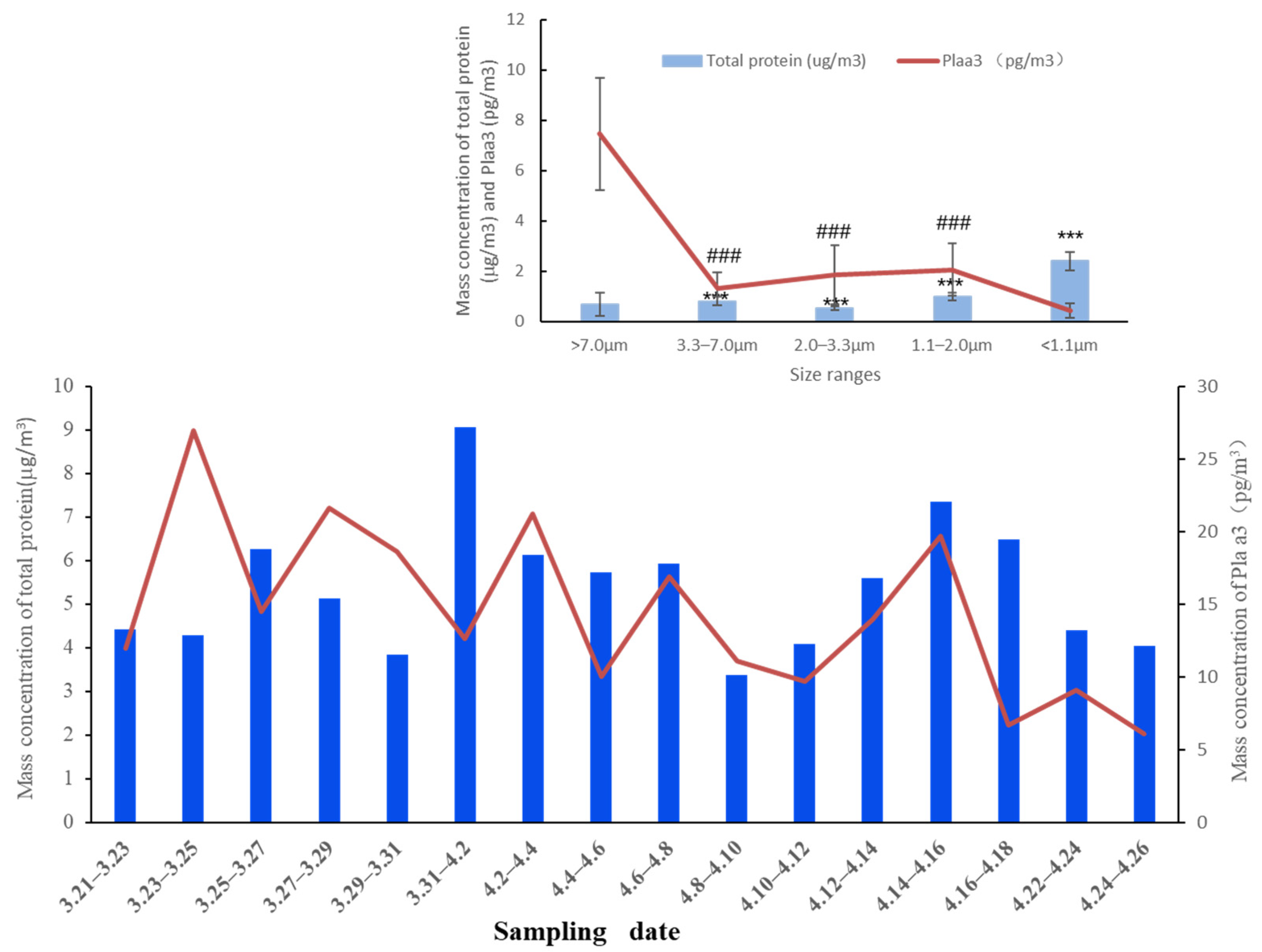
3.1. Daily Mass Level of Pla a3 in the Size-Resolved Particles
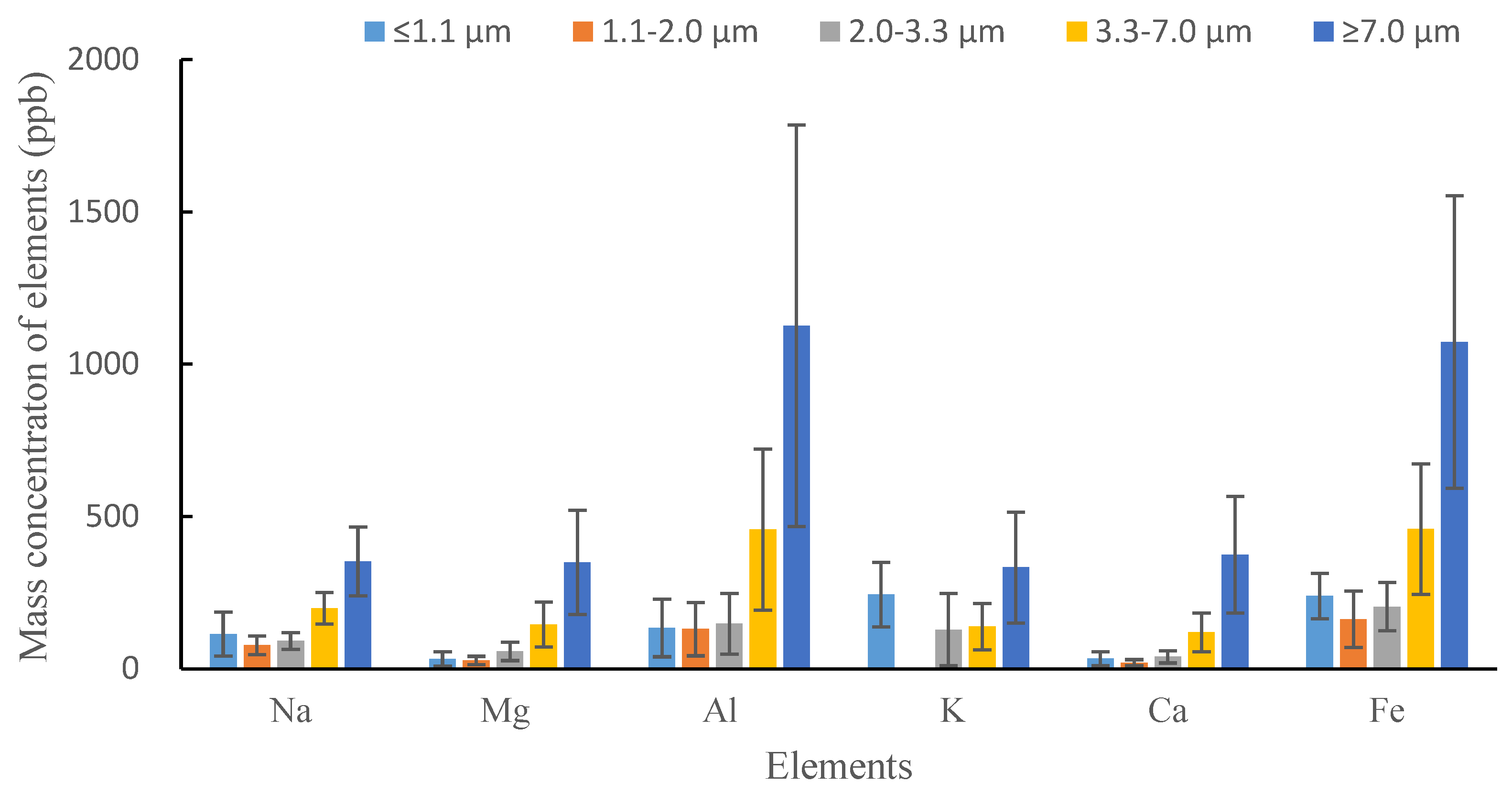
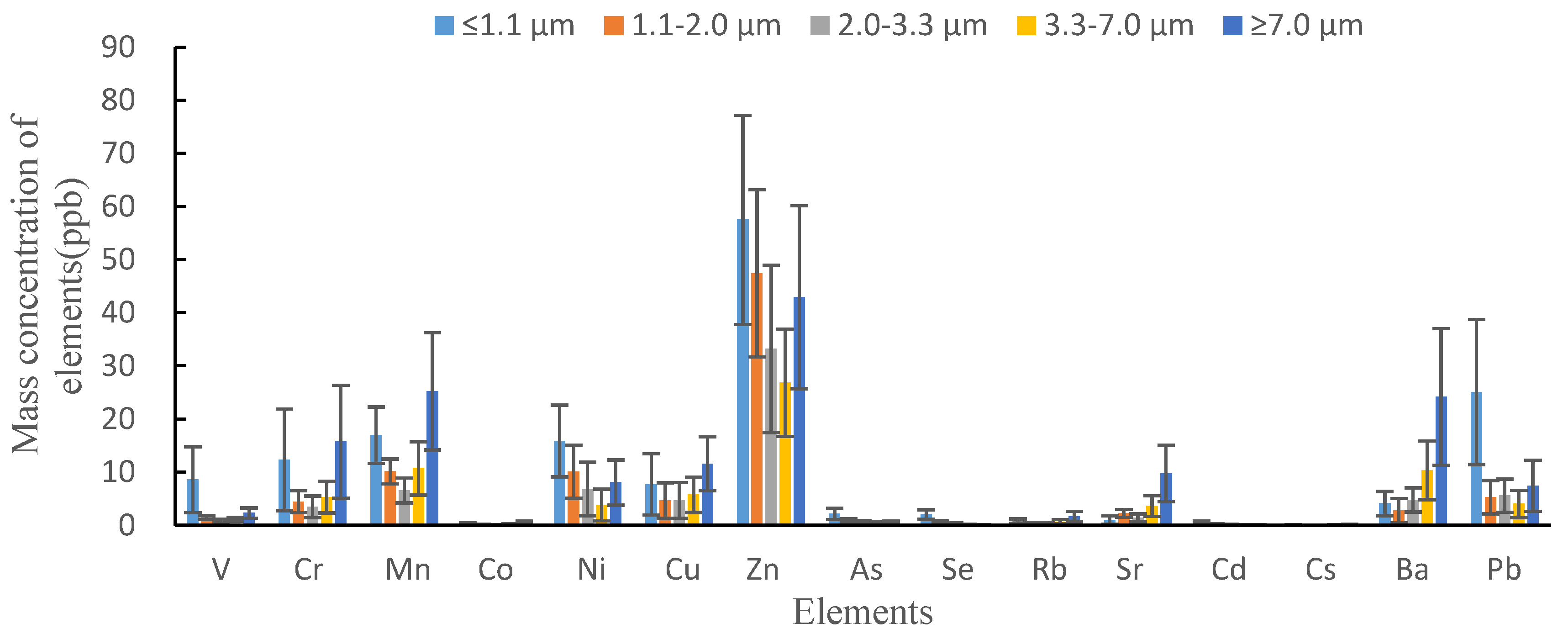
3.2. Mass Concentration of Redox Trace Metals in the Size-Resolved Particles
3.3. Relationship of Mass Concentration of Redox Trace Metals and Pla a3 in the Size-Resolved Particles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fajersztajn, L.; Mariana, V.; Ligia, V.B.; Paulo, S. Air pollution: A potentially modifiable risk factor for lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Hao, X.; Liu, D.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Liu, P.; Zhang, R.; Yu, S.; Pan, R.; Wu, M.; et al. Mineralogical characterization of ambient fine/ultrafine particles emitted from Xuanwei C1 coal combustion. Atmos. Res. 2015, 169, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, N.; Saliba, N.; Shihadeh, A.; Jaafar, M.; Baalbaki, R.; Shafer, M.; Schauer, J.; Sioutas, C. Oxidative potential and chemical speciation of size-resolved particulate matter (PM) at near-freeway and urban background sites in the greater Beirut area. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinmuth-Selzle, K.; Kampf, C.J.; Lucas, K.; Lang-Yona, N.; Frohlich-Nowoisky, J.; Shiraiwa, M.; Lakey, P.S.J.; Lai, S.; Liu, F.; Kunert, A.T.; et al. Air pollution and climate change effects on allergeies in the anthropocene: Abundance interaction and modification of allergens and adjuvants.Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4119–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shumin, Z.; Luying, Z.; Senlin, L.; Jiaxian, P.; Yang, L.; Lanfang, R.; Tingting, X.; Wei, Z.; Shuijun, L.; Weqian, W.; et al. Ambient particulate matter-associated autophagy alleviates pulmonary inflammation induced by Platanus pollen protein 3 (Pla3). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 758, 143696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poschl, U. Atmospheric aerosol: Composition, Transformation, Climate and Health Effects. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 7520–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancia, A.; Capone, P.; Vonesch, N.; Pelliccioni, A.; Grandi, C.; Magri, D.; D’Ovidio, M.C. Research Progress on Aerobiology in the Last 30 Years: A Focus on Methodology and Occupational Health. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiljanic, K.; Apostolovic, D.; Trifunovic, S.; Ognjenovic, J.; Perusko, M.; Mihajlovic, L.; Burazer, L.; van Hage, M.; Velickovic, T.C. Subpollen particles are rich carriers of major short ragweed allergens and NADH dehydrogenases: Quantitative proteomic and allergomic study. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2017, 47, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacsi, A.; Choudhury, B.K.; Dharajiya, N.; Sur, S.; Boldogh, I. Subpollen particles: Carriers of allergenic proteins and oxidases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Gong, X.; Suzuki, M.; Lu, S.; Sekiguchi, K.; Nakajima, D.; Miwa, M. Size-segregated Allergenic Particles Released from Airborne Cryptomeria japonica Pollen Grains during the Yellow Sand Events within the Pollen Scattering Seasons. Asian J. Atmospheric Environ. 2013, 7, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, C.; Luque, G.M.; Courchamp, F. The twenty most charismatic species. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fucheng, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Yichun, L.; Yang, L.; Luying, Z.; Jiaxian, P.; Wei, Z.; Shumin, Z.; Senlin, L. Subpollens delivery of Platanus acerifolia pollen allergen Pla a3 and nucleic acid into lungs and cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 513, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, Z.; Li, S. Characterization of two pollen allergens of the London plane tree in Shanghai. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015, 14, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ni, W.W.; Huang, W.; Wu, D.Q.; Zhou, Y.J.; Ji, C.M.; Cao, M.D.; Guo, M.; Sun, J.L.; Wei, J.F. Expression and purification of a major allergen, Pla a1, from Platanus acerifolia pollen and the preparation of its monoclonal antibody. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 2887–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhao, H.; Peng, J.; Hong, Q.; Xiao, K.; Shang, Y.; Lu, S.; Zhang, W.; Wu, M.; Li, S.; et al. Size distribution of Platanus acerifolia allergen 3 (Pla a3) in Shanghai ambient size-resolved particles and its allergenic effects. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 198, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buter, J.; Thibaudon, M.; Smith Mm Kennedy, R.; Rantio, A.; Albertini, R.; Reese, G.; Weber, B.; Galan, C.; Brandao, R.; Antunes, C.; et al. Release of Bet v 1 from birch pollen from 5 European countries. Results from the HIALINE study. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 55, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, X.; Tao, A.; Wang, G.; Wu, Y.; Li, M.; Shi, H.; Xie, M. Expression, purification and identification of Pla a1 in a codon-optimized Platanus pollen allergen. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 2197–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Yi, F.; Hao, X.; Yu, S. Physicochemical properties and ability to generate free radicals of ambient coarse, fine, and ultrafine particles in the atmosphere of Xuanwei, China, an area of high lung cancer incidence. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 97, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Ren, J.; Hao, X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, R.; Wu, M.; Yi, F.; Lin, J.; Shinich, Y.; Wang, Q. Characterization of protein expression of Platanus pollen following exposure to gaseous pollutants and vehicle exhaust particles. Aerobiologia 2014, 30, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Roh, Y.; Koh, D. Oxidation and reduction of redox-sensitive elements in the presence of humic substances in subsurface environments: A review. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Win, M.S.; Zeng, J.; Yao, C.; Zhao, M.; Xiu, G.; Lin, Y.; Xie, T.; Dai, Y.; Rao, L.; et al. A characterization of HULIS-C and the oxidative potential of HULIS and HULIS-Fe(II) mixture in PM2.5 during hazy and non-hazy days in Shanghai. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 219, 117058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Xie, Z.; Hu, Q. Ambient protein concentration in PM10 in Hefei, central China. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 54, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Feng, M.; Yao, Z.; An, J.; Zhong, Y.; Wu, M.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J.; Yonemochi, S.; Zhang, J.; et al. Physicochemical characterization and cytotoxicity of ambient coarse, fine, and ultrafine particulate matters in Shanghai atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, H.; Peng, J.; Li, Y.; Shang, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhang, W.; Lu, S.; Li, S.; et al. Allergenicity of recombinant Humulus j aponicus pollen allergen 1 after combined exposure to ozone and nitrogen dioxide. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Gonzalez, D.; Gonzalez-Parrado, Z.; Vega-Maray, A.M.; Valencia-Barrera, R.M.; Camazon-Izquierdo, B.; De Nuntiis, P.; Mandrioli, P. Platanus pollen allergen, Pla a1: Quantification in the atmosphere and influence on a sensitizing population. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2010, 40, 1701–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| ≤1.1 μm | 1.1–2.0 μm | 2.0–3.3 μm | 3.3–7.0 μm | ≥7.0 μm | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na | 114.19 ± 71.93 | 77.73 ± 30.63 | 90.83 ± 27.31 | 198.25 ± 51.87 | 352.47 ± 113.71 | 0.73 |
| Mg | 31.93 ± 23.53 | 27.64 ± 13.95 | 56.74 ± 29.73 | 145.30 ± 73.33 | 349.77 ± 170.82 | 0.83 |
| Al | 134.51 ± 94.57 | 130.26 ± 87.44 | 147.77 ± 99.71 | 456.99 ± 264.23 | 1126.22 ± 659.51 | 0.84 |
| K | 243.73 ± 105.77 | 0.11 ± 0.33 | 128.38 ± 188.83 | 138.20 ± 75.96 | 332.59 ± 181.87 | 0.32 |
| Ca | 33.07 ± 22.61 | 20.11 ± 9.87 | 39.46 ± 20.25 | 119.78 ± 63.72 | 374.67 ± 191.16 | 0.87 |
| Fe | 238.83 ± 74.72 | 162.59 ± 92.10 | 203.79 ± 79.62 | 458.20 ± 213.90 | 1073.32 ± 480.32 | 0.82 |
| V | 8.60 ± 6.21 | 1.44 ± 0.99 | 0.82 ± 0.37 | 1.14 ± 0.34 | 2.31 ± 0.98 | 0.09 |
| Cr | 12.33 ± 9.55 | 4.44 ± 3.17 | 3.47 ± 2.06 | 5.29 ± 2.98 | 15.73 ± 10.63 | 0.37 |
| Mn | 16.99 ± 5.32 | 10.14 ± 3.54 | 6.58 ± 2.36 | 10.73 ± 5.04 | 25.23 ± 11.03 | 0.54 |
| Co | 0.31 ± 0.19 | 0.19 ± 0.28 | 0.09 ± 0.05 | 0.21 ± 0.11 | 0.53 ± 0.25 | 0.60 |
| Ni | 15.88 ± 6.74 | 10.10 ± 13.43 | 6.85 ± 9.02 | 3.81 ± 2.99 | 8.06 ± 4.27 | 0.06 |
| Cu | 7.71 ± 5.76 | 4.66 ± 3.01 | 4.69 ± 3.36 | 5.76 ± 3.32 | 11.58 ± 5.09 | 0.61 |
| Zn | 57.53 ± 19.7 | 47.41 ± 16.82 | 33.21 ± 15.73 | 26.86 ± 10.10 | 42.97 ± 17.22 | 0.01 |
| As | 2.15 ± 1.08 | 0.90 ± 0.54 | 0.59 ± 0.33 | 0.47 ± 0.24 | 0.57 ± 0.27 | 0.21 |
| Se | 2.04 ± 0.89 | 0.75 ± 0.37 | 0.34 ± 0.16 | 0.17 ± 0.07 | 0.10 ± 0.05 | 0.30 |
| Rb | 0.77 ± 0.44 | 0.33 ± 0.19 | 0.34 ± 0.19 | 0.69 ± 0.41 | 1.67 ± 0.97 | 0.69 |
| Sr | 0.99 ± 0.77 | 2.25 ± 4.74 | 1.43 ± 0.74 | 3.62 ± 1.93 | 9.75 ± 5.30 | 0.91 |
| Cd | 0.51 ± 0.28 | 0.17 ± 0.12 | 0.14 ± 0.10 | 0.07 ± 0.06 | 0.07 ± 0.05 | 0.92 |
| Cs | 0.10 ± 0.06 | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.06 ± 0.04 | 0.13 ± 0.07 | 0.25 |
| Ba | 4.12 ± 2.28 | 2.77 ± 1.50 | 4.78 ± 2.27 | 10.36 ± 5.52 | 24.16 ± 12.85 | 0.82 |
| Pb | 25.07 ± 13.63 | 5.30 ± 3.08 | 5.57 ± 3.13 | 4.04 ± 2.57 | 7.44 ± 4.82 | 0.11 |
| Pla a3 | 0.41 ± 0.28 | 2.06 ± 1.04 | 1.84 ± 1.17 | 1.30 ± 0.66 | 7.46 ± 2.23 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, S.; Ma, T.; Zhang, L.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, W.; Yonemochi, S.; Liu, X.; Ebere, E.C.; Wang, W.; et al. Relationships between Mass Level of Allergenic Platanus acerifolia Protein 3 (Pla a3) and Redox Trace Elements in the Size-Resolved Particles in Shanghai Atmosphere. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101541
Lu S, Ma T, Zhang L, Feng Y, Zhou S, Zhang W, Yonemochi S, Liu X, Ebere EC, Wang W, et al. Relationships between Mass Level of Allergenic Platanus acerifolia Protein 3 (Pla a3) and Redox Trace Elements in the Size-Resolved Particles in Shanghai Atmosphere. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(10):1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101541
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Senlin, Teng Ma, Lu Zhang, Yule Feng, Shumin Zhou, Wei Zhang, Shinichi Yonemochi, Xinchun Liu, Enyoh Christian Ebere, Weiqian Wang, and et al. 2022. "Relationships between Mass Level of Allergenic Platanus acerifolia Protein 3 (Pla a3) and Redox Trace Elements in the Size-Resolved Particles in Shanghai Atmosphere" Atmosphere 13, no. 10: 1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101541
APA StyleLu, S., Ma, T., Zhang, L., Feng, Y., Zhou, S., Zhang, W., Yonemochi, S., Liu, X., Ebere, E. C., Wang, W., & Wang, Q. (2022). Relationships between Mass Level of Allergenic Platanus acerifolia Protein 3 (Pla a3) and Redox Trace Elements in the Size-Resolved Particles in Shanghai Atmosphere. Atmosphere, 13(10), 1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101541









