Abstract
The atmosphere over Lake Baikal covers a vast area (31,500 square meters) and has more significant differences in the composition and variability of gaseous and aerosol components in atmospheric air than in coastal continental areas and is still a poorly studied object. In recent years, the anthropogenic impact on the ecosystem of Lake Baikal has been increasing due to the development of industry in the region, the expansion of tourist infrastructure and recreational areas of the coastal zone of the lake. In addition, one of the significant sources of atmospheric pollution in the Baikal region is the emissions of smoke aerosol and trace gases from forest fires, the number of which is increasing in the region. This article presents the results of experimental studies of the dispersed composition of aerosols and gas impurities, such as ozone, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides during route ship measurements in the water area of Lake Baikal in the summer of 2020.
1. Introduction
The increase in total atmospheric pollution and the associated global climate changes have caused increased interest in the physicochemical properties and structure of atmospheric aerosols [1]. Certain information about the structure of atmospheric aerosols is required to solve theoretical and applied problems of atmospheric physics [1,2]. Aerosols, which largely determine many atmospheric processes and phenomena, are the most important object of research in almost all fields of atmospheric science. The spatial structure of aerosols changes noticeably over time as a result of the processes of generation, removal from the atmosphere, and the propagation of aerosol particles in it [3].
The processes of propagation and removal of aerosols from the atmosphere are determined by both meteorological (geophysical) factors and the properties of the aerosol particles themselves. The processes that are determined by meteorological factors include the ordered convective and advective transport of particles and, to a large extent, their mixing as a result of turbulent diffusion [4,5,6]. During the propagation or removal of particles from the atmosphere, the mass and composition of the latter are transformed as a result of coagulation and condensation growth, as well as heterogeneous reactions. Coagulation, condensation, and heterogeneous reactions form a spectrum of particle sizes, determining the type of particle size distribution function [7,8].
Due to the impact of fine particles on climate and health, with the development of reliable modern experimental methods and theoretical basis, in recent years, more and more research around the world has been focused on the nanometer region of aerosol size, in which the main amount of the particles in the atmosphere is concentrated [9,10].
Trace gases (ground-level ozone, sulfur oxide, nitrogen oxides, etc.) play an important role in the formation of new nanometer-sized aerosol particles from gaseous vapors as a result of physical and chemical transformations and meteorological processes [11]. Ozone molecules actively participate in the oxidation of various nitrogen and sulfur compounds [12], and variations in the content of aerosol-forming gases are ambiguously related to variations in the content of aerosols [7]. As a result, the temporal variations of aerosol-forming gases are of interest as an indicator of aerosol formation processes.
Fine aerosol solid particles, accumulating a number of chemicals of a wide spectrum, together with ozone and nitrogen dioxide are the most toxic air pollutants [13,14]. Despite the fact that new aerosol particles are formed from gaseous vapors in the atmosphere everywhere, studies of aerosol formation processes depending on geographical location, underlying surface, meteorological conditions, anthropogenic load in the region, transboundary transport of pollutants, as well as studies of various effects of microdispersed aerosols on atmospheric chemistry, climate, are still relevant. In this regard, the Lake Baikal region is of particular interest, since it can be characterized as representing natural conditions, but at the same time periods of anthropogenic impact are observed here due to the orographic isolation of the Baikal Basin and the specific nature of the circulation of air flows over the lake [15,16].
In recent years, the anthropogenic impact on the ecosystem of Lake Baikal has been increasing due to the development of industry in the Baikal region and the expansion of tourist infrastructure and recreational areas of the coastal zone of the lake. Enterprises of fuel energy, petrochemistry, smelting, woodworking, and paper industry dominate in this region. More than 300 thousand tons per year of pollutant emissions are related to the largest enterprises of the energy industry, such as thermal power plants using coal as a fuel [17]. Significant pollution sources for the atmosphere of the Baikal region are, in particular, emissions of smoke aerosol and trace gases from forest fires, which are growing in number in this region as a consequence of climate change [18,19,20,21]. After entering the upper tropospheric layers, smoke from forest fires may propagate great distances from Siberia to the Arctic Basin [22,23,24,25]. The transfer and accumulation of aerosol-gas impurities in the Baikal water area is observed every summer due to forest fires occurring in the boreal forests of Siberia [26,27]. The atmosphere above the lake covers a huge area (31,500 square meters) and is still a little-studied object.
Lake Baikal is the largest reservoir of fresh water with unique flora and fauna. In 1996, Lake Baikal was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Presently it is negatively affected by climate change, water warming, industrial emissions, shipping, touristic activities, and Siberian forest fires. The assessment of air pollution related to Baikal’s ecosystem damage is an unsolved problem [28,29,30,31,32,33]. In this case, the study of this article is focused on comprehensive observations of spatiotemporal distributions of the dispersed composition of aerosols and gas impurities, such as ozone, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides during the purposely designed expedition over Lake Baikal in the summer of 2020.
2. Materials and Methods
Complex expedition studies of spatial and temporal variability of physical, microphysical, and chemical characteristics of atmospheric aerosol, small gas impurities, and meteorological processes over the water area of Lake Baikal were carried out during the expedition on the research vessel (SRV) “Academician V.A. Koptyug” from 29 July to 11 August 2020. Figure 1 shows a map of Lake Baikal and the route of the vessel along the entire perimeter of Lake Baikal, as well as the main places with measurement dates. The total length of the route was about 2000 km. The coordinates of the measurement points were determined by the ship’s GPS system.
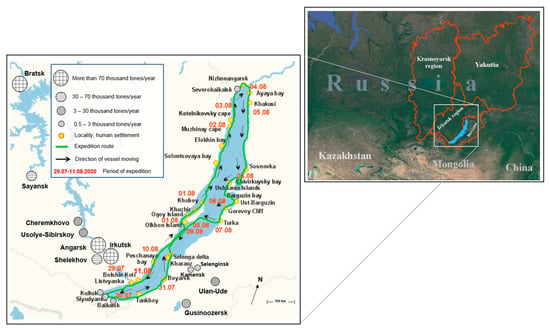
Figure 1.
The map of the vessel’s route along the entire perimeter of Lake Baikal and the main stops with dates in the water area of Baikal during the expedition on the research vessel (SRV) “Academician V.A. Koptyug” from 29 July to 11 August 2020.
Measurements of microphysical characteristics (aerosol particle number concentration N, cm−3 and particle distribution in the size range 0.005–10 microns) of atmospheric aerosol were carried out using a diffusion aerosol spectrometer Model DAS 2702 M (Aeronanotech, Moscow, Russia) [34].
The limits of the permissible relative error of measurements of aerosol particle sizes are ±15%. The time of one measurement was from 1 to 3 min, depending on the air parameters and the particle concentrations. The spectrometer has 2 operating modes: the mode of measuring of ultrafine atmospheric particles (UFA) with a size below 200 nm (40 ranges in 5 nm intervals) and the mode of measuring of submicron aerosol (SMA) with sizes above 200 nm (12 channels).
The 3.02 P-A, P-310A, and C-310A chemiluminescent gas analyzers (OPTEK Inc., St. Petersburg) were used to measure the concentrations of ozone, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur dioxide [35]. The P-310A and C-310A gas analyzers measured the concentrations in the range from 0 to 1000 μg m−3, with an error of ±25%, and the 3.02 P-A gas analyzers in the range from 0 to 500 μg m−3, with an error of ±20%. Calibration and zeroing were performed automatically with the help of built-in microflux sources according to commands from the gas analyzers’ processor, meeting ISO 9001:2015 [36]. The gas analyzer measurement accuracy was controlled using Mod. 8500 Monitor Labs calibrator (Monitor Labs. Inc., San Diego, CA, 920101, USA) [37].
The set of equipment for measuring the gas and aerosol composition of the Baikal near-water layer was installed in the lower deck of the vessel to exclude the influence of the ship’s emissions. Air samples for gas-aerosol instrumentation were taken using Teflon pipes at an altitude of 6 m above the water from the shipboard opposite to the exhaust plume direction. The acoustic meteorological complex EXMETEO [38] was installed on the upper deck of the vessel. The effect of the ship engine exhaust plume was eliminated through a constant control of wind direction and synchronization of measurements with meteorological parameters obtained from the meteorological complex.
All measurements of atmospheric impurities were recorded continuously and synchronously by the abovementioned gas analyzers and a diffusion spectrometer during the entire period of ship measurements in the Baikal water area. The data retrieved from the gas analyzers and diffusion aerosol spectrometer were postprocessed in order to remove outlier values. A value is considered as an outlier if it exceeds its previous value in the time-series by more than three times the standard deviation of the last 10 values. With this approach, extremely high concentrations that do not follow the general trend and can be attributed to local contamination (ship exhaust) were considered separately. If the direction of the apparent wind was blowing to the sampling site, we removed these extremely high concentrations from the database.
Along the entire route, aerosol samples (23 samples) were taken using a high-volume sampler PM10 of Andersen Instruments Inc. (45002, Cleves, OH, USA) on Watman-41 filters measuring 203 × 254 mm with a pumping speed of 17 L/min, which were subsequently analyzed for various pollutants by ion and high-performance liquid and gas chromatography, inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry in an Accredited Laboratory (No. ROSS RU. 0001.513855) of Limnological Institute SB RAS [39]. The laboratory complies with the requirements of International Organization for Standardization (ISO/IEC 17025-2019), as well as ISO 9001:2015 “Quality management systems—Requirements”. Samples of aerosol admixtures for chemical analysis were collected on filter packs with the use of the filterpack method, adopted in international monitoring networks [40]. The ionic composition of the aerosols was determined from the soluble fraction. The sampled matter was extracted from the filters with the available volume of deionized water (0.15–0.20 μS). A portion of the obtained solution was retained for pH measurements. The remainder of the solution was filtered through an acetate-cellulose filter with a 0.2-µm pore size. Ions of NH4+, Na+, K+, magnesium (Mg2+), and Ca2+ as well as SO42−, NO3−, hydrocarbonate (HCO3−), and chloride (Cl−) ions were determined from the filtrate. Atomic adsorption and ionic chromatography were used to determine the chemical composition of the soluble fraction. These techniques are recommended to provide correlation with data obtained in other areas of the world [40,41]. An atomic adsorption spectrometer (Carl Zeiss Jena, Jena, Germany), high performance fluid chromatographer (Milichrome A-02, Novosibirsk, Russia), and ionic chromatographer ICS-3000 (Sunnyvale, California 94088-3603, Dionex, USA) were employed. The introduction of ion determination through the ion chromatography method made it possible to obtain the measurement results with a confidence level of P = 0.95 accurately to within 4%. We note that the reliability of chemical analysis results, obtained with these methods and instruments, was repeatedly confirmed through participation of laboratory of Limnological Institute SB RAS in data quality control (QA/QC) as part of international programs [42,43,44]. The obtained data deviated from true values by no more than 10–15%, indicating the high quality of personnel and reliability of the results. The quality of the analyses was approved by inter-laboratory comparative experiments performed within the framework of international programs Global Atmosphere Watch [45] under the aegis of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and Acid Deposition Monitoring Network in East Asia (EANET). The sample collections were performed at anchorage and moving of the vessel from 6 h to 24 h during the expedition period. For the sampling, the proper precautionary measures were taken in order to prevent possible contamination from potential sources such as the ship exhaust and lake water droplets.
General synoptic processes over the region were analyzed on the basis of surface weather maps of the Federal State Budgetary Institution “AANI” [46]. The analysis of the direct trajectories of the movement of air masses using the HYSPLIT model was also carried out [47]. The trajectories were considered at three altitude levels—100, 500, and 1000 m.
3. Results and Discussion
The influence of atmospheric transport on the distribution pattern of aerosol and gas impurities in the Lake Baikal region is the most significant factor. Weather conditions on Lake Baikal change very quickly and can vary significantly across the lake’s water area.
Such situations were observed during the complex expedition in 2020 on the research vessel (SRV) “Academician V.A. Koptyug”. The synoptic situation in the Baikal water area during the expedition was characterized mainly as unstable cyclonic weather with a high cloud cover score (up to 10 points), with short-term clarifications on 30–31 July, 3 August, and 6 August during the change of circulation processes in the Lake Baikal region. The air temperature ranged from 14 to 25 °C. Prior to the expedition ship research, there were prolonged rains not only in the region but in the adjacent western regions.
It should be noted that, unlike in previous years, during the period of expeditionary research in 2020, forest fires were not observed in the Baikal region itself [27]; the main wildfires were concentrated in the northern regions of the Irkutsk region and Yakutia, i.e., they were remote.
The ultrafine particle number concentration in the size range from 5 to 200 nm (UFA) and the submicron aerosol in the size range from 0.3 to 10 microns (SMA), concentrations of ozone, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides, and meteorological parameters (temperature and pressure) were averaged over a 10-min measurement interval along the entire route of the vessel, as shown in Figure 2.
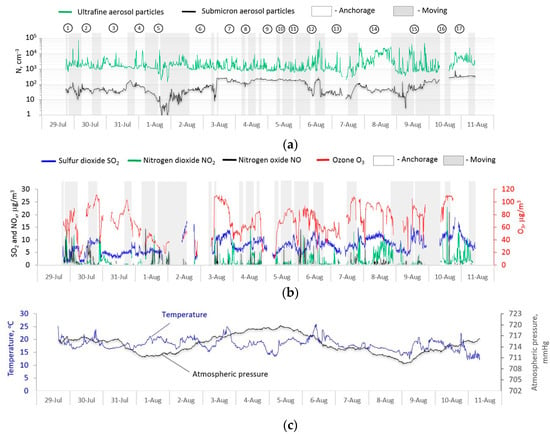
Figure 2.
The spatial-temporal variability along the route of the research vessel “Akademik V.A. Koptyug”: (a) the concentrations of the ultrafine and submicron atmospheric particles; (b) round-level of ozone, nitrogen oxide and dioxide, sulfur dioxide concentrations; (c) temperature and pressure; 1-Listvyanka, 2-Baikalsk, 3-Boyarsky, 4-Delta of River Selenga, 5-Island Ogoy, 6-Muzhinay cape, 7-Severobaikalsk, 8-Nizhneangarsk, 9-Ayaya bay, 10-Khakusi, 11-Kabaniu cape, 12-Zmeevaya bay,13-Ust-Barguzin, 14-Turka, 15-Aya bay, 16-Peschanaya bay, and 17-Kadilniy cape.
All data were obtained as a result of continuous synchronous measurements using automatic gas analyzers, a diffusion aerosol spectrometer DAS 2702 M, and an acoustic meteorological complex.
As can be seen from Figure 2, the spatial–temporal variability of the particle number concentration of the ultrafine dispersed and submicron aerosol fraction trace gases are extremely heterogeneous across the lake area. This is determined by the unevenness of the distribution of pollution sources, the short lifetime of most pollutants [48,49], the peculiarities of atmospheric circulation, and atmospheric processes of removing pollutants from the atmosphere.
In general, there are both extended areas up to 100–200 km with an elevated concentration of gas impurities, ultrafine and submicron atmospheric particles, as well as individual local bursts depending on the distribution of emissions, circulation features, and photochemical processes, and, in general, on weather conditions in a particular area. The average values for the measurement period of the ultrafine and submicron particles number concentration in the Baikal water area were, respectively, 2986 particles/cm3 and 98 particles/cm3.
Figure 3 shows the chemical compositions of the aerosols during all period of vessel cruising. Form 29 July to 11 August 2020, the total ionic concentrations varied from 0.5 to 2.9 μg/m3, and their upper limit was the highest over the entire long-term observation period in the southern basin of Lake Baikal. The SO42−, NH4+, Na+, Cl−, and NO3− ions dominated the chemical compositions in the atmosphere of Lake Baikal.
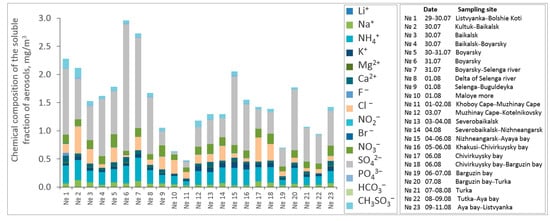
Figure 3.
Concentrations of soluble ions in the aerosols along route of the research vessel “Academician V.A. Koptyug”.
Based on the analysis of the measured data, we tried to separate the contributions to the pollution of the Baikal water area due to natural processes in the atmosphere, anthropogenic emissions, and fires, to identify the main patterns of spatial distribution of the particle number concentration of the microdispersed fraction of aerosol and trace gases.
So, for example, during the passage of the vessel, near large industrial centers on the route Kultuk–Slyudyanka–Baikalsk, located directly in the coastal zone of the lake, in rainy weather with westerly and northwesterly winds with a speed of 5–10 m s−1 and an increase to 15–20 m s−1, local elevated concentrations of fine dispersed and submicron aerosol fraction, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur dioxide were observed (Figure 2a,b). Figure 2a shows a fairly stable high distribution of SO2 concentration at the level of 9–11 μg m−3 also during the establishment of cloudy and calm weather, when the southeast of the water area during the movement of air masses was influenced by the emissions of the Irkutsk industrial zone according to the HYSPLIT trajectory model.
As is known, during mesoscale processes inside mesojet flows of the lower levels at altitudes of 100–600 m, plumes of atmospheric emissions from large industrial centers of the Irkutsk region are transferred to the water area of Lake Baikal [50]. The main pollutants in such plumes are sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, whose concentrations in the Baikal region can reach maximum permissible concentration (MPC) value and higher. It is in favor of such a mechanism that the duration of maintaining high levels of SO2 concentration along the entire route of the vessel’s movement in sparsely populated areas of the east coast testifies to, although precipitation during the measurement period made a certain contribution to the temporal dynamics of aerosol and gas components.
The results of the chemical analysis of the component composition of aerosol samples along the Baikalsk-Boyarsk route of the vessel also indicate the influence of anthropogenic outflows of industrial centers located on the lake shore. High content of sulfate ions SO42− (1.013 μg m−3), ammonium NH4+ (0.228 μg m−3), nitrate NO3− (0.142 μg m−3) were found in aerosol samples. Stoichiometry for NH4+, SO42−, and NO3- by molecular weight were equal to 30%, 25%, and 5.4%, respectively. A certain increase in the concentration of particles of the submicron fraction was noted.
The woodlands occupy a significant part in the coastal zone of Lake Baikal. In the Baikal region, a breeze phenomenon plays an important role in the circulation processes of air mass transfer. Constant air exchange occurs between land and water surface. Polluted air masses from the lake are affected by the influence of forest vegetation n the conditions of daytime breezes [26,51]. The contribution of forest vegetation to the absorption/emission of aerosol and gas impurities such as O3 and NOx, is high during the daytime when turbulent processes and photosynthetic activity of plants are activated.
During the long stay of the ship on 30–31 July opposite the research center of the Institute of Physical Materials Science SB RAS “Boyarsky”, located in a relatively clean area near a forest area close to the “background” conditions, the influence of breeze circulations on Lake Baikal on changes in the average values of atmospheric components was clearly manifested.
When the direction of the local wind changed from the shore to the lake during the night breeze, a decrease in the concentration of sulfur dioxide to the level of 5 μg m−3 and, at the same time, short-term spikes in the concentration of nitrogen dioxide were registered (Figure 2b), the most likely source of which was vehicle emissions due to the proximity of the federal highway R-258 on the lake shore.
Under the conditions of a night breeze, an increase in the concentration of ultrafine atmospheric particles was observed with a maximum of up to 10,000 particles/cm3 at 0:30–1:00 and, at the same time, a synchronous decrease in the concentration of submicron aerosol to 25–30 particles/cm3 (Figure 4), since volatile organic compounds VOC with ozone and OH and NO3 radicals make a significant contribution to the formation of not only oxidants but also organic aerosols (OA) [52,53]. The appearance of organic aerosols in gas-phase reactions occurs as a result of the fact that with a decrease in the vapor pressure, the solubility of the substance increases in comparison with that which existed for organic precursor compounds.
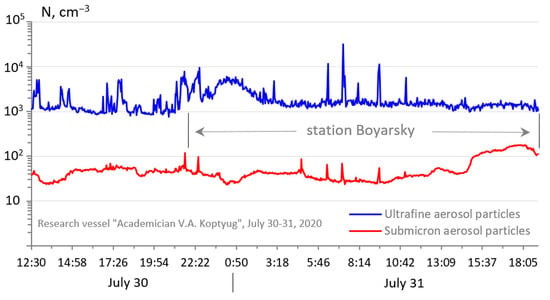
Figure 4.
Temporal variation of the concentration of ultrafine atmospheric particles (upper curve) and submicron particles (lower curve) in the driving layer of Lake Baikal, 30–31 July 2020.
Total concentrations of sulfate ions, nitrate ions, and ammonium cations in aerosol samples taken during the parking period near the station Boyarsk accounted for 88% of the total amount of ions.
Figure 5 shows the behavior of the microdispersed aerosol fraction in a clean atmosphere in the area of the Maloye More on Lake Baikal, located between the high mountain range of the Primorsky Ridge in the west and the island of Olkhon in the east. When the ship passed on 1 August 2020 in the Maloye More area, with weak northwestern and westerly winds and cloudy weather, the atmosphere along the entire route was washed out by precipitation and clean of anthropogenic impurities; moreover, there were heavy rains in the adjacent western territories.
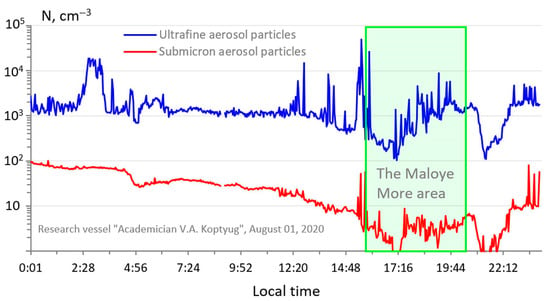
Figure 5.
Time course of the particle number concentration of the microdispersed aerosol fraction in the Maloye More area, 1 August 2020.
In conditions of a clean atmosphere, there was a sharp decrease in the concentration of submicron aerosol to the minimum values. In addition, the concentration of ultrafine atmospheric particles was also significantly reduced. Particles with an average size of 40–80 nm begin to predominate in the spectra of the ultrafine atmospheric particle’s distribution (Figure 6).
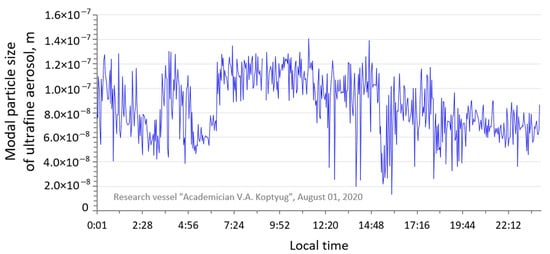
Figure 6.
Daily course of modal particle size of ultrafine aerosol in Maloye More area, 1 August 2020.
Low concentrations of trace gases SO2, NOx, and O3 were also noted along the entire route in the Maloye More area. In the aerosol samples taken in this area, the sum of the concentrations of the main ions was 0.646 μg m−3 and was one of the lowest for the entire measurement period on Lake Baikal. The results of calculating the particle deposition flux density on the lake surface under these background conditions indicate a decrease in the particle deposition rate of both ultrafine and submicron aerosols.
The features of the behavior of the flux density of aerosol particles during fogs and smoke emission from forest fires were considered. In the morning hours, when the vessel departed from Cape Muzhinay in Middle Baikal, under conditions of a high density of fog droplets in the coastal zone, a sharp decrease in submicron aerosol was noted (Figure 7) due to their humidification and coarsening to sizes beyond the range of sizes of the submicron fraction, since natural fogs usually consist of droplets with a diameter of up to 10 microns or more.
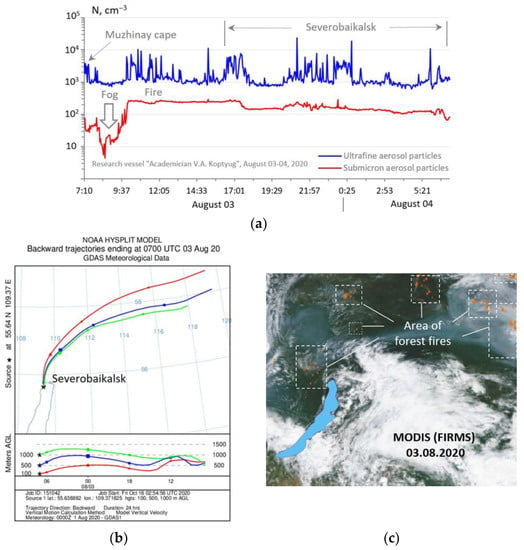
Figure 7.
Temporal variation of concentration of aerosol particles in the driving layer of Lake Baikal during fog and smoke emission in the period of 3–4 August 2020 (a); reverse trajectories of movement of air masses according to the HYSPLIT model (b); and map of wildfires according to MODIS satellite data (c).
Particles-droplets can grow under conditions of relatively low saturation, since already at r ≥ 0.5 μm the saturation moisture content above a convex surface E(r) is almost the same as the saturation moisture content above a flat surface E(∞), especially over fresh water [54]. On the other hand, large particles have a higher deposition rate on the water surface than small particles; therefore, the decrease in the concentration of ultrafine particles is manifested to a much lesser extent than the concentration of particles of the submicron fraction.
Deposition as a function of particle size is high for nanoparticles, moves through a minimum of about 0.5 um, and rises again from impaction or inertial forces. The results of calculating the density of sedimentation fluxes indicate that in some periods the sedimentation rate of large particles can be higher than that of ultrafine atmospheric particles (Figure 8). Sedimentation only affects particles >10–30 μm.
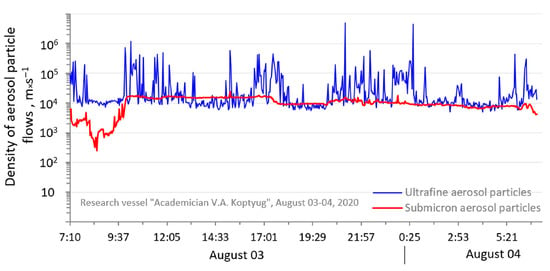
Figure 8.
Temporal variability of density of aerosol particle flows on the surface of Middle Baikal, 3–4 August 2020.
Forest fires can play a significant role in atmospheric chemistry and contribute to climate change [55,56,57,58,59,60]. With the appearance of smoke plumes in Northern Baikal from the centers of intense forest fires recorded in the north of the Irkutsk region and in Yakutia according to MODIS satellite data (FIRMS) [61] and calculations using the HYSPLIT model, a sharp increase in the concentration of submicron aerosol from 60 cm−3 to 300 cm−3 occurred and remained high, while fine particles remained on average at 1000 cm−3 with local bursts (more than 10,000 cm−3) in the morning, afternoon, and evening hours. Wildfire emissions can be important for local air pollution levels [62,63].
With long-distance transport of smoke aerosol, there is always a coagulated mode of submicron aerosol particles of high concentration, which eats away the ultrafine dispersed fraction of aerosol, preventing the formation of new particles, since larger particles, having a well-developed specific surface area, take on those atmospheric impurities that can serve the source of the formation of new particles [64]. Under the conditions of smoke emission along the entire route of the ship’s movement to Severobaikalsk, high concentrations of sulfur dioxide SO2 (12–14 μg m−3) with an increase up to 18 μg m−3 were also recorded (Figure 2b). The aerosol samples were dominated by sulfates (2.071 μg m−3), which accounted for 61% of the total amount of ions.
While maintaining high concentrations of submicron aerosol (over 200 cm−3) under the conditions of smoke outflows during the stay in Ayaya Bay near the eastern coast of Lake Baikal, local spikes in the concentration of ultrafine atmospheric particles were detected in the evening and in the morning (Figure 9b).
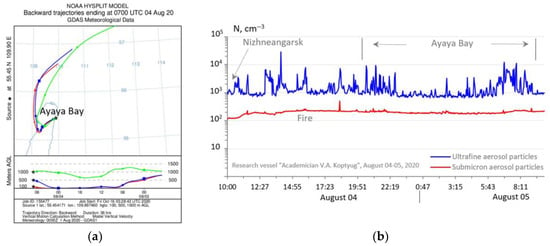
Figure 9.
Backward trajectories of the movement of air masses according to the HYSPLIT model (a); the time course of the concentration of ultrafine and submicron aerosol in the near-water of Lake Baikal in the period 4–5 August 2020 (b).
Here, the influence of breeze situations on Lake Baikal, associated with the transfer of organic matter from the forest vegetation of the coastal zone to the water area in the evening hours, was also clearly manifested
With the decrease in the influence of smoke emissions along the ship’s route along the eastern coast of Lake Baikal, a significant decrease in the concentration of submicron aerosol was noted, from 200 to 20 particles/cm3. When the wind direction changed to the east and southeast in the Chivyrkuisky Bay, anthropogenic sources of emissions from the settlements of Ust-Barguzin, Kurbulik, Monakhovo, and Katun, located on the eastern coast of Lake Baikal, began to influence the atmosphere of Baikal.
The influence of anthropogenic emissions leads to local increases in the concentrations of aerosol particles and sulfur dioxide when a vessel passes near emission sources. Thus, in Chivyrkuisky Bay, an increase in SO2 concentration was observed up to 10 μg m−3 in the area of Monakhovo settlement, in Zmeinaya Bay, and at the exit from the Chivyrkuisky Bay up to 15 μg m−3.
Upon arrival of the vessel “V.A. Koptyug” to the settlement Turka, one of the largest ports on the eastern coast of Lake Baikal, the concentration of nitrogen oxides increased sharply up to 10–12 μg m−3) and sulfur dioxide up to 12–14 μg m−3 (Figure 10).
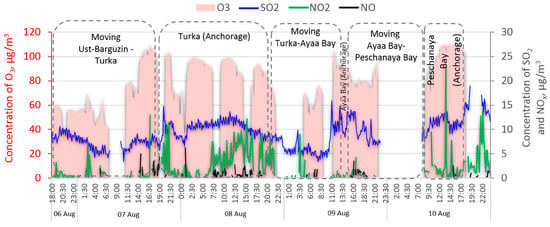
Figure 10.
The spatial–temporal variation of the concentration of trace gases in the near-water layer of Lake Baikal during the period of 6–10 August 2020.
The chemical composition of aerosol in the atmosphere of Turka shows its strong dependence on local sources of aerosols. The aerosol samples were dominated by sulfate ions (1.08 μg m−3), whose share was 55% of the total amount of ions, with nitrate ions (11%) and ammonium cations (13%) (Figure 11).
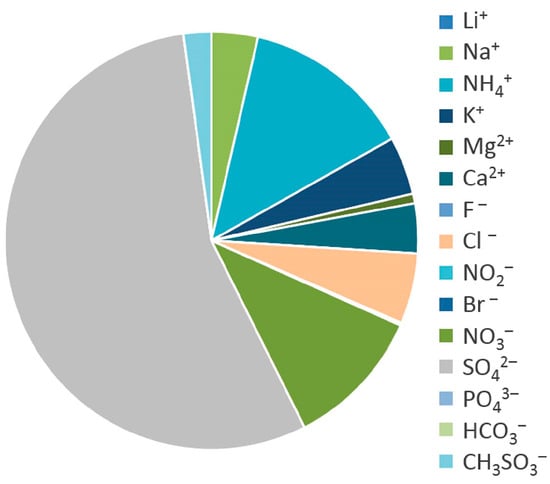
Figure 11.
Component composition of atmospheric aerosols in the settlement of Turka, 7–8 August 2020.
Against the background of an increase in the content of trace gases SO2 and NOx, there was simultaneously an increase in the concentration of ultrafine aerosol (Figure 12), since microdispersed fractions of nanoparticles, the so-called secondary aerosols, were formed as a result of photochemical and chemical reactions in the atmosphere not only from the products of organic compounds mentioned above but also from sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and some other gases with oxidizing agents, such as ozone and various radicals, as well as water vapor and aerosol particles [45,46].
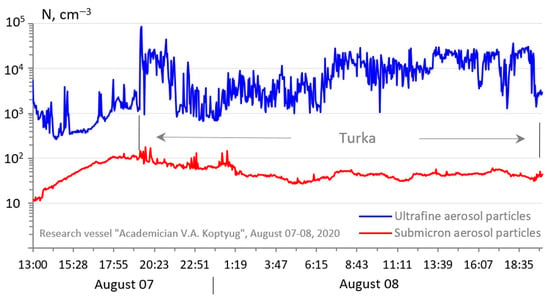
Figure 12.
Temporal variation of the concentration of ultrafine and submicron aerosol in the near-water layer of Lake Baikal in the period 7–8 August 2020 (Turka settlement).
In the daily course of the concentration of particles of the ultrafine aerosol, a pronounced night and evening minimum was observed; the maximum values were observed in the morning and afternoon hours (Figure 13a).
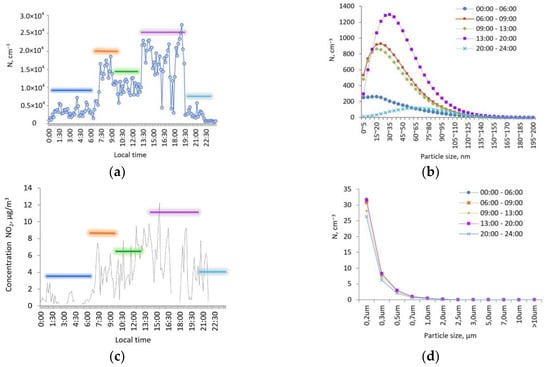
Figure 13.
The daily course: the particle number concentration of the microdisperse fraction (a); particle distribution spectra (b); concentration of NO2 (c); and particle distribution spectra of the submicron aerosol (d), 8 August 2020.
The main contribution to the concentration was made by particles from 5 to 80 nm. In the morning and afternoon hours, the concentration of an aerosol with a size of d < 80 nm dominated (Figure 13b) relative to concentrations at night and evening hours, since the formation of nanoparticles in the troposphere is closely related to solar activity initiating photochemical transformations in the atmosphere. Morning and midday peaks of the concentration of particles could be associated with morning primary emissions from human activity and ozone photochemistry peak later, just as well as NO2 correlation. The strongest relationship between the particle number concentration of ultrafine aerosol was manifested with the concentration of nitrogen dioxide NO2; the correlation coefficient was 0.61.
4. Conclusions
During the expedition on the research vessel (SRV) “Academician V.A. Koptyug” from 29 July to 11 August 2020, the studies of the spatial and temporal variability of physical, microphysical, and chemical characteristics of atmospheric aerosol, small gas impurities, and meteorological processes over the water area of Lake Baikal were carried out. The applied methods and approaches enabled evaluation of the interrelations between changes in the spatial structure of the gaseous and aerosol loading and aerosol particles size distribution with the meteorological and synoptic situations.
The atmosphere of Lake Baikal is significantly influenced by both anthropogenic emissions and smoke emissions from forest fires. The changes in the average values of atmospheric components clearly show the influence of breeze circulations on Lake Baikal. Under the conditions of a night breeze, an increase in the concentration of highly dispersed aerosol particles was observed with a maximum of up to 10,000 particles/cm3 at 0:30–1:00 and at the same time a synchronous decrease in the concentration of submicron aerosol to 25–30 particles/cm3.
With the appearance of smoke plumes from the centers of intense forest fires, a sharp increase in the concentration of submicron aerosol from 60 particles/cm3 to 300 particles/cm3 was observed, and it remained high, while highly dispersed particles remained on average at 1000 particles/cm3 with local bursts (more than 10,000 particles/cm3).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.Z. and A.Z.; methodology, A.Z. and G.Z.; data curation, A.Z., G.Z. and V.T.; software, V.T., T.B. and A.D.; investigation, A.Z., G.Z., T.B., A.D., T.K. and V.T.; resources, A.Z. and G.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, G.Z. and A.Z.; writing—review and editing, A.Z., G.Z. and V.T.; visualization, A.Z. and V.T.; supervision, G.Z., T.K.; project administration, G.Z., T.K. and A.Z.; funding acquisition, G.Z., T.K. and A.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by RFBR, project number 19-05-50005 «Micromir» and partly supported by budget funds for IPMS SB RAS within the State Assignment No. 0270-2021-0005 in organization of expedition on Lake Baikal.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Abbatt, J.P.D.; Leaitch, W.R.; Aliabadi, A.A.; Bertram, A.K.; Blanchet, J.P.; Boivin-Rioux, A.; Bozem, H.; Burkart, J.; Chang, R.Y.W.; Charette, J.; et al. Overview paper: New insights into aerosol and climate in the Arctic. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 2527–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leonardi, A.; Ricker, H.M.; Gale, A.G.; Ball, B.T.; Odbadrakh, T.T.; Shields, G.C.; Navea, J.G. Particle formation and surface processes on atmospheric aerosols: A review of applied quantum chemical calculations. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2020, 120, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warneck, P. Chemistry of the Natural Atmosphere; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, F.; Kärcher, B.; Fiebig, M.; Petzold, A. Aerosol states in the free troposphere at northern midlatitudes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, LAC-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Penner, J.E.; Andreae, M.; Annegarn, H.; Barrie, L.; Feichter, J.; Hegg, D.; Jayaraman, A.; Leaitch, R.; Murphy, D.; Nganga, J.; et al. Aerosols, their Direct and Indirect Effects. In Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis: Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Houghton, J.T., Ding, Y., Griggs, D.J., Noguer, M., van der Linden, P.J., Dai, X., Maskell, K., Johnson, C.A., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001; pp. 289–348. [Google Scholar]
- Hallquist, M.; Wenger, J.C.; Baltensperger, U.; Rudich, Y.; Simpson, D.; Claeys, M.; Dommen, J.; Donahue, N.M.; George, C.; Goldstein, A.H.; et al. The formation, properties and impact of secondary organic aerosol: Current and emerging issues. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5155–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivlev, L.S. Chemical Composition and Structure of Atmospheric Aerosols; Publishing House of Leningrad State University: Leningrad, Russia, 1982; pp. 233–278. [Google Scholar]
- Smirnov, V.V. Nature and evolution of ultrafine aerosol particles in the atmosphere. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2006, 42, 663–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miikka, D.M.; Markku, K.; Ilona, R.; Robert, W.; Tareq, H.; Pasi, P.A.; Kari, E.J. Formation and growth of fresh atmospheric aerosols: Eight years of aerosol size distribution data from SMEAR II, Hyytiälä, Finland. Boreal Environ. Res. 2005, 10, 323–336. [Google Scholar]
- Kulmala, M.; Vehkamäki, H.; Petäjä, T.; Dal Maso, M.; Lauri, A.; Kerminen, V.M.; Birmili, W.; McMurry, P. Formation and growth rates of ultrafine atmospheric particles: A review of observations. J. Aerosol Sci. 2004, 35, 143–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petaja, T.; Vakkari, V.; Pohja, T.; Nieminen, T.; Laakso, H.; Aalto, P.P.; Keronen, P.; Siivola, E.; Kerminen, V.M.; Kulmala, M.; et al. Transportable Aerosol Characterization Trailer with Trace Gas Chemistry: Design, Instruments and Verification. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hidy, G.M. Aerosols and Atmospheric Chemistry; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1972; pp. 120–127. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Air Quality Guidelines: Global Update 2005: Particulate Matter, Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, and Sulfur Dioxide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Guerreiro, C.B.B.; Foltescu, V.; de Leeuw, F. Air quality status and trends in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 98, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zagaynov, V.A.; Kulmala, M.; Lyubovtseva, Y.S.; Lushnikov, A.A.; Sogacheva, L.; Khodzher, T.V. Nucleation bursts in the atmosphere of Central Siberia. In Proceedings of the NOSA 2006 Aerosol Symposium, Helsinki, Finland, 8–10 November 2006; Finnish-Czech Aerosol Symposium: Helsinki, Finland, 2006; pp. 419–423. [Google Scholar]
- Zagaynov, V.A.; Lushnikov, A.A.; Nikitin, O.N.; Kravchenko, P.E.; Khodzher, T.V.; Petryanov-Sokolov, I.V. Background aerosol over Lake of Baikal. Dokl. Akad. Nauk. 1989, 308, 1087–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Documents of Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment of the Russian Federation. Available online: http://www.mnr.gov.ru/docs/gosudarstvennye_doklady (accessed on 2 September 2021).
- Izmest’eva, L.R.; Moore, M.V.; Hampton, S.E.; Ferwerda, C.J.; Gray, D.K.; Woo, K.H.; Pislegina, H.V.; Krashchuk, L.S.; Shimaraeva, S.V.; Silow, E.A. Lake-wide physical and biological trends associated with warming in Lake Baikal. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 0380–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shvidenko, A.Z.; Schepaschenko, D.G. Climate change and wildfires in Russia. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2013, 6, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov, M.Y.; Marinaite, I.I.; Golobokova, L.P.; Khuriganova, O.I.; Khodzher, T.V.; Semenov, Y.M. Source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Lake Baikal water and adjacent air layer. Chem. Ecol. 2017, 33, 977–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayakhanov, A.S.; Zhamsueva, G.S.; Tsydypov, V.V.; Balzhanov, T.S.; Balin, Y.S.; Kokhanenko, G.P.; Penner, I.E.; Nasonov, S.V. Features of the transport and transformation of aerosol and gas impurities in the atmosphere in the coastal zone of the Lake Baikal. Opt. Atmos. Okeana 2018, 31, 968–973. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.A.; Jacob, D.J.; Wang, Q.Q.; Bahreini, R.; Carouge, C.C.; Cubison, M.J.; Dibb, J.E.; Diehl, T.; Jimenez, J.L.; Leibensperger, E.M.; et al. Sources, distribution, and acidity of sulfate-ammonium aerosol in the Arctic in winter-spring. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 7301–7318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, L.; Li, Q.B.; Henze, D.K.; Tseng, H.L.; He, C.L. Sources of springtime surface black carbon in the Arctic: An adjoint analysis for April 2008. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 9697–9716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.; Ishizawa, M.; Chan, D.; Lavoue, D.; Andrews, E.; Eleftheriadis, K.; Maksyutov, S. 16-year simulation of Arctic black carbon: Transport, source contribution, and sensitivity analysis on deposition. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2013, 118, 943–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, A. Characteristics of atmospheric transport into the Arctic troposphere. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2006, 111, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayakhanov, A.S.; Zhamsueva, G.S.; Tcydypov, V.V.; Balzhanov, T.S.; Dementeva, A.L.; Khodzher, T.V. Investigation of Transport and Transformation of Tropospheric Ozone in Terrestrial Ecosystems of the Coastal Zone of Lake Baikal. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khodzher, T.V.; Zagaynov, V.A.; Lushnikov, A.A.; Chausov, V.D.; Zhamsueva, G.S.; Zayakhanov, A.S.; Tsydypov, V.V.; Potemkin, V.L.; Marinaite, I.I.; Maksimenko, V.V.; et al. Study of Aerosol Nano- and Submicron Particle Compositions in the Atmosphere of Lake Baikal During Natural Fire Events and Their Interaction with Water Surface. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravtsova, L.S.; Izhboldina, L.A.; Khanaev, I.V.; Pomazkina, G.V.; Rodionova, E.V.; Domysheva, V.M.; Sakirko, M.V.; Tomberg, I.V.; Kostornova, T.Y.; Kravchenko, O.S.; et al. Nearshore benthic blooms of filamentous green algae in Lake Baikal. J. Great Lakes Res. 2014, 40, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshkin, O.; Bondarenko, N.; Volkova, Y.A.; Tomberg, I.; Vishnyakov, V.; Malnik, V. Mass development of green filamentous algae of the genera Spirogyra and Stigeoclonium (Chlorophyta) in the littoral zone of the southern part of Lake Baikal. Hydrobiol. J. 2015, 51, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshkin, O.A.; Moore, M.V.; Kulikova, N.N.; Tomberg, I.V.; Malnik, V.V.; Shimaraev, M.N.; Troitskaya, E.S.; Shirokaya, A.A.; Sinyukovich, V.N.; Zaitseva, E.P.; et al. Groundwater contamination by sewage causes benthic algal outbreaks in the littoral zone of Lake Baikal (East Siberia). J. Great Lakes Res. 2018, 44, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuriganova, O.I.; Obolkin, V.A.; Golobokova, L.P.; Khodzher, T.V. Variability of gas impurities in the ground atmosphere of South-Eastern Siberia. In Proceedings of the 24th International Symposium on Atmospheric and Ocean Optics—Atmospheric Physics, Tomsk, Russia, 2–5 July 2018; Spie-Int Soc Optical Engineering: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2018; Volume 10833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obolkin, V.A.; Maysyuk, E.P.; Ivanova, I.Y.; Khodzher, T.V. Nitrogen oxides in the atmosphere of coastal areas of Lake Baikal. Sources and possible impact on the ecosystem of the lake. In Proceedings of the 24th International Symposium on Atmospheric and Ocean Optics—Atmospheric Physics, Tomsk, Russia, 2–5 July 2018; Spie-Int Soc Optical Engineering: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2018; Volume 10833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakirko, M.V.; Panchenko, M.V.; Domysheva, V.M.; Pestunov, D.A. Diurnal Rhythms of Carbon Dioxide Concentration in the Sea-level Air Layer and in the Surface Water of Lake Baikal in Different Hydrological Seasons. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2008, 33, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julanov, Y.V.; Lushnikov, A.A.; Zagaynov, V.A. Diffusion aerosol spectrometer. Atmos. Res. 2002, 62, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayakhanov, A.S.; Zhamsueva, G.S.; Tsydypov, V.V.; Ayurzhanaev, A.A. Automated system for monitoring atmospheric pollution. Meas. Tech. 2008, 51, 1342–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quality Management. Available online: https://www.iso.org/ru/iso-9001-quality-management.html (accessed on 14 December 2021).
- Zayakhanov, A.S.; Zhamsueva, G.S.; Tsydypov, V.V. A Hardware-Software System for Monitoring the Content of Atmospheric Impurities. Meas. Tech. 2015, 58, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azbukin, A.A.; Bogushevich, A.Y.; Korolkov, V.A.; Tikhomirov, A.A.; Shelevoi, V.D. A field version of the AMK-03 automated ultrasonic meteorological complex. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2009, 34, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golobokova, L.; Khodzher, T.; Obolkin, V.; Potemkin, V.; Khuriganova, O.; Onischuk, N. Aerosol in the atmosphere of the Baikal region: History and contemporary researches. Limnol. Freshw. Biol. 2018, 1, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EMEP. Manual for Sampling and Chemical Analysis. EMEP Cooperative Programme for Monitoring and Evaluation of the Long-range Transmission of Air Pollutant in Europe. Available online: http://www.itm.su.se (accessed on 11 October 2020).
- NILU. The European Monitoring and Evaluation Programme/CCC-Report 1/95. Reference: 0-7726. Available online: http://www.nilu.no (accessed on 11 October 2020).
- The Quality Assurance/Science Activity Centre—Americas (QA/SAC-Americas). Available online: https://www.qasac-americas.org/ (accessed on 14 November 2021).
- Asia Center for Air Pollution Research (ACAP). Available online: https://www.acap.asia/ (accessed on 14 November 2021).
- Norwegian Institute for Air Research. Available online: https://www.nilu.com/ (accessed on 14 November 2021).
- Allan, M.A. Manual for the GAW Precipitation Chemistry Programme: Guidelines, Data Quality Objectives and Standard Operating Procedures; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute. Available online: https://www.aari.ru/ (accessed on 14 November 2021).
- ARL NOAA. Atmospheric Resource Laboratory NOAA. Available online: http://www.arl.noaa.gov (accessed on 14 November 2021).
- Hanaoka, T.; Masui, T. Exploring effective short-lived climate pollutant mitigation scenarios by considering synergies and trade-offs of combinations of air pollutant measures and low carbon measures towards the level of the 2 degrees C target in Asia. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadrevu, K.P.; Ohara, T. Greenhouse gases, Short-Lived Climate Pollutants and aerosol pollution in South/Southeast Asia–Drivers, states and impacts. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 277, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obolkin, V.A.; Potemkin, V.L.; Makukhin, V.L.; Khodzher, T.V.; Chipanina, E.V. Long-distance transport of plumes of atmospheric emissions from regional coal-fired CHPPs to the water area of South Baikal. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2009, 22, 853–858. [Google Scholar]
- Zayakhanov, A.S.; Zhamsueva, G.S.; Tsydypov, V.V.; Balzhanov, T.S. Daily dynamics of ozone and other small gas impurities in the coastal zone of Lake Baikal (station Boyarsky). Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2017, 8, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, R.V.; Jacob, D.J.; Yantosca, R.M.; Chin, M.; Ginoux, P. Global and regional decreases in tropospheric oxidants from photochemical effects of aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshinov, M.Y.; Belan, B.D. Investigation of the dispersed aerosol composition during spring haze and forest fires. Opt. Atmos. Okeana J. 2011, 24, 468–477. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ivlev, L.S. Mechanisms of formation and decomposition of atmospheric aerosols and clouds and their ecological significance. Interdiscip. Sci. Appl. J. Biosph. 2013, 5, 82–210. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Reichstein, M.; Carvalhais, N. Aspects of Forest Biomass in the Earth System: Its Role and Major Unknowns. Surv. Geophys. 2019, 40, 693–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keywood, M.; Kanakidou, M.; Stohl, A.; Dentener, F.; Grassi, G.; Meyer, C.P.; Torseth, K.; Edwards, D.; Thompson, A.M.; Lohmann, U.; et al. Fire in the Air: Biomass Burning Impacts in a Changing Climate. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 43, 40–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccracken, M.C.; Cess, R.D.; Potter, G.L. Climatic effects of anthropogenic arctic aerosols—An illustration of climate feedback mechanisms with one-dimensional and two-dimensional climate models. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 1986, 91, 14445–14450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penner, J.E.; Ghan, S.J.; Walton, J.J. The role of biomass burning in the budget and cycle of carbonaceous soot aerosols and their climate impact. In Global Biomass Burning: Atmospheric, Climatic, and Biospheric Implications; Massachusetts Inst of Tech Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1991; pp. 387–393. [Google Scholar]
- Stohl, A.; Berg, T.; Burkhart, J.F.; Fjaeraa, A.M.; Forster, C.; Herber, A.; Hov, O.; Lunder, C.; McMillan, W.W.; Oltmans, S.; et al. Arctic smoke—Record high air pollution levels in the European Arctic due to agricultural fires in Eastern Europe in spring 2006. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 511–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobziar, L.N.; Thompson, G.R. Wildfire smoke, a potential infectious agent. Science 2020, 370, 1408–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satellite Monitoring of Fires in the Far East. Available online: http://fires-dv.kosmosnimki.ru/ (accessed on 14 November 2021).
- Vardy, M.; Oppenheimer, M.; Dubash, N.K.; O’Reilly, J.; Jamieson, D. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Challenges and Opportunities. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2017, 42, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andreae, M.O. Emission of trace gases and aerosols from biomass burning—An updated assessment. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 8523–8546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.H.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J.; von Hoyningen-Huene, W. Impact of the smoke aerosol from Russian forest fires on the atmospheric environment over Korea during May 2003. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).