Abstract
Particulate matter contributes much to the haze pollution in China. Meteorological conditions and environmental management significantly influenced the accumulation, deposition, transportation, diffusion, and emission intensity of particulate matter. In this study, temporal and spatial variations of PM10 and PM2.5—and the responses to meteorological factors and environmental regulation intensity—were explored in Xi’an, China. The concentrations of PM10 were higher than those of PM2.5, especially in spring and winter. The mean annual concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 markedly decreased from 2013 to 2017, but the decreasing trend has plateaued since 2015. The concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 exhibited seasonal differences, with winter being the highest and summer the lowest. Air quality monitoring stations did not reveal significant spatial variability in PM10 and PM2.5 concentrations. The concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 were significantly influenced by precipitation, relative humidity, and atmospheric temperature. The impact of wind speed was prominent in autumn and winter, while in spring and summer the impact of wind direction was obvious. Additionally, the emission intensity of SO2, smoke and dust could be effectively decreased with the increasing environmental regulation intensity, but not the concentrations of particulate matter. This study could provide a scientific framework for atmospheric pollution management.
1. Introduction
With rapid urbanization and industrialization, air quality has been deteriorating in many cities in China, resulting in major environmental problems [1,2,3]. Particulate matter, such as PM2.5 (particles with diameter less than 2.5 μm) and PM10 (particles with diameter less than 10 μm), are regarded as the dominant pollutants influencing air quality [4]. PM2.5 components are complex, predominantly generated by human activities and natural release, and the former is more harmful. PM2.5 are mainly chemically formed, or condensed from hot vapor (i.e., diesel exhaust) and coagulated into fine particles. PM10, mainly derived from natural processes and imperfect combustion, and commonly affected by the suspension and transport of sand and soil particles [5,6]. Given the negative effects of particulate matter on human health, governments have implemented strict pollutant reduction measures, which were deemed as an effective way for air quality improvement [7]. The concentrations of particulate matter across timescales can provide insight into the myriad causes of observed variations in air pollution [8]. Data at the annual scale can reflect the effects of mitigation strategies implemented by the government [9]. Seasonal variations of air quality are conducive to parsing the contribution of meteorological conditions, and the intensity of emissions [10,11]. Studies have shown that particulate matter exerts a serious impact on the air quality in spring and winter [12]. In addition, the spatial heterogeneity of air quality can reveal the effectiveness of environmental regulation practices [13,14]. Though local emissions contribute to the air pollution, the meteorological conditions are also at play, affecting the accumulation, deposition, transportation, and diffusion of air pollutants [2,15]. The meteorological factors showed a non-linear relationship with the concentrations of particulate matter [16]. Therefore, the temporal and spatial characteristics captured by air quality and the relationship with meteorological conditions and environmental management also deserve further investigation.
Unregulated local emissions elevate the concentrations of particulate matter, especially in developing regions [17]. For example, in China, the large-scale emission sources of PM10 and PM2.5 include coal combustion, traffic engine exhausts, biomass burning, industrial activities, fugitive dust from construction activities and sandstorms [18,19]. Particulate matter as the primary pollutant (i.e., the concentration is higher than other atmospheric pollutants) with a higher proportion [12], its improvement plays a key role in improving air quality, especially in cities of the semi-arid and arid regions in western and northwestern China, where fugitive dust is the major component of aerosol particles.
Xi’an, the capital city of Shaanxi province, with an area of 10,108 km2 and a population of 13.0 million, is the most urbanized region in northwestern China. Due to the topography, meteorological conditions, and tremendous amount of atmospheric pollutants emissions derived from urbanization and industrialization, Xi’an has been plagued by severe air pollution over the last decade [6,20]. PM10 and PM2.5 contribute more than 90% of all air pollutants, which are regarded as the dominant controller of air quality in this region [12,21]. In recent years, atmosphere environment protection policies have been vigorously implemented in Xi’an, but few studies have assessed the effectiveness of environmental management in improving atmospheric pollution. The atmospheric pollution in Xi’an exhibits seasonal dependence. Bare surface and strong wind in spring, and biomass burning and coal combustion from intensive heating demand in winter—accompanied with meteorological factors closely related to atmospheric pollution—all promote an abundance of particulate matter and visibility impairment [1,6,22]. Evaluation and improvement of air quality in the context of changes in energy consumption and rapid urbanization is conducive to the future development and sustainability of other megacities in northwest China.
In this study, PM10 and PM2.5 from 13 air monitoring stations in Xi’an from 2013 to 2017 were analyzed. We aimed to: (1) characterize the temporal and spatial variations of PM10 and PM2.5 in Xi’an; (2) analyze the relationships between particulate matter and meteorological conditions; and (3) explore the response of the concentration and emission intensity of atmospheric pollutants to the environmental management. This study aims to provide a scientific framework for atmospheric pollution management.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Xi’an, the capital of Shaanxi Province, is a megacity in western China, located at the central part of the Guanzhong Plain, with the Loess Plateau to the north, and the Qingling Mountains to the south. Xi’an is situated in a sub-humid and warm temperate region under the influence of the East Asian monsoon with hot and humid summers, and cold winters. During the warm period (May–October), winds blow in from southern China; during the cold period (November–April), winds from the desert regions of north-western and western China are dominant. Over the period of 2001–2017, the average annual temperature was 13.6 °C, and the annual precipitation was 558.2 mm (http://data.cma.cn/, accseed on 1 March 2020).
2.2. Particulate Matter Datasets
The atmospheric environment monitoring network in Xi’an is composed of 13 national air quality real-time monitoring stations: the Voltage Switchgear Factory (VS), the Xingqing Community (XQ), Textile City (TC), Xiaozhai (XZ), People’s Stadium (PS), High-tech District (HT), the Economic Development District (ED), Chang’an District (CA), Yanliang District (YL), Lintong District (LT), Caotan (CT), Qujiang (QJ), and Guangyun Lake (GY) (Figure 1). The daily mean concentrations of particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5) at each station, from 1 January 2013 to 31 December 2017, were used in the analysis. These data are publicly available at the Xi’an Ecology and Environment Bureau (http://xaepb.xa.gov.cn/, accessed on 9 July 2021).
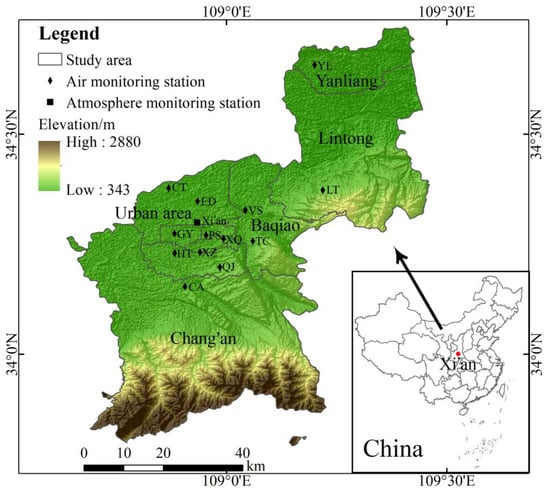
Figure 1.
Distribution of air monitoring stations and atmosphere monitoring station.
According to the emissions standards of air pollutants from the Ambient Air Quality Standard (GB 3095-2012) [23]. Grade 1 concentration limits (24 h average) of PM10 and PM2.5 are 50 μg/m3 and 35 μg/m3, which are the maximum concentrations healthy for humans. Grade 3 concentration limits of PM10 and PM2.5 are 150 μg/m3 and 75 μg/m3, which are unhealthy for humans.
2.3. Meteorological Datasets
The meteorological datasets for Xi’an covers 5 years from 2013 to 2017, obtained from the National Meteorological Information Centre (http://data.cma.cn/, accessed on 8 June 2019). Six meteorological indices were selected to study the influence of meteorological conditions on atmospheric pollutants, including mean daily total precipitation, atmospheric pressure, relative humidity, atmospheric temperature, wind speed, and wind direction.
2.4. Environmental Management
Environmental management in this study refers to the calculated emission intensity, environmental regulation intensity. The emission intensity is targeted at Xi’an, based on the ratio of the SO2, soot, and dust emissions to GDP. The environmental regulation intensity is targeted at Shaanxi province, based on the emissions and environmental investment.
The environmental regulation intensity is measured by environmental governance investment per unit of atmospheric pollutant emissions. The calculation formula is
where ERI represents the strength of environmental regulations; Inv. represents the investment in atmospheric environmental improvement; Pollu. represents the concentrations of atmospheric pollutants.
ERI = Inv./Pollu.
Environmental management datasets were obtained from the Statistical Yearbook (http://www.stats.gov.cn/, accessed on 6 May 2020), including the emission intensity (t/104 RMB) and the environmental regulation investment (108 RMB) in Xi’an, Shaanxi province.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test was used to confirm that the datasets followed a normal distribution, and the analysis method was dependent on the results of the K-S test. Spearman correlation analysis was carried out between the concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5. Spearman correlation coefficients were also calculated for the relationships between atmospheric pollutants and the meteorological factors, environmental regulation intensity. One-way ANOVA and t-pair test were conducted to analyze differences at different monitoring sites and time scales (annual, seasonal, and monthly). All data analyses and figure drawings were performed in SPSS 20.0 and MATLAB R2019a.
3. Results
3.1. Temporal Variations in the Concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5
The mean annual, seasonal, and monthly concentrations of PM10 were all higher than those of PM2.5 (Figure 2). Intra-annual variations in the concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 exhibited similar characteristics during 2013–2017. From 2013 to 2017, the mean annual concentration of PM10 in Xi’an declined from 186.3 μg/m3 to 131.7 μg/m3, with the lowest value in 2015 (128.0 μg/m3). The highest inter-annual decline rate was 19.2%, which occurred during 2013–2014. There was no significant difference (p > 0.05) between the mean annual concentrations of PM10 in 2015, 2016, and 2017 (Figure 2A). Similarly, the mean annual concentration of PM2.5 in Xi’an declined from 107.4 μg/m3 in 2013 to 73.7 μg/m3 in 2017, and the lowest value occurred in 2015 (58.1 μg/m3). The highest inter-annual decline rate was 27.9%, which occurred during 2013–2014. The differences between 2015, 2016, and 2017 were also nonsignificant (p > 0.05) (Figure 2B).
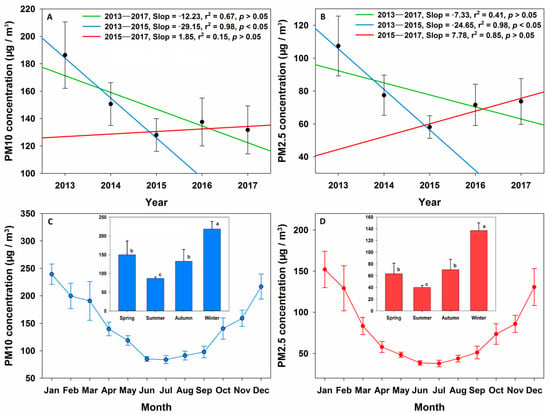
Figure 2.
Annual, seasonal, and monthly variations in the concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5. (A): interannual variation of PM10; (B): interannual variation of PM2.5; (C): intraannual variation of PM10; (D): intraannual variation of PM2.5.
The maximum seasonal concentrations of PM10 (218.5 μg/m3) and PM2.5 (137.2 μg/m3) were recorded in winter, and the minimum (86.7 and 40.0 μg/m3) in summer. The seasonal concentrations of PM10 in spring were higher than those in autumn, while the concentrations of PM2.5 in spring were lower than those in autumn, and the differences were all nonsignificant (p > 0.05) (Figure 2C,D). The maximum monthly concentrations of both PM10 (239.2 μg/m3) and PM2.5 (151.9 μg/m3) occurred in January. The monthly concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 decreased from January to June, with the lowest concentrations recorded in June (85.0 and 38.5 μg/m3). Concentrations then increased from June to December. The maximum inter-monthly decrease rate of PM10 and PM2.5 occurred during March–April (26.7% and 30.6%), while the maximum inter-monthly increase rates of PM10 and PM2.5 occurred during November–December (36.3% and 52.1%).
3.2. The Concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 at Different Air Monitoring Stations in Xi’an
As a whole, the concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 exhibited positive correlations (p < 0.05) during the days that exceeded the Grade 3 concentration limits (24 h average); and negative correlations (p < 0.05) during the days with Grade 1 concentration limits (24 h average) or lower (Table 1 and Figure 3).

Table 1.
Spearman correlation coefficients between concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 and the days that PM10 > 150 μg/m3, PM10 < 50 μg/m3, PM2.5 > 75 μg/m3, PM2.5 < 35 μg/m3.
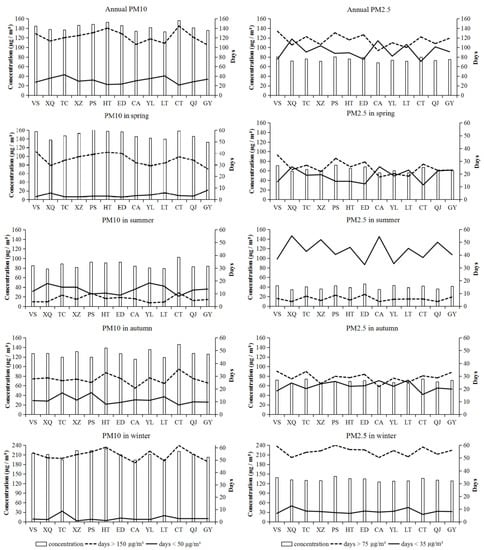
Figure 3.
Annual and seasonal concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 and the days that the concentrations lower than Grade 1 and higher than Grade 3 at different monitoring stations in Xi’an.
The concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 from all 13 of the air monitoring stations were involved to analyze the spatial differences in Xi’an. The concentrations of PM10, as well as PM2.5, among the 13 air monitoring stations were nonsignificant (p > 0.05), exhibiting similar characteristics of annual and seasonal concentrations (Figure 3).
The concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 among monitoring stations varied across temporal scales (Table 2). Annually, PM10 concentrations in Caotan (CT, 156.4 μg/m3) and High-Tech District (HT, 156.4 μg/m3) exceeded the Grade 3 concentration limit (>150 μg/m3); while PM2.5 concentrations in Voltage Switchgear Factory (VS, 80.2 μg/m3) (TC, 76.0 μg/m3), People’s Stadium (PS, 80.6 μg/m3), High-Tech District (HT, 76.4 μg/m3), Economic development District (ED, 79.2 μg/m3), and Caotan (CT, 76.9 μg/m3) exceeded the Grade 3 concentration limit (>75 μg/m3). Seasonally, in spring, PM10 concentrations in Voltage Switchgear Factory (VS, 157.1 μg/m3), Xiaozhai (XZ, 152.5 μg/m3), People’s Stadium (PS, 161.2 μg/m3), High-Tech District (HT, 157.3 μg/m3), Economic development District (ED, 156.4 μg/m3), and Caotan (CT, 158.3 μg/m3) exceeded the Grade 3 concentration limit; for PM2.5 concentrations, no station exceeded the Grade 3 concentration limit. In summer and autumn, neither the PM10 nor the PM2.5 exceeded the Grade 3 concentration limit. Whereas in winter, both PM10 and PM2.5 exceeded the Grade 3 concentration limit, with no monitoring station reaching the Grade 1 concentration limit for PM10 (<50 μg/m3). However, Xingqing Community (XQ, 34.5 μg/m3) and Chang’an District (CA, 35.0 μg/m3) meet the Grade 1 PM2.5 concentration limit (<35 μg/m3) in summer. The maximum PM10 concentration difference between seasons was identified in Xiaozhai (XZ, 142.1 μg/m3), the minimum in Textile City (TC, 106.0 μg/m3). The maximum PM2.5 concentration difference was found in People’s Stadium (PS, 100.4 μg/m3), the minimum in Yanliang District (YL, 84.5 μg/m3).

Table 2.
The concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 among monitoring stations in Xi’an annually and seasonally.
Overall, the concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 were highest in People’s Stadium (PS) and Caotan (CT), and lowest in the Xingqing Community (XQ), the Chang’an District (CA), the Lintong District (LT), and Guangyun Lake (GY).
3.3. Relationships between the Concentrations of Particulate Matter and Meteorological Factors
Spearman correlation coefficients between PM10 (and PM2.5) and meteorological factors varied across seasons, indicating that the dominant meteorological factors and their influence on PM10 and PM2.5 vary over time (Table 3 and Table 4).

Table 3.
Spearman correlations and multivariate progressive linear regression between PM10 and meteorological factors in Xi’an.

Table 4.
Spearman correlations and multivariate progressive linear regression between PM2.5 and meteorological factors in Xi’an.
Precipitation was negatively correlated with PM10 and PM2.5 (p < 0.01), except for PM2.5 in winter (p > 0.05). Atmospheric pressure was negatively correlated with PM10 and PM2.5 in summer and winter (p < 0.05), and positively correlated with the annual PM10 and PM2.5 (p < 0.05). Relative humidity showed a negative correlation (p < 0.05) with the annual and seasonal concentrations of PM10, except in winter. This same correlation with relative humidity was also exhibited for PM2.5 in spring and autumn, though a positive correlation was found with PM10 and PM2.5 in winter. Atmospheric temperature exhibited a negative correlation with PM10 and PM2.5 in spring and autumn, and a positive correlation in summer and winter. Wind speed only exhibited a negative correlation (p < 0.05) with PM10 and PM2.5 in autumn and winter. Finally, wind direction exhibited a negative correlation (p < 0.05) with PM10 and PM2.5 in all seasons except for autumn.
3.4. Response of Atmospheric Pollutants to the Environmental Management
Figure 4 displayed the emission intensity of SO2, smoke, and dust, and environmental regulation intensity in 2013–2017 in Xi’an. With the growth of economy, the emission intensity of SO2, smoke and dust exhibited declining trends during 2013–2017, especially SO2. In 2015–2016, the emission intensity of these atmospheric pollutants sharply declined from 9.49 to 1.20 t/108 RMB. However, the environmental regulation intensity (ERI) exhibited increasing trends during 2013–2017. In 2015–2016, ERI dramatically increased from 3.27 to 9.98.
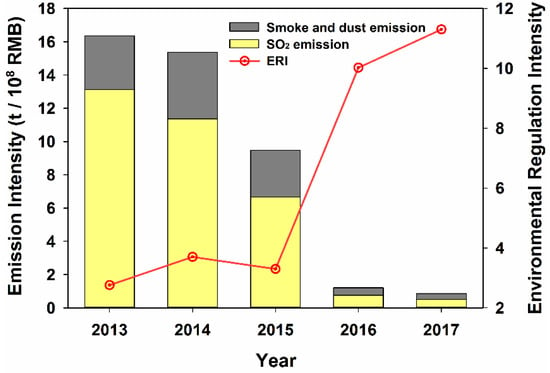
Figure 4.
Environmental regulation intensity and the emission intensity of SO2, smoke, and dust.
ERI was significantly and negatively correlated with the emission intensity of SO2, smoke and dust (p < 0.05), but not significantly correlated with the concentration of PM10 and PM2.5 (p > 0.05).
4. Discussion
4.1. Temporal and Spatial Variations of PM10 and PM2.5
The mean annual concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 decreased significantly from 2013 to 2017, while concentrations during 2015–2017 did not exhibit any significant variations. Studies have shown that improvements in air quality in megacities are significant in the early stages of governance and then stalled. The improvement of environmental quality rarely accompanies urbanization and industrialization [21]. The inter-annual variation may be attributed to human activities, including auto emissions and steel productions. Additionally, the demand for housing intensified by the expansion of urban land could increase construction dust emissions. The observed variations in the concentrations of PM2.5 and PM10 may thus be a result of specific weather conditions, combined with changes in land use and the increased development of urban infrastructure [2,24].
Regarding the seasonal variations in PM10 and PM2.5, both the highest concentrations occurred in winter and the lowest in summer, the second-highest in spring and autumn. This phenomenon might be attributable to frequent sandstorms originating in northwestern China with bare land cover and strong wind, which produced anomalously high concentrations of mineral dust, resulting in a prominent rise of particulate matter in spring [6]. In autumn, straw burning after agricultural harvests results in the rise in particulate matter concentrations. In addition, meteorological factors also play an important role in these processes. Cloudy weather and low wind speed could contribute to the elevated particulate matter concentrations [25]. Many cities seek to alter meteorological conditions to some extent by changing the urban landscape [26]. Wind and turbulence within the urban canopy can play an important role in local measurements of meteorological conditions. This is especially true if pollutants are frequently capped by a statically stable atmospheric layer [2,14]. Such stable conditions may contribute to the lack of spatial variations observed in the downtown area. Our results showed nonsignificant difference for the concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 among the 13 stations. Zhang et al. [27] analyzed the particulate matter at six sites in Xi’an, and also found nonsignificant spatial variations. However, the concentrations of particulate matter were lower in the stations that locate near places with higher tree coverage rates and large water bodies. Meanwhile, the concentrations were higher in the stations surrounded by high energy consumption and bare land. Based on these observations, we believe that the spatial homogeneity of the air quality is also affected by human activities (i.e., pollutant emissions and land use).
4.2. Effects of Meteorological Conditions and Environmental Management on Atmospheric Pollution
Affecting the formation, diffusion, dilution, transformation, transportation, and accumulation of airborne pollutants, meteorological conditions are crucial for establishing air quality levels [11,12]. In this study, the meteorological factors significantly influenced the seasonal variations of particulate matter concentrations. This is partly because of the stable interaction between particulate matter and meteorological factors. Precipitation, for example, can remove particulate matter in the atmosphere and reducing the concentrations across seasons [27,28]. However, there are also some unstable interactions. Within a certain range, the wind can dilute the concentrations of particulate matter, otherwise the effect could be the opposite. In spring, for instance, strong winds from the northwest can easily bring sandstorms from Loess Plateau and increase the concentrations of particulate matter. The increased relative humidity caused by precipitation can reduce the concentrations of particulate matter, whereas high relative humidity can accumulate water-soluble ions, such as NH4+, NO3−, and SO42−, which are major aerosol components during haze episodes [29,30]. In addition, there may be a combination of other factors, such as vegetation cover, which can adsorb the particulate matter. Vegetation cover is regulated by phenology, such as atmospheric temperature [14]. This may result in the different relationships between particulate matter and atmospheric temperature across seasons.
The environmental management could determine the pollution intensity and the types of pollutants. In this study, we found that the environmental regulation intensity could significantly alleviate the emissions of SO2, smoke and dust, neither the particulate matter (Table 5). Compared with SO2, smoke and dust, the composition, chemical process, and the influence factors of particulate matter are more complicated [30,31]. It may be ineffective by simply increasing the environmental regulation intensity in a short period. Therefore, further exploration and verification are needed in terms of environmental management.

Table 5.
Correlation coefficients between the environmental regulation intensity and the concentration and emission of atmospheric pollutants.
Considering the difficulty of artificial control of meteorological conditions, more attention has been paid to the environmental management, which has been confirmed as the effective way to the improvement of atmospheric pollution. A one-size-fits-all management model may also have side effects on the development of socio-economics in a developing region. To reduce atmospheric pollution, effective environmental management should factor in the seasonal meteorological conditions. For instance, increasing relative humidity is an effective measure to reduce airborne pollution in spring and autumn. In winter, it is quite clear that improving ventilation and reducing relative humidity may ameliorate some of the effects of atmospheric pollution [25,32]. It is necessary to implement the intensity of targeted atmospheric governance under specific meteorological conditions to achieve the sustainability of socio-economic development and environmental protection.
4.3. Further Work
Our results suggest that the worsening of air quality in Xi’an is mainly caused by the combination of human activities and natural sources. Many regulators believe that local air quality can be improved by efforts to reduce anthropogenic emissions, and controlling trans-boundary pollutants from the Gobi desert through increasing vegetation cover. It is necessary to investigate the effects of different types of human activities on air quality in the urban environment, and this will form the basis of our future work. Air monitoring stations that cover different environments are also needed. Further research should involve more monitoring systems by factoring in local land use, while involving both the downtown and suburban areas.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we explored the temporal and spatial trends of the concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 in Xi’an, China, and the response to the meteorological factors and environmental regulation intensity. The concentrations of PM10 were higher than those of PM2.5, especially in spring and winter. The annual, seasonal, and monthly variations of PM10 and PM2.5 were striking. In terms of seasonal variations, the air quality is best in summer, and worst in winter. The spatial characteristics of air quality did not reveal any significant spatial differences due to the air monitoring stations being concentrated in the downtown area.
Among the meteorological factors, precipitation, relative humidity, and atmospheric temperature had impacts on atmospheric pollution. Conversely, wind speed affected concentration only in autumn and winter, and wind direction affected them only in spring and summer. In addition, the effects of environmental regulation intensity were prominent (i.e., environmental governance investment per unit of air pollutant emissions).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.T. and H.S.; methodology, Y.T. and L.Z.; software, Y.T. and Y.W.; validation, Y.T., L.Z. and H.S.; formal analysis, Y.T. and L.Z.; investigation, Y.T. and L.Z.; resources, Y.T., L.Z. and J.S.; data curation, Y.T., L.Z. and Y.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.T.; writing—review and editing, Y.T. and H.S.; visualization, Y.T. and L.Z.; supervision, J.S.; project administration, J.S.; funding acquisition, J.S. and H.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi, grant number 2019ZDLSF05-02; the Open Research Fund of Key Laboratory for Ecology and Environment of River Wetlands in Shaanxi Province, grant number SXSD202002.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Huang, R.; Zhang, Y.L.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.; Cao, J.; Han, Y.M.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, C.; Liu, Y. Effects of China’s urban form on urban air quality. Urban Stud. 2016, 53, 2607–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, J.N.; Yung, Y.L.; Li, G.H.; Seinfeld, J.H. Unexpected air pollution with marked emission reductions during the COVID-19 outbreak in China. Science 2020, 369, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbai, S.E.; Li, C.L.; Boreave, A.; Charbonnel, N.; Perrier, S.; Vernoux, P.; Bentayeb, F.; George, C.; Gil, S. Atmospheric photochemistry and secondary aerosol formation of urban air in Lyon, France. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 99, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.J.; Qiao, Z.; Xu, X.L. Characteristics of particulate matter (PM10) and its relationship with meteorological factors during 2001-2012 in Beijing. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 192, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Huang, R.J.; Yang, L.; Ni, H.Y.; Wang, T.; Cao, W.J.; Duan, J.; Guo, J.; Huang, H.B.; Hoffmann, T. Concentrations, optical properties and sources of Humic-Like Substances (HULIS) in fine particulate matter in Xi’an, Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, L.; Rea, W.; Smith-Willis, P.; Fenyves, E.; Pan, Y.Q. Adverse health effects of outdoor air pollutants. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 815–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, Y.Q.; Guo, Z.H.; Li, Q.; Wu, D.; Ding, X.; Liu, A.L.; Huang, D.; Qiu, G.K.; Wu, M.M.; Zhao, Z.J.; et al. Chemical fingerprinting of HULIS in particulate matters emitted from residential coal and biomass combustion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 3593–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.J.; Cao, H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, C.Z.; Tao, H.; Fan, H.L. Spatial and temporal characteristics of air quality and air pollutants in 2013 in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 13996–14007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.J.; Wu, F.; Chow, J.; Lee, S.C.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.W.; An, Z.S.; Fung, K.K.; Watson, J.G.; Zhu, C.S.; et al. Characterization and source apportionment of atmospheric organic and elemental carbon during fall and winter of 2003 in Xi’an, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 3127–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, W.H.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, Y.; Wei, J.; Lu, T.W.; Che, Y.F.; Tian, Y.L. Spatiotemporal variations and relationships of aerosol-radiation-ecosystem productivity over China during 2001–2014. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.L.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xu, D.X.; Zhao, S.D.; He, L.H.; Liu, H.J.; Xu, H. Temporal and spatial trends in air quality in Beijing. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 185, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopke, P.K.; Cohen, D.D.; Begum, B.A.; Biswas, S.K.; Ni, B.F.; Pandit, G.G.; Santoso, M.; Chung, Y.; Rahman, S.A.; Hamzah, M.S.; et al. Urban air quality in the Asian region. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 404, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Yao, X.A.; Sun, R.H.; Chen, L.D. Effect of urban green patterns on surface urban cool islands and its seasonal variations. Urban For. Urban Gree. 2014, 13, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landguth, E.L.; Holden, Z.A.; Graham, J.; Stark, B.; Mokhtari, E.B.; Kaleczyc, E.; Anderson, S.; Urbanski, S.; Jolly, M.; Semmens, E.O.; et al. The delayed effect of wildfire season particulate matter on subsequent influenza season in a mountain west region of the USA. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Cao, J.J.; Shen, Z.X.; Han, Y.M.; Lee, S.C.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, C.S.; Wang, Q.Y.; Xu, H.M.; Huang, R.J. Spatial and seasonal variations of PM2.5 mass and species during 2010 in Xi’an, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 508, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Jing, J.; Tao, J.; Hsu, S.C.; Wang, G.; Cao, J.; Lee, C.S.L.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Chemical characterization and source apportionment of PM2.5 in Beijing: Seasonal perspective. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 7053–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Z.Z.; Yang, Y.Y.; Lu, J.L.; Zhang, C.X. Atmospheric particle characterization, distribution, and deposition in Xi’an, Shaanxi Province, Central China. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, A.; Vogt, U.; Panta, A.; Uprety, D. Vertical distribution of particulate matter, black carbon and ultra-fine particles in Stuttgart, Germany. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.X.; Hu, J.L.; Xu, Y.; Lv, D.; Xie, X.Y.; Kleeman, M.; Xing, J.; Zhang, H.L.; Ying, Q. Source contributions to primary and secondary inorganic particulate matter during a severe wintertime PM2.5 pollution episode in Xi’an, China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 97, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.H.; Wei, J.; Zhang, J.; Sun, L.; Che, Y.F.; Yuan, M.; Hu, X. Inferring near-surface PM2.5 concentrations from the VIIRS deep blue aerosol product in China: A spatiotemporally weighted random forest model. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Kong, S.F.; Wu, F.Q.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, S.R.; Qin, S.; Liu, X.; Yan, Q.; Zheng, H.; Zheng, M.M.; et al. The moving of high emission for biomass burning in China: View from multi-year emission estimation and human-driven forces. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Repblic of China. The Ambient Air Quality Standard (GB 3095-2012). 2012. Available online: http://www.mee.gov.cn/ (accessed on 4 August 2018).
- Elminir, H.K. Dependence of urban air pollutants on meteorology. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 350, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Liu, D.Y.; Yan, W.L. A Simple new method for calculating precipitation scavenging effect on particulate matter: Based on five-year data in Eastern China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Q.Z.; Li, B.; Ye, C.H.; Zhang, X.S.; Zhang, Y. Preliminary analysis about impacts of urban 3D landscape pattern on regional meteorological condition in Beijng. Ecology Environ. Sci. 2019, 28, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Cao, J.J.; Tie, X.X.; Shen, Z.X.; Liu, S.X.; Ding, H.; Han, Y.M.; Wang, G.H.; Ho, K.F.; Qiang, J.; et al. Water-soluble ions in atmospheric aerosols measured in Xi’an, China: Seasonal variations and sources. Atmos. Res. 2011, 102, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, S.X.; Wu, X. Meteorological change and impacts on air pollution: Results from North China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.X.; Cao, J.J.; Arimoto, R.; Han, Z.W.; Zhang, R.J.; Han, Y.M.; Liu, S.X.; Okuda, T.; Nakao, S.; Tanaka, S. Ionic composition of TSP and PM2.5 during dust storms and air pollution episodes at Xi’an, China. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2911–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Yang, L.; Shen, J.C.; Yuan, W.; Gong, Y.Q.; Guo, J.; Cao, W.J.; Duan, J.; Ni, H.Y.; Zhu, C.S.; et al. Water-insoluble organics dominate brown carbon in wintertime urban aerosol of China: Chemical characteristics and optical properties. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7836–7847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.H.; Han, J.Z.; Hopke, P.K.; Hu, J.G.; Shu, Q.; Chang, Q.; Ying, Q. Quantifying primary and secondary humic like substances in urban aerosol based on emission source characterization and a source-oriented air quality model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 2327–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beaver, S.; Tanrikulu, S.; Palazoglu, A.; Singh, A.; Soong, S.T.; Jia, Y.Q.; Tran, C.; Ainslie, B.; Steyn, D.G. Pattern-based evaluation of coupled meteorological and air quality models. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2010, 49, 2077–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).