Speciation of Magnesium in Aerosols Using X-ray Absorption Near-Edge Structure Related to Its Contribution to Neutralization Reactions in the Atmosphere
Abstract
1. Introduction
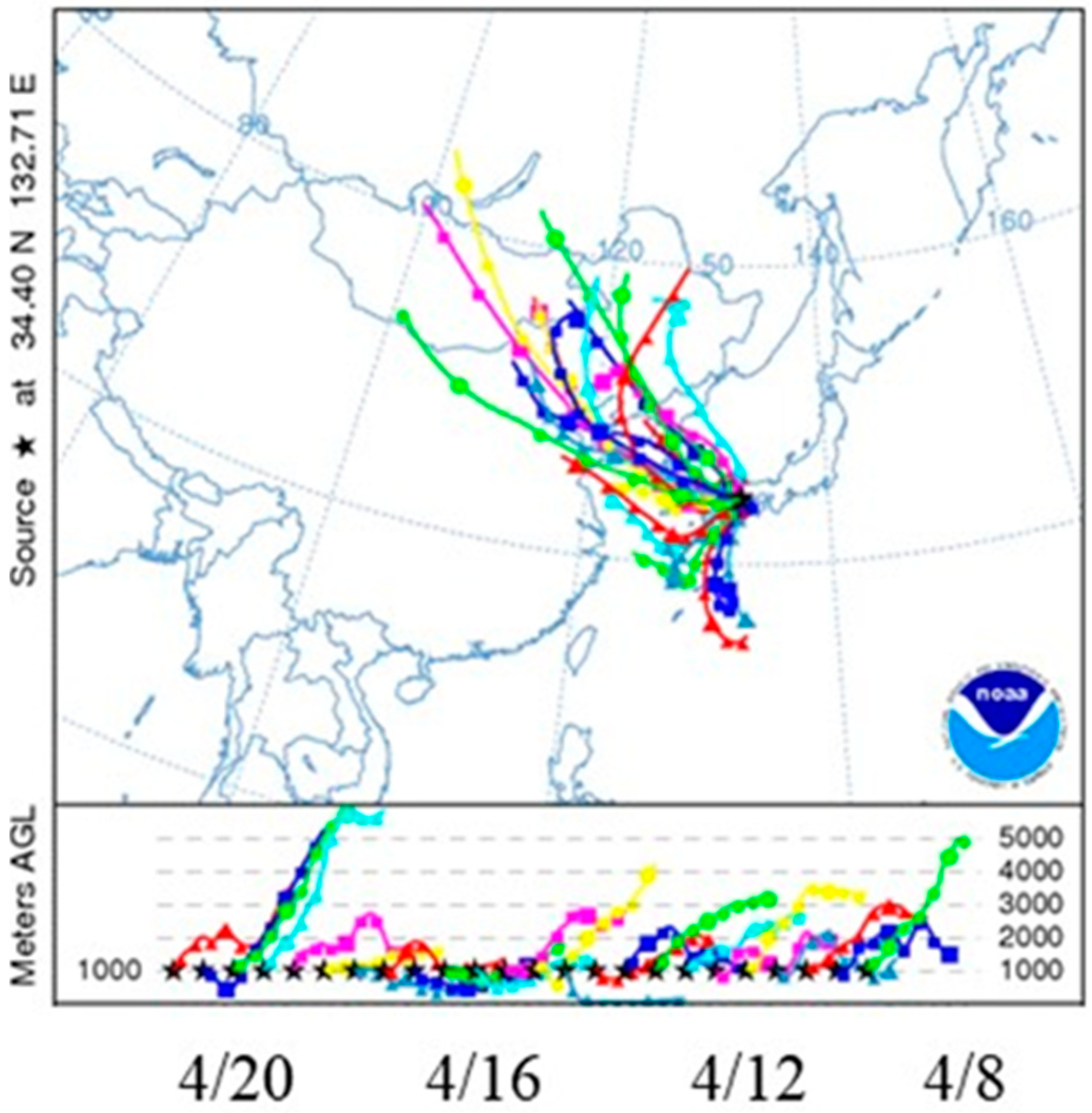
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
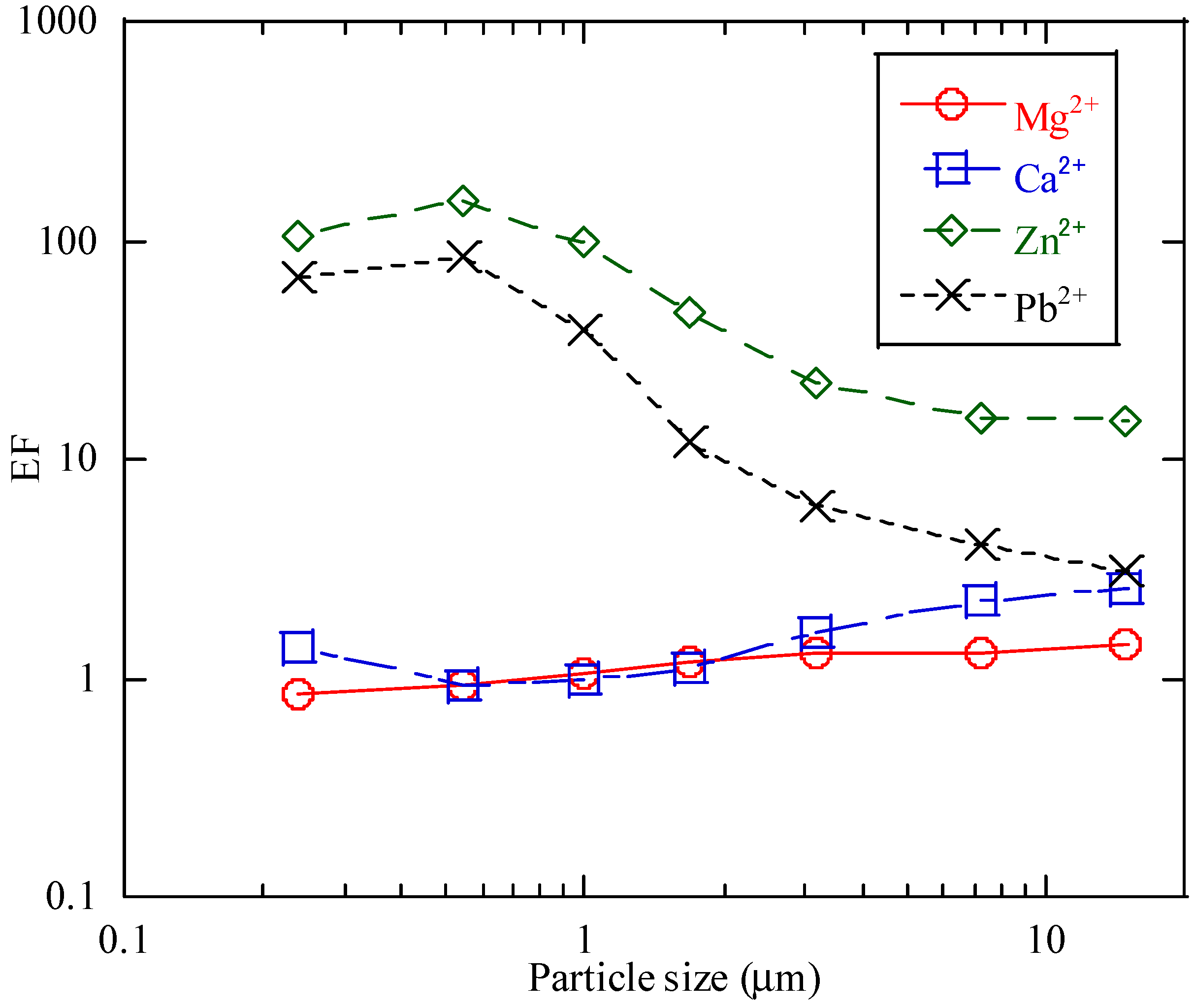
3.1. Concentrations of Various Elements in the Aerosol Samples
3.2. Speciation of Ca by Ca K-Edge XANES
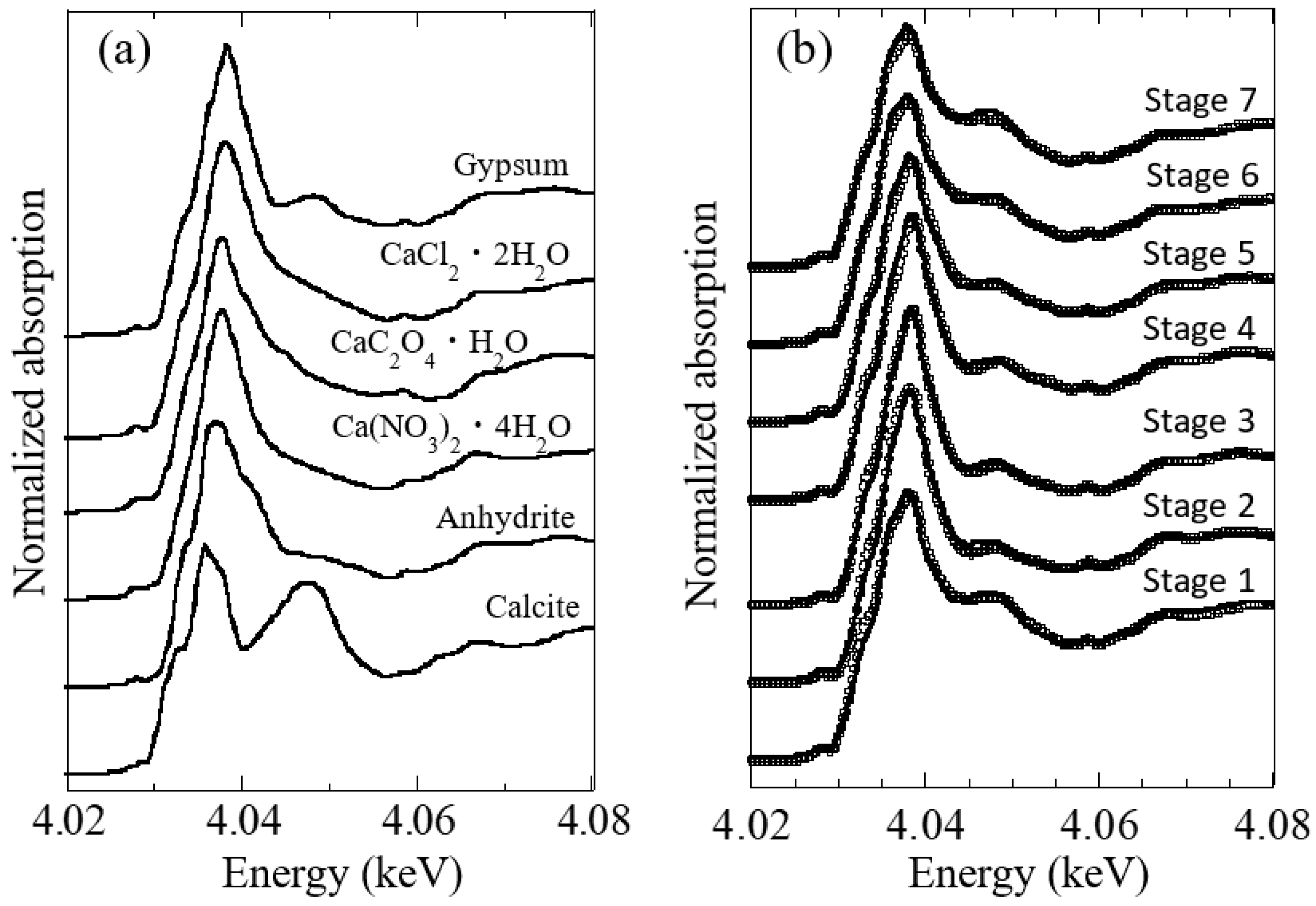
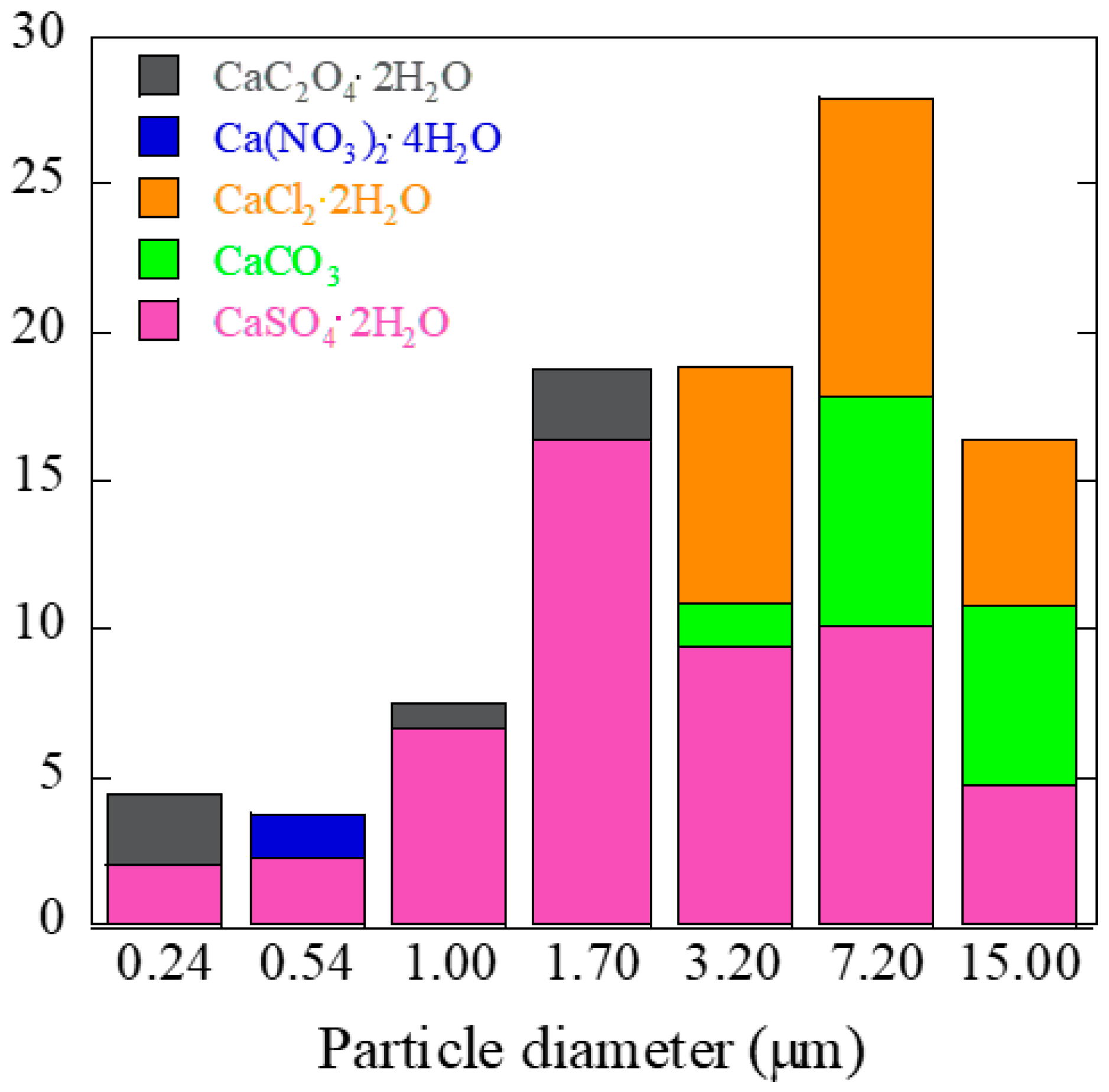
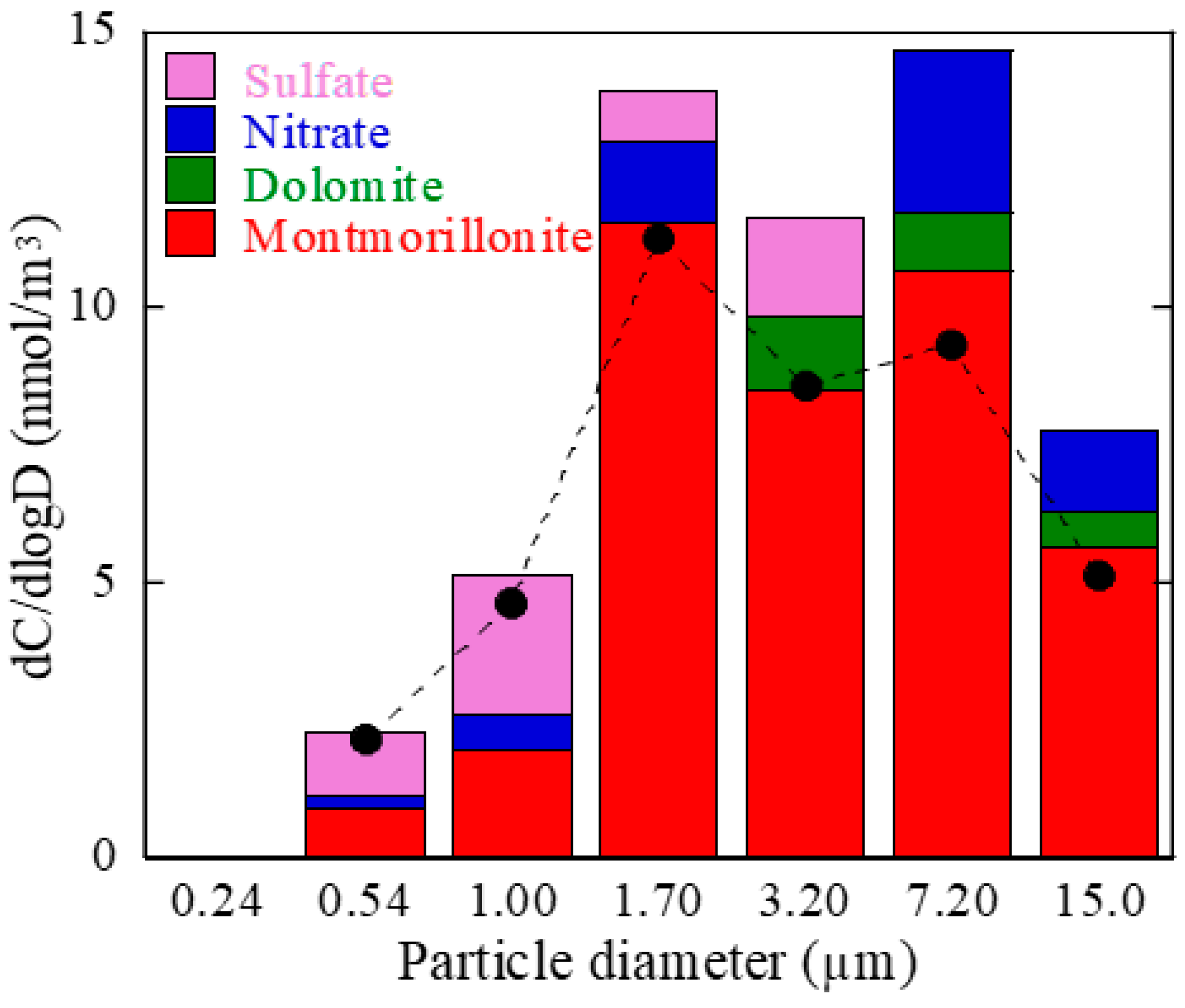
3.3. Speciation of Mg by Mg K-Edge XANES
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takahashi, Y.; Miyoshi, T.; Yabuki, S.; Inada, Y.; Shimizu, H. Observation of transformation of calcite to gypsum in mineral aerosols by CaK-edge X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES). Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6535–6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Miyoshi, T.; Higashi, M.; Kamioka, H.; Kanai, Y. Neutralization of Calcite in Mineral Aerosols by Acidic Sulfur Species Collected in China and Japan Studied by Ca K-edge X-ray Absorption Near-Edge Structure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6535–6540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; ISBN 1118591364. [Google Scholar]
- Dentener, F.J.; Carmichael, G.R.; Lelieveld, J.; Crutzen, P.J. Role of mineral aerosol as a reactive surface in the global troposhere. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 22869–22889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell-Meier, K.; Weber, R.; Song, C.; Orsini, D.; Ma, Y.; Carmichael, G.R.; Streets, D.G. Inorganic composition of fine particles in mixed mineral dust-pollution plumes observed from airborne measurements during ACE-Asia. J. Geophys. Res. D Atmos. 2004, 109, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, T.; Takahashi, Y. Oxalate metal complexes in aerosol particles: Implications for the hygroscopicity of oxalate-containing particles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 4289–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, C.; Sakata, K.; Yamakawa, Y.; Takahashi, Y. Determination of calcium and sulfate species in aerosols associated with the conversion of its species through reaction processes in the atmosphere and its influence on cloud condensation nuclei activation. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.Z. Studying the effects of calcium and magnesium on size-distributed nitrate and ammonium with EQUISOLV II. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 3635–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.S.; Meskhidze, N. Atmospheric dissolved iron deposition to the global oceans: Effects of oxalate-promoted Fe dissolution, photochemical redox cycling, and dust mineralogy. Geosci. Model Dev. 2013, 6, 1137–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Shi, Z. Delivery of anthropogenic bioavailable iron from mineral dust and combustion aerosols to the ocean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myriokefalitakis, S.; Daskalakis, N.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Baker, A.R.; Nenes, A.; Kanakidou, M. Changes in dissolved iron deposition to the oceans driven by human activity: A 3-D global modelling study. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 3973–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, J.W.; Bideaux, R.A.; Bladh, K.W.; Nichols, M.C. Handbook of Mineralogy; Mineralogical Society of America: Chantilly, VA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Journet, E.; Balkanski, Y.; Harrison, S.P. A new data set of soil mineralogy for dust-cycle modeling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 3801–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickovic, S.; Vukovic, A.; Vujadinovic, M.; Djurdjevic, V.; Pejanovic, G. Technical Note: High-resolution mineralogical database of dust-productive soils for atmospheric dust modeling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye, K. Aeolian Dust and Dust Deposits; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, Y.; Kanai, Y.; Kamioka, H.; Ohta, A.; Maruyama, H.; Song, Z.; Shimizu, H. Speciation of sulfate in size-fractionated aerosol particles using sulfur K-edge X-ray absorption near-edge structure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 5052–5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, K.; Sakaguchi, A.; Yokoyama, Y.; Terada, Y.; Takahashi, Y. Lead speciation studies on coarse and fine aerosol particles by bulk and micro X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. Geochem. J. 2017, 51, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurisu, M.; Adachi, K.; Sakata, K.; Takahashi, Y. Stable Isotope Ratios of Combustion Iron Produced by Evaporation in a Steel Plant. ACS Earth Sp. Chem. 2019, 3, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.R.; Hess, G.D. Description of the HYSPLIT_4 Modeling System. In NOAA Technical Memorandum ERL ARL-224; NOAA Air Resource Laboratory: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kurisu, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Iizuka, T.; Uematsu, M. Very low isotope ratio of iron in fine aerosols related to its contribution to the surface ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 11119–11136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.D.; Hesterberg, D.; Ravel, B. Analysis of Soils and Minerals using X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy. In Methods of Soil Analysis Part 5—Mineralogical Methods; Drees, L.R., Uler, A.K., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America Book Series: Madison, WI, USA, 2008; No. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Piel, C.; Weller, R.; Huke, M.; Wagenbach, D. Atmospheric methane sulfonate and non-sea-salt sulfate records at the European Project for Ice Coring in Antartica (EPICA) deep-drilling site in Dronning Maud Land, Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; Mclennan, S.M. The geochemical the continental evolution crust. Rev. Geopysics 1995, 33, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Higashi, M.; Furukawa, T.; Mitsunobu, S. Change of iron species and iron solubility in Asian dust during the long-range transport from western China to Japan. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 11237–11252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Tazaki, K. Seasonal variation of gypsum in aerosol and its effect on the acidity of wet precipitation on the Japan Sea side of Japan. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 3301–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Qi, F.; Tao, W.; Yanwu, Z.; Jianhua, S. Physicochemistry and mineralogy of storm dust and dust sediment in northern China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 21, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vespa, M.; Dähn, R.; Huthwelker, T.; Wieland, E. Soft X-ray absorption near-edge investigations of Mg-containing mineral phases relevant for cementitious materials. Phys. Chem. Earth 2017, 99, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, D. Aqueous Environmental Geochemistry; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, Z.; Chan, C.K. The Water Activities of MgCl2, Mg(NO3)2, MgSO4, and Their Mixtures. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1999, 31, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Morin, C.; Li, L.; Hitchcock, A.P.; Scholl, A.; Doran, A. Radiation damage in soft X-ray microscopy. J. Electron. Spectros. Relat. Phenom. 2009, 170, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zänker, H.; Hüttig, G.; Arnold, T.; Nitsche, H. Formation of iron-containing colloids by the weatheringof phyllite. Aquat. Geochem. 2006, 12, 299–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, F.; Bosbach, D.; Krawczyk-Barsch, E.; Arnold, T.; Bernhard, G. Chlorite dissolution in the acid ph-range: A combined microscopic and macroscopic approach. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochert, H. Chemical Oceanography; Academic Press: London, UK, 1965. [Google Scholar]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kawai, T.; Yamakawa, Y.; Takahashi, Y. Speciation of Magnesium in Aerosols Using X-ray Absorption Near-Edge Structure Related to Its Contribution to Neutralization Reactions in the Atmosphere. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050586
Kawai T, Yamakawa Y, Takahashi Y. Speciation of Magnesium in Aerosols Using X-ray Absorption Near-Edge Structure Related to Its Contribution to Neutralization Reactions in the Atmosphere. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(5):586. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050586
Chicago/Turabian StyleKawai, Takahiro, Yoshiaki Yamakawa, and Yoshio Takahashi. 2021. "Speciation of Magnesium in Aerosols Using X-ray Absorption Near-Edge Structure Related to Its Contribution to Neutralization Reactions in the Atmosphere" Atmosphere 12, no. 5: 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050586
APA StyleKawai, T., Yamakawa, Y., & Takahashi, Y. (2021). Speciation of Magnesium in Aerosols Using X-ray Absorption Near-Edge Structure Related to Its Contribution to Neutralization Reactions in the Atmosphere. Atmosphere, 12(5), 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050586





