Chemical Characteristics and Sources of Water-Soluble Organic Nitrogen Species in PM2.5 in Nanjing, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. PM2.5 Sample Collection
2.2. Chemical Analyses
2.3. Data Analyses
2.4. Source Apportionment of WSOM and WSON
3. Results and Discussion
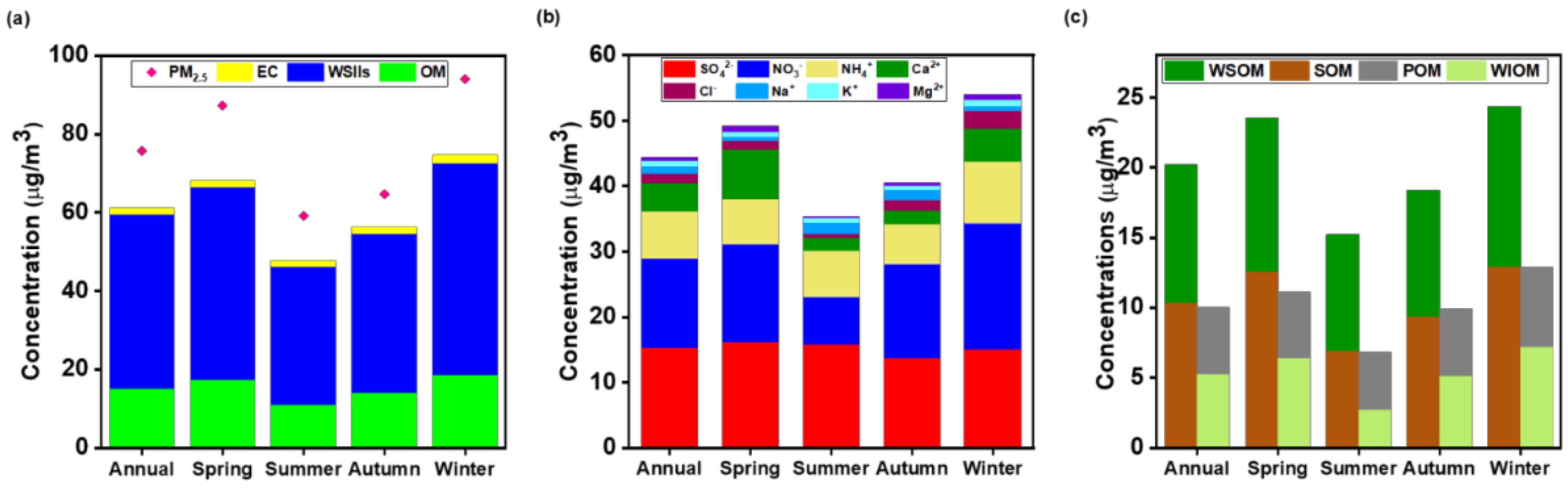
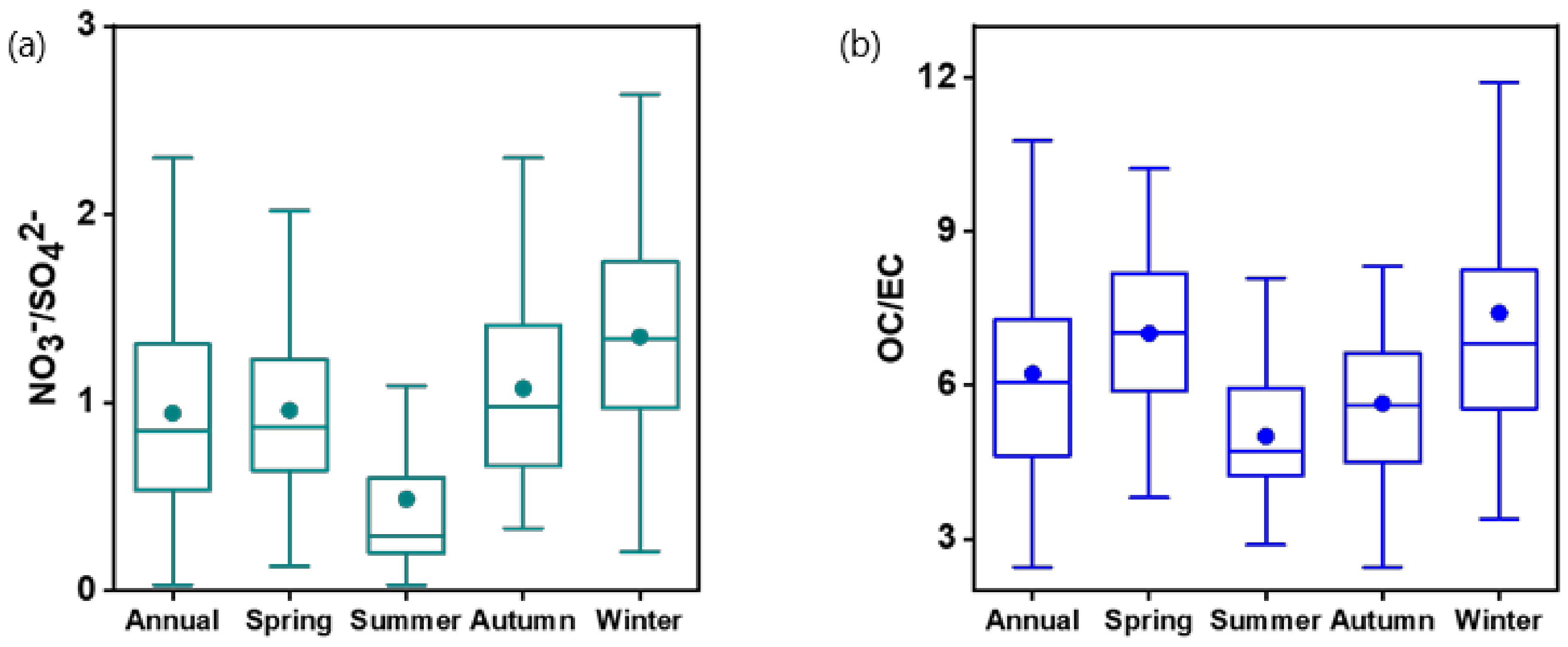
3.1. Overview of PM2.5 Concentration and Composition
3.2. Characteristics of WSON
3.2.1. Seasonal Variations of WSON and WSTN Concentrations
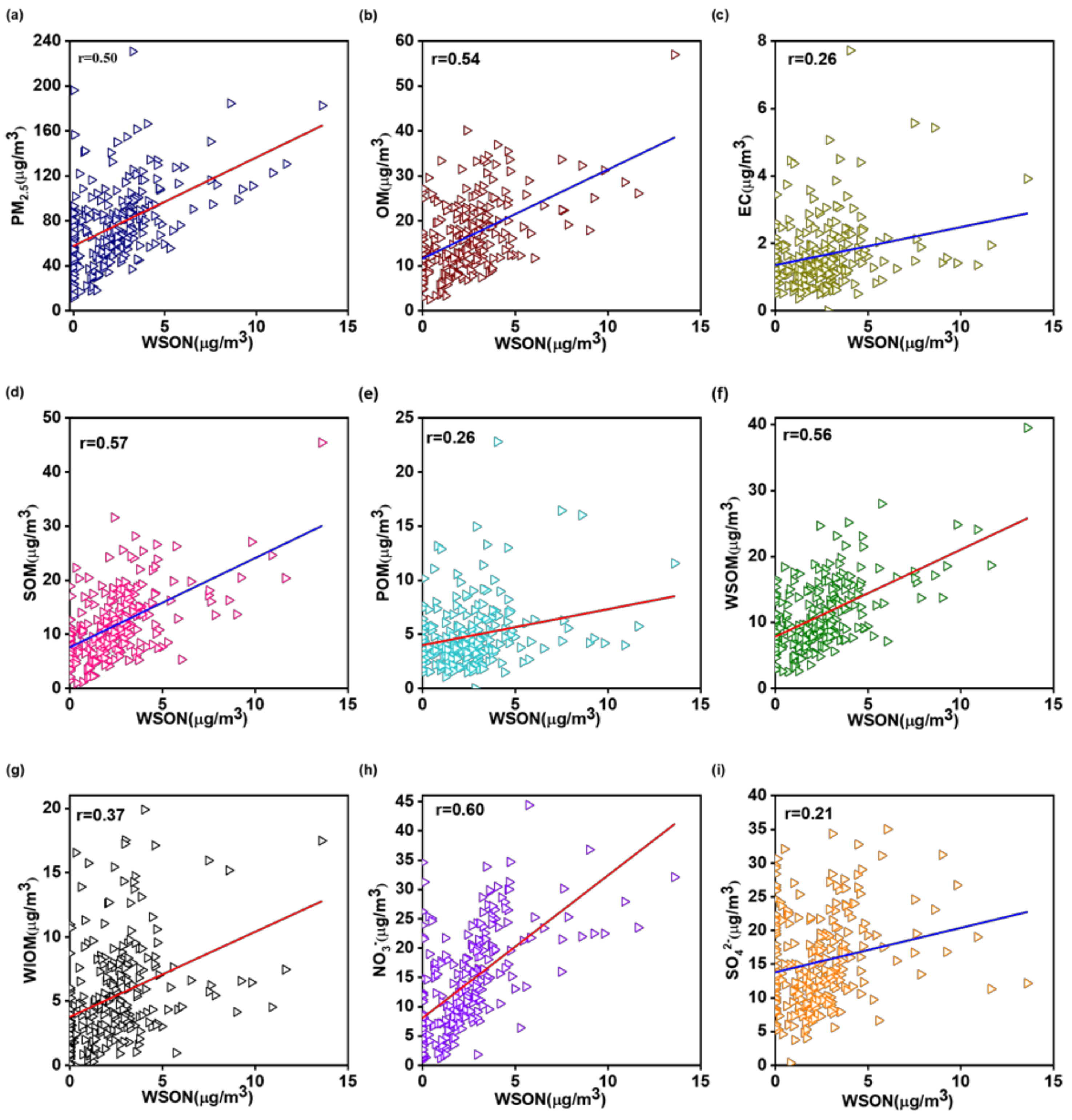
3.2.2. Relationships of WSON with PM2.5 Components
3.3. Bulk Composition and Source Apportionment of WSON
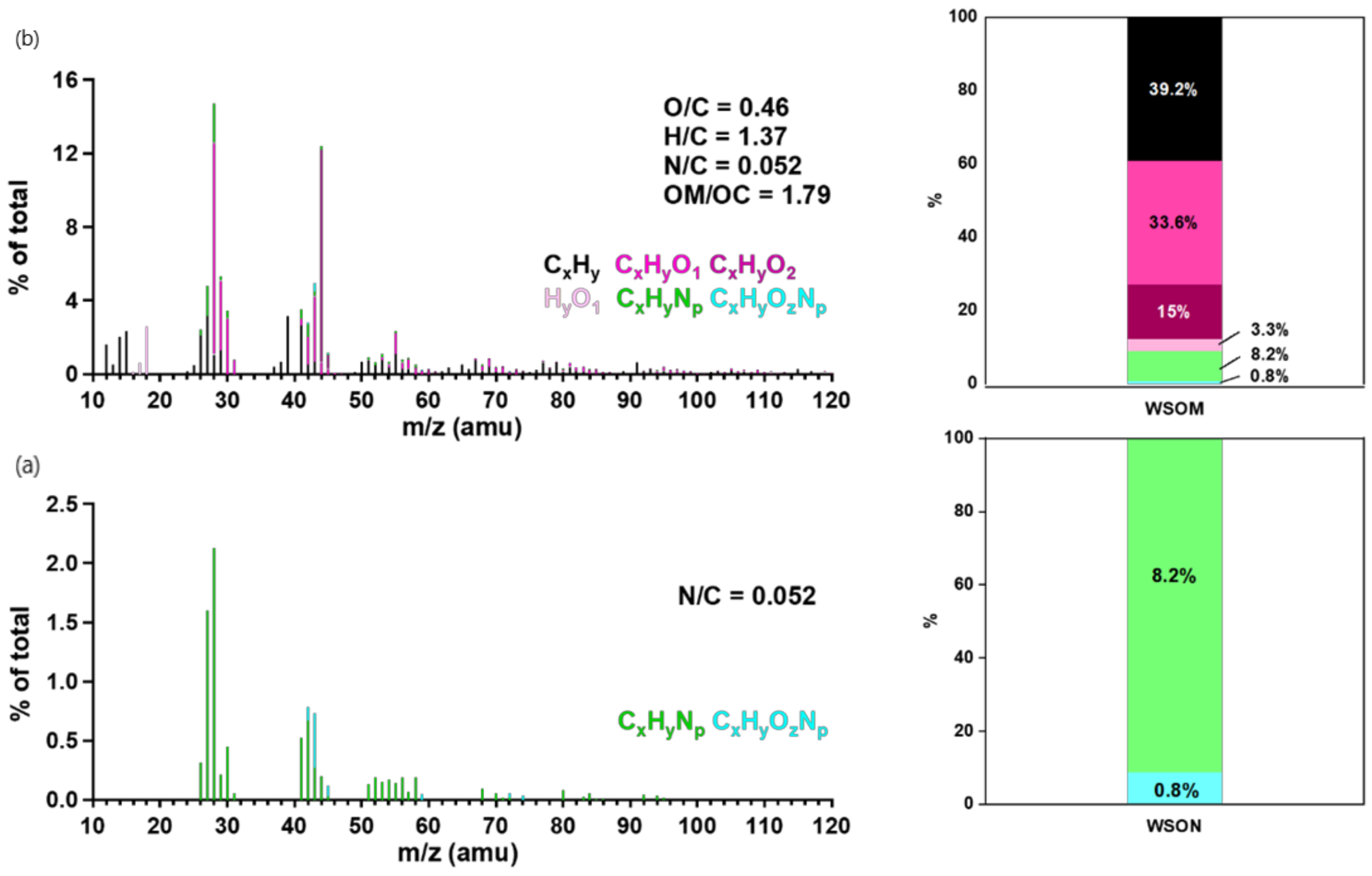
3.3.1. Bulk Composition of WSON
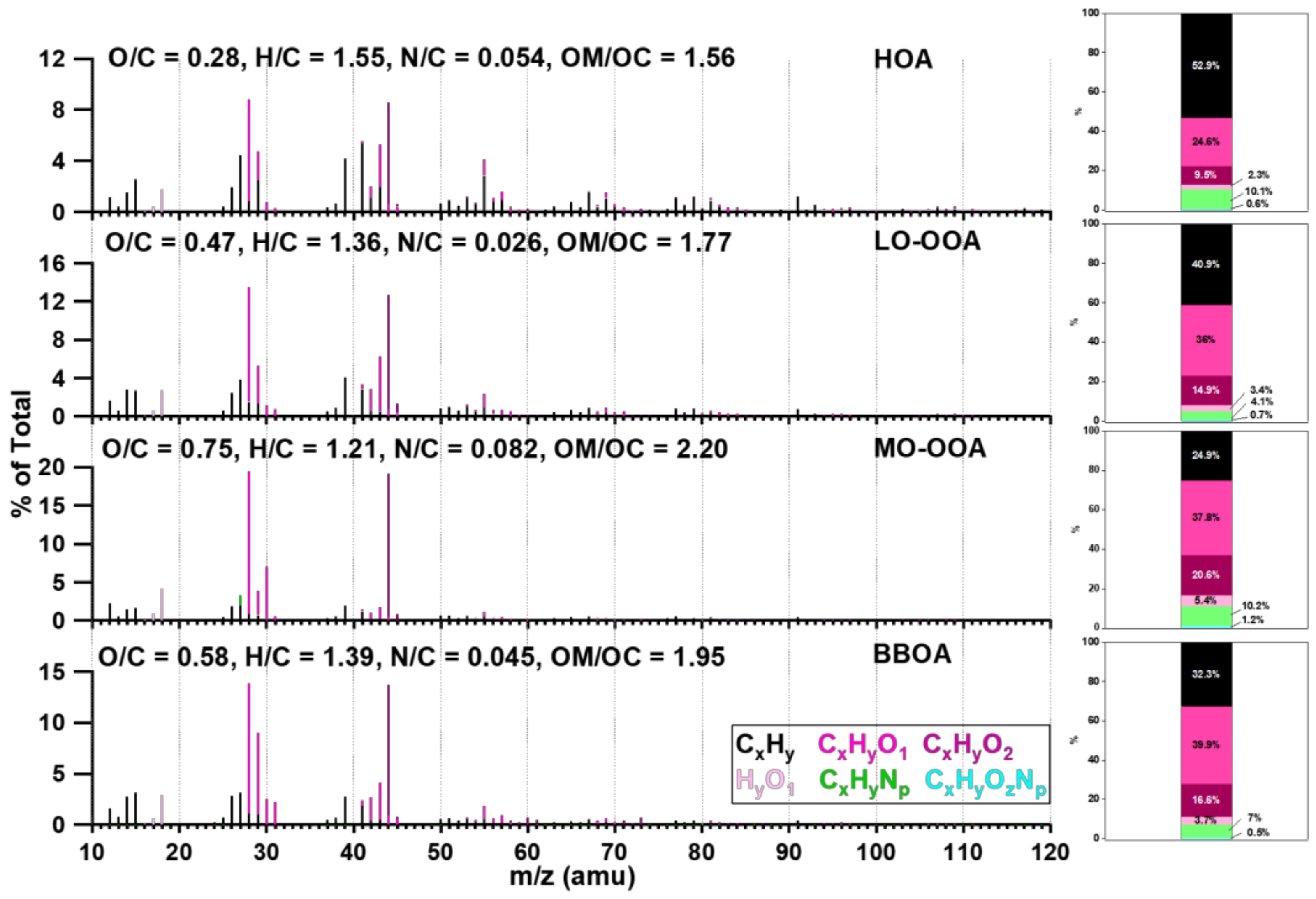
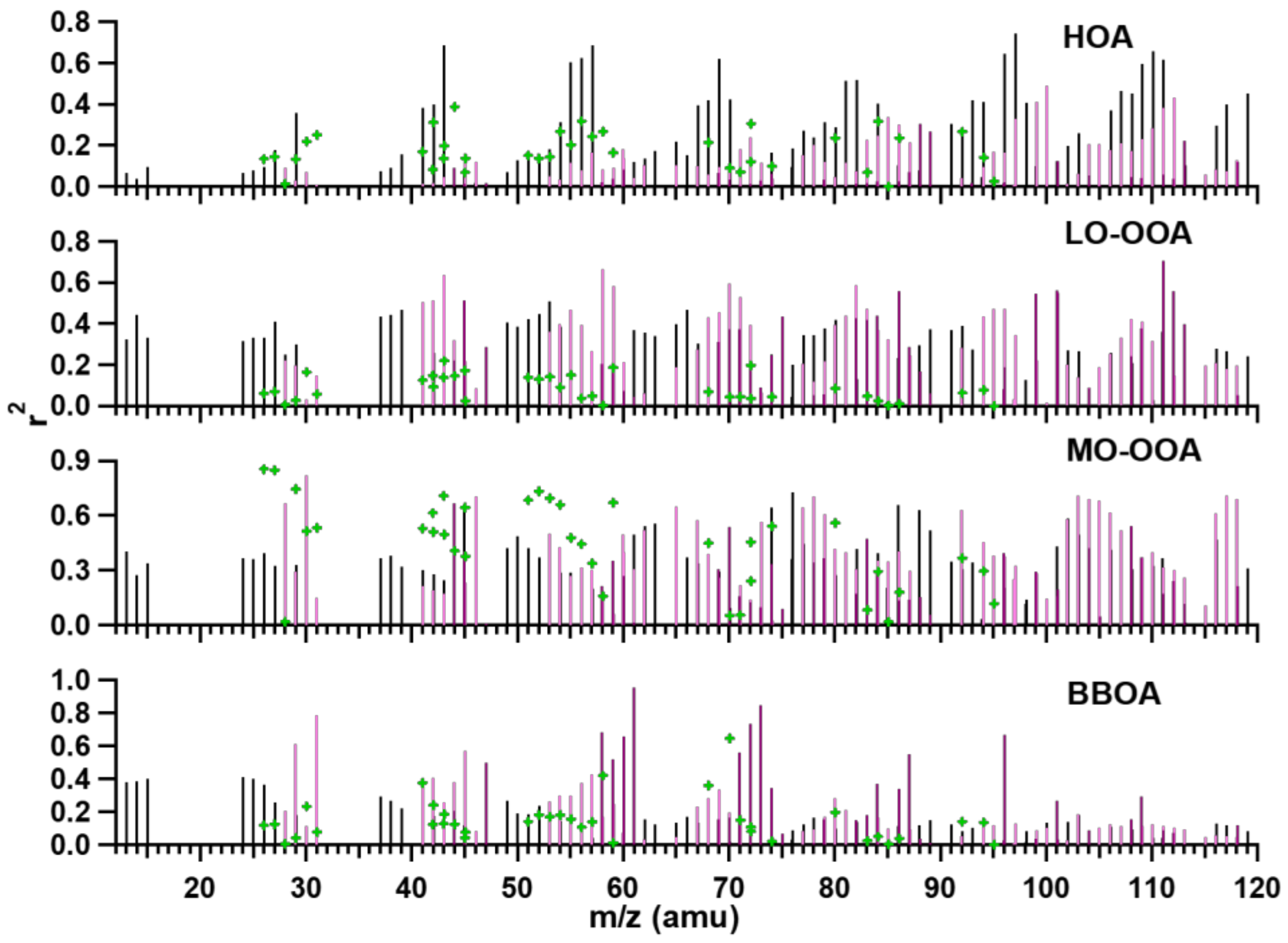
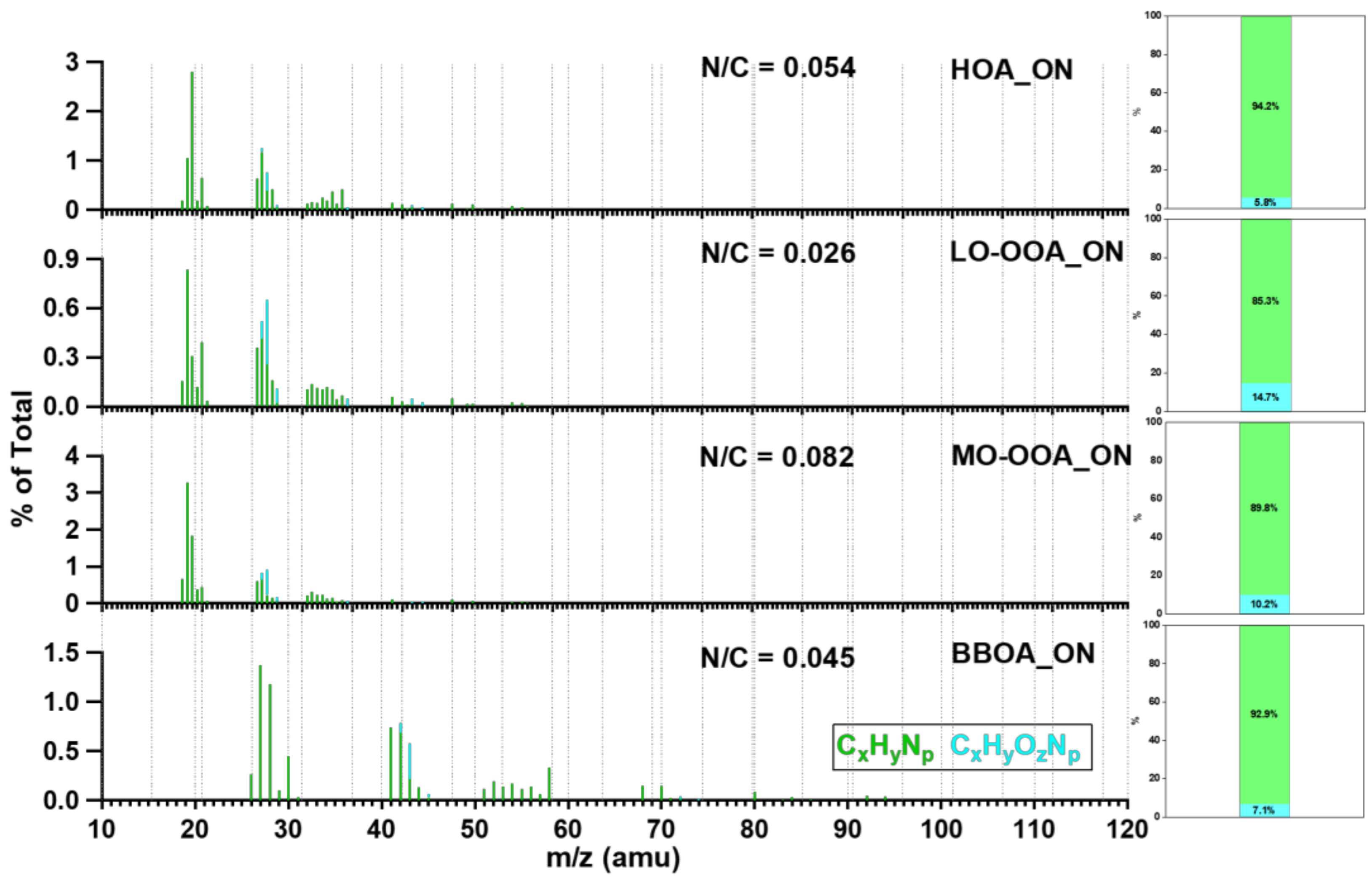
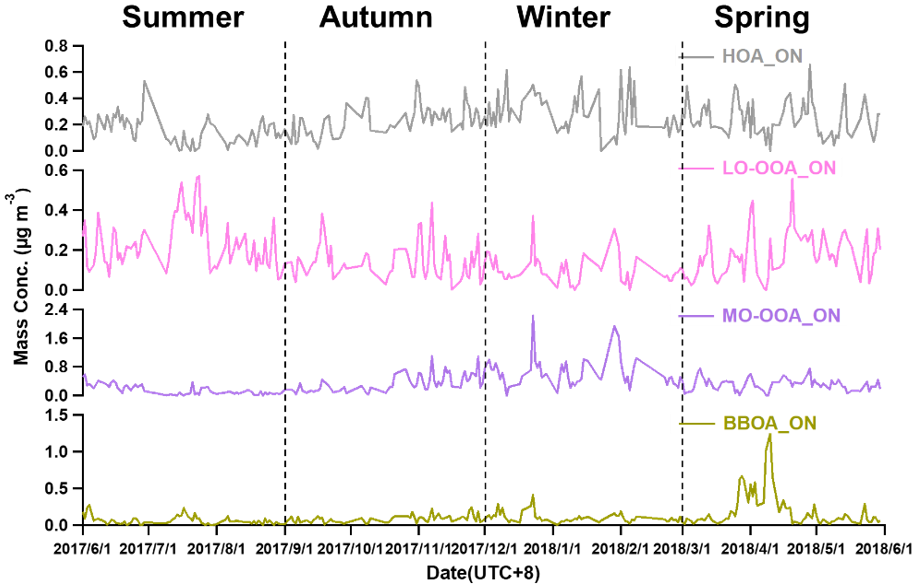
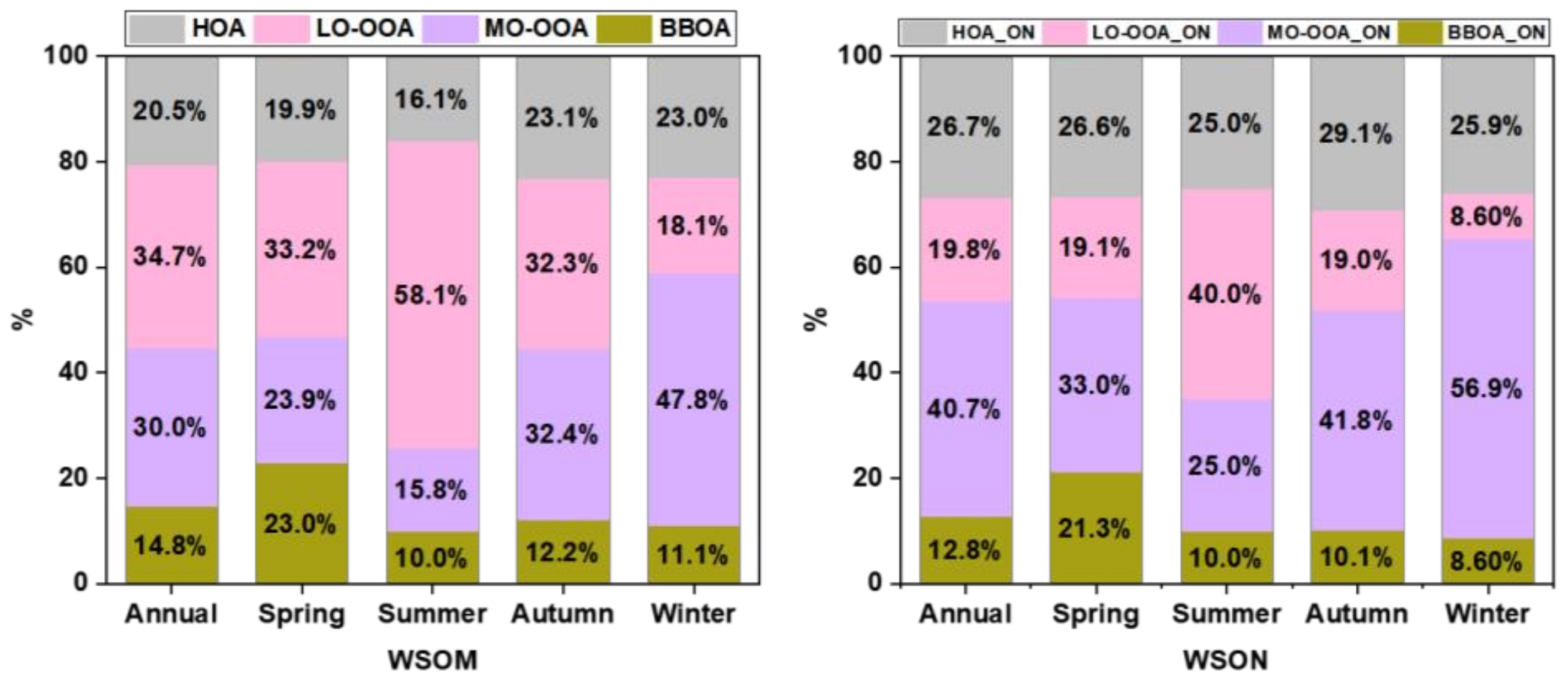
3.3.2. Source Apportionments of WSOM and WSON
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cornell, S.; Randell, A.; Jickells, T. Atmospheric inputs of dissolved organic nitrogen to the oceans. Nature 1995, 376, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, J.; Cape, J.N.; Heal, M.R. Gaseous and particulate water-soluble organic and inorganic nitrogen in rural air in southern Scotland. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Rodríguez, G.J.; Gioda, A.; Mayol-Bracero, O.L.; Collet, J.L., Jr. Organic carbon, total nitrogen, and water-soluble ions in clouds from a tropical montane cloud forest in Puerto Rico. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4171–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudlark, J.R.; Russell, K.M.; Galloway, J.N.; Church, T.M.; Keene, W.C. Organic nitrogen in precipitation at the mid-Atlantic U.S. Coast—Methods Evaluation and Preliminary Measurements. Atmos. Env. 1998, 32, 1719–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasio, C.; McGregor, K.G. Photodestruction of Dissolved Organic Nitrogen Species in Fog Waters. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2000, 32, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesworth, T.; Baker, A.R.; Jickells, T. Aerosol organic nitrogen over the remote Atlantic Ocean. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1887–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Balasubramanian, R.; Burger, D.F.; Hicks, K.; Kuylenstierna, J.C.I.; Palani, S. Dry and wet atmospheric deposition of nitrogen and phosphorus in Singapore. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2760–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neff, J.C.; Holland, E.A.; Dentener, F.J.; McDowell, W.H.; Russell, K.M. The origin, composition and rates of organic nitrogen deposition: A missing piece of the nitrogen cycle? Biogeochemistry 2002, 57, 99–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, Y.; Kawamura, K.; Jung, J.; Furutani, H.; Uematsu, M. Latitudinal distributions of organic nitrogen and organic carbon in marine biologically influenced aerosols over the western North Pacific in summer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, F.K.; Liu, X.D.; He, K.B.; Dong, S.P. Measurements and Characteristics of Nitrogen-Containing Compounds in Atmospheric Particulate Matter in Beijing, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 82, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xie, X.; Shi, Z.; Li, Y.; Gai, X.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, M.; et al. Brown carbon in atmospheric fine particles in Yangzhou, China: Light absorption properties and source apportionment. Atmos. Res. 2020, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ge, X.; Chen, H.; Xie, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Ye, Z.; Bao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M. Seasonal light absorption properties of water-soluble brown carbon in atmospheric fine particles in Nanjing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 187, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Erisman, J.W.; Bekunda, M.; Cai, Z.C.; Freney, J.R.; Martinelli, L.A.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Sutton, M.A. Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: Recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 2008, 320, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovallius, A.; Bucht, B.; Roffey, R.; Anäs, P. Three year investigation of the natural airborne bacterial flora at four localities in Sweden. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1978, 35, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindemann, J.; Constantinidou, H.A.; Barchet, W.R.; Upper, C.D. Plants as source of airbone bacteria, including ice nucleation-active bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1982, 44, 1059–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antia, N.J.; Harrison, P.J.; Oliveira, L. The role of dissolved organic nitrogen in phytoplankton nutrition, cell biology and ecology. Phycologia 1991, 30, 1–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Wexler, A.; Clegg, S. Atmospheric amines—Part I. A review. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 524–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherrier, J.; Bauer, J.E. Bacterial utilization of transient plankton-derived dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen inputs in surface ocean waters. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 35, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.; Sorooshian, A.; Kroll, J.; Ng, N.; Chhabra, P.; C, T.; Surratt, J.; Knipping, E.; Flagan, R.; Seinfeld, J. Secondary aerosol formation from atmospheric reactions of aliphatic amines. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 2313–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskin, A.; Smith, J.; Laskin, J. Molecular Characterization of Nitrogen-Containing Organic Compounds in Biomass Burning Aerosols Using High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3764–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R.; Arey, J. Gas-phase tropospheric chemistry of biogenic volatile organic compounds: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 197–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleindienst, T.E.; Jaoui, M.; Lewandowski, M.; Offenberg, J.H.; Lewis, C.W.; Bhave, P.V.; Edney, E.O. Estimates of the contributions of biogenic and anthropogenic hydrocarbons to secondary organic aerosol at a southeastern US location. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 8288–8300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Updyke, K.M.; Nguyen, T.B.; Nizkorodov, S.A. Formation of brown carbon via reactions of ammonia with secondary organic aerosols from biogenic and anthropogenic precursors. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 63, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, Y.; Fu, P.Q.; Ono, K.; Tachibana, E.; Kawamura, K. Seasonal cycles of water-soluble organic nitrogen aerosols in a deciduous broadleaf forest in northern Japan. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 1440–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.J.; Sullivan, A.P.; Peltier, R.E.; Russell, A.; Yan, B.; Zheng, M.; Gouw, J.D.; Warneke, C.; Brock, C.; Holloway, J.S. A study of secondary organic aerosol formation in the anthropogenic-influenced southeastern United States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D13302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.M. The atmospheric chemistry of organic nitrates. Atmos. Environ., Part A 1990, 24, 243–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, P.; Hildemann, L.M. Water-soluble organics in atmospheric particles: A critical review of the literature and application of thermodynamics to identify candidate compounds. J. Atmos. Chem. 1996, 24, 57–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieber, R.J.; Hydro, L.H.; Seaton, P.J. Photooxidation of Triglycerides and Fatty Acids in Seawater: Implication Toward the Formation of Marine Humic Substances. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1454–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüssler, W.; Nitschke, L. Nitrophenols in precipitation. Chemosphere 2001, 42, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsapakis, M.; Stephanou, E.G. Diurnal cycle of PAHs, nitro-PAHs, and oxy-PAHs in a high oxidation capacity marine background. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 8011–8017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakkanen, T.A. Study of formation of coarse particle nitrate aerosol. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 2475–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.M.; Pio, C.A. Size-differentiated composition of inorganic atmospheric aerosols of both marine and polluted continental origin. Atmos. Environ. 1983, 17, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xie, X.; Ye, Z.; Chen, M. Chemical Characteristics of PM2.5 and Water-Soluble Organic Nitrogen in Yangzhou, China. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onasch, T.B.; Trimborn, A.; Fortner, E.C.; Jayne, J.T.; Kok, G.L.; Williams, L.R.; Davidovits, P.; Worsnop, D.R. Soot Particle Aerosol Mass Spectrometer: Development, Validation, and Initial Application. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 804–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Cui, S.; Huang, D.D.; Ge, X. Aerosol Measurements by Soot Particle Aerosol Mass Spectrometer: A Review. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ge, X.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Xu, J.; Ge, S.; Yu, H.; Chen, M. Highly time-resolved urban aerosol characteristics during springtime in Yangtze River Delta, China: Insights from soot particle aerosol mass spectrometry. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 9109–9127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.L.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.F.; Chen, H.; Wu, D.; Wang, J.F.; Xie, X.C.; Ge, S.; Ye, Z.L.; Xu, J.Z.; et al. Aerosol characteristics and sources in Yangzhou, China resolved by offline aerosol mass spectrometry and other techniques. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.L.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.S.; Luo, S.P.; Zhou, Q.F.; Bi, C.L.; Ma, S.S.; Chen, Y.F.; Chen, H.; Li, L.; et al. Investigation of submicron aerosol characteristics in Changzhou, China: Composition, source, and comparison with co-collected PM2.5. Chemosphere 2017, 183, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.Y.; Ge, X.L.; Xiao, C.D.; Ren, J.W.; Qin, D.H. Dissolved Organic Matter and Inorganic Ions in a Central Himalayan Glacier-Insights into Chemical Composition and Atmospheric Sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6181–6188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Shaw, S.L.; Zhang, Q. Toward Understanding Amines and Their Degradation Products from Postcombustion CO2 Capture Processes with Aerosol Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 5066–5075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.L.; Qu, Z.X.; Ma, S.S.; Luo, S.P.; Chen, Y.T.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.F.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Chen, M.D.; Ge, X.L. A comprehensive investigation of aqueous-phase photochemical oxidation of 4-ethylphenol. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.C.; Ge, X.L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Xie, X.C.; Ou, Y.; Ye, Z.L.; Chen, M.D. Significant secondary organic aerosol production from aqueous-phase processing of two intermediate volatility organic compounds. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 211, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, J.C.; Chen, Y.F.; Liu, Y.; Ye, Z.L.; Ge, X.L. Aqueous-Phase Production of Secondary Organic Aerosols from Oxidation of Dibenzothiophene (DBT). Atmosphere 2020, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.L.; Zhuang, Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Ma, S.S.; Huang, H.Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Ge, X.L. Aqueous-phase oxidation of three phenolic compounds by hydroxyl radical: Insight into secondary organic aerosol formation yields, mechanisms, products and optical properties. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canonaco, F.; Crippa, M.; Slowik, J.G.; Baltensperger, U.; Prevot, A.S.H. SoFi, an IGOR-based interface for the efficient use of the generalized multilinear engine (ME-2) for the source apportionment: ME-2 application to aerosol mass spectrometer data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 3649–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canagaratna, M.R.; Jimenez, J.L.; Kroll, J.H.; Chen, Q.; Kessler, S.H.; Massoli, P.; Hildebrandt Ruiz, L.; Fortner, E.; Williams, L.R.; Wilson, K.R.; et al. Elemental ratio measurements of organic compounds using aerosol mass spectrometry: Characterization, improved calibration, and implications. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 253–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiken, A.C.; Decarlo, P.F.; Kroll, J.H.; Worsnop, D.R.; Huffman, J.A.; Docherty, K.S.; Ulbrich, I.M.; Mohr, C.; Kimmel, J.R.; Sueper, D.; et al. O/C and OM/OC ratios of primary, secondary, and ambient organic aerosols with high-resolution time-of-flight aerosol mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4478–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, M.; Ding, X.; Edgerton, E.S.; Wang, X. Characterization and Source Apportionment of Water-Soluble Organic Matter in Atmospheric Fine Particles (PM2.5) with High-Resolution Aerosol Mass Spectrometry and GC-MS. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4854–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulbrich, I.M.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Zhang, Q.; Worsnop, D.R.; Jimenez, J.L. Interpretation of organic components from Positive Matrix Factorization of aerosol mass spectrometric data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 2891–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzetti, C.; El Haddad, I.; Salameh, D.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Fermo, P.; Gonzalez, R.; Minguillon, M.C.; Iinuma, Y.; Poulain, L.; Elser, M.; et al. Organic aerosol source apportionment by offline-AMS over a full year in Marseille. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 8247–8268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jimenez, J.L.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Ulbrich, I.M.; Ng, N.L.; Worsnop, D.R.; Sun, Y.L. Understanding atmospheric organic aerosols via factor analysis of aerosol mass spectrometry: A review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 3045–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.L.; Liu, J.S.; Gu, A.J.; Feng, F.F.; Liu, Y.H.; Bi, C.L.; Xu, J.Z.; Li, L.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.F.; et al. Chemical characterization of fine particulate matter in Changzhou, China, and source apportionment with offline aerosol mass spectrometry. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2573–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Ye, J.H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Y.Z.; Li, J.Y.; Liu, D.T.; Li, W.J.; Zhang, Y.G.; Wu, C.; et al. Aqueous production of secondary organic aerosol from fossil-fuel emissions in winter Beijing haze. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.Z.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, L.; Tang, M.Q.; Gai, X.Y.; Chen, M.D.; Ge, X.L. Temporal variations of six ambient criteria air pollutants from 2015 to 2018, their spatial distributions, health risks and relationships with socioeconomic factors during 2018 in China. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.L.; He, Y.A.; Sun, Y.L.; Xu, J.Z.; Wang, J.F.; Shen, Y.F.; Chen, M.D. Characteristics and Formation Mechanisms of Fine Particulate Nitrate in Typical Urban Areas in China. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Chan, C.K.; Fang, M.; Cadle, S.; Chan, T.; Mulawa, P.; He, K.; Ye, B. The water-soluble ionic composition of PM2.5 in Shanghai and Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 4223–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turpin, B.; Huntzicker, J. Identification of secondary organic aerosol episodes and quantitation of primary and secondary organic aerosol concentrations during SCAQS. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 3527–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Yu, J.Z. Determination of primary combustion source organic carbon-to-elemental carbon (OC/EC) ratio using ambient OC and EC measurements: Secondary OC-EC correlation minimization method. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.F.; Ho, S.S.H.; Huang, R.J.; Liu, S.X.; Cao, J.J.; Zhang, T.; Chuang, H.C.; Chan, C.S.; Hu, D.; Tian, L.W. Characteristics of water-soluble organic nitrogen in fine particulate matter in the continental area of China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 106, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Anastasio, C.; Jimenez-Cruz, M. Water-soluble organic nitrogen in atmospheric fine particles (PM2.5) from northern California. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Walker, J.; Geron, C.; Khlystov, A. Organic nitrogen in PM2.5 aerosol at a forest site in the Southeast US. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 2145–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noziere, B.; Cordova, A. A kinetic and mechanistic study of the amino acid catalyzed aldol condensation of acetaldehyde in aqueous and salt solutions. J. Phys. Chem. A 2008, 112, 2827–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noziere, B.; Dziedzic, P.; Cordova, A. Products and Kinetics of the Liquid-Phase Reaction of Glyoxal Catalyzed by Ammonium Ions (NH4+). J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, Y.; Duan, F.; Yang, F.; Shi, Z.; Chen, G. Spatial and seasonal variability of PM2.5 acidity at two Chinese megacities: Insights into the formation of secondary inorganic aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 1377–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.H.; Yang, L.X.; Zhou, X.H.; Xue, L.K.; Gao, X.M.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, W.X. Size-fractionated water-soluble ions, situ pH and water content in aerosol on hazy days and the influences on visibility impairment in Jinan, China. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4631–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, R.K.; Wu, W.S.; Wang, T. Summertime PM2.5 ionic species in four major cities of China: Nitrate formation in an ammonia-deficient atmosphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 1711–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xue, L.K.; Wang, T.; Gao, X.M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.F.; Zhang, J.M.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Wang, W.X. Characterization of aerosol acidity at a high mountain site in central eastern China. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 51, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.M.; Xie, Q.R.; Wang, J.F.; Xu, W.Q.; Li, L.J.; Wang, Q.Q.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.T.; Chen, Y.F.; Wu, Y.Z.; et al. Vertical Characterization and Source Apportionment of Water-Soluble Organic Aerosol with High-resolution Aerosol Mass Spectrometry in Beijing, China. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2019, 3, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, W.Q.; Collier, S.; Sun, Y.L.; Zhang, Q.; He, K.B. Characteristics and sources of water-soluble organic aerosol in a heavily polluted environment in Northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.L.; Wexler, A.S.; Clegg, S.L. Atmospheric amines—Part II. Thermodynamic properties and gas/particle partitioning. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 561–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Feng, L.M.; Hu, Q.J.; Zhu, Y.J.; Gao, H.W.; Gao, Y.; Yao, X.H. Concentration and size distribution of water-extracted dimethylaminium and trimethylaminium in atmospheric particles during nine campaigns - Implications for sources, phase states and formation pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.R.; Hu, Q.J.; Li, K.; Zhu, Y.J.; Liu, X.H.; Gao, H.W.; Yao, X.H. Characteristics of dimethylaminium and trimethylaminium in atmospheric particles ranging from supermicron to nanometer sizes over eutrophic marginal seas of China and oligotrophic open oceans. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.C.; Ren, L.L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, L.Y.; Dai, L.; Ge, X.L.; Kong, S.F.; Yan, Q.; Xu, H.H.; Jiang, Y.J.; et al. C1-C2 alkyl aminiums in urban aerosols: Insights from ambient and fuel combustion emission measurements in the Yangtze River Delta region of China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.H.; Hu, Y.Y.; Sun, M.Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Chen, Y.T.; Zong, C.L.; Chen, J.Q.; Ge, X.L. Characteristics and potential source areas of aliphatic amines in PM2.5 in Yangzhou, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.Q.; Sun, Y.L.; Wang, Q.Q.; Du, W.; Zhao, J.; Ge, X.L.; Han, T.T.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zhou, W.; Li, J.; et al. Seasonal Characterization of Organic Nitrogen in Atmospheric Aerosols Using High Resolution Aerosol Mass Spectrometry in Beijing, China. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2017, 1, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiken, A.C.; DeCarlo, P.F.; Jimenez, J.L. Elemental analysis of organic species with electron ionization high-resolution mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 8350–8358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewnick, F. Speciation analysis in on-line aerosol mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404, 2127–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Chen, M.D.; Ge, X.L.; Gu, C.X.; Yu, W.T.; Nie, D.Y. Validation of a sensitive high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometric method for measuring carbohydrates in aerosol samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1619, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskin, A.; Laskin, J.; Nizkorodov, S.A. Mass spectrometric approaches for chemical characterisation of atmospheric aerosols: Critical review of the most recent advances. Environ. Chem. 2012, 9, 163–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, K.A.; Prather, K.A. Mass spectrometry of atmospheric aerosolsuRecent developments and applications. Part I: Off-line mass spectrometry techniques. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2012, 31, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Zhou, Z.; Chan, C.K. Real-time chemical characterization of atmospheric particulate matter in China: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 158, 270–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Tang, L.L.; Wang, Z.; Yu, H.X.; Sun, Y.L.; Liu, D.; Qin, W.; Canonaco, F.; Prevot, A.S.H.; Zhang, H.L.; et al. Insights into characteristics, sources, and evolution of submicron aerosols during harvest seasons in the Yangtze River delta region, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 1331–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, M.; Collier, S.; Zhou, S.; Ge, X.; Xu, J.; Shi, J.; Xie, C.; Hu, J.; et al. First Chemical Characterization of Refractory Black Carbon Aerosols and Associated Coatings over the Tibetan Plateau (4730 m a.s.l). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 14072–14082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Ye, J.H.; Liu, D.T.; Wu, Y.Z.; Zhao, J.; Xu, W.Q.; Xie, C.H.; Shen, F.Z.; Zhang, J.; Ohno, P.E.; et al. Characterization of submicron organic particles in Beijing during summertime: Comparison between SP-AMS and HR-AMS. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 14091–14102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, J.L.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Donahue, N.M.; Prevot, A.; Zhang, Q. Evolution of Organic Aerosols in the Atmosphere. Science 2009, 326, 1525–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.Q.; Han, T.T.; Du, W.; Wang, Q.Q.; Chen, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Li, J.; Fu, P.Q.; Wang, Z.F.; et al. Effects of Aqueous-Phase and Photochemical Processing on Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation and Evolution in Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.Z.; Ge, X.L.; Wang, J.F.; Shen, Y.F.; Ye, Z.L.; Ge, S.; Wu, Y.; Yu, H.; Chen, M.D. Responses of secondary aerosols to relative humidity and photochemical activities in an industrialized environment during late winter. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 193, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Cui, S.; Nie, D.; Chen, Y.; Ge, X. Chemical Characteristics and Sources of Water-Soluble Organic Nitrogen Species in PM2.5 in Nanjing, China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050574
Liu Y, Li H, Cui S, Nie D, Chen Y, Ge X. Chemical Characteristics and Sources of Water-Soluble Organic Nitrogen Species in PM2.5 in Nanjing, China. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(5):574. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050574
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yue, Haiwei Li, Shijie Cui, Dongyang Nie, Yanfang Chen, and Xinlei Ge. 2021. "Chemical Characteristics and Sources of Water-Soluble Organic Nitrogen Species in PM2.5 in Nanjing, China" Atmosphere 12, no. 5: 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050574
APA StyleLiu, Y., Li, H., Cui, S., Nie, D., Chen, Y., & Ge, X. (2021). Chemical Characteristics and Sources of Water-Soluble Organic Nitrogen Species in PM2.5 in Nanjing, China. Atmosphere, 12(5), 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050574






