Characterization of Products from the Aqueous-Phase Photochemical Oxidation of Benzene-Diols
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Aqueous-Phase Oxidation Experiments
2.2. Decay Kinetics of Benzene-Diols
2.3. Light Absorptive Properties of Products
2.4. Chemical Analyses of Products by the SP-AMS
2.5. Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) of the Aqueous-Phase Products
2.6. Oxidative Potential (OP) of Products Based on Dithiothreitol (DTT) Assay
3. Results and Discussion
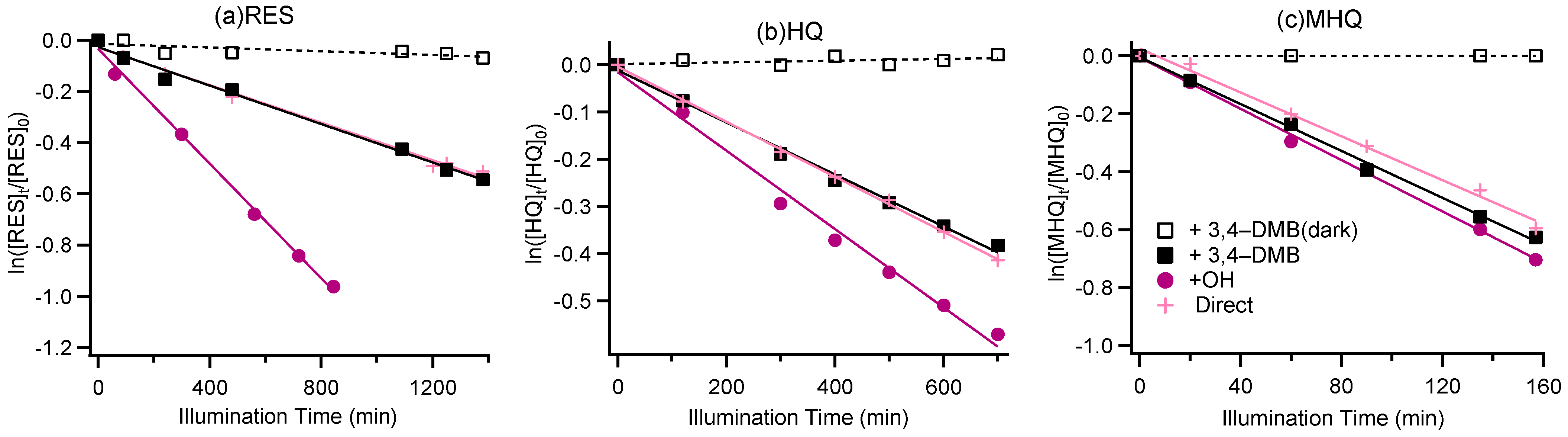
3.1. Kinetic Study
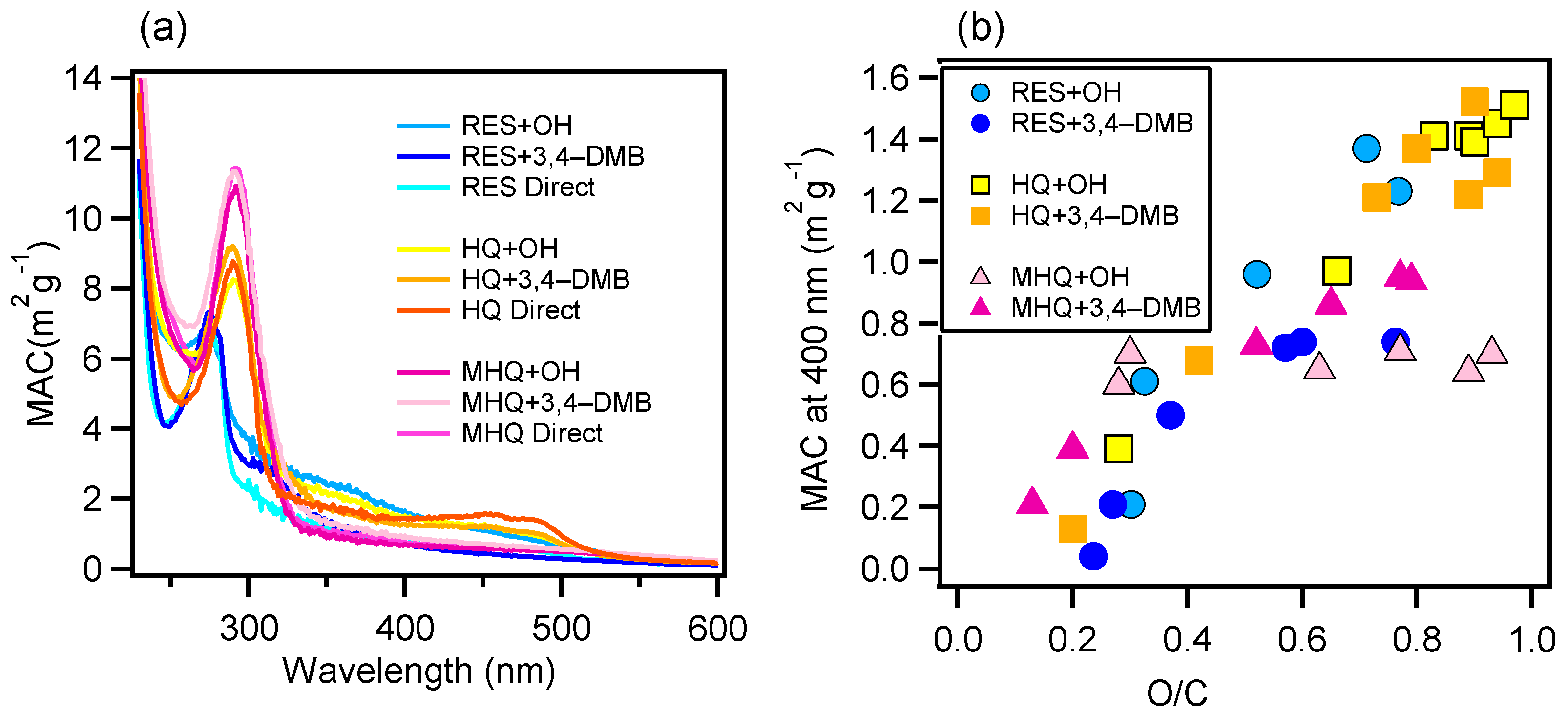
3.2. Light Absorption Properties
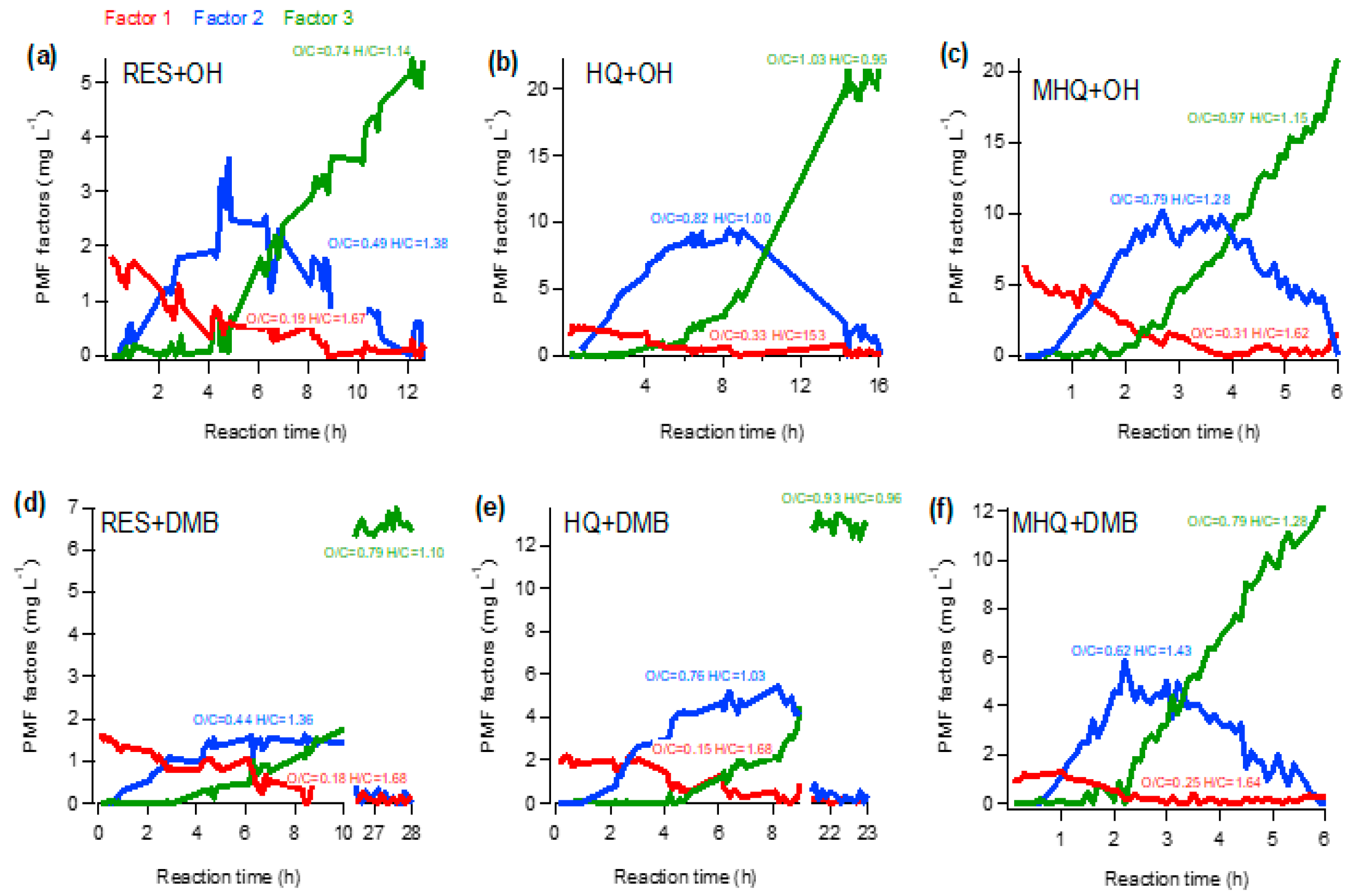
3.3. Chemical Properties and Evolution of Aqueous Oxidation Products
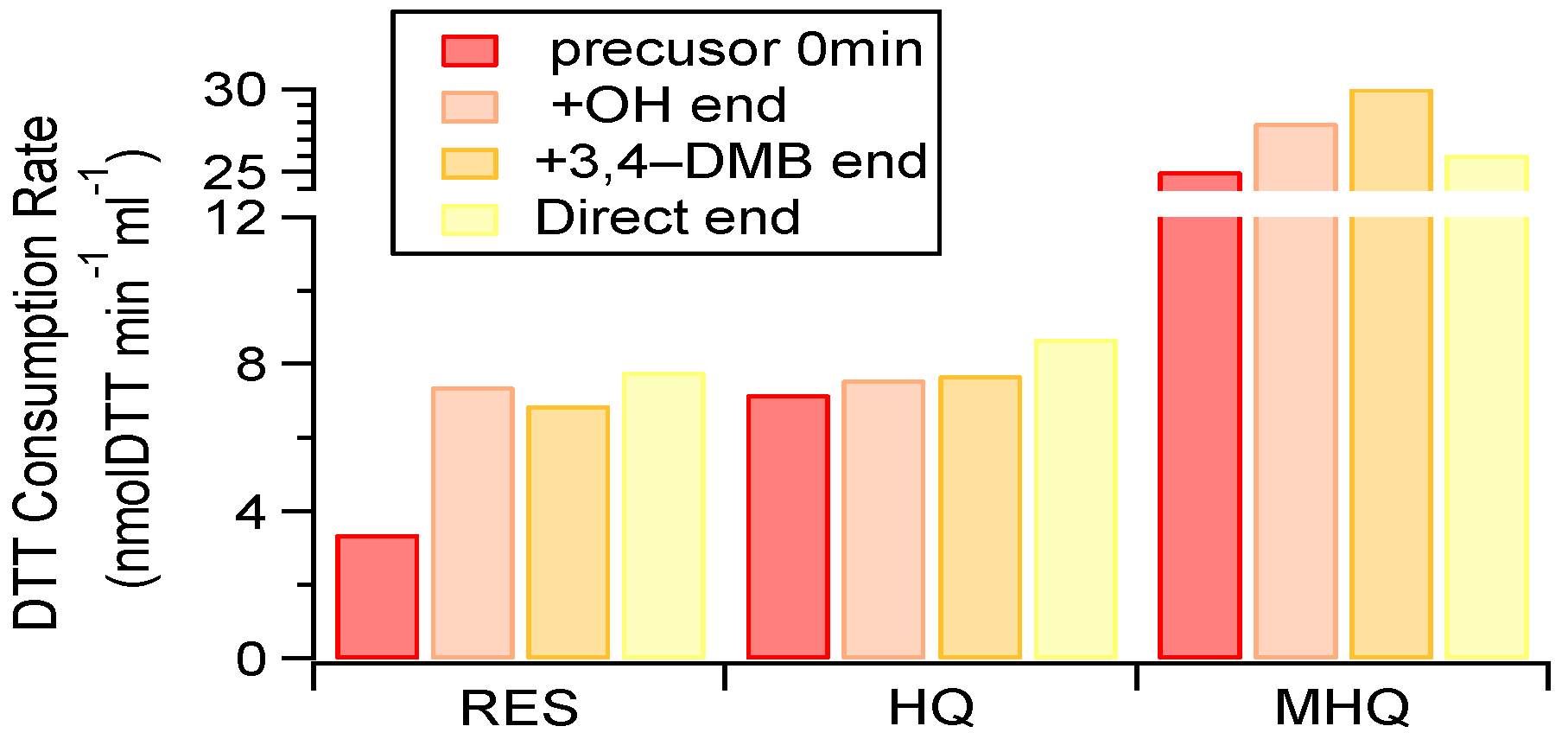
3.4. Oxidative Potential of Aqueous-Phase Products Compared with the Precursor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Q.; Jimenez, J.L.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Allan, J.D.; Coe, H.; Ulbrich, I.; Alfarra, M.R.; Takami, A.; Middlebrook, A.M.; Sun, Y.L.; et al. Ubiquity and dominance of oxygenated species in organic aerosols in anthropogenically-influenced Northern Hemisphere midlatitudes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 29979–29986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ying, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. Characterizing multi-pollutant air pollution in China: Comparison of three air quality indices. Environ. Int. 2015, 84, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, D.; Chen, M.; Wu, Y.; Ge, X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, K.; Ge, P. Characterization of Fine Particulate Matter and Associated Health Burden in Nanjing. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, D.; Wu, Y.; Chen, M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, K.; Ge, P.; Yuan, Y.; Ge, X. Bioaccessibility and health risk of trace elements in fine particulate matter in different simulated body fluids. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 186, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayorga, R.J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H. Formation of secondary organic aerosol from nitrate radical oxidation of phenolic VOCs: Implications for nitration mechanisms and brown carbon formation. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 244, 117910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gao, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, D.; Lou, S.; Wu, Z.; Guo, S.; et al. Atmospheric Processing of Nitrophenols and Nitrocresols From Biomass Burning Emissions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, 33401–33413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akherati, A.; He, Y.; Coggon, M.M.; Koss, A.R.; Hodshire, A.L.; Sekimoto, K.; Warneke, C.; A De Gouw, J.; Yee, L.D.; Seinfeld, J.H.; et al. Oxygenated Aromatic Compounds are Important Precursors of Secondary Organic Aerosol in Biomass-Burning Emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 8568–8579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilardoni, S.; Massoli, P.; Paglione, M.; Giulianelli, L.; Carbone, C.; Rinaldi, M.; Decesari, S.; Sandrini, S.; Costabile, F.; Gobbi, G.P.; et al. Direct Observation of Aqueous Secondary Organic Aerosol from Biomass-Burning Emissions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10013–10018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Wu, C.; Li, J.; Cao, C.; Li, J.; Xie, Y.; Ge, S.; Chen, J.; Zeng, L.; et al. Enhanced aqueous-phase formation of secondary organic aerosols due to the regional biomass burning over North China Plain. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Ge, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xie, X.; Ou, Y.; Ye, Z.; Chen, M. Significant secondary organic aerosol production from aqueous-phase processing of two intermediate volatility organic compounds. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 211, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhart, G.J.; Hennigan, C.J.; Miracolo, M.A.; Robinson, A.L.; Pandis, S.N. Cloud condensation nuclei activity of fresh primary and aged biomass burning aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2012, 12, 7285–7293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Du, W.; Wu, C.; Cheng, C.; Meng, J.; Li, D.; Ho, K.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G. Summertime atmospheric dicarboxylic acids and related SOA in the background region of Yangtze River Delta, China: Implications for heterogeneous reaction of oxalic acid with sea salts. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Huang, R.-J.; Gu, Y.; Lin, C.; Zhong, H.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, W.; Ni, H.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; et al. The formation and evolution of secondary organic aerosol during summer in Xi’an: Aqueous phase processing in fog-rain days. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 144077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ervens, B.; Turpin, B.J.; Weber, R.J. Secondary organic aerosol formation in cloud droplets and aqueous particles (aqSOA): A review of laboratory, field and model studies. Atmos. Chem. Physics. 2011, 11, 11069–11102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ye, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, D.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; et al. Aqueous production of secondary organic aerosol from fossil-fuel emissions in winter Beijing haze. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Ruehl, C.R.; Setyan, A. Effect of aqueous-phase processing on aerosol chemistry and size distributions in Fresno, California, during wintertime. Environ. Chem. 2012, 9, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ervens, B. Modeling the Processing of Aerosol and Trace Gases in Clouds and Fogs. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4157–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.L.; Zhang, Q.; Anastasio, C.; Sun, J. Insights into secondary organic aerosol formed via aqueous-phase reactions of phenolic compounds based on high resolution mass spectrometry. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2010, 10, 4809–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Smith, J.; Laskin, A.; Anastasio, C.; Laskin, J.; Zhang, Q. Chemical characterization of SOA formed from aqueous-phase reactions of phenols with the triplet excited state of carbonyl and hydroxyl radical. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2014, 14, 13801–13816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Smith, J.; Laskin, A.; George, K.M.; Anastasio, C.; Laskin, J.; Dillner, A.M.; Zhang, Q. Molecular transformations of phenolic SOA during photochemical aging in the aqueous phase: Competition among oligomerization, functionalization, and fragmentation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2016, 16, 4511–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.D.; Zhang, Q.; Cheung, H.H.Y.; Yu, L.; Zhou, S.; Anastasio, C.; Smith, J.D.; Chan, C.K. Formation and Evolution of aqSOA from Aqueous-Phase Reactions of Phenolic Carbonyls: Comparison between Ammonium Sulfate and Ammonium Nitrate Solutions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 9215–9224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ge, X.; Ye, Z. Aqueous-Phase Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation Via Reactions with Organic Triplet Excited States—a Short Review. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2018, 4, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Schaefer, T.; Otto, T.; Kroflič, A.; Herrmann, H. Kinetic and Theoretical Study of the Atmospheric Aqueous-Phase Reactions of OH Radicals with Methoxyphenolic Compounds. J. Phys. Chem. A 2019, 123, 7828–7838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veres, P.; Roberts, J.M.; Burling, I.R.; Warneke, C.; De Gouw, J.; Yokelson, R.J. Measurements of gas-phase inorganic and organic acids from biomass fires by negative-ion proton-transfer chemical-ionization mass spectrometry. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2010, 115, 14033–14047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desyaterik, Y.; Sun, Y.; Shen, X.; Lee, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Collett, J.L. Speciation of “brown” carbon in cloud water impacted by agricultural biomass burning in eastern China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 7389–7399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.M.; Doherty, R.M.; O’Connor, F.M.; Mann, G.W. The impact of biogenic, anthropogenic, and biomass burning volatile organic compound emissions on regional and seasonal variations in secondary organic aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2018, 18, 7393–7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillar, E.A.; Zhou, R.; Guzman, M.I. Heterogeneous Oxidation of Catechol. J. Phys. Chem. A 2015, 119, 10349–10359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillar, E.A.; Guzman, M.I. Oxidation of Substituted Catechols at the Air–Water Interface: Production of Carboxylic Acids, Quinones, and Polyphenols. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4951–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Li, F.; Tsona, N.T.; Lu, C.; Wang, X.; Du, L. Aqueous-Phase Photooxidation of Vanillic Acid: A Potential Source of Humic-Like Substances (HULIS). ACS Earth Space Chem. 2020, 4, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Guo, Y.; Niu, J. Photochemical degradation of nebivolol in different natural organic matter solutions under simulated sunlight irradiation: Kinetics, mechanism and degradation pathway. Water Res. 2020, 173, 115524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasio, C.; Faust, B.C.; Rao, C.J. Aromatic Carbonyl Compounds as Aqueous-Phase Photochemical Sources of Hydrogen Peroxide in Acidic Sulfate Aerosols, Fogs, and Clouds. 1. Non-Phenolic Methoxybenzaldehydes and Methoxyacetophenones with Reductants (Phenols). Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, J.J.; Kleeman, M.J.; Cass, G.R.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Measurement of Emissions from Air Pollution Sources. 3. C1−C29Organic Compounds from Fireplace Combustion of Wood. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1716–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauer, J.J.; Cass, G.R. Source Apportionment of Wintertime Gas-Phase and Particle-Phase Air Pollutants Using Organic Compounds as Tracers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 1821–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte, C.G.; Schauer, J.J.; Cass, G.R.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Highly Polar Organic Compounds Present in Wood Smoke and in the Ambient Atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1912–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakaki, T.; Anastasio, C.; Kuroki, Y.; Nakajima, H.; Okada, K.; Kotani, Y.; Handa, D.; Azechi, S.; Kimura, T.; Tsuhako, A.; et al. A General Scavenging Rate Constant for Reaction of Hydroxyl Radical with Organic Carbon in Atmospheric Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8196–8203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.D.; Kinney, H.; Anastasio, C. Phenolic carbonyls undergo rapid aqueous photodegradation to form low-volatility, light-absorbing products. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 126, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, L. Kinetics and mechanism of syringic acid degradation initiated by hydroxyl radical and sulphate radical in the aqueous phase. Chemosphere 2020, 256, 126997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.D.; Kinney, H.; Anastasio, C. Aqueous benzene-diols react with an organic triplet excited state and hydroxyl radical to form secondary organic aerosol. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 10227–10237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, J.; Chen, Y.; Ye, Z.; Ge, X. Aqueous-Phase Production of Secondary Organic Aerosols from Oxidation of Dibenzothiophene (DBT). Atmosphere 2020, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.K.Y.; Zhao, R.; Gao, S.S.; Abbatt, J.P.D. Aqueous-Phase OH Oxidation of Glyoxal: Application of a Novel Analytical Approach Employing Aerosol Mass Spectrometry and Complementary Off-Line Techniques. J. Phys. Chem. A 2011, 115, 10517–10526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Zhuang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, S.; Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Ge, X. Aqueous-phase oxidation of three phenolic compounds by hydroxyl radical: Insight into secondary organic aerosol formation yields, mechanisms, products and optical properties. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onasch, T.B.; Trimborn, A.; Fortner, E.C.; Jayne, J.T.; Kok, G.L.; Williams, L.R.; Davidovits, P.; Worsnop, D.R. Soot Particle Aerosol Mass Spectrometer: Development, Validation, and Initial Application. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 804–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Zeng, X.; Zhi, G.; Gligorovski, S.; Sheng, G.; Yu, Z.; Wang, X.; Peng, P. Molecular composition and photochemical evolution of water-soluble organic carbon (WSOC) extracted from field biomass burning aerosols using high-resolution mass spectrometry. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2020, 20, 6115–6128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, D.; Wang, J.; Xie, X.; Ge, S.; Ye, Z.; Xu, J.; et al. Aerosol characteristics and sources in Yangzhou, China resolved by offline aerosol mass spectrometry and other techniques. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, N.; Li, X.; Tao, Y.; Luo, S.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, S.; Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Ye, Z.; et al. Secondary organic aerosol formation from 3C⁎-initiated oxidation of 4-ethylguaiacol in atmospheric aqueous-phase. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 137953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiken, A.C.; Decarlo, P.F.; Kroll, J.H.; Worsnop, D.R.; Huffman, J.A.; Docherty, K.S.; Ulbrich, I.M.; Mohr, C.; Kimmel, J.R.; Sueper, D.; et al. O/C and OM/OC Ratios of Primary, Secondary, and Ambient Organic Aerosols with High-Resolution Time-of-Flight Aerosol Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4478–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canagaratna, M.R.; Jimenez, J.L.; Kroll, J.H.; Chen, Q.; Kessler, S.H.; Massoli, P.; Ruiz, L.H.; Fortner, E.C.; Williams, L.R.; Wilson, K.R.; et al. Elemental ratio measurements of organic compounds using aerosol mass spectrometry: Characterization, improved calibration, and implications. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2015, 15, 253–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Qu, Z.; Ma, S.; Luo, S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, M.; Ge, X. A comprehensive investigation of aqueous-phase photochemical oxidation of 4-ethylphenol. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ren, H.; Sun, Y.; Cao, F.; Chang, Y.; Liu, S.; Lee, X.; Agrios, K.; Kawamura, K.; Liu, D.; et al. High Contribution of Nonfossil Sources to Submicrometer Organic Aerosols in Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7842–7852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Zhang, Q.; Heo, J. Influence of intense secondary aerosol formation and long-range transport on aerosol chemistry and properties in the Seoul Metropolitan Area during spring time: Results from KORUS-AQ. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2018, 18, 7149–7168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Aljawhary, D.; Lee, A.K.Y.; Abbatt, J.P.D. Rapid Aqueous-Phase Photooxidation of Dimers in the α-Pinene Secondary Organic Aerosol. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Mulholland, J.A.; Russell, A.G.; Weber, R.J. Characterization of water-insoluble oxidative potential of PM2.5 using the dithiothreitol assay. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 224, 117327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, R.; Hennigan, C.J.; Mcmeeking, G.R.; Chuang, W.K.; Robinson, E.S.; Coe, H.; Donahue, N.M.; Robinson, A.L. Absorptivity of brown carbon in fresh and photo-chemically aged biomass-burning emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2013, 13, 7683–7693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ge, X.; Chen, H.; Xie, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Ye, Z.; Bao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M. Seasonal light absorption properties of water-soluble brown carbon in atmospheric fine particles in Nanjing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 187, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Laskin, J.; Nizkorodov, S.A.; Laskin, A. Revealing Brown Carbon Chromophores Produced in Reactions of Methylglyoxal with Ammonium Sulfate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14257–14266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskin, A.; Laskin, J.; Nizkorodov, S.A. Chemistry of Atmospheric Brown Carbon. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4335–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambe, A.T.; Cappa, C.D.; Massoli, P.; Onasch, T.B.; Forestieri, S.D.; Martin, A.T.; Cummings, M.J.; Croasdale, D.R.; Brune, W.H.; Worsnop, D.R.; et al. Relationship between Oxidation Level and Optical Properties of Secondary Organic Aerosol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6349–6357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vione, D.; Albinet, A.; Barsotti, F.; Mekic, M.; Jiang, B.; Minero, C.; Brigante, M.; Gligorovski, S. Formation of substances with humic-like fluorescence properties, upon photoinduced oligomerization of typical phenolic compounds emitted by biomass burning. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 206, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Han, T.; Du, W.; Wang, Q.; Chen, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Fu, P.; Wang, Z.; et al. Effects of Aqueous-Phase and Photochemical Processing on Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation and Evolution in Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wu, S.-D.; Shen, L.-J.; Zhao, T.-X.; Wei, Y.; Tang, X.-L.; Long, C.-L.; Zhou, Y.; He, D.-W.; Lin, T.; et al. Spermatogenesis dysfunction induced by PM2.5 from automobile exhaust via the ROS-mediated MAPK signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 167, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Yue, J.; Xu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yung, K.K.L.; Li, R. Fine particulate matter induces mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in human SH-SY5Y cells. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Liu, W.; Xu, Y.; Yi, K.; Zhou, M.; Tao, S.; Liu, W. Characteristics and oxidative potential of atmospheric PM2.5 in Beijing: Source apportionment and seasonal variation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, P.H.; He, Q.; Male, T.L.; Brune, W.H.; Rudich, Y.; Pardo, M. Exposure of Lung Epithelial Cells to Photochemically Aged Secondary Organic Aerosol Shows Increased Toxic Effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zotter, P.; Bruns, E.A.; Stefenelli, G.; Bhattu, D.; Brown, S.; Bertrand, A.; Marchand, N.; Lamkaddam, H.; Slowik, J.G.; et al. Particle-bound reactive oxygen species (PB-ROS) emissions and formation pathways in residential wood smoke under different combustion and aging conditions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2018, 18, 6985–7000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ou, Y.; Nie, D.; Chen, H.; Ye, Z.; Ge, X. Characterization of Products from the Aqueous-Phase Photochemical Oxidation of Benzene-Diols. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050534
Ou Y, Nie D, Chen H, Ye Z, Ge X. Characterization of Products from the Aqueous-Phase Photochemical Oxidation of Benzene-Diols. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(5):534. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050534
Chicago/Turabian StyleOu, Yang, Dongyang Nie, Hui Chen, Zhaolian Ye, and Xinlei Ge. 2021. "Characterization of Products from the Aqueous-Phase Photochemical Oxidation of Benzene-Diols" Atmosphere 12, no. 5: 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050534
APA StyleOu, Y., Nie, D., Chen, H., Ye, Z., & Ge, X. (2021). Characterization of Products from the Aqueous-Phase Photochemical Oxidation of Benzene-Diols. Atmosphere, 12(5), 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050534





