Seasonal Variations of Carbonyls and Their Contributions to the Ozone Formation in Urban Atmosphere of Taiyuan, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
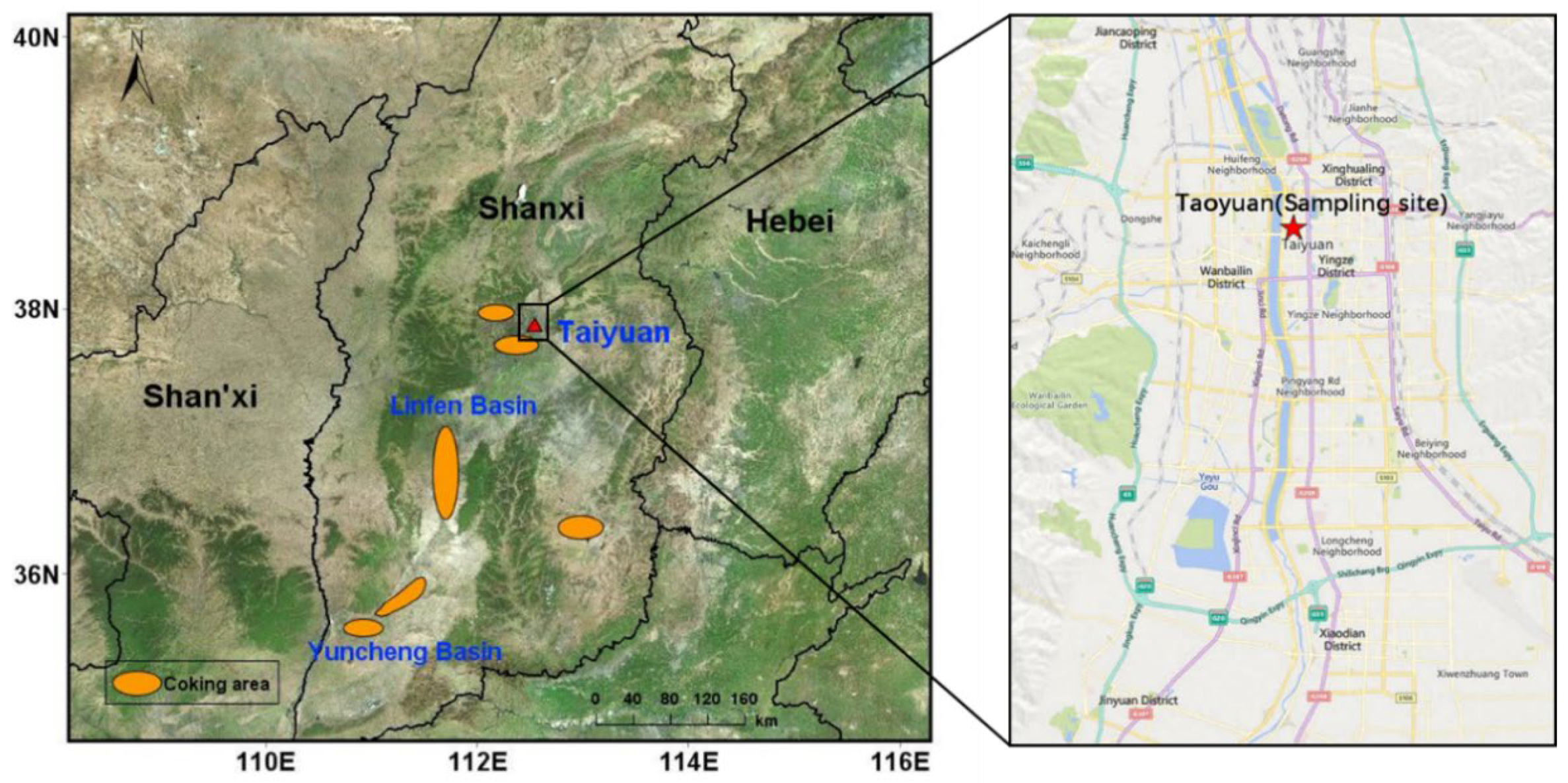
2.1. Sampling Description
2.2. Chemical Analysis
2.3. O3 Formation Potential
3. Results and Discussion
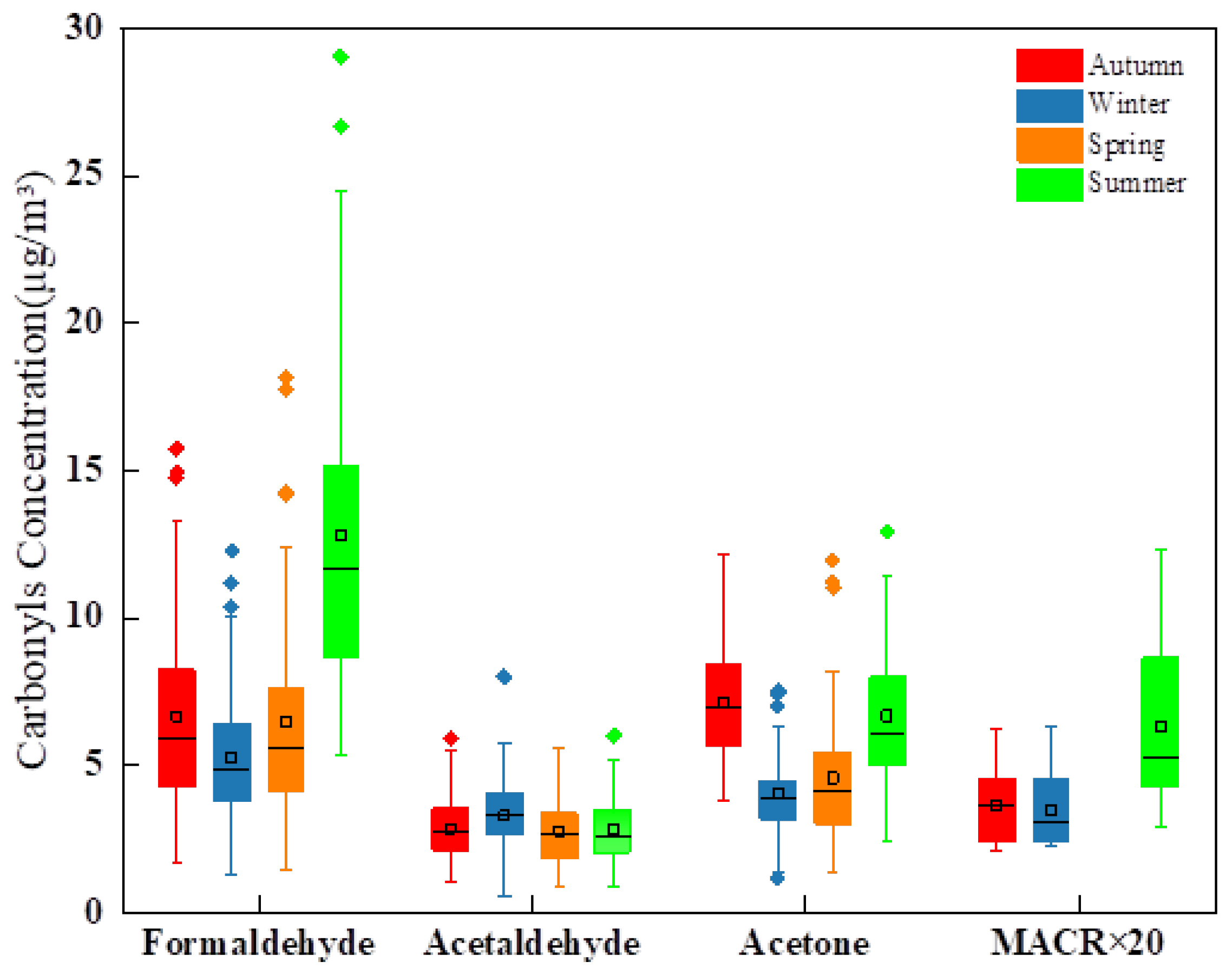
3.1. Atmospheric Carbonyl Levels
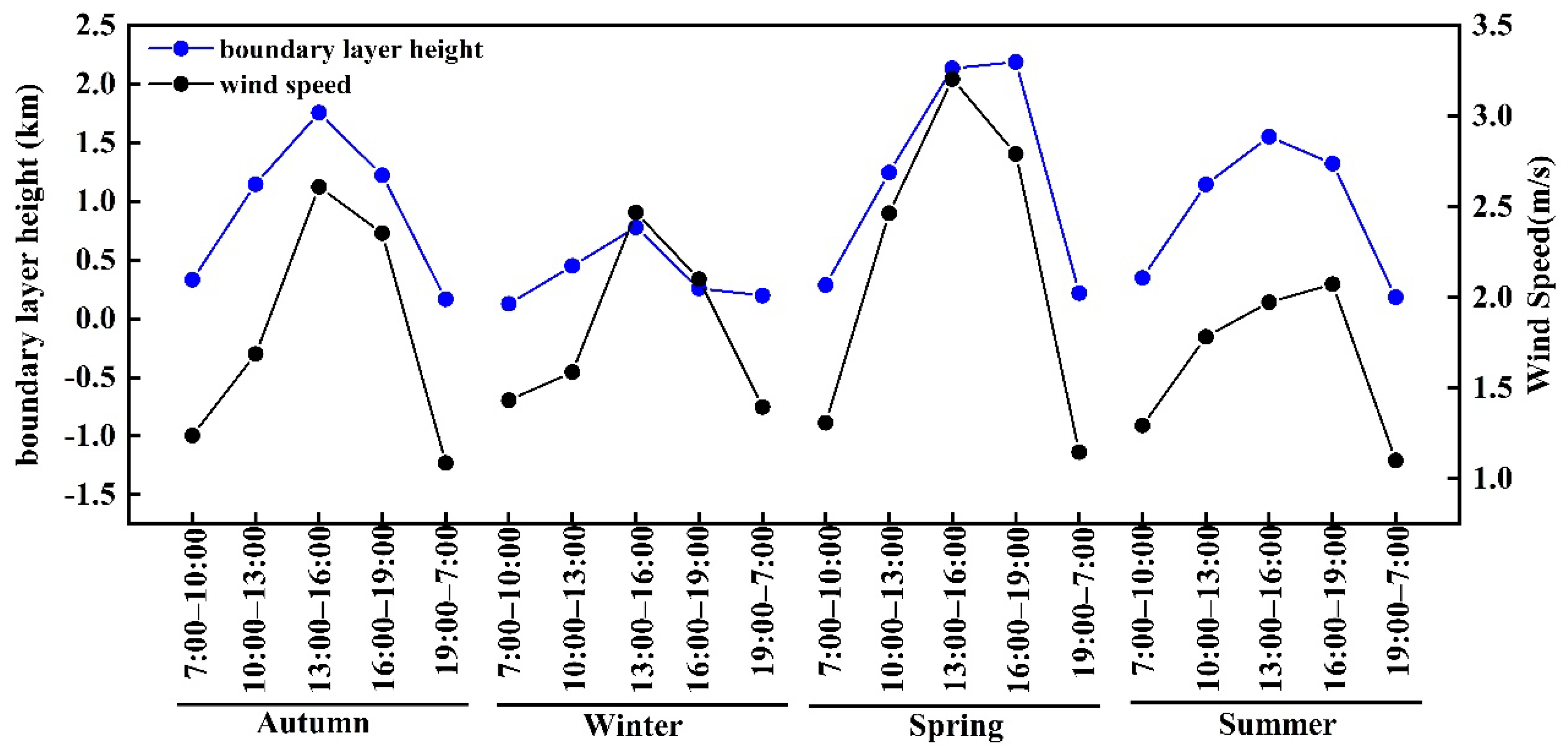
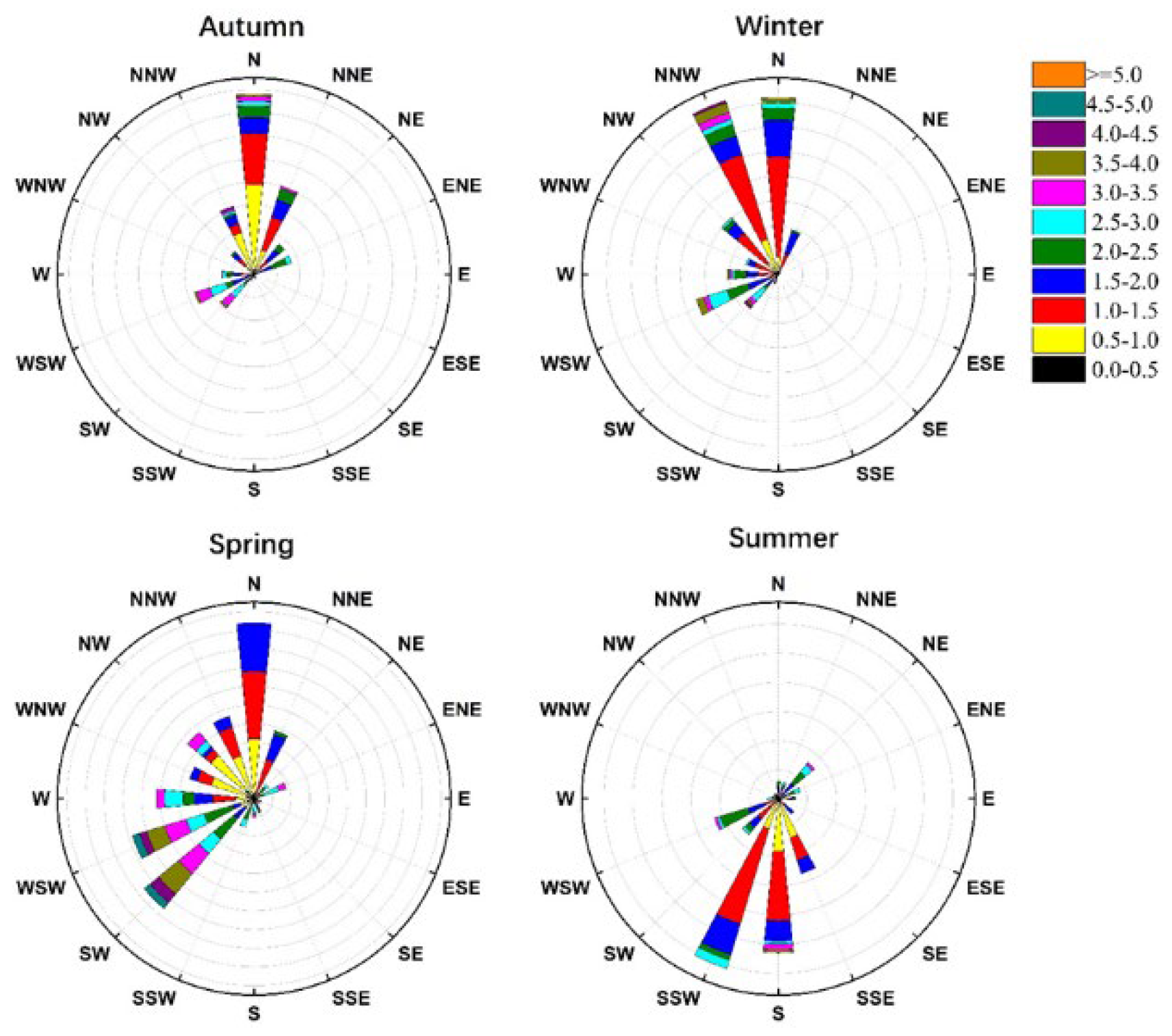
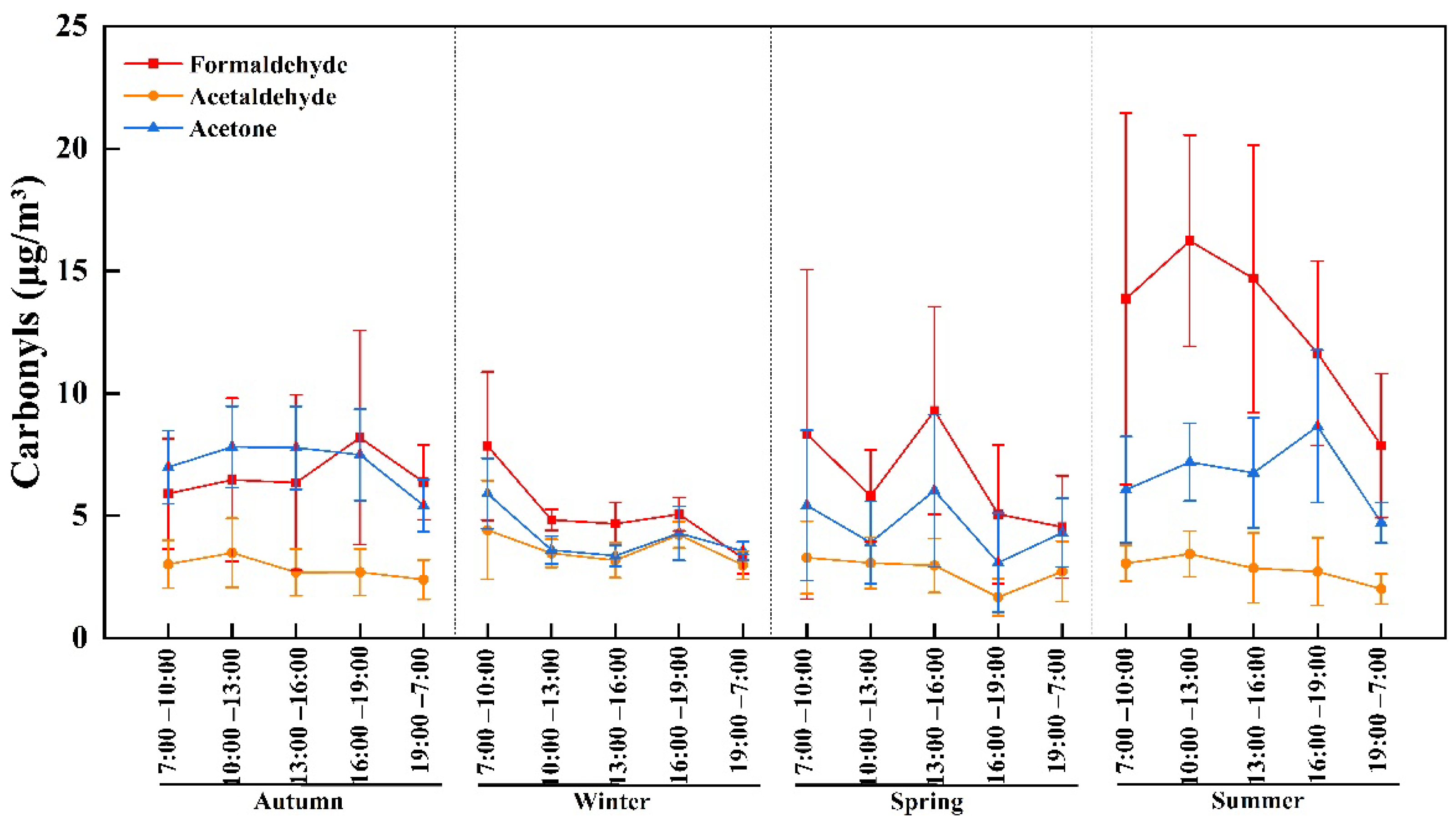
3.2. Seasonal and Diurnal Variations
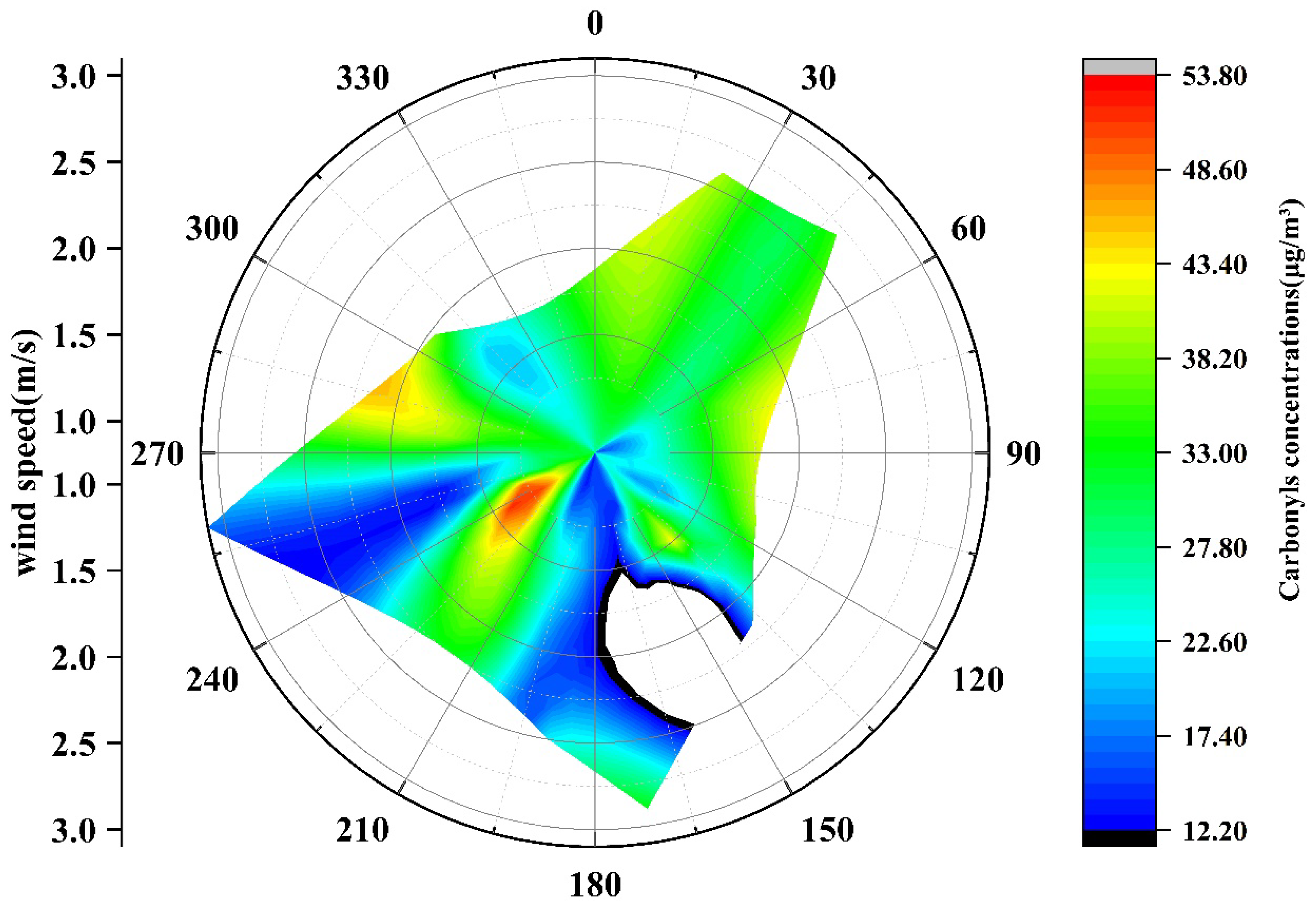
3.3. Ratios and Correlation Analysis
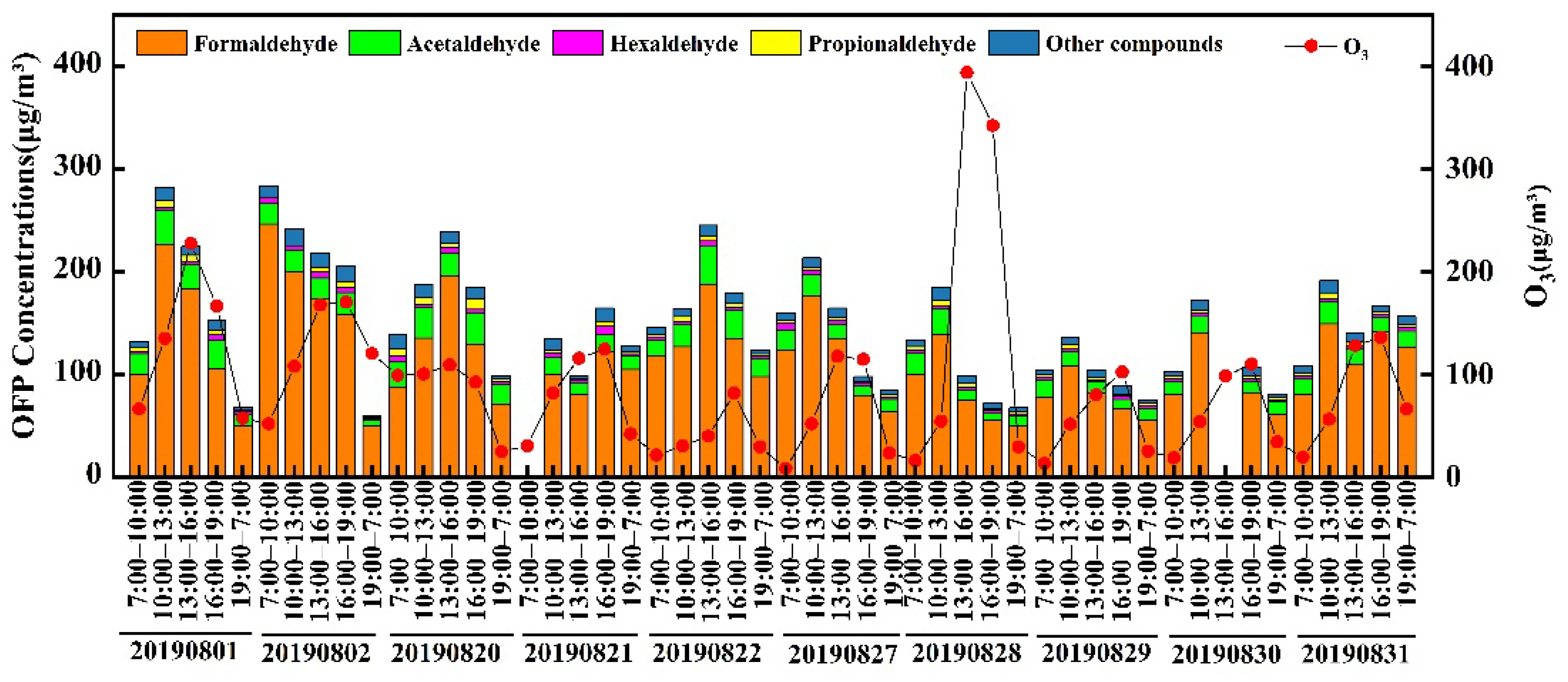
3.4. Ozone Formation Potential
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Autumn | Winter | Spring | Summer | Whole Year | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | MDL | |
| Formaldehyde | 6.66 ± 3.16 | 5.28 ± 2.42 | 6.50 ± 3.66 | 12.82 ± 5.68 | 7.70 ± 4.78 | 0.06 |
| Acetaldehyde | 2.86 ± 1.06 | 3.29 ± 1.40 | 2.77 ± 1.13 | 2.82 ± 1.12 | 2.95 ± 1.20 | 0.09 |
| Acetone | 7.10 ± 1.77 | 4.07 ± 1.47 | 4.57 ± 2.37 | 6.68 ± 2.43 | 5.57 ± 2.41 | 0.07 |
| Acrolein | 0.18 ± 0.05 | 0.24 ± 0.11 | 0.35 ± 0.15 | 0.30 ± 0.22 | 0.23 ± 0.12 | 0.13 |
| Propionaldehyde | 0.49 ± 0.17 | 0.55 ± 0.21 | 0.47 ± 0.19 | 0.53 ± 0.26 | 0.51 ± 0.21 | 0.14 |
| Crotonaldehyde | 0.28 ± 0.07 | 0.22 ± 0.02 | ND | ND | 0.24 ± 0.06 | 0.20 |
| Butanone | 0.62 ± 0.25 | 0.71 ± 0.55 | 1.15 ± 0.58 | 1.13 ± 0.83 | 0.89 ± 0.62 | 0.11 |
| Methacrolein | 0.18 ± 0.06 | 0.19 ± 0.08 | ND | 0.32 ± 0.14 | 0.23 ± 0.12 | 0.15 |
| Butyraldehyde | 0.32 ± 0.15 | 0.31 ± 0.13 | 0.30 ± 0.17 | 0.33 ± 0.17 | 0.32 ± 0.15 | 0.11 |
| Benzaldehyde | 0.63 ± 0.23 | 0.61 ± 0.40 | 0.44 ± 0.30 | 0.69 ± 0.45 | 0.59 ± 0.36 | 0.16 |
| Valeraldehyde | 0.30 ± 0.08 | 0.28 ± 0.07 | 0.36 ± 0.14 | 0.54 ± 0.25 | 0.40 ± 0.20 | 0.21 |
| m/p-Tolualdehyde | 0.73 ± 0.27 | 0.47 ± 0.13 | 0.41 ± 0.14 | 0.67 ± 0.47 | 0.64 ± 0.31 | 0.32 |
| Hexaldehyde | 0.84 ± 0.34 | 0.50 ± 0.24 | 0.67 ± 0.41 | 0.84 ± 0.36 | 0.71 ± 0.37 | 0.16 |
| Total carbonyls | 20.28 ± 6.30 | 15.59 ± 6.12 | 17.05 ± 7.88 | 26.40 ± 9.71 | 19.67 ± 8.56 |
| Season | Sampling Period | Temperature (°C) | Relative Humidity (%) | Wind Speed (m/s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Average | Range | Average | Range | Average | ||
| Autumn | 2018/10/1–10/11 | 4.40–23.10 | 13.96 | 19–70 | 43.17 | 0.30–4.20 | 1.54 |
| Winter | 2018/12/9–12/20 | −9.90–9.90 | −0.48 | 19–58 | 33.99 | 0.70–4.40 | 1.62 |
| Spring | 2019/4/1–4/8, 4/15–4/18 | 4–32 | 15.68 | 9–96 | 32.15 | 0.30–4.90 | 1.78 |
| Summer | 2019/8/1–8/2, 8/20–8/22, 8/27–8/31 | 16.40–32.70 | 23.53 | 22–100 | 59.20 | 0.30–3.70 | 1.46 |
| MIR (gO3/gVOCs) | Autumn | Winter | Spring | Summer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | ||
| Formaldehyde | 9.24 | 62.51 ± 28.04 | 47.72 ± 20.54 | 60.01 ± 33.83 | 118.48 ± 52.48 |
| Acetaldehyde | 6.34 | 18.30 ± 6.67 | 20.32 ± 7.89 | 17.56 ± 7.16 | 17.91 ± 7.12 |
| Acetone | 0.35 | 2.44 ± 0.66 | 1.41 ± 0.50 | 1.60 ± 0.83 | 2.34 ± 0.85 |
| Acrolein | 7.24 | 1.25 ± 0.38 | 1.73 ± 0.77 | 2.50 ± 1.10 | 2.18 ± 1.59 |
| Propionaldehyde | 6.83 | 3.40 ± 1.16 | 3.54 ± 1.46 | 3.20 ± 1.30 | 3.46 ± 1.88 |
| Crotonaldehyde | 9.39 | 2.35 ± 1.04 | 1.86 ± 0.69 | 1.96 ± 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Butanone | 1.18 | 0.73 ± 0.30 | 0.84 ± 0.65 | 1.36 ± 0.68 | 1.31 ± 0.99 |
| Methacrolein | 5.84 | 1.05 ± 0.36 | 0.98 ± 0.37 | 0.00 | 1.84 ± 0.80 |
| Butyraldehyde | 5.75 | 1.84 ± 0.87 | 1.70 ± 0.73 | 1.65 ± 1.00 | 1.89 ± 0.96 |
| Benzaldehyde | −0.67 | −0.42 ± 0.16 | −0.40 ± 0.27 | −0.30 ± 0.20 | −0.46 ± 030 |
| Valeraldehyde | 4.89 | 1.41 ± 0.43 | 1.34 ± 0.40 | 1.76 ± 0.67 | 2.64 ± 1.24 |
| m/p-Tolualdehyde | −0.59 | −0.42 ± 0.16 | −0.27 ± 0.09 | −0.24 ± 0.09 | −0.39 ± 0.28 |
| Hexaldehyde | 4.18 | 3.52 ± 1.45 | 2.03 ± 1.00 | 2.80 ± 1.73 | 3.51 ± 1.52 |
| Total carbonyls | 93.71 ± 37.30 | 78.58 ± 30.62 | 89.00 ± 43.93 | 151.78 ± 62.24 |

References
- Carlier, P.; Hannachi, H.; Mouvier, G. The chemistry of carbonyl compounds in the atmosphere—A review. Atmos. Environ. 1986, 20, 2079–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R. Atmospheric chemistry of VOCs and NOx. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 2063–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possanzini, M.; Di Palo, V.; Cecinato, A. Sources and photodecomposition of formaldehyde and acetaldehyde in Rome ambient air. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 3195–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCR. Formaldehyde and Other Aldehydes; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- CEPA. Acetaldehyde as a Toxic Air Contaminant; Part A: Exposure; Part B: Health Assessment; Air Resources Board, Stationary Source Division: Sacramento, CA, USA, 1993.
- WHO. Air Quality Guidelines for Europe; Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Grosjean, E.; Grosjean, D.; Fraser, M.P.; Cass, G.R. Air Quality Model Evaluation Data for Organics. 2. C1−C14 Carbonyls in Los Angeles Air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 2687–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possanzini, M.; Di Palo, V.; Petricca, M.; Fratarcangeli, R.; Brocco, D. Measurements of lower carbonyls in Rome ambient air. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 3757–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Grosselin, B.; Daële, V.; Mellouki, A.; Mu, Y. Seasonal, diurnal and nocturnal variations of carbonyl compounds in the semi-urban environment of Orléans, France. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 40, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzettj, N.A.; Bryan, R.J. Atmospheric Sampling for Aldehydes and Eye Irritation in Los Angeles Smog—1960. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1961, 11, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Feng, Y.; Li, J.; Xiong, B.; Feng, J.; Wen, S.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J.; Wu, M. Characteristics of carbonyl compounds in ambient air of Shanghai, China. J. Atmos. Chem. 2008, 61, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, H.; Cai, Q.-Y.; Wen, S.; Chi, Y.; Guo, S.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J. Seasonal and diurnal variations of carbonyl compounds in the urban atmosphere of Guangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3523–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-F.; Zhang, B.; Xia, S.-Y.; Han, Y.; Wang, C.; Yu, G.-H.; Feng, N. Sources of oxygenated volatile organic compounds (OVOCs) in urban atmospheres in North and South China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Sun, M.; Wang, L.; Guo, J.; Xie, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, R. Gas-particle partitioning of carbonyls and its influencing factors in the urban atmosphere of Zhengzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 142027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Chen, M.; Tan, J. Seasonal and diurnal characteristics of atmospheric carbonyls in Nanning, China. Atmos. Res. 2016, 169, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Cheng, H.; Wang, Z.; Peng, J.; Zhu, J.; Lyu, X.; Guo, H. Chemical characteristics of atmospheric carbonyl compounds and source identification of formaldehyde in Wuhan, Central China. Atmos. Res. 2019, 228, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Shen, H.; Chen, Z. Characterizing summer and winter carbonyl compounds in Beijing atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 214, 116845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Huang, X.-F.; Han, Y.; Zhu, B.; He, L.-Y. Sources and Potential Photochemical Roles of Formaldehyde in an Urban Atmosphere in South China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 11934–11947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Mu, Y.; Lee, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z. Influences of characteristic meteorological conditions on atmospheric carbonyls in Beijing, China. Atmos. Res. 2009, 93, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Guo, S.; Tan, J.; Wang, S.; Chai, F. Characteristics of atmospheric carbonyls during haze days in Beijing, China. Atmos. Res. 2012, 114–115, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Guo, L.; Cao, R.; Gao, B.; Yan, Y.; He, Q. A wintertime study of PM2.5-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Taiyuan during 2009–2013: Assessment of pollution control strategy in a typical basin region. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 140, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Yan, Y.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X. Characterization and source analysis of water-soluble inorganic ionic species in PM2.5 in Taiyuan city, China. Atmos. Res. 2017, 184, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TEEB. Bulletin of Environmental Status in Taiyuan City 2016–2020. Available online: http://hbj.taiyuan.gov.cn (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Li, J.; Li, H.; He, Q.; Guo, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y.; Chai, F. Characteristics, sources and regional inter-transport of ambient volatile organic compounds in a city located downwind of several large coke production bases in China. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 233, 117573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wen, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Lü, H.; Bi, X.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J. Ambient levels of carbonyl compounds and their sources in Guangzhou, China. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 1789–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, W.P.L. Development of Ozone Reactivity Scales for Volatile Organic Compounds. Air Waste 1994, 44, 881–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, W. Updated maximum incremental reactivity scale and hydrocarbon bin reactivities for regulatory applications. Calif. Air Resour. Board Contract 2010, 1, 307–339. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, K.F.; Ho, S.S.H.; Dai, W.T.; Cao, J.J.; Huang, R.-J.; Tian, L.; Deng, W.J. Seasonal variations of monocarbonyl and dicarbonyl in urban and sub-urban sites of Xi’an, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 2835–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Xue, Z.; Duan, L.; Kou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X. Pollution Characteristics of Atmospheric Carbonyls in Urban Linfen in Winter. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CWarneke, W.; de Gouw, J.A.; Holloway, J.S.; Peischl, J.; Ryerson, T.B.; Atlas, E.; Blake, D.; Trainer, M.; Parrish, D.D. Multiyear trends in volatile organic compounds in Los Angeles, California: Five decades of decreasing emissions. J. Geophys. Res. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xue, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Lee, S.; Blake, D.R.; Chai, F.; Wang, W. Observations and Explicit Modeling of Summertime Carbonyl Formation in Beijing: Identification of Key Precursor Species and Their Impact on Atmospheric Oxidation Chemistry. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 1426–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiyuan Municipal Bureau of Statistics (TMBS). Taiyuan Statistical Yearbook of 2020. 2020. Available online: https://www.yearbookchina.com/ (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- Feng, Y.; Wen, S.; Wang, X.; Sheng, G.; He, Q.; Tang, J.; Fu, J. Indoor and outdoor carbonyl compounds in the hotel ballrooms in Guangzhou, China. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesenthal, T.A.; Shepson, P.B. Observations of anthropogenic inputs of the isoprene oxidation products methyl vinyl ketone and methacrolein to the atmosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 1375–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Zhai, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Z. Seasonal and diurnal characteristics of carbonyls in the urban atmosphere of Changsha, a mountainous city in south-central China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Lee, X. Temporal variations of atmospheric carbonyls in urban ambient air and street canyons of a Mountainous city in Southwest China. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2098–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepson, P.; Hastie, D.; Schiff, H.; Polizzi, M.; Bottenheim, J.; Anlauf, K.; Mackay, G.; Karecki, D. Atmospheric concentrations and temporal variations of C1▯C3 carbonyl compounds at two rural sites in central Ontario. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1991, 25, 2001–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wen, S.; Wang, X.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J.; Hu, P.; Yu, Y. Carbon isotope analysis for source identification of atmospheric formaldehyde and acetaldehyde in Dinghushan Biosphere Reserve in South China. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 3489–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duane, M.; Poma, B.; Rembges, D.; Astorga, C.; Larsen, B. Isoprene and its degradation products as strong ozone precursors in Insubria, Northern Italy. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 3867–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, G.; An, T. Theoretical study of the reaction mechanism and kinetics of low-molecular-weight atmospheric aldehydes (C1–C4) with NO2. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 54, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, S.G.; El-Fadel, M.; Saliba, N.A. Seasonal, diurnal and nocturnal behaviors of lower carbonyl compounds in the urban environment of Beirut, Lebanon. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 2459–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cui, Y.; He, Q.; Guo, L.; Tian, X.; Zhang, K.; Wang, X. Predominant effects of emission reduction by recording 8-year water-soluble ions in precipitation in Taiyuan, North China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1922–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wu, B.; Liu, S.; Shao, P.; Liu, X.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xue, Y.; Gao, J.; et al. A regional high-resolution emission inventory of primary air pollutants in 2012 for Beijing and the surrounding five provinces of North China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 181, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Shao, M.; De Gouw, J.; Parrish, D.D.; Lu, S.; Wang, M.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in urban air: How chemistry affects the interpretation of positive matrix factorization (PMF) analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2012, 117, 24302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Location | Sampling Periods | Formaldehyde | Acetaldehyde | Acetone | Total | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taiyuan | Whole year | 7.70 ± 4.78 | 2.95 ± 1.20 | 5.57 ± 2.41 | 19.67 ± 8.56 | This study |
| Linfen | 2019.01 | 4.59 ± 2.64 | 4.47 ± 2.22 | 3.24 ± 1.82 | 16.90 ± 7.65 | [29] |
| Beijing | 2018.08 | 8.49 ± 2.11 | 2.97 ± 0.79 | 6.72 ± 1.58 | 21.05 ± 4.9 | [17] |
| 2017.11 | 3.18 ± 2.40 | 2.50 ± 2.06 | 2.57 ± 1.62 | 9.56 ± 6.63 | ||
| Xi’an | 2010.01 | 3.64 ± 1.40 | 3.45 ± 1.50 | 5.15 ± 2.95 | 14.24 ± 6.83 | [28] |
| 2010.07 | 4.62 ± 1.43 | 2.07 ± 0.72 | 0.69 ± 0.42 | 9.16 ± 3.67 | ||
| Zhengzhou | 2019.01 | 4.87 | 4.13 | 3.80 | 13.89 | [14] |
| 2019.07 | 8.34 | 5.03 | 4.99 | 20.03 | ||
| Wuhan | 2017.02–11 | 6.57 | 4.63 | 7.46 | 20.80 | [16] |
| Shanghai | 2007.01–10 | 19.40 | 15.9 | 11.86 | 62.70 | [11] |
| Nanning | 2011.10–2012.07 | 6.79 ± 3.39 | 15.81 ± 10.48 | 5.43 ± 6.91 | 33.21 ± 15.12 | [15] |
| Guangzhou | 2005.01–11 | 7.49 | 7.67 | 11.95 | 43.55 | [12] |
| Los Angeles, USA | 2008–2010 | 7.94 | 7.41 | 24.63 | / | [30] |
| Rome, Italy | 1994.07–1995.01 | 18.73 | 15.02 | 14.48 | / | [8] |
| Period | C1/C2 | C2/C3 | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taiyuan | Spring | 2.39 | 6.03 | This study |
| Summer | 4.68 | 5.63 | ||
| Autumn | 2.34 | 5.91 | ||
| Winter | 1.68 | 6.34 | ||
| Wuhan | Summer | 4.33 | 10.28 | [16] |
| Winter | 1.15 | 2.65 | ||
| Beirut | Summer | 2.30 | 2.00 | [41] |
| Nanning | Summer | 0.75 | 24.49 | [15] |
| Winter | 0.40 | 18.23 | ||
| Guangzhou | Summer | 1.32 | 5.90 | [12] |
| Winter | 1.04 | 7.70 | ||
| Beijing | Summer | 2.69 | 6.29 | [20] |
| Xi’an | Summer | 2.32 | / | [28] |
| Winter | 1.10 | / |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Cui, Y.; He, Q.; Guo, L.; Gao, X.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Seasonal Variations of Carbonyls and Their Contributions to the Ozone Formation in Urban Atmosphere of Taiyuan, China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12040510
Liu Z, Cui Y, He Q, Guo L, Gao X, Feng Y, Wang Y, Wang X. Seasonal Variations of Carbonyls and Their Contributions to the Ozone Formation in Urban Atmosphere of Taiyuan, China. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(4):510. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12040510
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zeqian, Yang Cui, Qiusheng He, Lili Guo, Xueying Gao, Yanli Feng, Yuhang Wang, and Xinming Wang. 2021. "Seasonal Variations of Carbonyls and Their Contributions to the Ozone Formation in Urban Atmosphere of Taiyuan, China" Atmosphere 12, no. 4: 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12040510
APA StyleLiu, Z., Cui, Y., He, Q., Guo, L., Gao, X., Feng, Y., Wang, Y., & Wang, X. (2021). Seasonal Variations of Carbonyls and Their Contributions to the Ozone Formation in Urban Atmosphere of Taiyuan, China. Atmosphere, 12(4), 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12040510







