Refined Characteristics of Moisture Cycling over the Inland River Basin Using the WRF Model and the Finer Box Model: A Case Study of the Heihe River Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Region, WRF Model Configuration, and Methods
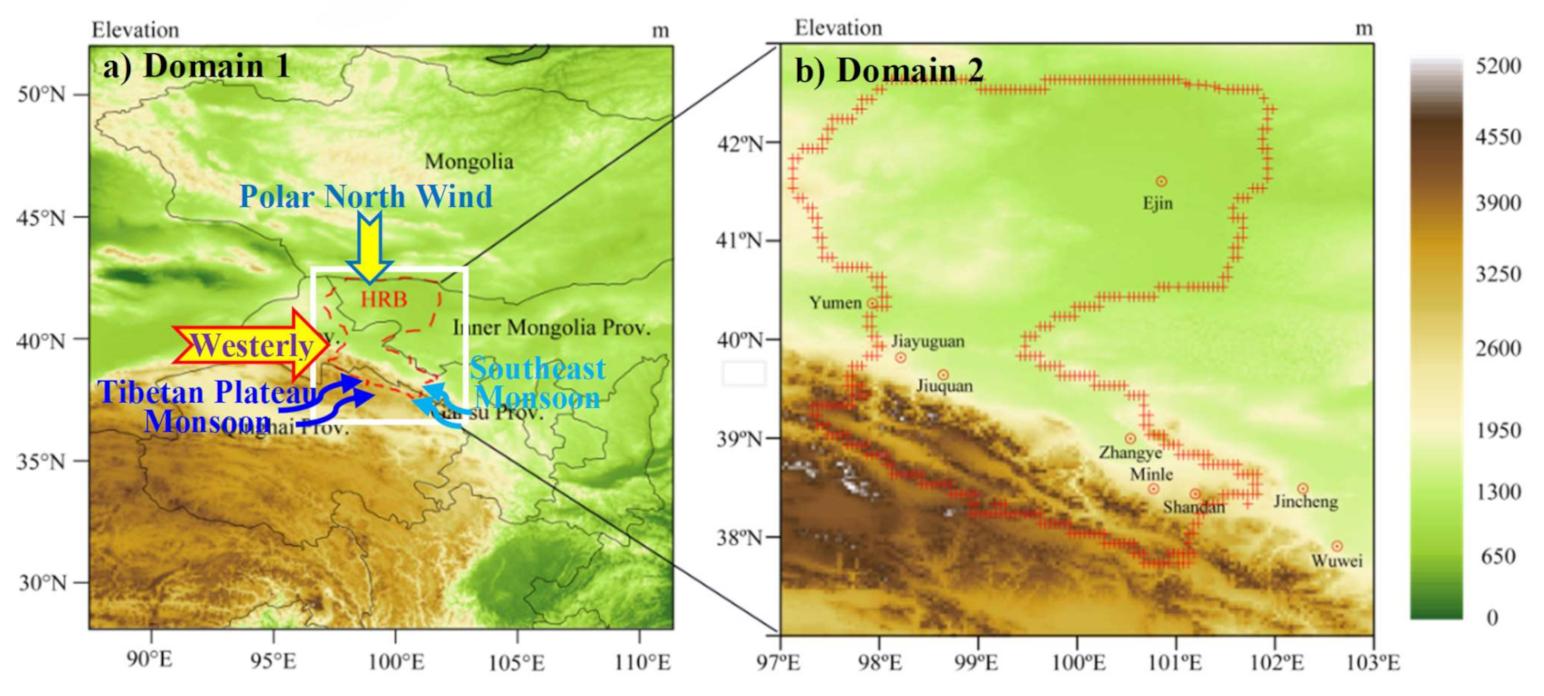
2.1. Research Region
2.2. WRF Model Configuration
2.3. Moisture Recycling Estimation Method
2.4. Finer Box Model for Calculating the Net Water Vapor Flux
3. Results
3.1. Atmospheric Water Storage
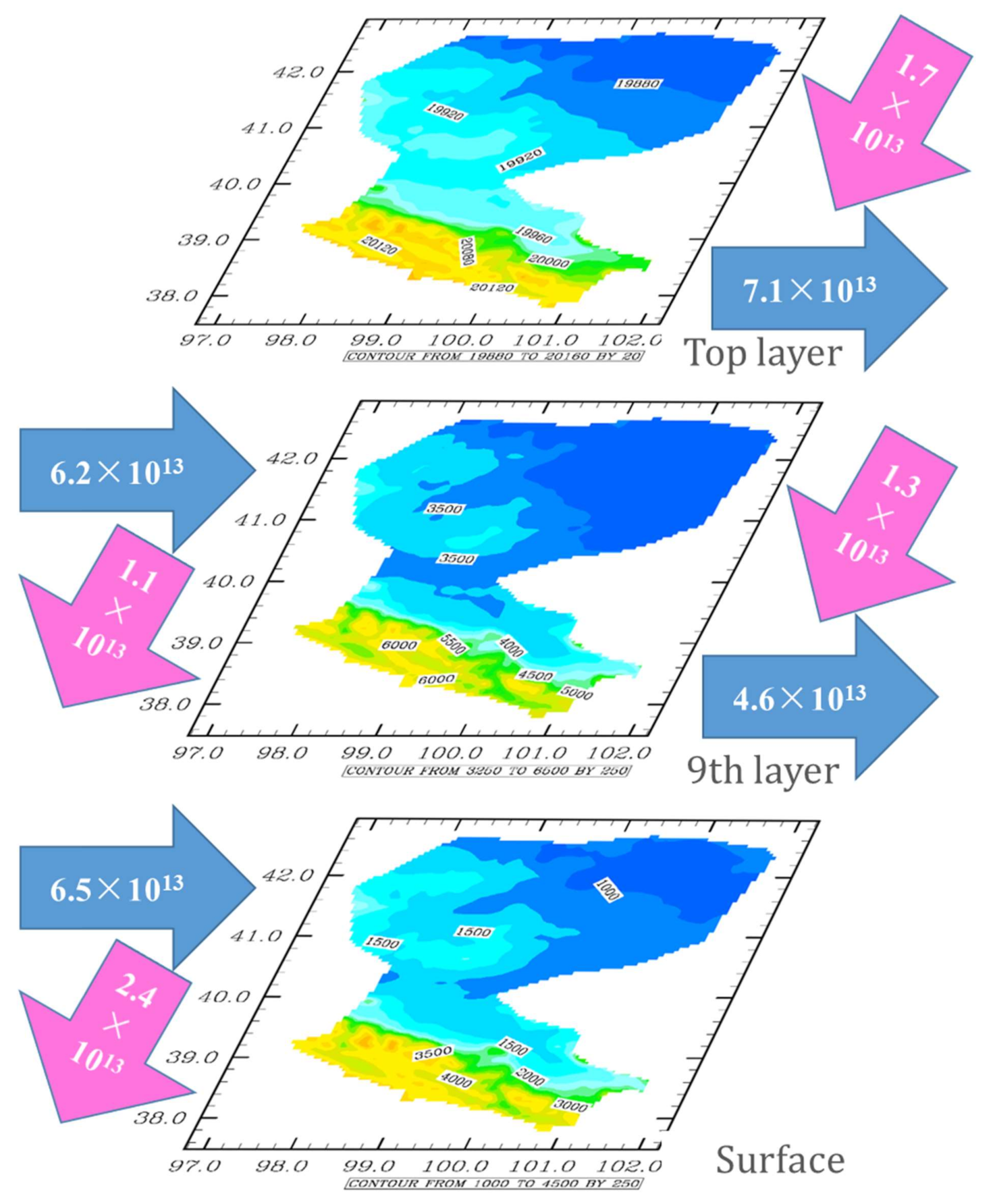
3.2. Net Water-Vapor Transport in the X and Y Directions
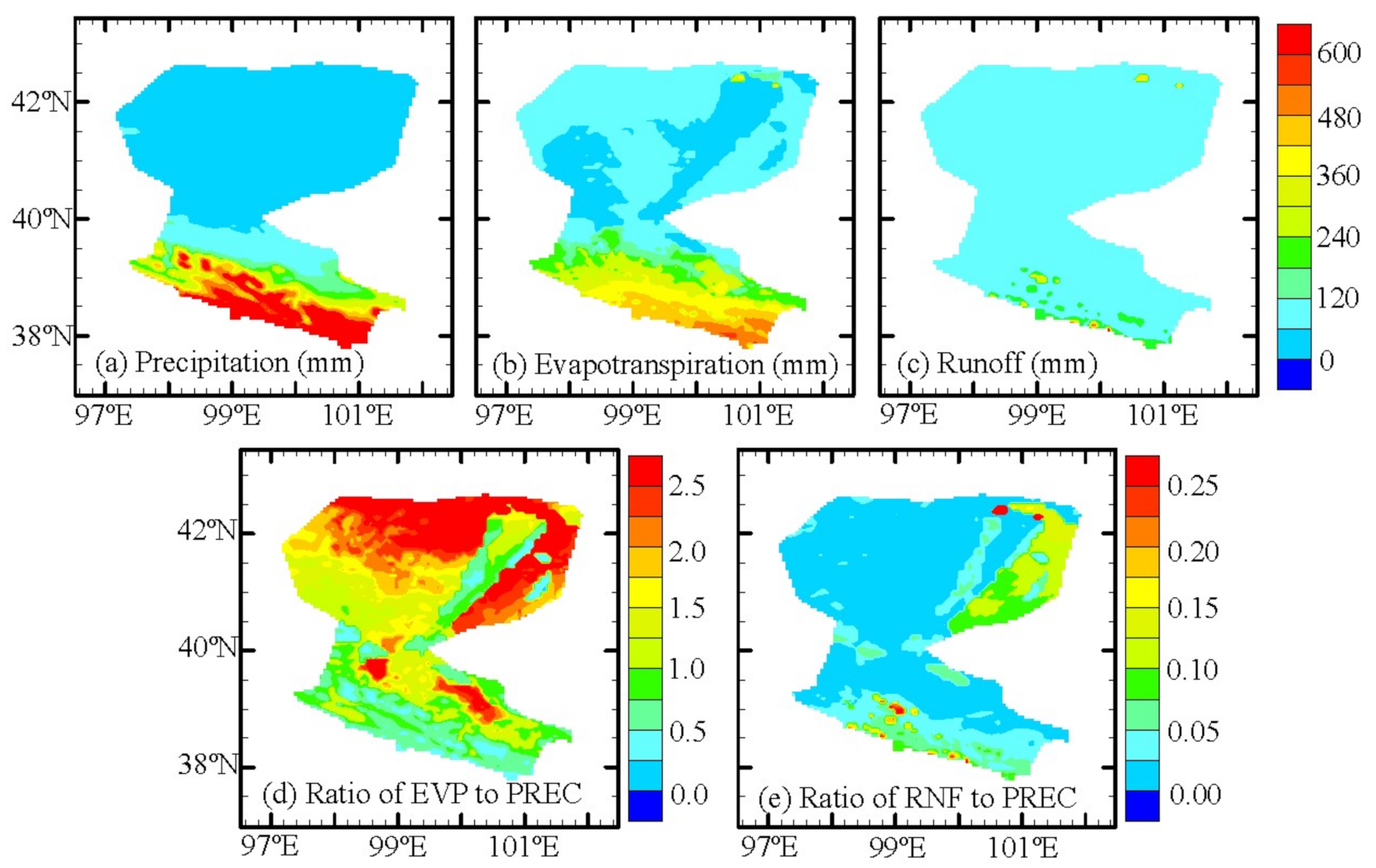
3.3. Precipitation, Evapotranspiration, and Runoff
3.4. Moisture Recycling
4. Discussion
4.1. Water-Vapor Transport in the HRB
4.2. Accuracy of the Moisture Recycling Estimation
4.3. Higher Moisture Recycling over the Inland River Basin
4.4. Tuning Layer and Other Issues
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The water vapor of the HRB was dominantly transported by the wind from west and from the north, and the west wind was much larger than the north wind. The net vapor transported by the west wind was positive, and by north wind was negative;
- (2)
- The precipitation over the HRB was triggered mainly by the vapor from the west, which arose from the lower vertical layer to the higher one during transport from west to east. The vapor from the north sank from a higher layer to a lower one, and crossed the south edge of the HRB;
- (3)
- The moisture-recycling ratio of evapotranspiration to precipitation over the HRB was much higher than in the other regions, which may be due to the strong land–atmosphere interaction in the arid inland river basin.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brubaker, K.L.; Entekhabi, D.; Eagleson, P.S. Estimation of continental precipitation recycling. J. Clim. 1993, 6, 1077–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltahir, E.A.B.; Bras, R.L. Precipitation recycling in the Amazon basin. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1994, 120, 861–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, R.; Jouzel, J.; Suozzo, R.; Russell, G.; Broecker, W.; Rind, D.; Eagleson, P. Global sources of local precipitation as determined by the Nasa/Giss GCM. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1986, 13, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E. Atmospheric moisture recycling: Role of advection and local evaporation. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 1368–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosilovich, M.G.; Schubert, S.D. Water vapor tracers as diagnostics of the regional hydrologic cycle. J. Hydrometeorol. 2002, 3, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirmeyer, P.A.; Brubaker, K.L. Contrasting evaporative moisture sources during the drought of 1988 and the flood of 1993. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1999, 104, 19383–19397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirmeyer, P.A.; Brubaker, K.L. Characterization of the global hydrologic cycle from a back-trajectory analysis of atmospheric water vapor. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, L.; Zhong, L.; Ke, Z. Characteristics of the precipitation recycling ratio and its relationship with regional precipitation in China. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2015, 127, 513–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zheng, C.; Tian, Y.; Liu, J.; Zheng, Y. Numerical modeling of regional groundwater flow in the Heihe River Basin, China: Advances and new insights. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciric, D.; Stojanovic, M.; Drumond, A.; Nieto, R.; Gimeno, L. Tracking the origin of moisture over the Danube river basin using a Lagrangian approach. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Rojí, S.J.; Sáenz, J.; De Argandoña, J.D.; Ibarra-Berastegi, G. Moisture recycling over the Iberian Peninsula: The impact of 3DVAR data assimilation. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorí, R.; Nieto, R.; Drumond, A.; Gimeno, L. The Niger river basin moisture sources: A Lagrangian analysis. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.J.; Yu, B.; Gao, X.Q.; Li, J. Change of large scale circulation and its impact on the water vapor over north china. Plateau Meteorol. 2008, 27, 517–523. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, N.; Kong, Y.; Song, Y.; He, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L. Contribution of recycled moisture to local precipitation in the inland Heihe River Basin. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 271, 316–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Li, X. Integrated research methods in watershed science. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.D.; Zhao, C.Y. An integrated study of ecological and hydrological processes in the inland river basin of the arid regions, China. Adv. Earth Sci. 2008, 23, 1005–1012. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; 1535p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA. National Centers for Environmental Information, State of the Climate: Global Climate Report for January 2016. Available online: https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/sotc/global/201601 (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- Olsson, J.; Berg, P.; Kawamura, A. Impact of RCM Spatial Resolution on the Reproduction of Local, Subdaily Precipitation. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prein, A.F.; Gobiet, A.; Suklitsch, M.; Truhetz, H.; Awan, N.K.; Keuler, K.; Georgievski, G. Added value of convection permitting seasonal simulations. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 41, 2655–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.K.; Cui, Z.; Domen, J. Appendix A—Emission factors for air pollutants related to mining and mineral processing. In Environmental Impact of Mining and Mineral Processing; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 271–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Kinzelbach, W.; Li, W.; Dong, X. Box model and 1D longitudinal model of flow and transport in Bosten Lake, China. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mareddy, A.R. 5—Impacts on air environment. In Impacts on Air Environment; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 171–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.; Navarro-Esbrí, J.; Belman-Flores, J.; Pérez, J.A.R. A simplified black-box model oriented to chilled water temperature control in a variable speed vapour compression system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2011, 31, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Li, X.; Cheng, G.; Li, H.; He, X. Development and evaluation of a river-basin-scale high spatio-temporal precipitation data set using the WRF Model: A case study of the Heihe River Basin. Remote. Sens. 2015, 7, 9230–9252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Li, X.; Shi, X.; Han, X.; Luo, L.; Wang, L. Dynamic downscaling of near-surface air temperature at the basin scale using WRF-a case study in the Heihe River Basin, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2012, 6, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.; Xu, Z.; Feng, Q.; Xiao, S.; Xiao, H. Integrated study of the water–ecosystem–economy in the Heihe River Basin. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2014, 1, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, G.; Liu, S.; Xiao, Q.; Ma, M.; Jin, R.; Che, T.; Liu, Q.; Wang, W.; Qi, Y.; et al. Heihe watershed allied telemetry experimental research (HiWATER): Scientific objectives and experimental design. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xiang, X. Spatial variation of reference crop evapotranspiration on Tibetan Plateau. Water Sci. Eng. 2009, 2, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yin, L.; Xiao, H.; Cheng, G.; Zhou, M.; Yang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhou, J. Isotopic evidence for the moisture origin and composition of surface runoff in the headwaters of the Heihe River Basin. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Liu, X.H.; Ma, Y.M. Turbulence structure and transfer characteristics in the surface layer of HEIFE Gobi area. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 1992, 6, 92–104. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Ma, M.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, Q.; Che, T.; Chen, E.; Yan, G.; et al. Watershed allied telemetry experimental research. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K. The westerly fluctuation and water vapor transport over the Qilian-Heihe valley. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2004, 47, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, K.L.; Cheng, G.D.; Li, H.Y.; Yu, T. Temporal variation and spatial structure of the water vapor transport and budget over the Heihe drainage area. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2009, 31, 311–317. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.H.; Dong, X.; He, H. Characteristics of water vapor transportation and budget over the Heihe drainage basin. J. Nat. Resour. 2012, 27, 510–521. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B. A time-split nonhydrostatic atmospheric model for weather research and forecasting applications. J. Comput. Phys. 2008, 227, 3465–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.Y.; Dudhia, J.; Chen, S.H. A revised approach to ice microphysical processes for the bulk parameterization of clouds and precipitation. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, J.S.; Kain, J. The Kain—Fritsch convective parameterization: An update. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A new vertical diffusion package with an explicit treatment of entrainment processes. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2006, 134, 2318–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudhia, J. Numerical study of convection observed during the Winter Monsoon Experiment using a mesoscale two-dimensional model. J. Atmos. Sci. 1989, 46, 3077–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlawer, E.J.; Taubman, S.J.; Brown, P.D.; Iacono, M.J.; Clough, S.A. Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 16663–16682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CGIP. Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment (GEWEX) Continental-Scale International Project: A Review of Progress and Opportunities; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; pp. 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Xiong, Z.; Yan, X. Modeling precipitation changes in the Heihe River Basin, Northwest China, from 1980 to 2014 with the Regional Integrated Environment Modeling System (RIEMS) nested with ERA-Interim reanalysis data. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2018, 137, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.L.; Cheng, G.D.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, L.J. Atmospheric hydrologic cycle over the Qilian-Heihe valley. Adv. Water Sci. 2003, 14, 91–97. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.R.; Zou, S.B.; Du, D.Y.; Xiong, Z.; Lu, Z.X.; Ruan, H.W.; Xiao, H.L. Variation of tropospheric specific humidity upon the middle-lower reaches of the heihe river during 1981–2010. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2016, 38, 57–68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.J.; Wang, K.L.; Jiang, H.; Li, Z.G.; Sun, J.; Luo, X.P.; Zhu, Q.L. A numerical simulation of the effects of westerly and monsoon on precipitation in the Heihe River Basin. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2010, 32, 489–496. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.J.; Zhang, S.Q. Study on water internal recycle process and mechanism in typical mountain areas of inland basins, Northwest China: Progress and Challenge. Adv. Earth Sci. 2018, 33, 719–728. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.D.; Li, X. Impact of spatial resolution on WRF model in Heihe river basin. eScience Technol. Appl. 2011, 2, 126–137. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.D.; Li, X.; Ran, Y.H.; Liu, C. Impact of underlying surface information on WRF modeling in Heihe River Basin. Plateau Meteorol. 2012, 31, 657–667. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bonekamp, P.N.J.; Collier, E.; Immerzeel, W.W. The impact of spatial resolution, land use, and spinup time on resolving spatial precipitation patterns in the Himalayas. J. Hydrometeorol. 2018, 19, 1565–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, L.; Vázquez, M.; Eiras-Barca, J.; Sorí, R.; Stojanovic, M.; Algarra, I.; Nieto, R.; Ramos, A.M.; Durán-Quesada, A.M.; Dominguez, F. Recent progress on the sources of continental precipitation as revealed by moisture transport analysis. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 201, 103070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-P.; Shen, Y.; Larry, P.; Li, B. Possible physical mechanism of water vapor transport over Tarim River Basin. Ecol. Complex. 2012, 9, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keys, P.W.; Barnes, E.A.; Van Der Ent, R.J.; Gordon, L.J. Variability of moisture recycling using a precipitationshed framework. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 3937–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keys, P.W.; Porkka, M.; Wang-Erlandsson, L.; Fetzer, I.; Gleeson, T.; Gordon, L.J. Invisible water security: Moisture recycling and water resilience. Water Secur. 2019, 8, 100046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zongxing, L.; Qi, F.; Wang, Q.; Song, Y.; Jianguo, L.; Yongge, L.; Yamin, W. Quantitative evaluation on the influence from cryosphere meltwater on runoff in an inland river basin of China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2016, 143, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gui, J.; Wang, X.; Feng, Q.; Zhao, T.; Ouyang, C.; Guo, X.; Zhang, B.; Shi, Y. Water resources in inland regions of central Asia: Evidence from stable isotope tracing. J. Hydrol. 2019, 570, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wekker, S.F.J.; Kossmann, M. Convective boundary layer heights over mountainous terrain—A review of concepts. Front. Earth Sci. 2015, 3, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Physics Processes | Domain 1 (25 km) | Domain 2 (5 km) |
|---|---|---|
| Horizontal | 60 × 60 | 130 × 130 |
| Time step | 150 s | 30 s |
| Microphysics | single-moment 5-class scheme | single-moment 5-class scheme |
| Cumulus | Kain–Fritsch scheme | Kain–Fritsch scheme |
| PBL | YSU scheme | YSU scheme |
| Shortwave radiation | Dudhia scheme | Dudhia scheme |
| Longwave radiation | Rapid radiative transfer model | Rapid radiative transfer model |
| Surface–land | 5-layer thermal diffusion | 5-layer thermal diffusion |
| Initial and boundary | NCEP/FNL analysis | Domain 1 |
| Wind | Layer | Input (kg/year) | Output (kg/year) | Net (kg/year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| West wind | Surface—9th layer | 6.5 × 1013 | 4.6 × 1013 | 1.9 × 1013 |
| 10th layer—Top | 6.2 × 1013 | 7.1 × 1013 | −0.9 × 1013 | |
| North wind | Surface—9th layer | 1.3 × 1013 | 2.4 × 1013 | −1.1 × 1013 |
| 10th layer—Top | 1.7 × 1013 | 1.1 × 1013 | 0.6 × 1013 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, X.; Ma, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. Refined Characteristics of Moisture Cycling over the Inland River Basin Using the WRF Model and the Finer Box Model: A Case Study of the Heihe River Basin. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12030399
Pan X, Ma W, Zhang Y, Li H. Refined Characteristics of Moisture Cycling over the Inland River Basin Using the WRF Model and the Finer Box Model: A Case Study of the Heihe River Basin. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(3):399. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12030399
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Xiaoduo, Weiqiang Ma, Ying Zhang, and Hu Li. 2021. "Refined Characteristics of Moisture Cycling over the Inland River Basin Using the WRF Model and the Finer Box Model: A Case Study of the Heihe River Basin" Atmosphere 12, no. 3: 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12030399
APA StylePan, X., Ma, W., Zhang, Y., & Li, H. (2021). Refined Characteristics of Moisture Cycling over the Inland River Basin Using the WRF Model and the Finer Box Model: A Case Study of the Heihe River Basin. Atmosphere, 12(3), 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12030399








