Impact of Urbanization on Sunshine Duration from 1987 to 2016 in Hangzhou City, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Preprocesses
2.3. Classification of Meteorological Stations
2.4. Estimation of Urbanization Effects on SSD Trends
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
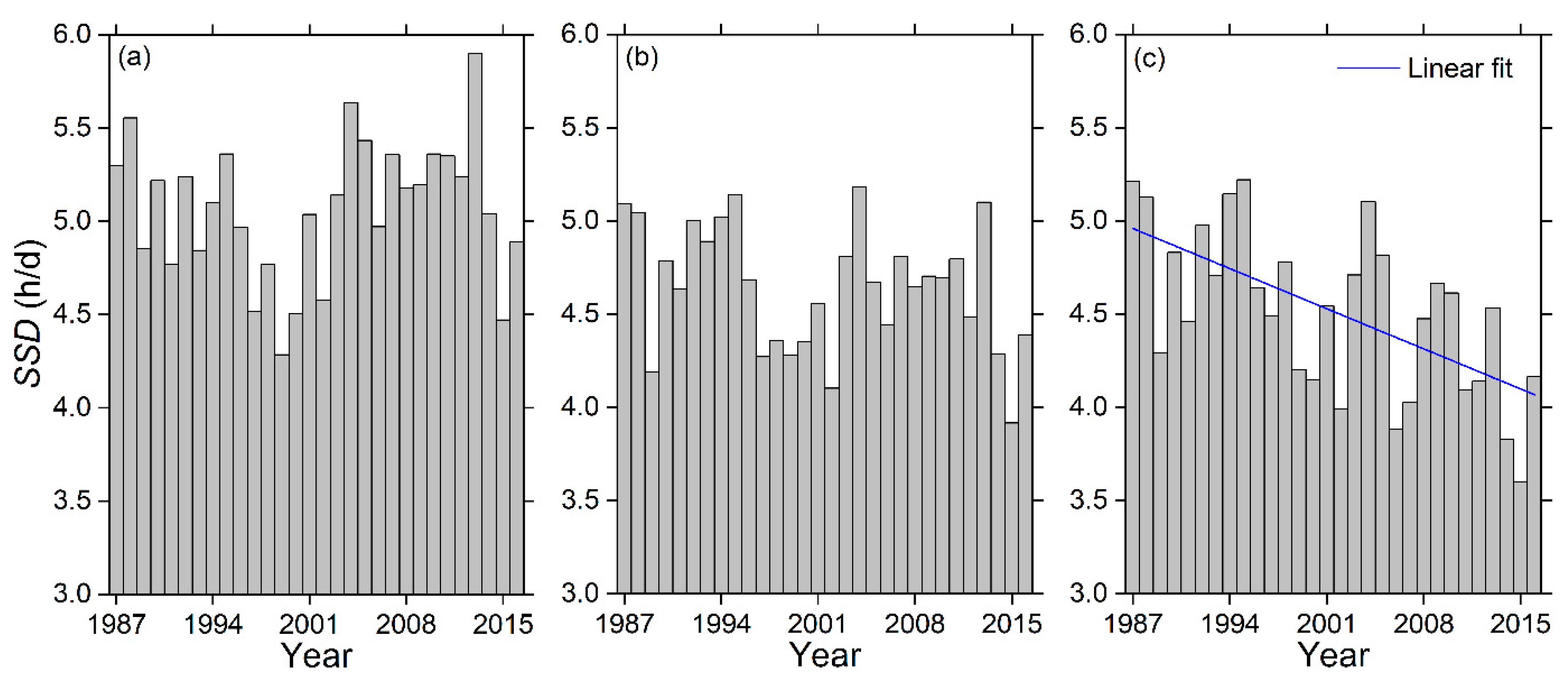
3.1. Temporal Changes in SSD
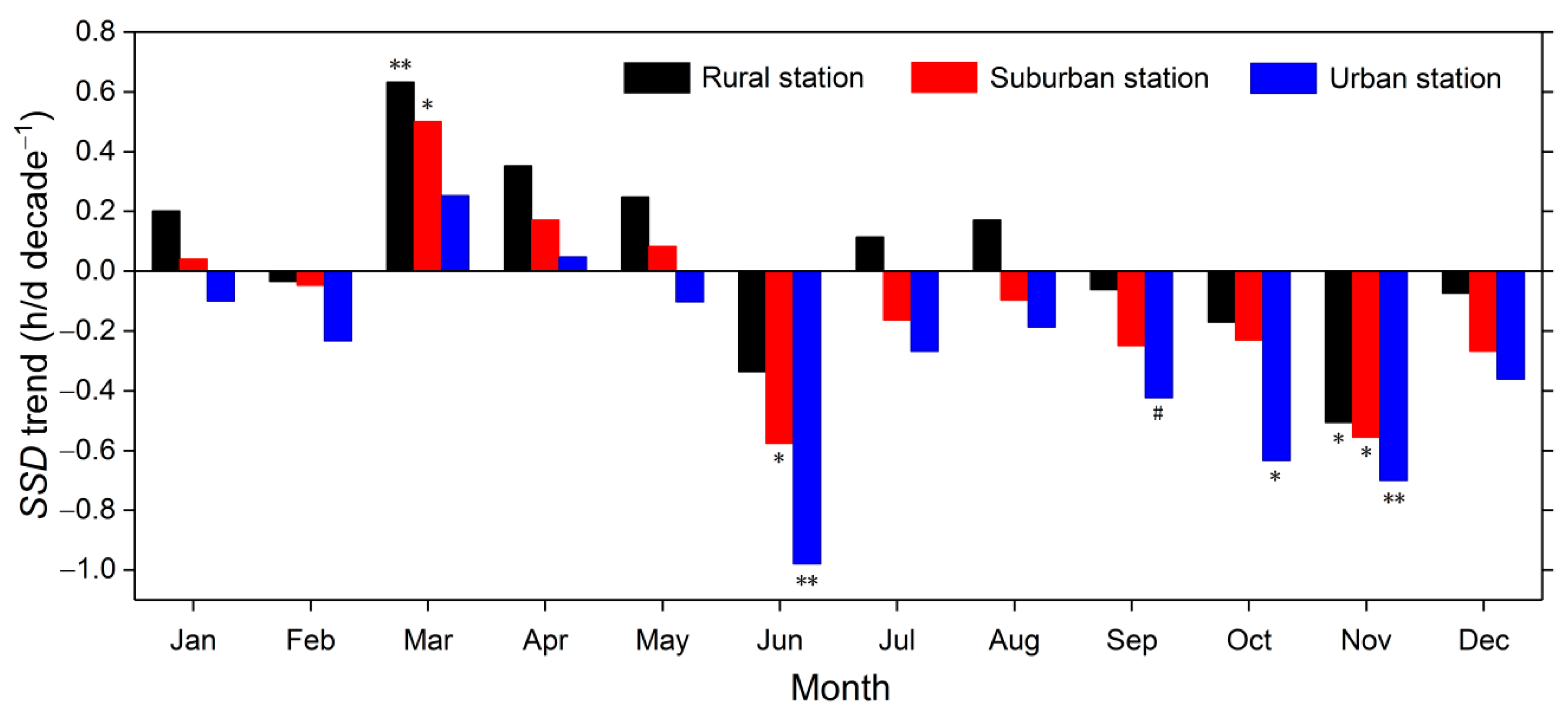
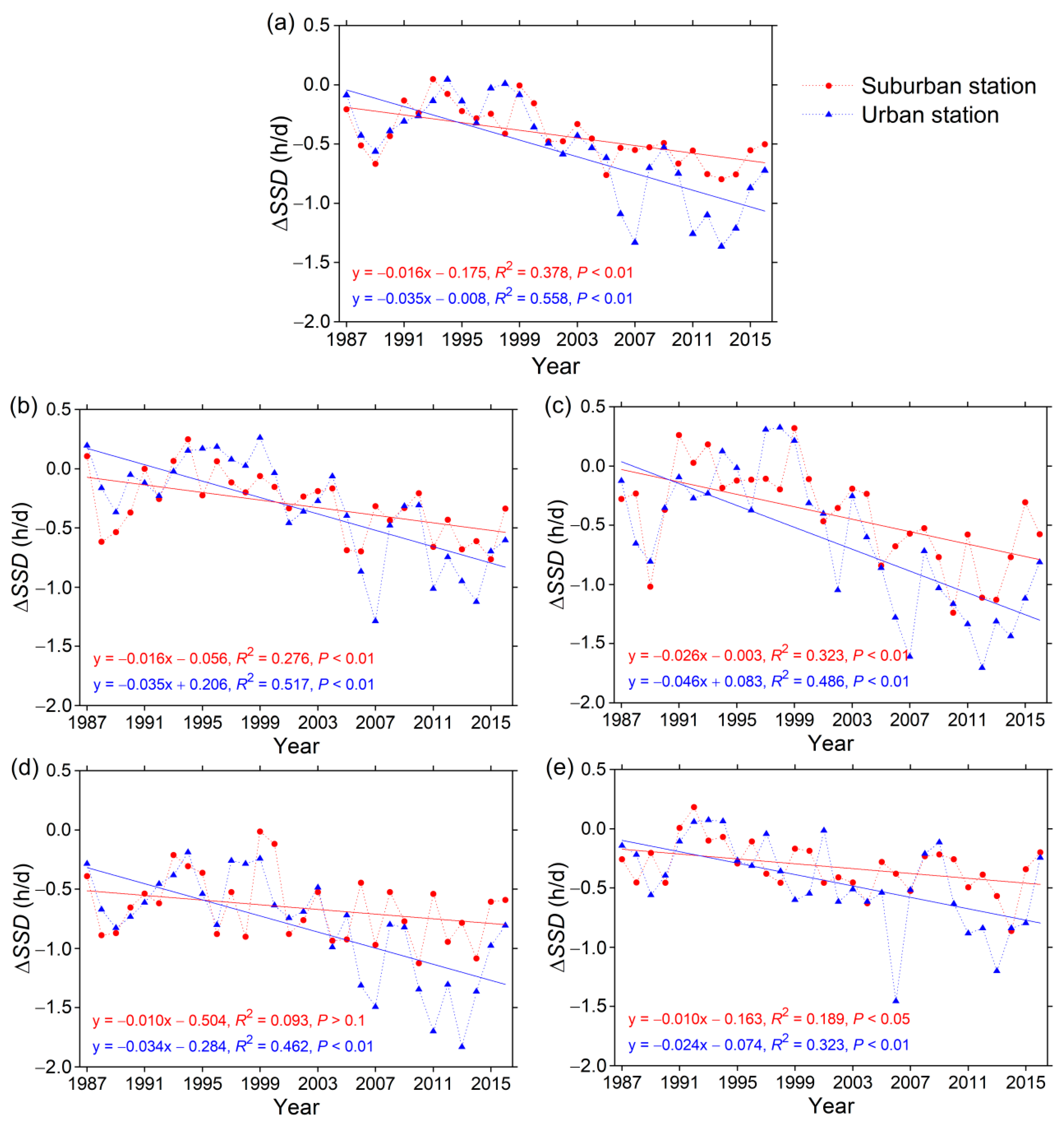
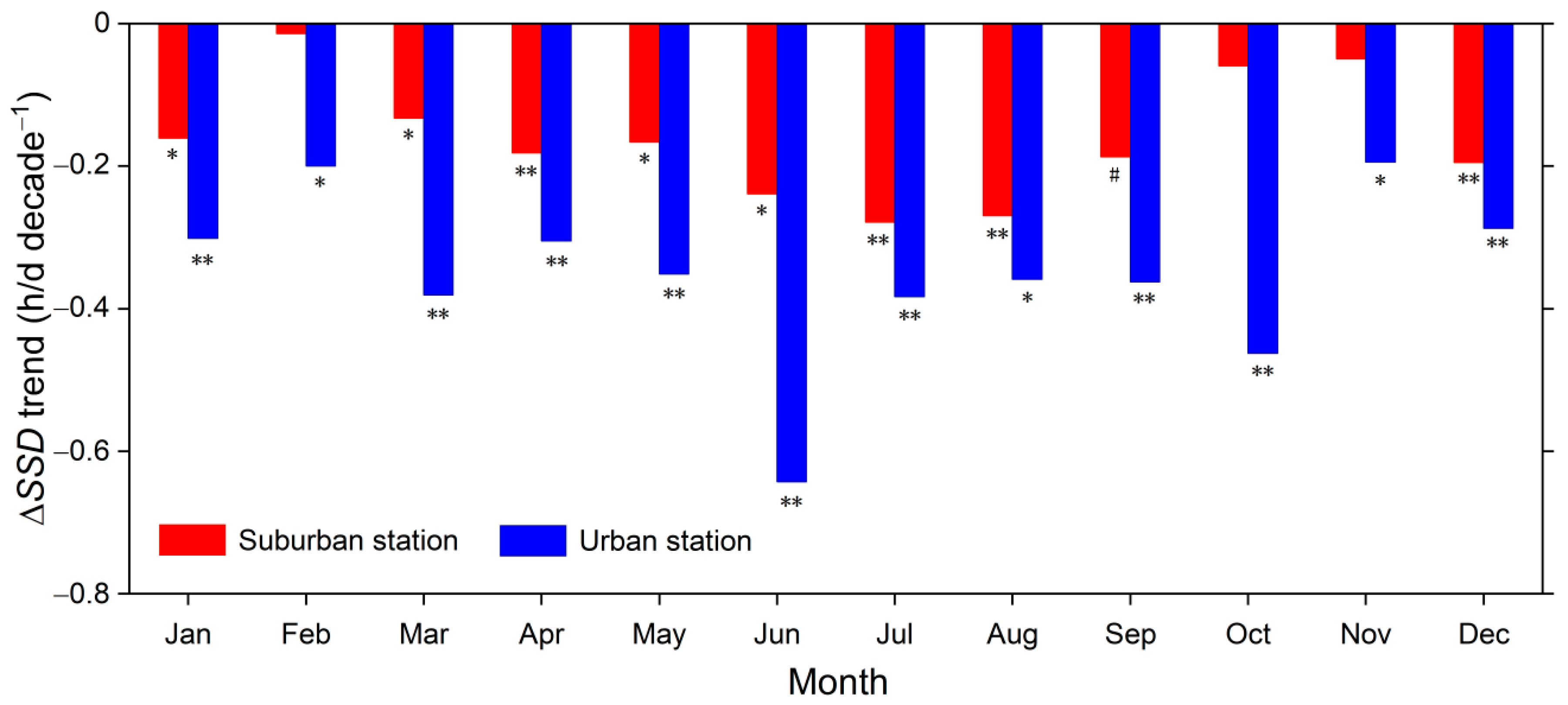
3.2. Urbanization Effects on SSD Change
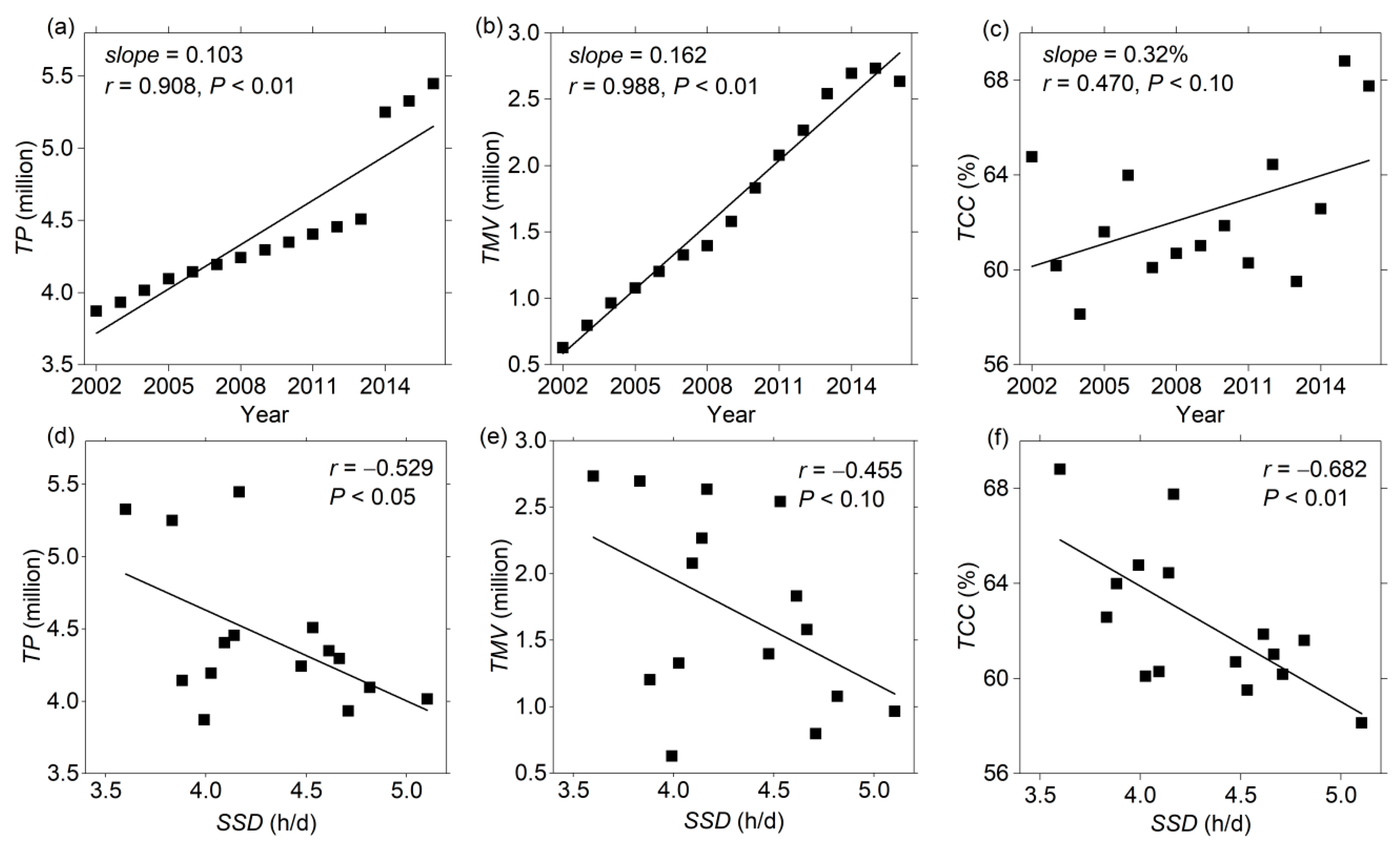
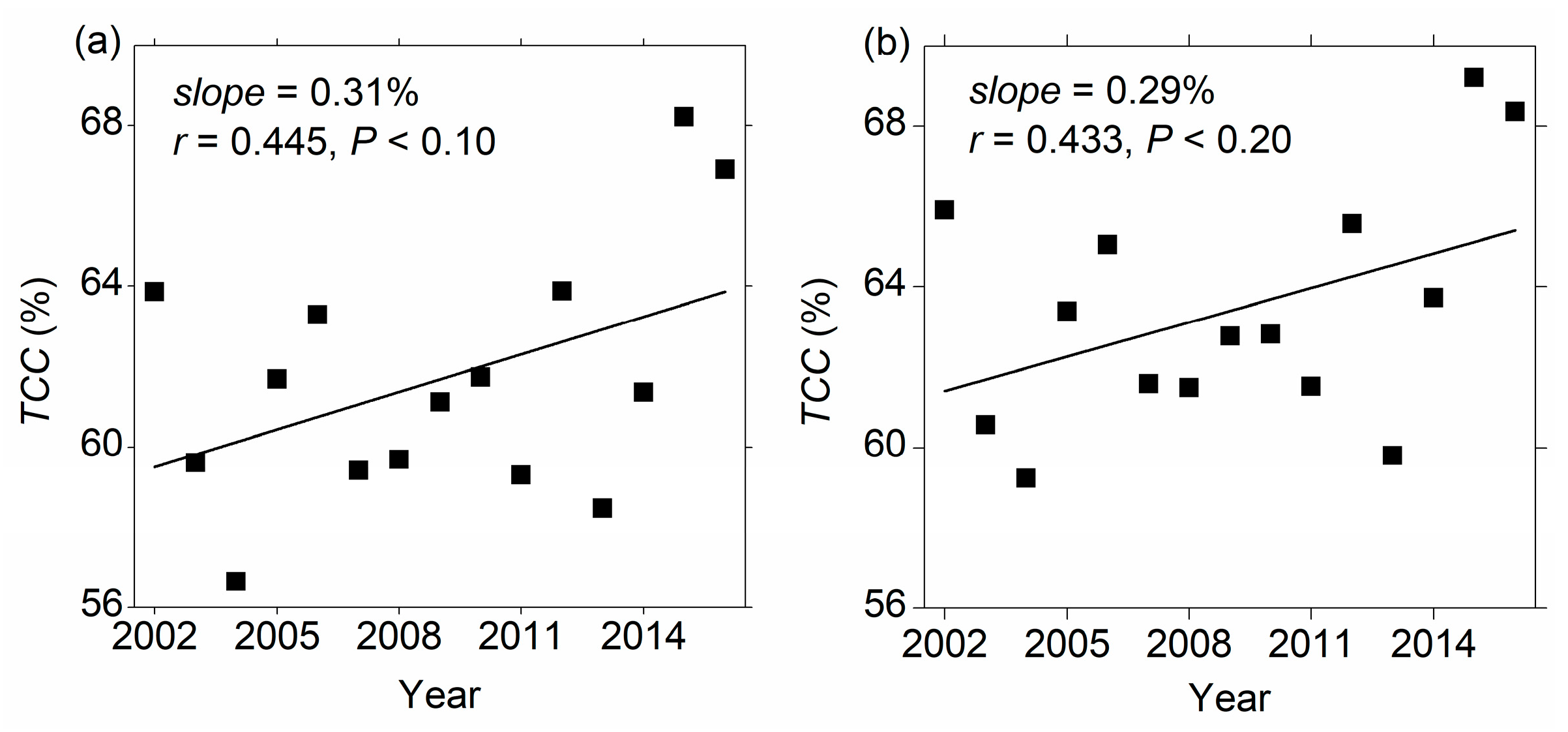
3.3. Environmental Variations Associated with SSD in Hangzhou City
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, T.B.; Li, C.X.; Zuo, Z.Y. Contributions of anthropogenic and external natural forcings to climate changes over China based on CMIP5 model simulations. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2016, 59, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.; Bai, X.; Briggs, J.M. Global Change and the Ecology of Cities. Science 2008, 319, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Wang, F.; Wang, S. Assessing the spatiotemporal variation in anthropogenic heat and its impact on the surface thermal environment over global land areas. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 63, 102488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.B.; Dan, L.; Chen, Y.L.; Tang, J.X. Trends of the sunshine duration and diffuse radiation percentage on sunny days in urban agglomerations of China during 1960–2005. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 34, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeill, V.F. Atmospheric Aerosols: Clouds, Chemistry, and Climate. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2017, 8, 427–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.J.; Yang, K.; Qin, J.; Cheng, C.C.K.; He, J. Solar radiation trend across China in recent decades: A revisit with quality-controlled data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Lorenzo, A.; Calbó, J.; Wild, M. Global and diffuse solar radiation in Spain: Building a homogeneous dataset and assessing their trends. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 100, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Linderholm, H.; Chen, D.; Zhou, X.; Flerchinger, G.; Yu, Q.; Du, J.; Wu, D.; Shen, Y.; Yang, Z. Changes in the relationship between solar radiation and sunshine duration in large cities of China. Energy 2015, 82, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, M. Decadal changes in radiative fluxes at land and ocean surfaces and their relevance for global warming. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2016, 7, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ma, Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Wild, M. Urban impacts on mean and trend of surface incident solar radiation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 4664–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manara, V.; Beltrano, M.C.; Brunetti, M.; Maugeri, M.; Sanchez-Lorenzo, A.; Simolo, C.; Sorrenti, S. Sunshine duration variability and trends in Italy from homogenized instrumental time series (1936–2013). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 3622–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wild, M.; Sanchez-Lorenzo, A.; Manara, V. Urbanization effect on trends in sunshine duration in China. Ann. Geophys. 2017, 35, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C. Impact of land use/land cover change on changes in surface solar radiation in eastern China since the reform and opening up. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 123, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.Y.; Chen, L.T.; Wang, Y.J.; Liu, X.P.; Lin, L.J.; Luo, M. Effects of urbanization on the decrease in sunshine duration over eastern China. Urban Clim. 2019, 28, 100471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raichijk, C. Observed trends in sunshine duration over South America. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 32, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Meier, F.; Lee, X.; Chakraborty, T.; Liu, J.; Schaap, M.; Sodoudi, S. Interaction between urban heat island and urban pollution island during summer in Berlin. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanhill, G.; Cohen, S. Is solar dimming global or urban? Evidence from measurements in Israel between 1954 and 2007. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Li, J.; Ren, Y.; Chu, Z.; Zhang, A.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Bian, T. An integrated procedure to determine a reference station network for evaluating and adjusting urban bias in surface air temperature data. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2015, 54, 1248–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.L. Characteristics of Precipitation in Hangzhou City from 1951 to 2014. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2018, 35, 25–29. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, L.; Huang, B.; Yang, Y.; Jones, P.; Cheng, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, Q. A new evaluation of the role of urbanization to warming at various spatial scales: Evidence from the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau region, China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL089152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, T.; Ren, G.; Yue, Y. Effect of Urbanization on Land-Surface Temperature at an Urban Climate Station in North China. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2017, 165, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tysa, S.K.; Ren, G.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, P.; Ren, Y.; Jia, W.; Wen, K. Urbanization effect in regional temperature series based on a remote sensing classification scheme of stations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 10646–10661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yan, Z.W. Urbanization-related warming in local temperature records: A review. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2016, 9, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Wang, F.; Yu, Q.; Gou, J.; Liu, H. Varied degrees of urbanization effects on observed surface air temperature trends in China. Clim. Res. 2018, 76, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanhill, G.; Cohen, S. Solar radiation changes in Japan during the 20th century: Evidence from sunshine duration measurements. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2008, 86, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, P.; Kishcha, P.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Schwarzbard, R. Global dimming or local dimming?: Effect of urbanization on sunlight availability. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L17802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, N.; Liu, C.; Wang, Q. The magnitude of the effect of air pollution on sunshine hours in China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D00V14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Ding, Y. The Long-term Variation of Extreme Heavy Precipitation and Its Link to Urbanization Effects in Shanghai during 1916–2014. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 34, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robaa, S.M. A study of solar radiation climate at Cairo urban area, Egypt and its environs. Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 26, 1913–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Song, K.; Da, L. The Diversity Distribution Pattern of Ruderal Community under the Rapid Urbanization in Hangzhou, East China. Diversity 2020, 12, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R. Investigating wintertime air pollution in Hangzhou, China. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2020, 13, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Wang, F.; Zong, Q.; Qin, P.; Liu, C. An Updated Estimate of the Urban Heat Island Effect on Observed Local Warming Trends in Mainland China’s 45 Urban Stations. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2020, 98, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Liu, J.; Kuang, W.; Xu, X.; Zhang, S.; Yan, C.; Li, R.; Wu, S.; Hu, Y.; Du, G.; et al. Spatio-temporal patterns and characteristics of land-use change in China during 2010-2015. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.L.; Wang, D.G.; Liu, X.P.; Wang, G.L.; Zhang, J.B. Estimated influence of urbanization on surface warming in Eastern China using time-varying land use data. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 3197–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ge, Q.S. Estimation of urbanization bias in observed surface temperature change in China from 1980 to 2009 using satellite land-use data. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 1708–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ge, Q.S.; Wang, S.W.; Li, Q.X.; Jones, P.D. A new estimation of urbanization’s contribution to the warming trend in China. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 8923–8938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Yang, Y.H. China’s dimming and brightening: Evidence, causes and hydrological implications. Ann. Geophys. 2014, 32, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liley, J.B. New Zealand dimming and brightening. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D00D10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Hou, M.; Xin, J. Low-cloud and sunshine duration in the low-latitude belt of South China for the period 1961–2005. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2011, 104, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Founda, D.; Kalimeris, A.; Pierros, F. Multi annual variability and climatic signal analysis of sunshine duration at a large urban area of Mediterranean (Athens). Urban Clim. 2014, 10, 815–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoszek, K.; Matuszko, D.; Soroka, J. Relationships between cloudiness, aerosol optical thickness, and sunshine duration in Poland. Atmos. Res. 2020, 245, 105097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ye, H.; Chen, F.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, C. Urbanization effect on the diurnal temperature range: Different roles under solar dimming and brightening. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.; Zhan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xing, J.; Li, J. Emission-driven changes in anthropogenic aerosol concentrations in China during 1970–2010 and its implications for PM2.5 control policy. Atmos. Res. 2018, 212, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X. Spatiotemporal changes in sunshine duration and cloud amount as well as their relationship in China during 1954–2005. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D00K06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Bai, L. Spatio-temporal characteristics of urban air pollutions and their causal relationships: Evidence from Beijing and its neighboring cities. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Wang, Z.; Cui, L.; Fu, H.; Zhang, L.; Kong, L.; Chen, W.; Chen, J. Air pollution characteristics in China during 2015–2016: Spatiotemporal variations and key meteorological factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 902–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
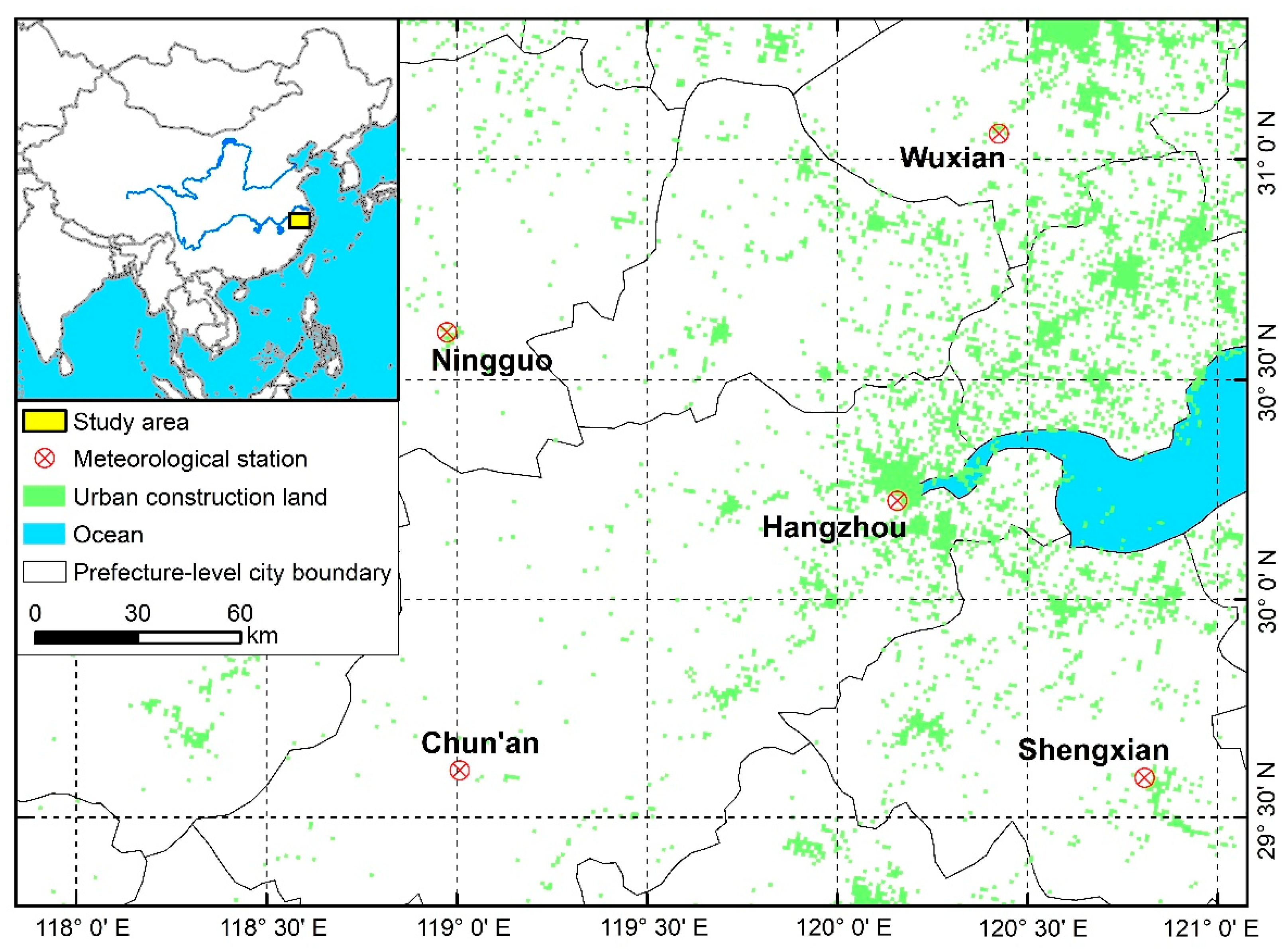
| Station Name | Latitude (degree) | Longitude (degree) | Altitude (m) | Distance 1 (km) | SSD 2 (h/d) | UF1990 3 (%) | UF2015 4 (%) | Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chun’an | 29.62 | 119.02 | 171.4 | 130 | 5.0 | 0.6 | 1.3 | Rural |
| Hangzhou | 30.23 | 120.17 | 41.7 | - | 4.5 | 29.2 | 55.2 | Urban |
| Ningguo | 30.62 | 118.98 | 89.4 | 120 | 4.6 | 5.8 | 11.0 | Suburban |
| Shengxian | 29.60 | 120.82 | 104.3 | 94 | 4.7 | 9.1 | 16.2 | Suburban |
| Wuxian | 31.07 | 120.43 | 17.5 | 97 | 5.1 | 3.2 | 7.8 | Rural |
| Trend in SSD (h/d decade−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rural Station | Suburban Station | Urban Station | All Stations | |
| Annual | 0.05 | −0.12 | −0.31 ** | −0.09 |
| Spring | 0.41 ** | 0.25 * | 0.07 | 0.28 * |
| Summer | −0.02 | −0.28 | −0.48 * | −0.21 |
| Autumn | −0.25 | −0.35 * | −0.59 ** | −0.35 * |
| Winter | 0.11 | 0.01 | −0.13 | 0.02 |
| Period | Suburban Station (h/d) | Urban Station (h/d) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | Annual | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | |
| 1987–2001 | −0.27 | −0.16 | −0.16 | −0.54 | −0.23 | −0.24 | −0.03 | −0.18 | −0.51 | −0.23 |
| 2002–2016 | −0.58 | −0.45 | −0.66 | −0.77 | −0.42 | −0.87 | −0.63 | −1.09 | −1.11 | −0.67 |
| 1987–2016 | −0.42 | −0.30 | −0.41 | −0.66 | −0.32 | −0.55 | −0.33 | −0.63 | −0.81 | −0.45 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, K.; Qin, P.; Liu, C.; Zong, Q.; Wang, S. Impact of Urbanization on Sunshine Duration from 1987 to 2016 in Hangzhou City, China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020211
Jin K, Qin P, Liu C, Zong Q, Wang S. Impact of Urbanization on Sunshine Duration from 1987 to 2016 in Hangzhou City, China. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(2):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020211
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Kai, Peng Qin, Chunxia Liu, Quanli Zong, and Shaoxia Wang. 2021. "Impact of Urbanization on Sunshine Duration from 1987 to 2016 in Hangzhou City, China" Atmosphere 12, no. 2: 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020211
APA StyleJin, K., Qin, P., Liu, C., Zong, Q., & Wang, S. (2021). Impact of Urbanization on Sunshine Duration from 1987 to 2016 in Hangzhou City, China. Atmosphere, 12(2), 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020211






