Carbon Dioxide and Methane Emissions during the Composting and Vermicomposting of Sewage Sludge under the Effect of Different Proportions of Straw Pellets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Experimental Setup
Composting and Vermicomposting
2.3. Carbon Dioxide (CO2) and Methane (CH4) Measurements during Composting and Vermicomposting
2.4. Analysis of Total Carbon (TC), Total Nitrogen (TN), pH, and EC
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussions
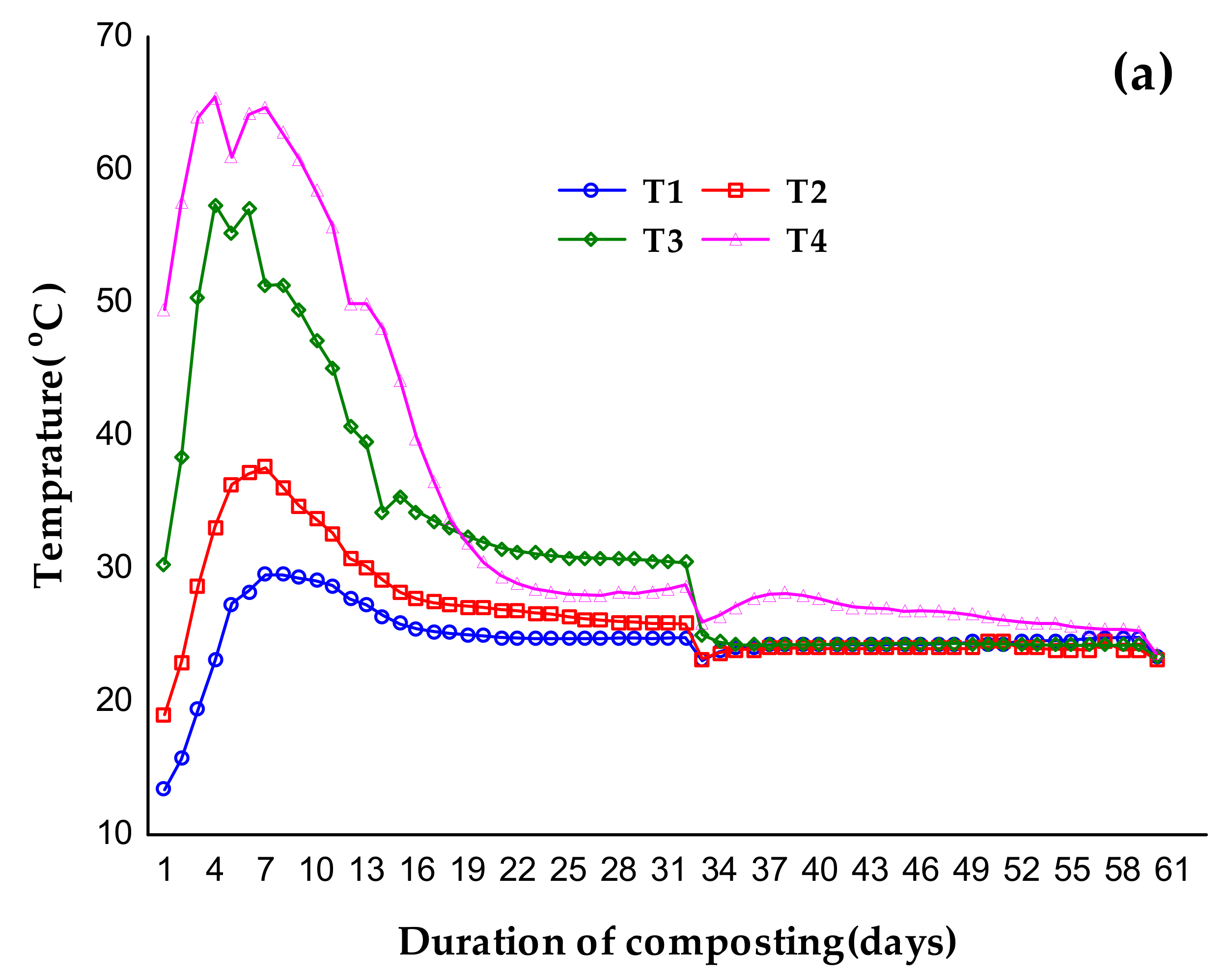
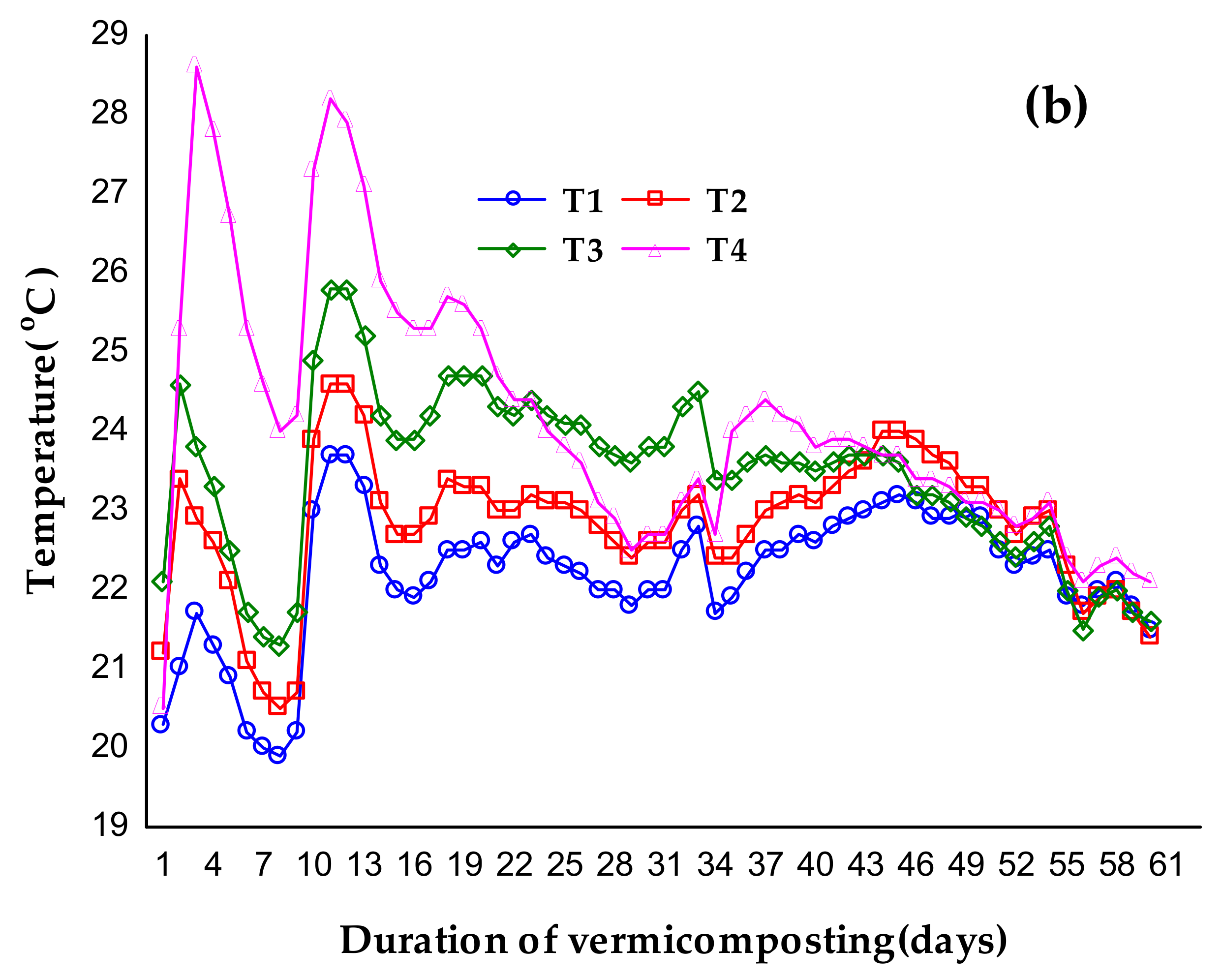
3.1. Temperature during Composting and Vermicomposting
3.2. pH and EC
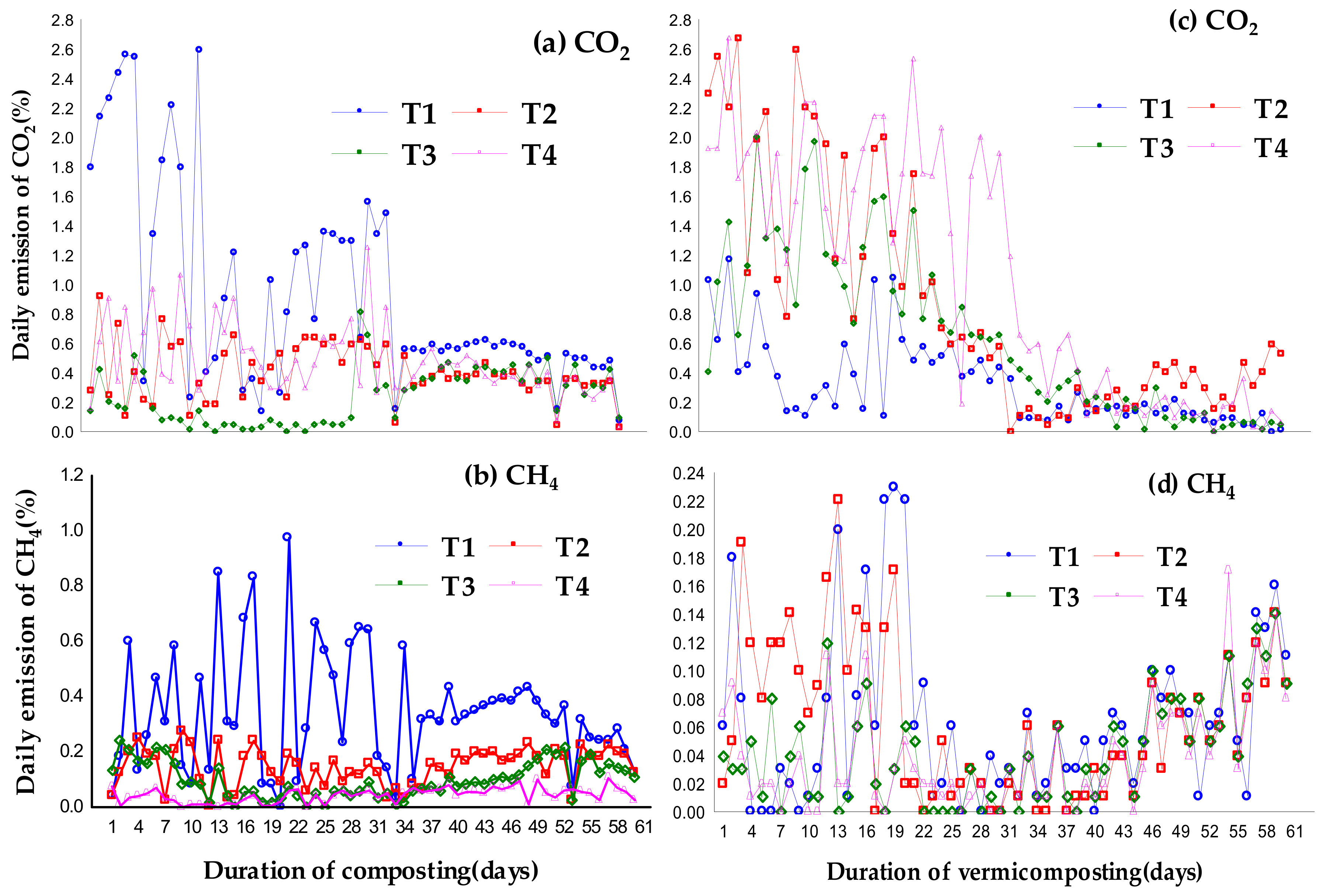
3.3. Carbon Dioxide(CO2) and Methane(CH4) Emissions during Composting and Vermicomposting
3.3.1. Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
3.3.2. Methane (CH4)
3.4. Total Carbon(TC), Total Nitrogen(TN), and the C:N Ratio
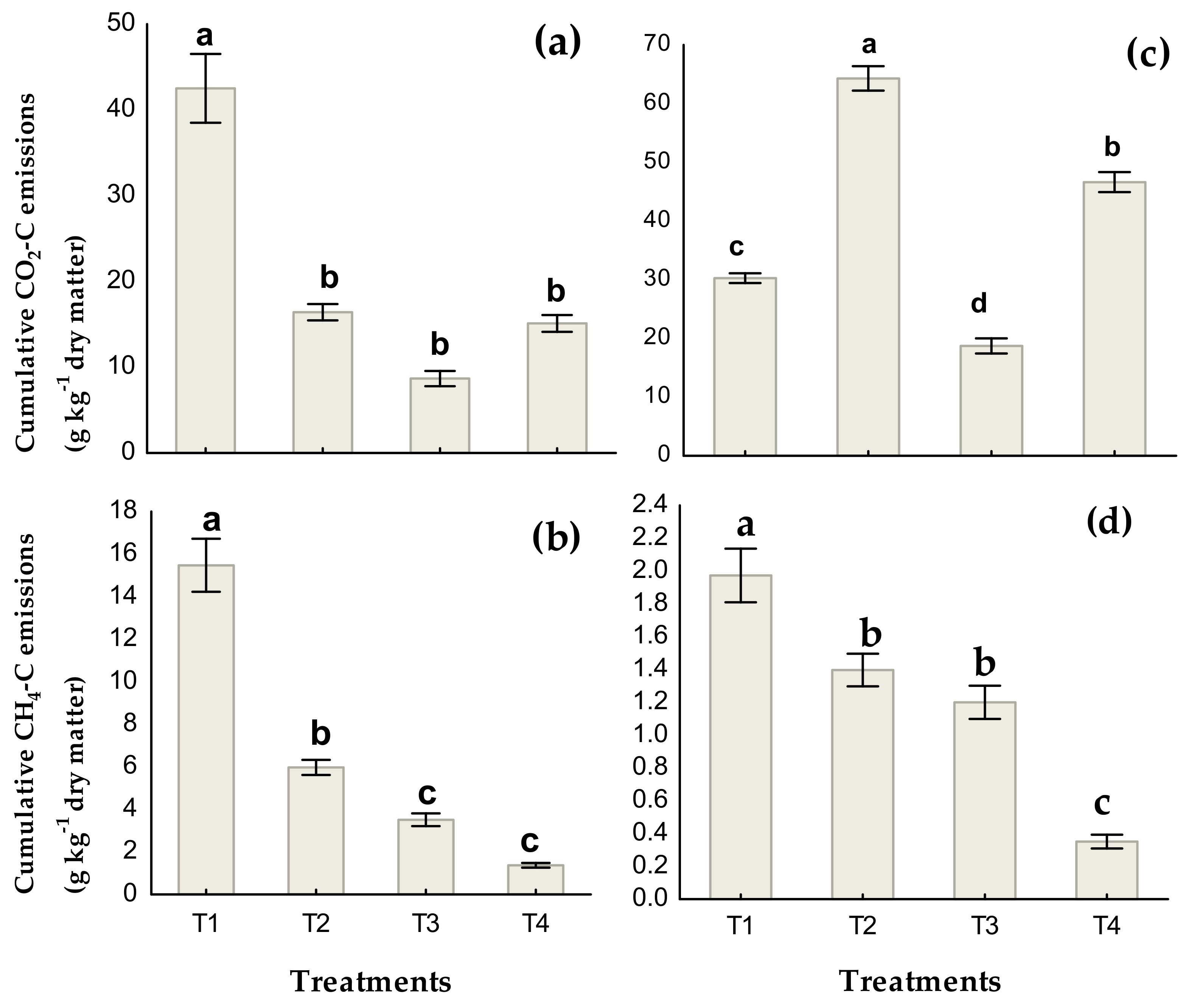
3.5. Carbon Balances
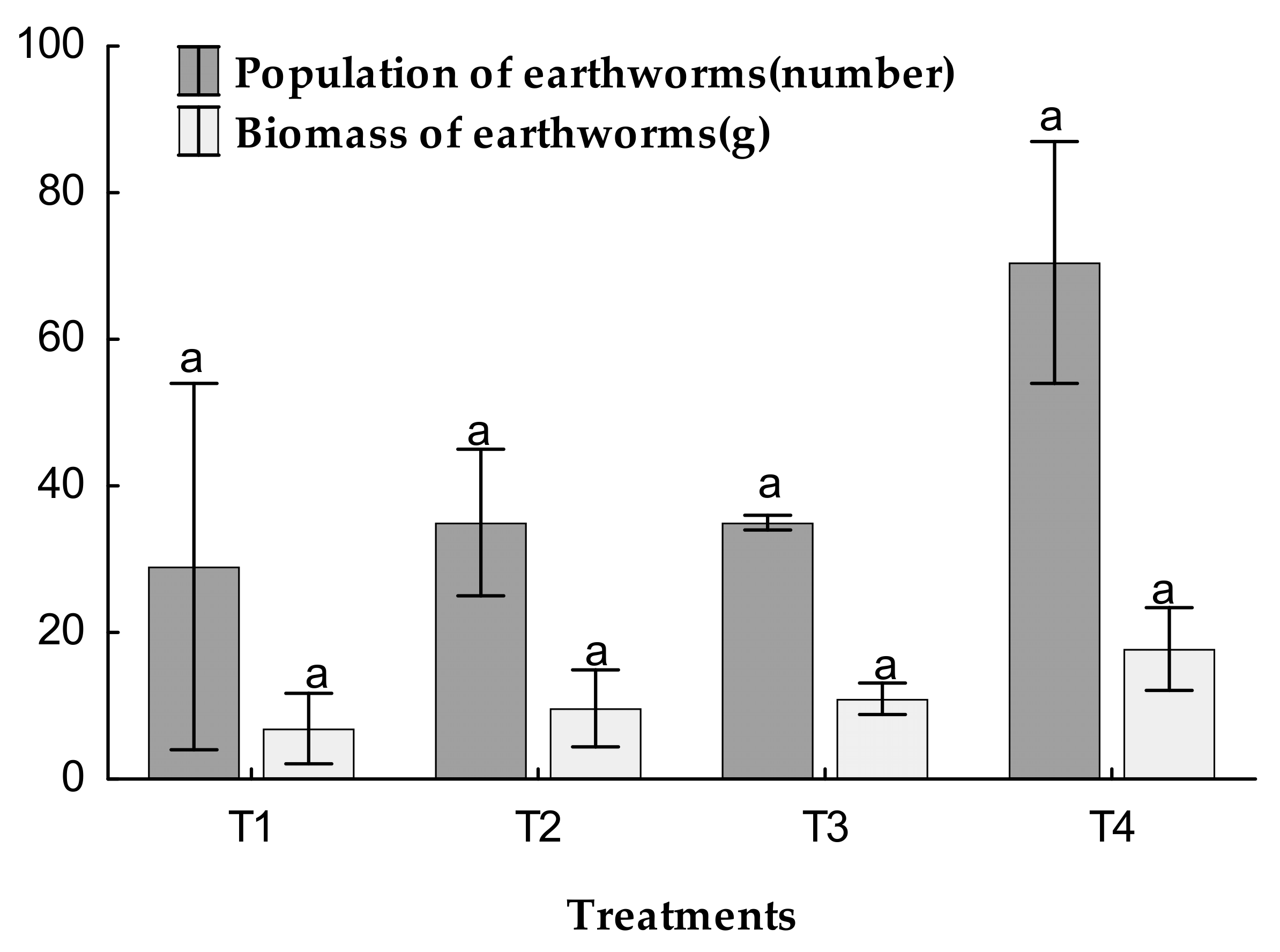
3.6. Population and Biomass of Earthworms
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hobson, A.M.; Frederickson, J.; Dise, N.B. CH4 and N2O from mechanically turned windrow and vermicomposting systems following in-vessel pre-treatment. Waste Manag. 2005, 25, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoornweg, D.; Bhada-Tata, P.; Kennedy, C. Waste production must peak this century. Nature 2013, 502, 615–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papageorgiou, A.; Barton, J.R.; Karagiannidis, A. Assessment of the greenhouse effect impact of technologies for energy recovery from municipal waste: A case for England. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2999–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoornweg, D.; Bhada-Tata, P. What a Waste: A Global Review of Solid Waste Management; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Baoyi, L.; Zhang, D.; Yuxue, C.; Fang, Y. Effects of C/N ratio and earthworms on greenhouse gas emissions during vermicomposting of sewage sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 268, 408–414. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Sui, Q.W.; Li, K.; Chen, M.X.; Tong, J.; Qi, L.; Wei, Y.S. Influence of natural zeolite and nitrification inhibitor on organics degradation and nitrogen transformation during sludge composting. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 1324–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.W.; Dai, X.H.; Takahashi, J.; Li, N.; Jin, J.W.; Dai, L.L.; Dong, B. New insight into chemical changes of dissolved organic matter during anaerobic digestion of dewatered sewage sludge using EEM-PARAFAC and two-dimensional FTIR correlation spectroscopy. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 159, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadef, Y.; Poulsen, T.G.; Habib, K.; Iqbal, T.; Nizami, A.S. Uncertainty in degradation rates for organic micro-pollutants during full-scale sewage sludge composting. Waste Manag. 2016, 56, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Chen, C.L.; Giannis, A.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.Y. Hydrothermal gasification of sewage sludge and model compounds for renewable hydrogen production: A review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2014, 39, 1127–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NBSC (National Bureau of Statistics of China). China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, M.S.; Jambhulkar, R.; Kalamdhad, A.S. Biochar amendment for batch composting of nitrogen rich organic waste: Effect on degradation kinetics, composting physics and nutritional properties. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 253, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Mao, H.L.; Li, X.K. Functional characteristics and influence factors of microbial community in sewage sludge composting with inorganic bulking agent. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridle, T.; Skrypski-Mantele, S. Assessment of sludge reuse options: A life cycle approach. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 4, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Xu, L. Eco-efficiency optimization for municipal solid waste management. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 104, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.Q.; Zhang, S.M.; Gong, H.N.; Zhang, X.C.; Wu, C.D.; Li, W.G. Improving sewage sludge composting by addition of spent mushroom substrate and sucrose. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 253, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.S.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, M.H.; Rong, H.W.; Zhang, K.F. Influence of inoculating white-rot fungi on organic matter transformations and mobility of heavy metals in sewage sludge based composting. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.; Goufo, P.; Fonseca, J.; Pereira, J.L.S.; Ferreira, L.; Coutinho, J.; Trindade, H. Effect of lignocellulosic and phenolic compounds on ammonia, nitric oxide and greenhouse gas emissions during composting. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Selvam, A.; Lau, S.; Wong, J. Influence of lime and struvite on microbial community succession and odour emission during food waste composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awasthi, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Awasthi, S.K.; Wang, M.J.; Chen, H.Y.; Ren, X.N.; Zhao, J.C.; Zhang, Z.Q. Influence of medical stone amendment on gaseous emissions, microbial biomass and abundance of ammonia oxidizing bacteria genes during biosolids composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermolaev, E.; Sundberg, C.; Pell, M.; Jönsson, H. Greenhouse gas emissions from home composting in practice. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 151, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change. Mitigation of Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Awasthi, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Chen, H.Y.; Wang, M.J.; Awasthi, S.K.; Ren, X.N.; Cai, H.Z.; Li, R.H.; Zhang, Z.Q. In-vessel co-composting of biosolid: Focusing on mitigation of greenhouse gases emissions and nutrients conservation. Renew. Energy 2018, 129, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, A.; Artola, A.; Font, X.; Gea, T.; Barrena, R.; Gabriel, D.; Sanchez-Monedero, M.A.; Roig, A.; Cayuela, M.L.; Mondini, C. Greenhouse gas emissions from organic waste composting. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2015, 13, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lubbers, I.M.; van Groenigen, K.J.; Fonte, S.J.; Six, J.; Brussaard, L.; van Groenigen, J.W. Greenhouse gas emissions from soils increased by earthworms. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapuis-Lardy, L.; Brauman, A.; Bernard, L.; Pablo, A.L.; Toucet, J.; Mano, M.J.; Weber, L.; Brunet, D.; Razafimbelo, T.; Chotte, J.L.; et al. Effect of the endogeic earthworm Pontoscolex corethrurus on the microbial structure and activity related to CO2 and N2O fluxes from a tropical soil (Madagascar). Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 45, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speratti, A.B.; Whalen, J.K. Carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide fluxes from soil as influenced by anecic and endogeic earthworms. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2008, 38, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.C.; Sinha, R.K.; Wang, W. Emission of greenhouse gases from home aerobic composting, anaerobic digestion and vermicomposting of household wastes in Brisbane, Australia. Waste Manag. Res. 2011, 29, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, W.; Deng, L.; Wu, G.; Wu, L.; Han, P.; Miao, Y.; Yao, B. Atmospheric monitoring of methane in Beijing using a mobile observatory. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belikov, D.; Arshinov, M.; Belan, B.; Davydov, D.; Fofonov, A.; Sasakawa, M.; Machida, T. Analysis of the diurnal, weekly, and seasonal cycles and annual trends in atmospheric CO2 and CH4 at Tower Network in Siberia from 2005 to 2016. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bradley, R.L.; Chroňáková, A.; Elhottová, D.; Šimek, M. Interactions between land-use history and earthworms control gross rates of soil methane production in an overwintering pasture. Soil Biol Biochem. 2012, 53, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, Z. Methane emissions from a rice agroecosystem in South China: Effects of water regime, straw incorporation and nitrogen fertilizer. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2012, 93, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BSI EN 15933. Sludge, Treated Biowaste and Soil Determination of pH; The British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2012.
- Hanc, A.; Castkova, T.; Kuzel, S.; Cajthaml, T. Dynamics of a vertical-flow windrow vermicomposting system. Waste Manag. Res. 2017, 35, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.P.; Lai, C.; Zeng, G.M.; Liang, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, J.J.; Dai, J.; Li, X.D.; Liu, J.F.; Chen, M.; et al. The interactions of composting and biochar and their implications for soil amendment and pollution remediation: A review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.K.; Herat, S.; Agarwal, S.; Asadi, R.; Carretero, E. Vermiculture technology for environmental management: Study of action of earthworms Elsinia foetida, Eudrilus euginae and Perionyx excavatus on biodegradation of some community wastes in India and Australia. Environmentalist 2002, 22, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Hu, Z.; Xu, X.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, B.; Liu, X.; Pan, X.; Kardol, P. Emissions of ammonia and greenhouse gases during combined pre-composting and vermicomposting of duck manure. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1546–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Garg, V. Comparative analysis of vermicompost quality produced from rice straw and paper waste employing earthworm Eisenia fetida (Sav.). Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandar, R.; Baskaran, L.; Yuvaraj, A.; Thangaraj, R.; Subbaiya, R.; Ravindran, B.; Chang, S.W.; Karmegam, N. Enriched pressmud vermicompost production with green manure plants using Eudrilus eugeniae. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 299, 122578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suthar, S. Pilot-scale vermireactors for sewage sludge stabilization and metal remediation process: Comparison with small-scale vermireactors. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigliotti, G.; Proietti, P.; Said-Pullicino, D.; Nasini, L.; Pezzolla, D.; Rosati, L.; Porceddu, P.R. Co-composting of olive husks with high moisture contents: Organic matter dynamics and compost quality. Int. Biodeterior. 2012, 67, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, M.; Zeng, G.; Zhou, M.; Li, M. Effect of vermicomposting on concentration and speciation of heavy metals in sewage sludge with additive materials. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, P.; Gupta, A.; Satya, S. Vermicomposting of different types of waste using Eisenia foetida: A comparative study. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tognetti, C.; Laos, F.; Mazzarino, M.J.; Hernandez, M.T. Composting vs. vermicomposting: A comparison of end product quality. Comp. Sci. Util. 2005, 13, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Haddad, M.E.; Zayed, M.S.; El-Sayed, G.A.M.; Hassanein, M.K.; El-Satar, A.M.A. Evaluation of compost, vermicompost and their teas produced from rice straw as affected by addition of different supplements. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2014, 59, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramnarain, Y.I.; Ansari, A.A.; Ori, L. Vermicomposting of different organic materials using the epigeic earthworm Eisenia foetida. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2019, 8, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jadia, C.D.; Fulekar, M.H. Vermicomposting of vegetable wastes: A biophysicochemical process based on hydro-operating bioreactor. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 3723–3730. [Google Scholar]
- Awasthi, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Huang, H.; Li, R.; Shen, F.; Lahori, A.H.; Wang, P.; Guo, D.; Guo, Z.; Jiang, S.; et al. Effect of biochar amendment on greenhouse gas emission and bio-availability of heavy metals during sewage sludge cocomposting. J. Clean Prod. 2016, 135, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lleó, T.; Albacete, E.; Barrena, R.; Font, X.; Artola, A.; Sánchez, A. Home and vermicomposting as sustainable options for biowaste management. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 47, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, T.; Ma, X.G.; Tang, Q.; Yang, J.; Li, G.X.; Schuchardt, F. Combined use of nitrification inhibitor and struvite crystallization to reduce the NH3 and N2O emissions during composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 217, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.; Fonseca, J.; Aires, A.; Coutinho, J.; Trindade, H. Effect of different rates of spent coffee grounds (SCG) on composting process, gaseous emissions and quality of end-product. Waste Manag. 2017, 59, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, M.A.; Restrepo, A.P.; Alburquerque, J.A.; Pérez-Murcia, M.D.; Paredes, C.; Moral, R.; Bernal, M.P. Recycling of anaerobic digestates by composting: Effect of the bulking agent used. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 47, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Fang, C.; Sun, X.; Han, L.; He, X.; Huang, G. Bacterial community succession during pig manure and wheat straw aerobic composting covered with a semi-permeable membrane under slight positive pressure. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 259, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Awasthi, M.K.; Ren, X.N.; Zhao, J.C.; Li, R.H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, M.J.; Chen, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.Q. Combining biochar, zeolite and wood vinegar for composting of pig manure: The effect on greenhouse gas emission and N conservation. Waste Manag. 2018, 74, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manios, T.; Maniadakis, K.; Boutzakis, P.; Naziridis, Y.; Lasaridi, K.; Markakis, G.; Stentiford, E.I. Methane and carbon dioxide emission in a two-phase olive oil mill sludge windrow pile during composting. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awasthi, M.K.; Wang, M.J.; Chen, H.Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, J.C.; Ren, X.N.; Li, D.S.; Awasthi, S.K.; Shen, F.; Li, R.H.; et al. Heterogeneity of biochar amendment to improve the carbon and nitrogen sequestration through reduce the greenhouse gases emissions during sewage sludge composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sugir, M.E.; Li, Y.; Yuan, L.; Zhou, M.; Lv, P.; Yu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhou, D. Effects of vermicomposting on the main chemical properties and bioavailability of Cd/Zn in pure sludge. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 20949–20960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, V.; Goel, G.; Thakur, V.K.; Singh, R.P.; Ferreira de Araujo, A.S.; Singh, P. Analysis and advanced characterization of municipal solid waste vermicompost maturity for a green environment. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 255, 109914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharana, P.C.; Biswas, D.R. Assessment of maturity indices of rock phosphate enriched composts using variable crop residues. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 222, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biruntha, M.; Karmegam, N.; Archana, J.; Karunai Selvi, B.; John Paul, J.A.; Balamuralikrishnan, B.; Chang, S.W.; Ravindran, B. Vermiconversion of biowastes with low-to-high C/N ratio into value added vermicompost. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, A.; Khoram, M.R.; Gholami, M.; Eslami, H. Pistachio waste management using combined composting-vermicomposting technique: Physico-chemical changes and worm growth analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigussie, A.; Kuyper, T.W.; Bruun, S.; De, N.A. Vermicomposting as a technology for reducing nitrogen losses and greenhouse gas emissions from small-scale composting. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 139, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, J.; Desfontaines, L.; Faverial, J.; Loranger-Merciris, G.; Boval, M. Composting and vermicomposting of cattle manure and green wastes under tropical conditions: Carbon and nutrient balances and end-product quality. Soil Res. 2013, 51, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.A.; de Neergaard, A.; Jensen, L.S. Potential of aeration flow rate and bio-char addition to reduce greenhouse gas and ammonia emissions during manure composting. Chemosphere 2014, 97, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, Q.D.; de Neergaard, A.; Tran, T.D.; Hoang, H.T.T.; Vu, V.H.K.; Jensen, L.S. Greenhouse gas emissions from passive composting of manure and digestate with crop residues and biochar on small-scale livestock farms in Vietnam. Environ. Technol. 2015, 36, 2925–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Sewage Sludge (SS) | Pelletized Wheat Straw (PWS) |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.99 ± 0.017 | 8.30 ± 0.300 |
| EC (mS/cm) | 0.617 ± 0.064 | 0.680 ± 0.040 |
| TC (%) | 32.95 ± 0.150 | 42.6 ± 0.207 |
| TN (%) | 5.36 ± 0.017 | 0.8 ± 0.069 |
| C:N | 6.15 ± 0.011 | 53.2 ± 4.388 |
| Treatments | pH | EC(mS/cm) | TC (%) | TN (%) | C:N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 6.99 ± 0.017 | 0.617 ± 0.064 | 32.9 ± 0.150 | 5.36 ± 0.017 | 6.15 ± 0.023 |
| T2 | 7.32 ± 0.064 | 0.633 ± 0.046 | 35.36 ± 0.133 | 1.98 ± 0.121 | 18.03 ± 1.11 |
| T3 | 7.64 ± 0.144 | 0.649 ± 0.035 | 37.77 ± 0.139 | 1.34 ± 0.040 | 28.17 ± 0.826 |
| T4 | 7.97 ± 0.219 | 0.664 ± 0.029 | 40.18 ± 0.167 | 1.05 ± 0.029 | 38.36 ± 1.172 |
| Composting Method | Treatments | pH | EC (mS/cm) | TC (%) | TN (%) | C:N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composting | T1 | 8.4 ± 0.069 | 1.90 ± 0.098 | 29.52 ± 0.421 | 4.55 ± 0.081 | 6.50 ± 0.012 |
| T2 | 8.3 ± 0.052 | 1.43 ± 0.052 | 32.43 ± 0.456 | 3.69 ± 0.017 | 8.84 ± 0.185 | |
| T3 | 8.4 ± 0.046 | 1.94 ± 0.081 | 34.45 ± 0.883 | 3.27 ± 0.029 | 10.57 ± 0.375 | |
| T4 | 8.0 ± 0.035 | 0.80 ± 0.035 | 37.95 ± 0.012 | 2.76 ± 0.087 | 13.88 ± 0.462 | |
| Vermicomposting | T1 | 6.7 ± 0.670 | 0.644 ± 0.023 | 28.43 ± 0.185 | 4.22 ± 0.127 | 6.77 ± 0.150 |
| T2 | 6.5 ± 0.866 | 1.186 ± 0.127 | 31.96 ± 0.514 | 3.58 ± 0.023 | 8.94 ± 0.202 | |
| T3 | 6.5 ± 0.081 | 0.802 ± 0.225 | 34.38 ± 0.652 | 2.95 ± 0.087 | 11.72 ± 0.537 | |
| T4 | 6.6 ± 0.179 | 1.21 ± 0.069 | 35.32 ± 0.214 | 3.08 ± 0.035 | 12.15 ± 0.185 |
| Total C Emission during Composting | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trts | Initial C (g kg−1) | Ending C (g kg−1) | CH4-C (g kg−1) | CO2-C (g kg−1) | C Loss (%) | CH4-C Loss (%) | CO2-C Loss (%) | Unaccounted C (%) |
| T1 | 329.53 | 295.2 | 5.48 | 28.51 | 10.42 | 1.66 | 8.65 | 0.11 |
| T2 | 353.62 | 324.38 | 5.97 | 16.42 | 8.29 | 1.69 | 4.64 | 1.96 |
| T3 | 377.70 | 344 | 3.51 | 8.68 | 8.92 | 0.93 | 2.30 | 5.69 |
| T4 | 401.78 | 379.5 | 1.37 | 15.11 | 5.54 | 0.34 | 3.76 | 1.44 |
| Total C Emission during Vermicomposting | ||||||||
| Trts | Initial C (g kg−1) | Ending C (g kg−1) | CH4-C (g kg−1) | CO2-C (g kg−1) | C Loss (%) | CH4 -C Loss (%) | CO2-C Loss (%) | Unaccounted C (%) |
| T1 | 329.53 | 284.3 | 1.97 | 30.28 | 13.73 | 0.60 | 9.19 | 3.94 |
| T2 | 353.62 | 305.6 | 0.35 | 44.31 | 13.58 | 0.1 | 12.53 | 0.95 |
| T3 | 377.70 | 343.8 | 1.20 | 18.73 | 8.98 | 0.32 | 5.03 | 3.63 |
| T4 | 401.78 | 353.2 | 1.40 | 46.64 | 12.09 | 0.35 | 11.61 | 0.13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dume, B.; Hanc, A.; Svehla, P.; Míchal, P.; Chane, A.D.; Nigussie, A. Carbon Dioxide and Methane Emissions during the Composting and Vermicomposting of Sewage Sludge under the Effect of Different Proportions of Straw Pellets. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111380
Dume B, Hanc A, Svehla P, Míchal P, Chane AD, Nigussie A. Carbon Dioxide and Methane Emissions during the Composting and Vermicomposting of Sewage Sludge under the Effect of Different Proportions of Straw Pellets. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(11):1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111380
Chicago/Turabian StyleDume, Bayu, Ales Hanc, Pavel Svehla, Pavel Míchal, Abraham Demelash Chane, and Abebe Nigussie. 2021. "Carbon Dioxide and Methane Emissions during the Composting and Vermicomposting of Sewage Sludge under the Effect of Different Proportions of Straw Pellets" Atmosphere 12, no. 11: 1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111380
APA StyleDume, B., Hanc, A., Svehla, P., Míchal, P., Chane, A. D., & Nigussie, A. (2021). Carbon Dioxide and Methane Emissions during the Composting and Vermicomposting of Sewage Sludge under the Effect of Different Proportions of Straw Pellets. Atmosphere, 12(11), 1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111380







