Abstract
Shopping malls in Hong Kong are usually located near major roads. Indoor air quality (IAQ) in these buildings is subject to infiltration of outdoor traffic-related pollutants, such as PM10, PM2.5, CO, and NO2. Furthermore, the existence of indoor sources and building geometry added to the complexity of variations in IAQ. To understand outdoor infiltration and spatial heterogeneity of these pollutants, we conducted fixed and cruise indoor sampling, together with simultaneous outdoor measurements, in a typical mall in Hong Kong. The cruise sampling was conducted indoors on a predesigned route and repeated 15 times. Outdoor infiltration was quantified based on regression analysis between indoor and outdoor sampling. Results showed that 75% of PM2.5, 53% of PM10, and 59% of NO2 were infiltrated into the mall during opening hours. Elevated PM2.5 and CO were observed during the dinner period, suggesting an impact from cooking. Substantial spatial variations were observed for PM10, PM2.5, and NO2, particularly at locations near entrances and restaurants. Measures are needed to reduce pollution intrusion from building openings and cooking-related sources to improve air quality in the selected mall. Fixed and cruise sampling methods used in this study provide insights on sensor deployment for future air quality monitoring in buildings.
1. Introduction
Shopping malls are one of the important activity nodes in which people spend their time. Based on a survey conducted earlier in Hong Kong, residents spend on average 1 to 2 h in shopping malls per day [1]. Hong Kong has been recognized as a shopping paradise since 1999 [2]. There are over 26,000 employees in Hong Kong currently working in retail locations [3]. People spend on average 40 h per week in their workplace environment [4]. Indoor air quality is one of the key factors affecting people’s health and productivity in the workplace environment [5,6,7]. Most shopping malls are located near major roads due to convenience. The proximity to heavy-traffic areas transporting a high number of passengers makes them subjected to traffic-related pollutants, such as particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter less than 10 μm (PM10) and 2.5 μm (PM2.5), as well as gases such as nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and carbon monoxide (CO).
People’s exposure to particles and gaseous air pollutants is associated with many adverse health effects. For example, exposure to PM10 is associated with pneumonia and chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases [8,9]. Breathing air with a high level of CO reduces the amount of oxygen that is transported to organs such as the brain and leads to a higher chance of heart diseases [10,11]. Exposure to nitrogen dioxide (NO2) may increase susceptibility to infection and hence increase the risk of having pulmonary disease [12,13]. Understanding variability in these pollutants and contribution from outdoor infiltration is critical for identifying key factors affecting indoor air quality in shopping malls and thus developing strategies to protect public health.
Compared with other places that people spend time, such as home and schools [14,15,16,17], fewer efforts have been made to understand air quality in shopping malls. Only one study was found in Hong Kong, which was conducted in the 1990s. The study reported an indoor average of 200 µg/m3 of PM10 at measured malls, which was the second-most polluted indoor environment among selected offices, schools, homes, shopping malls, and restaurants in Hong Kong [18]. Around 55% of PM10 samples collected from weekdays failed to comply with Hong Kong Indoor Air Quality (HKIAQ) 8 h guideline of 180 µg/m3 at that time [19]. The highest CO concentration at one mall near a major road was found to be 4.2 ppm, which was two times higher than the HKIAQ 8 h guideline of 1.7 ppm [19]. This study highlighted the severity of indoor air quality in shopping malls; however, it may not reflect current situations given that it was conducted 20 years ago. In addition, these studies did not include PM2.5 and NO2, which have been shown to be critical for public health. For example, fine particles (PM2.5), which are much smaller than PM10, can penetrate deeply into the lung region and cause severe cardiovascular, respiratory diseases, and even death [20,21]. In Hong Kong, road traffic is the major source of PM2.5 and NO2 [22,23]. Thus, exposure to PM2.5 and NO2 in these places may substantially be the result of the outdoor environment.
The impact of outdoor-infiltrated pollutants on indoor air quality is less understood with regard to shopping malls. In the mentioned Hong Kong study, indoor concentrations were compared with outdoor concentrations, but no further analysis to quantify how much outdoor pollution was infiltrated indoor. A study conducted in the city of Changsha found the indoor-to-outdoor ratio (I/O ratio) of PM2.5 concentrations in a shopping mall ranging from 0.46 to 0.52 [24]. However, pollutant concentrations observed in shopping malls composed of pollutants infiltrated from outdoor and pollutants generated through indoor activities, such as cooking. The I/O ratio does not separate outdoor contributions from indoor concentrations, and thus, it is not useful in evaluating the impact of the outdoor environment on the mall’s IAQ [25]. In enclosed microenvironments, the contribution of outdoor infiltration can be quantified using linear regression based on simultaneous indoor and outdoor measurements [14,15,16,17,26]. The infiltration factor (IF), which is a slope from linear regression, can be used to infer the infiltration of outdoor pollution. Studies conducted in other microenvironments, such as homes and schools, have demonstrated that IF is useful to separate impact from outdoor pollution and indoor sources [14,15,26] and can be used in microenvironmental models to estimate people’s exposure to air pollutants.
With the development of sensor technology, routine air quality monitoring in buildings may become possible [27]. However, it is less clear how we should deploy sensors to better represent the indoor air quality in buildings. Especially for shopping malls, there is a knowledge gap on spatial heterogeneity of air pollution inside building to guide the design sensor network so that it can help identify pollution hot spots and provide useful information for managers to prioritize control measures.
In this study, we conducted simultaneous indoor and outdoor measurements of PM10, PM2.5, CO, and NO2 at fixed locations together with cruise samplings along predesigned routes at a shopping mall adjacent to a major road in Hong Kong, with aims to (1) examine the indoor abundance of traffic-related air pollutants, (2) quantify the impact of outdoor air pollution on indoor air quality, and (3) examine the spatial heterogeneity of air pollutants.
2. Methodology
The methodology includes (1) description of the sampling site; (2) study design and field measurement; (3) instrumentation and quality control; (4) statistical analysis.
2.1. Sampling Site
The selected shopping mall is located in an urban area of Hong Kong, surrounded by major trunk roads, as shown in Figure 1. There are bus and minibus terminals around the mall to facilitate transportation. Nearby the mall, with a 160 m distance, there is an Air Quality Monitoring Station (AQMS) operated by the government.
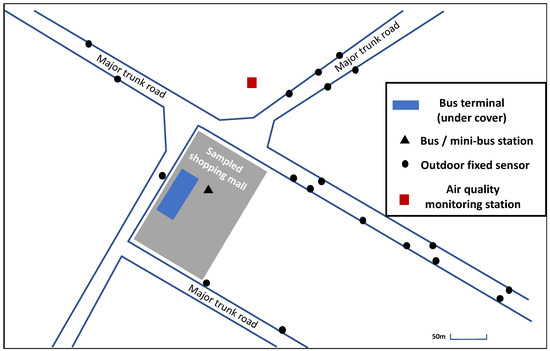
Figure 1.
Aerial view of the sampled mall and its surrounding environment.
The selected sampling site has 162 shops located on 3 floors—namely, G/F, UG/F (upper-ground floor), and 1/F, occupying 300,000 sq. ft. in total. There are escalators and lifts on both sides, which allow people to move from one floor to another. Facilities on G/F included food court, bakeries, and restaurants, while UG/F and 1/F mainly are used for retails and exhibition purposes. Smoking is prohibited at the mall. The opening hours of this mall is from 10:00 to 22:00 on both weekday and weekend.
Similar to numerous other malls in Hong Kong [28], the selected shopping mall uses centralized ventilation and air-conditioning system, which operate together with an integrated heat, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system. The HVAC system operates during opening hours and is turned off during non-opening hours. During operation, the outdoor air is mixed with indoor air at a constant ratio of approximately 10%. The ventilation rate and chiller volume can be adjusted through fan and temperature settings either locally by users or centrally by managers. Washable aluminum filters are installed in the ventilation ducts to prevent dust blockage, which has a filtering efficiency of approximately 40% for PM10 [29]. The mall staff takes shifts in the roster for 24 h. The major cleaning work occurs in the early morning and during the night when the mall is closed, which is one of the major infiltration pathways of outdoor air pollutants into indoors. Other than that, outdoor air can also enter indoors through multiple entrances that connect the mall with transportation hubs, outdoors, and above-ground footbridges to other locations. The glass door of these entrances is open from time to time based on entrance and exit, which may introduce outdoor air pollutants to the indoor environment.
2.2. Study Design and Field Measurement
Simultaneous outdoor and indoor measurements were conducted continuously at the selected shopping mall from 7 to 14 October 2017. The outdoor sampling location was set near the air intake of the ventilation system. The indoor sampling was conducted in parallel with two study designs, including (1) indoor sampling at a fixed location and (2) indoor sampling with a cruise route. The fixed sampling location was set up nearby the customer service center, which is a large open indoor area allowing air exchange among 3 floors, aiming to represent the general IAQ. The cruise sampling route, as shown in Figure 2, started from the top floor (1/F) and covered all functional areas to the ground floor (G/F). It was designed to cover the most spatial area in the selected shopping mall so as to reflect the spatial heterogeneity of air pollutants.
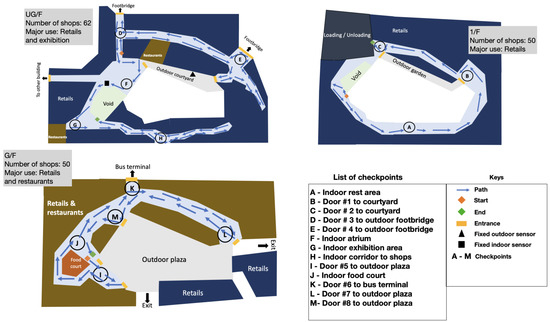
Figure 2.
Cruise sampling route over 3 floors and checkpoints along the route.
The outdoor and fixed indoor samplings were continuously conducted during the sampling period, while the cruise sampling was conducted by an investigator from time to time carrying a portable sensor box. A total of 13 checkpoints were set along the cruise route—namely, A, B, and C on 1/F; D, E, F, G, and H on UG/F; I, J, K, L, and M on G/F, which required a 5 min stay upon the researchers’ arrival. Among these points, 8 points were located near to entrance or exit to the outdoor, 2 points at the open indoor area, 2 points at a relatively crowded area, and 1 point at a food court, as listed in Table 1. Each trip of the cruise sampling took around 2 h to complete, which is comparable to the time people spend in a shopping mall in Hong Kong. In this study, 15 trips of cruise sampling, with a spread of sampling schedule in weekday/weekend, morning/afternoon, meal/non-meal hours, during the measurement period, were completed.

Table 1.
Checkpoints of cruise sampling route inside the selected shopping mall.
2.3. Instrument and Quality Control
Pollutants of PM10, PM2.5, CO, and NO2 were selected for all indoor and outdoor measurements. Indoor and outdoor PM2.5 and PM10 levels were sampled by Aerocet 831 Handheld Particle Counter (Met One, Grants Pass, OR, USA) and model 212 Ambient Particulate Profiler (Met One, Grants Pass, OR, USA), respectively. These counters measure particulate matter by light-scattering methods. CO and NO2 were measured by sensor models NO2-B4 and CO-B4 (Alphasense Ltd., Great Notley, UK). Indoor and outdoor portable systems were developed by assembling these sensors on the same sensor boards. The sensing systems were connected to the cloud platform for real-time data transmission. Data obtained from sensors were in 1 min time resolution. Details of the detection range, data resolution, and accuracy of sensors can be found in Table A1 in the Appendix A.
To assure data quality, laboratory and field performance tests were conducted. The testing procedure was reported in previous studies [14,15,30]. In brief, during the laboratory test, known concentrations of standard gases were supplied to NO2 and CO sensors to check the consistency. For the field performance test, all sensors were compared with the reference method in the AQMS operated by the Hong Kong Environmental Protection Department. In both tests, the indoor and outdoor sensors achieved the accuracy defined as specified. All indoor and outdoor portable systems were collocated for one hour before and after the mall’s measurement campaign to further check consistency between sensors. During collocation before and after the measurement, differences in average concentrations of pollutants (PM10, PM2.5, CO, and NO2) recorded among sensors were less than 10%.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The data collected at indoor and outdoor locations were merged into a database and averaged on an hourly basis to enable comparison with data recorded at AQMS station, which were obtained from governmental websites. Mean concentrations of selected pollutants and their correlations were calculated during the opening period (10 a.m.–10 p.m.) and non-opening period (10 p.m.–10 a.m.) and were compared between indoor, outdoor, and AQMS.
The indoor air pollutant concentrations were compared with HKIAQ, which was set up by Hong Kong Environmental Protection Department in 2001 to promote IAQ awareness and provide information on IAQ to the public. The latest version was released in 2019 [31]. HKIAQ is targeted for short-term pollution assessment, with most guidelines set for 8 h or 1 h average concentration.
Outdoor infiltration is determined by many factors, including air exchange rates, penetration, removal by deposition, filtration, and other loss mechanisms [32]. However, these factors are difficult to achieve or obtain in the real world. A typical practice of quantifying outdoor infiltrations is using the infiltration factor (IF), which is an average fraction of outdoor pollutants that exist indoors over a period. IF can be inferred as the slope from a linear regression between simultaneous indoor and outdoor concentrations of a pollutant [32]:
where, ; ; hourly indoor concentration of nonambient origin for pollutant p at time t .
IF accounts for the overall impact of direct outdoor penetration and deposition, filtration, and/or decay of the infiltrated pollutants over a period [15]. Such an equation is also applied in calculating IF for other microenvironments such as home and school [14,15,17,26,32,33,34]. The IF in Equation 1 ranges from 0 to 1. The goodness of fit was assessed using the coefficient of determination (R2), which indicates how much variability in indoor concentrations can be explained by outdoor pollution.
The cruise sampling collected data in sequences, which reflect both spatial variations along the sampling route as well as temporal variations during the sampling period. The data were normalized by dividing corresponding measurements at the fixed indoor location to remove impact from temporal variations, which was recommended for sequential measurements [26]. For each trip, normalized ratios were calculated along the sampling route for each pollutant using Equation (2).
where, ; ; ; P = pollutant, e.g., PM10, PM2.5, CO, NO2; .
The calculated ratios were then averaged among 15 trips and were spatially plotted for each pollutant.
3. Result and Discussion
This section includes (1) a summary of measurements, (2) assessment of outdoor infiltration, (3) indoor spatial variations of particle and gaseous concentrations, and (4) implications for indoor air quality management and IAQ sensor deployment.
3.1. Summary of Air Pollutant Measurements
In total, we collected 1344 h of pollution concentration data (168 h * 4 pollutants * 2 locations) from fixed sampling and 15 trips of repeated route pollution concentration, with each around 2 h. The data collected from fixed sampling were continuously conducted including weekday and weekend, opening hours, and non-opening hours. Compared with previous IAQ study at malls [35], which was conducted in a segment of time such as one hour, the long and continuous measurement in this study provided useful information on understanding the variations of pollutants in the mall, such as opening and non-opening period, meal times, and cleaning events, as shown in Figure 3.
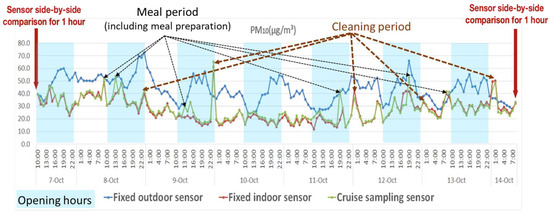
Figure 3.
Hourly data of PM10 during the side-by-side comparison period and parallel sampling period. Note: The cruise sampling sensor was put near the fixed indoor sensor when it was not in use for walkthrough inspection.
Figure 4 summarizes the hourly concentrations of PM10, PM2.5, CO, and NO2 sampled at fixed indoor and outdoor locations, together with concentrations recorded at AQMS, using box and whisker plots. The average PM10 concentrations during the sampling period were 27.0 µg/m3, 43.2 µg/m3, and 30.8 µg/m3 at mall indoor, outdoor, and AQMS, respectively. Compared with the previous study conducted in the 1990s [35], PM10 concentrations measured in this study were substantially lower. This may be related to a few reasons. First, smoking is banned in shopping malls in Hong Kong since 2006 [36], which was expected to be one of the indoor sources of PM10 within malls [18]. Second, outdoor PM10 concentration has been improved due to governments’ efforts in reducing pollution in recent years, especially measures in reducing vehicular emissions. For example, 82,000 pre-Euro IV diesel commercial vehicles were phased out between 2014 to 2019 to reduce PM pollution [37]. Together with other measures such as the enforcement of tighter emission standards, replacement of catalytic converters, as well as oxygen sensors of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) taxis and light buses [38], the PM10 concentrations measured at roadside has dropped by approximately 30% from 2013 to 2018, based on government monitoring stations [39]. Moreover, the mean indoor PM10 concentrations were 39% lower than outdoor during opening hours, which is equivalent to the filtration efficiency of the installed filter. The improved outdoor PM10 air quality, together with filters installed in the ventilation system, contributes to the lower indoor PM10 concentrations observed in the selected shopping mall, which complied with the “Good class” of HKIAQ guideline for 8 h PM10 concentration of 100 µg/m3 during the whole sampling period [31]. As shown in Table A2, indoor PM10 concentrations were moderately correlated with outdoor concentration (r = 0.5) during opening hours but weakly correlated (r = 0.21) during non-opening hours, suggesting closer correlation with outdoor pollution when mechanical ventilation was turned on.
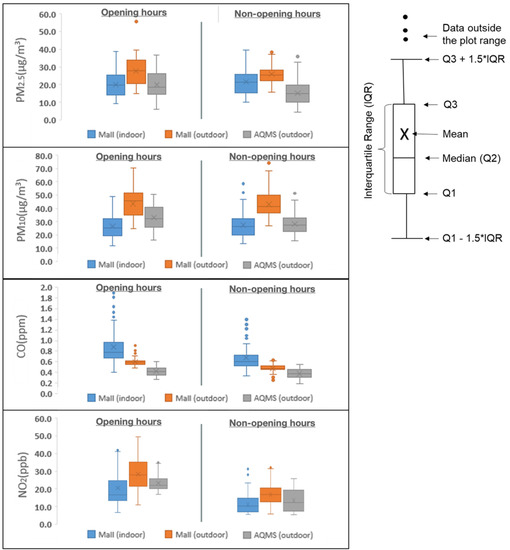
Figure 4.
The air quality of mall (indoor), mall (outdoor), and nearby air quality monitoring stations using hourly data during the sampling period.
The mean PM2.5 concentrations during opening hours were 20.1 µg/m3 and 27.7 µg/m3, respectively, at the fixed indoor and outdoor locations of the selected shopping mall. Indoor and outdoor PM2.5 concentrations were highly correlated with a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.81. Indoor PM2.5 concentrations were, on average, 20% higher during the dinner period (7 pm to 9 pm) than other periods, suggesting intensified emissions from indoor sources, such as cooking and resuspension of particles due to increased people traffic. Occupancy was not recorded in this study due to concerns of intrusiveness and being labor intensive. Further research is needed to investigate the impacts of this parameter with feasible indicative methods. The correlation coefficient of indoor and outdoor PM2.5 concentrations was 0.6 during the non-opening period, which was lower than that observed during opening hours, indicating that fine particles were less affected by outdoor during non-opening hours. This is probably due to the closure of the ventilation system during non-opening hours, which blocked the main channel of infiltration from outdoor pollution.
The mean indoor and outdoor CO concentrations were 0.9 ppm and 0.6 ppm during opening hours, respectively, with a low correlation of 0.15. The indoor CO concentrations were higher than outdoor indicating there were indoor sources. CO is generated mainly from combustion, such as cooking from food services. The indoor CO concentrations were observed to be right skewed, as reflected by the median position in the box plot. The average CO concentration was 1.4 ppm during the dinner period, which was 75% higher than that of 0.8 ppm in other periods, suggesting intensified indoor generation of CO during cooking periods. Compared with previous studies, which reported indoor CO concentrations from 0.8 ppm to 4.5 ppm [35], the CO concentrations at the selected shopping mall were relatively lower, ranging from 0.4 ppm to 1.9 ppm. The lower concentrations observed in this study may be caused by the smoking ban and improvement in outdoor air quality, similar to those of PM10. The indoor CO concentrations observed in this study complied with the “Excellent Class” of the HKIAQ guideline during the whole sampling period.
The mean NO2 concentrations during opening hours were 16.8 ppb and 28.1 ppb, respectively, at the fixed indoor and outdoor locations of the selected shopping mall, with moderate correlation (r = 0.61). The indoor NO2 concentrations were 40% lower than outdoors during opening hours and 27% lower than outdoors during non-opening hours. There were no specific gas filters installed in the ventilation system. However, previous studies indicate that NO2 may be consumed by reacting with indoor surfaces [40]. Thus, the reduction in indoor NO2 may be related to the reactions with surfaces in the shopping mall, as well as surfaces in the ventilation system. The hourly indoor NO2 concentrations complied with the “Excellent Class” of the HKIAQ guideline on hourly NO2 of 100 µg/m3 (approximately 53 ppb) during the whole sampling period.
Low-to-moderate correlations (r = 0.32~0.64) of pollutants concentrations were found between the fixed sampling location of the mall and AQMS in both opening and non-opening periods. The outdoor concentrations of PM10, PM2.5, CO, and NO2 were generally higher than those recorded at the nearby air quality monitoring station (AQMS). Although close in proximity (<200 m), the outdoor sampling location at the selected shopping mall is much closer to the road traffic conditions than the AQMS. The sampling height of the outdoor sensor is one floor (approximately 4 m) above the ground, while the AQMS is four floors above the ground. The lower sampling height of the outdoor sensor makes it closer to traffic-related pollutants, such as PM, CO, and NO2. Since the outdoor sensor was allocated in close proximity to the air intake of the ventilation system in the selected shopping mall, the higher pollution concentrations observed from the outdoor sensor indicated that the mall is more subjected to the near-ground air pollution, and the results would be underestimated if using AQMS as an indicator of its air quality.
3.2. Outdoor Infiltration of Pollutants
Outdoor infiltrations during opening hours were estimated based on linear regression, as shown in Figure 5, with scatter plots of the hourly indoor and outdoor concentrations for each pollutant. As observed in Section 3.1., the indoor emission was intensified during the dinner period, which may impair the fitting power of the linear regression models. For a better understanding of the impact of outdoor pollution, infiltration factors were estimated using data collected beyond the dinner period.

Figure 5.
Scatter plot of hourly indoor and outdoor pollutant concentrations together with infiltration estimated during the opening period (dinner data excluded).
The estimated infiltration factor for PM10 and PM2.5 was 0.53 and 0.75 for the selected shopping mall during opening hours, indicating 53% and 75% of the outdoor PM10 and PM2.5 infiltrated into the selected shopping mall. The filters installed in the HVAC system are less efficient in capturing fine particles than coarse particles, which may contribute to the higher infiltration found for PM2.5. Further, particles with different sizes may differ in their penetration and deposition, which may also contribute to the differences in overall infiltration. The infiltrated outdoor PM10 and PM2.5, which are estimated based on the infiltration factor multiplied by the outdoor concentration, contributed to more than 80% of the indoor observed indoor concentrations during the non-dinner period. This indicates that the indoor PM concentrations in the selected mall were dominantly affected by outdoor particle pollution.
The PM infiltration factors observed at the selected site were comparable with our measurements at homes and schools in Hong Kong. For example, the mean PM2.5 infiltration factor was 0.75 among 49 measured homes in Hong Kong, which is similar to the infiltration observed in this study [15]. Infiltration factors ranged from 0.44 to 0.63 for PM10 and from 0.53 to 0.79 for PM2.5 among 32 public schools in Hong Kong [14]. The filters installed at these microenvironments were typically low-efficiency filters, which may contribute to a generally high infiltration of PM observed in these studies. In contrast, the PM infiltrations were much lower in an office building that installed high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters, with infiltration less than 0.3 for PM10 and less than 0.4 for PM2.5 [41]. This indicates that efficient filters may help to reduce outdoor infiltration of particle pollution, which is a serious health threat in urban areas.
The estimated infiltration factor for NO2 was 0.57, indicating that 57% of the outdoor NO2 infiltrated into the selected shopping mall during the opening period. The intercept was not significantly different from zero, suggesting the contribution from indoor sources was minor, as seen in Table S1. The estimated NO2 infiltration was comparable to the average infiltration of 0.53 in our home study [15] but was higher than those observed at schools (0.24–0.36) [14]. As mentioned in the previous section and our previous studies [14,15], low outdoor infiltration of NO2 could be related to indoor chemistry. NO2 is reactive and could be removed with a wide range of species through complex chemical reactions that occur on the building envelope and indoor surfaces [42,43]. Additional measurements with experiments on specific factors are needed for an in-depth understanding of the underlying mechanisms behind outdoor infiltration.
The goodness of fit of the linear regression for CO is relatively low, with an R2 of 0.11, leaving a large portion of variations unexplained. The CO concentrations were lower than 1 ppm most of the time during the sampling period, which did not give a sufficient concentration span to build a model. Since the measurement period is relatively short, longer field measurements are recommended in the future to better capture the variations in air pollution. However, mean indoor CO concentrations were higher than outdoor concentrations during the non-dinner period, suggesting a contribution from indoor sources.
3.3. Spatial Heterogeneity Analysis
The spatial distribution of pollutant concentration ratio at the selected shopping mall was calculated based on 15 trips and plotted for PM10, PM2.5, CO, and NO2 in Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9, respectively.
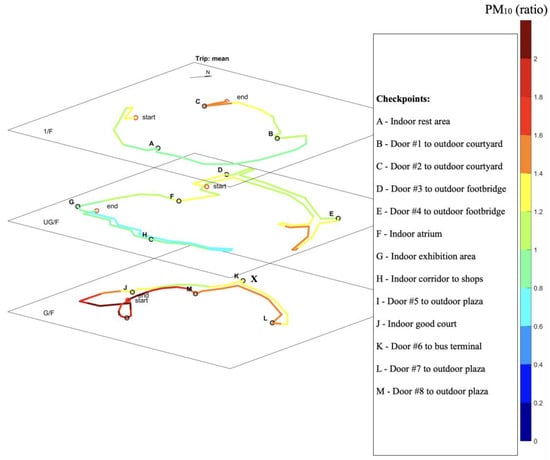
Figure 6.
Map of average PM10 normalized ratio based on 15 trips of cruise sampling.
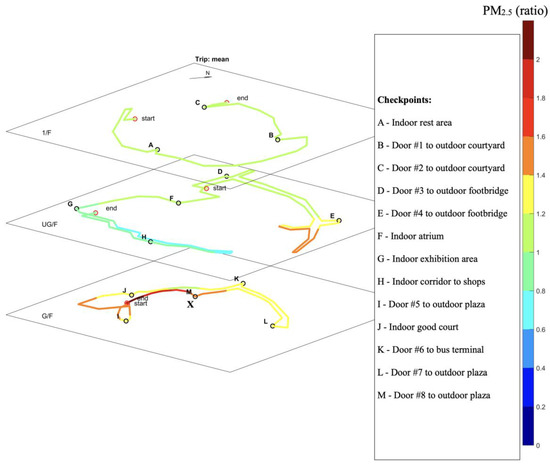
Figure 7.
Map of average PM2.5 normalized ratio based on 15 trips of cruise sampling.
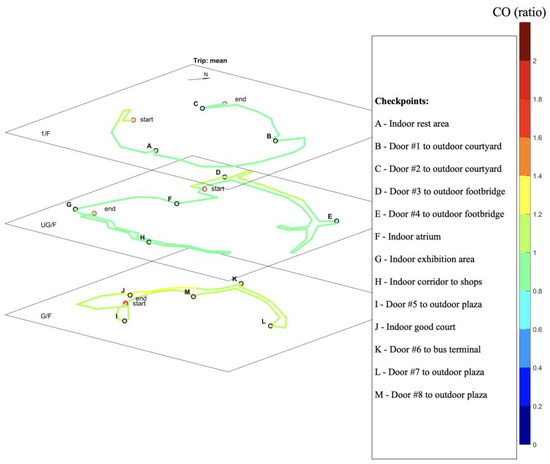
Figure 8.
Map of average CO normalized ratio based on 16 trips of cruise sampling.
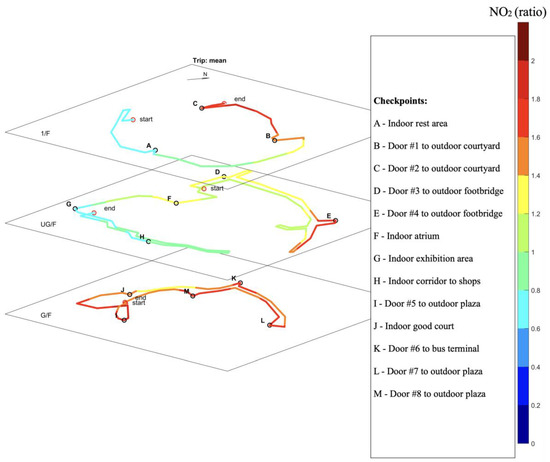
Figure 9.
Map of average NO2 normalized ratio based on 15 trips of cruise sampling.
Substantial spatial variations were observed for PM10, with an average normalized concentration ratio between 0.79 and 1.79 along the sampling route. Locations with normalized ratios higher than 1 indicate higher pollutant concentrations at those places compared to the reference point, which was the fixed sampling site near the customer service counter. Higher PM10 concentrations were found at places where higher people traffic was observed, such as food court (checkpoint J) and major entrances (checkpoints M, K, and L). PM10 can be generated through the resuspension of pre-loaded dust. Higher people traffic may lead to a larger portion of resuspended particles and thus contribute to higher PM10 concentrations. Another hot spot with high PM10 concentrations was found in a goods delivery area (checkpoint C), which may be related to the particle generation through mechanical processes related to loading and unloading goods. The PM10 concentration at checkpoint C was 33% higher than average, indicating the impact of duty-related activities on nearby particle concentration. High PM10 concentrations were also observed in an area near checkpoint E, which is the end of the shopping pathway and could be related to an accumulation of dust.
Spatial variations were also found for PM2.5, with an average normalized concentration ratio between 0.88 and 1.42 along the sampling route. PM2.5 concentrations on the ground floor were, on average, 27% higher than the other two floors. The major dining area was located at G/F, where restaurants were mainly gathered. Indoor PM2.5 was likely to be generated by the cooking activities, which was supported by the higher PM2.5 concentrations observed during the dinner period. High PM2.5 concentrations were also observed in the corner area near checkpoint E, which is similar to PM10. However, PM2.5 concentrations in the goods delivery area were not substantially higher, which indicated that the mechanical process is not a major source for fine particles.
The average CO concentration varied from 0.5 ppm to 1.2 ppm, with average normalized concentration ratio between 0.85 and 1.22 along the sampling route. CO concentrations on the ground floor were, on average, 29% higher than the other two floors, indicating the impact of cooking activities of the food court. The intra-floor variations in CO concentrations were limited, suggesting the mixed nature of gases.
Substantial spatial heterogeneity of NO2 was observed, with an average normalized ratio between 0.66 and 1.83 along the sampling route. Higher NO2 concentrations were found at areas near to entrances from outdoor, indicating impact from outdoor pollution. Larger spatial variations were found for NO2 than other selected pollutants. NO2 can react with a series of chemicals presented indoor. Part of the spatial heterogeneity of NO2 concentrations may be related to the intensity of NO2 chemistry, which would be of interest for further investigation.
Figure 10 shows the group mean and standard deviation of ratios between concentrations measured at checkpoints and the fixed location at the customer service center for PM10, PM2.5, CO, and NO2. The ratios for pollutant concentrations at checkpoints in the general area were not significantly different than unity, indicating they are similar to the air quality measured at the fixed point. However, the ratios for checkpoints near to door were 30% to 60% higher than unity for PM10, PM2.5, and NO2, suggesting higher pollutant concentrations at these locations compared with the general area. These places were subject to frequent indoor and outdoor air exchange, which may introduce more outdoor air pollutants. During the measurements, the entrance doors were sometimes left open, which may increase the intrusion of outdoor pollution. Ratios for CO were close to 1 at all checkpoints, indicating well-mixed nature and dominant impact from indoor sources.
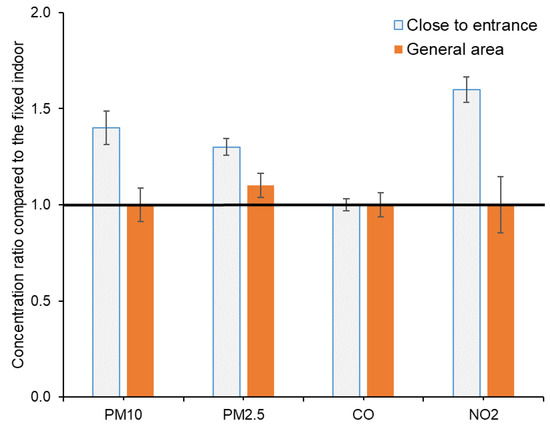
Figure 10.
Mean and standard deviation of concentration ratio between checkpoints and fixed indoor location.
3.4. Implications for Indoor Air Quality Management and IAQ Sensor Deployment
Regression analysis on the observed data showed that outdoor pollution is a dominant contributor to pollutants inside the selected mall, especially for PM. The cruise sampling data further demonstrated that PM concentrations at entrances, where un-filtered air may be introduced through the use of doors, were substantially higher than other indoor locations. Therefore, measures to reduce outdoor infiltration at entrances, such as installing automatic doors, should be prioritized for indoor air improvement in the selected building. Some pollution hot spots were identified for PM and CO, which were related to cooking and good delivery. Measures either to reduce source emission or enhance the removing process are needed for air quality concerns of these pollutants. For example, adding a filtering facility at hot spots may help to further reduce the intrusion of outdoor pollution. A study suggested that a vertical air curtain with a filtration function at bus stops may help to filter PM2.5 up to 70% [44]. It would be of interest to investigate how such an air curtain can help improve air quality at hot spots, as well as door entrances in a building setup.
Monitoring air quality in buildings has received increasing attention in recent years. However, questions remain on how to set up such a monitoring system that can better represent building air quality. With the limited data collected from a single site, we did not attempt to develop guidelines that would work for all mechanically ventilated buildings; however, results in this study provide useful insights on this issue. Similar temporal trends were found for both PM and gases between cruise sampling and fixed sampling, as seen in Figure 11, with differences in a trip average concentration less than 25% in the majority of the time for PM10 (12 out of 15 tips), PM2.5 (13 out of 15 tips), CO (14 out of 15 tips), and NO2 (8 out of 15 tips). This indicates that by carefully selecting the sampling location, one fixed sensor would be able to reflect general air quality in a building. However, spatial variations were also observed in pollutants’ concentrations during cruise sampling. Higher pollutant concentrations were observed at places near doors or indoor sources, on average 30% to 60% higher than general areas. Such differences may be enlarged during emission periods, as illustrated by trips 8 and 9, which were conducted during dinner hours. These places can be potential monitoring locations when additional sensors are available for a better understanding of the intensity and impact of indoor sources. A cruise sampling design with a few repeated measurements was able to identify hot spots, which would be useful in suggesting possible monitoring locations before sensor deployment.
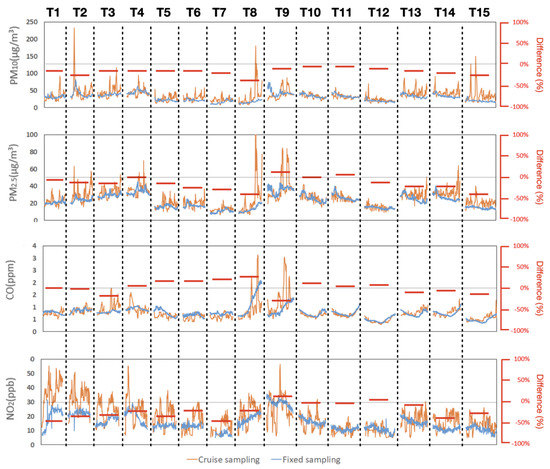
Figure 11.
Time-series of pollutants concentrations (in 1 min interval), together with trip average differences (%) of 15 trips (T).
4. Conclusions
Shopping malls are one of the important activity nodes in which people spend their time and thus are critical for understanding people’s exposure to air pollution. This study addressed the knowledge gaps of outdoor infiltration and spatial heterogeneity for particles and gases in shopping malls by a comprehensive indoor and outdoor air quality evaluation. Compared with the last reported shopping mall measurements in Hong Kong, which were conducted 20 years ago, pollutant concentrations were substantially lower in this study. This could be attributed to the improvement of outdoor air quality, as well as indoor source controls such as the smoking ban. Nevertheless, outdoor pollution still dominates indoor air quality. Regression analysis on simultaneous indoor and outdoor measurements suggests that 75% of PM2.5, 53% of PM10, and 59% of NO2 were infiltrated into the mall during opening hours. Measures to reduce outdoor infiltration, such as installing filters with higher filtration efficiency and air purification at entrances, should be prioritized for air quality improvement inside shopping malls. Our fixed and cruise sampling provides unique information on spatial heterogeneity in shopping malls and thus may provide insights on sensor deployment for routine air quality monitoring. Concentration differences between fixed and cruise sampling were less than 25% for most of the trips conducted in the selected mall, indicating that by carefully selecting the sampling location, one fixed sensor would be able to reflect general air quality in a shopping mall. Meanwhile, a few hot spots were identified near entrances and indoor sources, with concentrations higher than general areas by 30% to 60% on average. These places can be potential monitoring locations when additional sensors are available for a better understanding of the intensity and impact of indoor sources. Our study provides new data and methods to advance the understanding of indoor air quality in shopping malls.
Supplementary Materials
The following is available online at www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/atmos12101313/s1, Table S1: Sensitivity of infiltration estimates to the averaging time of indoor and outdoor concentrations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.-W.C. and A.K.-H.L.; methodology W.-W.C. and A.T.-Y.L.; software, Y.-S.S.; validation, A.T.-Y.L., Y.-S.S. and W.-W.C.; formal analysis, A.T.-Y.L.; investigation, A.T.-Y.L., Y.-S.S. and W.-W.C.; resources, A.K.-H.L. and J.C.-K.T.; data curation, A.T.-Y.L. and W.-W.C.; writing—original draft preparation, A.T.-Y.L.; writing—review and editing, W.-W.C. and J.C.-K.T.; visualization, A.T.-Y.L. and Y.-S.S.; supervision, W.-W.C., A.K.-H.L. and J.C.-K.T.; project administration, W.-W.C.; funding acquisition, A.K.-H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was sponsored by the HSBC 150th Anniversary Charity Programme through the PRAISE-HK project.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Detection range, data resolution, and accuracy of sensors.
Table A1.
Detection range, data resolution, and accuracy of sensors.
| Air Parameter | Detection Range | Data Resolution | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | 0–1000 μg/m3 | 0.1 μg/m3 | ±10% to calibration aerosol |
| PM10 | 0–1000 μg/m3 | 0.1 μg/m3 | ±10% to calibration aerosol |
| CO | 0–1000 ppm | 0.01 ppm | ±0.05 ppm or 15% of measured concentration |
| NO2 | 0–20 ppm | 1 ppb | ±10 ppb or 15% of measured concentration |

Table A2.
Pearson correlation coefficients of pollutants concentration between mall (indoor) with mall (outdoor), and mall (outdoor) with AQMS during the sampling period.
Table A2.
Pearson correlation coefficients of pollutants concentration between mall (indoor) with mall (outdoor), and mall (outdoor) with AQMS during the sampling period.
| Pollutants | Mall (Indoor) and Mall (Outdoor) | Mall (Outdoor) and AQMS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opening | Non-Opening | Opening | Non-Opening | |
| PM10 | 0.50 | 0.21 | 0.64 | 0.59 |
| PM2.5 | 0.81 | 0.60 | 0.64 | 0.57 |
| CO | 0.15 | 0.60 | 0.40 | 0.32 |
| NO2 | 0.61 | 0.30 | 0.41 | 0.42 |
Note: AQMS refers to the nearby air quality monitoring station shown in Figure 1.
References
- Chau, C.K.; Tu, E.Y.; Chan, D.W.T.; Burnett, J. Estimating the total exposure to air pollutants for different population age groups in Hong Kong. Environ. Int. 2002, 27, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heung, V.C.S.; Qu, H. Tourism shopping and its contributions to Hong Kong. Tour. Manag. 1998, 19, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Census and Statistics Department. Hong Kong Annual Digest of Statistics. 2020. Available online: https://www.censtatd.gov.hk/en/data/stat_report/product/B1010003/att/B10100032020AN20B0100.pdf (accessed on 3 August 2021).
- Muckenhuber, J. Working Time Around the World: Trends in Working Hours, Laws and Policies in a Global Comparative Perspective. Work. Employ. Soc. 2009, 23, 384–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.X.; Ou, D.Y.; Mak, C.M. The impact of indoor environmental quality on work productivity in university open-plan research offices. Build. Environ. 2017, 124, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunekreef, B.; Holgate, S.T. Air pollution and health. Lancet 2002, 360, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, F.J.; Fussell, J.C. Improving indoor air quality, health and performance within environments where people live, travel, learn and work. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 200, 90–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Ramón, M.; Zanobetti, A.; Schwartz, J. The Effect of Ozone and PM10 on Hospital Admissions for Pneumonia and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A National Multicity Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 163, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tecer, L.H.; Alagha, O.; Karaca, F.; Tuncel, G.; Eldes, N. Particulate Matter (PM2.5, PM10-2.5, and PM10) and Children’s Hospital Admissions for Asthma and Respiratory Diseases: A Bidirectional Case-Crossover Study. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2008, 71, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, N. Noninvasive Measurement of Blood Carboxyhemoglobin with Pulse CO-Oximetry. In Carbon Monoxide Poisoning; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 739–744. [Google Scholar]
- Allred, E.N.; Bleecker, E.R.; Chaitman, B.R.; Dahms, T.E.; Gottlieb, S.O.; Hackney, J.D.; Pagano, M.; Selvester, R.H.; Walden, S.M.; Warren, J. Short-Term Effects of Carbon Monoxide Exposure on the Exercise Performance of Subjects with Coronary Artery Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 321, 1426–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linares, C.; Falcon, I.; Ortiz, C.; Diaz, J. An approach estimating the short-term effect of NO2 on daily mortality in Spanish cities. Environ. Int. 2018, 116, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanbari Ghozikali, M.; Heibati, B.; Naddafi, K.; Kloog, I.; Conti, G.O.; Polosa, R.; Ferrante, M. Evaluation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) attributed to atmospheric O3, NO2, and SO2 using Air Q Model (2011–2012 year). Environ. Res. 2016, 144, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, W.W.; Li, A.T.Y.; Frey, H.C.; Tang, K.T.J.; Sun, L.; Wei, P.; Hossain, M.S.; Hohenberger, T.L.; Leung, K.W.; Lau, A.K.H. Factors affecting variability in gaseous and particle microenvironmental air pollutant concentrations in Hong Kong primary and secondary schools. Indoor Air 2021, 31, 170–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Che, W.W.; Frey, H.C.; Lau, A.K.H. Factors affecting variability in infiltration of ambient particle and gaseous pollutants into home at urban environment. Build. Environ. 2021, 206, 108351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.M.; Sarnat, J.A. Indoor-outdoor relationships and infiltration behavior of elemental components of outdoor PM2.5 for Boston-area homes. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekey, B.; Bozkurt, Z.B.; Pekey, H.; Dogan, G.; Zararsiz, A.; Efe, N.; Tuncel, G. Indoor/outdoor concentrations and elemental composition of PM10/PM2.5 in urban/industrial areas of Kocaeli City, Turkey. Indoor Air 2010, 20, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-C.; Guo, H.; Li, W.M.; Chan, L.Y. Inter-comparison of air pollutant concentrations in different indoor environments in Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 1929–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HKEPD. A Guide on Indoor Air Quality Certification Scheme for Offices and Public Places; The Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region: Hong Kong, China, 2003.
- Lu, F.; Xu, D.Q.; Cheng, Y.B.; Dong, S.X.; Guo, C.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, X.Y. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the adverse health effects of ambient PM2.5 and PM10 pollution in the Chinese population. Environ. Res. 2015, 136, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polichetti, G.; Cocco, S.; Spinali, A.; Trimarco, V.; Nunziata, A. Effects of particulate matter (PM10, PM2.5 and PM1) on the cardiovascular system. Toxicology 2009, 261, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HKEPD. Air Quality in Hong Kong 2017—A Report on the Results from the Air Quality Monitoring Network (AQMN); The Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region: Hong Kong, China, 2017.
- Chan, K.L.; Wiegner, M.; Wenig, M.; Pohler, D. Observations of tropospheric aerosols and NO2 in Hong Kong over 5 Years using ground based MAX-DOAS. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 1545–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, N. Variation of PM2.5 Concentrations in Shopping Malls in Autumn, Changsha. Procedia Eng. 2015, 121, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, I.; Viana, M.; Moreno, T.; Bouso, L.; Pandolfi, M.; Alvarez-Pedrerol, M.; Forns, J.; Alastuey, A.; Sunyer, J.; Querol, X. Outdoor infiltration and indoor contribution of UFP and BC, OC, secondary inorganic ions and metals in PM2.5 in schools. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 106, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, W.W.; Frey, H.C.; Li, Z.Y.; Lao, X.Q.; Lau, A.K.H. Indoor Exposure to Ambient Particles and Its Estimation Using Fixed Site Monitors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawska, L.; Thai, P.K.; Liu, X.T.; Asumadu-Sakyi, A.; Ayoko, G.; Bartonova, A.; Bedini, A.; Chai, F.H.; Christensen, B.; Dunbabin, M.; et al. Applications of low-cost sensing technologies for air quality monitoring and exposure assessment: How far have they gone? Environ. Int. 2018, 116, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HKPlanD. Hong Kong Planning Standards and Guidelines-Retail Facilities; Planning Department, Ed.; The Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region: Hong Kong, China, 2009.
- Smith Filter Corporation. Multiple Layers of Expanded Aluminum. 2021. Available online: https://smithfilter.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/Lifetime.pdf (accessed on 3 August 2021).
- Sun, L.; Wong, K.C.; Wei, P.; Ye, S.; Huang, H.; Yang, F.H.; Westerdahl, D.; Louie, P.K.K.; Luk, C.W.Y.; Ning, Z. Development and Application of a Next Generation Air Sensor Network for the Hong Kong Marathon 2015 Air Quality Monitoring. Sensors 2016, 16, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HKEPD. A Guide on Indoor Air Quality Certification Scheme for Offices and Public Places; The Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region: Hong Kong, China, 2019.
- Chen, C.; Zhao, B. Review of relationship between indoor and outdoor particles: I/O ratio, infiltration factor and penetration factor. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoli, E. Short-term effects of nitrogen dioxide on mortality: An analysis within the APHEA project. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 27, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hänninen, O.O.; Lebret, E.; Ilacqua, V.; Katsouyanni, K.; Kunzli, F.; Sram, R.J.; Jantunen, M. Infiltration of ambient PM2.5 and levels of indoor generated non-ETS PM2.5 in residences of four European cities. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 6411–6423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-M.; Lee, S.C.; Chan, L.Y. Indoor air quality at nine shopping malls in Hong Kong. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 273, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.P.M. Tobacco control policy in Hong Kong. Hong Kong Med. J. 2016, 22, 96–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- HKEPD. Phasing Out Pre-Euro IV Diesel Commercial Vehicles. Available online: https://www.epd.gov.hk/epd/english/environmentinhk/air/prob_solutions/Phasing_out_diesel_comm_veh.html (accessed on 24 September 2020).
- HKEPD. Cleaning the Air at Street Level. Available online: https://www.epd.gov.hk/epd/english/environmentinhk/air/prob_solutions/cleaning_air_atroad.html (accessed on 24 September 2020).
- HKEPD. An overview on air quality and air pollution control in Hong Kong. Available online: https://www.epd.gov.hk/epd/english/environmentinhk/air/air_maincontent.html (accessed on 24 September 2020).
- Weschler, C.J.; Shields, H.C.; Nalk, D.V. Indoor Chemistry Involving O3, NO, and NO2 as evidenced by 14 months of measurements at a site in Southern California. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 2120–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, W.W.; Tso, C.Y.; Sun, L.; Ip, D.Y.K.; Lee, H.; Chao, C.Y.H.; Lau, A.K.H. Energy consumption, indoor thermal comfort and air quality in a commercial office with retrofitted heat, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) system. Energy Build. 2019, 201, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weschler, C.J. Roles of the human occupant in indoor chemistry. Indoor Air 2016, 26, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weschler, C.J.; Wells, J.; Poppendieck, D.; Hubbard, H.; Pearce, T.A. Workgroup report: Indoor chemistry and health. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tong, J.C.; Ng, D.W.; Cheng, V.S.; Tsui, R.Y. Purifying City Air in Densely Urban Environment. the World Sustainable Built Environment Conference. Hong Kong, 5–7 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).