Impacts of the Tree Canopy and Chemical Reactions on the Dispersion of Reactive Pollutants in Street Canyons
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Governing Equations of the CFD
2.2. Tree Canopy Model
2.3. Chemical Reaction Model
3. Simulation Setup
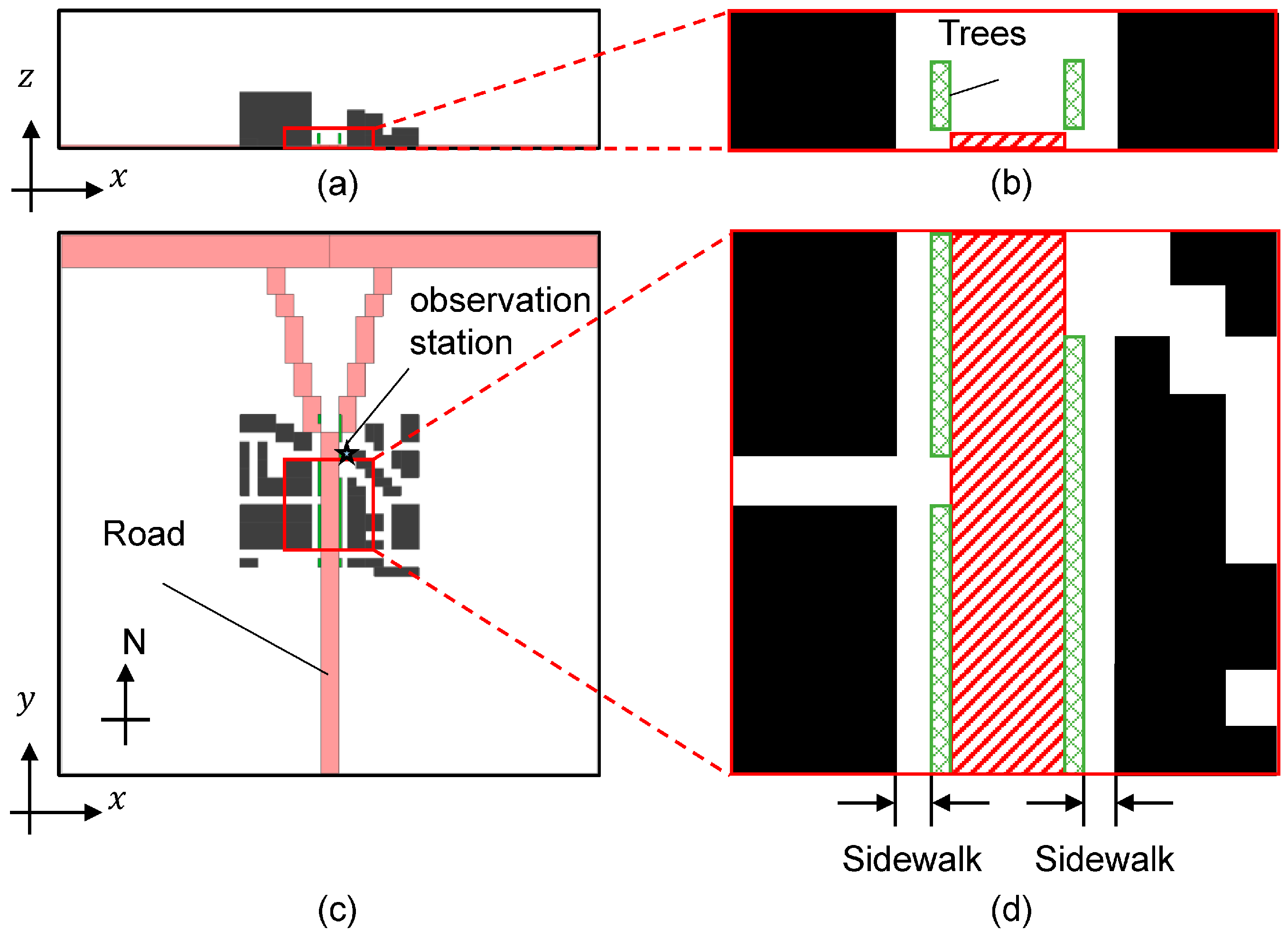
3.1. Calculation Domain and Period
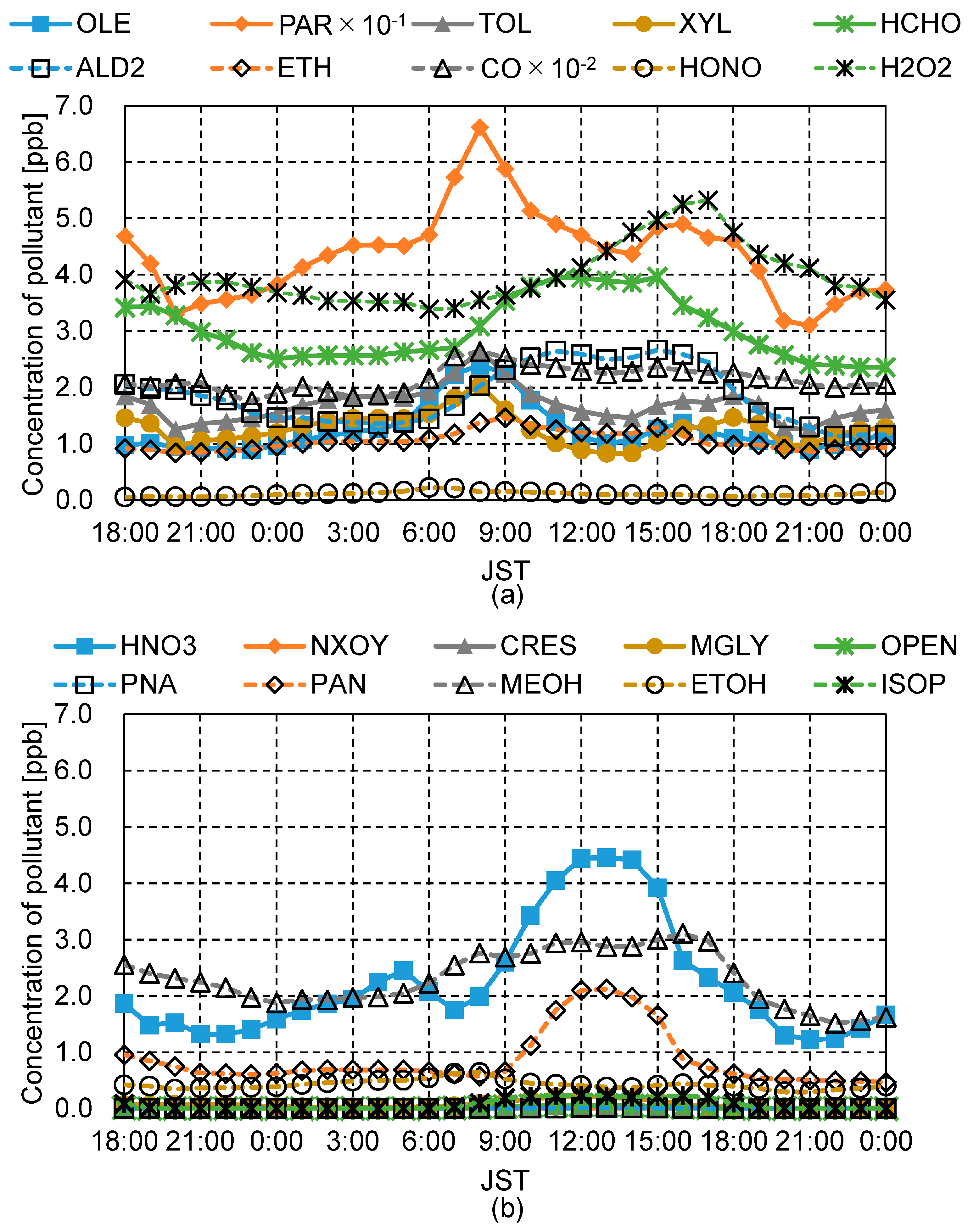
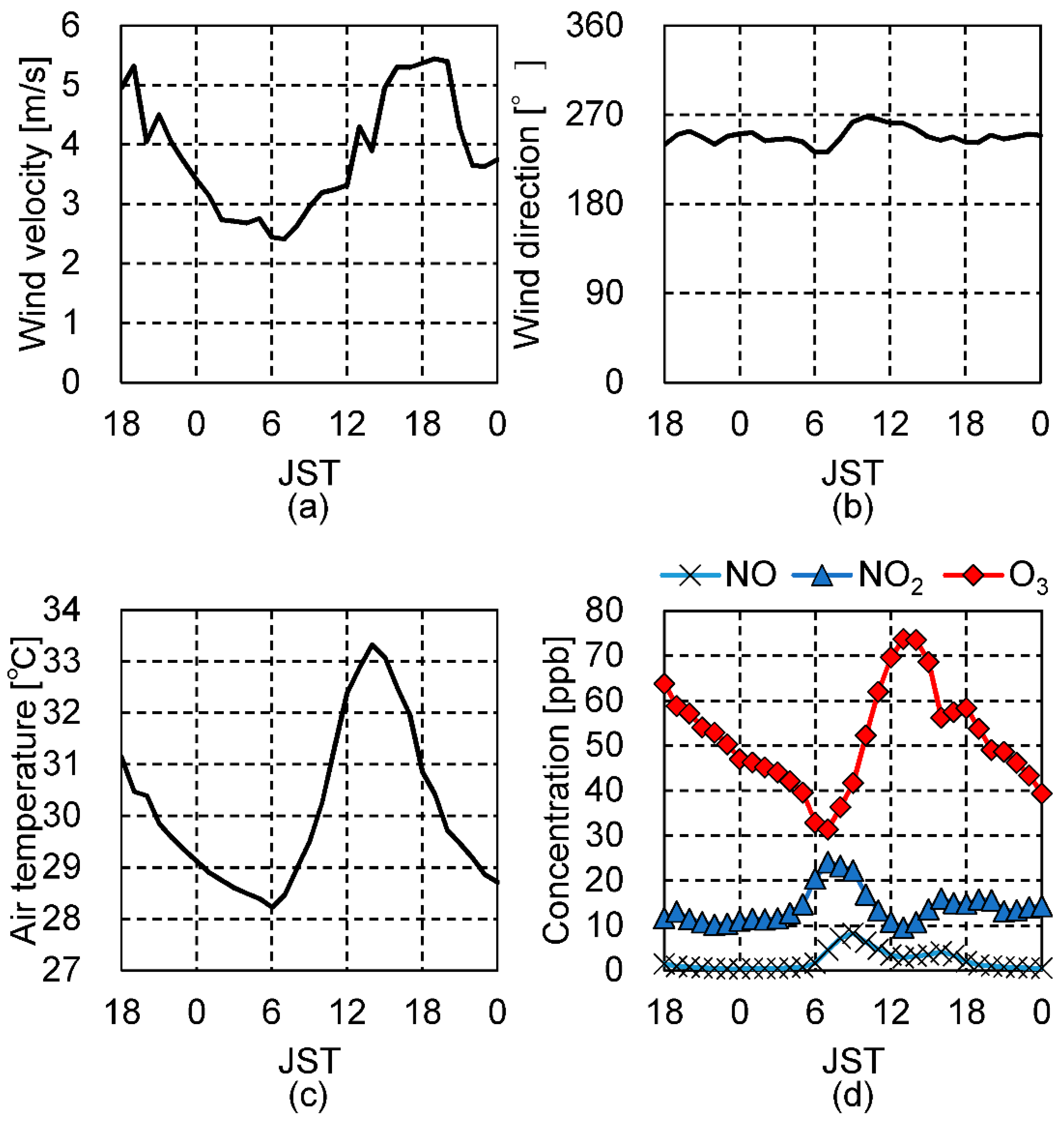
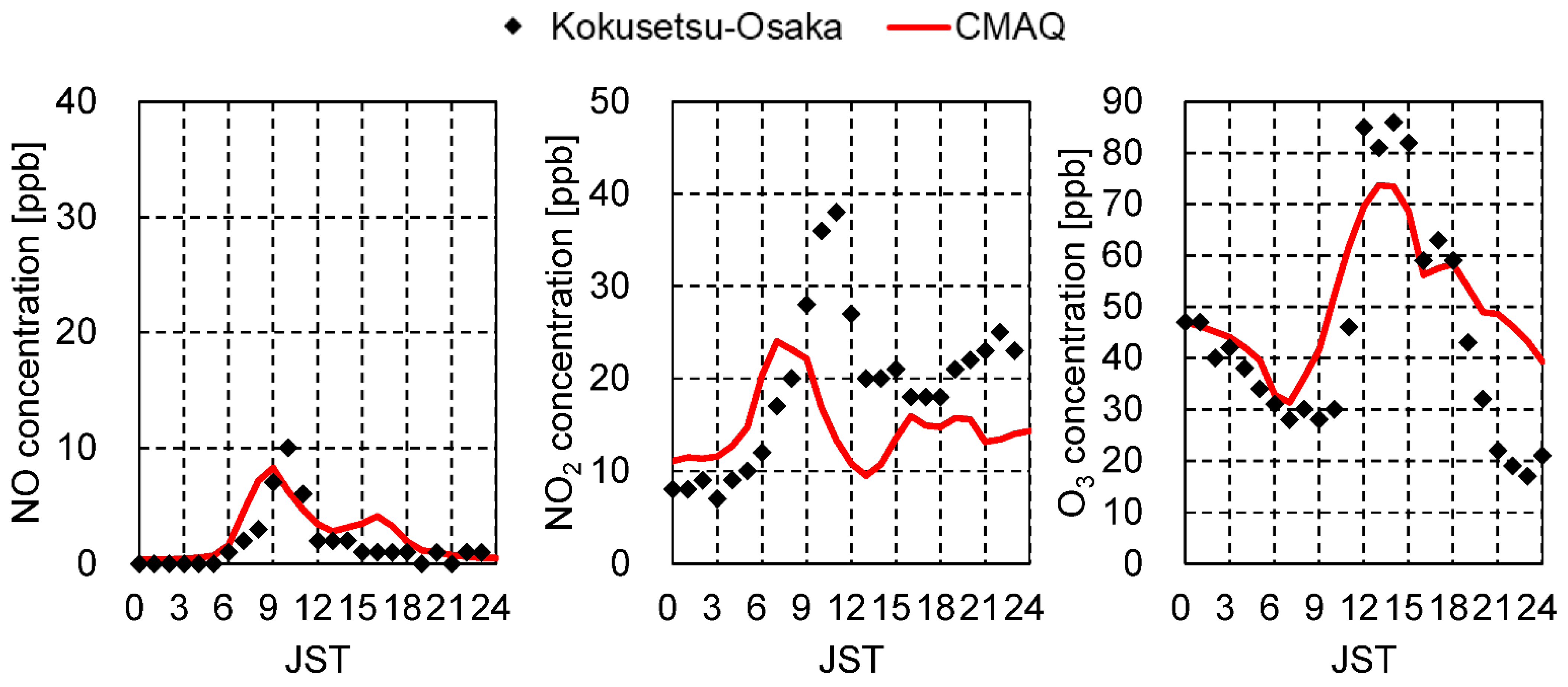
3.2. Boundary Conditions
3.3. CFD Tool Setup
3.4. Calculation Cases
4. Results and Discussion
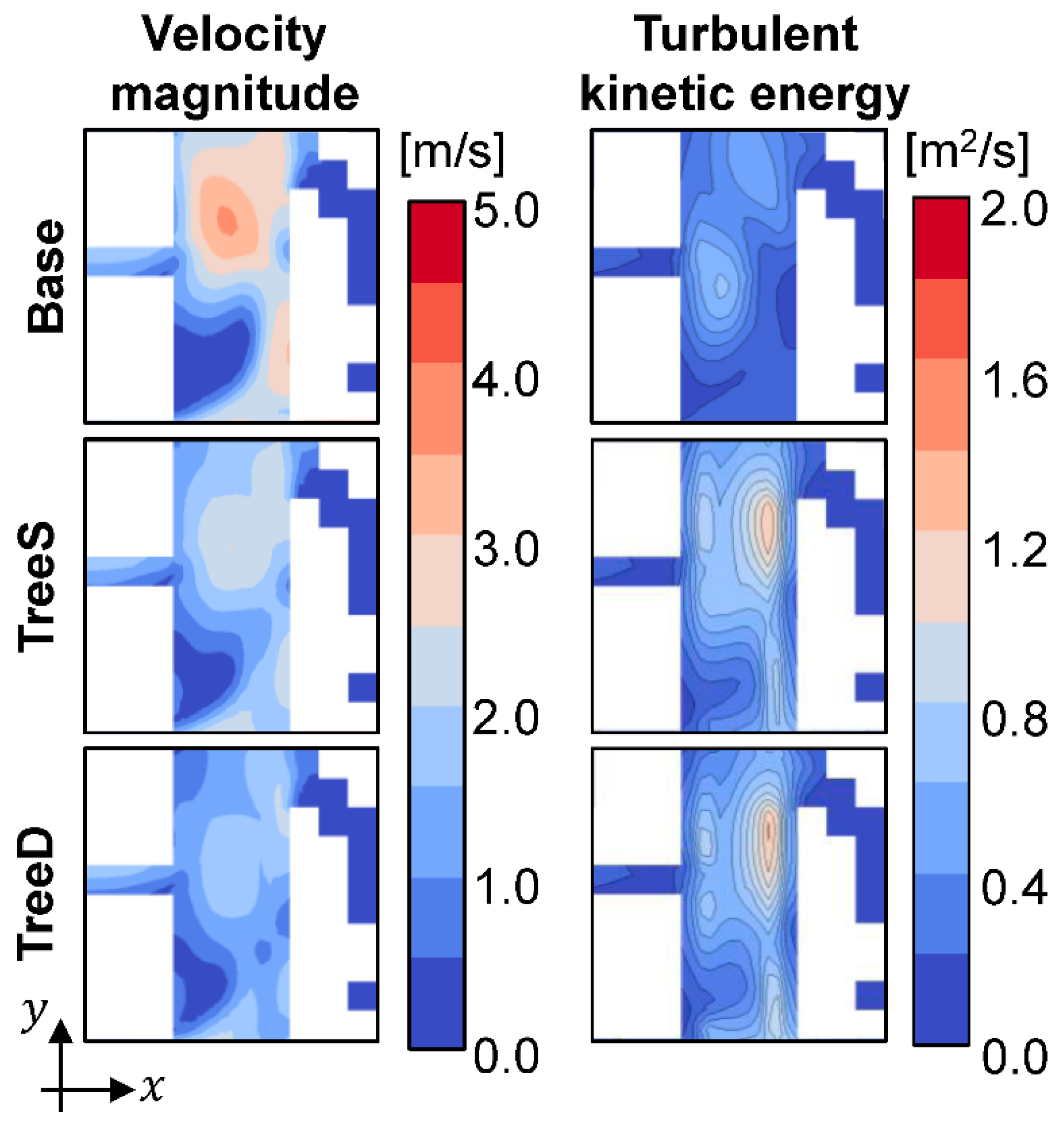
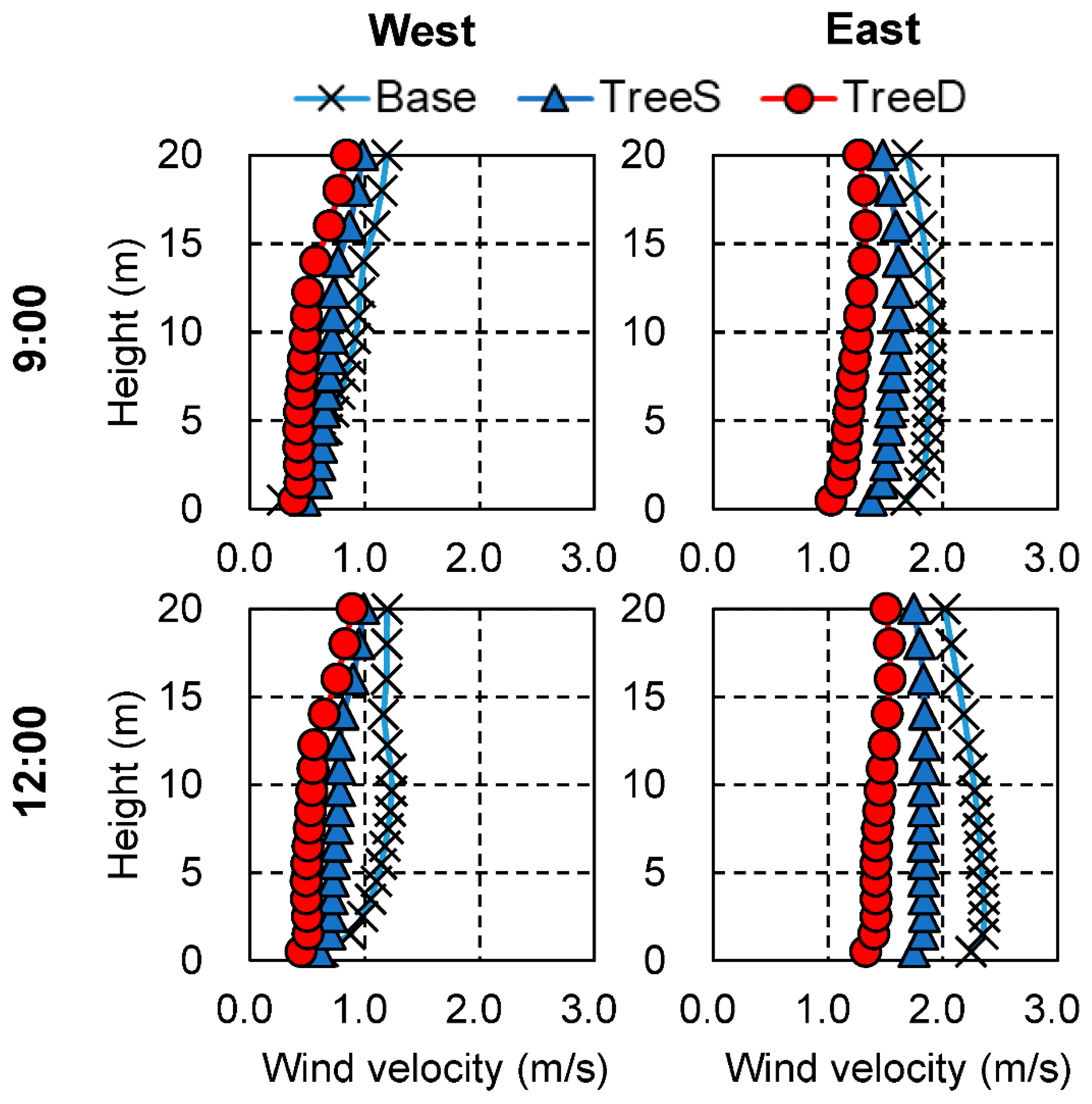
4.1. Impact of the Aerodynamic Effect of Trees on the Flow Field
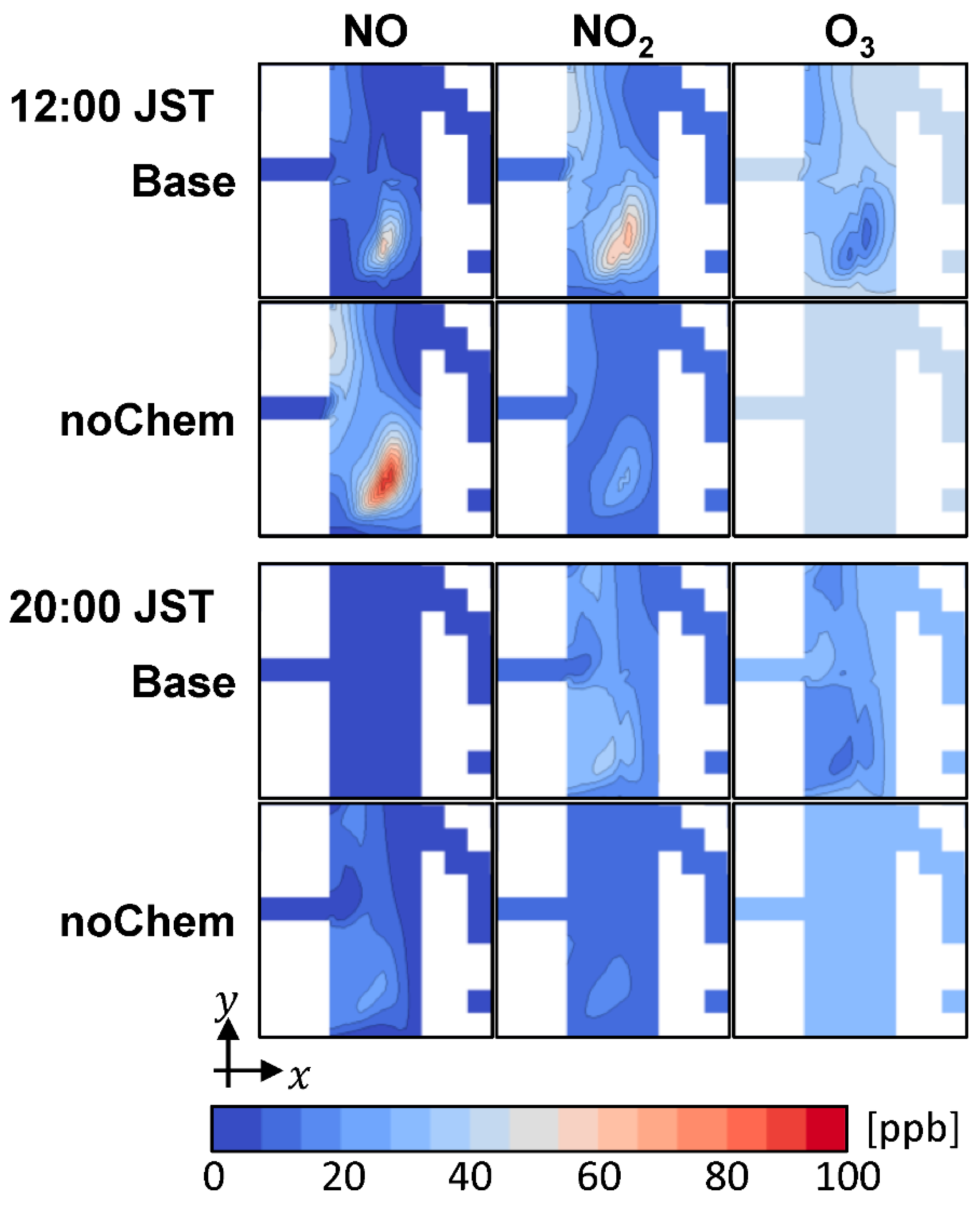
4.2. Impact of the Chemical Reactions on Pedestrian-Level Pollutant Concentrations
4.3. Impact of the Trees on Pedestrian-Level Pollutant Concentrations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Species | Short Names |
|---|---|
| Nitric oxide | NO |
| Nitrogen dioxide | NO2 |
| Nitrogen oxide | NXOY |
| Nitrous acid | HONO |
| Nitric acid | HNO3 |
| Peroxynitric acid | PNA |
| Ozone | O3 |
| Hydrogen peroxide | H2O2 |
| Carbon monoxide | CO |
| Formaldehyde | HCHO |
| High molecular weight aldehydes (RCHO, R>H) | ALD2 |
| Peroxyacyl nitrate | PAN |
| Paraffin carbon bond | PAR |
| Olefinic carbon bond | OLE |
| Ethene | ETH |
| Toluene | TOL |
| Cresol and higher molecular weight phenols | CRES |
| High molecular weight aromatic oxidation ring fragment | OPEN |
| Xylene | XYL |
| Methylglyoxal | MGLY |
| Isoprene | ISOP |
| Methanol | MEOH |
| Ethanol | ETOH |

References
- Leung, K.K.; Liu, C.H.; Wong, C.C.C.; Lo, J.C.Y.; Ng, G.C.T. On the Study of Ventilation and Pollutant Removal Over Idealized Two-Dimensional Urban Street Canyons. Build. Simul. 2012, 5, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Leung, D.Y.C.; Liu, C.H.; Lam, K.M. Physical Modeling of the Flow Field Inside Urban Street Canyons. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2008, 47, 2058–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegrini, J. A Wind Tunnel Study on Three-Dimensional Buoyant Flows in Street Canyons With different Roof Shapes and Building Lengths. Build. Environ. 2018, 143, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wen, C.Y.; Yang, A.S.; Juan, Y.-H. Effects of Height-Asymmetric Street Canyon Configurations on Outdoor Air Temperature and Air Quality. Build. Environ. 2020, 183, 107195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiminger, N.; Vazquez, J.; Blond, N.; Dufresne, M.; Wertel, J. CFD Evaluation of Mean Pollutant Concentration Variations in Step-Down Street Canyons. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2020, 196, 104032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegrini, J.; Dorer, V.; Carmeliet, J. Buoyant Flows in Street Canyons: Validation of CFD Simulations with Wind Tunnel Measurements. Build. Environ. 2014, 72, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.Y.; Li, Z.; Tao, W.Q. Wind-Tunnel Measurements for Thermal Effects on the Air Flow and Pollutant Dispersion Through Different Scale Urban Areas. Build. Environ. 2016, 97, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, L.W.; Glicksman, L.R.; Norford, L.K. Buoyant Flows in Street Canyons: Comparison of RANS and LES at Reduced and Full Scales. Build. Environ. 2018, 146, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertwig, D.; Efthimiou, G.C.; Bartzis, J.G.; Leitl, B. CFD-RANS Model Validation of Turbulent Flow in a Semi-Idealized Urban Canopy. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2012, 111, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, Y.; Stathopoulos, T. CFD Modeling of Pollution Dispersion in a Street Canyon: Comparison between LES and RANS. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2011, 99, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, J.-J.; Kang, Y.-S.; Kim, J.-J. Modeling Reactive Pollutant Dispersion in an Urban Street Canyon. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 934–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.; Walker, H.L.; Cai, X. A Study of the Dispersion And transport of Reactive Pollutants in and above Street Canyons—A Large Eddy Simulation. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 6883–6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez Olivardia, F.G.; Qi, Z.; Matsuo, T.; Shimadera, H.; Kondo, A. Analysis of Pollutant Dispersion in a Realistic Urban Street Canyon Using Coupled CFD and Chemical Reaction Modeling. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, K.-H.; Baik, J.-J. A CFD Modeling Study of the Impacts of NOx and VOC Emissions on Reactive Pollutant Dispersion in and above a Street Canyon. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 46, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, K.-H.; Baik, J.-J. Diurnal Variation of NOx and Ozone Exchange between a Street Canyon and the Overlying Air. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 86, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munera, F.; Favale, G.; Vardoulakis, S.; Solazzo, E. Modelling Dispersion of Traffic Pollution in a Deep Street Canyon: Application of CFD and Operational Models. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2303–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launder, B.E.; Spalding, D.B. The Numerical Computation of Turbulent Flows. Comp. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1974, 3, 269–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhot, V.; Orszag, S.A. Renormalization Group Analysis of Turbulence. I. Basic Theory, J. Sci. Comput. 1986, 1, 3–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, T.; Liou, W.W.; Shabbir, A.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, J. A New k-e Eddy Viscosity Model for High Reynolds Number Turbulent Flows. Comput. Fluids 1995, 24, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menter, F.R. Eddy Viscosity Transport Equations and Their Relation to the k-e Model. J. Fluids Eng. 1997, 119, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, G.E.; Ngan, K. Analysins Urban Ventilation in Building Arrays with the Age Spectrum and Mean Age of Pollutants. Build. Environ. 2018, 131, 288–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, N.; Montazeri, H.; Wigo, H.; Neophytou, M.K.-A.; Blocken, B.; Sandberg, M. CFD and Wind-Tunnel Analysis of Outdoor Ventilation in a Real Compact Heterogeneous Urban Area: Evaluation Using “Air Delay”. Build. Environ. 2017, 126, 255–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Buccorieri, R.; Gao, Z.; Ding, W. Indices Employed for the Assessment of “Urban Outdoor Ventilation”—A Review. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blocken, B.; Stathopoulos, T.; van Beeck, J.P.A.J. Pedestrian-Level Wind Conditions around Buildings: Review of Wind-Tunnel and CFD Techniques and Their Accuracy for Wind Comfort Assessment. Build. Environ. 2016, 100, 50–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, H. Modeling of Turbulent Flows within Plant/Urban Canopies. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1993, 46–47, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T. A Numerical Model Study of Turbulent Airflow in and above a Forest Canopy. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1982, 60, 439–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, I.; Ueda, H.; Wakamatsu, S. Numerical Modeling of the Nocturnal Urban Boundary Layer. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1989, 49, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.R. Modelling Turbulent Air Flow in a Stand of Widely-Spaced Trees. PHOENICS J. Comput. Fluid Dyn. Appl. 1992, 5, 294–312. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, F.; Li, X. The Impact of Roadside Trees on Traffic Released PM10 in Urban Street Canyon: Aerodynamic and Deposition Effects. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 30, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, W.-K.; Park, J.-H. Characteristics of Roadside Air Pollution in Korean Metropolitan City (Daegu) over Last 5 to 6 Years: Temporal Variations, Standard Exceedances, and Dependence on Meteorological Conditions. Chemosphere 2005, 59, 1557–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gery, M.W.; Whitten, G.Z.; Killus, J.P.; Dodge, M.C. A Photochemical Kinetics Mechanism for Urban and Regional Scale Computer Modeling. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 12925–12956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, K.-H.; Baik, J.-J.; Ryu, T.-H.; Lee, S.-H. Urban Air Quality Simulation in a High-Rise Building Area Using a CFD Model Coupled with Mesoscale Meteorological and Chemistry-Transport Models. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 100, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Xiang, S.; Liu, Y.; Yu, J.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Tao, S. High-Resolution Simulation of Local Traffic-Related NOx Dispersion and Distribution in a Complex Urban Terrain. Envion. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varatti, G.; Fabbi, S.; Bigi, A.; Lupascu, A.; Tinarelli, G.; Teggi, S.; Brusasca, G.; Mutler, T.M.; Ghermandi, G. Towards the Coupling of a Chemical Transport Model with a Micro-Scale Lagrangian Modelling System for Evaluation of Urban NOx Levels in a European Hotspot. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, R.S.; Perez, J.L.; Gonzalez-Barras, R.M. Assessment of Mesoscale and Microscale Simulations of a NO2 Episode Supported by Traffic Modelling at Microscopic Level. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimadera, H.; Kojima, T.; Kondo, A. Evaluation of Air Quality Model Performance for Simulating Long-Range Transport and Local Pollution of PM2.5 in Japan. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 5694251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uranishi, K.; Ikemori, F.; Shimadera, H.; Kondo, A.; Sugata, S. Impact of Field Biomass Burning on Local Pollution and Long-Range Transport of PM2.5 in Northeast Asia. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Japan Petroleum Energy Center. Technical Report of the Japan Auto-Oil Program: Emission Inventory of Road Transport in Japan; JPEC-2011AQ-02-06; Japan Petroleum Energy Center (JPEC): Tokyo, Japan, 2012; p. 136. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Patankar, S.V.; Spalding, D.B. A Calculation Procedure for Heat, Mass and Momentum Transfer in Three-Dimensional Parabolic Flows. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1972, 15, 1787–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, R.I.; Gosman, A.D.; Watkins, A.P. The Computation of Compressible and Incompressible Recirculating Flows by a Non-Iterative Implicit Scheme. J. Comput. Phys. 1986, 62, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gonzalez Olivardia, F.G.; Matsuo, T.; Shimadera, H.; Kondo, A. Impacts of the Tree Canopy and Chemical Reactions on the Dispersion of Reactive Pollutants in Street Canyons. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12010034
Gonzalez Olivardia FG, Matsuo T, Shimadera H, Kondo A. Impacts of the Tree Canopy and Chemical Reactions on the Dispersion of Reactive Pollutants in Street Canyons. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(1):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12010034
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzalez Olivardia, Franchesca G., Tomohito Matsuo, Hikari Shimadera, and Akira Kondo. 2021. "Impacts of the Tree Canopy and Chemical Reactions on the Dispersion of Reactive Pollutants in Street Canyons" Atmosphere 12, no. 1: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12010034
APA StyleGonzalez Olivardia, F. G., Matsuo, T., Shimadera, H., & Kondo, A. (2021). Impacts of the Tree Canopy and Chemical Reactions on the Dispersion of Reactive Pollutants in Street Canyons. Atmosphere, 12(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12010034





