Abstract
The PM10 concentrations in the studied region (Ostravsko-karvinská agglomeration, Czech Republic) exceed air pollution limit values in the long-term and pose a significant problem for human health, quality of life and the environment. In order to characterize the pollution in the region and identify the pollution origin, Instrumental Neutron Activation Analysis (INAA) was employed for determination of 34 elements in PM10 samples collected at a height of 90 m above ground level. From April 2018 to March 2019, 111 PM10 samples from eight basic wind directions and calm and two smog situations were sampled. The elemental composition significantly varied depending on season and sampling conditions. The contribution of three important industrial sources (iron and steelworks, cement works) was identified, and the long-range cross-border transport representing the pollution from the Polish domestic boilers confirmed the most important pollution inflow during the winter season.
1. Introduction
The studied area—Ostravsko-karvinská agglomeration—is situated in the northeast part of the Czech Republic, in the Moravian-Silesian Region. The region, together with the adjacent cross-border Polish region of Silesia, is historically connected with the accumulation of black coal mining and heavy industry, namely energetics, coking plants and ironworks [1,2]. The particular industrial character of the region along with its topography (basin surrounded by fairly high mountain ranges) and local meteorological conditions [3] causes its specific air pollution problems. The strategic industrial development of the region in the 1950s [4,5] initiated intensive population growth connected with substantial emissions from households. This effect has persisted until the present, as coal is still the most widely used fuel in the Polish border area [6,7]. Thus, the region is one of the most polluted in Europe [8]. The air pollution significantly exceeds the limit values of particulate matter (PM10, PM2.5), benzo[a]pyrene and ozone [4,8,9] according to European legislation [10] and World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines [11,12]. Both daily and long-term exposure to the substances mentioned above has a number of substantiated adverse biological effects [5,13]. Airborne particles increase mortality and morbidity, especially of the respiratory system, even at short-term exposures. The population exposed to PM shows a higher incidence of infectious diseases [14,15,16], and atmospheric pollution and PM pollution are factors classified as proven human carcinogens (category 1) [17]. Being one of the most densely populated regions in the Czech Republic (except its capital city) [18], the air pollution here poses an essential and long-term environmental problem.
Substantial pollution in the region has challenged researchers to identify causes and look for solutions, starting in the 1990s with the US EPA project Silesia [19,20]; later on, the effort continued with projects AIR SILESIA [21,22] and AIR TRITIA [6,23]. Moreover, numerous case studies focused on the pollution origin were performed [24,25,26] together with the recently published study of the Czech Hydrometeorological Institute (CHMI) [27,28]. All the studies emphasized the role of both the industry and the transboundary pollution from Poland (caused mainly by domestic boilers). According to these studies and state air quality monitoring [9,29], the highest PM concentrations occur near the Czech–Polish border (characterized by more prominent growth in the colder half of the year and during smog events) and also close to important industrial sources where the limit values of PM happened to be reached not only during the winter season. The air quality in the region is significantly influenced by the rate and nature of cross-border pollution transmission along the most frequent wind directions (typically SW/NE), together with the inverse character of the weather with steady atmosphere and subsequently worsened dispersion conditions, which significantly contribute to increased air pollution during the winter. According to the available studies [6,22,27,30], the contribution of the cross-border PM pollution to the annual average values can vary from 20–40% depending on the location in the region, emissions and meteorological conditions in the year.
The air quality monitoring presented in this study was performed within the AIR BORDER project focused on the cross-border pollution transport from Poland to the Ostravsko-karvinská agglomeration (the Czech borderland) and vice versa. The aim of the study was to run a special monitoring campaign in order to characterize the transmission of the PM10 particles from different groups of air pollution sources specific for the region, excluding the influence of the local sources [31]. This presumption was possible by locating a monitoring device on the top of a tower that reaches a height of over 85 m above the ground level. The device collects the PM10 particles depending on the wind direction, which enables one to investigate from which directions and from which sources the pollution comes and to more precisely quantify its transfer within the region.
2. Experiments
2.1. Sampling
The monitoring device was situated on the top of a former mining tower (90 m above ground level) located in Horní Suchá village in the centre of the Ostravsko-karvinská agglomeration.
(World Geodetic System 1984 coordinates 49.805166 N, 18.473954 E). The location of the tower in the region can be seen in Figure 1, the tower in Figure 2.
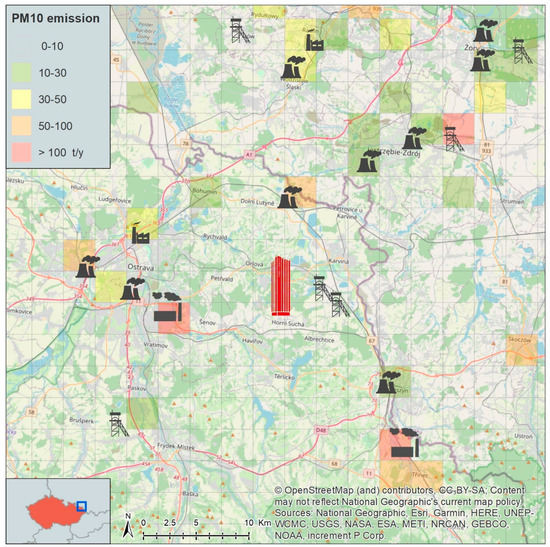

Figure 1.
The location of the tower at a regional scale with plotted industrial PM10 emissions.

Figure 2.
The tower in the operation period of the 1980s (a) and presently (b).
For the particulate matter sampling, the high-volume sampler SAM Hi 30 AUTO WIND (Baghirra Ltd., Prague, Czech Republic) was used. The sampler operates respecting the Guidelines on high-volume sampling methods that can be found in the Compendium of Methods for the Determination of Inorganic Compounds in Ambient Air compiled by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) [32]; a summary of the research of high-volume samplers performance can be found elsewhere [33].
The SAM Hi 30 AUTO WIND is a fully automatic, remote-controlled sampler intended for gravimetric and chemical analyses of aerosol particles. The device samples particulate matter with a <10 μm diameter (PM10) using the DIGITEL DPM10/30/00 PM10 pre-separator for 30 m3/h according to EN 12341 [34]. The sampler was designed to work depending on wind conditions. It has a magazine of 15 filters (glass microfiber, Whatman GF/A, Ø 150 mm) stretched in filter holders that are automatically changed to the sampling position according to actually evaluated wind conditions. Thus the sampler was able to collect PM10 particles from eight basic wind directions (N, NE, E, SE, S, SW, W, NW) and CALM (wind speed < 0.2 m·s−1). The sampler can be seen in Figure 3. Both wind speed and wind direction were measured via the WindSonic™ SDI-12 anemometer (Gill Instruments Ltd., Lymington, UK). The wind direction and wind speed for selecting a particular sampling filter from the magazine were determined according to one-hour moving averages calculated from 10-min data in accordance with US EPA guidance [35]. Thus, the actual wind may be different. The wind roses representing the measured wind direction in comparison with the sampled sector can be seen in Figure 4. Moreover, a special filter was designed for the episodes with extreme air pollution, defined as three successive average hourly PM10 concentrations exceeding 100 µg·m−3, using 10-min data from continuous ground monitoring.
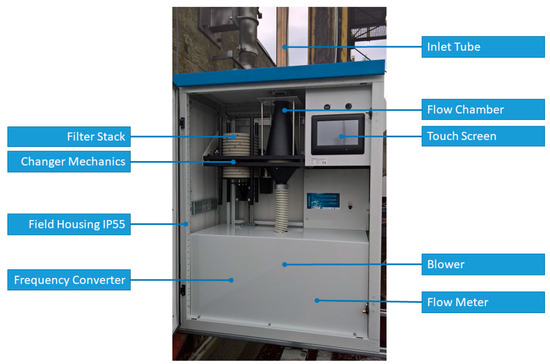
Figure 3.
The SAM Hi 30 AUTO WIND sampler.
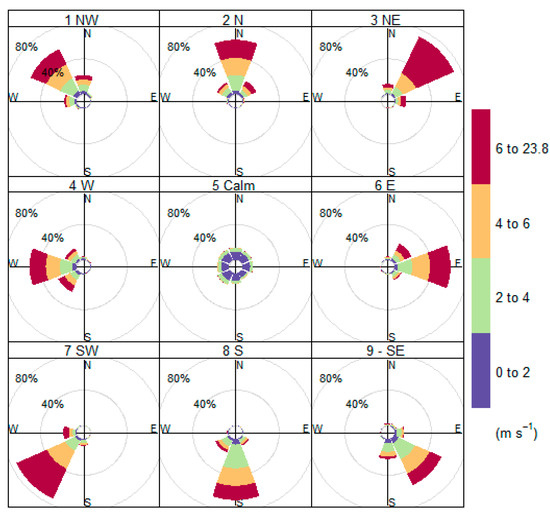
Figure 4.
Matching of sampled sectors and measured wind directions.
Employing this method, 111 PM10 samples from eight wind directions and calm (and extreme air pollution if occurring) were collected for each month from April 2018 to March 2019 (total of 12 months).
2.2. Determination of PM10 Mass Concentrations
PM10 mass concentrations were determined following the guidelines of EN 12341 [34]. Filters were weighed using an analytical balance (Sartorius MC 210P) before and after sampling. The filters were conditioned for ≥ 48 h under controlled relative humidity (50% ± 5%) and temperature (20 °C ± 1 °C), then weighed for a first time, followed by a second weighing after additional conditioning for ≥ 12 h for filters prior to the sampling and for 24 to 72 h for filters after the sampling. In accordance with the requirements, the difference of weighing results was ≤40 µg for filters prior to the sampling and ≤60 µg for filters after the sampling. The filter weight was calculated as an average of the two results. Weights for the blank filters were also recorded. The collected PM10 mass was calculated by subtracting pre-weight from the post-weight of the filters.
2.3. Element Content Determination Using Neutron Activation Analysis
One of the premises of this study was to apply NAA at the IBR-2 reactor of the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (Russia) for the characterisation of sampled PM. Thus, the testing of filters convenient for the analyses preceded the sampling campaign. Six different filters comprising five different materials were tested (glass microfiber, quartz, PTFE membrane, cellulose and paper). Only glass microfiber filters were determined as being fully suitable; a quartz filter was more problematic for repacking and considering the price, the glass microfiber filters were chosen to be used for the sampling.
Before subjecting the samples to NAA, the preparation of the subsamples of exposed and blank filters was done, as the irradiation capsules of the applied pneumatic transport system have limited volume (Ø 18 mm) and the whole filter is not able to fit in it. This also allows putting more subsamples in one capsule so the subsamples from one month and the corresponding blank filter can be irradiated all together under the same conditions. For this purpose, a special automatic punching head was designed and made (used materials: stainless steel, Teflon and surface finish synthetic rubber). Prior to cutting, filters were folded in half to avoid the loss of collected material, and then 4 circles (Ø 16 mm) were cut from the folded filter using the layering of subsamples. This way, one subsample of each filter (counting eight layers of the filter) was prepared reaching a weight of 0.06–0.07 g depending on the exposure. The preparation of the filters took place under a relative humidity of 50% (±5%) and temperature of 20 °C (±1 °C). After the preparation, each subsample was vacuum-packed to be transported for NAA.
The NAA procedure started with unpacking the subsamples and weighing them under controlled relative humidity and temperature. Then the subsamples were immediately packed in polyethylene and aluminium cups for short-term and long-term irradiation, respectively. Once packed, they were put into irradiation capsules and transported to the reactor.
The employed NAA provides the activation with thermal and epithermal neutrons at low temperatures convenient for this type of samples. Complete information about samples irradiation, measurement and quality can be found elsewhere [36,37].
For short-term irradiation, Channel 2 (epithermal neutrons, flux density φepi = 2.0 × 1011 cm−2·s−1) was used with an irradiation time of about 3 min. Samples were measured with 3–5 min. decay after irradiation for 15 min. Al, Ca, Cl, I, Mg, Mn, Si, Ti and V isotopes were determined in this way. For long-term irradiation, Cd screened Channel 1 (epithermal neutrons, flux density φepi = 2.0 × 1011 cm−2·s−1) was used with an irradiation time of around 4 days. After 4-days cooling, the samples were repacked and measured twice. The first time, they were measured directly after repacking for 30 min to determine As, Br, K, La, Na, Mo, Sm, U and W, and the second time 20 days after the end of irradiation for 1.5 h to determine Ba, Ce, Co, Cr, Cs, Eu, Fe, Hf, Ni, Rb, Sb, Si, Sc, Se, Sr, Ta, Tb, Th, W, Zn and Zr.
Gamma spectra of activated samples were measured on HPGe detectors (resolution of 1.9 keV for the 60Co 1332 keV line, efficiency 40%). The gamma spectra obtained were then processed using GENIE-2K software (CANBERRA) with the verification of the peak fit in an interactive mode. The concentrations of elements were calculated using certified reference materials irradiated simultaneously with samples via “CalcConc” software developed in the Frank Laboratory of Neutron Physics, Joint Institute for Nuclear Research [37]. The element concentrations were calculated by subtracting the corresponding blank filter values from determined values of the element in the subsample and recalculating using the mass concentrations of PM10. In cases of values below the detection limit, half of the detection limit was used. In case of missing values (no data) caused by technical problems during the analysis, the data imputation was employed in order to retain the information in the dataset and allow the proper multivariate assessment [38]. The k-nearest neighbours algorithm (knn) [39] was applied for the missing non-sub-limit data.
Recommendations of US EPA [40] were kept with respect to the workplace standard operating procedures. The quality control of the NAA results was ensured by triplicating standards per batch of unknown samples and carrying out simultaneous analysis. For filter analyses, standard reference materials were used: 2709a–San Joaquin Soil Baseline Trace Element Concentrations from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), 2710a–Montana I Soil Highly Elevated Trace Element Concentrations (NIST), 2711a–Montana II Soil Moderately Elevated Trace Element Concentrations (NIST), 1632c Trace Elements in Coal (Bituminous) (NIST), 1633c Trace Elements in Coal Fly Ash (NIST), AGV-2 Andesite from the United States Geological Survey and 433 from the Institute for Reference Materials and Measurements (IRMM). Satisfying agreement between the experimental results and certified material was obtained. The accuracy was formulated as the percentage deviation from the certified value amount up to 10%.
2.4. Statistical Analyses and Visualization
Pearson correlations calculation, Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and the visualizations of the results were performed in the R environment [41], package FactoMineR [42,43], Openair [44] and ggplot2 [45]. Prior to the PCA, the data were transformed according to the compositional data analysis (CoDa) principles [46] using the centred log-ratio (clr) transformation [47]. Only the clr-transformed elemental concentration data were used for the construction of the model, and the information on the wind direction, calm and inversion situation were added as supplementary variables.
3. Results
3.1. PM10 Mass Concentrations
The values of PM10 concentrations corresponding to wind directions, calm and inversion situations are shown for year average, warm (from April to September) and cold (from October to March) seasons for the period of observation (04/2018–03/2019) in Table 1 and Figure 5a. The values recorded during inversion events are not included in the calculation of means for respective wind directions considering the set-up function of the sampling device (see Section 2.1). For the PM10 concentration synopsis, see Table S1 the Supplementary materials.

Table 1.
Average PM10 concentrations for the observed period (µg·m−3).
Figure 5.
The average PM10 concentrations (a) and wind rose for the observed period (b).
The lowest PM10 values were observed from the SW and NW directions regardless of the season. The concentrations were below average in the warm part of the year, with the exception of the west direction due to the peak concentration in August 2018 (Figure 6). The highest concentrations were sampled from the east and north during the cold season, though prevailing wind direction in the season was SW Figure 5b. This wind direction in the cold season was the prevailing wind direction for the whole period of observation, as Figure 5b shows (expressed as a sampled air volume). Calm was recorded for 12% of the sampling time.
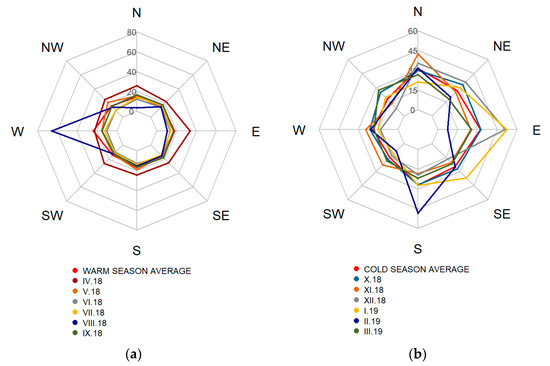
Figure 6.
The monthly average PM10 concentrations for warm (a) and cold (b) season.
Despite the peak concentration in August 2018, there was, in general, no directionality of the pollution in the warm season, as the concentration rose in Figure 6a shows. The peak August concentration originated most likely from the metallurgical complex in the west of the sampling site (see Figure 1), as the elemental composition of this sample also suggests (see Section 3.2). According to the meteorological data, this high concentration occurred in the period of steady cyclonic airflow (wind speed from calm to 2 m/s) preceding an upcoming cold front (see Figure 7). The meteorological situation for this event is illustrated via the ICON EU model data 10 m AGL and the Skew-T diagram as the global model (ICON, NOAA) in this situation was in total disagreement with recorded wind speed and wind direction data on the sampling site.
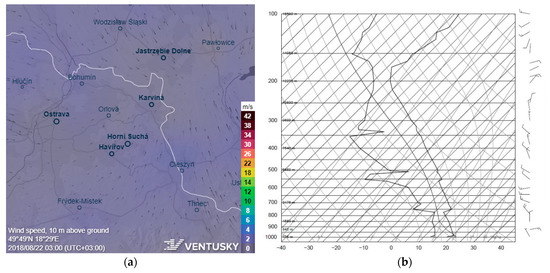
Figure 7.
The modelled wind fields (a) and the Skew-T diagram at the Prostějov sounding station (b) for August 2018 peak concentrations [48,49].
The April concentration rose has a similar course to the one for March (Figure 6). Considering the elements found in samples of these two months and the results of PCA (see Section 3.3), a similar origin of the pollution is expected. Thus, the April concentrations should be considered to appertain rather to the cold-season-related pollution sources.
During the winter season, the pollution came predominantly from the north, northeast and east directions, as the monthly average PM10 concentrations show in Figure 6b. This clearly confirms the importance of the PM inflow from the Polish borderland. The increase of PM10 concentrations from these directions in the winter season average 14 µg·m−3 though the prevailing airflow in winter is from the inverse direction (Figure 5b).
High PM10 concentration was sampled in this season also from the south direction in February 2019. As there is no important pollution source in this direction (mountainous rural area), this peak was investigated closer. According to the meteorological data, the airflow was steady (wind speed 1–2 m/s), coming from the southwest via the Moravian Gate for more than one day, accompanied by a radiation inversion (see Figure 8). This indicates that the peak concentration originated from an important pollution source in the south part of the Moravian Gate, directing to the cement works near the city of Hranice (about 50 km from the sampling site), as the elemental composition of this sample confirms (see below in Section 3.2).
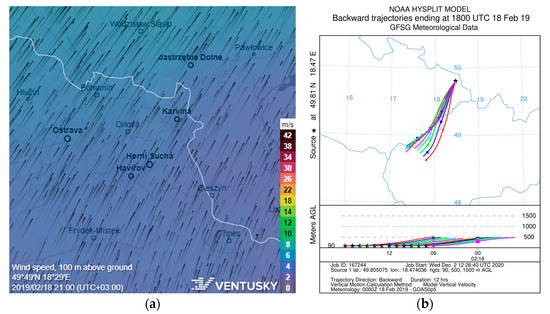
Figure 8.
The modelled wind fields (a) and backward trajectories (b) for February 2019 peak concentrations [48,50,51].
During the winter season, there were two smog events sampled, the first on 19 and 23 November 2018 (sampled on the same filter), with the PM10 concentration reaching 60.5 µg·m−3, and the second on 23 March 2019, with a PM10 concentration of 57.4 µg·m−3. In both cases, there was a temperature inversion connected with a steady airflow (measured wind speed < 1 m/s). In November, the prevailing airflow was from the NE, E and SE directions. Most likely representing the inflow of the pollution from the metallurgical complex on the southeast of the sampling site as confirmed by models (see Figure 9). For the March smog situation, the modelled airflow indicates the direction from the NE and E, suggesting the origin of pollution in the Polish borderland (see Figure 10). The elemental composition of these samples is stated in the next chapter.
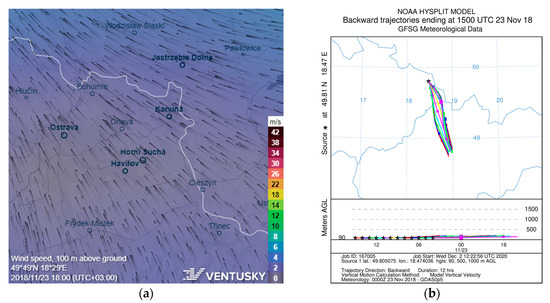
Figure 9.
The modelled wind fields (a) and backward trajectories (b) for the smog situations in November 2018 [48,50,51].
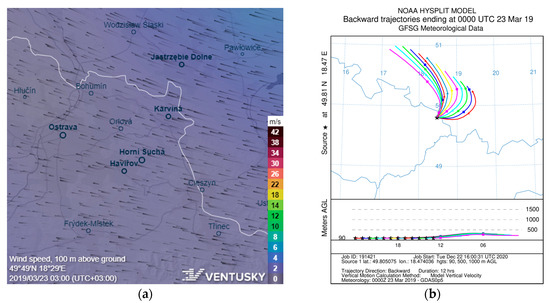
Figure 10.
The modelled wind fields (a) and backward trajectories (b) for the smog situations in March 2019 [48,50,51].
3.2. Element Content Characterization
The basis of the study was to characterise the sampled PM10 using NAA. Though this method enables the determination of a wide range of elements, it has specific limitations. Therefore, some of the important markers that would facilitate the source identification are lacking in the obtained dataset of element composition. Thus, the data of Pb (impossible to determine), Cd, Cu, Ni and Ti (determinable only if high concentrations are present) are absent. However, Cd, Ni and Ti were determined in a few samples, but the concentrations were below the minimal detectable concentrations and hence not included in further assessment.
Minimum and maximum levels, mean concentration values, medians and standard deviations of the elements determined in the PM10 are shown in Table 2; the correlation of the analysed elements can be found in Table 3. Element contents and concentrations vary depending on the season; thus, the data were investigated separately. To see the element concentrations for the respective directions and seasons, see Table S2 and Figures S1 and S2 in the Supplementary Materials.

Table 2.
Synoptic table (minimum, maximum value, mean, median and standard deviation) of elements concentration (ng·m−3) determined in the PM10 using INAA.

Table 3.
Elements with Pearson correlation coefficients >0.7 determined for the respective seasons.
The correlation between the analysed element contents was also season-dependent, thus confirming the variability of the sources and the different origin of the pollution. A strong positive correlation (R > 0.7) was determined between As and Cr, Mn, Br and I in the warm season, and As correlated with La, Sm, Sr and U in winter. This suggests—together with the directionality of the concentrations of these elements—that As occurrence in the warm season is connected to the metallurgical processes [52,53,54], while in winter samples, its source appears to be black coal burning [52,55,56,57].
The element content of coal combustion products, or more precisely, fly ash plays an important role in this study for the determination of pollution origin mainly during the cold season. The distribution of elements during this process is well described in many works [56,58,59,60], and numerous factors need to be taken into account. First are the element content and its bonding in coal, as well as boiling points of elements and their compounds (in connection to a combustion temperature). Other important factors affecting the resulting emissions are also the type of furnace, rated capacity, combustion temperature, exposure time, the type of separator and its operating temperature, physic-chemical reactions with other substances (additives, sulphur or halogens) and others. Depending on these conditions, different elemental compositions of fly ash emission are described in the literature [56,61,62,63,64]. The elements presented in bituminous coal fly ash in the majority of information sources are As, Cd, Se, Pb and Hg; other elements vary. Thus, named elements can be considered as strong markers of this process. Regarding the limitations of NAA mentioned above, other less common elements also need to be investigated. Consequently, while determining the main sources of pollution depending on weaker element markers, the element composition of emissions appertaining to particular sources in the region was taken into consideration [52,57]. Thus, a presence or absence of an element can indicate or exclude an origin in a certain source.
In the warm season, Fe was strongly correlated with Br, Sm and Th, while in winter, it was correlated only with Sc. Considering the direction where the highest concentrations of these elements originated (E, NE), it can be assumed that their occurrence is associated with the primary metallurgy [52,53]. Cr correlated with As, I and Mg in the warm season, while in the winter samples, no significant correlation was found. The highest concentrations of these elements in the warm season came from the west direction, suggesting the relation with a steel and iron production [54,65,66] as a relatively high concentration of Br and I was found also in a local coking plant emission [52]. For more correlations, see Table 3. It should be noted that the Rare Earth Element (REE) levels were in good correlation, which is important for both evaluating the data quality and understanding the mass transport events [67,68].
Special attention was paid to the samples with the PM10 peak concentrations above those mentioned. The sample collected in August 2018 from the west sector was characterized by high concentrations of Cr, Mg and I (the highest of all the set) and relatively high concentrations of Mn and Co. Cr and Co are important solutes for steel alloying in order to obtain special properties of steel; both Cr and Mg form important refractories used as lining in metallurgical facilities [65,69]. Moreover, Mg (with Ca) constitutes a base additive used in almost every step of the steel-making process from agglomeration and blast furnaces (dolomitic limestone, dolomite) to final steel-making (magnesite). Mn is a common element in austenitic steels produced in local steelworks [52,54,65,69]. The presence of iodine can be also connected with steel alloying as it is used for the production of certain transition metals, among them Co, Cr or Ti. Another possible source is coking [52]. Considering all these facts, the steelworks west of the sampling site are the most likely origin of the peak PM10 concentration (see Figure 1 above).
The elemental composition of the south sample in February 2019 was characterized by high concentrations of Ca, Se and V (the highest of all the set) and relatively high concentrations of I and Sb. The high concentration of Ca is, in all probability, connected with a cement plant [52,70,71,72], and regarding the meteorological conditions discussed above, this peak concentration most likely originated from the cement plant quite far (about 50 km) to the southwest of the sampling tower. This hypothesis can be confirmed by the fact that, in this factory, alternative fuels based on waste and tar are used during the process of clinker firing besides coal, explaining the high concentrations of the other elements determined.
The two samples collected during the smog events significantly differed in their elemental composition. The PM10 sampled in November 2018 was characterized by high concentrations of Ba, Ce, Fe, Hf, Rb, Sc, Ta, Th, U and Zr (the highest of all the set), while the sample in March 2019 by high concentrations of Si, Sr, Zn and Eu. The elemental composition of the first sample indicates two sources of pollution: coal burning and metallurgy [28,52,54,57]. These high concentrations were sampled during steady airflow from the NE, E and SE directions, suggesting the origin of the pollution in the steel plant southeast to the sampling site (see Figure 1 above) together with residential coal burning. The origin of the pollution in the case of the second inversion situation is not as clear; nevertheless, the modelled airflow points to the Polish borderland (see Figure 10) [52,54,65,69].
3.3. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
The samples were investigated using a PCA (see Section 2.4) to understand the variability of the element composition and thus also the pollution origin. The results of PCA performed on the untransformed dataset with the variables season and sector taken as supplementary qualitative variables indicate that the factor season separates the plane and the individual measurements distinctively. This separation of the plane was confirmed by the Wilks test (p-value of 9.108346 × 10−11). Similar separation also occurs when PCA is performed on the whole dataset with the clr-transformed concentration data (p-value of 5.219250 × 10−8), only it is realized alongside the second dimension. Thus, PCA results confirm that the season is a determining factor both for the elemental composition of the entirety of the measurements and for the directionality of the elements expressed as the change in the sectors with similar analysed concentrations. For more details, see Section 3.3.1 and Section 3.3.2. According to the analysis (chi-squared goodness-of-fit test), the elements varying the most depending on the season are Sr (p < 0.001), Cl (p < 0.001), Th (p < 0.001), Na (p = 0.001), Zn (p = 0.01), Cs (p = 0.015), Rb (p = 0.02) and Co (p = 0.04) with higher concentrations in the cold season and Mg (p < 0.001), Hf (p < 0.001), Sm (p < 0.001) and Ba (p = 0.015) in the warm season.
3.3.1. PCA of The Warm Season Measurements
According to the PCA results, the first two dimensions express over 81% of the dataset inertia, meaning that the first factor plane represents a major part of the total variability and that no other dimensions need to be considered. Moreover, the first axis itself represents almost 75% of the data; hence, it can be concluded that only this axis carries real information. The variability explained by this axis alone exceeds the reference value of 10.26%; this value is equal to 0.95-quantile of inertia percentages derived from the simulation of 10,000 data tables of equivalent size (normal distribution). The percentages of explained variance of the first five axes were 74.93, 6.52, 4.74, 2.46 and 2.1, respectively. A visualization of the PCA results of the warm season data is presented in Figure 11.
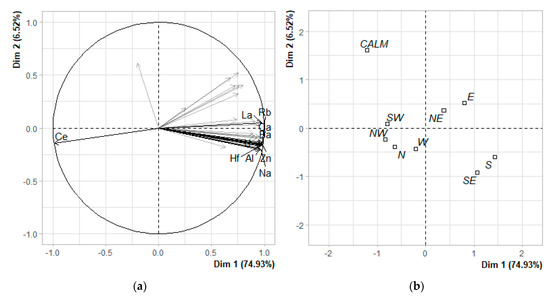
Figure 11.
The warm season PCA results for the first two dimensions; (a) correlation circle of clr-transformed elemental concentrations; 10 most contributing variables are presented; (b) qualitative factor map of the sectors.
The elements most positively correlated with this dimension were Ba, Zn, Ca, Rb, La, Sm, Na, Hf and Al (Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.98, 0.98, 0.98, 0.98, 0.98, 0.98, 0.97, 0.97 and 0.96, respectively), while Ce was negatively correlated (Pearson correlation coefficient of −0.98). Thus, can be assumed that these elements describe this dimension well. Figure 8b shows that the sectors (from where the particulate matter was sampled) are divided alongside this axis mostly to the east and south group on its right and west and north group on its left. The calm has a high score on this axis, while having a high score also on the second axis.
3.3.2. PCA of the Cold Season Measurements
In the case of the cold season measurements, the PCA results show that the first dimensions express over 66% of the dataset inertia, meaning that while the first-factor plane represents a significant part of the total variability. The variability explained by this plane is higher than the reference value of 18.75%, and the increase in explained inertia for the second axis is also higher than the reference value for this axis (8.61%); hence, both dimensions carry real information. The percentages of explained variance of the first five axes were 54.87, 11.67, 7.2, 5.8 and 3.3, respectively. A visualization of the PCA results of the cold season data is presented in Figure 12.
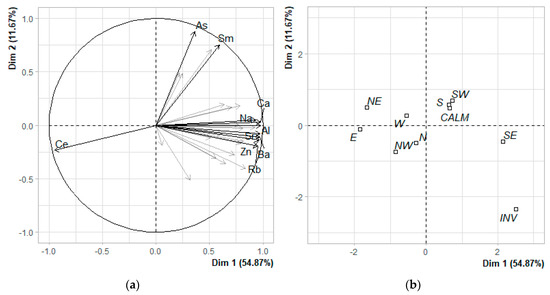
Figure 12.
The cold season–PCA results for the first two dimensions; (a) correlation circle of clr-transformed elemental concentrations; 10 most contributing variables are presented; (b) qualitative factor map of the sectors.
The elements most positively correlated with the first dimension are Ca, Al, Sr, Ba, Zn, Rb, Na, Hf and Th (Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.98, 0.98, 0.97, 0.97, 0.96, 0.95, 0.93, 0.92 and 0.84, respectively), while concentrations of Ce are, once again, correlated negatively with this dimension (Pearson correlation coefficient of −0.95). As and Sm are the elements most positively correlated with the second dimension (Pearson correlation coefficients of 0.88 and 0.75, respectively). Figure 9b shows that the sectors are divided alongside these axes in a different manner than in the case of the warm season. Samples from the southeast, south, and southwest directions form a cluster with calm on the right of the first axis and the northwest, west, east and northeast located on its left. The inversion event (INV) measurements simultaneously have a high positive score on the first and high negative scores on the second axis.
4. Discussion
Within the study, the elemental composition of sampled PM10 was determined with NAA, and the origin of the pollution was interpreted using specific pollutants as markers of pollution sources, multivariate statistics and meteorological models. More commonly, the pollution origin is investigated by means of receptor modelling [25,28,71,73,74]. However, specifics of the dataset concerned (long sampling period, small number of samples within each sector), an irregular time resolution of samples and a questionable construction of uncertainty matrix (different weights of respective samples) make this method inappropriate.
Despite the limitations of the methods used, the study confirmed that the region has specific types of pollution sources, including two metallurgical complexes (west and southeast to the sampling site), which, in specific meteorological conditions, increase the pollution load in the region and contribute to the pollution transfer in the higher atmospheric levels. However, in certain situations, this transfer is not detected by the ground pollution monitoring stations (in comparison to [9]). This corroborates locating the sampling device at 90 m AGL. By sampling in such height, the contribution of the local sources (residential emission, transport, constructions, autumnal waste biomass burning and others) [28,75] is excluded from the sampling, and the pollution transfer within the region can be more properly investigated.
The other specific type of pollution in the region is the pollution connected to the trans-boundary transfer coming from Poland during the winter season originating from coal burning in domestic boilers. In the cold part of the year, the PM10 concentrations originating in the Polish borderland (the north, northeast and east direction) increased by almost 50%, despite the prevailing wind in this season blowing in the opposite direction. This fact has already been stated in many previous studies [3,21,26,27,29] and confirms once again the importance of the cross-border PM pollution in this region, emphasizing that it is not just a problem of directly adjacent areas but of the region as a whole.
For the determination of elemental content in the samples, neutron activation analysis was applied, and a wide spectrum of elements was analysed. This, on the one hand, brought specific limitations, but on the other hand, helped to identify the origin of element concentrations in samples using data on less commonly determined elements. Though it should be noted that NAA does not provide information on important elements such as Cd, Cu, Hg or Pb, the obtained information is, in the majority of cases, sufficient to identify the pollution source.
To collect more data on the pollution transfer in the region during meteorologically different years and to render the assessment more precise, the monitoring on the tower continues. In addition to the sampling device used in this study, the PM continual monitoring is now operated both on the top of the tower and on the ground level.
5. Conclusions
A specially designed high-volume sampler (SAM Hi 30 AUTO WIND) was used to collect PM10 samples depending on airflow conditions. The sampler was located on the top of a former mining tower in 90 m AGL. This allowed the elimination of the influence of local sources and investigation of the regional pollution transport. The sampled particulate matter was analysed using the neutron activation analysis, which provided information on the content of 34 elements. This information—together with the PM10 concentrations and meteorological data (measured and modelled)—was used to characterize the pollution origin in the region. A significant difference in the element composition was observed: elemental concentrations were dependent on both the season and the sampling direction. Contribution of three industrial sources, two ironworks (in the west and in the southeast) and a cement plant (southwest from the sampling site) was identified, showing that—though not detected by ground air pollution monitoring—these sources have a significant impact on the pollution transfer in the region. The measurements also confirmed that the PM10 cross-border pollution inflow from Poland plays a crucial role during the winter season and contributes significantly to the air pollution in the whole studied region.
Currently, the air quality management and decision-making in the region are performed just on a local level without considering the cross-border impacts. However, to assure that the air quality meets the air pollution limit values, international cooperation and the legitimacy of the joint interregional approach to the air quality management is imperative, as proven herein [9].
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4433/12/1/29/s1, Figure S1: The element concentration roses for the warm season (ng·m−3), Figure S2: The element concentration roses for the cold season (ng·m−3), Figure S3: The average element concentration according to the wind direction for the warm (plain) and cold seasons (shaded) (ng·m−3), Figure S4: The average element concentration according to the wind direction for the cold season (plain) and smog events (shaded) (ng·m−3), Table S1: Synoptic table (minimum, maximum value, mean, median and standard deviation) of elements concentration (ng·m−3) determined in PM10 using INAA. Table S2: Synoptic table (minimum, maximum value, mean and standard deviation) of PM10 concentration (µg·m−3).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.P.; validation, I.P., D.H. and O.M.; formal analysis, O.M.; investigation, D.H. and I.P.; data curation, O.M. and D.H.; resources (performing NAA), K.N.V., L.P.S. and M.S.S.; writing—original draft preparation, I.P. and O.M.; writing—review and editing, I.P., O.M. and D.H.; visualization, D.H. and O.M.; supervision, I.P.; project administration, I.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was carried out within the project “AIR BORDER–Joint Czech–Polish Measurements of Cross-border Transmission of Air Pollutants” funded by the cooperation programme Interreg V-A in the Czech Republic and Poland co-financed by European Regional Development Fund (ERDF), grant number CZ.11.4.120/0.0/0.0/15_006/0000118. The NAA performance was funded within the “3+3 Project” for the cooperation with the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research by Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, grant number 29/209, theme No. 03-4-1128-2017/2019. The work was supported by European Regional Development Fund/European Social Fund—New Composite Materials for Environmental Applications (No. CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/17_048/0007399).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in article and supplementary materials.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Petr Jančík, the coordinator of the AIR BORDER project (VSB—Technical University of Ostrava, Ostrava, Czech Republic); Marina V. Frontasyeva (Joint Institute of Nuclear Research, Dubna, Russia), the coordinator of the 3 + 3 project on the side of Joint Institute of Nuclear research; Sergey S. Pavlov (Joint Institute of Nuclear Research, Dubna, Russia) for the methodological leadership of the team performing the Neutron Activation Analyses and analysis results processing. Further, we would like to thank Petra Šutarová (VSB—Technical University of Ostrava, Ostrava, Czech Republic) for financial management and administrative support of the projects. The authors also gratefully acknowledge the NOAA Air Resources Laboratory (ARL) for the provision of the HYSPLIT transport and dispersion model and/or READY website (https://www.ready.noaa.gov) used in this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Klusácek, P. Downsizing of bituminous coal mining and the restructuring of steel works and heavy machine engineering in the Ostrava region. Moriv. Geogr. Rep. 2005, 13, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Cabala, J.; Cmiel, S.R.; Idziak, A.F. Environmental impact of mining activity in the upper silesian coal basin. Geol. Belg. 2004, 7, 225–229. [Google Scholar]
- Blažek, Z.; Černikovsky, L.; Krejči, B.; Osrodka, L.; Volna, V.; Wojtylak, M. Vliv Meteorologických Podmínek Na Kvalitu Ovzduší V Přeshraniční Oblasti Slezska A Moravy—Wpływ Warunków Meteoro-Logicznych Na Jakość Powietrza W Obszarze Przygranicznym Śląska I Moraw [The Influence of Meteorological Conditions on Air Quality in the Border Region of Silesia and Moravia], 1st ed.; Český Hydrometeorologický Ústav: Prague, Czech Republic; Instytut Meteorologii i Gospodarki Wodnej, Państwowy Instytut Badawczy: Warsaw, Poland, 2013; ISBN 978-80-87577-15-8. (In Czech/Polish). [Google Scholar]
- Hůnová, I. Ambient air quality in the Czech Republic: Past and present. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuskova, P.; Gingrich, S.; Krausmann, F. Long term changes in social metabolism and land use in Czechoslovakia, 1830–2000: An energy transition under changing political regimes. Ecol. Econ. 2008, 68, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ďurčanská, D.; Drličiak, M.; Jandačka, D.; Bitta, J.; Bizek, V.; Foldynová, I.; Hladký, D.; Hrušková, A.; Hruška, L.; Chovanec, P.; et al. Riadenie Kvality Ovzdušia [Air Quality Management]; Žilinská Univerzita V Žiline—EDIS—Vydavate’ské Centrum ŽU: Žilina, Slovakia, 2020; ISBN 978-80-554-1658-8. (In Czech, Slovaque/Polish). [Google Scholar]
- Główny Urząd Statystyczny. Zużycie Energii w Gospodarstwach Domowych w 2018 Roku [Energy Consumption in Households in 2018]; Główny Urząd Statystyczny—Statistics Poland: Warsaw, Poland, 2019; Volume 2019. [Google Scholar]
- European Environment Agency. Air Quality in Europe—2019 Report; Number 10; European Environment Agency: Luxembourg, 2019; ISBN 978-92-9480-088-6.
- Czech Hydrometeorological Institute. Summary Tabular Survey. 2018. Available online: http://portal.chmi.cz/files/portal/docs/uoco/isko/tab_roc/2018_enh/index_GB.html (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- European Council. Directive 2008/50/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 May 2008 on Ambient Air Quality and Cleaner Air for Europe; OJEC L 152; European Council: Brussel, Belgium, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Air Quality Guidelines: Global Update 2005: Particulate Matter, Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, and Sulfur Dioxide; World Health Organization: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2006; ISBN 978-92-890-2192-0. [Google Scholar]
- WHO Regional Office for Europe. Evolution of WHO Air Quality Guidelines Past, Present and Future; WHO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2017; ISBN 978-92-890-5230-6. [Google Scholar]
- Jiřík, V.; Hermanová, B.; Dalecká, A.; Pavlíková, I.; Bitta, J.; Jančík, P.; Ośródka, L.; Krajny, E.; Sładeczek, F.; Siemiątkowski, G.; et al. Wpływ Zanieczyszczenia Powietrza Na Zdrowie Ludności W Obszarze Polsko-Czeskiego Pogranicza. Dopad Znečištění Ovzduší Na Zdravotní Stav Obyvatelstva V Česko-Polském Příhraničí [Impact of Air Pollution on the Health Status of the Population in the Czech-Polish Border]; Sieć Badawcza Łukasiewicz—Instytut Ceramiki i Materiałów Budowlanych Instytut Meteorologii i Gospodarki Wodnej—Państwowy Instytut Badawczy Ostravská Univerzita Vysoká Škola Báňská—Technická Univerzita Ostrava: Ostrava, Czech Republic, 2020; ISBN 978-80-248-4406-0. (In Czech/Polish). [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Ambient Air Pollution: A Global Assessment of Exposure and Burden of Disease; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-92-4-151135-3. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Review of Evidence on Health Aspects of Air Pollution—REVIHAAP Project; Technical Report; World Health Organization: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jiřík, V.; Machaczka, O.; Miturová, H.; Tomášek, I.; Šlachtová, H.; Janoutová, J.; Velická, H.; Janout, V. Air pollution and potential health risk in Ostrava region—A review. Cent. Eur. J. Public Health 2016, 24, S4–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.; Samet, J.M.; Straif, K. (Eds.) Air Pollution and Cancer; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2013; Volume 161, ISBN 978-92-832-2161-6. [Google Scholar]
- The Czech Statistical Office. Czech Demographic Handbook—2018. Available online: https://www.czso.cz/csu/czso/czech-demographic-handbook (accessed on 29 June 2020).
- Pinto, J.P.; Stevens, R.K.; Willis, R.D.; Kellogg, R.; Mamane, Y.; Novak, J.; Šantroch, J.; Beneš, I.; Lenicek, J.; Bureš, V. Czech air quality monitoring and receptor modeling study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čížová, H. Projekt Slezsko/Silesia [The Silesia Project]. Zprav. Minist. Životn. Prostředí ČR 1994, 3, 6–7. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Jančík, P.; Pavlíková, I.; Bitta, J.; Hladký, D. Atlas Ostravského Ovzduší; Vysoká Škola Báňská—Technická Univerzita Ostrava: Ostrava, Czech Republic, 2013; ISBN 978-80-248-3006-3. [Google Scholar]
- Air TRITIA—Uniform Approach to the Air Polution Management System for Functional Urban Areas in TRITIA Region. Available online: http://www.interreg-central.eu/Content.Node/AIR-TRITIA.html (accessed on 17 April 2020).
- Mikuška, P.; Křůmal, K.; Večeřa, Z. Characterization of organic compounds in the PM2.5 aerosols in winter in an industrial urban area. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 105, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorná, P.; Hovorka, J.; Klán, M.; Hopke, P.K. Source apportionment of size resolved particulate matter at a European air pollution hot spot. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoni, C.; Pokorná, P.; Hovorka, J.; Masiol, M.; Topinka, J.; Zhao, Y.; Křůmal, K.; Cliff, S.; Mikuška, P.; Hopke, P.K. Source apportionment of aerosol particles at a european Air Pollution hot spot using particle number size distributions and chemical composition. Environ. Pollut. Barking Essex 1987 2018, 234, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aglomerace Ostrava/Karviná/Frýdek-Místek. Český Hydrometeorologický Ústav Aktualizace Programů Zlepšovaní Kvality Ovzduší 2020+; Ministerstvo Životního Prostředí ČR: Prague, Czech Republic, 2019.
- Seibert, R.; Nikolova, I.; Volná, V.; Krejčí, B.; Hladký, D. Air pollution sources’ contribution to PM2.5 concentration in the northeastern part of the Czech Republic. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech Hydrometeorological Institute. Summary Tabular Survey. 2015. Available online: http://portal.chmi.cz/files/portal/docs/uoco/isko/tab_roc/2015_enh/index_GB.html (accessed on 23 April 2020).
- Černikovský, L.; Krejčí, B.; Blažek, Z.; Volná, V. Transboundary air-pollution transport in the Czech-Polish border region between the cities of Ostrava and Katowice. Cent. Eur. J. Public Health 2016, 24, S45–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volná, V.; Hladký, D. Detailed assessment of the effects of meteorological conditions on PM10 concentrations in the northeastern part of the Czech Republic. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Compendium of Methods for the Determination of Inorganic Compounds in Ambient Air: Sampling of Ambient Air for Total Suspended Particulate Matter (Spm) and PM10 Using High Volume (Hv) Sampler; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1999.
- Krug, J.D.; Dart, A.; Witherspoon, C.L.; Gilberry, J.; Malloy, Q.; Kaushik, S.; Vanderpool, R.W. Revisiting the size selective performance of EPA’s high-volume total suspended particulate matter (Hi-Vol TSP) sampler. Aerosol. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Committee for Standardization. Ambient Air. Standard Gravimetric Measurement Method for the Determination of the PM10 or PM2,5 Mass Concentration of Suspended Particulate Matter; EN 12341:2014; NSAI: Dublin, Ireland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Office of Air and Radiation. Office of Air Quality Planning and Standards Meteorological Monitoring Guidance for Regulatory Modeling Applications; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2000.
- Frontasyeva, M.V.; Pavlov, S.S.; Shvetsov, V.N. NAA for applied investigations at FLNP JINR: Present and future. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2010, 286, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, S.; Dmitriev, A.; Frontasyeva, M. Automation system for neutron activation analysis at the reactor IBR-2, Frank Laboratory of Neutron Physics, Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna, Russia. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2016, 309, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dray, S.; Josse, J. Principal component analysis with missing values: A comparative survey of methods. Plant. Ecol. 2015, 216, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hron, K.; Templ, M.; Filzmoser, P. Imputation of missing values for compositional data using classical and robust methods. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2010, 54, 3095–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Compendium Method IO-3.7—Determination of Metals in Ambient Particulate Matter Using Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA) Gamma Spectrometry; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1999.
- The R Foundation. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 25 December 2020).
- Lê, S.; Josse, J.; Husson, F. FactoMineR: An R package for multivariate analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husson, F.; Josse, J.; Le, S.; Mazet, J. Package ‘FactoMineR’—Multivariate Exploratory Data Analysis and Data Mining. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/FactoMineR/index.html (accessed on 25 December 2020).
- Carslaw, D.; Ropkins, K. Package ‘Openair’—Tools for the Analysis of Air Pollution Data. Available online: https://davidcarslaw.github.io/openair/ (accessed on 25 December 2020).
- Wickham, H.; Chang, W.; Henry, L.; Pedersen, T.L.; Takahashi, K.; Wilke, C.; Woo, K.; Yutani, H.; Dunnington, D. Package ‘Ggplot2′—Create Elegant Data Visualisations Using the Grammar of Graphics. Available online: https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org/reference/ggplot2-package.html (accessed on 25 December 2020).
- Pawlowsky-Glahn, V.; Buccianti, A. (Eds.) Compositional Data Analysis: Theory and Applications; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2011; ISBN 978-0-470-71135-4. [Google Scholar]
- Aitchison, J. The Statistical Analysis of Compositional Data; Blackburn Press: Caldwell, NJ, USA, 2003; ISBN 978-1-930665-78-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ventusky. Available online: https://www.ventusky.com/?p=49.8;18.5;5&l=wind-10m (accessed on 25 December 2020).
- University of Wyoming Atmospheric Soundings. Available online: http://weather.uwyo.edu/upperair/sounding.html (accessed on 2 December 2020).
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolph, G.; Stein, A.; Stunder, B. Real-time Environmental Applications and Sisplay sYstem: READY. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 95, 210–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureš, V.; Velíšek, J. Omezování Emisí Znečišťujících Látek Do Ovzduší: II. Etapa, Rok 2005 [Reduction of Emissions of Pollutants into the Air: 2nd Stage, Year 2005]; TESO: Prague, Czech Republic, 2005. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Alleman, L.Y.; Lamaison, L.; Perdrix, E.; Robache, A.; Galloo, J.-C. PM10 metal concentrations and source identification using positive matrix factorization and wind sectoring in a French industrial zone. Atmos. Res. 2010, 96, 612–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvestre, A.; Mizzi, A.; Mathiot, S.; Masson, F.; Jaffrezo, J.L.; Dron, J.; Mesbah, B.; Wortham, H.; Marchand, N. Comprehensive chemical characterization of industrial PM2.5 from steel industry activities. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 152, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, R.W.; Davis, T.E.; Elseewi, A.A. Strontium isotopes as tracers of coal combustion residue in the environment. Eng. Geol. 1991, 30, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritz, M.; Bartoňová, L.; Klika, Z. Emissions of Heavy Metals and Polyaromatic Hydrocarbons During Coal Combustion in Industrial and Small Scale Furnaces. Sborník Věd. Pr. Vysoké Šk. Báňské Tech. Univerzity Ostrava 2003, 49, 69–82. [Google Scholar]
- Horák, J.; Kuboňová, L.; Bajer, S.; Dej, M.; Hopan, F.; Krpec, K.; Ochodek, T. Composition of ashes from the combustion of solid fuels and municipal waste in households. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 248, 109269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramme, B.W.; Tharaniyil, M.P. Coal Combustion Products Utilization Handbook, 3rd ed.; We Energies: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Robl, T.L.; Oberlink, A.; Jones, R. (Eds.) Coal Combustion Products (CCPs): Characteristics, Utilization and Beneficiation; Woodhead Woodhead Publishing: Duxford, UK; Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-0-08-100945-1. [Google Scholar]
- Juda-Rezler, K.; Kowalczyk, D. Size distribution and trace elements contents of coal fly ash from pulverized boilers. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2013, 22, 25–40. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Qin, S.; Panchal, B.; Sun, Y.; Niu, H. Distribution characteristics and migration patterns of hazardous trace elements in coal combustion products of power plants. Fuel 2019, 258, 116062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, C.D.; Strum, M.; Simon, H.; Riddick, L.; Kosusko, M.; Menetrez, M.; Hays, M.D.; Rao, V. An assessment of important SPECIATE profiles in the EPA emissions modeling platform and current data gaps. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 207, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernigotti, D.; Belis, C.A.; Spanò, L. SPECIEUROPE: The European data base for PM source profiles. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2016, 7, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, H.; Beck, L.; Bhave, P.V.; Divita, F.; Hsu, Y.; Luecken, D.; Mobley, J.D.; Pouliot, G.A.; Reff, A.; Sarwar, G.; et al. The development and uses of EPA’s SPECIATE database. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2010, 1, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Chatterjee, A. Ironmaking and Steelmaking: Theory and Practice; Eastern Economy 3rd ed.; PHI Learning: New Delhi, India, 2010; ISBN 978-81-203-3289-8. [Google Scholar]
- Mohiuddin, K.; Strezov, V.; Nelson, P.F.; Stelcer, E. Characterisation of trace metals in atmospheric particles in the vicinity of iron and steelmaking industries in Australia. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 83, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beijer, K.; Jernelov, A. Sources, transport and transformation of metals in the environment. Environ. Sci. 1986, 1, 68. [Google Scholar]
- Avino, P.; Capannesi, G.; Rosada, A. Heavy metal determination in atmospheric particulate matter by instrumental neutron activation analysis. Microchem. J. 2008, 88, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bažan, J.; Socha, L. Základy Teorie a Technologie Výroby Železa a Oceli: Část II—Základy Teorie a Technologie Výroby Oceli; VŠB—Technická Univerzita Ostrava: Ostrava, Czech Republic, 2013; ISBN 978-80-248-3353-8. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, B.R.; Gilardoni, S.; Stenström, K.; Niedzialek, J.; Jimenez, J.; Belis, C.A. Sources for PM air pollution in the Po Plain, Italy: II. Probabilistic uncertainty characterization and sensitivity analysis of secondary and primary sources. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 50, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samara, C.; Kouimtzis, T.; Tsitouridou, R.; Kanias, G.; Simeonov, V. Chemical mass balance source apportionment of PM10 in an industrialized urban area of Northern Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatkin, S.; Bayram, A. Determination of major natural and anthropogenic source profiles for particulate matter and trace elements in Izmir, Turkey. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, G.; Duvall, R.; Brown, S.; Bai, S. Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) 5.0 Fundamentals and User Guide; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- European Commission. European Guide on Air Pollution Source Apportionment with Receptor Models: Revised Version 2019; JRC Technical Reports; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2019.
- Bernardoni, V.; Vecchi, R.; Valli, G.; Piazzalunga, A.; Fermo, P. PM10 source apportionment in Milan (Italy) using time-resolved data. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 4788–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombi, C.; Gianelle, V.; Belis, C.; Larsen, B. Determination of local source profile for soil dust, brake dust and biomass burning sources. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2010, 22, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).