Atmospheric Dynamics and Numerical Simulations of Six Frontal Dust Storms in the Middle East Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
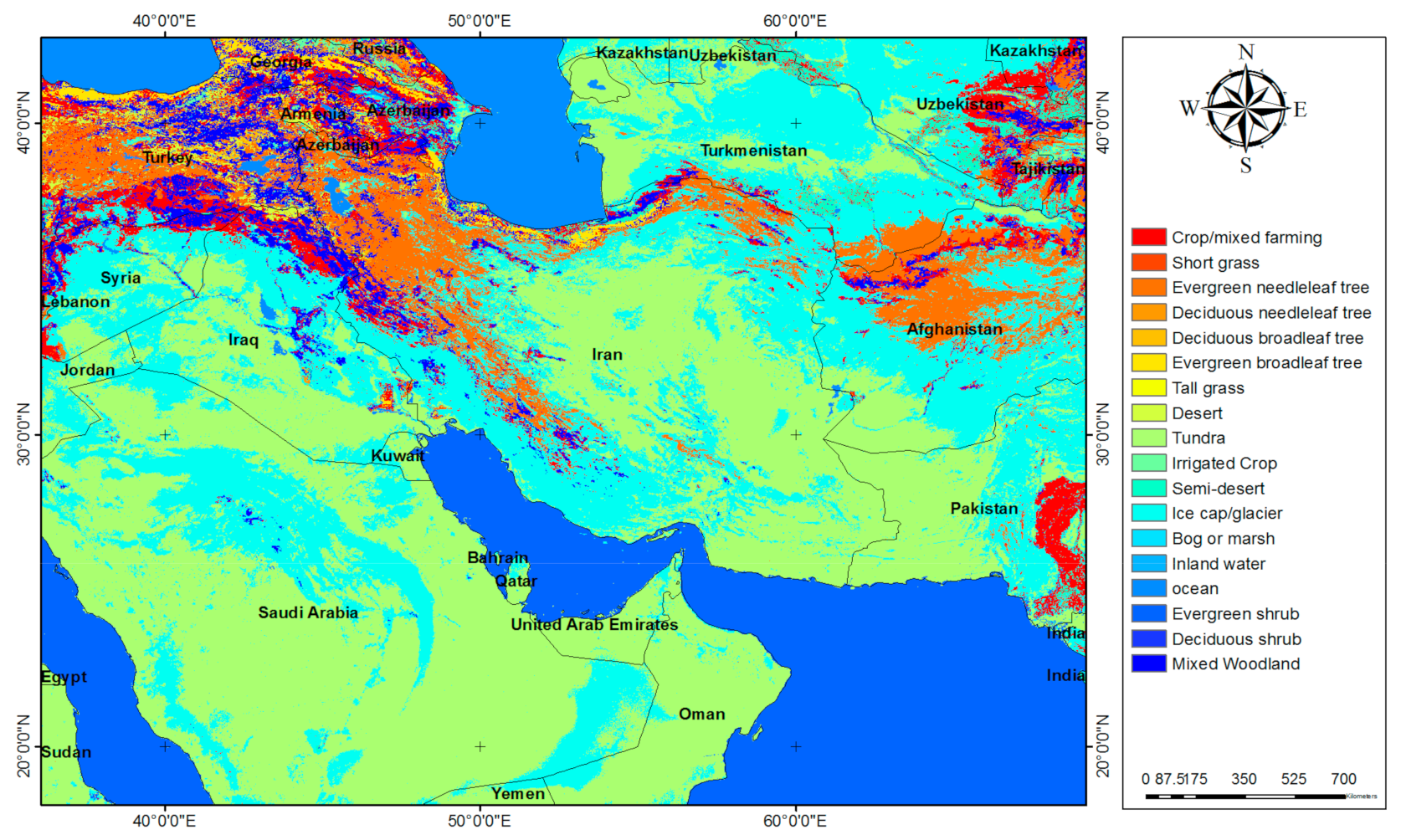
2. Study Area and Dust Storms
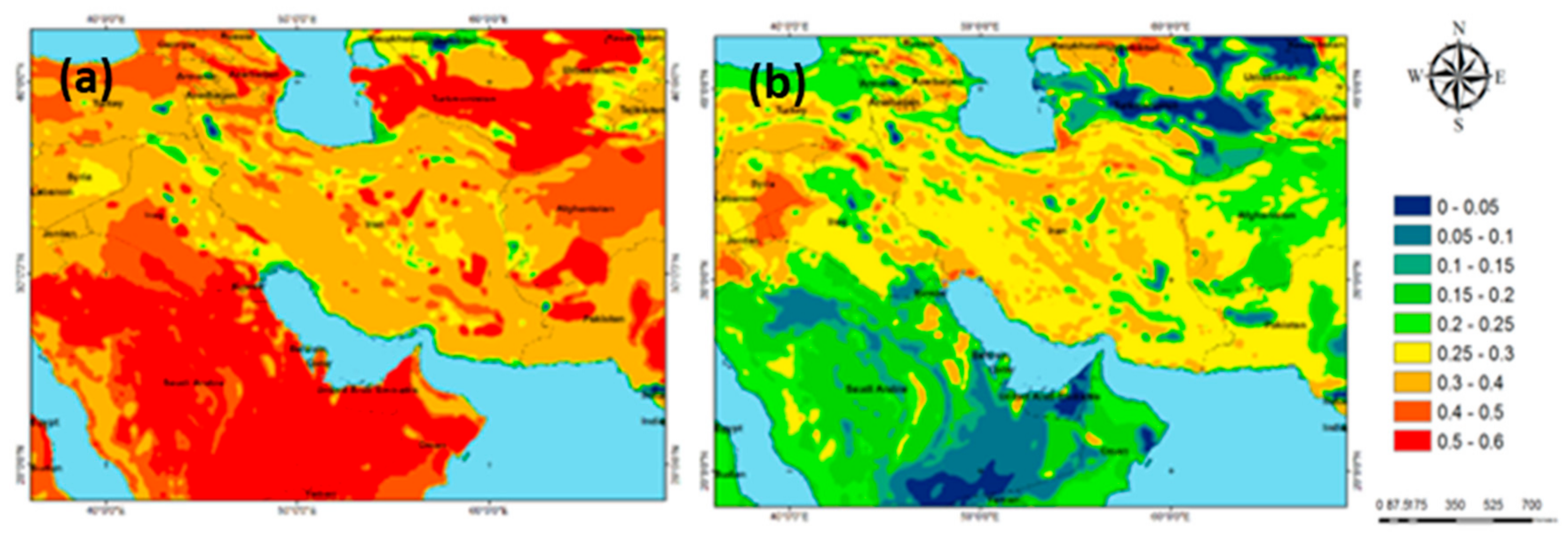
3. Data Set and Methodology
4. Model Simulations
4.1. WRF-Chem Model
4.2. CAMS Model
4.3. RegCM4 Model
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Satellite Observations
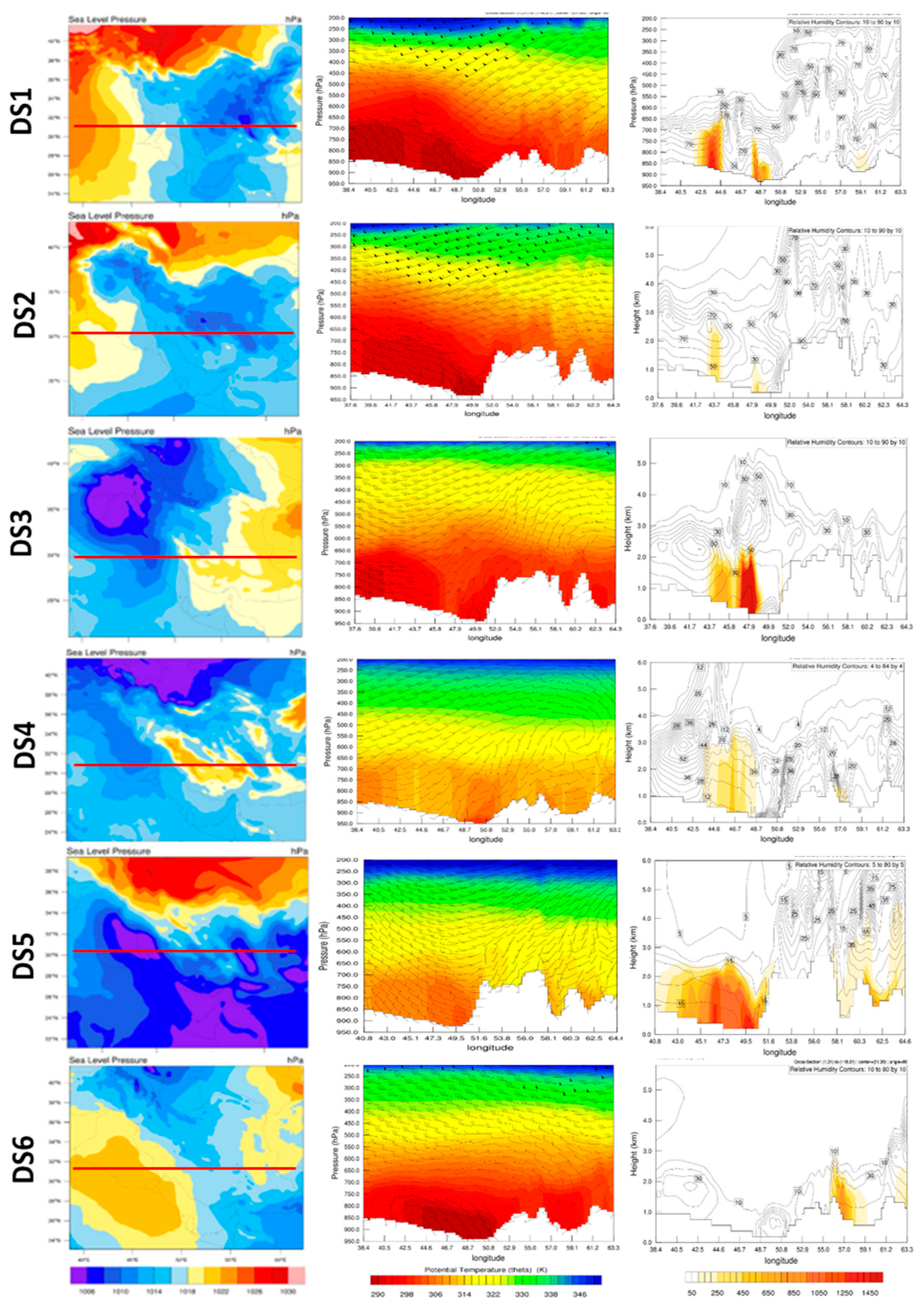
5.2. Synoptic Meteorology
5.3. Spatial Distribution of the AOD
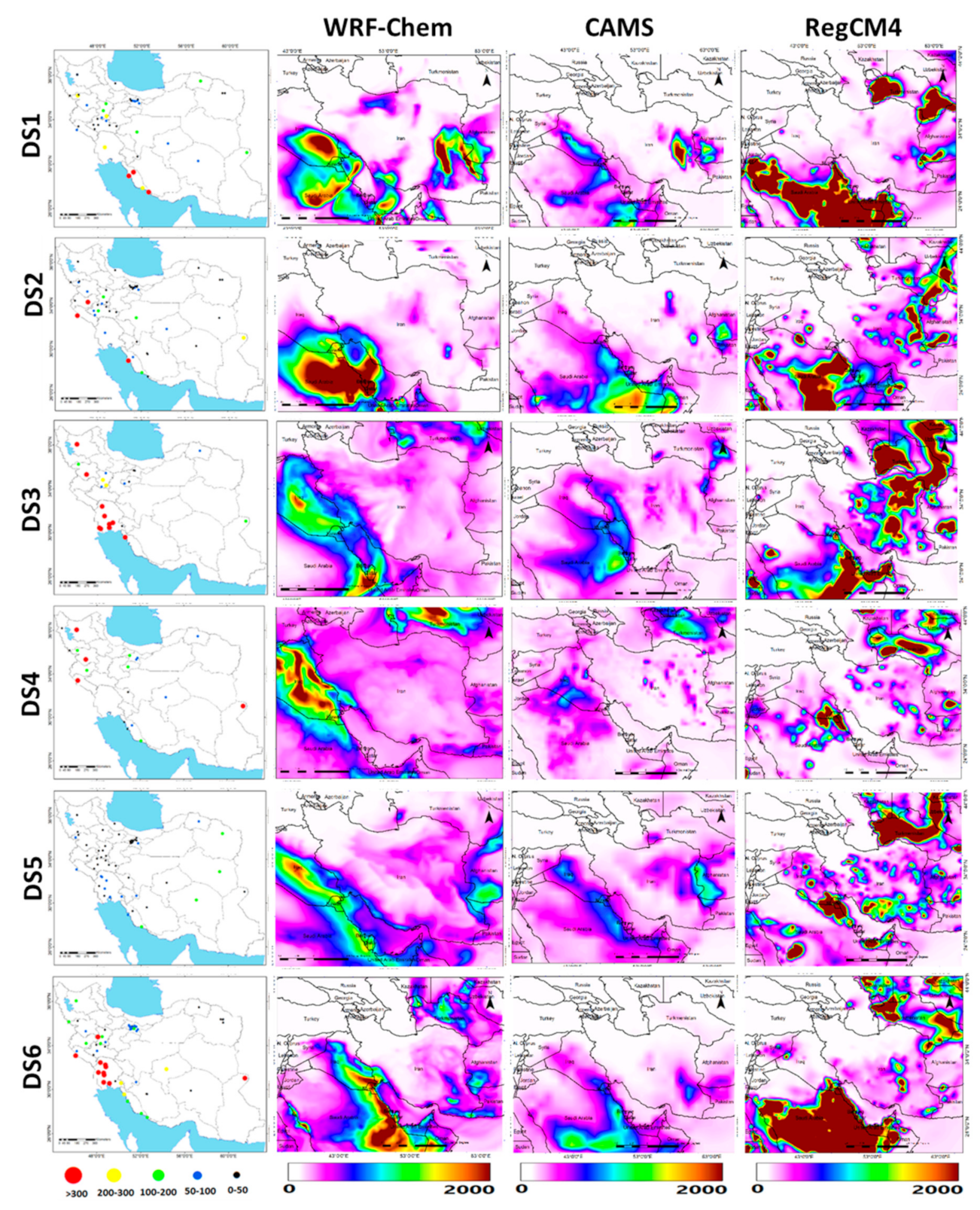
5.4. Simulations of PM10 Concentrations
5.5. Differences between the Model Simulations
5.6. Meteorological Dynamics and Dust Concentrations via WRF-Chem Model
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahowald, N.M.; Baker, A.R.; Bergametti, G.; Brooks, N.; Duce, R.A.; Jickells, T.D.; Kubilay, N.; Prospero, J.M.; Tegen, I. Atmospheric global dust cycle and iron inputs to the ocean. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2005, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, N.; Kang, U. Sand and dust storms: Impact mitigation. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepanski, K. Transport of mineral dust and its impact on climate. Geosciences 2018, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkan, J.; Alpert, P.; Kutiel, H.; Kishcha, P. Synoptics of dust transportation days from Africa toward Italy and central Europe. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D07208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.J.; Sicard, M.; Costa, M.J.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; Gómez-Amo, J.L.; Molero, F.; Barragán, R.; Basart, S.; Bortoli, D.; Bedoya-Velásquez, A.E.; et al. Extreme, wintertime Saharan dust intrusion in the Iberian Peninsula: Lidar monitoring and evaluation of dust forecast models during the February 2017 event. Atmos. Res. 2019, 228, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, J.; Yao, F.; Zhang, D.; Guo, H. Drivers to dust emissions over dust belt from 1980 to 2018 and their variation in two global warming phases. Sci. Total Environ. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, M.F.; Almutairi, S.K.; Al-Hemoud, A. Dust storms backward Trajectories’ and source identification over Kuwait. Atmos. Res. 2018, 212, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandham, H.; Dasari, H.P.; Langodan, S.; Karumuri, R.K.; Hoteit, I. Major changes in extreme dust events dynamics over the Arabian Peninsula during 2003–2017 driven by atmospheric conditions. J. Geophys. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, K.; Sciortino, M.; Saligheh, M.; Raziei, T.; Boloorani, A.D. Spatiotemporal regionalization of atmospheric dust based on multivariate analysis of MACC model over Iran. Atmos. Res. 2020, 249, 105322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Wyrwoll, K.H.; Chappell, A.; Huang, J.; Lin, Z.; McTainsh, G.H.; Mikami, M.; Tanaka, T.Y.; Wang, X.; Yoon, S. Dust cycle: An emerging core theme in Earth system science. Aeol. Res. 2011, 2, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, D.; Chaboureau, J.-P.; Nelli, N.; Cuesta, J.; Alshamsi, N.; Temimi, M.; Pauluis, O.; Xue, L. Summertime dust storms over the Arabian Peninsula and impacts on radiation, circulation, cloud development and rain. Atmos. Res. 2020, 105364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jish Prakash, P.; Stenchikov, G.; Kalenderski, S.; Osipov, S.; Bangalath, H. The impact of dust storms on the Arabian Peninsula and the Red Sea. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 199–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Yang, Z.L.; Wei, J. Seasonal responses of Indian summer monsoon to dust aerosols in the Middle East, India, and China. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 6329–6349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solmon, F.; Nair, V.S.; Mallet, M. Increasing Arabian dust activity and the Indian Summer Monsoon. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 8051–8064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamehr, S.; Sabetghadam, S. Estimation of global solar radiation data based on satellite-derived atmospheric parameters over the urban area of Mashhad, Iran. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherboudj, I.; Ghedira, H. Assessment of solar energy potential over the United Arab Emirates using remote sensing and weather forecast data. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 55, 1210–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, A.; Ameri, M.; Zandi, M.; Ghoachani, R.G.; Eslami, S.; Pierfederici, S. Photovoltaic Potential Assessment and Dust Impacts on Photovoltaic Systems in Iran: Review Paper. IEEE J. Photov. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshan, D.R.; Koc, M.; Abdallah, A.; Martin-Pomares, L.; Isaifan, R.; Fountoukis, C. UV Index Forecasting under the Influence of Desert Dust: Evaluation against Surface and Satellite-Retrieved Data. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miri, A.; Ahmadi, H.; Ekhtesasi, M.R.; Panjehkeh, N.; Ghanbari, A. Environmental and socio-economic impacts of dust storms in Sistan Region, Iran. Intern. J. Environ. Stud. 2009, 66, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifikia, M. Environmental challenges and drought hazard assessment of Hamoun Desert Lake in Sistan region, Iran, based on the time series of satellite imagery. Nat. Hazards 2013, 65, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, S.J.; Ebrahimzadeh, L.; Eslami, A.; Bidarpoor, F. Effects of dust storm events on emergency admissions for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases in Sanandaj, Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleimani, Z.; Teymouri, P.; Darvishi Boloorani, A.; Mesdaghinia, A.; Middleton, N.; Griffin, D.W. An overview of bioaerosol load and health impacts associated with dust storms: A focus on the Middle East. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingmüller, K.; Pozzer, A.; Metzger, S.; Stenchikov, G.L.; Lelieveld, J. Aerosol optical depth trend over the Middle East. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 5063–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notaro, M.; Yu, Y.; Kalashnikova, O.V. Regime shift in Arabian dust activity, triggered by persistent Fertile Crescent drought. J. Geophys. Res. 2015, 120, 10229–10249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miri, A.; Maleki, S.; Middleton, N. An investigation into climatic and terrestrial drivers of dust storms in the Sistan region of Iran in the early twenty-first century. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashki, A.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Eriksson, P.G.; Rautenbach, C.D.W.; Flamant, C.; Vishkaee, F.A. Spatio-temporal variability of dust aerosols over the Sistan region in Iran based on satellite observations. Nat. Hazards 2014, 71, 563–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Notaro, M.; Kalashnikova, O.V.; Garay, M.J. Climatology of summer Shamal wind in the Middle East. J. Geophys. Res. 2016, 121, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Notaro, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, F.; Alkolibi, F.; Fadda, E.; Bakhrjy, F. Climatic controls on the interannual to decadal variability in Saudi Arabian dust activity: Toward the development of a seasonal dust prediction model. J. Geophys. Res. 2015, 120, 1739–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labban, A.H.; Mashat, A.S.; Awad, A.M. The variability of the Siberian High Ridge over the Middle East. Intern. J. Climat. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashki, A.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Mofidi, A.; Minvielle, F.; Chiapello, I.; Legrand, M.; Dumka, U.C.; Francois, P. Effects of Monsoon, Shamal and Levar winds on dust accumulation over the Arabian Sea during summer–The July 2016 case. Aeol. Res. 2019, 36, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomos, S.; Abuelgasim, A.; Spyrou, C.; Binietoglou, I.; Nickovic, S. Development of a dynamic dust source map for NMME-DREAM v1.0 model based on MODIS Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) over the Arabian Peninsula. Geosci. Model Dev. 2019, 12, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezazadeh, M.; Irannejad, P.; Shao, Y. Climatology of the Middle East dust events. Aeol. Res. 2013, 10, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, A.; Rappenglueck, B.; Eltahir, E.A.B. The climatology of dust aerosol over the Arabian Peninsula. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2015, 15, 1523–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.M.; Mashat, A.W.S. Synoptic characteristics of spring dust days over northern Saudi Arabia. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2016, 9, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, T.M.; Al-Dashti, H.; Spyrou, C. Aerosol’s optical and physical characteristics and direct radiative forcing during a shamal dust storm, a case study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 3751–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, D.; Flamant, C.; Chaboureau, J.P.; Banks, J.; Cuesta, J.; Brindley, H.; Oolman, L. Dust emission and transport over Iraq associated with the summer Shamal winds. Aeol. Res. 2017, 24, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beegum, S.N.; Gherboudj, I.; Chaouch, N.; Temimi, M.; Ghedira, H. Simulation and analysis of synoptic scale dust storms over the Arabian Peninsula. Atmos. Res. 2018, 199, 62–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, D.; Alshamsi, N.; Cuesta, J.; Gokcen Isik, A.; Dundar, C. Cyclogenesis and density currents in the Middle East and the associated dust activity in September 2015. Geosciences 2019, 9, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knippertz, P.; Todd, M.C. Mineral dust aerosols over the Sahara: Meteorological controls on emission and transport and implications for modeling. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, M.; Kavianpour, M.R.; Shao, Y. Synoptic analysis of dust storms in the Middle East. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 49, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghrabi, A.; Alharbi, B.; Tapper, N. Impact of the March 2009 dust event in Saudi Arabia on aerosol optical properties, meteorological parameters, sky temperature and emissivity. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2164–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, M.; Kavianpour, M.R.; Shao, Y. A quantitative evaluation of the 3–8 July 2009 Shamal dust storm. Aeol. Res. 2017, 24, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalenderski, S.; Stenchikov, G.; Zhao, C. Modeling a typical winter-time dust event over the Arabian Peninsula and the Red Sea. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 1999–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K.; Trautmann, T.; Blaschke, T.; Subhan, F. Changes in aerosol optical properties due to dust storms in the Middle East and Southwest Asia. Rem. Sens. Environ. 2014, 143, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, M.S.; Khoshakhllagh, F.; Zamanzadeh, S.M.; Shirazi, M.H.; Samadi, M.; Hajikhani, S. Characteristics of TSP loads during the Middle East springtime dust storm (MESDS) in Western Iran. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 5367–5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibzadeh, M.; Alam, K.; Bidokhti, A.A.; Abedini, Y.; Masoumi, A. Radiative Effects and Optical Properties of Aerosol during Two Dust Events in 2013 over Zanjan, Iran. Aeros. Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D.L.; Gupta, P.; Wang, K.; Jena, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Z.F.; Streets, D.G. Using gapfilled MAIAC AOD and WRF-Chem to estimate daily PM2.5 concentrations at 1 km resolution in the Eastern United States. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 199, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beegum, S.N.; Gherboudj, I.; Chaouch, N.; Couvidat, F.; Menut, L.; Ghedira, H. Simulating aerosols over Arabian Peninsula with CHIMERE: Sensitivity to soil, surface parameters and anthropogenic emission inventories. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 128, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, G.; Fast, J.; Gustafson, W.I.; Peckham, S.E.; McKeen, S.; Salzmann, M.; Freitas, S. On-line chemistry within WRF: Description and evaluation of a State-of-the-Art multiscale air quality and weather prediction model. In Integrated Systems of Meso-Meteorological and Chemical Transport Models; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 41–54. [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti, A.; Morcrette, J.J.; Boucher, O.; Dethof, A.; Engelen, R.J.; Fisher, M.; Flentje, H.; Huneeus, N.; Jones, L.; Kaiser, J.W.; et al. Aerosol analysis and forecast in the European centre for medium-range weather forecasts integrated forecast system: 2. Data assimilation. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakey, A.S.; Solmon, F.; Giorgi, F. Implementation and testing of a desert dust module in a regional climate model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 4687–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginoux, P.; Prospero, J.M.; Gill, T.E.; Hsu, N.C.; Zhao, M. Global-scale attribution of anthropogenic and natural dust sources and their emission rates based on MODIS Deep Blue aerosol products. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, G.; Yang, G.; Luo, L. Identification of sand and dust storm source areas in Iran. J. Arid Land 2015, 7, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, H.R.; Opp, C.; Groll, M.; Rohipour, H.; Khosroshahi, M.; Khaksarian, F.; Gohardoust, A. Spatial and temporal variation of the aeolian sediment transport in the ephemeral Baringak Lake (Sistan Plain, Iran) using field measurements and geostatistical analyses. Z. Geomorphol. 2018, 61, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, N.; Namdari, S.; Sorooshian, A.; Bilal, M.; Heidary, P. Evaluation and modification of SARA high-resolution AOD retrieval algorithm during high dust loading conditions over bright desert surfaces. Atmos. Poll. Res. 2019, 10, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroughani, M.; Pourhashemi, S.; Hashemi, H.; Salehi, M.; Amirahmadi, A.; Asadi, M.A.Z.; Berndtsson, R. Application of remote sensing techniques and machine learning algorithms in dust source detection and dust source susceptibility mapping. Ecolog. Inform. 2020, 56, 101059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashki, A.; Middleton, N.J.; Goudie, A.S. Dust storms in Iran–Distribution, causes, frequencies and impacts. Aeol. Res. 2021, 48, 100655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashki, A.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Francois, P.; Kosmopoulos, P.G.; Legrand, M. Dust-storm dynamics over Sistan region, Iran: Seasonality, transport characteristics and affected areas. Aeol. Res. 2015, 16, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, H.; Opp, C.; Groll, M.; Gohardoust, A. Wind regime and sand transport in the Sistan and Registan regions (Iran/Afghanistan). Z. Geomorphol. 2019, 62 (Suppl. 1), 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khusfi, E.Z.; Moatamednia, M. Evaluating different functions of artificial neural networks for predicting the hourly variations of horizontal visibility under dry and humid conditions (case study: Zabol City). Desert Ecos. Engin. J. 2019, 3, 55–69. [Google Scholar]
- Khusfi, Z.E.; Khosroshahi, M.; Roustaei, F.; Mirakbari, M. Spatial and seasonal variations of sand-dust events and their relation to atmospheric conditions and vegetation cover in semi-arid regions of central Iran. Geoderma 2020, 365, 114225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazroui, M.; Islam, M.N.; Jones, P.D.; Athar, H.; Rahman, M.A. Recent climate change in the Arabian Peninsula: Seasonal rainfall and temperature climatology of Saudi Arabia for 1979–2009. Atmos. Res. 2012, 111, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patlakas, P.; Stathopoulos, C.; Flocas, H.; Kalogeri, C.; Kallos, G. Regional Climatic Features of the Arabian Peninsula. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghrabi, A.H.; Al-Dosari, A.F. Effects on surface meteorological parameters and radiation levels of a heavy dust storm occurred in Central Arabian Peninsula. Atmos. Res. 2016, 182, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, S.; Ranjbar, A.; Mohebalhojeh, A.R.; Moradi, M. A rare case of haboob in Tehran: Observational and numerical study. Atmos. Res. 2017, 185, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi Vishkaee, F.; Flamant, C.; Cuesta, J.; Oolman, L.; Flamant, P.; Khalesifard, H.R. Dust transport over Iraq and northwest Iran associated with winter Shamal: A case study. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D03201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermida, L.; Merino, A.; Sánchez, J.L.; Fernández-González, S.; García-Ortega, E.; López, L. Characterization of synoptic patterns causing dust outbreaks that affect the Arabian Peninsula. Atmos. Res. 2018, 199, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woollen, J.; et al. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.M.; Hsu, N.C.; Lee, J.; Kim, W.V.; Dutcher, S.T. Validation, stability, and consistency of MODIS Collection 6.1 and VIIRS Version 1 Deep Blue aerosol data over land. J. Geophys. Res. 2019, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Hunt, W.H.; McGill, M.J. Initial performance assessment of CALIOP. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, I.; Yumimoto, K.; Shimizu, A.; Hara, Y.; Sugimoto, N.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Winker, D.M. 3D structure of Asian dust transport revealed by CALIPSO lidar and a 4DVAR dust model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeGrand, S.L.; Polashenski, C.; Letcher, T.W.; Creighton, G.A.; Peckham, S.E.; Cetola, J.D. The AFWA dust emission scheme for the GOCART aerosol model in WRF-Chem v3.8.1. Geosc. Model Develop. 2019, 12, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginoux, P.; Chin, M.; Tegen, I.; Prospero, J.M.; Holben, B.; Dubovik, O.; Lin, S.J. Sources and distributions of dust aerosols simulated with the GOCART model. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 20255–20273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Barth, M.C.; Pfister, G.G.; Naja, M.; Brasseur, G.P. WRF-Chem simulations of a typical pre-monsoon dust storm in northern India: Influences on aerosol optical properties and radiation budget. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 2431–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Sokolik, I.N. Quantifying the anthropogenic dust emission from agricultural land use and desiccation of the Aral Sea in Central Asia. J. Geophys. Res. 2016, 121, 12270–12281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroushani, M.A.; Opp, C.; Groll, M.; Nikfal, A. Evaluation of WRF-Chem Predictions for Dust Deposition in Southwestern Iran. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marticorena, B.; Bergametti, G. Modeling the atmospheric dust cycle: 1. Design of a soil-derived dust emission scheme. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 16415–16430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, R. Study on sand movement by wind. Rept. Inst. Sci. Technol. 1951, 5, 95–112. [Google Scholar]
- Kok, J.F.; Albani, S.; Mahowald, N.M.; Ward, D.S. An improved dust emission mode–Part 2: Evaluation in the Community Earth System Model, with implications for the use of dust source functions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 13043–13061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, S.O.; Haimberger, L.; Samimi, C. Sensitivity of WRF-chem predictions to dust source function specification in West Asia. Aeol. Res. 2017, 24, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillette, D.A. Environmental Factors Affecting Dust Emissions by Wind Erosion, in Saharan Dust; Morales, C., Ed.; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 71–94. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, C.; Singh, S.K.; Chauhan, P.; Budakoti, S. Simulation of an extreme dust episode using WRF-CHEM based on optimal ensemble approach. Atmos. Res. 2021, 249, 105296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh Choobari, O.; Zawar-Reza, P.; Sturman, A. Low level jet intensification by mineral dust aerosols. Ann. Geophys. 2013, 31, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, K.; Motlagh, M.S.; Neyestani, S.E. Dust storms modeling and their impacts on air quality and radiation budget over Iran using WRF-Chem. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2017, 10, 1059–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukowski, J.; van den Heever, S.C. Convective distribution of dust over the Arabian Peninsula: The impact of model resolution. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 2967–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, M.; Kavianpour, M.R.; Shao, Y. Numerical simulation of dust events in the Middle East. Aeol. Res. 2014, 13, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inness, A.; Ades, M.; Agusti-Panareda, A.; Barré, J.; Benedictow, A.; Blechschmidt, A.M.; Dominguez, J.; Engelen, R.; Eskes, H.; Flemming, J.; et al. The CAMS reanalysis of atmospheric composition. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 3515–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmopoulos, P.G.; Kazadzis, S.; Taylor, M.; Athanasopoulou, E.; Speyer, O.; Raptis, P.I.; Marinou, E.; Proestakis, E.; Solomos, S.; Gerasopoulos, E.; et al. Dust impact on surface solar irradiance assessed with model simulations, satellite observations and ground-based measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 2435–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, A.; Tripathi, S.N.; Sembhi, H.; Boesch, H. Validation of CAMS AOD using AERONET Data and Trend Analysis at Four Locations in the Indo-Gangetic Basin. Ann. Geophys. Discuss. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toon, O.B.; Ackerman, T.P. Algorithms for the calculation of scattering by stratified spheres. Appl. Opt. 1981, 20, 3657–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Marinucci, M.; Bates, G. Development of a second generation regional climate 15 model (RegCM2). Part I: Boundary layer and radiative transfer processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 1993, 121, 2794–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, J.S.; Giorgi, F.; Bi, X.; Elguindi, N.; Solmon, F.; Gao, X.J.; Francisco, R.; Zakey, A.; Winter, J.; Ashfaq, M.; et al. Regional climate modeling for the developing world: The ICTP RegCM3 and RegCNET. Bull. Amer. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 1395–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Coppola, E.; Solmon, F.; Mariotti, L.; Sylla, M.B.; Bi, X.; Elguindi, N.; Diro, G.T.; Nair, V.; Giuliani, G.; et al. RegCM4: Model description and preliminary tests over multiple CORDEX domains. Clim. Res. 2012, 52, 7–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, G.; Dudhia, J.; Stauffer, D. A description of the fifth generation Penn State/mesoscale model (MM5). In NCAR Technical Note-398+ STR; 1994; p. 117. [Google Scholar]
- Kamali, S.; Mofidi, A.; Zarrin, A.; Nazaripour, H. Sensitivity studies of the forth-generation regional climate model simulation of dust storms in the Sistan plain, Iran. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2017, 3, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Houssos, E.E.; Solmon, F.; Legrand, M.; Rashki, A.; Dumka, U.C.; Francois, P.; Gautam, R.; Singh, R.P. Impact of atmospheric circulation types on southwest Asian dust and Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Atmos. Res. 2018, 201, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voudouri, K.A.; Siomos, N.; Michailidis, K.; Papagiannopoulos, N.; Lucia, M.; Cornacchia, C.; Nicolae, D.; Balis, D. Comparison of two automated aerosol typing methods and their application to an EARLINET station. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 10961–10980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashki, A.; Arjmand, M.; Kaskaoutis, D.G. Assessment of dust activity and dust-plume pathways over Jazmurian Basin, southeast Iran. Aeol. Res. 2017, 24, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Rashki, A.; Francois, P.; Dumka, U.C.; Houssos, E.E.; Legrand, M. Meteorological regimes modulating dust outbreaks in southwest Asia: The role of pressure anomaly and Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone on the 1–3 July 2014 case. Aeol. Res. 2015, 18, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, H.; Mohammadifar, A.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Collins, A.L. A new integrated data mining model to map spatial variation in the susceptibility of land to act as a source of aeolian dust. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2020, 27, 42022–42039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, H.; Mohamadifar, A.; Sorooshian, A.; Jansen, J.D. Machine-learning algorithms for predicting land susceptibility to dust emissions: The case of the Jazmurian Basin, Iran. Atmos. Poll. Res. 2020, 11, 1303–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Suresh, K.; Rahaman, W. Geochemical characterization of modern aeolian dust over the Northeastern Arabian Sea: Implication for dust transport in the Arabian Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmabadi, H.; Khalidy, R.; Saeedi, M. Transport routes and potential source regions of the Middle Eastern dust over Ahvaz during 2005–2017. Atmos. Res. 2020, 104947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geravandi, S.; Yari, A.R.; Jafari, M.; Goudarzi, G.; Vosoughi, M.; Dastoorpoor, M.; Farhadi, M.; Mohammadi, M.J. Effects of dust phenomenon and impacts with emphasis on dust problems and present solutions in Khuzestan (Iran). Arch. Hyg. Sci. 2018, 7, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahsavani, A.; Tobías, A.; Querol, X.; Stafoggia, M.; Abdolshahnejad, M.; Mayvaneh, F.; Guo, Y.; Hadei, M.; Hashemi, S.S.; Khosravi, A.; et al. Short-term effects of particulate matter during desert and non-desert dust days on mortality in Iran. Environ. Intern. 2020, 134, 105299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, S.D.; Grasso, L.D.; Bian, Q.; Kreidenweis, S.M.; Dostalek, J.F.; Solbrig, J.E.; Bukowski, J.; van den Heever, S.C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; et al. A Tale of Two Dust Storms: Analysis of a complex dust event in the Middle East. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 5101–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamzade Ledari, D.; Hamidi, M.; Shao, Y. Evaluation of the 13 April 2011 frontal dust storm in west Asia. Aeol. Res. 2020, 44, 100592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, H.; Rahimi, S.; Fathabadi, A.; Habibi, S.; Collins, A.L. Mapping the spatial sources of atmospheric dust using GLUE and Monte Carlo simulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 138090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmati, O.; Mohammadi, F.; Ghiasi, S.S.; Tiefenbacher, J.; Moghaddam, D.D.; Coulon, F.; Nalivan, O.A.; Bui, D.T. Identifying sources of dust aerosol using a new framework based on remote sensing and modelling. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notaro, M.; Alkolibi, F.; Fadda, E.; Bakhrjy, F. Trajectory analysis of Saudi Arabian dust storms. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 6028–6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, E.; Noohi, K.; Shiravand, H. Study of dust storm synoptical patterns in southwest of Iran. Desert 2012, 17, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Namdari, S.; Karimi, N.; Sorooshian, A.; Mohammadi, G.; Sehatkashani, S. Impacts of climate and synoptic fluctuations on dust storm activity over the Middle East. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 173, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomos, S.; Kalivitis, N.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Amiridis, V.; Kouvarakis, G.; Gkikas, A.; Binietoglou, I.; Tsekeri, A.; Kazadzis, S.; Kottas, M.; et al. From Tropospheric Folding to Khamsin and Foehn Winds: How Atmospheric Dynamics Advanced a Record-Breaking Dust Episode in Crete. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, B.H.; Maghrabi, A.L.; Tapper, N. The March 2009 dust event in Saudi Arabia: Precursor and supportive environment. Bull. Amer. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Gao, Z. Validation and Accuracy Assessment of MODIS C6.1 Aerosol Products over the Heavy Aerosol Loading Area. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Wei, J. Validation and Comparison of MODIS C6.1 Aerosol Products over Beijing, China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Peng, Y.; Sun, L. MODIS Collection 6.1 aerosol optical depth products over land and ocean: Validation and comparison. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 201, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Peng, Y.; Guo, J.; Sun, L. Performance of MODIS Collection 6.1 Level 3 aerosol products in spatial temporal variations over land. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 206, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Li, T.; Shen, H.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, L. Evaluation and comparison of MODIS Collection 6.1 aerosol optical depth against AERONET over regions in China with multifarious underlying surfaces. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 200, 280–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Remer, L.A.; Patadia, F.; Levy, R.C.; Christopher, S.A. High-Resolution Gridded Level 3 Aerosol Optical Depth Data from MODIS. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; He, Q.; Liu, T.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; et al. Validation and Accuracy Analysis of the Collection 6.1 MODIS Aerosol Optical Depth over the Westernmost City in China Based on the Sun Sky Radiometer Observations from SONET. Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, J.; Yao, F.; Zhang, D.; Guo, H. Temporal variation of dust emissions in dust sources over Central Asia in recent decades and the climate linkages. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 222, 117176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.; Nichol, J.E.; Bilal, M.; Qiu, Z.; Mazhar, U.; Wahiduzzaman, M.; Almazroui, M.; Islam, M.N. Classification of aerosols over Saudi Arabia from 2004–2016. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 241, 117785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xie, L.; Yang, X.; Wu, H.; Cai, L.; Qi, P. Aerosol optical properties at seven AERONET sites over Middle East and Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 243, 117884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabetghadam, S.; Alizadeh, O.; Khoshsima, M.; Pierleoni, A. Aerosol properties, trends and classification of key types over the middle-east using satellite-derived atmospheric optical datasets. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 118100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahat, A.; El-Askary, H.; Al-Shaibani, A. Study of aerosols’ characteristics and dynamics over the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia using a multisensor approach combined with ground observations. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 247531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroushani, M.; Opp, C.; Groll, M. Chemical Characterization of Aeolian Dust Deposition in Southern and Western Iran. Asian J. Geogr. Res. 2019, 2, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, A.; Wu, R.; Aldabash, M. Long-term AOD trend assessment over the Eastern Mediterranean region: A comparative study including a new merged aerosol product. Atmos. Environ. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrooz, R.D.; Esmaili-Sari, A.; Bahramifar, N.; Kaskaoutis, D.G. Analysis of the TSP, PM10 concentrations and water-soluble ionic species in airborne samples over Sistan, Iran during the summer dusty period. Atmos. Poll. Res. 2017, 8, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsani, M.H.; Shirmardi, M.; Alavi, N.; Maleki, H.; Sorooshian, A.; Babaei, A.; Asgharnia, H.; Marzouni, M.B.; Goudarzi, G. Evaluation of the relationship between PM10 concentrations and heavy metals during normal and dusty days in Ahvaz, Iran. Aeol. Res. 2018, 33, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motaghi, F.A.; Hamzehpour, N.; Abasiyan, S.M.A.; Rahmati, M. The wind erodibility in the newly emerged surfaces of Urmia Playa Lake and adjacent agricultural lands and its determining factors. Catena 2020, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basart, S.; Vendrell, L.; Baldasano, J.M. High-resolution dust modelling over complex terrains in West Asia. Aeol. Res. 2016, 23, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, P.; Mahalov, A.; Li, J. Simulating the meteorology and PM10 concentrations in Arizona dust storms using the Weather Research and Forecasting model with Chemistry (WRF-Chem). J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2018, 68, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, S.P.; Yang, Z.L.; Kocurek, G. Mapping erodibility in dust source regions based on geomorphology, meteorology, and remote sensing. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 1977–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, S.P.; Stenchikov, G.L.; Ukhov, A.; Kim, H. Dust emission modeling using a new high-resolution dust source function in WRF-Chem with implications for air quality. J. Geophys. Res. 2019, 124, 10109–10133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menut, L.; Pérez, C.; Haustein, K.; Bessagnet, B.; Prigent, C.; Alfaro, S. Impact of surface roughness and soil texture on mineral dust emission fluxes modeling. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 6505–6520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Francis, D.; Rashki, A.; Chaboureau, J.P.; Dumka, U.C. Atmospheric Dynamics from Synoptic to Local Scale During an Intense Frontal Dust Storm over the Sistan Basin in Winter 2019. Geosciences 2019, 9, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bou Karam, D.; Flamant, C.; Cuesta, J.; Pelon, J.; Williams, E. Dust emission and transport associated with a Saharan depression: February 2007 case. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D00H27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagulian, F.; Temimi, M.; Ghebreyesus, D.; Weston, M. Analysis of a severe dust storm and its impact on air quality conditions using WRF-Chem modeling, satellite imagery, and ground observations. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2019, 12, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karegar, E.; Hamzeh, N.H.; Jamali, J.B.; Abadi, A.R.S.; Moeinaddini, M.; Goshtasb, H. Numerical simulation of extreme dust storms in east of Iran by the WRF-Chem model. Nat. Hazards 2019, 99, 769–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Cheng, Y.M.; Goto, D.; Schutgens, N.A.J.; Kikuchi, M.; Yoshida, M.; Shi, G.Y.; Nakajima, T. Inverting the East Asian Dust Emission Fluxes Using the Ensemble Kalman Smoother and Himawari-8 AODs: A Case Study with WRF-Chem v3.5.1. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathe, Y.; Kulkarni, S.; Gupta, P.; Kaginalkar, A.; Islam, S.; Gargava, P. Application of Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) and Weather Research Forecasting (WRF) model meteorological data for assessment of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) over India. Atmos. Poll. Res. 2018, 10, 418–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
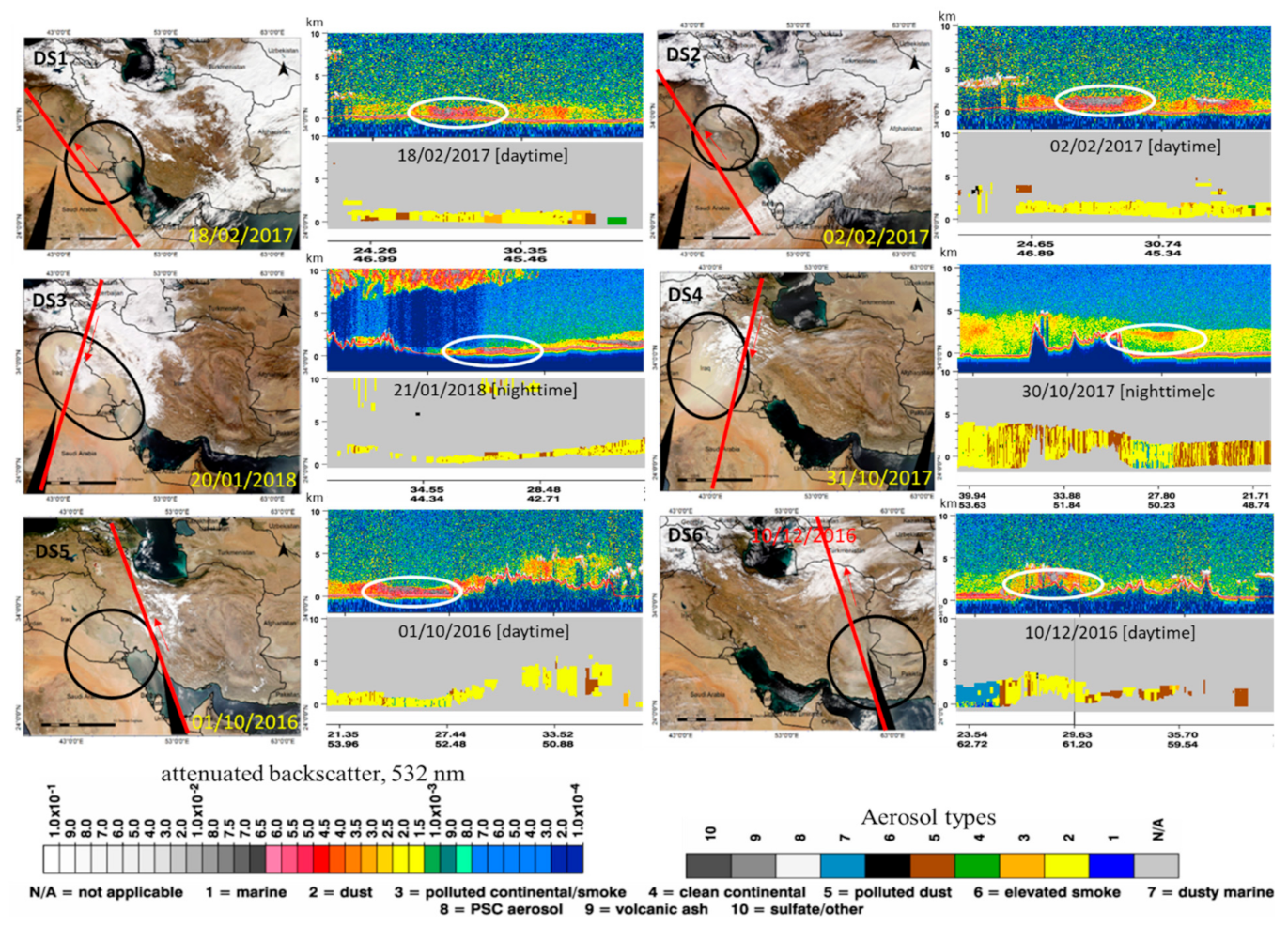
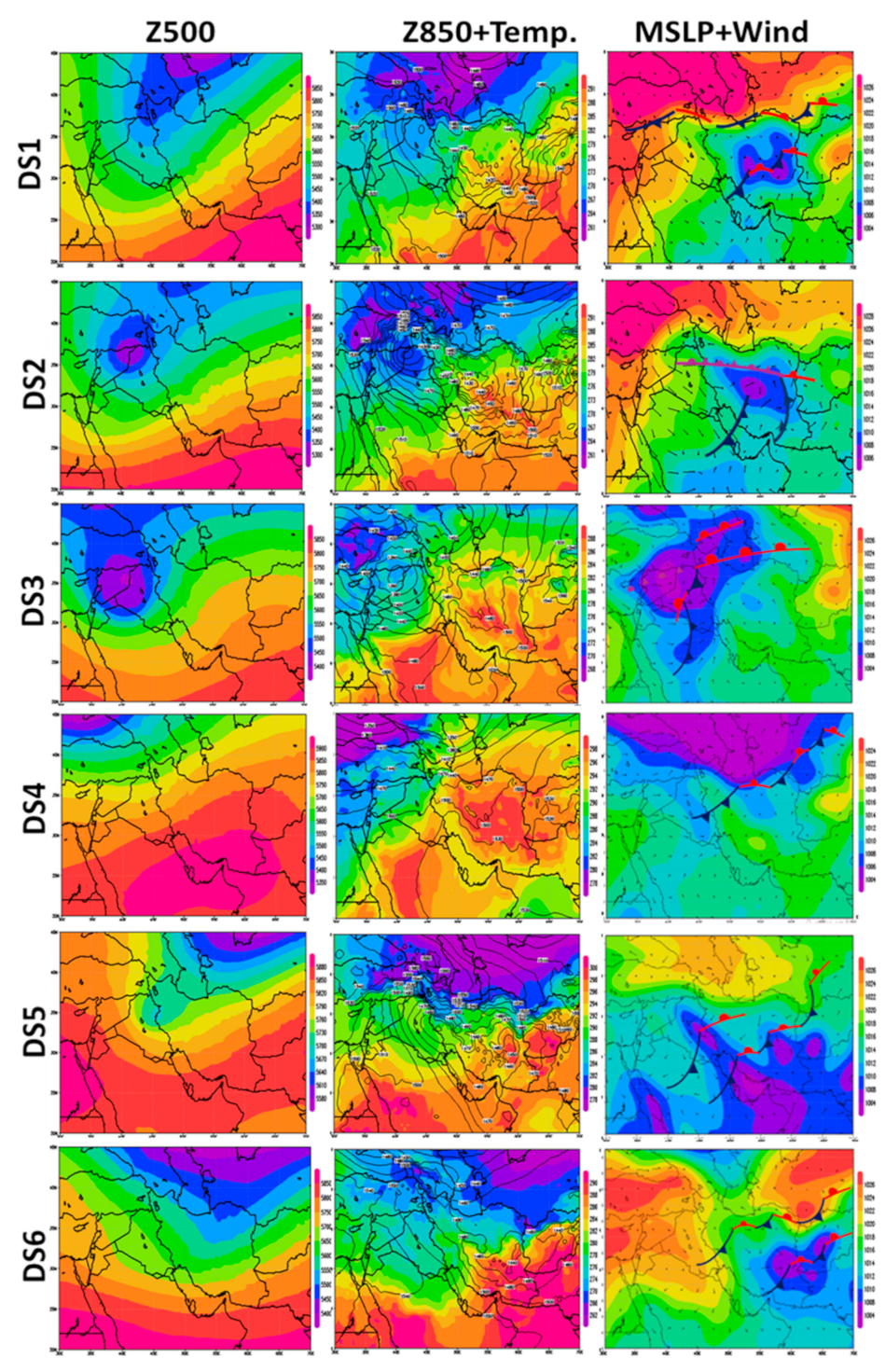
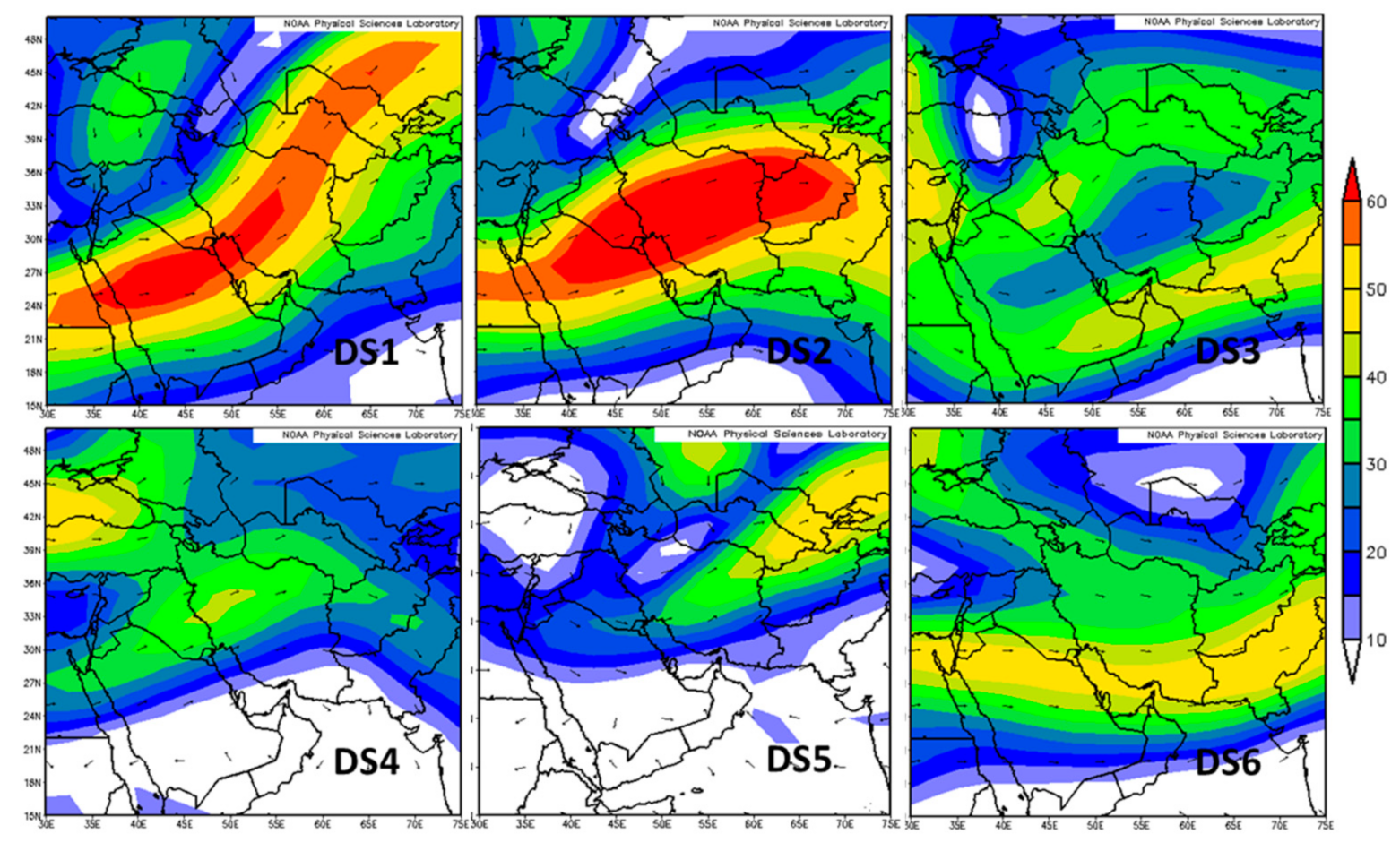
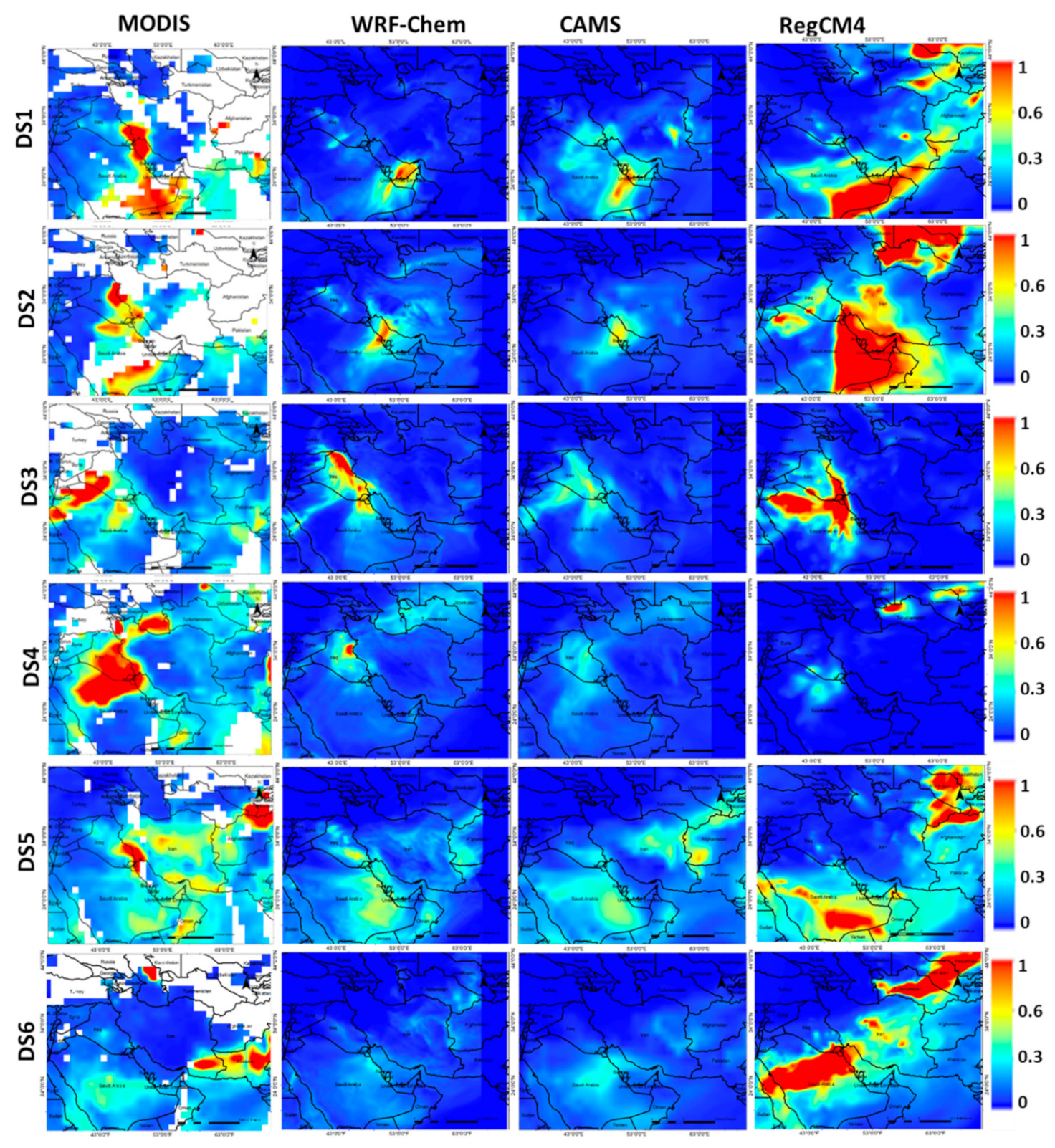
| Case ID | Time | Min.Visibility (m) | Affected Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| DS1 | 17–20 February 2017 | 100 | West and southwest of Iran, East Iraq |
| DS2 | 1–3 February 2017 | 100 | West Iran, East Iraq |
| DS3 | 18–21 January 2018 | 100 | Western half of Iran, Iraq, northeast of Saudi Arabia |
| DS4 | 29 October–1 November 2017 | 100 | West Iran, Iraq, North Saudi Arabia |
| DS5 | 30 September–2 October 2016 | 100 | West and southwest Iran |
| DS6 | 9–10 December 2016 | 100 | West Afghanistan, West Pakistan and East Iran |
| Model | Scale | Institute | Emission Scheme | Horizontal Resolution | Vertical Coordinate | Vertical Layers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WRF-Chem | Regional | UCAR | AFWA [72] | 21 km | sigma | 30 |
| CAMS-ECMWF | Global | UCAR | Uplifting [73] | 8–10 km | sigma | 137 |
| RegCM4 | Regional | EMA | Saltation and sandblasting [51] | 45 km | sigma | 18 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamzeh, N.H.; Karami, S.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Tegen, I.; Moradi, M.; Opp, C. Atmospheric Dynamics and Numerical Simulations of Six Frontal Dust Storms in the Middle East Region. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12010125
Hamzeh NH, Karami S, Kaskaoutis DG, Tegen I, Moradi M, Opp C. Atmospheric Dynamics and Numerical Simulations of Six Frontal Dust Storms in the Middle East Region. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(1):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12010125
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamzeh, Nasim Hossein, Sara Karami, Dimitris G. Kaskaoutis, Ina Tegen, Mohamad Moradi, and Christian Opp. 2021. "Atmospheric Dynamics and Numerical Simulations of Six Frontal Dust Storms in the Middle East Region" Atmosphere 12, no. 1: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12010125
APA StyleHamzeh, N. H., Karami, S., Kaskaoutis, D. G., Tegen, I., Moradi, M., & Opp, C. (2021). Atmospheric Dynamics and Numerical Simulations of Six Frontal Dust Storms in the Middle East Region. Atmosphere, 12(1), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12010125








