Diagnosing ISO Forecast from GloSea5 Using Dynamic-Oriented ISO Theory
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Mean Climate in the Boreal Winter
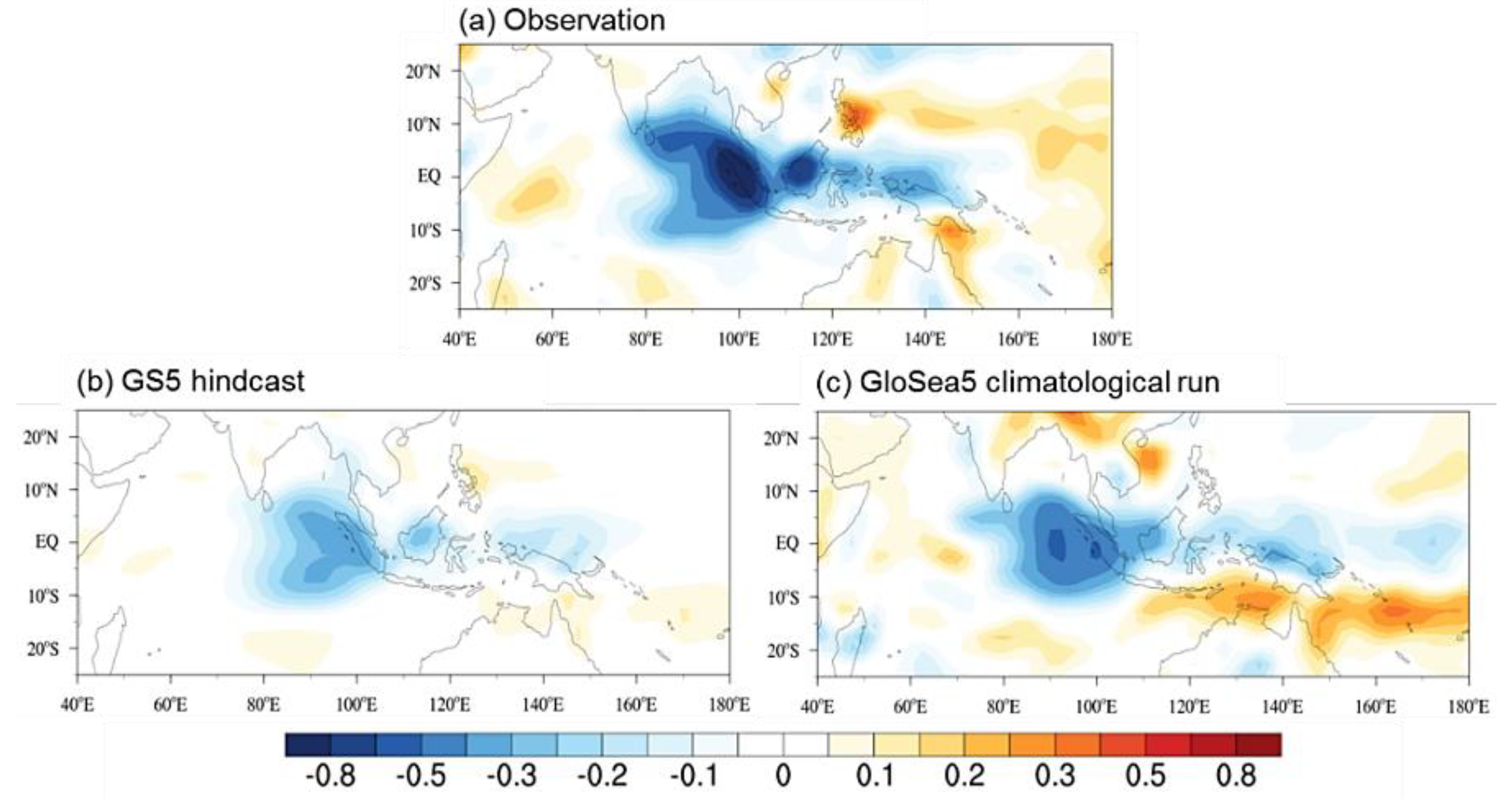
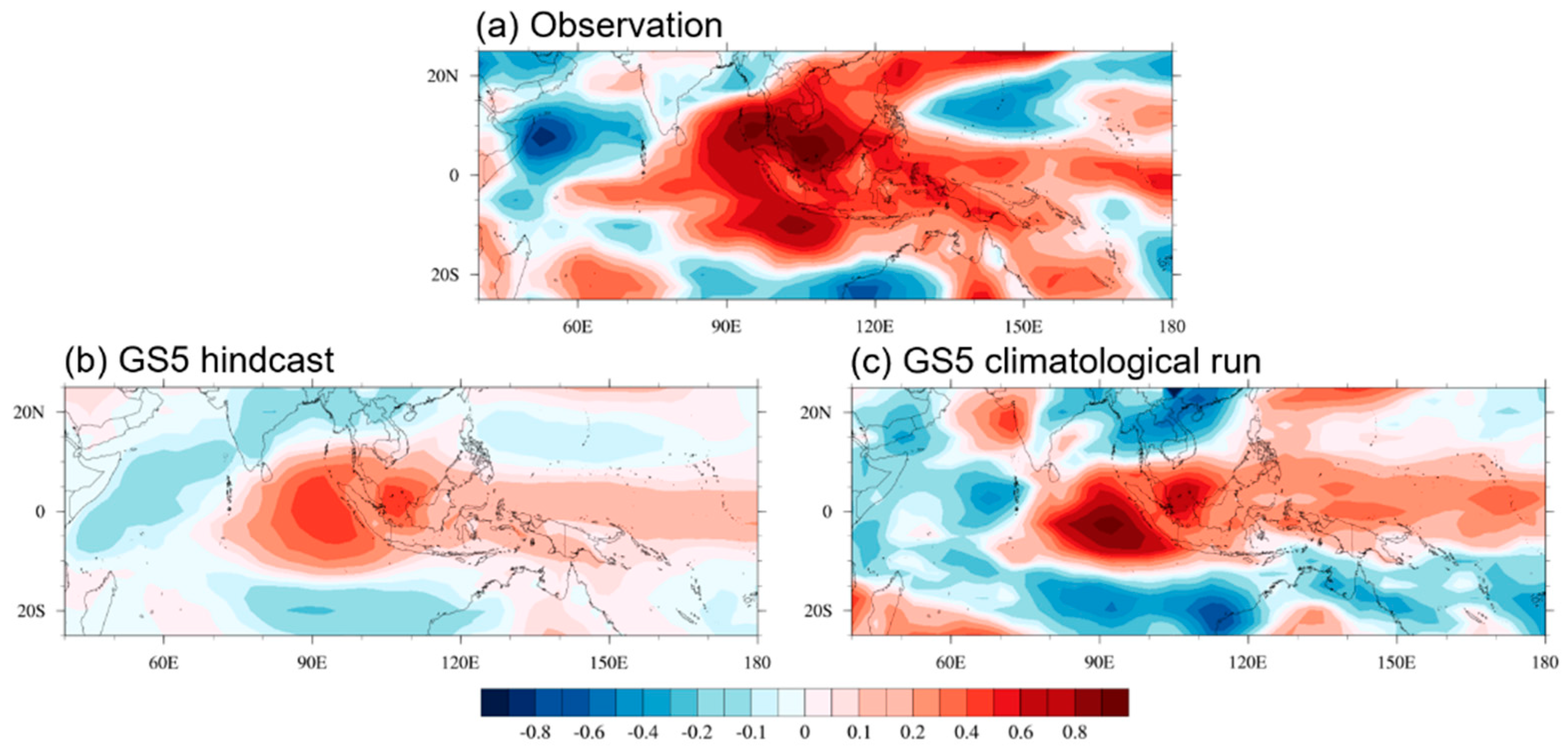
3.2. Basic Diagnostics in MJO Properties
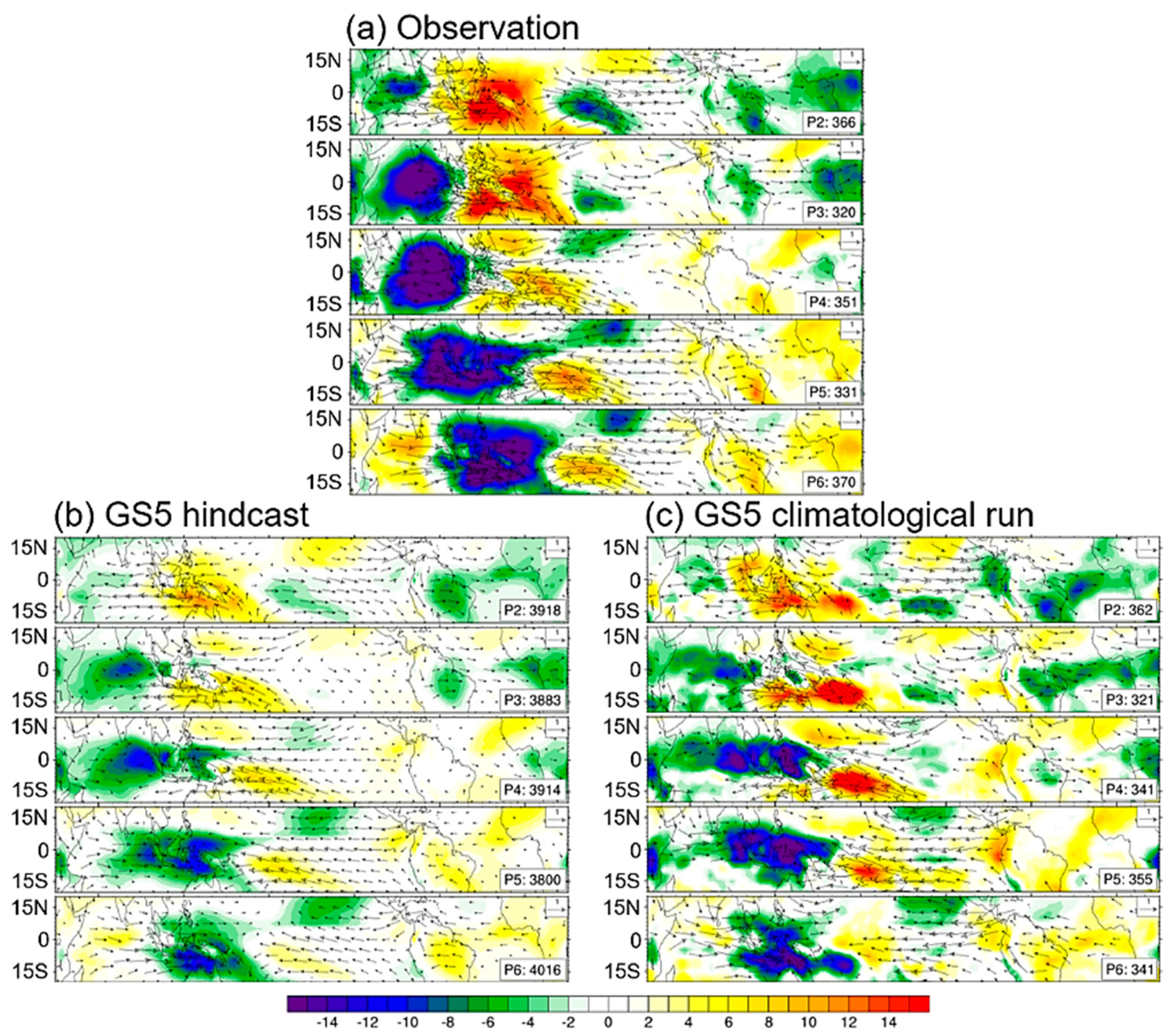
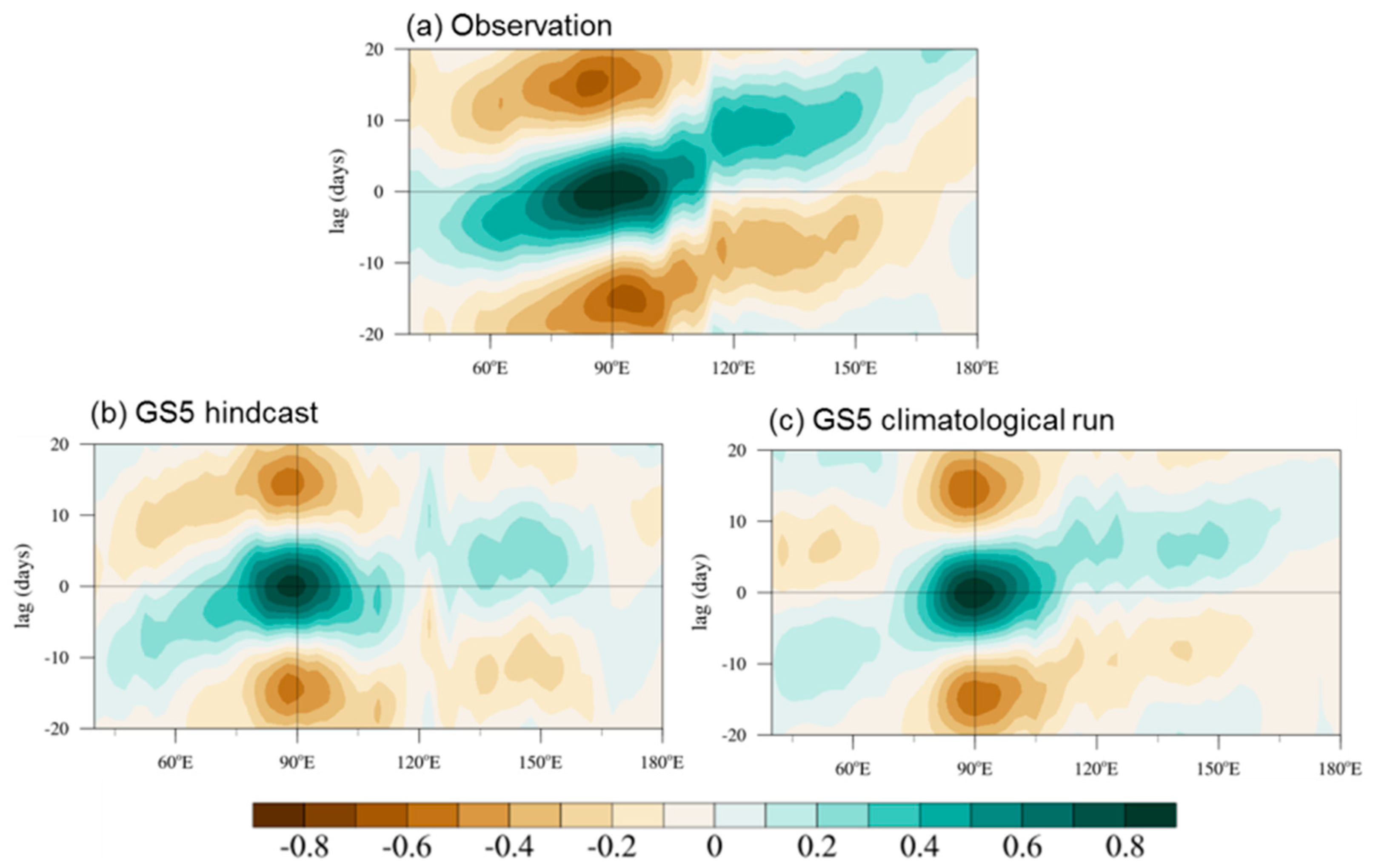
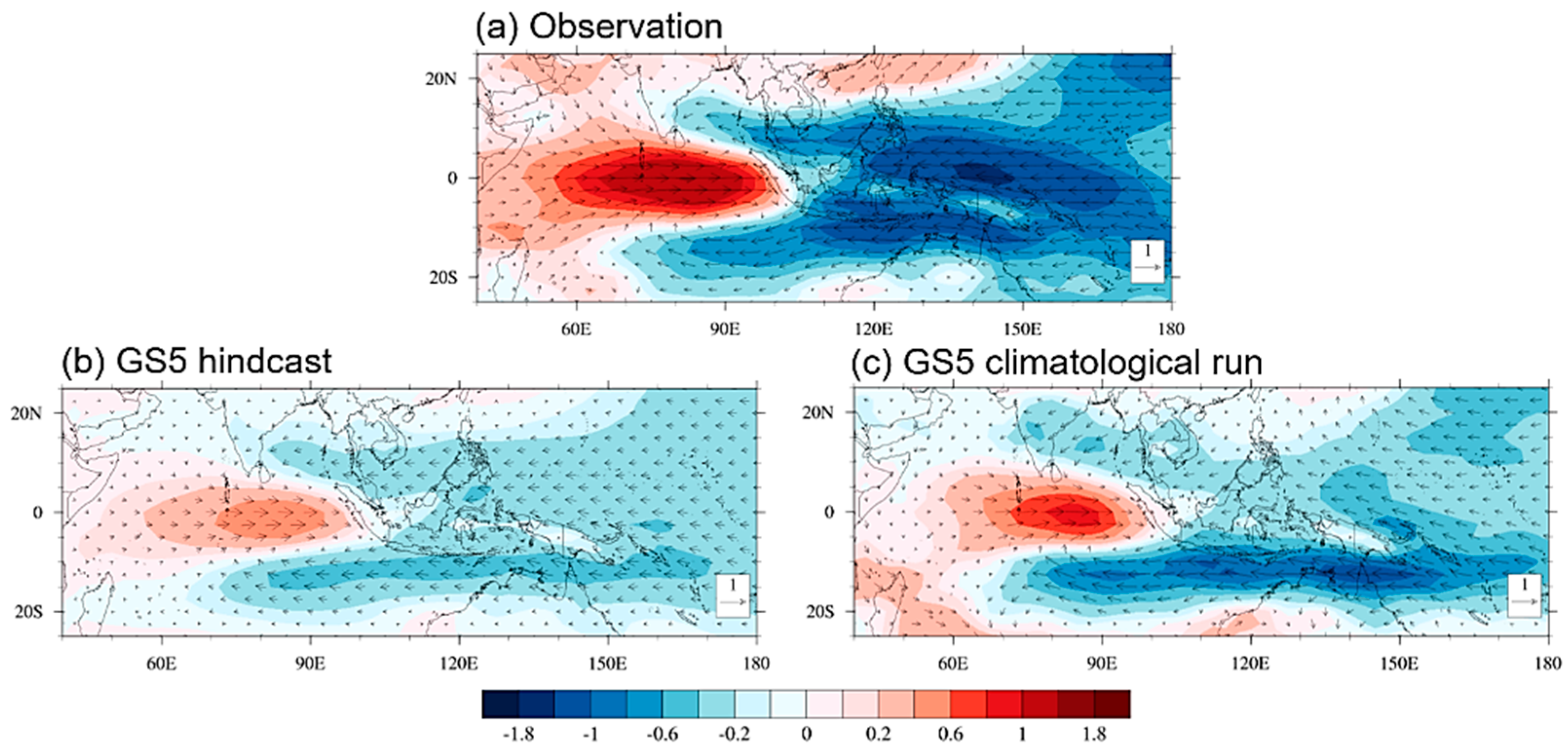
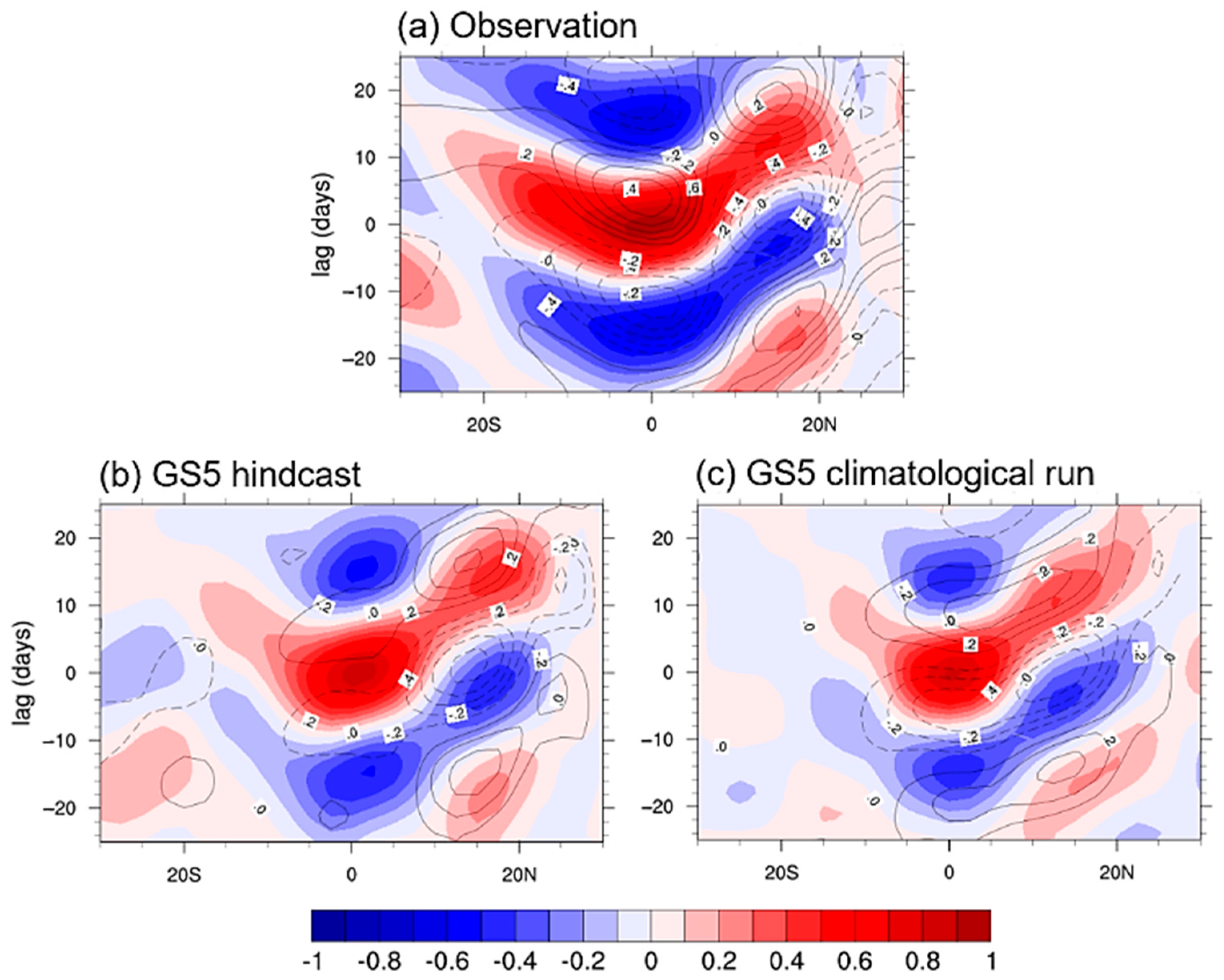
3.3. Evaluation of MJO Simulations Using Dynamic-Oriented Diagnostics
3.4. Diagnosing BSISO Simulations
4. Summary and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, L.; Alves, O.; Hendon, H.H.; Wang, G.; Anderson, D. The role of stochastic forcing in ensemble forecasts of the 1997/98 El Nino. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 2526–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitart, F.; Molteni, F. Simulation of the Madden–Julian Oscillation and its teleconnections in the ECMWF forecast system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 136, 842–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waliser, D.E. Intraseasonal variability. In The Asian Monsoon; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 203–257. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Waliser, D.E.; Xavier, P.K.; Petch, J.; Klingaman, N.P.; Woolnough, S.J.; Guan, B.; Bellon, G.; Crueger, T.; DeMott, C.; et al. Vertical structure and physical processes of the Madden–Julian Oscillation: Exploring key model physics in climate simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 4718–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, E.D.; Sobel, A.H.; Hannah, W.M. Intraseasonal variability in an aquaplanet general circulation model. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2010, 2, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, J.J.; Benedict, J.J.; Maloney, E.D.; Sobel, A.H.; Frierson, D.M.W. Gross moist stability and MJO simulation skill in three full-physics GCMs. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 71, 3327–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B. Dynamics of tropical low-frequency waves: An analysis of the moist Kelvin wave. J. Atmos. Sci. 1988, 45, 2051–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Rui, H. Dynamics of the coupled moist Kelvin–Rossby wave on an equatorial β-plane. J. Atmos. Sci. 1990, 47, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, K.; Takayabu, Y.N. The development of organized convection associated with the MJO during TOGA COARE IOP:trimodal characteristics. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L10104131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsumata, M.; Johnson, R.H.; Ciesielski, P.E. Observed synoptic-scale variability during the developing phase of an ISO over the Indian Ocean during MISMO. J. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 66, 3434–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Z. A moisture–stratiform instability for convectively coupled waves. J. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 65, 834–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wang, B. Critical roles of the stratiform rainfall in sustaining the Madden–Julian Oscillation: GCM experiments. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 3939–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.I.; Kang, I.-S.; Kim, J.-K.; Mapes, B.E. Influence of cloud–radiation interaction on simulating tropical intraseasonal oscillation with an atmospheric general circulation model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 14219–14233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, D.J. A new model of the Madden–Julian Oscillation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 58, 2807–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, F.; Chen, G. A trio-interaction theory for Madden–Julian Oscillation. Geosci. Lett. 2016, 3, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-M.; Lee, J.-Y.; Wang, B. The Tibetan Plateau uplift is crucial for eastward propagation of Madden–Julian Oscillation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-M.; Wang, B.; Lee, J.-Y. Mechanisms of northward propagation of boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation revealed by climate model experiments. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 3417–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lee, S.-S.; Waliser, D.E.; Zhang, C.; Sobel, A.; Maloney, E.; Li, T.; Jiang, X.; Ha, K.-J. Dynamics-oriented diagnostics for the Madden–Julian Oscillation. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 3117–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Webster, P.J.; Toma, V.E.; Kim, D. Predictability and prediction skill of the MJO in two operational forecasting systems. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 5364–5378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.; Son, S.; Kim, D. MJO prediction skill of the subseasonal-to-seasonal prediction models. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 4075–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, E.D.; Hartmann, D.L. The Madden-Julian oscillation, Barotropic dynamics, and North Pacific tropical cyclone formation. Part I: Observations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 58, 2545–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.-Y.; Wang, B.; Ha, K.-J.; Lee, J.-Y. Teleconnections associated with Northern Hemisphere summer monsoon intraseasonal oscillation. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 40, 2761–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xie, X. A model for the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation. J. Atmos. Sci. 1997, 54, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, T.; Wang, B. Structures and mechanisms of the northward propagating boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 1022–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-M.; Lee, J.-Y.; Wang, B. Dominant Process for Northward Propagation of Boreal Summer Intraseasonal Oscillation Over the Western North Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL089808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMott, C.A.; Stan, C.; Randall, D.A. Northward propagation mechanisms of the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation in the ERA-Interim and SP-CCSM. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 1973–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, B.; Kang, I.-S. Role of barotropic convective momentum transport in the intraseasonal oscillation. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 4908–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhao, J.; Fu, X.; Huang, G. The role of shallow convection in promoting the northward propagation of boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 131, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogensen, K.; Balmaseda, M.; Weaver, A.T.; Martin, M.; Vidard, A. NEMOVAR: A variational data assimilation system for the NEMO ocean model. In ECMWF Newsletter; Walter, Z., Ed.; ECMWF: Reading, UK, 2009; Volume 120, pp. 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen, K.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Weaver, A.T. The NEMOVAR ocean data assimilation system as implemented in the ECMWF ocean analysis for System 4. In Technical Report TR-CMGC-12-30; CERFACS: Toulouse, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bowler, N.; Arribas, A.; Beare, S.; Mylne, K.E.; Shutts, G. The local ETKF and SKEB:Upgrades to the MOGREPS short-range ensemble prediction system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 135, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, K.D.; Harris, C.M.; Bodas-Salcedo, A.; Camp, J.; Comer, R.E.; Copsey, D.; Fereday, D.; Graham, T.; Hill, R.; Hinton, T.; et al. The Met Office Global Coupled model 2.0 (GC2) configuration. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 1509–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, R.F.; Huffman, G.J.; Chang, A.; Ferraro, R.; Xie, P.P.; Janowiak, J.; Rudolf, B.; Schneider, U.; Curtis, S.; Bolvin, D.; et al. The version-2 global precipitation climatology project (GPCP) monthly precipitation analysis (1979–present). J. Hydrometeorol. 2003, 4, 1147–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebmann, B.; Catherine, A.S. Description of a Complete (Interpolated) Outgoing Longwave Radiation Dataset. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 1275–1277. [Google Scholar]
- Valcke, S. The OASIS3 coupler: A European climate modelling community software. Geosci. Model Dev. 2013, 6, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, D.; Rowntree, P.R. A massflux convection scheme with representation of cloud ensemble characteristics and stability dependent closure. Mon. Weather Rev. 1990, 118, 1483–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.-C.; Li, T. Role of the boundary layer moisture asymmetry in causing the eastward propagation of the Madden–Julian Oscillation. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 4914–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.H.; Ciesielski, P.E.; Ruppert, J.H., Jr.; Katsumata, M. Sounding-based thermodynamic budgets for DYNAMO. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 72, 598–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.-M.; Shim, T.; Moon, J.-Y.; Kim, K.-Y.; Hyun, Y.-K. Diagnosing ISO Forecast from GloSea5 Using Dynamic-Oriented ISO Theory. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12010114
Yang Y-M, Shim T, Moon J-Y, Kim K-Y, Hyun Y-K. Diagnosing ISO Forecast from GloSea5 Using Dynamic-Oriented ISO Theory. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(1):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12010114
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Young-Min, Taehyoun Shim, Ja-Yeon Moon, Ki-Young Kim, and Yu-Kyung Hyun. 2021. "Diagnosing ISO Forecast from GloSea5 Using Dynamic-Oriented ISO Theory" Atmosphere 12, no. 1: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12010114
APA StyleYang, Y.-M., Shim, T., Moon, J.-Y., Kim, K.-Y., & Hyun, Y.-K. (2021). Diagnosing ISO Forecast from GloSea5 Using Dynamic-Oriented ISO Theory. Atmosphere, 12(1), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12010114




