Abstract
Methane (CH4) emission and environmental controls of CH4-cycling microorganisms are unclear in inland floodplains. Here, we examined soil CH4 emissions and the community composition of CH4-cycling microorganisms under three vegetation types—mudflat (MF, no vegetation cover), Carex meadow (CM, mainly Carex brevicuspis), and reed land (RL, mainly Miscanthus sacchariflorus)—from water-adjacent areas to higher-elevation land in the Dongting Lake floodplain, China. The results showed that CH4 emission is the highest in CM, while significant absorption was observed in the RL site. The abundance ratio of methanogen/methanotroph was the highest in CM, intermediate in MF, and lowest in RL. The Methanosarcinaceae family represented the dominant methanogens in the three sampling sites (41.32–75.25%). The genus Methylocystis (60.85%, type II methanotrophs) was dominant in CM, while Methylobacter and Methylosarcina (type I methanotrophs) were the dominant genera in MF (51.00%) and RL (50.24%), respectively. Structural equation model analysis showed that methanogen and methanotroph abundance were affected by water table depth, soil water content, and pH indirectly through soil organic content, total nitrogen, microbial biomass carbon, and microbial biomass nitrogen. These results indicated that the Dongting Lake floodplain may change from a CH4 source to a CH4 sink with vegetation succession with an increase in elevation, and the methanogen/methanotroph ratio can be used as a proxy for CH4 emission in wetland soils. The continuous increase in reed area combined with the decrease in Carex meadow may mitigate CH4 emission and enhance the CH4 sink function during the non-flood season in the Dongting Lake floodplain.
1. Introduction
Methane (CH4) is an important greenhouse gas with a global warming potential 28 times higher than that of carbon dioxide (CO2) on a 100-year scale [1]. Natural wetlands are considered the main natural CH4 source for the atmosphere because of their high productivity and low redox capacity. The annual CH4 emission from natural wetlands is reported to be 172 Tg CH4•y−1 (1σ SD, ± 12 Tg CH4•y−1), accounting for approximately 62% of the annual global (natural) CH4 budget [2,3]. Although CH4 emissions and microbial production mechanisms from high-latitude peatlands have been well studied [4,5,6,7,8], relatively little data have been published on the low-latitude wetlands, which is the most important source of uncertainty on the methane budget [2].
Low-latitude seasonal floodplains are prolific sources of CH4 because of their substantial net primary productivity and high seasonal temperatures [9]. For example, the large CH4 emission in the Amazon floodplain trees adapted to permanent or seasonal inundation can account for about 15% of the global wetland CH4 emission [10]. Water regime, i.e., water table depth (WTD), soil water content (SWC), etc., and C and N concentrations in the soil, i.e., soil organic content (SOC), nitrogen, dissolved organic carbon (DOC), etc., along with the elevation gradient, may act as critical factors influencing CH4 production and emission in floodplains [11,12,13]. It has been documented that the water regime was a predominant factor affecting the methanogenic archaea (methanogens) and CH4-oxidizing microbes (methanotrophs) community over regional and seasonal variations [14]. Plant zonation along an elevation is a common phenomenon in floodplain wetlands. Vegetation type can also play a critical role in determining the community structures of methanogens and methanotrophs because it can provide sufficient substrates (i.e., soil C, N, etc.) for the growth of CH4-cycling microorganisms by plant litter decomposition and root exudate [15,16]. Nevertheless, with an increase in elevation, methanogen should be unlikely to survive owing to the WTD and SWC decline and increase in oxygen availability [17]. Therefore, the effects of vegetation and water regime, along with an elevation gradient, on CH4-cycling microorganisms, are still conflicting.
Currently, under the double pressure of anthropogenic disturbances and global climate change, the vegetation distribution pattern in wetlands changes significantly owing to variation in the water regime, especially in river-connected floodplains [18,19]. For example, in the East Dongting Lake wetlands, the area covered by reed and forest increased significantly, but that of Carex meadow (CM) showed a sharply decreasing trend during 1995–2015, particularly after the implementation of the Three Gorges Dam (TGD) upstream of the Yangtze River [19]. In this study, we analyzed the CH4 flux and the community structure of methanogens and methanotrophs along an elevation gradient in the Dongting Lake floodplain. Three vegetation types—mudflat (MF, no vegetation cover), CM (dominated by Carex brevicuspis), and reed land (RL, dominated by Miscanthus sacchariflorus)—were distinctly distributed from water-adjacent areas to higher-elevation land. The objectives of our study were as follows: (1) to analyze the CH4 emission from three vegetation types along an elevation gradient; (2) to elucidate the diversity and community structure of methanogens and methanotrophs in three vegetation types and vertical soil profiles; and (3) to quantify the relationships between environmental variables and abundance of methanogens and methanotrophs in three vegetation types.
2. Experiments
2.1. Study Site
Dongting Lake (28°30′–30°20′ N, 111°40′–113°10′ E), with an area of 2625 km2, is the second-largest inland freshwater lake in China. It is connected to the Yangtze River by distributary channels (Songzi, Taiping, and Ouchi) and has four other water inlets (Rivers Xiang, Zi, Yuan, and Li) in the Hunan Province (Figure 1). The wetlands of this lake are characterized by large seasonal water level fluctuations (12–14 m), with the maxima in August and minima typically in January or February, which provide the basic hydrological regime for maintaining large areas of floodplain [20]. The floodplains are completely flooded from June to October and are exposed from November to the following May [21]. The study was conducted at a monitoring sampling site (29°30′ N, 112°48′ E) of Dongting Lake Station for Wetland Ecosystem Research, a member of the Chinese Ecosystem Research Network (CERN). The monitoring site has an area of 200 ha, and it is covered by mudflats (no vegetation cover), Carex communities (mainly Carex brevicuspis), and reed (mainly Miscanthus sacchariflorus), along with a small elevation gradient (22–26 m, Yellow Sea Datum 1985). The mean annual temperature in the study area is 16.4–17.0 °C, with the lowest temperatures in January (3.9–4.5 °C) and the highest in July (28.6–29.1 °C). The annual precipitation is 1382 mm, with more than 60% of rainfall occurring from April to August [22].
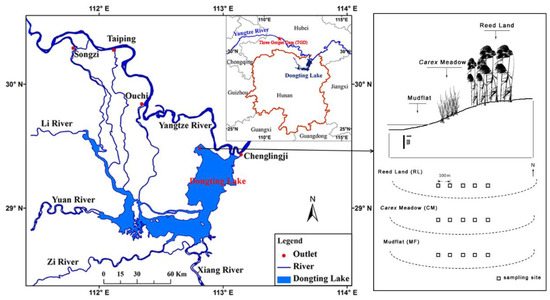
Figure 1.
Maps of Dongting Lake showing the location and elevation of the sampling area.
2.2. Soil Sampling Process
Soil samples were collected from three sampling sites—MF, CM, and RL—on 10 November 2016, after the flood season. Five sampling plots at intervals of 100 m in a parallel line were randomly selected at each site. Five 30-cm-deep soil cores at each sampling plot were collected using steel sediment samplers (d = 10 cm) and split into three depths: 0–10, 10–20, and 20–30 cm. Each collected soil sample (ca. 1000 g in fresh weight) was divided into two sub-samples. One was stored at 4 °C for physicochemical analysis (ca. 900 g in fresh weight), and the other was stored in liquid nitrogen for DNA extraction and molecular analysis (ca. 100 g in fresh weight).
2.3. Soil Physical and Chemical Analysis
Soil pH was determined using a pH meter (Mettler Toledo, Shanghai, China) with a soil-to-water ratio of 1:2.5. The SWC was determined by the mass ratio of the pore water to solids by drying the samples in the oven at 105 °C for 48 h [23]. The SOC was determined by wet oxidation with KCr2O7 + H2SO4 and titration with FeSO4. Ammonium (NH4+) and nitrate (NO3−) were determined by the Flow Injection Analyzer AA3 (SEAL, 22844 Norderstedt, Germany) after extraction with 2M K2SO4 solution. Total carbon (TC) and total nitrogen (TN) were measured by the Element Analyzer (Elementar, Munich, Germany). Soil DOC was measured as follows: each 10-g wet-soil sample was incubated with 50 mL of distilled water for 30 min on an end-over-end shaker and then centrifuged for 20 min at 1680× g (5000 rpm). The extracted solutions were passed through a 0.45-μm filter membrane and analyzed using a total organic carbon (TOC) Analyzer (TOC-VWP, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) [24]. The estimation of soil microbial biomass carbon (MBC) and microbial biomass nitrogen (MBN) was performed by the chloroform–fumigation–extraction method: 25 g of fresh soil was fumigated, and carbon dissolved in 0.5 M K2SO4 extracts was measured by automated analyses on a TOC Analyzer (TOC-VWP, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) [25].
2.4. Gas Sampling and CH4 Lux Calculation
The gas collection was carried out at the three sampling sites every 7 days from 5 November to 6 December 2016, using the static opaque chamber–gas chromatography method [26]. The chambers (40 cm in diameter and 50 cm in height) were made of 0.5-cm-thick opaque Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipe, with a volume and area of 0.0628 m3 and 0.1256 m2, respectively. Because the reeds were harvested for paper making during the non-flooding season of the Dongting Lake floodplain, the CH4 emission in RL during our sampling period only represents the emission in the soil and belowground plant tissues. The chambers were equipped with a small fan for gentle air circulation and wrapped with thermal insulating Styrofoam and radiation-reflecting tinfoil to prevent dramatic temperature changes in the headspace during chamber closure. A PVC chamber base (height = 10 cm; diameter = 41 cm) was permanently inserted into the soil at each spatial replicate.
On the day of observation, gas sampling at the three sites was simultaneously performed between 8:00 and 10:00 a.m., when the gas flux and air temperature were representatives of the daily averages. At each sampling time, the chamber was sealed, and five gas samples (30 mL each) were collected using a polypropylene syringe at 10-min intervals. The samples were injected into labeled evacuated Exetainers (Labco Ltd., London, UK). The CH4 concentrations were analyzed with a gas chromatograph (Agilent 7890A, Santa Clara CA, USA) equipped with a flame ionization detector (FID). The gas fluxes were calculated by the following formula:
where FCH4 is flux (μg C m−2 h−1), and dc/dt is the slope of the linear regression of gas concentration at time approaching zero. T is the absolute temperature (K) during sampling. P is the atmospheric pressure (KPa) during the sampling period. H is the height (m) of the chamber headspace.
FCH4 = dc/dt ∙ 0.53 ∙ 273/T ∙ P/1013 ∙ H ∙ 1000
2.5. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and High-Throughput Sequencing
DNA from soil samples was extracted according to the manufacturer’s instructions using the FastDNA® Spin Kit for Soil (MP Biomedicals, Irvine, CA, USA). The extracted DNA was evaluated by electrophoresis on a 1% agarose gel and quantified by spectrophotometry (NanoDrop, Waltham, MA, USA).
A 470-bp mcrA gene fragment, which generally represents methanogens community, was PCR-amplified from community DNA samples by means of a forward primer MLfF (5′-GGTGGTGTMGGATTCACACARTAYGCWACAGC-3′) and reverse primer MLrR (5′-TTCATTGCRTAGTTWGGRTAGTT-3′) [27]. A 472-bp pmoA gene fragment, which generally represents methanotrophs community, was PCR-amplified from community DNA samples by means of a forward primer A189F (5′-GGNGACTGGGACTTCTGG-3′) [28] and reverse primer mb661R (5′-CCGGMGCAACGTCYTTACC-3′) [29]. The mcrA and pmoA gene fragments were PCR-amplified by an ABI GeneAmp® 9700 PCR thermocycler (ABI, Vernon, CA, USA) with an eight-base sequence barcode unique to each sample at the 5′ end of the MLfF/MLrR and A189F/mb661R primer pairs, respectively. Amplification was performed in a 20-µL final volume containing 4 µL of 5 × FastPfu Buffer, 2 µL of 2.5 mM dNTPs, 0.4 µL of FastPfu Polymerase, 0.2 µL of BSA, 0.8 µL of each primer (final concentration 5 µM), and 10 ng of extracted DNA. The thermal cycling conditions were as follows: 95 °C for 3 min followed by 35 cycles (mcrA) and 36 cycles (pmoA) of denaturing at 95 °C for 30 s, annealing at 55 °C for 30 s, and extension at 72 °C for 45 s. Final extension reactions were carried out for 10 min at 72 °C. The PCR products were extracted and further purified using the AxyPrep DNA Gel Extraction Kit (Axygen Biosciences, New York, NY, USA). The resulted PCR products of the same sample were mixed and analyzed by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. Purified amplicons were pooled in equimolar concentrations and paired-end sequenced (2 × 300) on an Illumina MiSeq PE300 platform at Majorbio Bio-Pharm Technology Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China) (Figure S1). The raw reads were deposited into the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database (Accession Number: PRJNA497518).
2.6. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
Methanogens and methanotrophs were quantified by ABI 7500 Real-Time PCR software (ABI, California, USA) using the primer pair MLfF/ MLrR and A189F/mb661R. The PCR system contained a 2X ChamQ SYBR Color qPCR Master Mix (16.5 μL), the forward primer (5 μM, 0.8 μL), the reverse primer (5 μM, 0.8 μL), template DNA (19.1 ng for mcrA and 21.3 ng for pmoA, 2 μL), and ddH2O (7.4 μL). Quantitative PCR was carried out as follows: 5 min at 95 °C for initial denaturation, 35 cycles of 5 s at 95 °C, 30 s at 53 °C (mcrA) and 58 °C (pmoA), and 40 s at 72 °C. After the PCR procedure, three products were randomly selected to be analyzed on an agarose gel and sequenced to check the specificity of the products. Moreover, the melting-curve analysis for each sample was employed to ensure the specificity of each amplicon. A standard curve for the mcrA and pmoA genes was prepared using a 10-fold dilution series (102–109 copies) of the plasmids containing the target gene fragments. The efficiencies of qPCR for the mcrA and pmoA genes were 89.27% (R2 = 0.9999) and 97.24% (R2 = 0.9999), respectively. All qPCRs were run in triplicate with the DNA extracted from each soil sample.
2.7. Data Analysis
Quality control of the amplicon sequences was performed using QIIME pipeline (version 1.9.0). Briefly, low-quality sequences (<50 bp in length with an average quality score of <20) were excluded from further analyses. After the removal of the barcode and primer sequences, operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were defined with an identity threshold of 97% using Usearch (version 7.0). Taxa were assigned using the RDP fungene database (release 7.3). Subsequently, community bar plots and the plot of average CH4 flux (n = 5) were constructed using Origin V8.0 (Origin Lab, Northampton, MA, USA). The differences in soil properties (SWC, MBC, MBN, DOC, SOC, pH, NH4+, NO3−, TC, and TN) and the abundance of methane-cycling microorganisms (pmoA and mcrA gene copies) among the three soil layers and three sampling sites (mean value of the soil properties and methane-cycling microorganisms of the whole soil column) were tested by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) using R (version 3.4.3). Redundancy analysis (Koh, #46) with 999 Monte Carlo permutation tests was conducted by R (version 3.4.3). Phylogenetic trees were constructed by FastTree (version 2.1.3) using the approximately-maximum-likelihood method and then drawn by R (version 3.4.3). We further fitted a piecewise structural equation model (SEM) using R (version 3.4.3); the “piecewise SEM” package was used to infer the relative importance of environmental factors (WTD, SWC, and pH), C and N availability in the soil (SOC, TN), MBC, and MBN on the abundance of methanogens and methanotrophs. Compared with the traditional variance–covariance-based SEM, the piecewise SEM could (1) piece multiple separate (generalized) linear models together to a single causal network, (2) use Shipley’s test of d-separation to test whether any paths are missing from the model, and (3) use Akaike information criterion (AIC) to compare nested models and for small sample size [30].
3. Results
3.1. CH4 Flux and Abundance of Methanogens and Methanotrophs
The average CH4 flux was significantly higher in CM (57.42 ± 39.17 μg C m−2 h−1) than in MF (6.32 ± 4.12 μg C m−2 h−1) and RL (–14.80 ± 6.83 μg C m−2 h−1) (p < 0.01, Figure 2A).
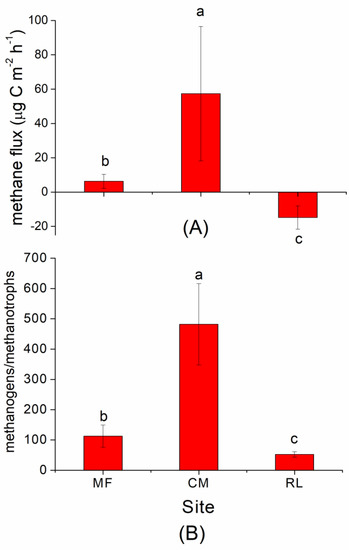
Figure 2.
Average methane flux (A) and the abundance ratio of methanogens and methanotrophs (B) from 5 November to 6 December 2016, at three sites in the Dongting floodplain. The data used in (B) is the average ratio of methanogens and methanotrophs gene abundance across the 0–30 cm soil profile. Site abbreviations: MF: mudflat, CM: Carex meadow, RL: reed land. Different lowercase letters in the same column within each sampling site indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) among the three soil layers.
For methanogens, the average abundance value in CM was (6.15 ± 1.16) ×107 gene copies g−1dws, which was significantly higher than in RL (1.43 ± 0.38) × 107 gene copies g−1dws and MF (0.32 ± 0.11) × 107 gene copies g−1dws (p < 0.05, Table 1). For methanotrophs, the average abundance values in CM and RL ((2.41 − 4.47) × 105 gene copies g−1dws) were significantly higher than that in MF (0.62 ± 0.32) × 105 gene copies g−1dws) (p < 0.05, Table 1). However, the difference in the abundance value of methanotrophs between CM and RL was insignificant (p > 0.05, Table 1). The abundance of methanogens and methanotrophs was the highest in soil depths of 0–10 cm, and both decreased with increase in soil depth. The abundance ratio of methanogens and methanotrophs was significantly higher in CM (481.96 ± 134.33) than in MF (112.81 ± 36.50) and RL (52.60 ± 8.78) (p < 0.01, Figure 2B).

Table 1.
The vertical pattern of the abundance of methanogens (gene copies g−1dws × 107) and methanotrophs (gene copies g−1dws × 105) in three sites of the Dongting Lake floodplain.
3.2. Diversity and Richness of Methanogens and Methanotrophs
After the amplification of mcrA genes (methanogen) and pmoA genes (methanotroph), the samples were sequenced by high-throughput sequencing. Among the three sampling sites, the average retrieved sequence amount of the mcrA genes and pmoA genes is 15422–16483 and 13368–14773, respectively. The average read lengths were 440 bp (ranging from 421 to 460 bp) and 488 bp (ranging from 481 to 500 bp) for the mcrA and pmoA genes, respectively (Table S1). The coverage index was higher than 98%, indicating that the sequencing effort encompassed a significant amount of biodiversity in the examined samples. For methanogens, the OTU number was the highest in MF (446–468) and lowest in RL (170–214). The ACE and Chao1, which represented methanogen richness, were highest in MF and lowest in RL. The Shannon diversity index was also highest in MF (4.68) and lowest in RL (2.95). However, for methanotrophs, the average OTU number was the highest in CM (212–258) and lowest in the MF (134–265) and RL sites (170–214). The richness, as suggested by the ACE and Chao1, and the diversity, as suggested by the Shannon index, were highest in the CM site (Table S1).
3.3. Community Composition of Methanogens and Methanotrophs
3.3.1. Methanogens
Methanosarcinaceae, Methanosaetaceae, Methanobacteriaceae, Methanoregulaceae, Methanomassiliicoccaceae, Methanocellaceae, and Methanomicrobiaceae were detected in the soil samples (Fig.S2A), and the family Methanosarcinaceae was the most abundant of the methanogens in the three sampling sites (Figure 3A). However, the composition of methanogens varied significantly in different vegetation types. The relative percentage of Methanosarcinaceae was the highest in the RL site (75.25%), followed by the CM site (66.19%), and was the lowest in the MF site (41.32%). On the contrary, the relative percentage of Methanomassiliicoccaceae and Methanomicrobiaceae was the highest in the MF site (22.07% vs. 12.01%) and lowest in the RL site (0.74% vs. 0.22%). The family Methanobacteriaceae showed a consistent relative percentage among the three sampling sites (14.9–19.9%, Figure 3A).
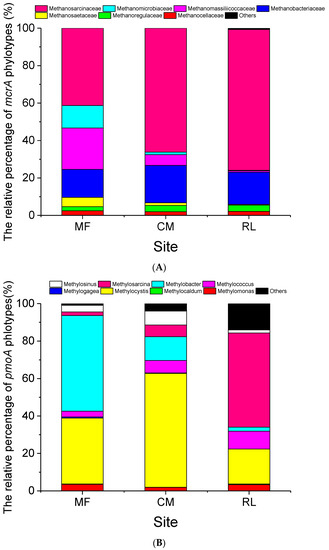
Figure 3.
The relative percentage of Methanogens (A) and Methanotrophs (B) phylotypes at three sites in the Dongting floodplain. The data is average value across a 0–30 cm soil profile. Site abbreviations: MF: mudflat, CM: Carex meadow, RL: reed land.
The relative percentage of Methanosarcinaceae (56.09%, 37.56%, and 30.31% at depths of 0–10 cm, 10–20 cm, and 20–30 cm, respectively) and Methanobacteriaceae (29.33%, 8.30%, and 7.20% at depths of 0–10 cm, 10–20 cm, and 20–30 cm, respectively) were decreased with increasing depth in MF. However, the relative percentage of Methanomassiliicoccaceae (2.88%, 27.31%, and 36.03% at depths of 0–10 cm, 10–20 cm, and 20–30 cm, respectively) and Methanomicrobiaceae (2.73%, 16.42%, and 16.88% at depths of 0–10 cm, 10–20 cm, and 20–30 cm, respectively) were increased with increasing depth in MF. In the CM and RL sites, Methanosarcinaceae showed a relatively higher abundance in the 10–20-cm soil layer (80.67% and 80.39% in CM and RL, respectively) than in the 0–10-cm (53.81% and 73.06%, respectively) and 20–30-cm soil layers (64.10% and 72.30%, respectively, Figure 4A). In the CM site, Methanobacteriaceae showed a relatively higher abundance in the 0–10-cm soil layer (40.08%) than that in the 10–30-cm soil layers (8.61–11.19%), but it showed relatively consistent abundance in the three soil layers in the RL site (14.46–19.89%, Figure 4A).
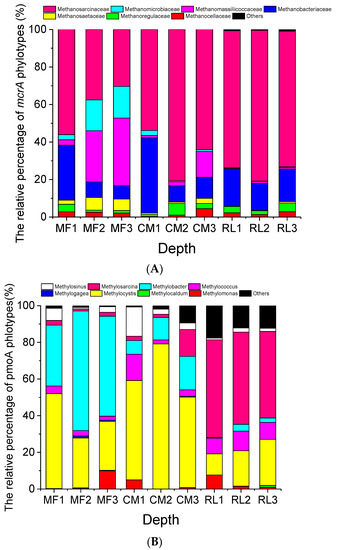
Figure 4.
The relative percentage of methanogen (A) and methanotroph (B) phylotypes across three sites and soil depths in the Dongting floodplain. Site abbreviations: MF: mudflat, CM: Carex meadow, RL: reed land. 1, 2, and 3 represent the three depths: 0–10 cm, 10–20 cm, and 20–30 cm, respectively.
3.3.2. Methanotrophs
The methanotroph groups detected in the three sampling sites included the Methylobacter, Methylosarcina, Methylogaea, Methylococcus, Methylocaldum, Methylocystis, Methylosinus, and Methylomonas genera (Figure S2B). The most common and dominant genus of methanotrophs in CM was Methylocystis (60.85%, type II methanotrophs, from the Rhizobiales order), the abundance of which was significantly higher than that in the MF (35%) and RL sites (18%). Methylobacter and Methylosarcina (type I methanotrophs, both from the Methylococcales order) were dominant in MF (51.00%) and RL (50.24%), respectively (Figure 3B).
The vertical patterns of the methanotroph community structure are shown in Figure 4B. The relative percentage of Methylobacter in MF was higher in the 10–30-cm soil layer (54.52–65.29%) than in the 0–10-cm (33.18%). The relative percentage of Methylocystis in CM was the highest in the 10–20-cm soil layer (79.08%). However, the relative percentage of Methylosarcina in RL was relatively constant among the three soil layers (47.23–53.22%, Figure 4B).
3.4. The Relationship between Methanogen and Methanotroph Communities and Environmental Factors
The soil environmental factors can be divided into two axes; the axes of RDA 1 (water regime condition, 80.31%) and RDA 2 (soil C and N availability, 14.65%) successfully explained the total variance for the methanogen–environment relationship, and the axes of RDA 1 (water regime condition) and RDA 2 (soil C and N availability) explained 81.29% and 13.87% of the total variance for the methanotroph–environment relationship, respectively (Figure 5A,B). WTD and pH were positively correlated with the Methanosarcinaceae distribution but negatively correlated with the distribution of Methanomassiliicoccaceae, Methanosaetaceae, and Methanomicrobiaceae. MBC, MBN, TC, SOC, and TN were positively correlated with the Methanobacteriaceae distribution (Figure 5A, Table 2). For methanotroph communities, WTD and pH were positively correlated with the Methylosarcina but negatively correlated with the distribution of Methylobacter and Methylocystis. MBC, MBN, TC, SOC, and TN were positively correlated with the distribution of Methylosinus and Methylococcus (Figure 5B, Table 2). Since the SWC was significantly negatively correlated with the WTD and pH, the effects of SWC on methanogen and methanotroph communities were contrary to that of WTD and pH.
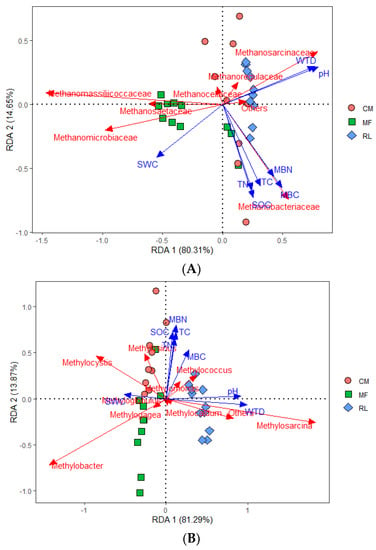
Figure 5.
RDA ordination diagrams of methanogen (A) and methanotroph (B) community composition and environmental variables. MF, CM, and RL represent the three sampling sites of mudflat, Carex meadow, and reed land, respectively. Arrows point to variables associated with community composition, and the length of the arrows indicates the percentage of data explained by that variable. The following abbreviations indicate environmental factors: SWC: soil water content, MBC: microbial biomass carbon, MBN: microbial biomass nitrogen, SOC: soil organic carbon, TC: total carbon, TN: total nitrogen, WTD: water table depth.

Table 2.
The coefficients of correlation (β) and determination (r2) between methanogen and methanotroph communities and environmental factors by redundancy analysis (Koh, #46).
3.5. Effect Pathways of Environmental Factors on CH4-Cycling Microorganisms
The effect pathways of WTD, SWC, and pH on the abundance of methanogens and methanotrophs through soil C (SOC), soil N (TN), MBC, and MBN were successfully fitted by the piecewise SEM (Table 3). For methanogens, the WTD, SWC, and pH affected the abundance of mcrA directly and indirectly through MBC and MBN or the SOC, TN, MBC, and MBN (Figure 6A). Overall, the WTD and SWC positively affected the abundance of methanogens (WTD: direct effect: −28.0%, indirect effect: 43.4%, total effect: 15.4%; SWC: direct effect: −52.0%, indirect effect: 75.7%, total effect: 23.7%). However, pH negatively affected the abundance of methanogens (direct effect: 48.0%, indirect effect: −67.0%, total effect: −19%).

Table 3.
Statistics of the structural equation model (SEM) of the relationship between the abundance of methanogens and methanotrophs and environmental factors in the three sites.
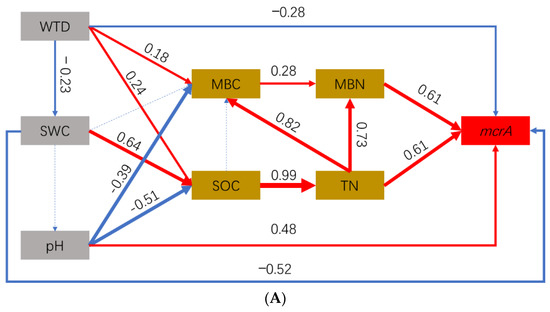
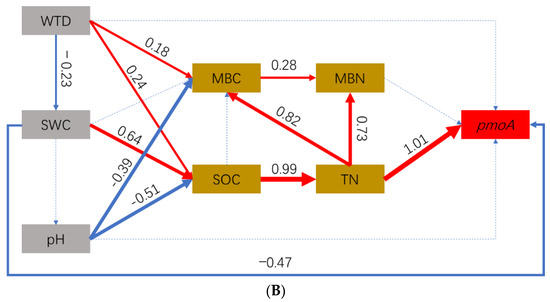
Figure 6.
Structural equation model (SEM) of the relationship between the abundance (qPCR) of methanogens (A) and methanotrophs (B) and environmental factors in the three sites. Solid red arrows represent positive paths (p < 0.05, piecewise s.e.m.), solid blue arrows represent negative path (p < 0.05, piecewise s.e.m.) and dotted blue arrows represent non-significant paths (p > 0.05, piecewise s.e.m.).
For methanotrophs, WTD positively affected the abundance of methanotrophs indirectly through the SOC and TN or the SWC (total effect: 34.8%). pH negatively affected the abundance of methanotrophs indirectly through SOC and TN (total effect: −51.0%). SWC positively affected the abundance of methanotrophs indirectly through SOC and TN (β = 0.64 × 0.99 × 1.01 = 0.64) but negatively affected the abundance of methanotrophs directly (β = −0.47, Figure 6B). Overall, SWC positively affected the abundance of methanotrophs (total effect: 17%).
4. Discussion
4.1. CH4 Flux and Abundance of CH4-Aycling Microorganisms
In this study, both the CM and MF sites showed a significant CH4 emission; however, the RL site exhibited a significant CH4 absorption. This result indicated that the plant zonation sites can change from a CH4 source to CH4 sink with an increase in elevation in the Dongting Lake floodplain. The abundance of methanogens was the highest in the CM sites, which may induce the highest CH4 emission in the CM site at an intermediate elevation. However, the abundance of methanotrophs was the highest in CM, indicating that CH4 consumption may also be significant in CM sites. Fundamentally, soil CH4 flux is responsible for the balance of CH4 production and consumption by methanogens and methanotrophs, respectively [31]. We found that the ratio of methanogen/methanotroph was the highest in CM and lowest in RL, which can explain the significant CH4 emission in CM and a noticeable CH4 absorption in the RL sites (Figure 2). Chen et al. (2017) also reported a linear relationship between CH4 emission and the methanogen/methanotroph ratio in the Chongxi wetland, a coastal restored wetland in eastern China [17]. Recently, Rey-Sanchez et al. (2019) also reported that the ratio of methanogens to methanotrophs in the upper portion of the peat was significantly correlated with CH4 exchange velocity from a peat bog located in northeastern Ohio [32]. Therefore, we can infer that the methanogen/methanotroph ratio might be a critical factor in determining CH4 emission in wetland soils. However, this conclusion still needs more evidence from other natural wetlands. In addition, the primer mb661r used in this study does not detect all the high-affinity methanotrophs [33], which might further explain the CH4 sink function of the RL site.
4.2. CH4-Cycling Microorganism Composition
4.2.1. Methanogen Composition in Three Vegetation Types
In this study, the Methanosarcinaceae was the most abundant family in the three vegetation types (Figure 3 and Figure 4), indicating that the Methanosarcinaceae are the main CH4-producing methanogens in the Dongting Lake floodplain. The relative percentage of Methanosarcinaceae was significantly increased in CM and RL sites, but the relative percentages of Methanomassiliicoccaceae and Methanomicrobiaceae (nonacetoclastic families) were decreased. This result indicated that the acetate pathway might be the dominant pathway for CH4 production in CM and RL sites since plenty of acetate could be accumulated in the wetland soil due to root secretion and root anaerobic respiration along with plant development [15,34,35]. Furthermore, some nutrient materials (SOC, TN, NH4-N, NO3-N, etc.) produced by root decomposition can also serve as a substrate for Methanosarcinaceae methanogens, leading to a higher relative percentage of Methanosarcinaceae in the CM and RL sites, especially in the 10–20-cm soil layers (Figure 4A). These phenomena were also found in other freshwater wetlands, such as the freshwater–brackish water gradients of the Min River [24], Zoige peatland, and Sanjiang Carex lasiocarpa marsh [36]. However, besides the Methanosarcinaceae, the Methanomicrobiaceae and Methanobacteriaceae are prevalent in MF, suggesting that an H2/CO2 pathway might be the main process for CH4 production in the frequently flooded MF site. These results were also confirmed by Kemnitz et al. (2004), who reported that Methanomicrobiaceae was only found in the permanently and frequently flooded soils in a riparian flooding gradient in the Netherlands [14].
Interestingly, the family Methanomassiliicoccaceae, which was recently discovered in human and animal gastrointestinal tracts (GITs) [37], was detected in the MF and CM sites in our study. One possible explanation for this is that Dongting Lake is an important wintering ground for migratory birds, and CM and MF sites are the main places for their feeding and inhabitation [38]. In this context, the inhabitation of migratory birds in the Dongting Lake floodplain might provide a positive feedback for CH4 production.
4.2.2. Methanotroph Composition in Three Vegetation Types Along an Elevation Gradient
The dominant methanotrophic genera detected in our study were Methylobacter, Methylosarcina (both belonging to type I methanotrophs), and Methylocystis (belonging to type II methanotrophs, Figure 3B). We found that Methylocystis represented the dominant methanotrophic bacteria in the CM site. However, Methylobacter and Methylosarcina were the dominant genera in the MF and RL sites, respectively. It has been documented that type I and type II methanotrophs generally have distinct life strategies, enabling them to predominate under different conditions and maintain functionality [39,40]. Generally, Type I methanotrophs, which respond rapidly to substrate availability and exist as the predominantly active community in many environments, can thus be classified as competitors (C) and competitors-ruderals (C-R). On the contrary, type II methanotrophs were found to persist in inactive states and show versatility in substrate utilization; they are classified as stress tolerators (S) and stress tolerator-ruderals (S-R) [40]. Therefore, the genus Methylocystis (type II methanotrophs), which has repeatedly been found to be associated with a wide variety of environments (such as rice paddies, different upland and hydromorphic soils, landfills, peatlands, and glacier fore fields) [41], was not only dominant in the CM site but also prevalent in the MF and RL sites in the Dongting Lake floodplain (Figure 3B). However, because of the frequent flooding disturbance and water shortage in MF and RL, the methanotrophs living in MF and RL should be more competitive for acquiring O2 and/or water. Therefore, Methylobacter and Methylosarcina (both are type I methanotrophs) act as competitors in MF and RL sites, respectively.
Further, the SWC may act as a critical factor for methanotroph distribution in different soil layers, since the SWC determines soil aeration along a soil profile [26]. In the MF site, the SWC was significantly higher in the 10–30 cm soil layer than in the 0–10 cm soil layer. In the CM site, the SWC was higher in the 0–10 cm and 20–30 cm soil layers, while in the RL site, the SWC was relatively consistent among the three soil layers (Table S2). According to the C-S-R functional classification of methanotrophs, the relative percentage of the genus Methylobacter in MF should be increasing for O2 competition with an increase in soil depth, while the relative percentage of the genus Methylosarcina was consistent in the RL site. Moreover, the diversity of nitrogen metabolism in methanotrophs is well documented [41,42,43]. Type II methanotrophs and members of the type I genus Methylococcus have been shown to be capable of nitrogen fixation, while other type I methanotrophs are not capable of performing this process [44]. Therefore, other factors, such as soil ammonium and nitrate, may also play important roles in selecting the methanotroph type in nature wetland soils, which should be considered in future studies.
4.3. Environmental Controls on CH4-Cycling Microorganisms
Redundancy analysis used multiple linear regressions to explain the variation between independent and dependent variables, and these calculations are performed within the iterative procedure to find the best ordination of the objects [45]. The results of the RDA analysis indicated that the WTD, SWC, and pH are critical factors influencing the methanogen and methanotroph community structure. From water-adjacent areas to higher-elevation lands, the WTD increased, but the SWC decreased, and the soil environment may change from anaerobic to aerobic. Further, the soil pH may also increase with a decrease in SWC [46]. These events may change the living conditions for CH4-cycling microorganisms and eventually reduce CH4 emission with an increase in elevation in a floodplain wetland [16,47].
Further, SEM analysis also showed that the WTD and SWC both had negative direct effects but positive indirect effects on the abundance of methanogens through the soil C and N concentration (i.e., SOC and TN), MBC, and MBN. In the Dongting Lake floodplain, the Carex and reed communities were distributed at 24–25 m and 25–28 m elevations, respectively, and the WTD was 1–1.5 m and 2–3 m in the Carex and reed communities, respectively (Table S2). On the one hand, with an increase in elevation, because of the plant growth and litter decomposition, the soil C and N concentration and microbial biomass were significantly increased, which can supply sufficient substrate for methanogen growth [7,16]. On the other hand, the continuous increase in elevation induced SWC decline; more oxygen can permeate into the soil profile through oxygen loss from rhizosphere [47], which may inhibit methanogen growth in the RL site. Moreover, due to a slower decomposition rate in RL, the complex organic compounds in the RL site cannot be directly utilized by methanogens, which may also result in a lower abundance of methanogens in the RL site [48,49]. Similarly, the continuous decrease in elevation induced SWC increase, but soil C and N shortage may cause a lower methanogen abundance in the MF site. Generally, methanogens are usually active over a pH range of 6.6–7.8, the optimum pH being 6.8, whereas most methanogens can be inhibited if the pH is lower than 6.1 or higher than 8.3 [50,51]; however, methanogen activity was occasionally found to be very high in considerably more acidic environments in ombrotrophic peats [6]. The soil pH in our study site ranged from 7.51–8.07 (Table S2). Therefore, the soil pH could have negatively affected methanogen abundance through its negative influence on SOC and MBC, as confirmed by our SEM results.
For methanotrophs, a higher SOC and TN content can facilitate methanotrophs to assimilate gaseous methane in the soil profiles [52]. The WTD and SWC also had positive indirect effects on the abundance of methanotrophs through their positive effects on the SOC and TN, which can explain the significantly higher abundance of methanotrophs in the CM site, especially in 0-10-cm soil layers. Additionally, more oxygen in the surface layers, combined with moderate SWC, also favors methanotroph growth (Table S2). Similar to the effect of the soil C and N on methanogens, the complex organic compounds in the RL site may also inhibit methanotroph growth, although there is an aerobic environment in the RL site. The soil pH had negative indirect effects on the abundance of methanotrophs, which suggested that methanotrophs may favor a neutral and/or relatively acidic environment [53]. Factually, different methanotrophs are known to have different pH optima [54], and pH can only be considered an indicator rather than a decisive factor for methanotroph abundance in this study.
Previous studies have shown emissions of CH4 from northern peatlands vary as a function of temperature, pH, substrate and nutrient availability, etc. [4]. However, in the subtropical floodplains, the emissions of CH4 combined with methanogens/methanotrophs composition are mainly influenced by WTD, SWC, and pH. The significant change in WTD, SWC, and pH not only determines soil redox potential for CH4 production but also controls substrate and nutrient availability by influencing biogeochemical cycles. Besides the environmental factors considered in this study, other environmental variables, such as the oxygen availability and concentration of metal ions (e.g., Fe3+, Mn4+, and SO42−) in the soil profile and different vegetation, are also reported as critical factors influencing CH4 emission and methane-cycling microorganisms [55,56,57,58]. These observations may account for the unexplained variance of methanogen/methanotroph–environment relationship in this study. This needs further study in the future.
5. Conclusions
This study provided fundamental insights into soil CH4 emissions, the community structure of CH4-cycling microorganisms, and their environmental controls in a subtropical inland floodplain. The Dongting Lake floodplain may change from a CH4 source to a CH4 sink with vegetation succession along an elevation gradient, and the methanogen/methanotroph abundance ratio can be used as a CH4 emission proxy in natural wetlands. In the Dongting Lake floodplain, Methanosarcinaceae is the main CH4-producing methanogen, Methylocystis (type II methanotrophs) represents the dominant methanotrophic bacteria in CM, and Methylobacter and Methylosarcina (type I methanotrophs) are the dominant genera in MF and RL. Methanogen and methanotroph community structures are mainly controlled by the WTD, SWC, and pH along the elevation gradient. The continuous increase in reed area combined with the decrease in CM, which is caused by the decrease in WTD, may mitigate CH4 emission and enhance the CH4 sink function during the non-flood season in the Dongting Lake floodplain.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4433/11/9/997/s1, Figure S1: Rarefaction curve for mcrA(A) and pmoA(B) sequences clustered at 97% similarity across the three site and soil depths in the Dongting floodplain. Figure S2: The phylogenetic trees of methanogens (A) and methanotrophs (B) using approximately-maximum-likelihood method on the basis of the mcrA and pmoA sequences in the soils of three sites in the Dongting floodplain, Table S1: Richness and diversity indices of methanogen (mcrA) and methanotroph (pmoA) at different soil depths in the Dongting Lake floodplain. Table S2: Physicochemical properties of soils at each sampling site on November 10, 2016, in the Dongting Lake floodplain.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology, Y.R. and Z.D.; investigation, Y.R., L.Z., F.L., X.C. (Xinsheng Chen) and Y.Z.; data curation, Y.X.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.R. and Z.D.; writing—review and editing, Y.R., L.Z., Z.D., C.Z., F.X., R.S., X.Z., X.C. (Xian Chen) and X.C. (Xinsheng Chen); visualization, Z.D.; supervision, Y.X.; funding acquisition, Z.D. and F.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Hunan innovative province construction projection (Hunan Key Research and Development Project, 2019NK2011), Training Program for Excellent Young Innovators of Changsha (kq1905048, kq1802026, kh1904002), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41601262), The National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFD0300201), Open Foundation of Key Laboratory of Agro-ecological Processes in Subtropical Region (ISA2019302).
Acknowledgments
The authors immensely thankful to Wei Li for her help in data analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Team, C.W., Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, L., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Saunois, M.; Bousquet, P.; Poulter, B.; Peregon, A.; Ciais, P.; Canadell, J.G.; Dlugokencky, E.J.; Etiope, G.; Bastviken, D.; Houweling, S.; et al. The global methane budget 2000–2012. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2016, 8, 697–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zimmermann, N.E.; Stenke, A.; Li, X.; Hodson, E.L.; Zhu, G.; Huang, C.; Poulter, B. Emerging role of wetland methane emissions in driving 21st century climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 9647–9652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basiliko, N.; Yavitt, J.B.; Dees, P.M.; Merkel, S.M. Methane biogeochemistry and methanogen communities in two northern peatland ecosystems, New York State. Geomicrobiol. J. 2003, 20, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadillo-Quiroz, H.; Brauer, S.; Yashiro, E.; Sun, C.; Yavitt, J.; Zinder, S. Vertical profiles of methanogenesis and methanogens in two contrasting acidic peatlands in central New York State, USA. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1428–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, M.A.; Matthies, C.; Küsel, K.; Schramm, A.; Drake, H.L. Hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis by moderately acid-tolerant methanogens of a methane-emitting acidic peat. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Rooney-Varga, J.N.; Giewat, M.W.; Duddleston, K.N.; Chanton, J.P.; Hines, M.E. Links between archaeal community structure, vegetation type and methanogenic pathway in Alaskan peatlands. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 60, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.T.; Crawford, R.L. Methanogenic bacteria, including an acid-tolerant strain, from peatlands. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 50, 1542–1544. [Google Scholar]
- Bloom, A.A.; Palmer, P.I.; Fraser, A.; Reay, D.S. Seasonal variability of tropical wetland CH4 emissions: The role of the methanogen-available carbon pool. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 2821–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Pangala, S.R.; Enrich-Prast, A.; Basso, L.S.; Peixoto, R.B.; Bastviken, D.; Hornibrook, E.R.C.; Gatti, L.V.; Marotta, H.; Braucks Calazans, L.S.; Sakuragui, C.M.; et al. Large emissions from floodplain trees close the Amazon methane budget. Nature 2017, 552, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batson, J.; Noe, G.B.; Hupp, C.R.; Krauss, K.W.; Rybicki, N.B.; Schenk, E.R. Soil greenhouse gas emissions and carbon budgeting in a short-hydroperiod floodplain wetland. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2015, 120, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, H.-S.; Ochs, C.; Yu, K. Hydrologic gradient and vegetation controls on CH4 and CO2 fluxes in a spring-fed forested wetland. Hydrobiologia 2009, 630, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, G.; Noormets, A.; Domec, J.-C.; Trettin, C.C.; McNulty, S.G.; Sun, G.; King, J.S. The effect of water table fluctuation on soil respiration in a lower coastal plain forested wetland in the southeastern U.S. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2013, 118, 1748–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemnitz, D.; Chin, K.J.; Bodelier, P.; Conrad, R. Community analysis of methanogenic archaea within a riparian flooding gradient. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narihiro, T.; Hori, T.; Nagata, O.; Hoshino, T.; Yumoto, I.; Kamagata, Y. The Impact of Aridification and Vegetation Type on Changes in the Community Structure of Methane-Cycling Microorganisms in Japanese Wetland Soils. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 75, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tian, J.; Chen, H.; Dong, X.; Wang, Y. Relationship between archaeal community structure and vegetation type in a fen on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2012, 48, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Wu, S.; Jiang, Y.; den Camp, H.J.O.; Li, Z.; Zhu, G.; Zheng, J.; Wang, Y. Shifts of archaeal community structure in soil along an elevation gradient in a reservoir water level fluctuation zone. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 2728–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire Silva, T.S.; Costa, M.P.F.; Novo, E.M.L.M.; Melack, J.M. A Multisensor, Multitemporal Approach for Monitoring Herbaceous Vegetation Growth in the Amazon Floodplain; IEEE: Banff, AB, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.-Y.; Xie, Y.-H.; Tang, Y.; Li, F.; Zou, Y.-A. Changes of vegetation distribution in the east Dongting Lake after the operation of the Three Gorges Dam, China. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 582. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.H.; Yue, T.; Xin-sheng, C.; Feng, L.; Zheng-miao, D. The impact of Three Gorges Dam on the downstream eco-hydrological environment and vegetation distribution of East Dongting Lake. Ecohydrology 2015, 8, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.-M.; Chen, X.-S.; Xie, Y.-H.; Xie, Y.-J.; Hou, Z.-Y.; Li, F. The role of seedling recruitment from juvenile populations of Carex brevicuspis (Cyperaceae) at the Dongting Lake wetlands, China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.S.; Li, X.; Xie, Y.H.; Li, F.; Hou, Z.Y.; Zeng, J. Combined influence of hydrological gradient and edaphic factors on the distribution of macrophyte communities in Dongting Lake wetlands, China. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 23, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Kelly, B.C. Accurate Determination of Moisture Content of Organic Soils Using the Oven Drying Method. Dry. Technol. 2004, 22, 1767–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; Cadillo-Quiroz, H.; Zeng, Z.H.; She, C.X.; Yang, P.; Huang, J.F. Changes of community structure and abundance of methanogens in soils along a freshwater-brackish water gradient in subtropical estuarine marshes. Geoderma 2017, 299, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Joergensen, R.; Pommerening, B.; Chaussod, R.; Brookes, P. Measurement of soil microbial biomass C by fumigation-extraction-an automated procedure. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1990, 22, 1167–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Li, Y.; Xie, Y.; Peng, C.; Chen, X.; Li, F.; Ren, Y.; Pan, B.; Zhang, C. Hydrologic and Edaphic Controls on Soil Carbon Emission in Dongting Lake Floodplain, China. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2018, 123, 3088–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luton, P.E.; Wayne, J.M.; Sharp, R.J.; Riley, P.W. The mcrA gene as an alternative to 16S rRNA in the phylogenetic analysis of methanogen populations in landfillb. Microbiology 2002, 148, 3521–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, A.J.; Costello, A.; Lidstrom, M.E.; Murrell, J.C. Evidence that participate methane monooxygenase and ammonia monooxygenase may be evolutionarily related. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1995, 132, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, A.M.; Lidstrom, M.E. Molecular characterization of functional and phylogenetic genes from natural populations of methanotrophs in lake sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 5066–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Sanders, N.J.; Shi, Y.; Chu, H.; Classen, A.T.; Zhao, K.; Chen, L.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, Y.; He, J.-S. The links between ecosystem multifunctionality and above- and belowground biodiversity are mediated by climate. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ma, H.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Liang, X.; He, C. Changes in methane emission and methanogenic and methanotrophic communities in restored wetland with introduction of Alnus trabeculosa. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Sanchez, C.; Bohrer, G.; Slater, J.; Li, Y.; Grau-Andrés, R.; Hao, Y.; Rich, V.; Davies, G. The ratio of methanogens to methanotrophs and water-level dynamics drive methane exchange velocity in a temperate kettle-hole peat bog. Biogeosciences 2019, 16, 3207–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, D.G.; McDonald, I.R.; Murrell, J.C. Comparison of pmoA PCR primer sets as tools for investigating methanotroph diversity in three Danish soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 3802–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galand, P.E.; Saarnio, S.; Fritze, H.; Yrjala, K. Depth related diversity of methanogen Archaea in Finnish oligotrophic fen. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2002, 42, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Jin, F.; Lu, C.H.; Baoyin, T.G.T.; Jia, Z.J. Shifts in the community composition of methane-cycling microorganisms during lake shrinkage. Geoderma 2018, 311, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Ding, W.; Jia, Z.; Cai, Z. The impact of dissolved organic carbon on the spatial variability of methanogenic archaea communities in natural wetland ecosystems across China. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollinger, A.; Schwab, C.; Weinmaier, T.; Loy, A.; Tveit, A.T.; Schleper, C.; Urich, T. Phylogenetic and genomic analysis of Methanomassiliicoccales in wetlands and animal intestinal tracts reveals clade-specific habitat preferences. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiv149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.-A.; Zhang, P.-Y.; Zhang, S.-Q.; Chen, X.-S.; Li, F.; Deng, Z.-M.; Yang, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, F.-Y.; Xie, Y.-H. Crucial sites and environmental variables for wintering migratory waterbird population distributions in the natural wetlands in East Dongting Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.; Kerckhof, F.M.; Luke, C.; Reim, A.; Krause, S.; Boon, N.; Bodelier, P.L. Conceptualizing functional traits and ecological characteristics of methane-oxidizing bacteria as life strategies. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, A.; Luke, C.; Frenzel, P. Recovery of methanotrophs from disturbance: Population dynamics, evenness and functioning. ISME J. 2011, 5, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dam, B.; Dam, S.; Blom, J.; Liesack, W. Genome Analysis Coupled with Physiological Studies Reveals a Diverse Nitrogen Metabolism in Methylocystis sp. Strain SC2. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoefman, S.; van der Ha, D.; Boon, N.; Vandamme, P.; De Vos, P.; Heylen, K. Niche differentiation in nitrogen metabolism among methanotrophs within an operational taxonomic unit. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, L.Y.; Klotz, M.G. Nitrifying and denitrifying pathways of methanotrophic bacteria. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011, 39, 1826–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auman, A.J.; Speake, C.C.; Lidstrom, M.E. nifH sequences and nitrogen fixation in type I and type II methanotrophs. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 4009–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramette, A. Multivariate analyses in microbial ecology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 62, 142–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Gao, P.; He, X. The water-level fluctuation zone of Three Gorges Reservoir—A unique geomorphological unit. Earth Sci. Rev. 2015, 150, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyos-Santillan, J.; Craigon, J.; Lomax, B.H.; Lopez, O.R.; Turner, B.L.; Sjogersten, S. Root oxygen loss from Raphia taedigera palms mediates greenhouse gas emissions in lowland neotropical peatlands. Plant Soil 2016, 404, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Xie, Y.; Xiao, H.; Chen, X.; Li, F. Controls on Litter Decomposition of Emergent Macrophyte in Dongting Lake Wetlands. Ecosystems 2017, 20, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgham, S.D.; Cadillo-Quiroz, H.; Keller, J.K.; Zhuang, Q. Methane emissions from wetlands: Biogeochemical, microbial, and modeling perspectives from local to global scales. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 1325–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, J.-J.; Li, Y.-Y.; Noike, T. Influences of pH and moisture content on the methane production in high-solids sludge digestion. Water Res. 1997, 31, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.P.; DeLaune, R.D.; Patrick, W.H.; Masscheleyn, P.H. Soil Redox and pH Effects on Methane Production in a Flooded Rice Soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1993, 57, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodelier, P.L.E. Interactions between nitrogenous fertilizers and methane cycling in wetland and upland soils. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2011, 3, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.F.U.; Crombie, A.T.; Ensminger, S.A.; Baciu, C.; Murrell, J.C. Facultative methanotrophs are abundant at terrestrial natural gas seeps. Microbiome 2018, 6, 118. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, R.S.; Hanson, T.E. Methanotrophic bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1996, 60, 439–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, M.S.; Wu, J.; Reed, B.C.; Kretz, C.B.; Belli, K.M.; Simister, R.L.; Henny, C.; Stewart, F.J.; DiChristina, T.J.; Brandes, J.A.; et al. Shifting microbial communities sustain multiyear iron reduction and methanogenesis in ferruginous sediment incubations. Geobiology 2017, 15, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, S.R.; Bandeppa, G.S.; Dubey, G.; Ahirwar, U.; Patra, A.K.; Bharati, K. Methane oxidation in response to iron reduction-oxidation metabolism in tropical soils. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2017, 78, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivan, O.; Shusta, S.; Valentine, D. Methanogens rapidly transition from methane production to iron reduction. Geobiology 2016, 14, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Zeng, C.-S.; Tong, C.; Huang, J.-F.; Chen, K.; Liu, F.-Q. Iron Reduction Along an Inundation Gradient in a Tidal Sedge (Cyperus malaccensis) Marsh: The Rates, Pathways, and Contributions to Anaerobic Organic Matter Mineralization. Estuaries Coasts 2016, 39, 1679–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).