Did ERA5 Improve Temperature and Precipitation Reanalysis over East Africa?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Study Approach
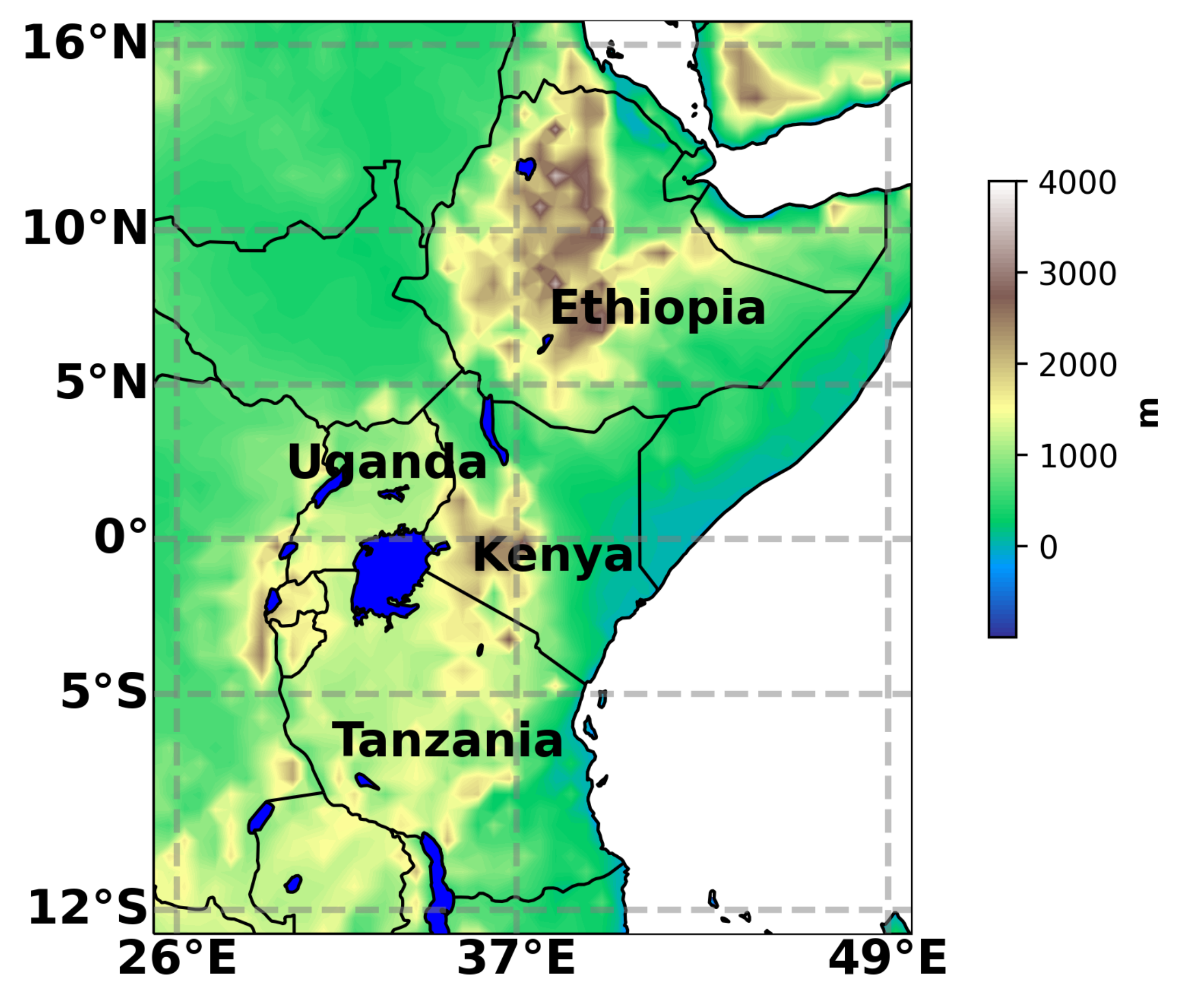
2.1. Study Region
2.2. ERA5 and ERA-interim Reanalysis Data
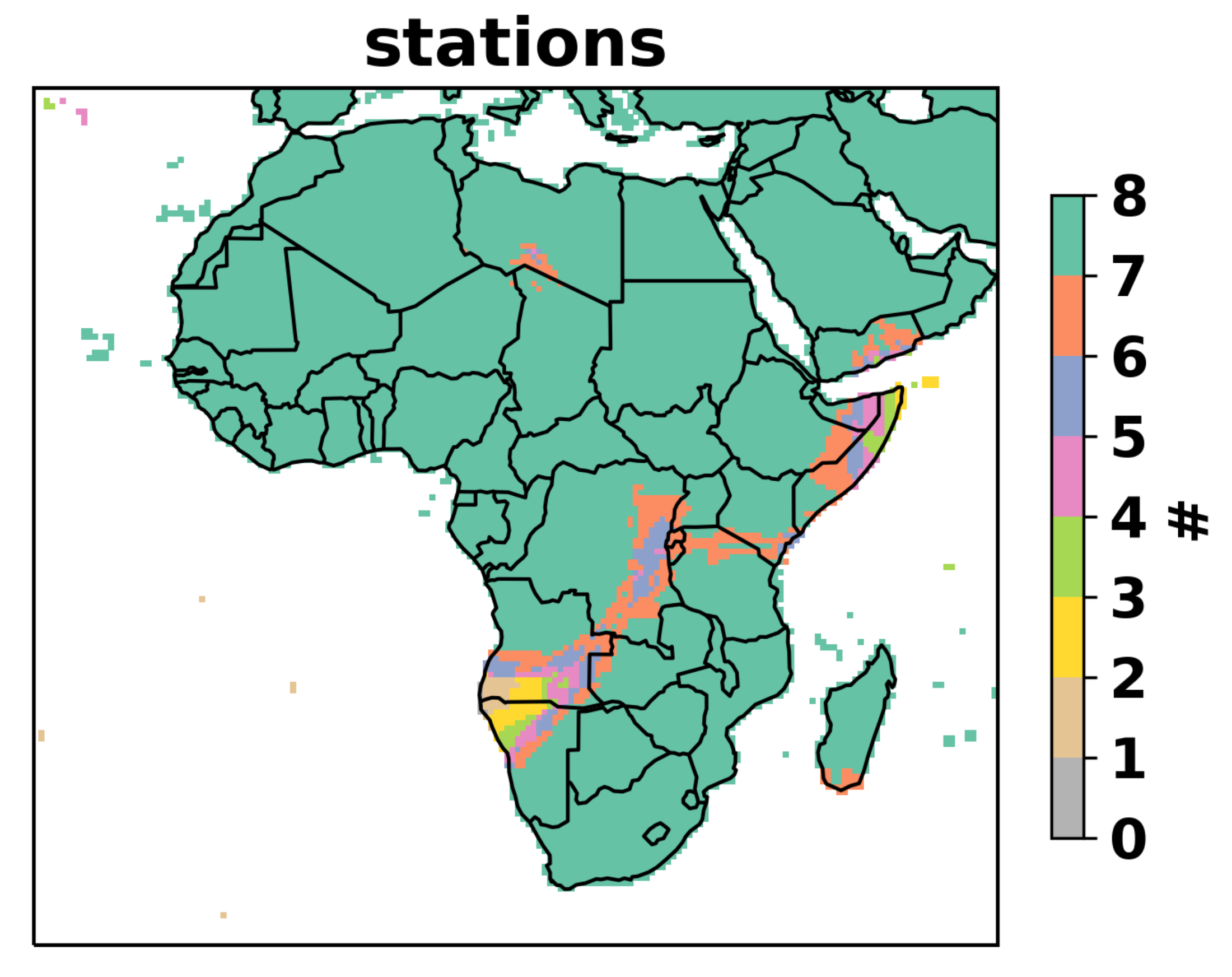
2.3. Observational Data for Evaluation
2.4. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
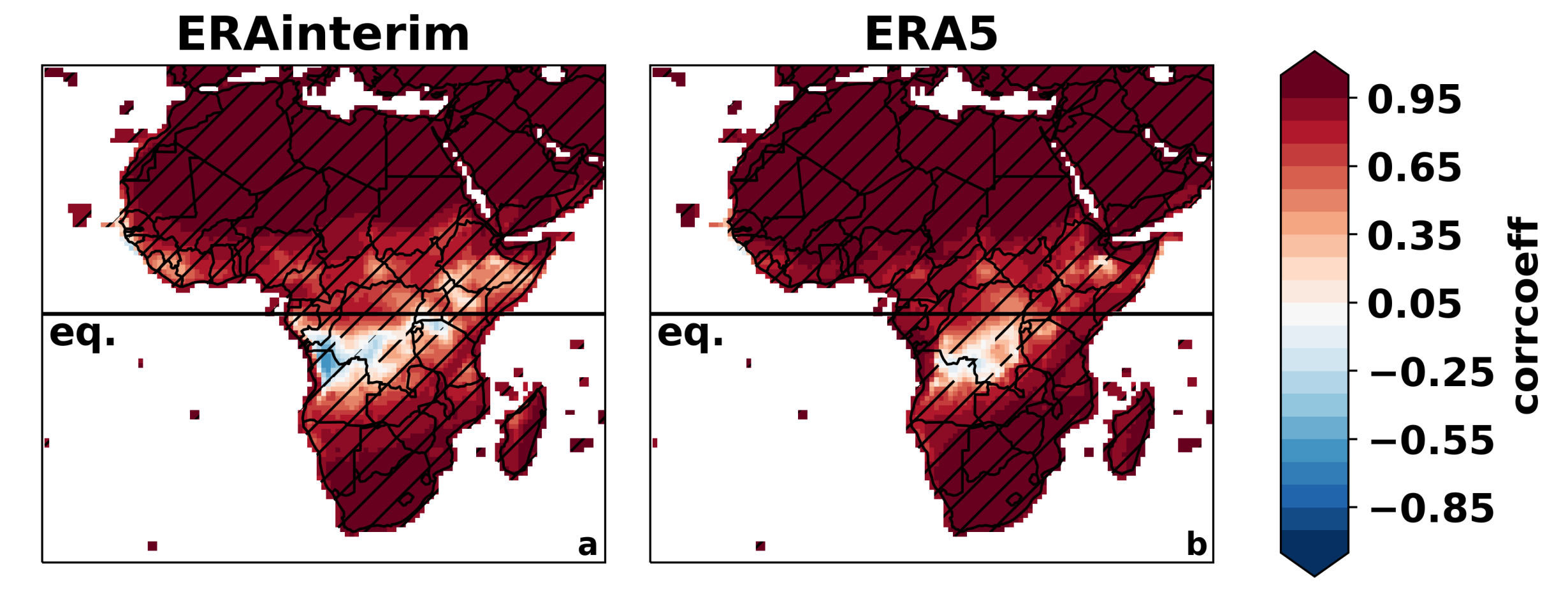
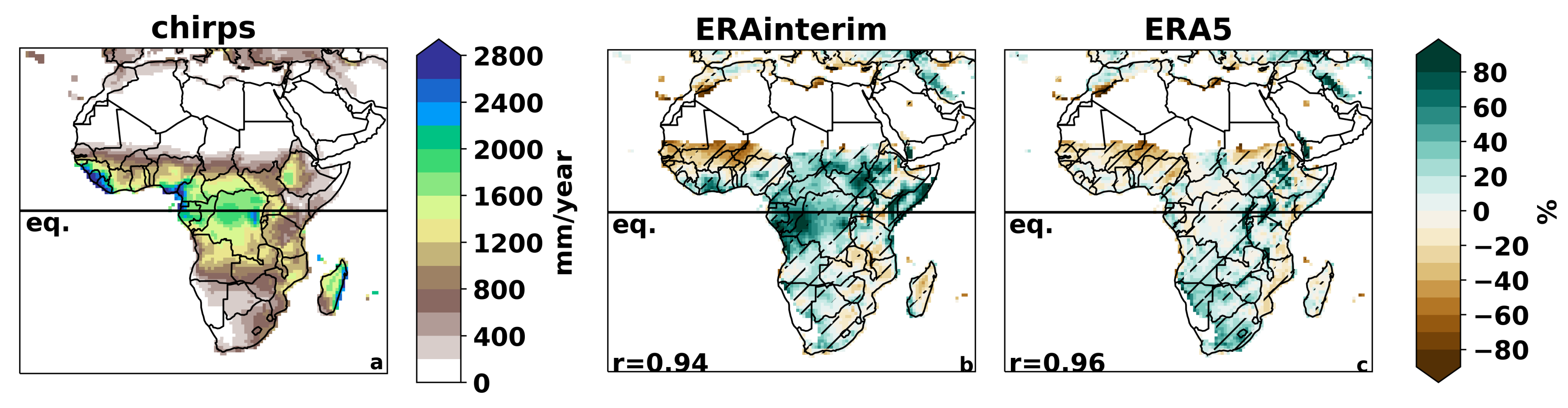
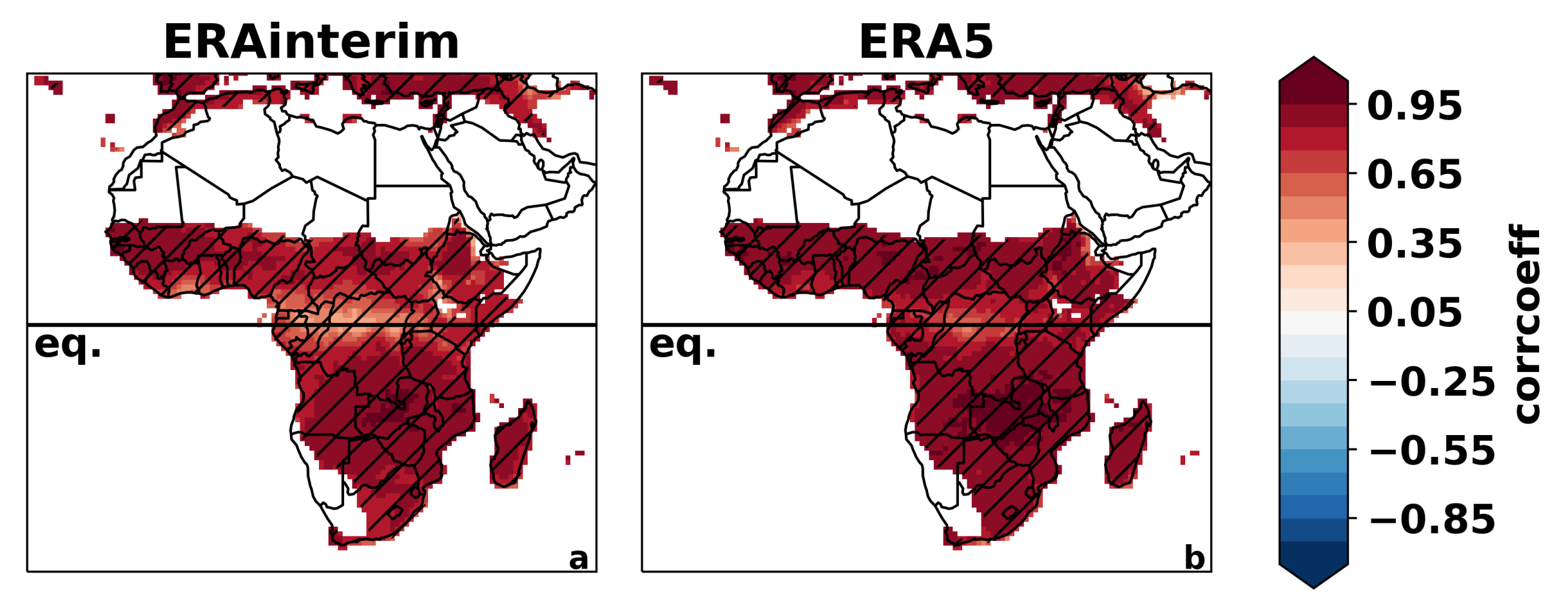
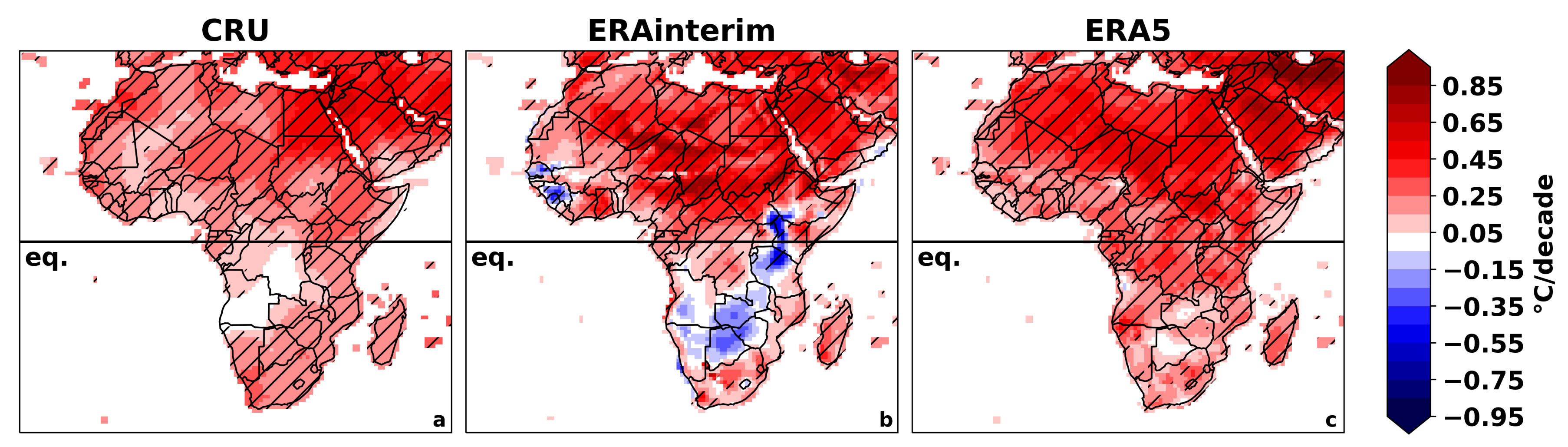
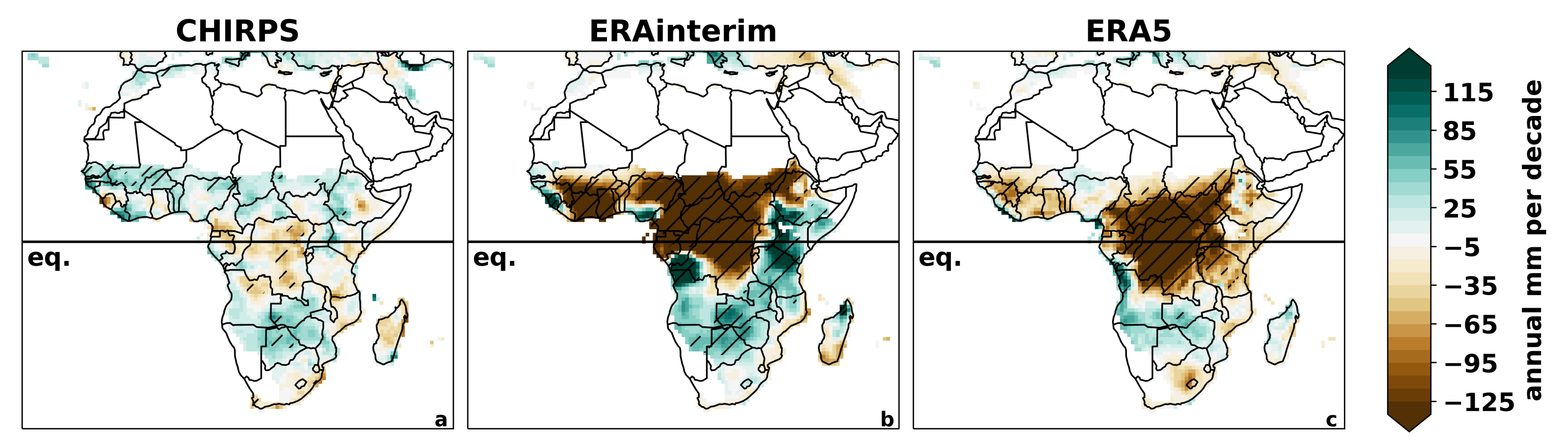
3.1. All-Africa Evaluation
3.1.1. Spatial and Temporal Variability of Temperature and Precipitation
3.1.2. Linear Trends
3.2. Regional Analysis
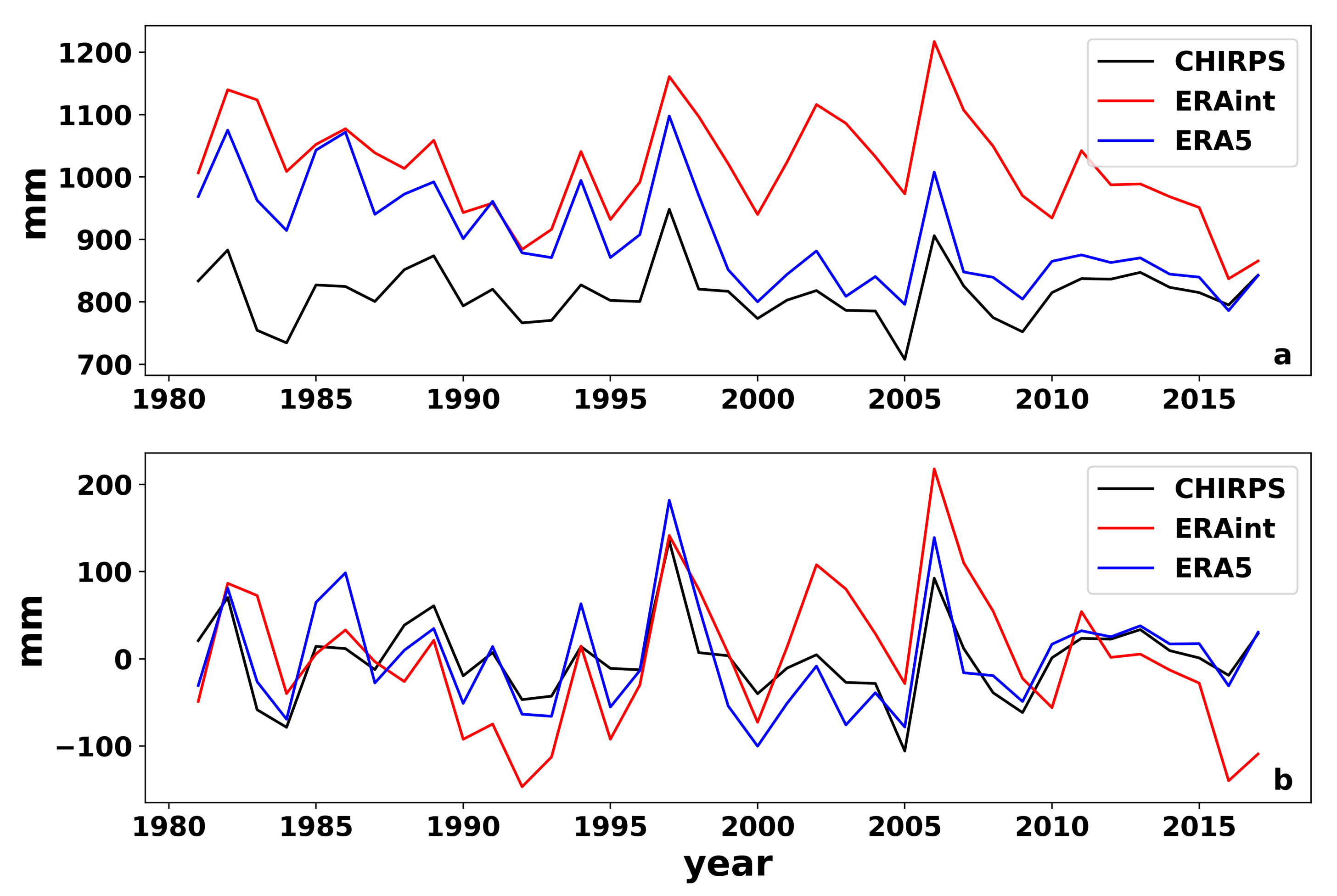
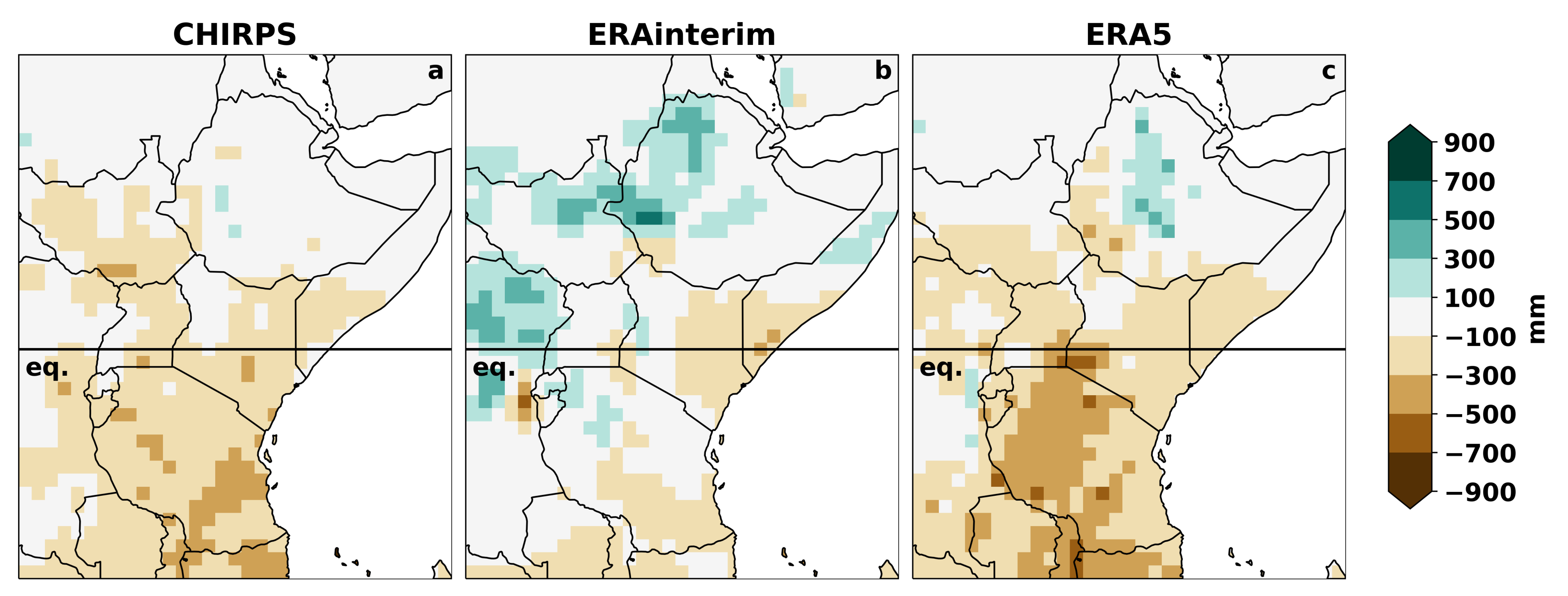
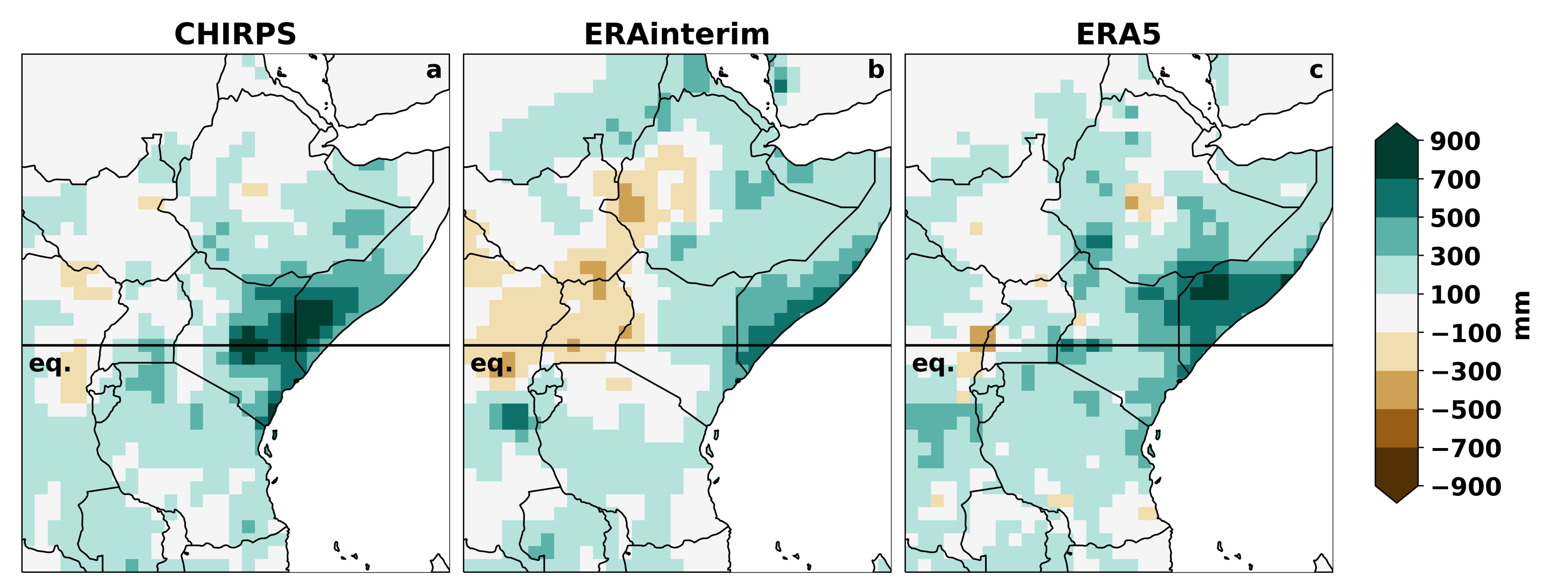
3.2.1. East African Precipitation Cycle
3.2.2. Extreme Precipitation Years
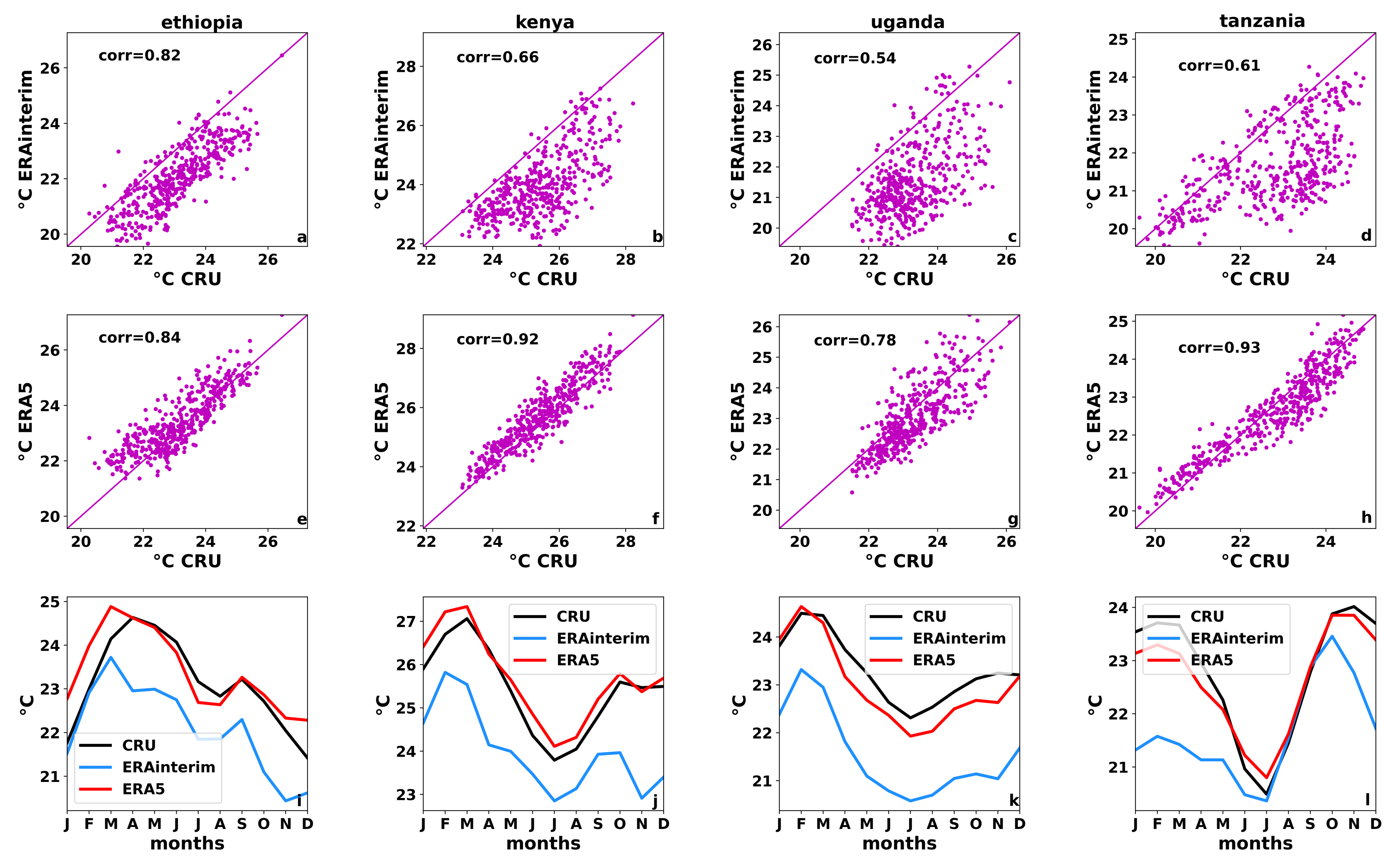
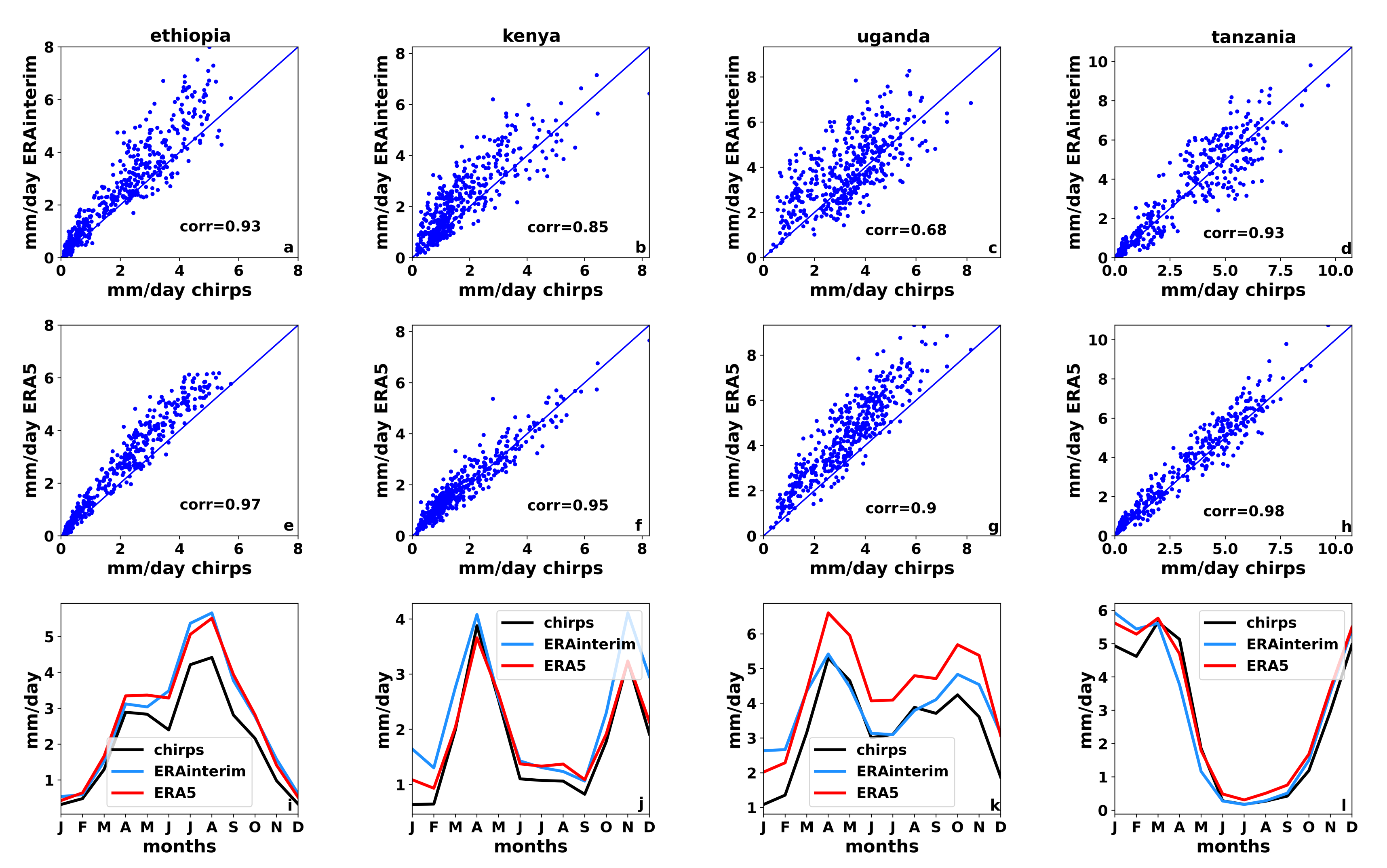
3.3. Country-Level Evaluation
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part B: Regional Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. In Climate Change 2014; Barros, V., Field, C., Dokken, D., Mastrandrea, M., Mach, K., Bilir, T.E., Ebi, K., Estrada, Y., Genova, R., Girma, B., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014; p. 688. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.A.; Diffenbaugh, N.S.; Hertel, T.W.; Lobell, D.B.; Ramankutty, N.; Rios, A.R.; Rowhani, P. Climate Volatility and Poverty Vulnerability in Tanzania; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hertel, T.W.; Burke, M.B.; Lobell, D.B. The poverty implications of climate-induced crop yield changes by 2030. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2010, 20, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. Agriculture for Development; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. Development and Climate Change. World Development Report 2010; Technical Report; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dinku, T. Challenges with availability and quality of climate data in Africa. In Extreme Hydrology and Climate Variability; Melesse, A.M., Abtew, W., Senay, G.B.T.E.H., Variability, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Chapter 7; pp. 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, I.; Jones, P.D.; Osborn, T.J.; Lister, D.H. Updated high-resolution grids of monthly climatic observations—The CRU TS3.10 Dataset. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 623–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maidment, R.I.; Grimes, D.; Black, E.; Tarnavsky, E.; Young, M.; Greatrex, H.; Allan, R.P.; Stein, T.; Nkonde, E.; Senkunda, S.; et al. A new, long-term daily satellite-based rainfall dataset for operational monitoring in Africa. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novella, N.S.; Thiaw, W.M. African rainfall climatology version 2 for famine early warning systems. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Maidment, R.I.; Tadesse, T.; Gadain, H.; Ceccato, P. Validation of the CHIRPS satellite rainfall estimates over eastern Africa. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 144, 292–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Rowland, J.; Romero, B.; Husak, G.; Michaelsen, J.; Verdin, A. A quasi-global precipitation time series for drought monitoring. U.S. Geol. Surv. Data Ser. 2014, 832, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, I.C.; Osborne, T.; Jones, P.; Lister, D. Version 4 of the CRU TS monthly high-resolution gridded multivariate climate dataset. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 2052–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, T.J.; Jones, P.D. The CRUTEM4 land-surface air temperature data set: Construction, previous versions and dissemination via Google earth. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2014, 6, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenssen, N.; Schmidt, G.; Hansen, J.; Menne, M.; Persin, A.; Ruedy, R.; Zyss, D. Improvements in the GISTEMP uncertainty model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmospheres. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 6307–6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.M.; Reynolds, R.W.; Peterson, T.C.; Lawrimore, J. Improvements to NOAA’s historical merged land-ocean surface temperature analysis (1880–2006). J. Clim. 2008, 21, 2283–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrimore, J.H.; Menne, M.J.; Gleason, B.E.; Williams, C.N.; Wuertz, D.B.; Vose, R.S.; Rennie, J. An overview of the Global Historical Climatology Network monthly mean temperature data set, version 3. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, M.; Brunke, M.A.; Wang, Z.; Sakaguchi, K.; Zeng, X.; Bosilovich, M.G. Evaluation of the reanalysis products from GSFC, NCEP, and ECMWF using flux tower observations. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 1916–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, A.J.; Jones, P.D.; da Costa Bechtold, V.; Beljaars, A.C.; Kållberg, P.W.; Saarinen, S.; Uppala, S.M.; Viterbo, P.; Wedi, N. Comparison of trends and low-frequency variability in CRU, ERA-40, and NCEP/NCAR analyses of surface air temperature. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, R.; Wensnahan, M.; Schweiger, A.; Zhang, J. Evaluation of Seven Different Atmospheric Reanalysis Products in the Arctic. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 2588–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Ge, F.; Yang, K.; Zhu, S.; Peng, T.; Cai, W.; Liu, X.; Tang, W. Assessment of ECMWF reanalysis data in complex terrain: Can the CERA-20C and ERA-interim data sets replicate the variation in surface air temperatures over Sichuan, China? Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 5619–5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlu, D.; Moges, S.A.; Nikolopoulos, E.I.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Hailu, D. Evaluation of High-Resolution Multisatellite and Reanalysis Rainfall Products over East Africa. Adv. Meteorol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. Performance of three reanalysis precipitation datasets over the qinling-daba mountains, eastern fringe of tibetan plateau, China. Adv. Meteorol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Wollen, J.; et al. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppala, S.M.; Kållberg, P.W.; Simmons, A.J.; Andrae, U.; da Costa Bechtold, V.; Fiorino, M.; Gibson, J.K.; Haseler, J.; Hernandez, A.; Kelly, G.A.; et al. The ERA-40 re-analysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 131, 2961–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollmann, R. Precipitation—Essential Climate Variable (ECV) Factsheet; Technical Report; GCOS: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, P.; Thorpe, A.; Brunet, G. The quiet revolution of numerical weather prediction. Nature 2015, 525, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legates, D.R. Climate Models and their Simulation of Precipitation. Energy Environ. 2014, 25, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poccard, I.; Janicot, S.; Camberlin, P. Comparison of rainfall structures between NCEP/NCAR reanalyses and observed data over tropical Africa. Clim. Dyn. 2000, 16, 897–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diro, G.; Grimes, D.I.F.; Black, E.; O’Neill, A.; Pardo-Iguzquiza, E. Evaluation of reanalysis rainfall estimates over Ethiopia. Int. J. Climatol. 2009, 29, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diro, G.; Toniazzo, T.; Shaffrey, L. Ethiopian rainfall in climate models. In African Climate and Climate Change; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 51–69. [Google Scholar]
- Lemma, E.; Upadhyaya, S.; Ramsankaran, R. Investigating the performance of satellite and reanalysis rainfall products at monthly timescales across different rainfall regimes of Ethiopia. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 4019–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsouris, A.J.; Chen, D.; Lyon, S.W. Comparing global precipitation data sets in eastern Africa: A case study of Kilombero Valley, Tanzania. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 2000–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Horányi, A.; Sabater, J.M.; Nicolas, J.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; Simmons, A.; Cornel Soci, D.D. Global reanalysis: Goodbye ERA-interim, hello ERA5. ECMWF Newsl. 2019, 159, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Martens, B.; Schumacher, D.L.; Wouters, H.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; Miralles, D.G. Evaluating the surface energy partitioning in ERA5. Geosci. Model Dev. Discuss. 2020, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urraca, R.; Huld, T.; Gracia-Amillo, A.; Martinez-de Pison, F.J.; Kaspar, F.; Sanz-Garcia, A. Evaluation of global horizontal irradiance estimates from ERA5 and COSMO-REA6 reanalyses using ground and satellite-based data. Sol. Energy 2018, 164, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, A.K.; Chan, D.Z.; Desjardins, R.L. Near-Surface Biases in ERA5 Over the Canadian Prairies. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarek, M.; Brissette, F.P.; Arsenault, R.; De, É.; West, N.D. Evaluation of the ERA5 reanalysis as a potential reference dataset for hydrological modelling over North America. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 2527–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Zimmermann, N.E.; McVicar, T.R.; Vergopolan, N.; Berg, A.; Wood, E.F. Present and future köppen-geiger climate classification maps at 1-km resolution. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, S. The Turkana low-level jet: Mean climatology and association with regional aridity. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 2598–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Seager, R.; Cane, M.A.; Lyon, B. The annual cycle of East African precipitation. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 2385–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, T.R.; Hain, C.R.; Anderson, M.C.; Crow, W.T. Cloud tolerance of remote-sensing technologies to measure land surface temperature. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 3263–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awange, J.L.; Ferreira, V.G.; Forootan, E.; Andam-Akorful, S.A.; Agutu, N.O.; He, X.F. Uncertainties in remotely sensed precipitation data over Africa. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 303–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Ceccato, P.; Grover-Kopec, E.; Lemma, M.; Connor, S.J.; Ropelewski, C.F. Validation of satellite rainfall products over East Africa’s complex topography. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 1503–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Ceccato, P.; Connor, S.J. Challenges of satellite rainfall estimation over mountainous and arid parts of east Africa. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 5965–5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, A.J.; Uppala, S.; Dee, D.; Kobayashi, S. ERA-interim: New ECMWF reanalysis products from 1989 onwards. ECMWF Newsl. 2007, 110, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennermann, K.; Giusti, M. ERA5: Data Documentation; Technical Report; ECMWF: Reading, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Weedon, G.P.; Balsamo, G.; Bellouin, N.; Gomes, S.; Best, M.J.; Viterbo, P. The WFDEI meteorological forcing data set: WATCH Forcing Data methodology applied to ERA-interim reanalysis data. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 7505–7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthoni, F.K.; Odongo, V.O.; Ochieng, J.; Mugalavai, E.M.; Mourice, S.K.; Hoesche-Zeledon, I.; Mwila, M.; Bekunda, M. Long-term spatial-temporal trends and variability of rainfall over Eastern and Southern Africa. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 137, 1869–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, S.I.; Lennon, J.J. Deriving meteorological variables across Africa for the study and control of vector-borne disease: A comparison of remote sensing and spatial interpolation of climate. Trop. Med. Int. Health 1999, 4, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylla, M.B.; Giorgi, F.; Coppola, E.; Mariotti, L. Uncertainties in daily rainfall over Africa: Assessment of gridded observation products and evaluation of a regional climate model simulation. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 1805–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, T.W.; Dhanya, C.; Gosain, A. Evaluation of ERA-interim, MERRA, NCEP-DOE R2 and CFSR Reanalysis precipitation Data using Gauge Observation over Ethiopia for a period of 33 years. AIMS Environ. Sci. 2017, 4, 596–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, A.J.; Willett, K.M.; Jones, P.D.; Thorne, P.W.; Dee, D.P. Low-frequency variations in surface atmospheric humidity, temperature, and precipitation: Inferences from reanalyses and monthly gridded observational data sets. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Zhou, T.; Qian, Y. Evaluation of Global Monsoon Precipitation Changes based on Five Reanalysis Datasets. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 1271–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jury, M.R. Climate trends in southern Africa. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2013, 109, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J.M. Temperature Variability over Africa. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 3649–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, L.; Hagemann, S.; Hodges, K.I. Can climate trends be calculated from reanalysis data? J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Koike, T.; Onogi, K. Progress and Prospects for Reanalysis for Weather and Climate. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2008, 89, 234–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, P.W.; Vose, R.S. Reanalyses Suitable for Characterizing Long-Term Trends. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, E.P.; Hendon, H.H. Causes and Predictability of the Negative Indian Ocean Dipole and Its Impact on La Niña During 2016. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henricksen, B.L. Reflections on drought: Ethiopia 1983–1984. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1986, 7, 1447–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparna, S.G.; McCreary, J.P.; Shankar, D.; Vinayachandran, P.N. Signatures of Indian Ocean Dipole and El Niño–Southern Oscillation events in sea level variations in the Bay of Bengal. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahaga, T.; Mengistu Tsidu, G.; Kucharski, F.; Diro, G. Potential predictability of the sea-surface temperature forced equatorial East African short rains interannual variability in the 20th century. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 141, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, D.; Tank, A.K.; Rusticucci, M.; Alexander, L.; Brönnimann, S.; Charabi, Y.; Dentener, F.; Dlugokencky, E.; Easterling, D.; Kaplan, A.; et al. Observations: Atmosphere and surface. In Climate Change 2013 the Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Hartmann, D.L., Klein Tank, A.M., Rusticucci, M., Alexander, L.V., Brönnimann, S., Charabi, Y.A.R., Dentener, F.J., Dlugokencky, E.J., Easterling, D.R., Kaplan, A., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 159–254. [Google Scholar]
- Hastenrath, S.; Polzin, D.; Mutai, C. Diagnosing the 2005 Drought in Equatorial East Africa. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 4628–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, G.D.; Halpert, M.S. Climate Assessment for 1997. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, S1–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Vergopolan, N.; Pan, M.; Levizzani, V.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Weedon, G.P.; Brocca, L.; Pappenberger, F.; Huffman, G.J.; Wood, E.F. Global-scale evaluation of 22 precipitation datasets using gauge observations and hydrological modeling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 6201–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.H.; Li, Q.X.; Yang, S.; Xu, Y. Overview of global monthly surface temperature data in the past century and preliminary integration. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2014, 5, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Dutra, E.; Balsamo, G.; Boussetta, S.; Zsoter, E.; Albergel, C.; Agusti-Panareda, A. ERA5-Land: An improved version of the ERA5 reanalysis land component. In Proceedings of the 8th Workshop-Joint ISWG and LSA-SAF Workshop, Lisbon, Portugal, 26–28 June 2018; pp. 26–28. [Google Scholar]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gleixner, S.; Demissie, T.; Diro, G.T. Did ERA5 Improve Temperature and Precipitation Reanalysis over East Africa? Atmosphere 2020, 11, 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090996
Gleixner S, Demissie T, Diro GT. Did ERA5 Improve Temperature and Precipitation Reanalysis over East Africa? Atmosphere. 2020; 11(9):996. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090996
Chicago/Turabian StyleGleixner, Stephanie, Teferi Demissie, and Gulilat Tefera Diro. 2020. "Did ERA5 Improve Temperature and Precipitation Reanalysis over East Africa?" Atmosphere 11, no. 9: 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090996
APA StyleGleixner, S., Demissie, T., & Diro, G. T. (2020). Did ERA5 Improve Temperature and Precipitation Reanalysis over East Africa? Atmosphere, 11(9), 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090996




