Characterization of Spatio-Temporal Trends and Periodicity of Precipitation over Malawi during 1979–2015
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area, Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Climate Data Quality Control and Homogenization
2.3.2. Empirical Orthogonal Function (EOF) Analysis
2.3.3. Linear Trend Test
2.3.4. Mann–Kendall Test
2.3.5. Wavelet Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Preliminary Analysis
3.2. Long-Term Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Rainfall
3.2.1. Analysis of Annual Mean Rainfall Cycle
3.2.2. Spatial Analysis of Wet Season Precipitation
3.3. Long-Term Monotonic Trends for Precipitation
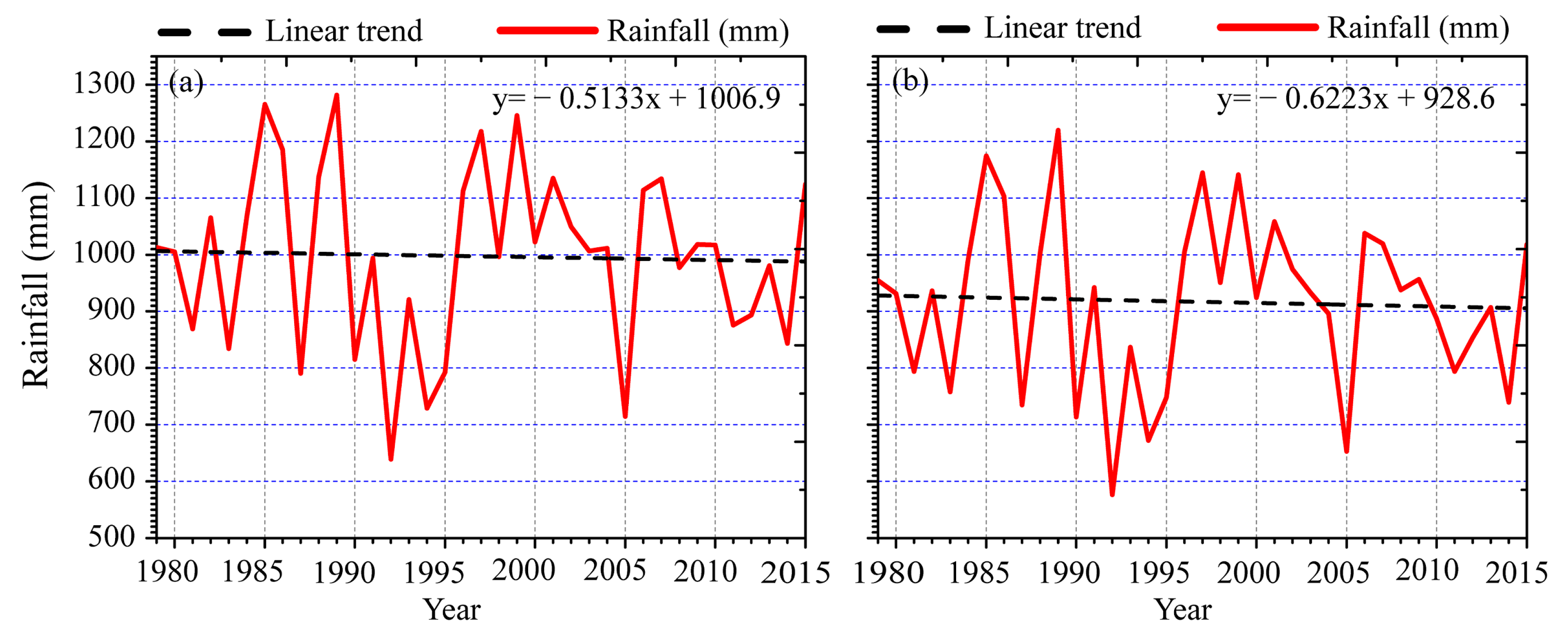
3.3.1. Temporal Trends of Seasonal and Annual Precipitation
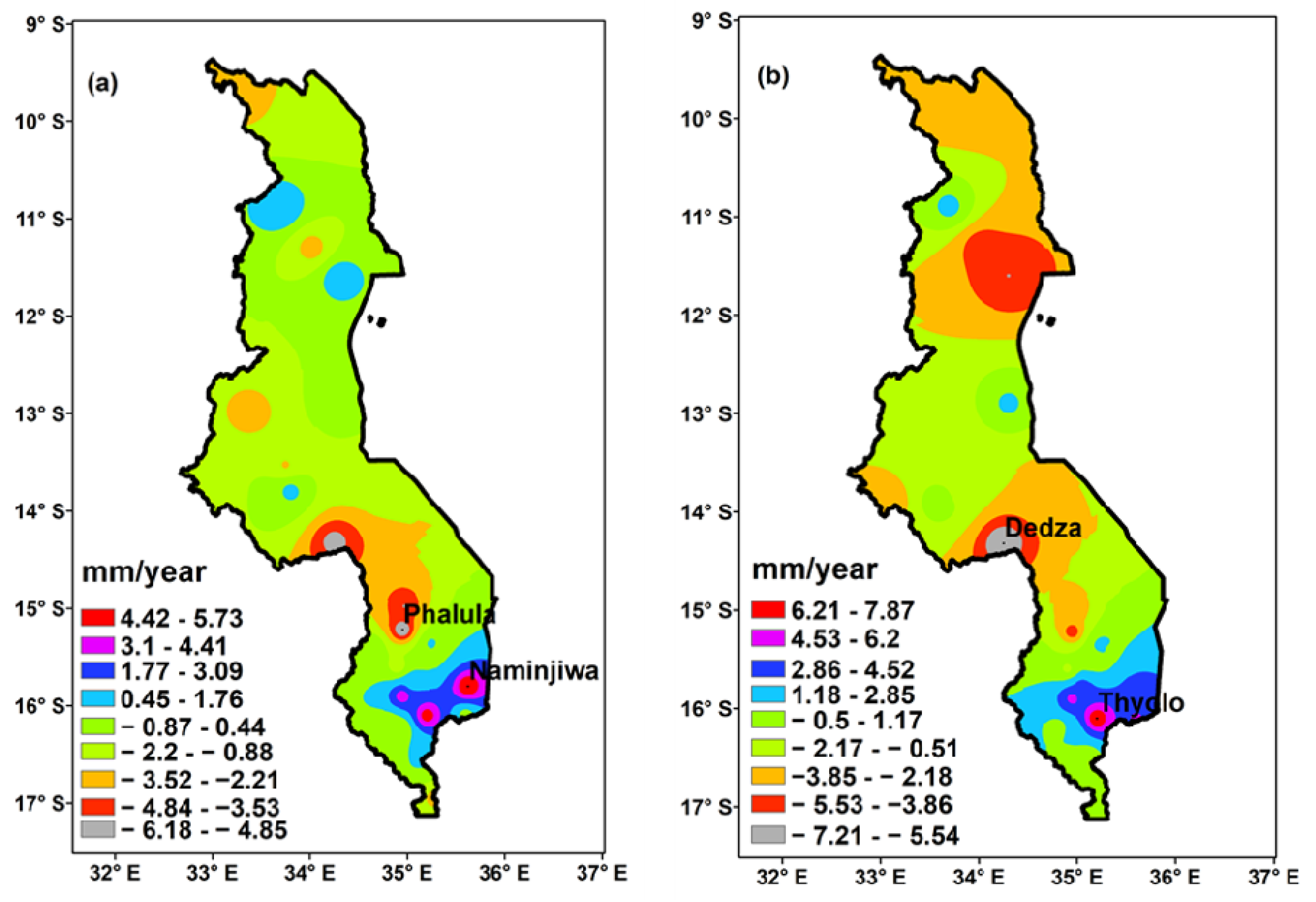
3.3.2. Spatial Variability of the Temporal Trends of Precipitation
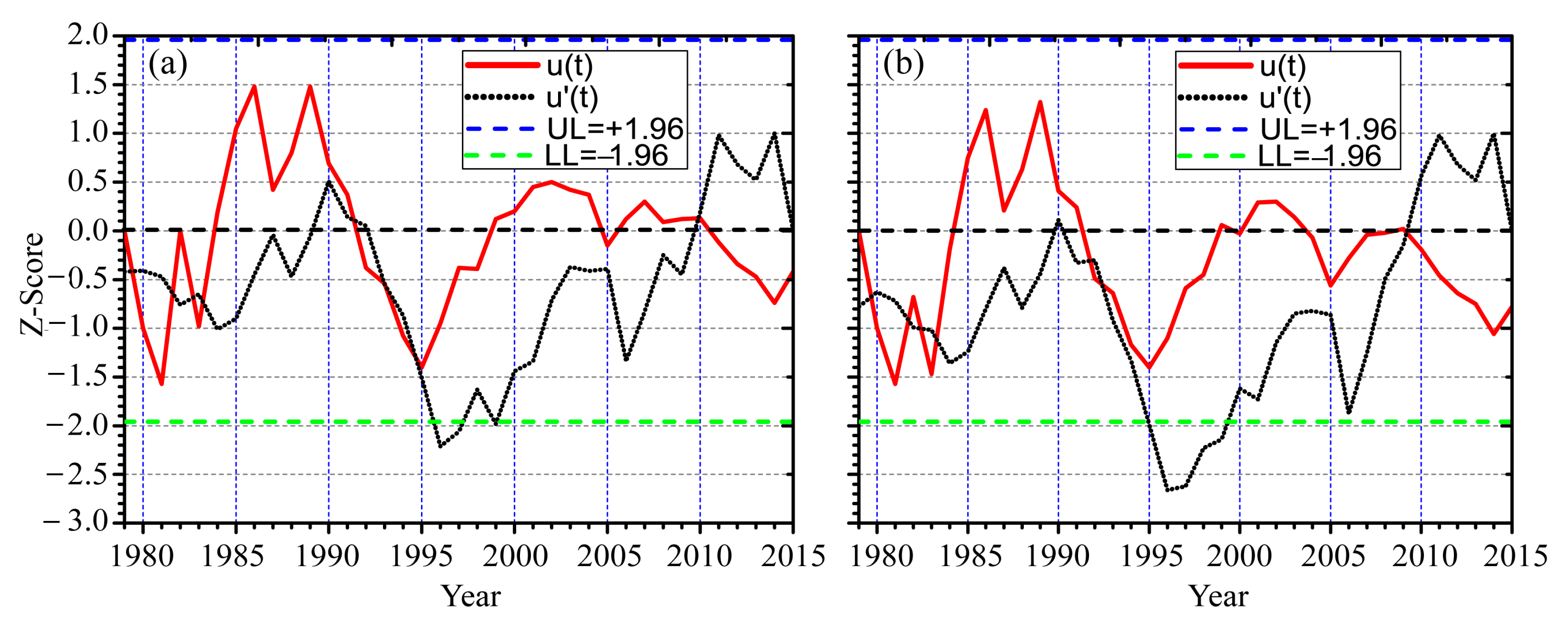
3.3.3. Sequential MK Test Results
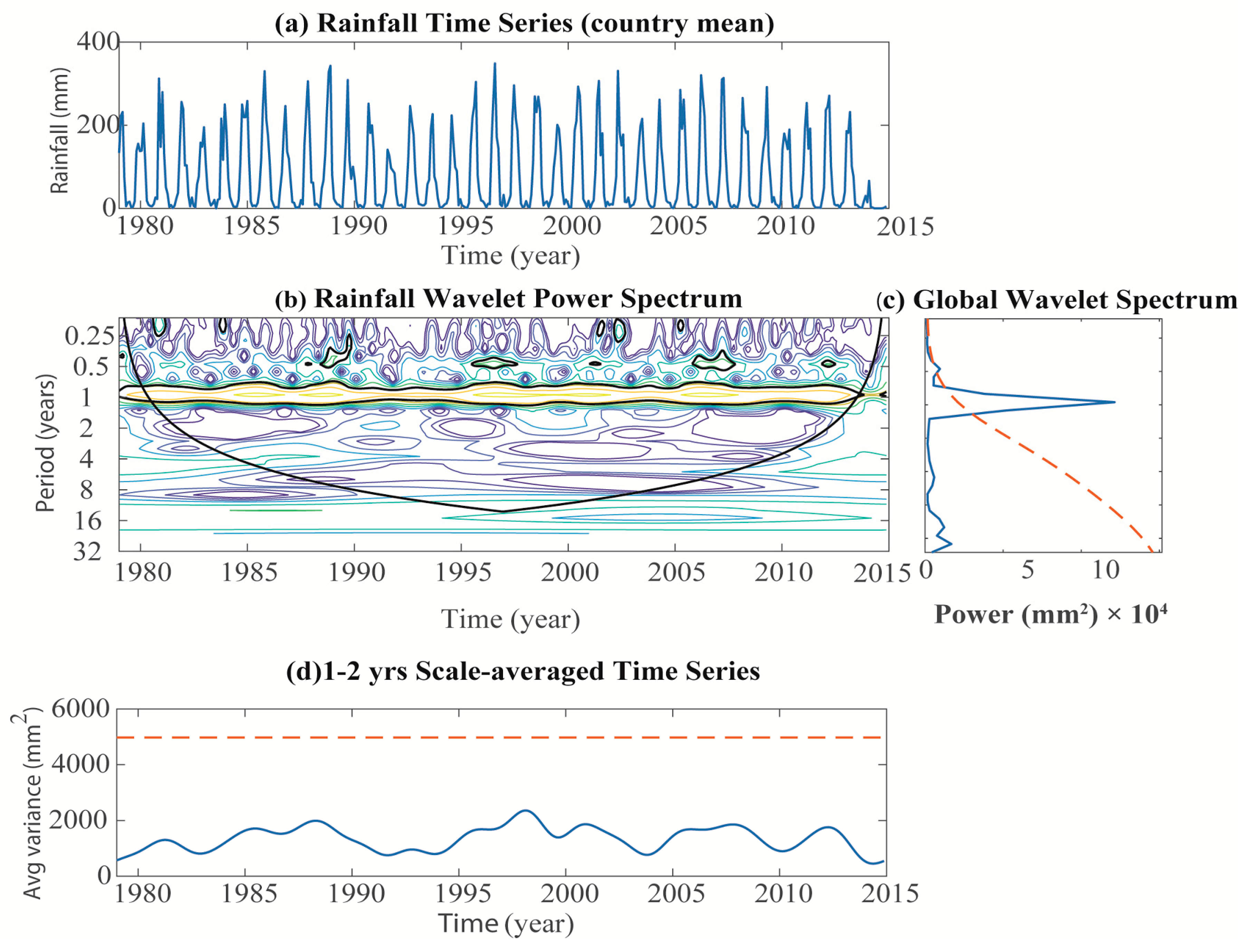
3.4. Wavelet Analysis of Rainfall Changes
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Malawi: Country Indicators. 2017. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#country/130 (accessed on 3 September 2019).
- Alemu, M.M.; Bawoke, G.T. Analysis of spatial variability and temporal trends of rainfall in Amhara region, Ethiopia. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayugi, B.O.; Tan, G.; Ongoma, V.; Mafuru, K.B. Circulations Associated with Variations in BorealSpring Rainfall over Kenya. Earth Syst. Environ. 2018, 2, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. 2014: Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Core Writing Team, Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, L.A., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015; p. 151. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. In Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Solomon, S., Qin, D., Manning, M., Chen, Z., Marquis, M., Averyt, K.B., Tignor, M., Miller, H.L., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007; p. 1007. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, S.; You, Q.; Ullah, W.; Ali, A. Observed changes in precipitation in China- Pakistan economic corridor during 1980–2016. Atmos. Res. 2018, 210, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, L.V.; Zhang, X.; Peterson, T.C.; Caesar, J.; Gleason, B.; Klein Tank, A.M.G.; Haylock, M.; Collins, D.; Trewin, B.; Rahimzadeh, F.; et al. Global observed changes in daily climate extremes of temperature and precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. 2012: Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation; A Special Report of Working Groups I and II of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Field, C.B., Barros, V., Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Dokken, D.J., Ebi, K.L., Mastrandrea, M.D., Mach, K.J., Plattner, G.-K., Allen, S.K., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2012; p. 582. [Google Scholar]
- Ongoma, V.; Chen, H.; Omony, G.W. Variability of extreme weather events over the equatorial East Africa, a case study of rainfall in Kenya and Uganda. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 131, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, L.V. Global observed long-term changes in temperature and precipitation extremes: A review of progress and limitations in IPCC assessments and beyond. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2016, 11, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate Communication. Current Extreme Weather and Climate Change. 2011, pp. 1–28. Available online: https://www.climatecommunication.org/new/features/extreme-weather/download-full-pdf/ (accessed on 21 August 2020).
- Trenberth, K.E. Changes in precipitation with climate change. Clim. Res. 2011, 47, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumo, L.; Yu, J.; Ayugi, B. Evaluation of spatiotemporal variability of rainfall over Kenya from 1979 to 2017. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2019, 194, 105097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnatzsch, E.A.; Reay, D.S. Temperature and precipitation change in Malawi: Evaluation of CORDEX-Africa climate simulations for climate change impact assessments and adaptation planning. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 378–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghtalab, N.; Moore, N.; Ngongondo, C. Spatio-temporal analysis of rainfall variability and seasonality in Malawi. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2019, 19, 2041–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauw, K.; Thurlow, J.; van Seventer, D. Droughts and Floods in Malawi: Assessing the Economywide Effects. IFPRI Discuss. 2010, 00962. Available online: http://www.ifpri.org/publication/droughts-and-floods-malawi (accessed on 21 August 2020).
- Ongoma, V.; Chen, H. Temporal and spatial variability of temperature and precipitation over East Africa from 1951 to 2010. Meteor. Atmos. Phys. 2017, 129, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jury, M.R.; Mwafulirwa, N.D. Climate variability in Malawi part 1: Dry summers, statistical associations and predictability. Int. J. Climatol. 2002, 22, 1289–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbuyo, C.P.; Shimizu, K.; Yasuda, H.; Kitamura, Y. Linkage between Malawi Rainfall and Global Sea Surface Temperature. J. Rainwater Catchment Syst. 2015, 20, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ngongondo, C.; Xu, C.-Y.; Gottschalk, L.; Alemaw, B. Evaluation of spatial and temporal characteristics of rainfall in Malawi: A case of data scarce region. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2011, 106, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libanda, B.; Zheng, M.; Banda, N. Variability of extreme wet events over Malawi. Geogr. Pannonica. 2017, 214, 21–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayugi, B.O.; Wang, W.; Chepkemoi, D. Analysis of Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Rainfall Variations over Kenya. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 6, 69–83. [Google Scholar]
- Camberlin, P.; Okoola, R.E. The onset and cessation of the ‘long rains’ in eastern Africa and their interannual variability. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2003, 75, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettitt, A.N. A Non-Parametric Approach to the Change-Point Problem. Appl. Stat. 1979, 28, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandersson, H. A homogeneity test applied to precipitation data. J. Climatol. 1986, 6, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallakpour, I.; Villarini, G. A simulation study to examine the sensitivity of the Pettitt test to detect abrupt changes in mean. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumo, L.; Yu, J.; Fang, K. Assessing Impacts of Seasonal Climate Variability on Maize Yield in Kenya. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2018, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. Empirical Orthogonal Functions and Statistical Weather Prediction. Tech. Rep. Stat. Forecast Proj. Rep. 1 Dep. Meteorol. MIT 1956, 49, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Hannachi, A.; Jolliffe, I.T.; Stephenson, D.B. Empirical orthogonal functions and related techniques in atmospheric science: A review. Int. J. Climatol. 2007, 27, 1119–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.A.; Semazzi, F.H.M. The Role of the Dominant Modes of Precipitation Variability over Eastern Africa in Modulating the Hydrology of Lake Victoria. Adv. Meteorol. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkonen, L. Plotting positions in extreme value analysis. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 2006, 45, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the Regression Coefficient Based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 324, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Gong, T.; Lu, J.; Lou, D.; Hagan, D.F.T.; Chen, T. On the long-term changes of drought over China (1948-2012) from different methods of potential evapotranspiration estimations. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 2954–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods, 4th ed.; Charles Griffin: London, UK, 1975; p. 202. [Google Scholar]
- Araghi, A.; Mousavi-Baygi, M.; Adamowski, J. Detection of trends in days with extreme temperatures in Iran from 1961 to 2010. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 125, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongoma, V.; Chen, H.; Gao, C.; Nyongesa, A.M.; Polong, F. Future changes in climate extremes over Equatorial East Africa based on CMIP5 multimodel ensemble. Nat. Hazards. 2018, 90, 901–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayugi, B.; Tan, G.; Gnitou, G.T.; Ojara, M.; Ongoma, V. Historical evaluations and simulations of precipitation over East Africa from Rossby centre regional climate model. Atmos. Res. 2020, 232, 104705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A Practical Guide to Wavelet Analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, S.E.; Klotter, D.; Chavula, G. A detailed rainfall climatology for Malawi, Southern Africa. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taljaard, J.J. Change of rainfall distribution and circulation patterns over Southern Africa in summer. J. Climatol. 1986, 6, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jury, M.R. Climate prediction experiences in southern Africa 1990–2005 and key outcomes. Nat. Hazards. 2013, 65, 1883–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, B.; Janicot, S. Abrupt shift of the ITCZ over West Africa and intra-seasonal variability. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 3353–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwafulirwa, N.D. Climate variability and predictability in tropical southern africa with a focus on dry spells over Malawi. Master’s Thesis, University of Zululandno, Richards Bay, South Africa, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ratnam, J.V.; Behera, S.K.; Masumoto, Y.; Yamagata, T. Remote Effects of El Niño and Modoki Events on the Austral Summer Precipitation of Southern Africa. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 3802–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, M.; Abiodun, B.J.; Kucharski, F. Understanding the influence of ENSO patterns on drought over southern Africa using SPEEDY. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 54, 307–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinault, J.L. The Anticipation of the ENSO: What Resonantly Forced Baroclinic Waves Can Teach Us (Part II). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, R.; Preston, A. Extreme wet years over southern Africa: Role of Indian Ocean sea surface temperatures. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D15104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinsted, A.; Moore, J.C.; Jevrejeva, S. Application of the cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2004, 11, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okonkwo, C. An Advanced Review of the Relationships between Sahel Precipitation and Climate Indices: A Wavelet Approach. Int. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
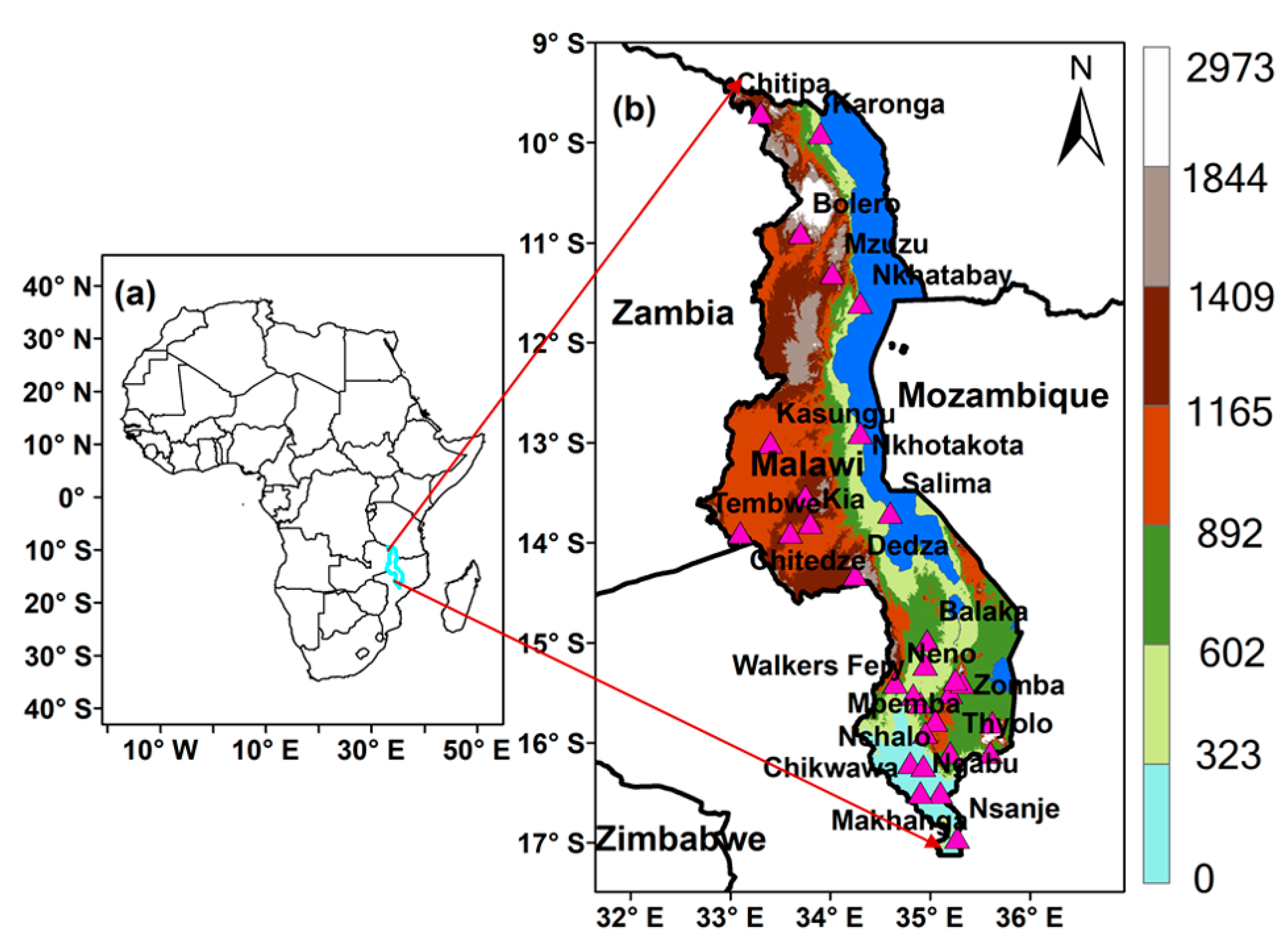
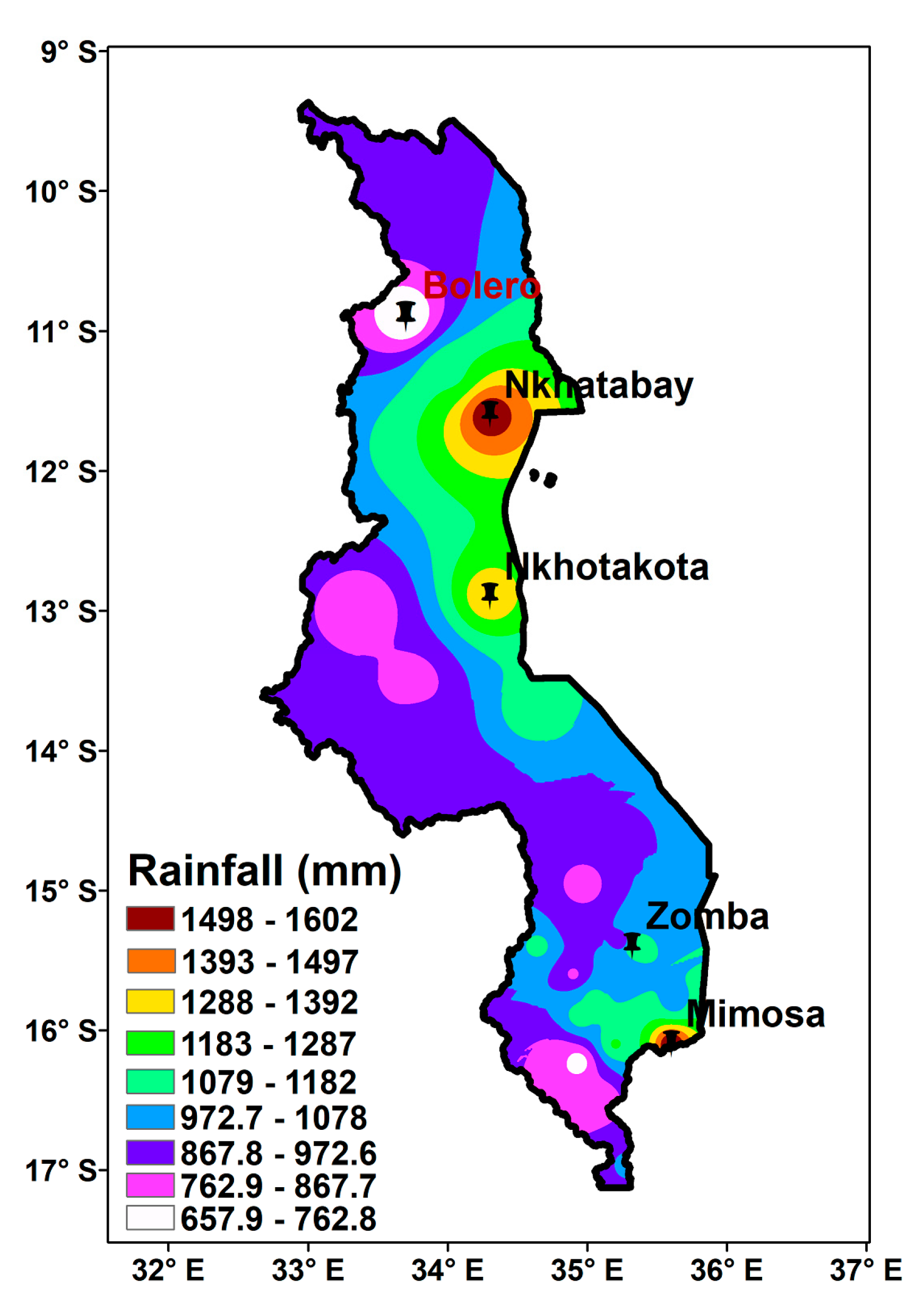
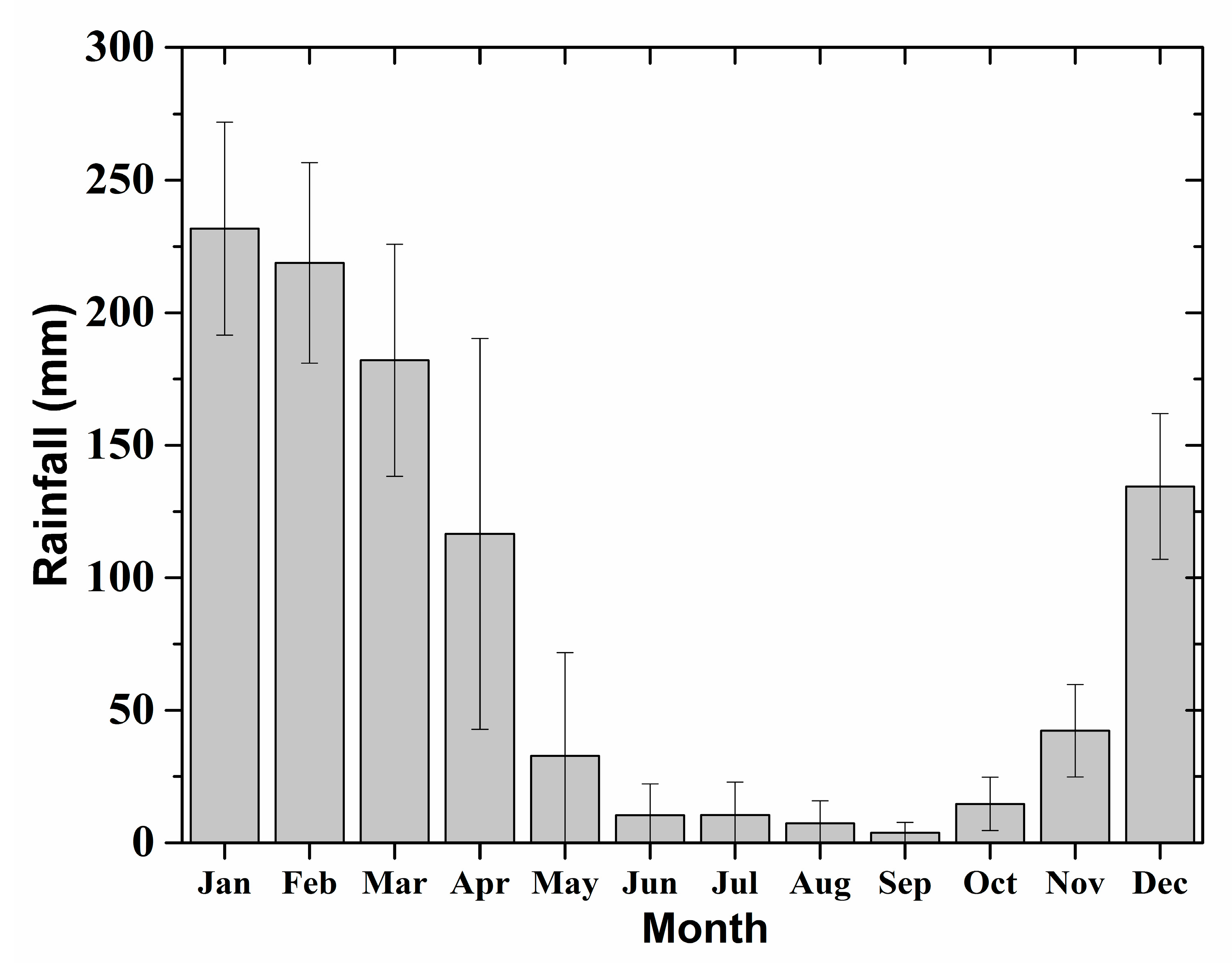


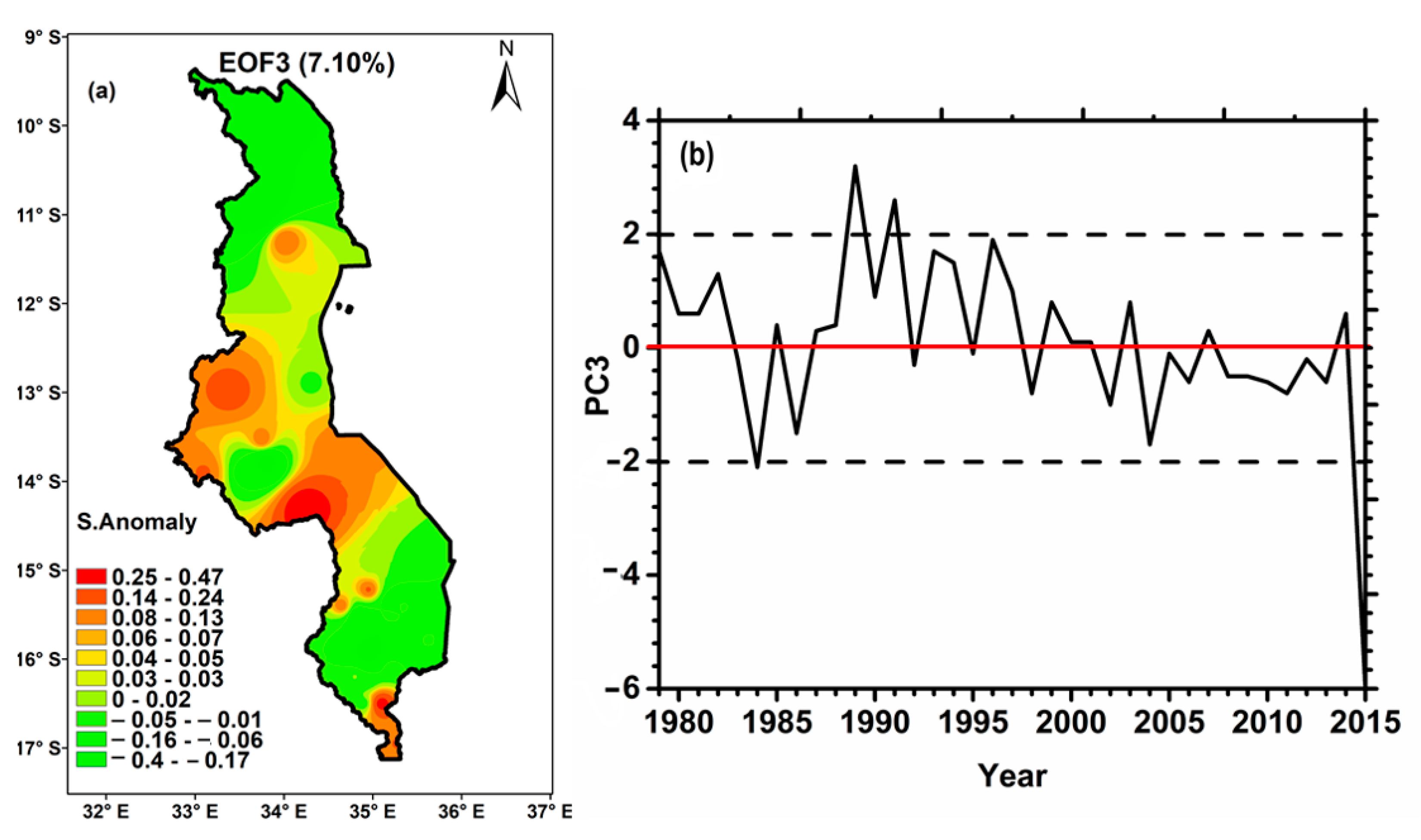

| No. | Station Name | Lon | Lat | Altitude (m) | Annual Mean Rainfall (mm) | SD | Pettitt’s Test | SNHT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Balaka | 34.97 | −14.98 | 625 | 801 | 299.4 | 0.07 | 0.10 |
| 2 | Bolero | 33.7 | −10.9 | 1100 | 657.72 | 164.3 | 0.15 | 0.03 |
| 3 | Chichiri | 35.02 | −15.78 | 1132 | 1122.96 | 283.0 | 0.54 | 0.95 |
| 4 | Chikwawa | 34.8 | −16.2 | 107 | 770.76 | 224.2 | 0.82 | 0.15 |
| 5 | Chileka | 34.9 | −16.6 | 767 | 847.8 | 183.2 | 0.45 | 0.59 |
| 6 | Chitedze | 33.6 | −13.9 | 1149 | 867.72 | 191.5 | 0.89 | 0.26 |
| 7 | Chitipa | 33.3 | −9.7 | 1285 | 920.64 | 160.2 | 0.26 | 0.20 |
| 8 | Dedza | 34.25 | −14.32 | 1632 | 899.4 | 198.5 | 0.05 | 0.20 |
| 9 | Kia | 33.8 | −13.8 | 1229 | 944.52 | 211.8 | 0.33 | 0.59 |
| 10 | Karonga | 33.9 | −9.9 | 529 | 964.68 | 256.8 | 0.59 | 0.02 |
| 11 | Kasungu | 33.4 | −13 | 1058 | 776.76 | 192.7 | 0.62 | 0.63 |
| 12 | Makhanga | 35.1 | −16.5 | 76 | 782.76 | 280.3 | 0.88 | 0.45 |
| 13 | Makoka | 35.2 | −15.5 | 1029 | 984.48 | 245.8 | 0.52 | 0.95 |
| 14 | Mimosa | 35.6 | −16.1 | 652 | 1602.6 | 367.9 | 0.89 | 0.59 |
| 15 | Mpemba | 34.95 | −15.9 | 866 | 1142.52 | 318.8 | 0.09 | 0.14 |
| 16 | Mponela | 33.75 | −13.53 | 1220 | 780.48 | 203.9 | 0.46 | 0.42 |
| 17 | Mwanza | 34.52 | 15.62 | 1260 | 1033.32 | 326.6 | 0.35 | 0.67 |
| 18 | Mzuzu | 34.02 | −11.3 | 1254 | 1165.8 | 260.4 | 0.47 | 0.83 |
| 19 | Naminjiwa | 35.62 | −15.8 | 773 | 1040.16 | 293.7 | 0.01 | 0.11 |
| 20 | Nchalo | 34.93 | −16.23 | 52 | 684.24 | 203.1 | 0.52 | 0.89 |
| 21 | Neno | 34.65 | −15.4 | 899 | 1111.68 | 358.4 | 0.86 | 0.73 |
| 22 | Ngabu | 34.9 | −16.5 | 105 | 780.96 | 215.8 | 0.94 | 0.96 |
| 23 | Nkhatabay | 34.3 | −11.6 | 500 | 1572.6 | 321.1 | 0.48 | 0.78 |
| 24 | Nkhotakota | 34.3 | −12.9 | 500 | 1370.52 | 318.8 | 0.69 | 0.02 |
| 25 | Nsanje | 35.27 | −16.95 | 200 | 978.72 | 330.7 | 0.44 | 0.59 |
| 26 | Phalula | 34.95 | −15.22 | 585 | 876.84 | 303.8 | 0.01 | 0.10 |
| 27 | Salima | 34.6 | −13.7 | 512 | 1165.2 | 314.5 | 0.42 | 0.23 |
| 28 | Tembwe | 33.1 | −13.9 | 1097 | 941.16 | 204.7 | 0.49 | 0.56 |
| 29 | Thyolo | 35.2 | −16.2 | 820 | 1196.88 | 272.8 | 0.14 | 0.16 |
| 30 | Zomba | 35.32 | −15.4 | 915 | 1223.28 | 336.1 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| 31 | Chingale | 35.25 | −15.37 | 610 | 879.12 | 261.0 | 0.77 | 0.68 |
| Decades | Annual | Seasonal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (mm) | Trend (mm/decade) | Mean (mm) | Trend (mm/decade) | |
| 1979–1988 | 1023.284 | 155.6 | 925.26 | 59.5 |
| 1989–1998 | 949.98 | 226.8 | 857.9 | 233.5 |
| 1999–2008 | 1040.92 | −119.6 | 928.8 | −157.8 |
| 2009–2015 | 964.64 | −94.25 | 850.33 | −121.7 |
| Trend Analysis | MK Rainfall (mm) | |
|---|---|---|
| Annual Rainfall | Seasonal Rainfall | |
| S Trend | −30.000 | −60.000 |
| Z | 0.37929 | 0.77165 |
| Kendall’s tau | −0.045 | −0.090 |
| P | 0.70447 | 0.4403 |
| α | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Significance | Insignificant decreasing trend | Insignificant decreasing trend |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tadeyo, E.; Chen, D.; Ayugi, B.; Yao, C. Characterization of Spatio-Temporal Trends and Periodicity of Precipitation over Malawi during 1979–2015. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090891
Tadeyo E, Chen D, Ayugi B, Yao C. Characterization of Spatio-Temporal Trends and Periodicity of Precipitation over Malawi during 1979–2015. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(9):891. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090891
Chicago/Turabian StyleTadeyo, Edwin, Dan Chen, Brian Ayugi, and Chunzhen Yao. 2020. "Characterization of Spatio-Temporal Trends and Periodicity of Precipitation over Malawi during 1979–2015" Atmosphere 11, no. 9: 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090891
APA StyleTadeyo, E., Chen, D., Ayugi, B., & Yao, C. (2020). Characterization of Spatio-Temporal Trends and Periodicity of Precipitation over Malawi during 1979–2015. Atmosphere, 11(9), 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090891







