Abstract
A Chinese Ka-band solid-state transmitter cloud radar (CR) was employed to investigate clouds and precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau (TP) in summer 2014. After performing quality control and merging the output from the three work modes of CR, the Doppler spectral density data were analyzed to estimate the vertical air motion (Vair) and particle fall speed (Vfall) in clouds. The reproduced radar reflectivity was employed to retrieve the ice water content (IWC) and ice effective radius (Re). The cloud type classification algorithm was developed to classify cloud conditions into eight different categories. The vertical and daily variations of reflectivity, Vair, Vfall, IWC, and Re were then analyzed, and as a result, four conclusions were formulated. First, the clouds with reflectivity less than −10 dBZ were mainly located above 7 km, and the precipitable particles were formed below this layer (rain echo top) due to the abundant supercooled water therein. Second, the weak updraft in the range of 2–4 km caused the high occurrence of weak clouds during 04:00–12:00 Beijing local time (BT), and the rain echo top did not exceed 7 km due to the existing downdraft in 4–6 km. After 14:00 BT, convective clouds quickly developed, and the averaged updraft, reflectivity, and the echo top notably increased. Third, particular cloud types commonly exhibited weak reflectivity, low IWC, and less vertical variations, while the others more obvious vertical variations with larger IWC and Re. Last, compared with the radar sensitivity and range from radar, Vair biases that were introduced by the Doppler spectra broadening due to turbulence, wind shear, and radar beam width, could be neglected.
1. Introduction
The Tibetan Plateau (TP) located in the southwest region of China is the highest plateau with the most complex terrain in the world. The average elevation of the TP (~4000 m) can reach the heights up to the mid-troposphere. Owing to its thermodynamic forcing, the TP significantly influences the atmospheric circulation, the surface–atmosphere momentum exchange, and the hydrologic cycle in its surrounding areas, as well as in Eastern Asia [1,2,3]. Clouds and precipitation impose a considerable impact on atmospheric moisture transfer and surface heating over the plateau. Microphysics processes underlying the changes in the atmosphere above the TP often differ from those over low altitude areas (1000 m above sea level). Due to strong surface heating, convection often develops quickly after noon. Unlike in the downstream plain areas, convective processes are more frequently triggered in the TP. However, the horizontal scales of the convective systems are always small, and their maximum reflectivity are weak.
Due to the relatively rare field experiments and observations of clouds and precipitation in the TP, the current understanding of the microphysical processes in clouds and precipitation over the plateau still contains multiple gaps. During the first TP atmospheric science experiment conducted in 1979, two conventional X-band 711 type radars were employed to observe precipitation at Naqu, central Tibet Plateau, and Lasa, southern Plateau. The statistical characteristics of convective precipitations and the relationship between the vertical distributions of the moist static energy and convective development were analyzed [4,5]. In the second TP atmospheric science experiment conducted in 1998, a Japanese X-band Doppler radar, rain gauges, and radiosondes were deployed to observe precipitation. The characteristics of the radar reflectivity corresponding to convective precipitation were analyzed, and the variations of the convective processes before and after a monsoon onset were explored [6,7,8,9,10].
The precipitation radar observations gathered during the tropical rainfall measuring mission (TRMM) were also used to compare the differences in precipitation between the TP and other regions of East Asia. The deep convective precipitations over the TP had weak reflectivity and minor horizontal scale due to the relatively dry environmental conditions and the low convective available potential energy (CAPE) [11,12,13]. The microphysical structure of stratus clouds formed over Qinghai and the eastern TP were also analyzed based on in situ observations obtained from the aircraft and radar observations [14,15].
In the third TP atmospheric science experiment performed in 2014 and 2015, the vertically pointing Ka-band cloud radar (CR), micro-rain radar (MRR), microwave radiometer, and disdrometer were utilized to observe the microphysical and thermodynamic parameters of clouds in Naqu [16]. Then, the experiment on clouds and precipitation and its preliminary results were discussed and summarized [17,18,19]. The characteristics of convective clouds and precipitation including the rain rate, cloud-top height, and raindrop size distribution (DSD) during summertime at Naqu over central Tibetan Plateau were analyzed using CR, disdrometer, laser imaging detection and ranging (LIDAR) ceilometer, and Fengyun 2E (FY-2E) satellite data [20]. Zhao et al. analyzed the microphysical properties of the high ice clouds focusing on the raw reflectivity observed by CR cirrus mode using the empirical regression equations for cloud parameter retrievals [21]. In these studies, only the raw CR reflectivity data were utilized to analyze microphysical parameters. Considering that the radial Doppler velocity was defined as the sum of air motion and the raindrop terminal velocity, it was difficult to decompose air motion from the radial Doppler velocity measurements. The Doppler spectrum observations obtained using a vertically pointing CR were useful to identify and quantify microphysical properties and to estimate vertical air velocities. However, the Doppler density data were not used to retrieve the information about vertical air motion and the terminal fall speed in the work. A method to identify vertical air velocities in convective clouds over the TP based on the CR Doppler density data obtained in the single-work mode was reported, only some convective precipitation processed were analyzed, however, the statistical analysis of microphysical and dynamical parameters for clouds and precipitation were not done [22].
Although considerable efforts were made to obtain the information about cloud macrophysics (for example, cloud cover) and microphysics (for example, water content) over the TP [23,24,25], the microphysical characteristics of different cloud types are still unknown, and the dynamic processes and their relationships with the microphysical ones have not been thoroughly investigated. Deeper knowledge about cloud properties from the viewpoint of the high spatiotemporal resolution observations is required to accurately evaluate and monitor the thermodynamic processes in clouds and precipitation. This is important to understand the special characteristic properties of cloud and precipitation processed and improve the forecasting ability of numerical models.
In the present study, the Doppler density data obtained using the three work modes are qualified and merged to produce an optimized hybrid Doppler density dataset. It is utilized to evaluate post-processed reflectivity, and to retrieve the vertical air motion and the terminal fall speed. The post-processed reflectivity data are compared with those from the observed surface raindrop size distribution (DSD) registered using a disdrometer. The statistical microphysical and dynamic characteristics and their relationships for different cloud types are first retrieved with Doppler spectral data from CR in China. Microphysical and dynamical parameters for clouds are compared with those in low altitude regions like South China. The paper is organized as follows: Section 2 describes the observed data, a data processing method, and a cloud type classification method. Section 3 presents the results of analyzing microphysical and dynamical parameters for clouds over the TP and difference with those in South China. Section 4 discusses the vertical air motion (Vair) biases corresponding to the Doppler spectra broadening and radar sensitivity. A concluding summary is provided in Section 5.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data and Instrument Descriptions
Intensive cloud and precipitation observations were conducted in Naqu of the Tibetan Plateau (31.48° N, 92.01° E, and 4507 m above the sea level) from 1 July to 31 August 2014, with continuous observations in July. However, CR did not work for 3 days in August. The Ka-band CR with a solid-state transmitter used in this experiment relies on a Doppler radar and polarization radar technology. It works in a vertically pointing mode to obtain the vertical profiles of reflectivity (Z), radial velocity (Vr), velocity spectrum width (Sw), and the linear depolarization ratio (LDR) in the cloud and light precipitation. The observational errors of Z, Vr, and Sw are 1.0 dB, 1.0 m/s, and 1.0 m/s, respectively. As an output, it records Doppler spectral density data. Table 1 lists the major technical parameters of the considered CR. The main purpose of using a solid-state transmitter is to realize continuous measurements, as evaluating statistical characteristics is specifically important in cloud and precipitation physics.

Table 1.
Major technical parameters of the Ka-band solid-state transmitter cloud radar (CR).
The pulse compression, as well as coherent and incoherent integration techniques are required to improve the detection of weak clouds due to the low peak power of the solid-state transmitter. The data from the different operating modes are combined to yield a comprehensive and accurate evaluation of most clouds. To improve the radar detection capability in terms of identifying clouds and precipitation, three operating modes: boundary mode (M1), cirrus mode (M2), and precipitation mode (M3), are applied (see Table 2 for the major operational parameters). The velocity resolutions for Doppler spectral density data by M1, M2, and M3 are 0.036, 0.0722, and 0.145 m s−1, respectively. In principle, it is desirable to run all three modes and combine their outputs to observe weak clouds and precipitations in the range from near-ground to the height of approximately 15 km. Once the radial measurement is completed in one mode, the radar immediately switches to the other one. The dwell times corresponding to the three operational modes (namely, the time to obtain a radial measurement) are about 2 s, while the conversion time between the two modes is approximately 1 s. Therefore, one cycle of the three operational modes takes 9 s, and 500 radial measurements require approximately 1.25 h to complete.

Table 2.
Major operational parameters for the three operational modes.
An MP-3000A 35-channel microwave radiometer produced by U.S. Radiometrics Corp. was deployed to observe temperature, relative humidity, liquid water profile, and total liquid water content (LWC). An HSC-PS32 disdrometer was used to monitor the surface raindrop size distribution (DSD). The disdrometer data were applied to examine and adjust the CR reflectivity data. An MRR-2 micro-rain radar produced by METEK Meteorologische Messtechnik GmbH (Elmshorn, Germany) was employed to measure reflectivity, DSD, and rainfall.
The CR calibrations included a radar system test, as well as calibration with the manufacturer before field experiment. The antenna parameters, including the beam width, the gains of main lobe and side lobes, and the degree of isolation between the horizontal and vertical channel were measured in a microwave chamber. The transfer parameters, such as the pulse width, peak output power, noise ratio, and dynamic range were captured using a signal generator, an oscilloscope, and an attenuator. The reflectivity was calibrated according to the radar meteorological equation. The signal input with different frequencies was fed into the receiver, and the theoretical velocity was calculated and compared with the radar measurement. In addition, the reflectivity bias between the CR and the HSC-PS32 disdrometer was analyzed to correct it, as it was mainly caused by CR hardware and antenna water cover attenuation [26].
2.2. Data Processing Methods
The M1 mode has high sensitivity and velocity resolution in terms of observing the boundary layer clouds. The M2 mode with the highest sensitivity is suitable for weakly reflective high-altitude cloud monitoring. The M3 mode has large Nyquist velocity, large maximum reflectivity, and low minimum range, facilitating the observation of light precipitation. However, coherent integration introduces large negative biases in reflectivity and reflectivity spectra (SZ) at the high Doppler velocities in M2. To obtain a complete picture of the vertical distributions of hydrometeors and air speed, it is necessary to merge the Doppler spectral density data from the three modes.
The coherent integration and pulse compression techniques increase the CR sensitivity; however, the former reduces the Nyquist velocity, introduces Doppler spectral density aliasing, and leads to the underestimation of the Doppler spectral density in the case of large velocity (larger than 6.0 m s−1). The raw Doppler spectral density data generated using the three work modes are then post-processed and used to reevaluate reflectivity and to retrieve the vertical air motion, the hydrometeor fall speed, and ice water content (IWC). The data post-processing includes quality control (QC), merging to the Doppler spectra, and recalculating Doppler moments [27]. QC for Doppler spectra implies de-aliasing the aliased Doppler spectral density data, as well as detecting and removing the artifacts produced by pulse compression. To merge the Doppler spectral density data from three observation modes, we individually compare, evaluate, and select the best bins to compose a Doppler spectral density dataset. QC and merging processing for the Doppler spectral density data are applied to fill in the gaps in the individual spectra during the weakly cloud periods, to reduce the effects of coherent integration and pulse compression in liquid precipitation, to mitigate the aliasing of Doppler velocity, and to remove artefacts, aiming to yield a comprehensive and accurate representation of most cloud and precipitation patterns. However, it is difficult to deal with the aliasing of Doppler velocity and artefacts in raw data.
Reflectivity attenuation correction is conducted according to Wang’s algorithm [28]. In the attenuation correction, the Z-K relationships for a nonprecipitating liquid cloud, a precipitating liquid cloud, and snow used in the paper are expressed as follows:
for non-precipitating liquid cloud.
for snow.
for precipitating cloud.
where Z is reflectivity and K is attenuation coefficient. After QC and merging, the integrated retrieval technique with the merged Doppler spectra is applied to estimate the vertical air velocity [22]. The method relies on the “small-particle-traced” idea and its associated data processing procedure. Spectral broadening corrections and uncertainty estimations are also conducted to ensure accurate results.
The reflectivity after QC is used to calculate IWC and the ice effective radius Re [21] as follows:
It is useful to note that the reflectivity bias and the variations of the coefficients in Equations (1)–(5) introduce errors of assessed attenuation coefficient, IWC and Re.
2.3. Cloud Clustering and Classification Algorithm Description
The International Satellite Cloud Climatology Project (ISCCP) suggested to focus on the combination of the cloud top pressure and cloud optical depth to classify clouds. As a result, the following classification groups were identified: cumulus (Cu), stratocumulus (Sc), stratus (St), altocumulus (Ac), altostratus (As), nimbostratus (Ns), cirrostratus (Cs), cirrocumulus (Cc), and deep convective clouds (Dc) [29]. Wang and Sassen presented a cloud classification method to categorize clouds into St, Sc, Cu, Ns, Ac, As, Dc, or high-level cloud based on the data from multiple remote sensors, including polarization Laser Imaging Detection and Ranging system (LiDAR), millimeter-wave radar, infrared radiometers, etc. [30]. The cloud classification products (for example, 2B-cldclass-lidar), released jointly for the CLOUDSAT and CALIPSO satellites, rely on the principles of this cloud classification method. A ground-based radar can observe the cloud base and top, cloud thickness, retrieved water content, and vertical air motion. These meso-scale microphysical and dynamic characteristics are useful for cloud classification. However, it is difficult to observe the horizontal scale of cloud systems in such a way. According to particular features of the considered radar and the scientific requirements associated with cloud classification, we design a cloud classification algorithm to categorize clouds into eight types: circus (Cir), Ac, As, Sc, St, Ns, Cu, or Dc.
We apply the following procedure to cluster and classify clouds. First, storm cell identification and the tracking algorithm based on the weather Doppler radar volume scanned data are used to cluster the cloud echoes with time-height section reflectivity through the CR [31]. The boundary for each cloud cluster is defined using the cloud classification algorithm, and the parameters for cloud classification are calculated. The fuzzy logic method is then applied to determine the first guessed membership value (T) as follows:
where subscript i represents the cloud type; subscript j denotes the characteristic parameter; Wj is the weight coefficient. We select the eight following characteristic parameters from the CR for cloud classification: the averaged cloud top height (Htop), the height of maximum reflectivity (Hmaxz), the lowest cloud base height (Hbase), the averaged cloud depth (Dh), the maximum cloud depth (Dhmax), the maximum reflectivity (Zmax), the last period of the cloud echo (Chr), and the maximum air updraft velocity (Vmax), which is the averaged value of all maximum air motion estimates along the radar beam. A trapezoid-shaped fuzzy membership function is defined as follows:
where P is the membership function; "0" means no, "1" means yes; a is the characteristic parameter; A1, A2, A3, and A4 are the coefficients of the membership functions for each characteristic parameter in cloud classification. The initial guess of A1–A4 shown in Table 3 is from Huo’s research work [32]. The types of clouds were derived from the used schemes and analyzed by experts. The scheme was improved and approved by these experts. The final values of A1–A4 were determined by experts.

Table 3.
A1, A2, A3, A4, and the weights for eight characteristic parameters and eight cloud types.
The first guessed membership value is modified through the following method (Figure 1). The cloud types are divided into precipitation and nonprecipitating ones according to the maximum reflectivity and the low boundary of a cloud segment in each beam. If the beam number in which the maximum reflectivity of each beam is larger than −10.0 dBZ or the reflectivity reaches the ground, the cloud type is set to precipitation. Then, the nonprecipitating cloud types are divided to low, middle, and high clouds corresponding to Htop and Hbase. In each cloud type, some of the first guessed membership values (T) are set to zero. Finally, the cloud type with maximum T is determined as the cloud classification.
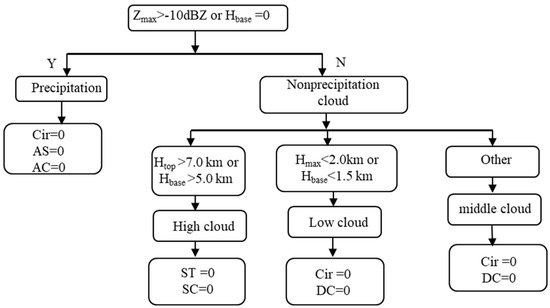
Figure 1.
Scheme of cloud classification. The first guessed membership value is modified using the proposed method.
3. Results
3.1. Base and Spectral Data Quality Control and Post Processing
To examine the reflectivity bias introduced by CR, the reflectivity for Ka-band in the DSD data observed by the disdrometer was calculated based on back-scattering cross sections using the extended boundary condition method [33]. Figure 2 represents the scattering figure for minutely averaged reflectivity (averaged in 1 min) at the height of 300 m above the radar station generated by CR (ZCR) and the reflectivity derived based on the raindrop size distribution (DSD) data (ZDSD). The error, standard correlation coefficient, and root mean square error are 0.5 dB, 0.87, and 6.5 dB, respectively.
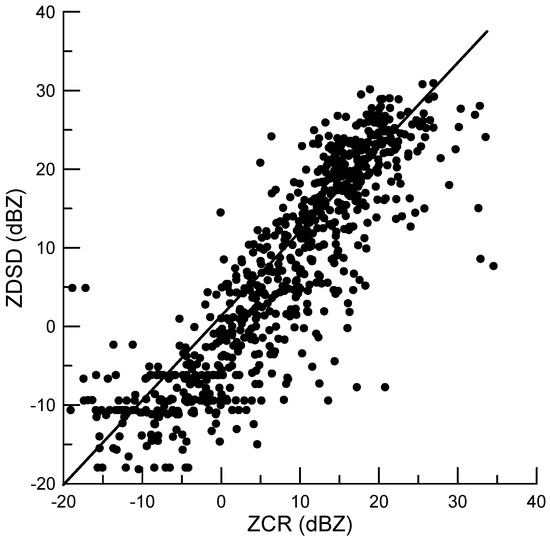
Figure 2.
Scattering figure of minutely averaged reflectivity at the height of 300 m by CR (ZCR) and the reflectivity calculated based on the DSD data (ZDSD) for 24 July and 14 July.
Figure 3 illustrates the time-height cross sections corresponding to 500 profiles of raw reflectivity and radial velocity obtained by the three modes from 02:53 to 04:08 Beijing local time (BT) on 11 July 2014. The Beijing time is 2 h earlier then the Naqu local time. The precipitation case is stratified cloud, most of echo was located below 7 km. As the M3 mode did not perform pulse compression and coherent integration, the data from this mode were the least affected by bias. Therefore, we compared the results corresponding to the other two modes with those for the M3 mode. The three modes captured similar reflectivity and velocity values above the bright band at the height of 1.2 km. Below this altitude, the M1 mode velocity was aliased, and reflectivity was underestimated in liquid precipitation. Accordingly, the full gain of coherent integration was not applicable to the large Doppler velocity, which caused the radar returns that rapidly got uncorrelated over time. The long pulse width in the case of M2 increased the minimum range and improved the radar sensitivity. Figure 4 represents the reflectivity and velocity corresponding to the Doppler spectral density SZ after quality control and merging. The M1 velocity below the bright band was correctly de-aliased, and the artificial reflectivity induced by the pulse compression side lobe in the cloud top was eliminated. The reflectivity and velocity in Figure 4 were recalculated based on SZ after quality control. The raw SZ and the SZ after quality control are represented in Figure 5. In addition to all spectral points of artificial SZ in the cloud top, the spectral points with larger positive velocity above and produced by liquid precipitation below the bright band, respectively, were also eliminated.
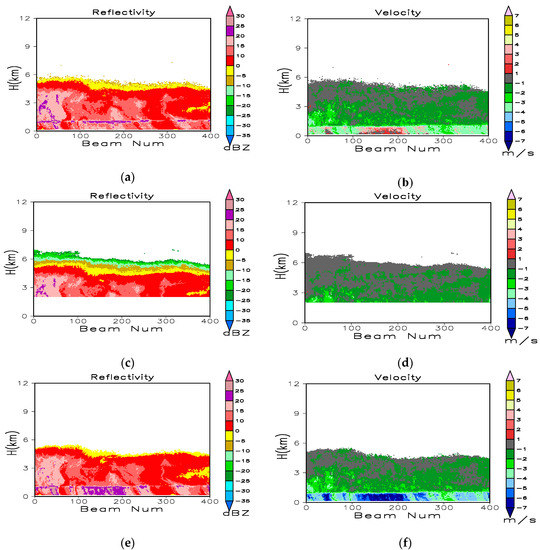
Figure 3.
Time–height cross sections of 500 profiles for raw (a) reflectivity and (b) velocity observed by the M1 mode; (c) reflectivity and (d) velocity observed by the M2 mode; (e) reflectivity and (f) velocity observed by the M3 mode from 02:53 to 04:07 Beijing local time (BT) on 11 July 2014.
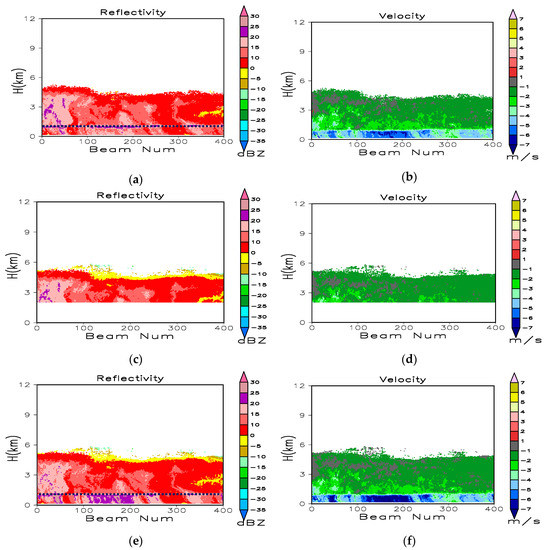
Figure 4.
Time–height cross sections of 500 profiles for quality controlled (a) reflectivity and (b) velocity observed by M1 mode; (c) reflectivity and (d) velocity observed by M2 mode; (e) reflectivity and (f) velocity for merged results from 02:53 to 04:07 BT on 11 July 2014. The dotted lines in (a) and (e) stand for 0 isotherm.
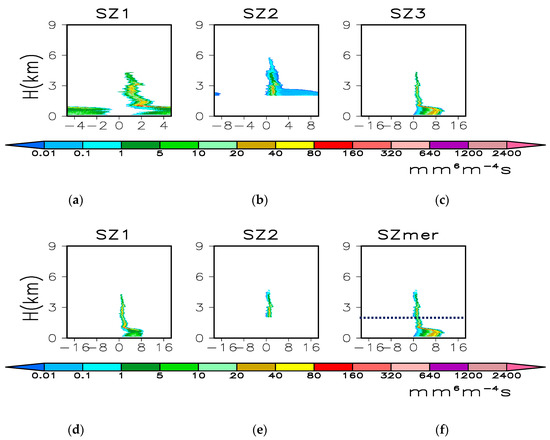
Figure 5.
Raw reflectivity spectra (SZ) alone with the 85th beam by (a) M1, (b) M2, (c) M3; the quality control (QC) SZ by (d) M1, (e) M2, and (f) merged SZ. The dotted line in (f) stands for 0 isotherm.
3.2. Vertical Distributions of Reflectivity and the Retrieved Microphysical and Dynamical Parameters
The vertical distributions of monthly averaged radar reflectivity (Z), particle terminal fall speed (Vfall), and vertical air motion (Vair) were analyzed using the merged data gathered in July 2014. The results indicated the preliminary statistical characteristics of cloud and precipitation in the central region of the TP in the summer. Figure 6 presents the contoured frequency altitude diagrams (CFADs) of Z, Vfall, and Vair for the precipitation and non-precipitating clouds, respectively. Above the height of 8 km from the ground (considering that CR was placed 4507 m above the sea level), the radar reflectivities were commonly less than −5.0 dBZ. The air temperature therein was less than −40 °C; and therefore, homogeneous ice nucleation regularly occurred, and many small ice crystals formed into cirrus. Deep convection and Rossby waves were noted as the important dynamical processes over the Tibetan Plateau [24], meaning that the anvil cirrus outflowing from convective clouds, as well as the large-scale cold perturbations in upper troposphere, dominated the variation in cirrus. Less precipitation clouds (namely, Z > −10 dBZ) were located above 7 km, which was consistent with the results reported by Pan and Fu [34]. Based on the sounding data, they found that 7 km corresponded to the rain echo top, and the atmospheric layer above 7.0 km was the dividing line between shallow and deep convective precipitation.
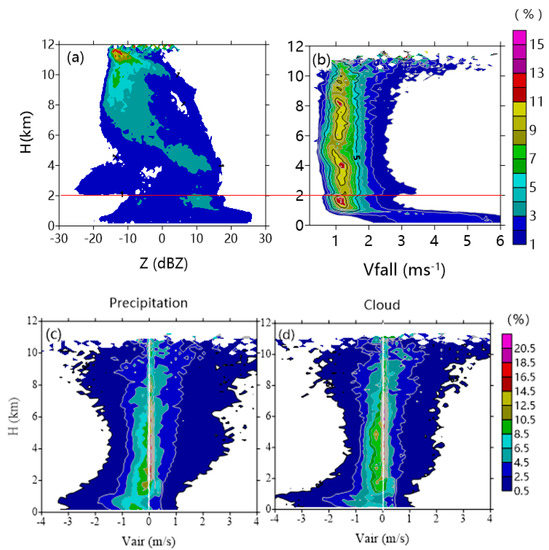
Figure 6.
Contoured frequency altitude diagrams (CFADs, %) of (a) reflectivity, (b) particle fall speed (Vfall), (c) vertical air motion (Vair) for precipitation, and (d) Vair for non-precipitating clouds during July 2014. The solid red line in (a) and (b) indicates the minimum observation range of M2, and the dotted white lines in (c) and (d) are zero of Vair.
From the area with larger CFADs then 3%, we can see that the reflectivity in the range of 4–7 km increased significantly with a decline in the height, along with the frequent positive Vair in 4–6 km for the precipitation and non-precipitation clouds (Figure 6c,d). More air updraft motions occurred in precipitation clouds in the range of 2–4 km. Most of reflectivities were within the range of −5 and 15 dBZ due to the microphysical processes, such as deposition of water vapor and aggregation between ice particles. The entrainment process near the cloud tops, leading to the mixing of dry air into saturated clouds and then into smaller-size hydrometeors, also contributed to this decreasing trend. Specifically, it was noted that the abundant supercooled liquid water was observed above the 0 °C layer using the ground-based microwave radiometer (Figure 7). The maximum LWC located at the height of 3.5 km with the value of ~0.12 g m−3 but with the minimum particle fall speed at 5 km (Figure 6b) indicated the presence of a strong growth process corresponding to the rimming of smaller-sized supercooled liquid water. The large ice hydrometeors were formed below this layer.
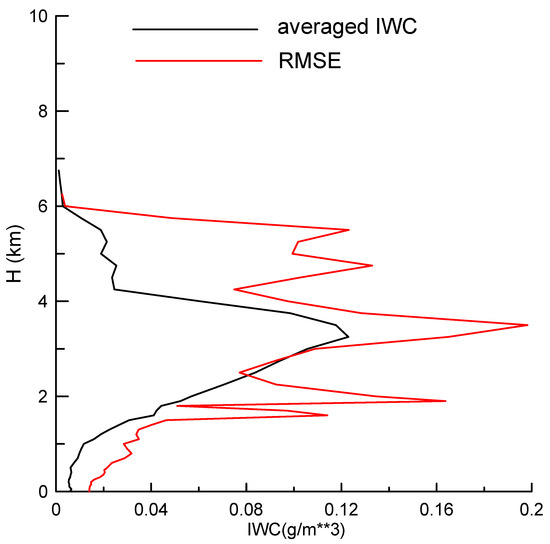
Figure 7.
Averaged ice water content (IWC) and its root-mean-square error (RMSE) profiles obtained by the microwave radiometer.
In the range of 2–4 km, stronger reflectivities (~10 dBZ) were observed. The clouds at this altitude should have comprised more orographic ice clouds compared with those at higher layers. These clouds generally could have stronger air uplifting motion (as represented in Figure 6c,d), and caused the growth of much larger ice particles. The Vfall of 1.0 m s−1 could correspond to the development of the solid particles with the diameter of 500–800 μm that could be regarded as the sixth type of ice particle shapes [35,36]. Indeed, the occurrence frequency of stronger Vair (namely, >1 m s−1) between 2 and 4 km steadily could increase, which caused greater LWC in 3–4 km. In addition, the layer of 0 °C was located approximately at the height of 1.5 km, and the maximum reflectivity in the liquid area was ~7 dB stronger than that of the solid area. A greater number of occurrences of air downdraft in liquid precipitation (between −2.0 and 0.5 m s−1) was due to the drag of liquid hydrometeors on air. Vfall corresponding to the ice particles over the top of the bright band increases after melting into liquid water (Figure 6b), which could be explained by different physical properties of hydrometeor particles (for example, density and shape). In addition, the sharp variations of reflectivity at the 2 km height appeared due to the higher sensitivity of the M2 mode at the minimum range of 2.1 km (marked with red line in Figure 6a,b). Most of the weak clouds were observed in the results generated by M2 compared with those obtained using M1 and M3.
Figure 8 represents CFADs of estimated IWC and Re retrieved from the recalculated reflectivity. As represented in the figure, most of the IWC was less than 0.1 g m−3. Most of the Re above 6 km were smaller than 60 µm, and particles larger than 60 µm formed below this level. The occurrence rate of large IWC (namely, <1.1%) below 4 km slightly augmented with an increase in height; for instance, from 0.25 g m−3 at 2 km to 0.3 g m−3 at 4 km. The reason was that when air mass moved upwards, adiabatic expansion occurred, and the water vapor transformed to solid particles, which caused an increase in the particle size and IWC. The IWC and Re values in the ice layers decreased with further increase in height, as the 1.1% occurrence rate of large IWC (Re) was ~0.28 g m−3 (76 µm) at 5 km, while 0.12 g m−3 (68 µm) at 9 km. This could be caused by the relatively stronger air exchanges in upper-level clouds. As noted, the ice particle sizes reached two peaks below 4 km: one was at 63–73 µm, and the other one was at 40–49 µm. The former was due to the strong riming and aggregation processes, and the latter could be caused by the occurrence of ice multiplication under the condition from −10 °C to −15 °C.
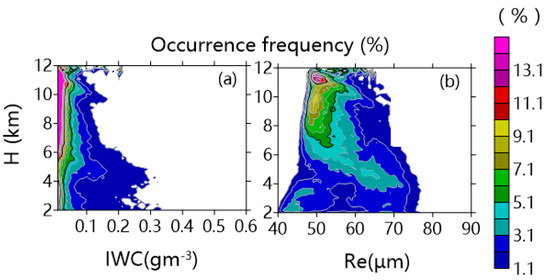
Figure 8.
CFADs (%) for (a) IWC and (b) radius (Re) above the bright band during July 2014.
3.3. Diurnal Variations of the Averaged Reflectivity, Vertical Air Motion, and Hydrometeor Terminal Fall Speed
In this section, we discuss the diurnal variations in the occurrence frequency of reflectivity, the averaged reflectivity, Vair, and Vfall in July 2014 with the temporal resolution of 10 min and the height resolution of 0.15 km (Figure 9). It is useful to note that Beijing time is 2 h earlier then the Naqu local time (LT). As shon in Figure 9a, the clouds over Naqu were widely distributed and could reach up to the 12 km height above the ground level. The maximum averaged reflectivity increased sharply after 13:00 BT, and the maximum echo top with the reflectivity of 0 dBZ occurred from 14:00 to 16:00 BT (12:00 to 14:00 LT). The echo top gradually descended during the period from 20:00 to 04:00 BT. This was caused by the diurnal variations of solar radiation and thermodynamics over the TP [20]. In this period, strong updrafts were observed above 4 km achieving the maximum value of ~4 m s−1, and the maximum height of strong updrafts could even reach up to 10 km above the ground level. Intense sensible heating induced the thermodynamic conditions suitable for the development of convective activities over the plateau in summer. The boundary layer reached the highest temperature in the afternoon, which caused the instability of atmospheric conditions after that and resulted in three peaks of reflectivity, updrafts, and Vfall (for example, 14:00–16:00, 17:00–19:00, 21:00–23:00 BT). It was beneficial to the convective activity and precipitation. Weak downdrafts were identified before and after each strong updraft. During the period from 04:00 to 14:00 BT, most clouds were located between 2–6 km, and it was difficult for them to develop at the altitude of 7 km due to weak updrafts during that period.
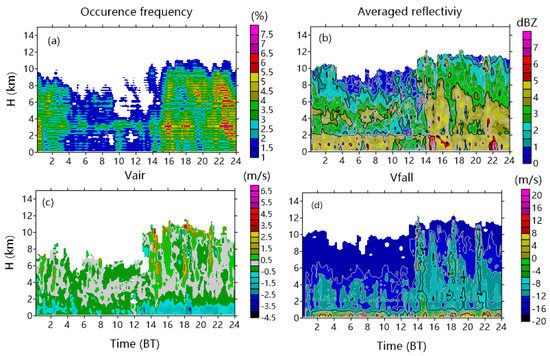
Figure 9.
Diurnal variations in the averaged (a) occurrence frequency of the valid merged reflectivity, (b) reflectivity, (c) Vair, and (d) Vfall at various altitudes during July 2014.
To compare the vertical structures of clouds and precipitation with those in the low altitude regions, the observed results using the same cloud radar in summer 2016 in South China are also represented in Figure 10 [37]. The band in Figure 10a is with the occurrence frequency of the valid merged reflectivity less than 0.05%. The averaged reflectivity in South China was obviously stronger than that in the central Tibetan Plateau due to the stronger convection in the mid-latitude plain, as well as weaker and more frequent convection generally existing in the TP. Many lower clouds and precipitations occurred below 2 km above the ground in South China; however, many high clouds above 8 km with the reflectivity in the range of −10 dBZ–5 dBZ were observed in the TP. In addition, convective precipitation commonly occurred between 10:00 and 20:00 BT in South China. The medium intensity of the convective precipitation was an important factor influencing total precipitation in the central Tibetan Plateau, where the high occurrence rate was from 13:00 to 04:00 BT, implying that precipitation during midnight occurred more frequently over the TP.
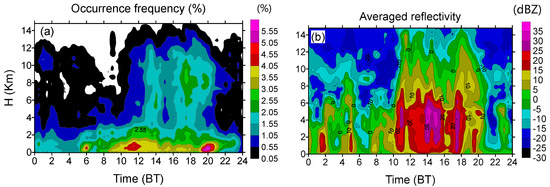
Figure 10.
Diurnal variations in (a) the occurrence frequency of the valid merged reflectivity and (b) averaged reflectivity at various altitudes in South China during July 2016.
3.4. The Characteristics and Diurnal Variations for Different Cloud Types
Two typical convection cases observed on 5 July and 11 July were utilized to investigate the structures of radar reflectivity, cloud types, and vertical air motion (Figure 11). There was not valid data by CR in the band in Figure 11. On 5 July, the echo top of minimum reflectivity (−15 dBZ) reached the height of ~11 km, and the maximum updraft of 7 m s−1 appeared at 7 km in the afternoon. Some of Cu, As, and a limited amount of Sc clouds emerged at 14:00. Dc steadily developed at 16:00 BT and lasted for approximately 8 h, corresponding to the second and third convective peaks, as represented in Figure 11a. Among the Dc clouds, Cu was found below the height of 4 km. The anvil cloud connected the Dc precipitation clouds and occurred in different periods. On 11 July, Cu was the dominate cloud type with the echo top of 9 km and an insignificantly weaker updraft. It dissipated gradually after the sunrise. As, Sc, and St clouds were also observed.
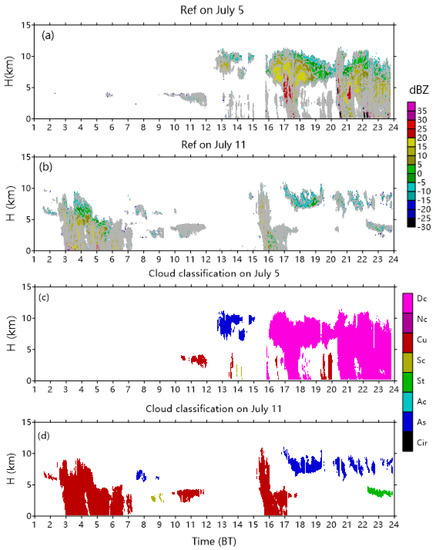
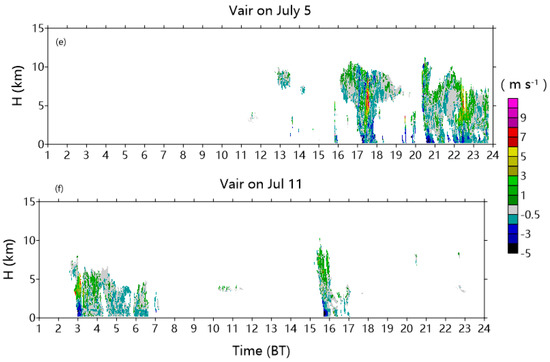
Figure 11.
Time–height cross-sections of (a,b) reflectivity, (c,d) cloud type, and (e,f) Vair on 5 and 11 July 2014.
Figure 12 represents the occurrence frequencies of the eight types of clouds based on the CR observations. The occurrence frequency was defined as the ratio of the number of beams within a specified cloud type to the total number of radar beams. The occurrence frequency was related to the minimum reflectivity observed by the radar, and with an increase in the sensitivity of CR, the amount of observed clouds augmented. Under the same condition, the occurrence frequency of clouds declined with an increase of height, as the detected minimum reflectivity increased with height. The merged reflectivity corresponding to the highly sensitive work mode at the high level allowed the improvement of the occurrence frequency for weak clouds. As there were more than one cloud type simultaneously, the total of occurrence frequencies for the eight types of clouds could exceed 100% in some cases.
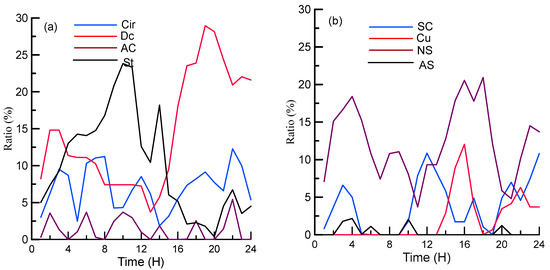
Figure 12.
Diurnal variations of the cloud occurrence frequencies corresponding to eight cloud types: (a) Cir, Dc, Ac, and St, (b) Sc, Cu, Ns, and As.
The results indicated that Dc, Cu, and Ns exhibited similar patterns, namely, the occurrence frequencies rapidly increased after 14:00 and declined at 04:00 BT, which mainly reflected the influence of solar radiation. The maximum frequency of the deep convective clouds (~30%) with larger particles and IWC was the most important factor influencing the surface precipitation, which was similar to the results reported by Fu et al. [11], indicating that summer convective activities reached their strongest state at ~16:00 BT, and less convection was presented in the morning. In contrast, during 04:00–12:00 BT, St exhibited the maximum occurrence frequency (up to 25%). It generally had smaller ice particles and low IWC. In addition to the thermodynamic features, the occurrence frequencies corresponding to As and Ac were less than 5% and were the lowest among all cloud types. The appearance of the high-layer cirrus clouds was more related to the status of atmospheric circulation and could appear in various weather systems; therefore, it did not exhibit obvious daily variation. From Figure 12, we can see that there are few chances for CR to detect Cu and As, possibly due to small areas of Cu and As. Cu and As occurrence frequencies observed by CR possibly have errors due to the short period of time for CR data.
Figure 13 further shows the profiles of averaged reflectivity, Vair, IWC, and Re for eight types of clouds. The IWC and Re were registered only above 2 km (the height of the bright band). The Cir and As commonly occurred above the 5 km height and had reflectivity less than −10 dBZ, IWC less than 0.03 g m−3, and Re less than 50 μm. Ac had the similar reflectivity as As; however, it could reach larger height. St and Sc exhibited similar reflectivity, IWC, and Re below 10 km; however, the averaged reflectivity and air updraft of Sc above the level were larger than those of St. The different vertical distributions of Sc and St reflected the roles of the convective process in cloud developments. Ac exhibited weaker reflectivity compared with that of St.
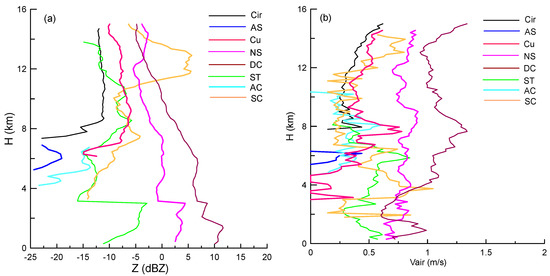
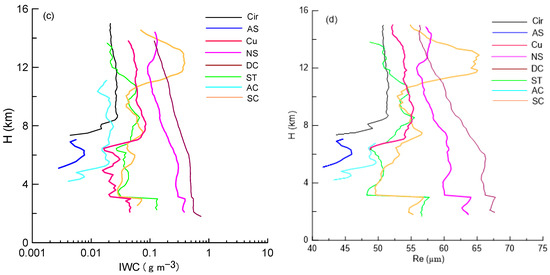
Figure 13.
Vertical profiles of (a) the averaged reflectivity, (b) Vair, (c) IWC, and (d) Re for eight types of clouds.
In general, the values of reflectivity profiles during the precipitation periods (namely, Ns, Cu, and Dc) were larger than those during the non-precipitation ones. Ns exhibited the vertical distribution patterns similar to those of Cu in terms of reflectivity, as well as IWC and Re above the 5 km height. However, their Vair profiles were different. The maximum updraft in Cu was located at 7.5 km, and its value was 1.2 m s−1, indicating the occurrence of weak convection; however, the value of Vair in Ns was approximately 0.7 m s−1 without obvious variations in height. As expected, Dc exhibited the strongest convection activity with the following parameters: ~5 dB of reflectivity, ~0.2 g m−3 of IWC, and ~4 µm of Re greater than those of Cu. This situation remained unchanged below 5 km except for significantly increased air updrafts reaching the height required for strong convection.
4. Discussion on Biases of Vertical Air Motion
Turbulence and wind shear exist in atmosphere and cloud systems [38,39,40]. In this section, the biases in Vair introduced by the Doppler spectra broadening and radar sensitivity are discussed. The vertically pointing radar-measured Doppler spectra are broadened due to turbulence, the vertical variance of the horizontal wind, and the radar beam width. According to previous research [41], vertical air motion bias δ (m s−1) can be estimated as follows:
where is the variance induced by the particle size distribution; is the variance caused by turbulence; is the variance due to wind shear; and is the variance introduced due to the finite radar beam width. The wind horizontal speed for calculation was estimated through sounding at the Naqu weather station. The averaged vertical air motion biases are shown in Figure 14. Most of averaged biases are less than 0.1 m s−1, being incomparably minor with respect to vertical air motion in Figure 9c, and therefore, they should be neglected.
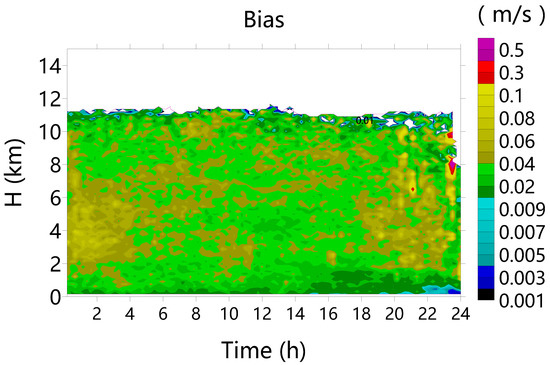
Figure 14.
Averaged vertical air motion biases introduced by turbulence, air horizontal wind speed, and the radar beam width.
The other bias in Vair is associated with the CR radar sensitivity (the minimum observable reflectivity). Coherent integration is performed for the M2 mode twice, and the pulse compression ratio is 60; therefore, theoretically, the sensitivity for M2 mode should be improved by 20.8 dB compared with M3. The Vair values observed simultaneously by M2 and M3 above 2.1 km at the same time are used to analyze the bias in estimated Vair by M2 and M3. The number of distributions with the bias in the retrieved Vair values are represented in Figure 15a. It can be seen that the underestimated vertical air motion of M3 is approximately 0.3 m s−1. The results can be considered to explain a sharp decrease in Vair at the height of 2.1 km in Figure 9c. Above this level, we can utilize the Doppler spectra corresponding to M2 aiming to retrieve air motion; below this level, only the M1 and M3 data are available.
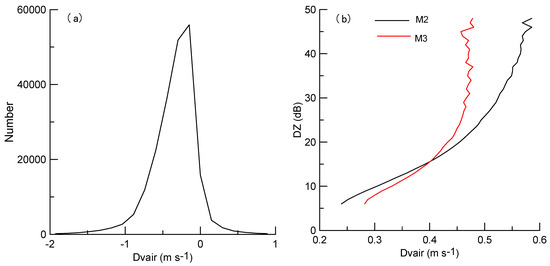
Figure 15.
Distributions of the biases of the vertical air motions retrieved by M2 and M3 (a); the variations of the averaged biases in vertical air motions with the signal level difference (b).
To evaluate the Vair biases introduced due to the range from the CR, we analyze the signal level differences (DZ) of Doppler density data between the first left edge of a valid Doppler spectral and the right points, as well as the corresponding velocity difference (Dvair). The variations of Dvair with DZ are shown in Figure 15b. Considering the same target, if the range from the CR is increased, the weak Doppler density in both of the edges is missed, and the observed left edge of a valid Doppler spectral moves to the right, which leads to underestimations in vertical air motions. Compared with 2.1 km, the signal level of the Doppler density at 10 km can decrease by 13.6 dB, which possibly may introduce the biases air vertical motions of 0.2 m s−1.
5. Conclusions
The raw Doppler density data obtained from the three work modes of CR were qualified, merged, and then used to retrieve the vertical air velocity, hydrometeor fall speed, ice water content, and ice effective radius concerning Naqu, and central Tibetan Plateau. The cloud type classification algorithm was introduced to categorize the observed cloud systems into St, Sc, Cu, Ns, Ac, As, Dc, and Cir types. The statistical characteristics of clouds and precipitation in the vertical and daily variations were analyzed. The major conclusions derived as a result of the conducted analysis were as follows:
(1) Based on the analysis of the vertical structures in clouds and precipitation in TP, we found that the observed clouds with reflectivity less than −5 dBZ were mainly located at a height over 7 km. Precipitation formed below this level, between 4 and 7 km, constituting the rain echo top with the increasing reflectivity where the air updraft and the strong rimming of the small-sized supercooled liquid water particles could have a considerable influence. Most of vertical motions corresponded to weak updrafts between 2 and 4 km, which led to the frequent occurrence of weak clouds in the period of 04:00–12:00 BT. The presence of updrafts at a smaller extent was observed at the height of 7 km, and therefore, most of the rain echo top conditions did not exceed 7 km.
(2) The daily variations, low occurrence rate, weak reflectivity, and low echo top were observed between 04:00 and 12:00 BT. In this period, the interfacial layered structures were usually identified. The high occurrence rates of weak clouds in the case of St were observed at 3 km height, leading to the weak updraft at this level. After 14:00 BT, the convective clouds (Cu and Dc), as well as Ns, quickly developed, and the averaged reflectivity, echo top, and vertical updraft increased. The strong updraft was accompanied with the weak downdraft over the 5 km height.
(3) The non-precipitation clouds (Cir, As, St, Sc, and Ac) exhibited weaker reflectivity, lower IWC, and less vertical variations compared with precipitation clouds (Ns, Cu, and Dc). The air updraft in Sc was larger than that of St. Ns had similar vertical distributions of reflectivity, IWC, and Re compared with those of Cu above the 5 km height. However, the maximum updraft in Cu was ~0.5 m s−1 stronger, indicating the occurrence of weak convection. Dc exhibited the strongest convection activity along with the averaged Z of −5–10 dBZ, air updraft of 0.5–1.8 m s−1, IWC of 0.1–0.6 g m−3, and Re of 57–67 μm.
(4) Compared with the radar sensitivity and range from the CR, the vertical air motion biases introduced by the Doppler spectra broadening due to the turbulence, wind shear, and radar beam width were deemed insignificant and therefore, were neglected.
It should be noted that IWC and Re retrieved from Z could have certain errors due to the complicated shape and phase of particles, as well as the relationships between IWC-Ze and Re-Ze. The attenuation of SZ within a precipitation area could cause the underestimation of updraft. The microphysical parameter retrieval for solid particles based on the Doppler density data will require considerable investigation in the future. We used automatic scheme for cloud classification and no manual observations were carried out at that time, hence there could be errors in cloud type determination in this paper.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: L.L.; data curation: W.G.; methodology: L.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported under the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91837310), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFC1505704), and China Meteorological Administration Special Public Welfare Research Fund (GYHY201406001).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Naqu Meteorological Bureau, and the 23rd Institute of China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation, for the observation data and producing the cloud radar.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wu, G.X.; Chen, S. The effect of mechanical forcing on the formation of a mesoscale vortex. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1985, 111, 1049–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, M.; Li, C.; Song, Z. Seasonal heating of the Tibetan Plateau and its effects on the evolution of the Asian summer monsoon. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1992, 70, 319–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boos, W.R.; Kuang, Z. Dominant control of the South Asian monsoon by orographic insulation versus plateau heating. Nature 2010, 463, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.D.; Liu, J.X. Statistical Characteristic of Radar Echo for Convective Precipitation. Collected Thesis on Meteorological Experiment in Qinghai-Xizang Plateau (in Chinese); Science Press: Beijing, China, 1984; pp. 258–268. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, H.D. Atmospheric static energy for convective processes at Naqu in Tibetan. Plateau Meteorol. 1983, 2, 61–65. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.P.; Chu, R.Z.; Song, X.M.; Zhou, Y.J.; Feng, J.M.; Chen, C.P.; Zhang, T.; Shimizu, S.; Ueno, K.; Koike, T.; et al. Summary and preliminary results of cloud and precipitation observation in Qinghai-Xizang Plateau in GAME-TIBET. Plateau Meteorol. 1999, 18, 441–450. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, S.; Ueno, K.; Fujii, H.; Yamada, H.; Shirooka, R.; Liu, L. Mesoscale characteristics and structure of stratiform precipitation on the Tibetan Plateau. J. Meteor. Soc. Jpn. 2001, 79, 435–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyeda, H.; Yamada, H.; Horikomi1, J. Characteristics of convective clouds observed by a Doppler radar at Naqu on Tibetan Plateau during the GAME-Tibet IOP. J. Meteor. Soc. Jpn. 2001, 79, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.P.; Feng, J.M.; Chu, R.Z.; Zhou, Y.J.; Ueno, K. Diurnal variation of precipitation in monsoon season in the Tibetan Plateau. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 19, 365–378. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.P. Simulation and analysis on observational errors of cloud intensity and structure with TRMM PR and ground-based radar. J. Meteor. Res. 2003, 17, 376–384. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.F.; Li, H.T.; Zi, Y. Case study of precipitation cloud structure viewed by TRMM satellite in a valley of the Tibetan Plateau. Plateau Meteorol. 2007, 26, 98–106. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Yu, X.; Liu, G.; Xu, X.; Yue, Z.; Sun, W.; Yang, F. Satellite retrieval analysis on microphysical property of thunderstorm with light precipitation over the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Plateau Meteorol. 2011, 30, 288–298. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Bai, A.J.; Huang, S.J. Characteristic analysis of a severe convective weather over Tibetan Plateau based on TRMM Data. Plateau Meteorol. 2012, 31, 304–311. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.G.; De, L. Analyses of microphysical features for spring precipitation cloud layers in east of Qinghai. Plateau Meteorol. 2001, 20, 191–196. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.X.; Chen, W.H.; Hang, H.Z. Analysis on precipitation altostratus microphysical structure in spring over north-east Qinghai. Plateau Meteorol. 2002, 21, 281–287. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Xu, X.; Chen, F.; Guo, X.; Zheng, X.; Lu, L.; Hong, Y.; Li, Y.; La, Z.; Peng, H.; et al. The third atmospheric scientific experiment for understanding the earth–atmosphere coupled system over the Tibetan Plateau and its effects. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2018, 99, 757–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.P.; Zheng, J.; Ruan, Z.; Cui, Z.; Hu, Z.; Wu, S.; Dai, G.; Wu, Y. Comprehensive radar observations of clouds and precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau and preliminary analysis of cloud properties. J. Meteor. Res. 2015, 29, 546–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Sui, C.; Fan, J.; Hu, Z.; Zhong, L. A study of cloud microphysics and precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau by radar observations and cloud-resolving model simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 13735–13752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Lu, C. The microphysical properties of convective precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau by a subkilometer resolution cloud-resolving simulation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 3212–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Guo, X.L. Characteristics of convective cloud and precipitation during summer time at Naqu over Tibetan Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 1706–1720. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.F.; Liu, L.P.; Wang, Q.Q.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y. Toward understanding the properties of high ice clouds at the Naqu site on the Tibetan Plateau using ground-based active remote sensing measurements obtained during a short period in July 2014. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2016, 55, 2493–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.F.; Liu, L.P.; Zhu, K.Y.; Wu, J.Y.; Wang, B.Y. A method for retrieving vertical air velocities in convective clouds over the Tibetan Plateau from TIPEX-III cloud radar Doppler spectra. Remote Sens. 2017, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujinami, H.; Yasunari, T. The seasonal and intraseasonal variability of diurnal cloud activity over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2001, 79, 1207–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.S.; Li, C.C.; Ma, J.Z.; Wang, H.Q.; Shi, G.M.; Liang, Z.R.; Luan, Q.; Geng, F.H.; Zhou, X.W. The properties and formation of cirrus clouds over the Tibetan Plateau based on summertime lidar measurements. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 70, 901–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, X.L. Comparative analyses of vertical structure of a deep convective cloud with multi-source satellite and ground-based radar observational data at Naqu over the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2018, 76, 996–1013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.P.; Xie, L.; Cui, Z. Examination and application of Doppler spectral density data in drop size distribution retrieval in weak precipitation by cloud radar. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 38, 223–236. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Zheng, J. Algorithms for Doppler Spectral Density Data Quality Control and Merging for the Ka-Band Solid-State Transmitter Cloud Radar. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Teng, X.; Ji, L.; Zhao, F. A study of the relationship between the attenuation coefficient and radar reflectivity factor for spherical particles in clouds at millimeter wavelengths (in Chinese with English abstract). Acta Meteor Sinica. 2011, 69, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Rossow, W.B.; Schiffer, R.A. Advances in understanding clouds from ISCCP. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 1999, 80, 2261–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sassen, K. Cloud type and macro-physical property retrieval using multiple remote sensors. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 1665–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.T.; MacKeen, P.L.; Witt, A.; Mitchell, E.D.W.; Stumpf, G.J.; Eilts, M.D.; Thomas, K.W. The storm cell identification and tracking algorithm: An enhanced WSR-88D algorithm. Wea. Forecasting 1988, 13, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Bi, Y.; Lü, D.; Duan, S. Cloud classification and distribution of cloud types in Beijing using Ka-band radar data. Adv. Atmos. Phys. 2019, 36, 793–803. [Google Scholar]
- Barber, P.; Yeh, C. Scattering of electromagnetic wave by arbitrarily shaped dielectric bodies. Appl. Opt. 1975, 14, 2864–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Fu, Y. Analysis on climatological characteristics of deep and shallow precipitation cloud in summer over Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Plateau Meteorol. 2015, 34, 1191–1203. [Google Scholar]
- Heymsfield, A.J.; Westbrook, C.D. Advances in the estimation of ice particle fall speeds using laboratory and field measurements. J. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 67, 2469–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, D.L. Use of mass- and area-dimensional power laws for determining precipitation particle terminal velocities. J. Atmos. Sci. 1996, 53, 1710–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Run, Z.; Zheng, J.; Gao, W. Comparing and Merging Observation Data from Ka-Band Cloud Radar, C-Band Frequency-Modulated Continuous Wave Radar and Ceilometer Systems. Remote. Sens. 2017, 9, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Heale, C.J.; Snively, J.B.; Cai, X.; Pautet, P.D.; Fish, C.; Zhao, Y.; Taylor, M.J.; Pendleton, W.R., Jr.; Wickwar, V.; et al. Evidence of dispersion and refraction of a spectrally broad gravity wave packet in the mesopause region observed by the Na lidar and Mesospheric Temperature Mapper above Logan, Utah. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; She, C.Y.; Liu, H.L.; Montgomery, M.T. Evidence of a gravity wave breaking event and the estimation of wave characteristics from sodium lidar observation over Fort Collins, CO (41° N, 105° W). Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 34, L05815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Yuan, T.; Zhao, Y.; Pautet, P.D.; Taylor, M.J.; Pendleton, W.R., Jr. A coordinated investigation of the gravity wave breaking and the associated dynamical instability by a Na lidar and an Advanced Mesosphere Temperature Mapper over Logan, UT (41.7° N, 111.8° W). J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 6852–6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shupe, M.D.; Koliias, P.; Matrosov, M.; Eloranta, E. On deriving vertical air motions from cloud radar Doppler spectra. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2008, 25, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).