Spatiotemporal Distribution of Major Aerosol Types over China Based on MODIS Products between 2008 and 2017
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Method
2.1. Study Domain
2.2. Data Involved in Aerosol-Type Classification
2.2.1. MODIS Data
2.2.2. Population Density
2.2.3. AERONET AOD Products
2.3. Aerosol-Type Classification Methods
2.4. Validation of Satellite Spectral AODs
3. Results
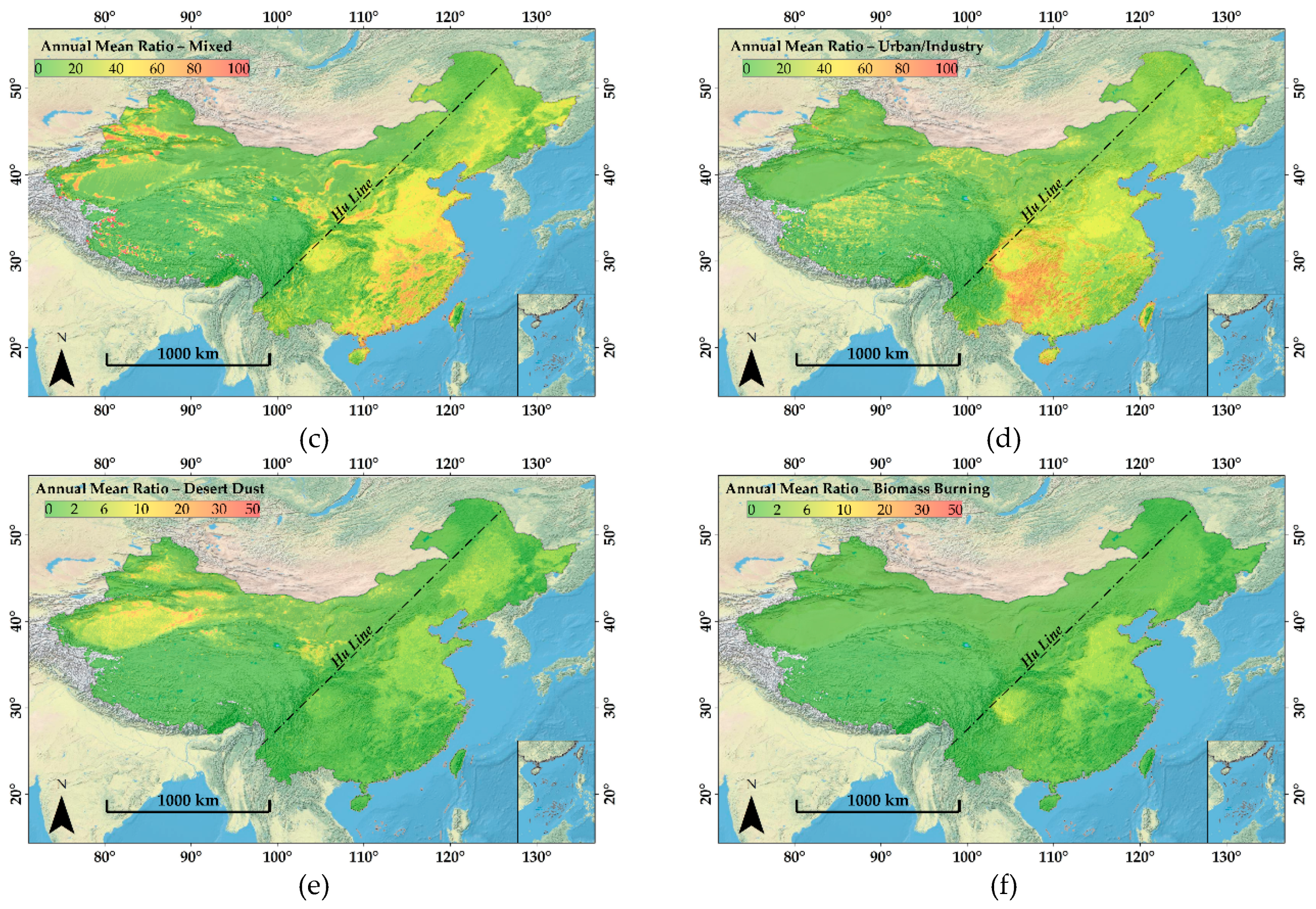
3.1. Spatial Distribution of Background Aerosol Subtypes across China
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Dominant Aerosol Types over China
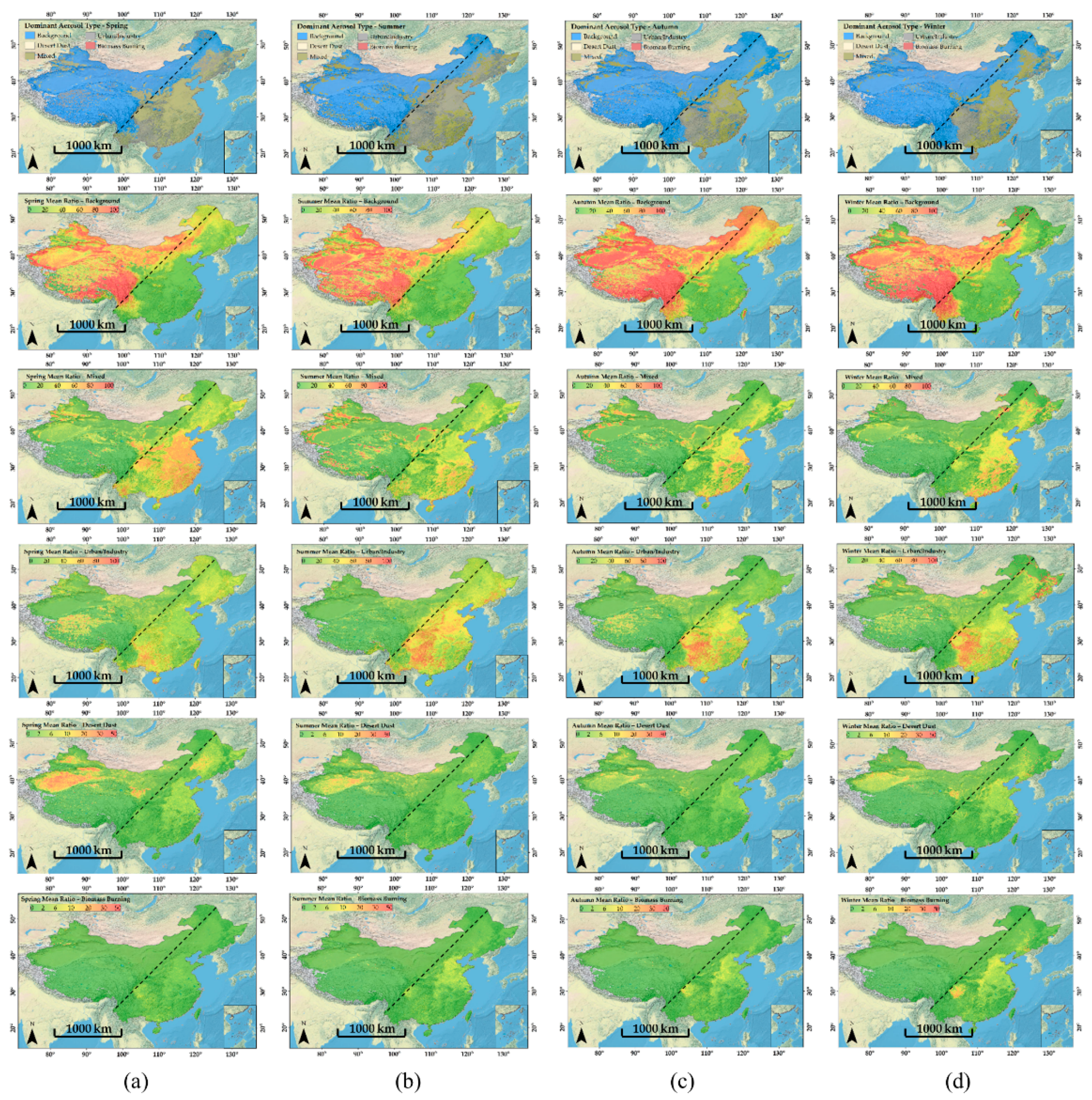
3.3. Seasonal Variation of Dominant Aerosol Types over China
3.4. Inter-Annual Variation of Aerosol Types in Typical Regions over China
3.5. Properties of Typical Aerosol Type over China
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moosmüller, H.; Chakrabarty, R.K.; Arnott, W.P. Aerosol light absorption and its measurement: A review. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2009, 110, 844–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Chin, M.; Feingold, G.; Remer, L.A.; Anderson, T.L.; Balkanski, Y.; Bellouin, N.; Boucher, O.; Christopher, S.; et al. A review of measurement-based assessments of the aerosol direct radiative effect and forcing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Andreae, M.O.; Asmi, A.; Chin, M.; de Leeuw, G.; Donovan, D.P.; Kahn, R.; Kinne, S.; Kivekäs, N.; Kulmala, M.; et al. Global observations of aerosol-cloud-precipitation-climate interactions. Rev. Geophys. 2014, 52, 750–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jimenez, J.L.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Ulbrich, I.M.; Ng, N.L.; Worsnop, D.R.; Sun, Y. Understanding atmospheric organic aerosols via factor analysis of aerosol mass spectrometry: A review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 3045–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Q.; Xu, H.; Li, K.T.; Li, D.H.; Xie, Y.S.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, X.F.; Zhao, W.; Tian, Q.J.; et al. Comprehensive Study of Optical, Physical, Chemical, and Radiative Properties of Total Columnar Atmospheric Aerosols over China: An Overview of Sun–Sky Radiometer Observation Network (SONET) Measurements. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 99, 739–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twomey, S. Aerosols, clouds and radiation. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1991, 25, 2435–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Wang, Y.; Rosenfeld, D.; Liu, X. Review of Aerosol–Cloud Interactions: Mechanisms, Significance, and Challenges. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 73, 4221–4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Liou, K.-N.; Jiang, J.H.; Fan, J.; Liu, X.; Huang, L.; Yung, Y.L. Ice nucleation by aerosols from anthropogenic pollution. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Kleidman, R.G.; Mattoo, S.; Ichoku, C.; Kahn, R.; Eck, T.F. Global evaluation of the Collection 5 MODIS dark-target aerosol products over land. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10399–10420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.; Remer, L.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, J. Variability of Major Aerosol Types in China Classified Using AERONET Measurements. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xia, X.; Wang, J.; Che, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Levy, R.; Oo, M.; Holz, R.; et al. Evaluation of Aerosol Optical Depth and Aerosol Models from VIIRS Retrieval Algorithms over North China Plain. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.H.; Gu, X.F.; Xie, D.H.; Li, Z.Q.; Yu, T.; Chen, X.F. Simultaneous retrieval of aerosol optical properties over the Pearl River Delta, China using multi-angular, multi-spectral, and polarized measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Gong, W.; Liu, B.; Shi, Y.; Chen, Z. Aerosol optical properties and radiative effects: Assessment of urban aerosols in central China using 10-year observations. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 182, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.-X.; Yuan, Y.; Shuai, Y.; Tan, H.-P. Graphical aerosol classification method using aerosol relative optical depth. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 135, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, B. Characteristics of Aerosol Types in Beijing and the Associations with Air Pollution from 2004 to 2015. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeisser, L.; Andrews, E.; Ogren, J.A.; Sheridan, P.; Jefferson, A.; Sharma, S.; Kim, J.E.; Sherman, J.P.; Sorribas, M.; Kalapov, I.; et al. Classifying aerosol type using in situ surface spectral aerosol optical properties. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 12097–12120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogacheva, L.; Rodriguez, E.; Kolmonen, P.; Virtanen, T.H.; Saponaro, G.; de Leeuw, G.; Georgoulias, A.K.; Alexandri, G.; Kourtidis, K.; van Der A, R.J. Spatial and seasonal variations of aerosols over China from two decades of multi-satellite observations-Part 2: AOD time series for 1995–2017 combined from ATSR ADV and MODIS C6.1 and AOD tendency estimations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 16631–16652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Che, H.; Xia, X.; Chen, H.; Goloub, P.; Zhang, W. Column-integrated aerosol optical and physical properties at a regional background atmosphere in North China Plain. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 84, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xia, X.; Che, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Duan, Y. Study of aerosol optical properties at Kunming in southwest China and long-range transport of biomass burning aerosols from North Burma. Atmos. Res. 2016, 169, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, X.; He, Z.; Tan, H. Assessment of column aerosol optical properties using ground-based sun-photometer at urban Harbin, Northeast China. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 74, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, H.; Qi, B.; Zhao, H.; Xia, X.; Eck, T.F.; Goloub, P.; Dubovik, O.; Estelles, V.; Cuevas-Agulló, E.; Blarel, L.; et al. Aerosol optical properties and direct radiative forcing based on measurements from the China Aerosol Remote Sensing Network (CARSNET) in eastern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Jiang, J.H.; Tackett, J.L.; Su, H.; Fu, R. Seasonal and diurnal variations of aerosol extinction profile and type distribution from CALIPSO 5-year observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 4572–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Jiang, J.H.; Diner, D.J.; Su, H.; Gu, Y.; Liou, K.-N.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, L.; Takano, Y.; Fan, X.; et al. Intra-annual variations of regional aerosol optical depth, vertical distribution, and particle types from multiple satellite and ground-based observational datasets. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 11247–11260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.R.; Kang, N.; Yin, Y. Classification of key aerosol types and their frequency distributions based on satellite remote sensing data at an industrially polluted city in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 320–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Liou, K.N.; Xue, Y.; Mechoso, C.R.; Li, W.; Luo, Y. Climatic effects of different aerosol types in China simulated by the UCLA general circulation model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, J.; Wong, M.S.; Yoon, J.; Lee, J.; Wu, D.; Chan, P.W.; Nichol, J.E.; Chung, C.-Y.; Ou, M.-L. Improvement of aerosol optical depth retrieval over Hong Kong from a geostationary meteorological satellite using critical reflectance with background optical depth correction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 142, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Kondragunta, S.; Laszlo, I.; Liu, H.; Remer, L.A.; Huang, J.; Superczynski, S.; Ciren, P. An enhanced VIIRS aerosol optical thickness (AOT) retrieval algorithm over land using a global surface reflectance ratio database. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 10–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalapureddy, M.C.R.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Ernest Raj, P.; Devara, P.C.S.; Kambezidis, H.D.; Kosmopoulos, P.G.; Nastos, P.T. Identification of aerosol type over the Arabian Sea in the premonsoon season during the Integrated Campaign for Aerosols, Gases and Radiation Budget (ICARB). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.N.; Dumka, U.C.; Babu, K.N.; Mathur, A.K. Aerosol characterization and radiative properties over Kavaratti, a remote island in southern Arabian Sea from the period of observations. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Eck, T.F.; Smirnov, A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; King, M.D.; Tanré, D.; Slutsker, I. Variability of Absorption and Optical Properties of Key Aerosol Types Observed in Worldwide Locations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 590–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, D.M.; Sinyuk, A.; Sorokin, M.G.; Schafer, J.S.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Lewis, J.R.; Campbell, J.R.; et al. Advancements in the Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Version 3 database – automated near-real-time quality control algorithm with improved cloud screening for Sun photometer aerosol optical depth (AOD) measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, R.; Yu, H.; Schwartz, S.; Chin, M.; Feingold, G.; Remer, L.; Rind, D.; Halthore, R.; DeCola, P. Atmospheric Aerosol Properties and Climate Impacts; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Cohen, J.B.; Lecoeur, E.; Hui Loong Ng, D. Decadal-scale relationship between measurements of aerosols, land-use change, and fire over Southeast Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 721–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Cohen, J.B.; Wang, S.; Lan, R. Application of a combined standard deviation and mean based approach to MOPITT CO column data, and resulting improved representation of biomass burning and urban air pollution sources. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 241, 111720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.L.; Kanaya, Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Liu, Y.; Pochanart, P.; Akimoto, H.; Sun, Y.L.; Dong, H.B.; Li, J.; Irie, H.; et al. Correlation of black carbon aerosol and carbon monoxide in the high-altitude environment of Mt. Huang in Eastern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 9735–9747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.X.; Shen, W.X.; Yuan, Y.; Xie, M.; Tan, H.P. Inferring Fine-Mode and Coarse-Mode Aerosol Complex Refractive Indices from AERONET Inversion Products over China. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mso, Q.J.; Huang, C.L.; Chen, Q.X.; Zhang, H.X.; Yuan, Y. Satellite-based identification of aerosol particle species using a 2D-space aerosol classification model. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 219, 117057–117069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.Q.; Gu, Y.F.; Zhang, M. Spatiotemporal patterns of aerosol optical depth throughout China from 2003 to 2016. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Fu, D.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Xia, X.; He, J.; Han, X.; Zhang, R.; Che, H. Diurnal and seasonal variability of PM2.5 and AOD in North China plain: Comparison of MERRA-2 products and ground measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 191, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Bo, Y.; Xie, S. High-resolution historical emission inventories of crop residue burning in fields in China for the period 1990–2013. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 138, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Kang, S.; Wang, Y.; Xin, J.; Liu, B.; Guo, Y.; Wen, T.; Zhang, G.; Cong, Z. Size distribution of carbonaceous aerosols at a high-altitude site on the central Tibetan Plateau (Nam Co Station, 4730ma.s.l.). Atmos. Res. 2015, 153, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhawish, A.; Banerjee, T.; Broday, D.; Misra, A.; Tripathi, S. Evaluation of MODIS Collection 6 aerosol retrieval algorithms over Indo-Gangetic Plain: Implications of aerosols types and mass loading. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 201, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gridded Population of the World (GPW), v4. Available online: https://sedac.ciesin.columbia.edu/data/collection/gpw-v4 (accessed on 22 June 2020).
- Omar, A.H.; Won, J.G.; Winker, D.M.; Yoon, S.C.; Dubovik, O.; McCormick, M.P. Development of global aerosol models using cluster analysis of Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Zhang, X.; Xia, X.; Goloub, P.; Holben, B.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Blarel, L.; Damiri, B.; et al. Ground-based aerosol climatology of China: Aerosol optical depths from the China Aerosol Remote Sensing Network (CARSNET) 2002–2013. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2015, 15, 7619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NT, O.N.; Ignatov, A.; Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F. The lognormal distribution as a reference for reporting aerosol optical depth statistics; Empirical tests using multi-year, multi-site AERONET Sunphotometer data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 3333–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Nichol, J.E.; Wang, L. New customized methods for improvement of the MODIS C6 Dark Target and Deep Blue merged aerosol product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 197, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Calvello, M.; Esposito, F.; Pavese, G.; Lin, M.; Cao, J.; Zhou, C.; Li, D.; et al. Regional transport of anthropogenic pollution and dust aerosols in spring to Tianjin—A coastal megacity in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, M.; Koepke, P.; Schult, I. Optical Properties of Aerosols and Clouds: The Software Package OPAC. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Li, D.; Xu, H.; Li, K. Aerosol Optical and Microphysical Properties of Four Typical Sites of SONET in China Based on Remote Sensing Measurements. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 9928–9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, L.; Che, H.; Xia, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, H.; Gui, K.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, T.; Li, X.; et al. Aerosol Optical Properties over an Urban Site in Central China Determined Using Ground-Based Sun Photometer Measurements. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 620–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Lü, R.; Liu, C.; Yuan, L.; Shao, Y.; Zhu, B.; Lei, L. Seasonal variation of columnar aerosol optical properties and radiative forcing over Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 166, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gong, W.; Xia, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, Z. Long-term observations of aerosol optical properties at Wuhan, an urban site in Central China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 101, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Cao, X.; Zhang, L.; Sun, N.; Sun, L.; Logan, T.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y.; Ji, Y.; Lin, Y.; et al. Aerosol vertical distribution and optical properties over China from long-term satellite and ground-based remote sensing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2509–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Cuesta, J.; Li, D.; Wei, P.; Xie, Y.; Li, L. Aerosol Column Size Distribution and Water Uptake Observed during a Major Haze Outbreak over Beijing on January 2013. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 945–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Flynn, C.; Welton, E.J.; Cribb, M. Transport, vertical structure and radiative properties of dust events in southeast China determined from ground and space sensors. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6469–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Shi, C.; Ma, J.; Zhu, B.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Kang, N. Aerosol optical properties during firework, biomass burning and dust episodes in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 81, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, R.; Zhou, R.; Li, D.; Wang, W.; Cheng, T.; Zhou, B. A study of aerosol optical properties during ozone pollution episodes in 2013 over Shanghai, China. Atmos. Res. 2015, 153, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Che, H.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, X.; Hong, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Aerosol Vertical Distribution and Typical Air Pollution Episodes over Northeastern China during 2016 Analyzed by Ground-based Lidar. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 918–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Yuan, X.; He, Q.; Yu, Y.; Cao, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W. Temporal-spatial analysis of crop residue burning in China and its impact on aerosol pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Che, H.; Xia, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, H.; Estellés, V.; An, L.; Gui, K.; Sun, T.; et al. A Comparative Analysis of Aerosol Microphysical, Optical and Radiative Properties during the Spring Festival Holiday over Beijing and Surrounding Regions. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 1774–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, Z.; Ding, A. Impact of Aerosol-PBL Interaction on Haze Pollution: Multiyear Observational Evidences in North China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 8596–8603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Shen, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, T.; Xie, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, H.; et al. The two-way feedback mechanism between unfavorable meteorological conditions and cumulative aerosol pollution in various haze regions of China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 3287–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.X.; Shen, W.X.; Yuan, Y.; Tan, H.P. Verification of aerosol classification methods through satellite and ground-based measurements over Harbin, Northeast China. Atmos. Res. 2019, 216, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Szyszkowicz, M.; Jovic, B.; Cakmak, S.; Austin, C.C.; Zhu, J.P. Aerosol types types and radiative forcing estimates over East Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 141, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.L.; Ge, B.Z.; Wang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Liu, H.; Wei, L.F.; Yue, S.Y.; Uno, I.; Kobayashi, H.; Nishizawa, T.; et al. Synergistic effect of water-soluble species and relative humidity on morphological changes in aerosol particles in the Beijing megacity during severe pollution episodes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Z.; Zhao, W.X.; Qian, X.D.; Wang, S.; Fang, B.; Zhang, Q.L.; Zhang, W.J.; Venables, D.S.; Chen, W.D.; Huang, Y.; et al. The influence of photochemical aging on light absorption of atmospheric black carbon and aerosol single-scattering albedo. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 16829–16844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Kim, Y.J. Satellite remote sensing of Asian aerosols: A case study of clean, polluted, and Asian dust storm days. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 1771–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.H.; Xu, H.; Zheng, F.J. Classifying Aerosols Based on Fuzzy Clustering and Their Optical and Microphysical Properties Study in Beijing, China. Adv. Meteorol. 2017, 2017, 4197652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
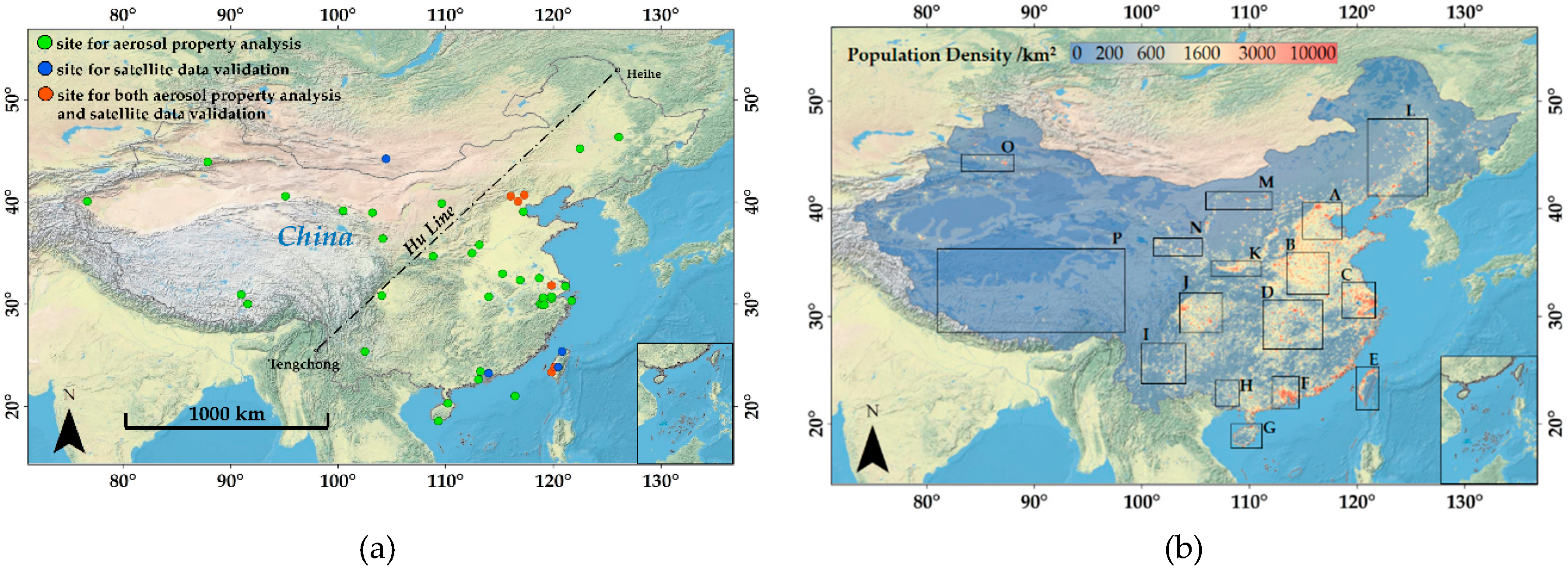
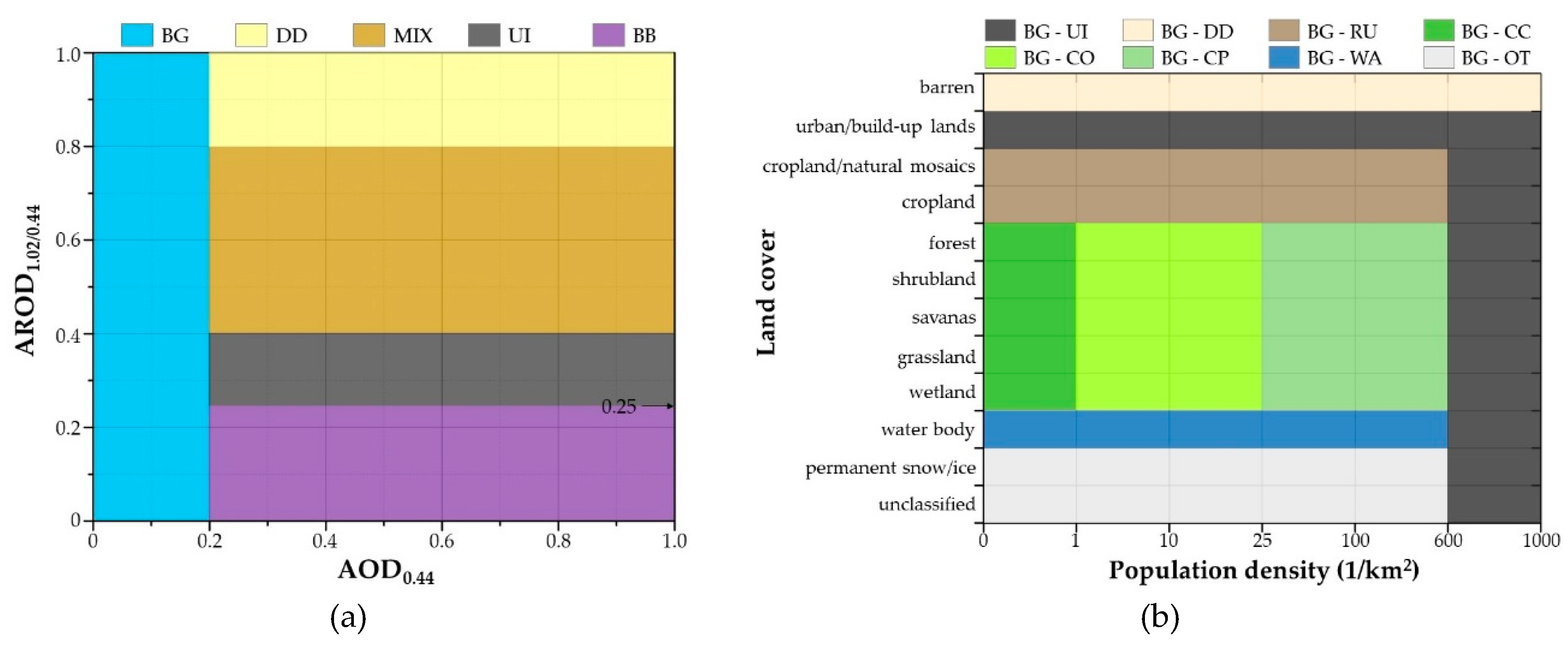

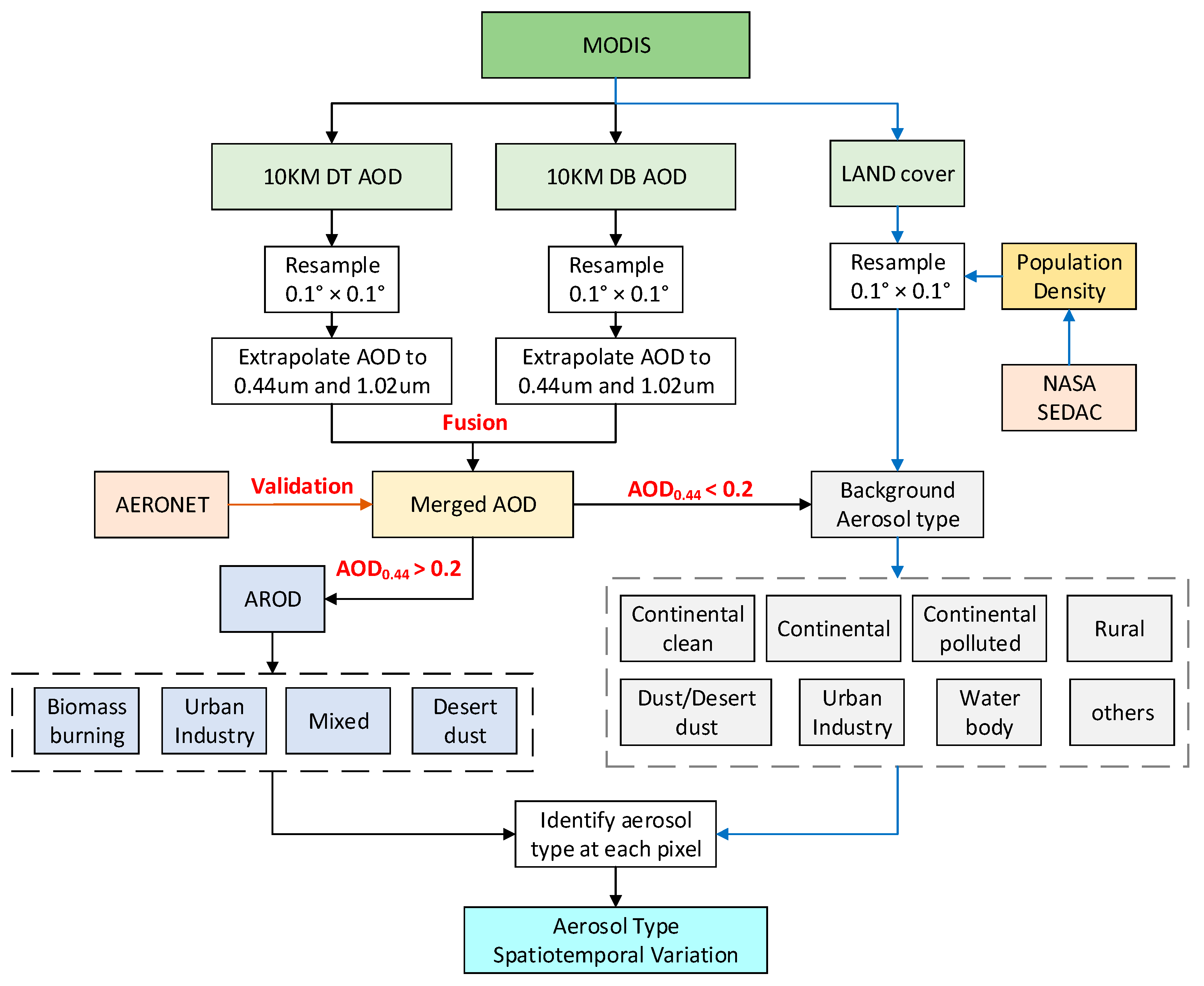
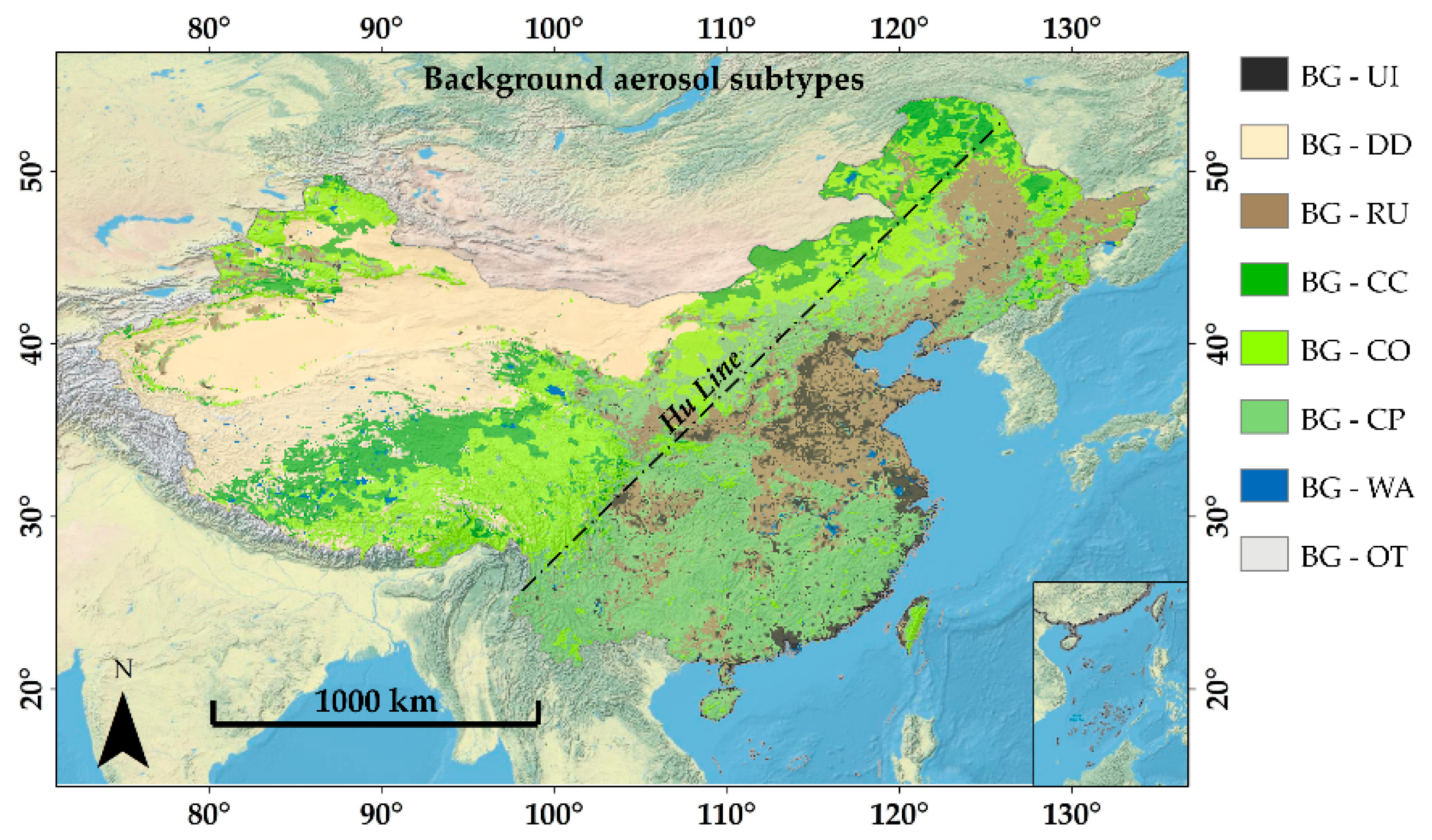

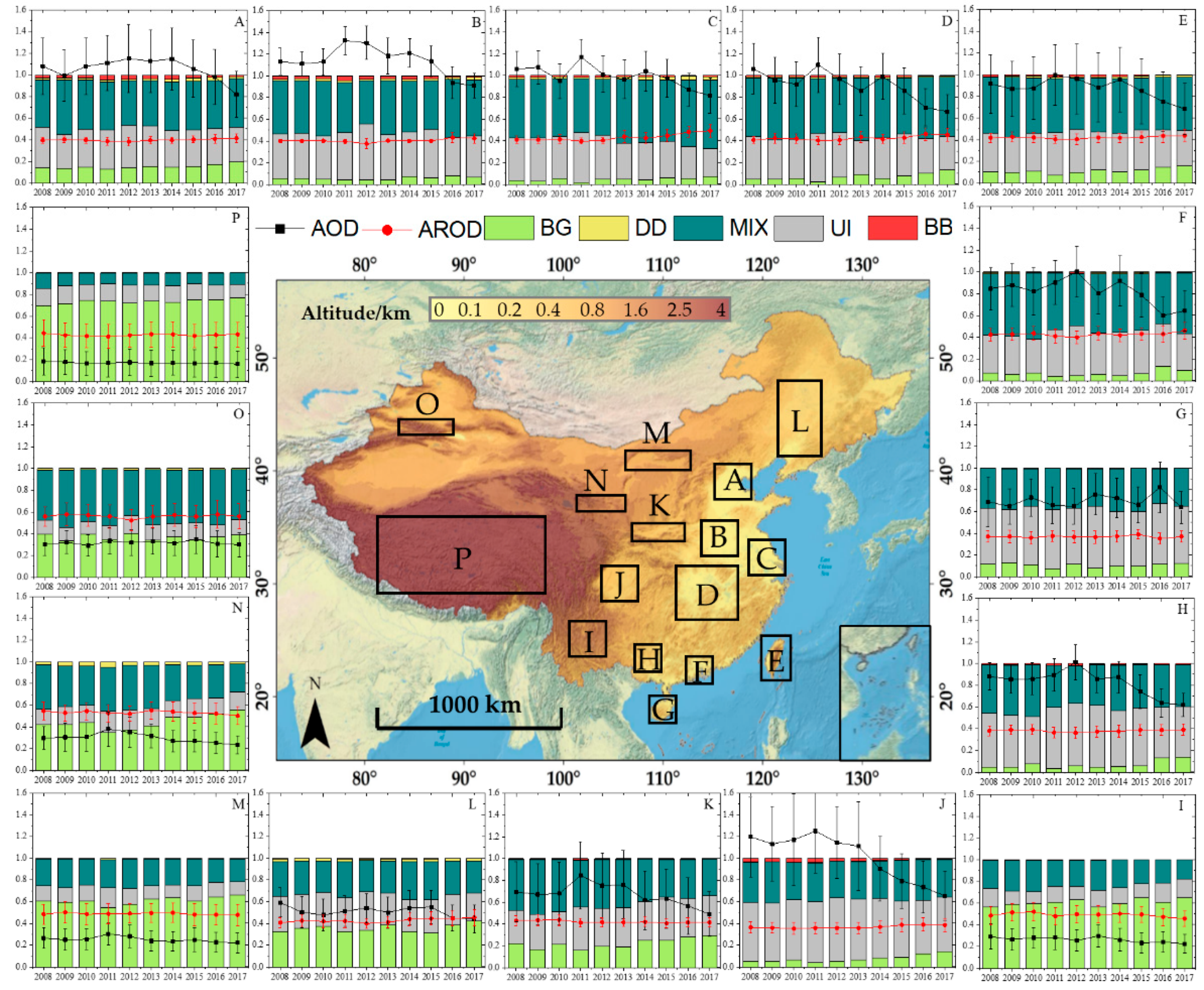
| Region | Name | Longitude (°) | Latitude (°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei | 36.5°N–40.1°N | 114.5°E–118.0°E |
| B | the Central Plain | 32.5°N–35.5°N | 113.0°E–117.5°E |
| C | Yangtze River Delta | 30.5°N–33.0°N | 118.5°E–122.0°E |
| D | Hunan and Hubei Province | 27.5°N–31.0°N | 111.7°E–116.5°E |
| E | Chinese Taiwan | 21.5°N–25.5°N | 119.5°E–112.5°E |
| F | Pearl River Delta | 21.5°N–23.7°N | 112.5°E–114.5°E |
| G | Hainan Province | 18.0°N–20.0°N | 108.5°E–111.1°E |
| H | Guangxi Province | 21.5°N–25.5°N | 107.5°E–111°E |
| I | Yunnan Province | 23.0°N–27.5°N | 101.0°E–104°E |
| J | Sichuan Basin | 28.5°N–32.0°N | 103.5°E–108.5°E |
| K | Central Shaanxi Plain | 34.0°N–35.5°N | 107.0°E–111.5°E |
| L | Northeast China Plain | 40.6°N–47.5°N | 121.5°E–128°E |
| M | Central and Western Inner Mongolia | 40.0°N–41.3°N | 106.8°E–112.5°E |
| N | Upstream of the Yellow River | 35.5°N–37.0°N | 101.5°E–104.0°E |
| O | Northern Piedmonts of Tianshan Mountains | 43.5°N–44.5°N | 84.5°E–87.7°E |
| P | Tibetan Plateau | 28.0°N–35.5°N | 80.0°E–93.0°E |
| Type | SSA | RIR | RII | C1/C2 | R1 | D1 | R2 | D2 | Reference | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UI | 0.91 | 1.46 | 0.0110 | 1.27 | 0.19 | 0.54 | 3.08 | 0.63 | This study | China |
| 0.92 | 1.41 | 0.0063 | 1.13 | 0.16 | 0.42 | 3.55 | 0.73 | Omar et al., 2005 [45] | Global | |
| 0.93 | 1.48 | 0.0099 | 1.42 | 0.26 | 0.54 | 2.58 | 0.57 | Lee et al., 2010 [69] | East Asia | |
| DD | 0.91 | 1.57 | 0.0070 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.51 | 3.06 | 0.65 | This study | China |
| 0.93 | 1.45 | 0.0072 | 0.29 | 0.12 | 0.40 | 2.83 | 0.65 | Omar et al., 2005 [45] | Global | |
| 0.89 | 1.5 | 0.0070 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.52 | 2.35 | 0.60 | Zhang et al., 2017 [70] | China, Beijing | |
| MIX(MA+UI) | 0.95 | 1.48 | 0.01 | 1.30 | 0.19 | 0.51 | 2.96 | 0.64 | This study * | China, coastal |
| MIX(DD+UI) | 0.92 | 1.50 | 0.0085 | 1.28 | 0.15 | 0.48 | 2.52 | 0.65 | This study * | China |
| 0.90 | 1.55 | 0.0049 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.62 | 2.24 | 0.53 | Lee et al., 2010 [69] | East Asia | |
| 0.88 | 1.51 | 0.0140 | 0.50 | 0.16 | 0.48 | 2.71 | 0.65 | Zhang et al., 2017 [70] | China, Beijing | |
| BB | 0.89 | 1.48 | 0.0230 | 1.25 | 0.17 | 0.51 | 4.01 | 0.63 | This study * | China |
| 0.9 | 1.44 | 0.0127 | 1.05 | 0.19 | 0.50 | 2.92 | 0.62 | Lee et al., 2010 [69] | East Asia | |
| 0.84 | 1.48 | 0.0230 | 0.82 | 0.16 | 0.51 | 2.79 | 0.63 | Zhang et al., 2017 [70] | China, Beijing | |
| BG-UI | 0.92 | 1.44 | 0.0070 | 1.78 | 0.26 | 0.57 | 2.94 | 0.55 | Zhang et al., 2017 * [70] | China, Beijing |
| BG-DD | 0.94 | 1.57 | 0.0080 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.52 | 2.52 | 0.64 | This study * | China |
| BG-CC | 0.94 | 1.48 | 0.0060 | 1.10 | 0.16 | 0.51 | 3.96 | 0.63 | This study * | China |
| BG-CO | 0.93 | 1.48 | 0.0075 | 1.25 | 0.16 | 0.51 | 2.84 | 0.63 | This study * | China |
| BG-CP | 0.92 | 1.48 | 0.0080 | 1.50 | 0.16 | 0.51 | 2.76 | 0.63 | This study * | China |
| BG-RU | 0.90 | 1.43 | 0.0120 | 1.00 | 0.17 | 0.50 | 2.73 | 0.60 | Zhang et al., 2017 * [70] | China, Beijing |
| BG-WA | 0.93 | 1.44 | 0.0072 | 0.94 | 0.19 | 0.49 | 2.84 | 0.64 | This study * | China, Taihu |
| BG-MA | 0.95 | 1.43 | 0.0060 | 1.21 | 0.21 | 0.48 | 2.87 | 0.63 | This study * | China, Dongsha Island |
| BG | 0.91 | 1.48 | 0.0080 | 0.94 | 0.17 | 0.52 | 2.72 | 0.63 | This study | China |
| BG | 0.93 | 1.39 | 0.0044 | 0.35 | 0.17 | 0.48 | 3.27 | 0.69 | Omar et al., 2005 [45] | Global |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Q.-X.; Huang, C.-L.; Yuan, Y.; Mao, Q.-J.; Tan, H.-P. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Major Aerosol Types over China Based on MODIS Products between 2008 and 2017. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11070703
Chen Q-X, Huang C-L, Yuan Y, Mao Q-J, Tan H-P. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Major Aerosol Types over China Based on MODIS Products between 2008 and 2017. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(7):703. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11070703
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Qi-Xiang, Chun-Lin Huang, Yuan Yuan, Qian-Jun Mao, and He-Ping Tan. 2020. "Spatiotemporal Distribution of Major Aerosol Types over China Based on MODIS Products between 2008 and 2017" Atmosphere 11, no. 7: 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11070703
APA StyleChen, Q.-X., Huang, C.-L., Yuan, Y., Mao, Q.-J., & Tan, H.-P. (2020). Spatiotemporal Distribution of Major Aerosol Types over China Based on MODIS Products between 2008 and 2017. Atmosphere, 11(7), 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11070703






