Variation of the Distribution of Atmospheric n-Alkanes Emitted by Different Fuels’ Combustion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Sampling Site Descriptions
2.2. Aerosol Collection and Chemical Analysis
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
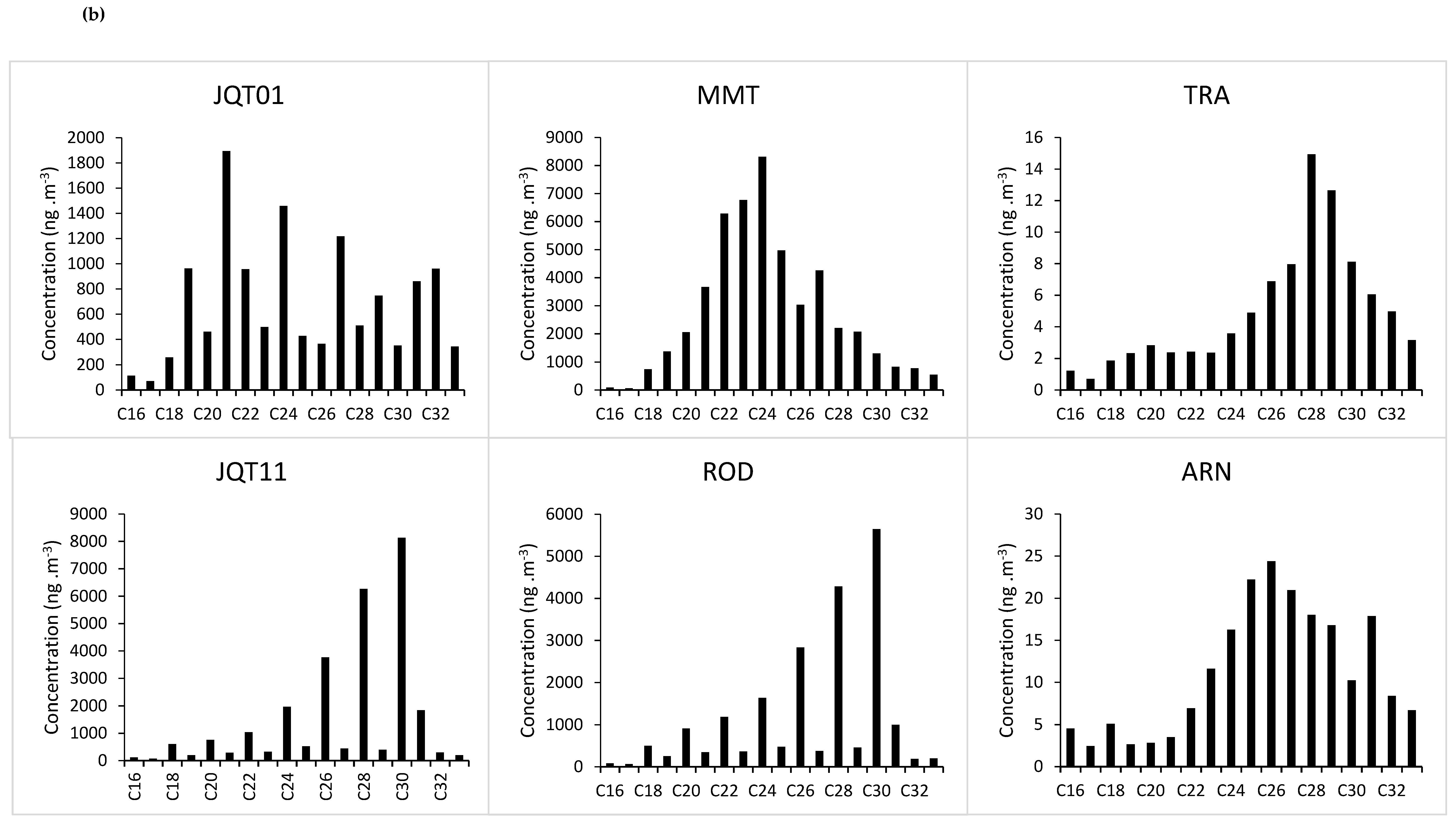
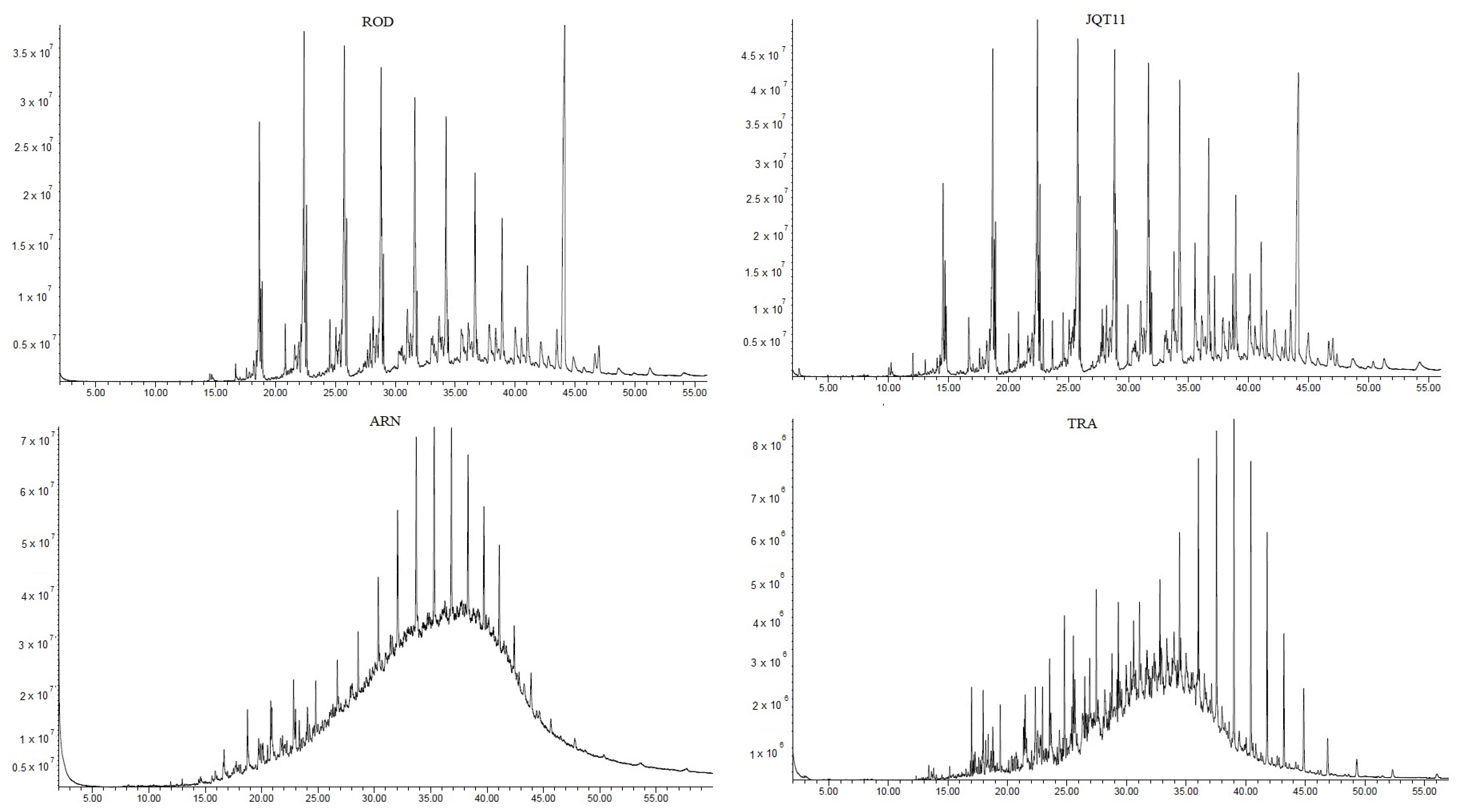
3.1. Particulate Matter and n-Alkane Concentrations in the Tunnels and at the Truck Depot
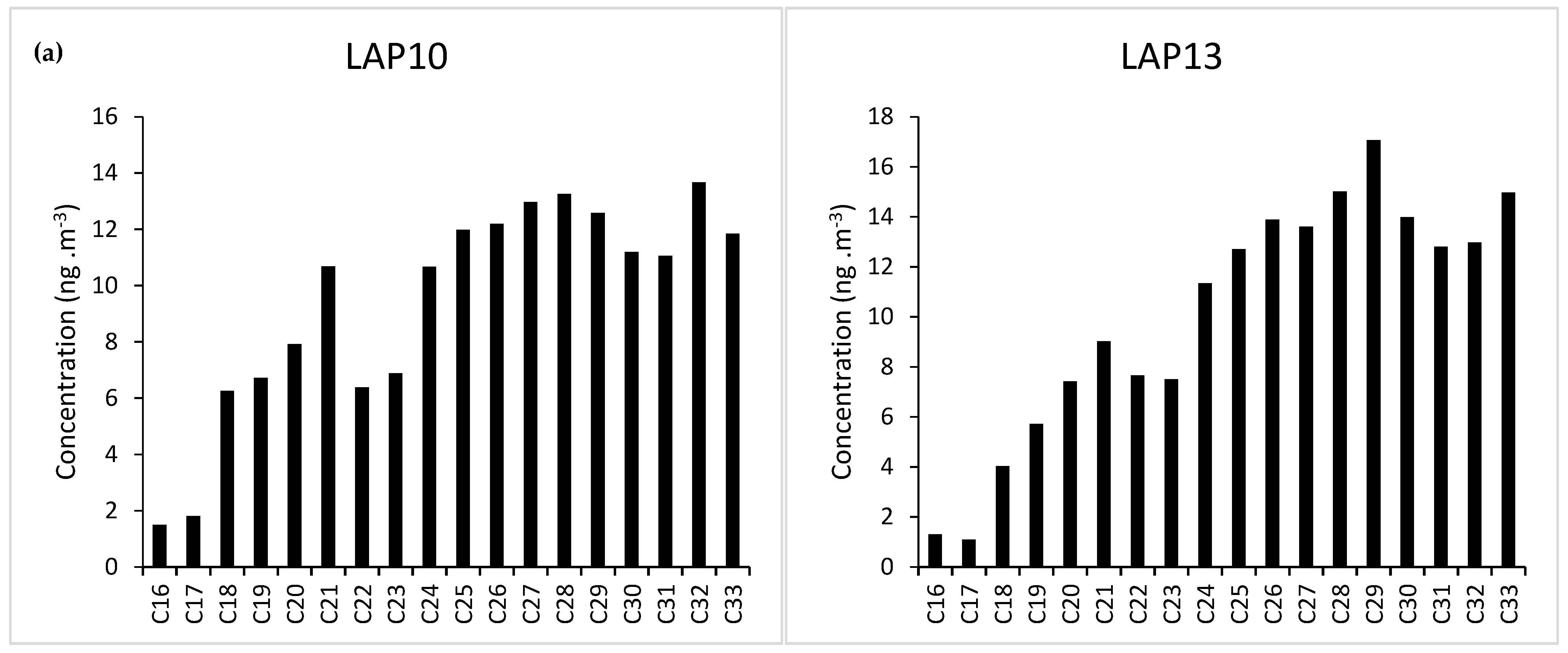
3.2. Particulate Matter and n-Alkanes Concentration in Bus Station (LAP) and Bus Corridor (ARN)
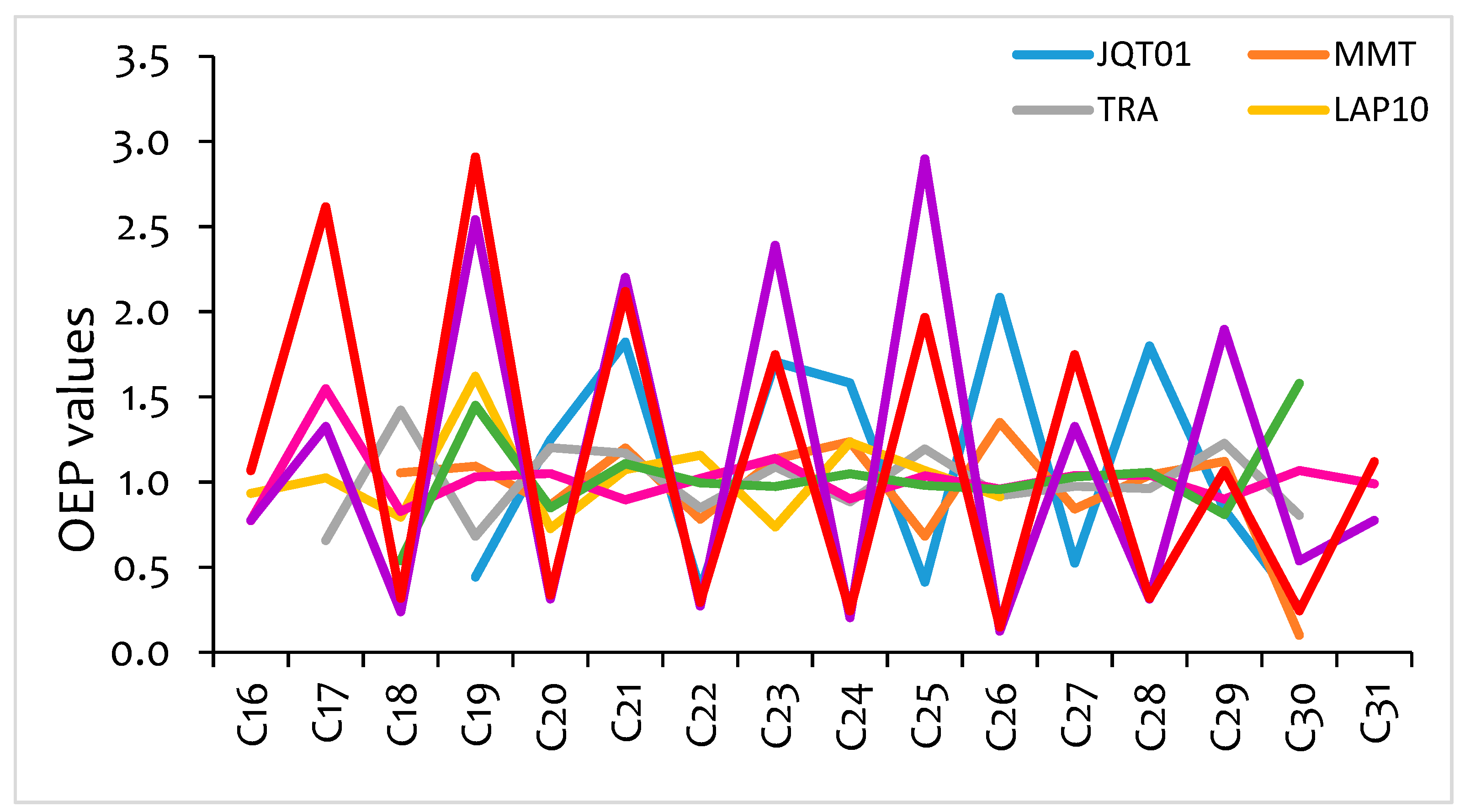
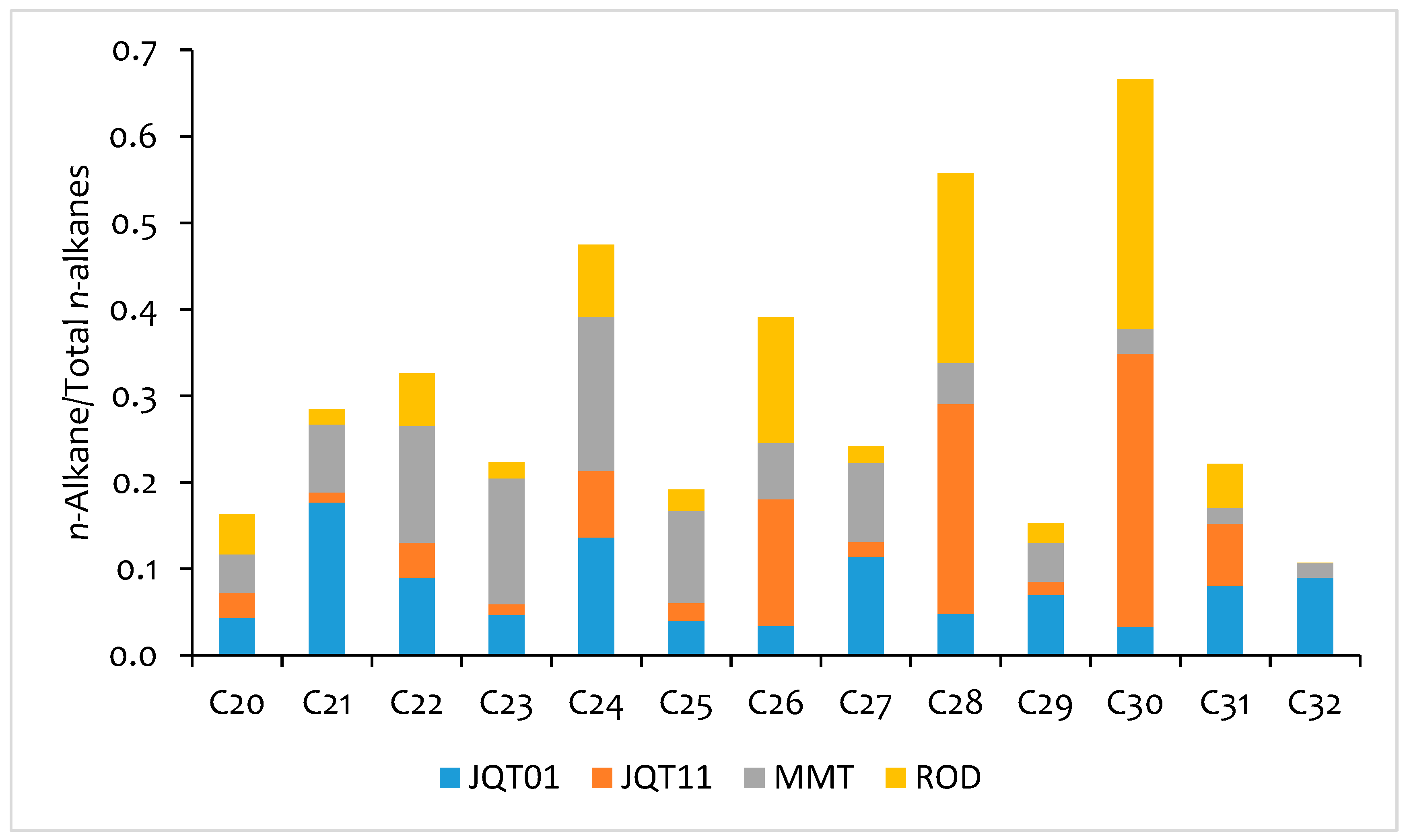
3.3. Species Contribution
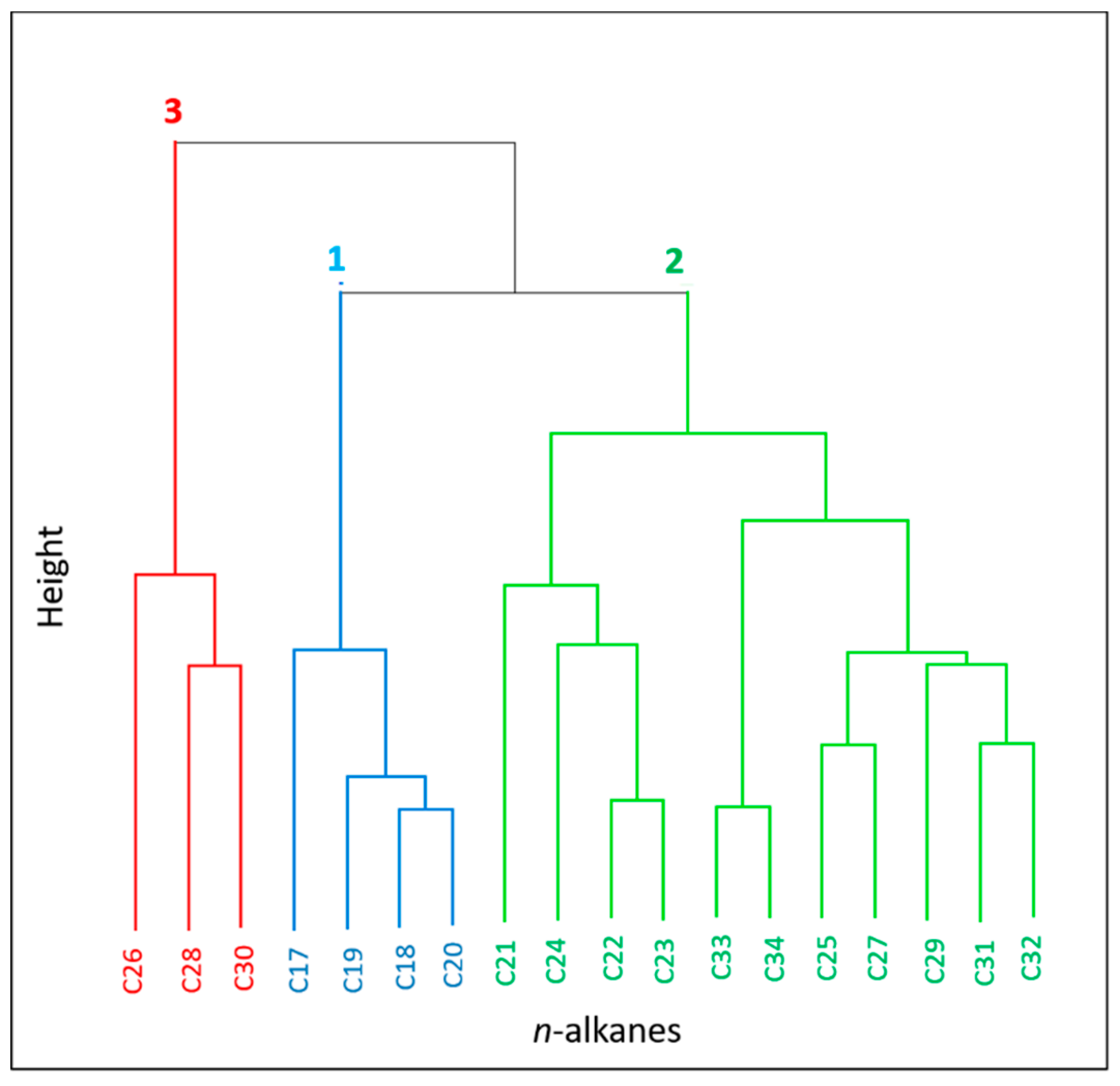
3.4. Statistical Correlations
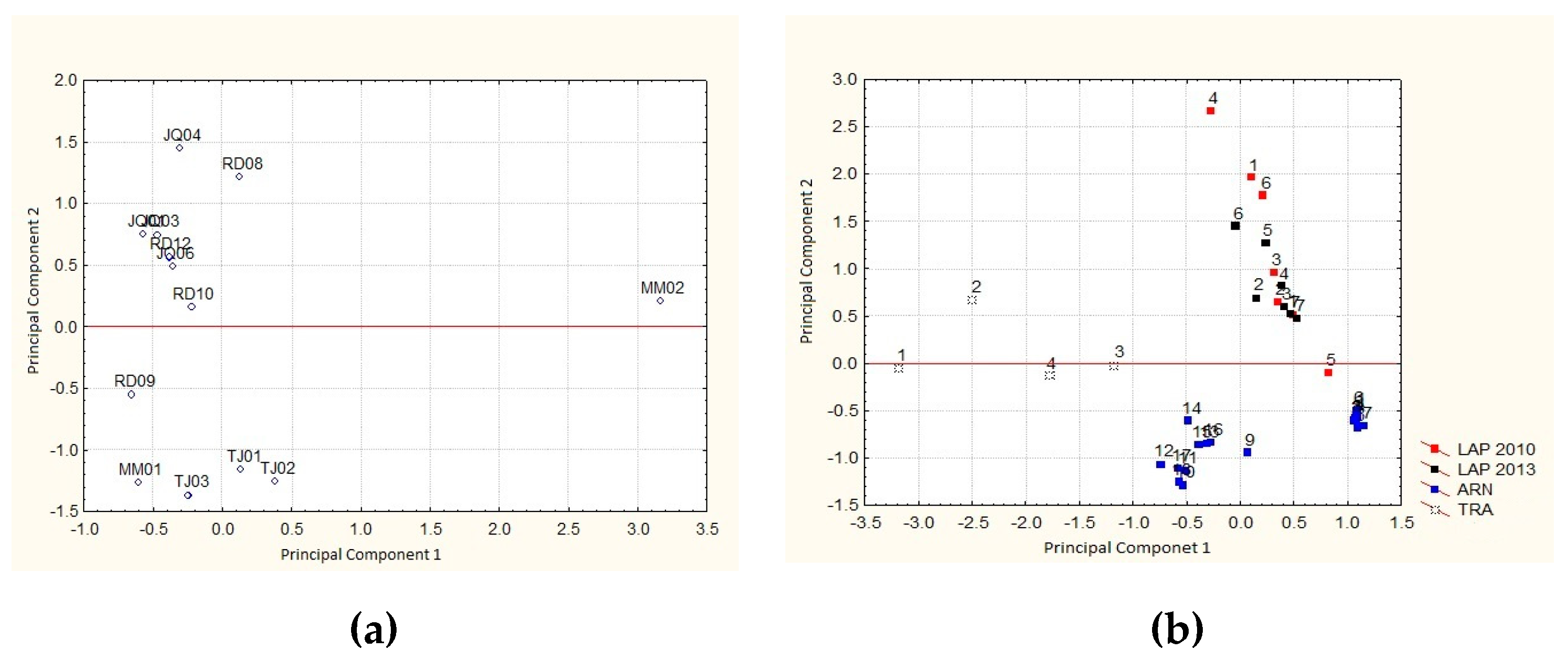
3.5. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Large Values | Small Values | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC1 | PC2 | ||
| C17 | - | - | C17 | −0.931 | - |
| C18 | 0.472 | 0.781 | C18 | −0.931 | - |
| C19 | 0.757 | 0.444 | C19 | −0.864 | 0.324 |
| C20 | 0.761 | 0.481 | C20 | −0.672 | 0.716 |
| C21 | 0.870 | −0.394 | C21 | −0.545 | 0.768 |
| C22 | 0.964 | - | C22 | −0.892 | - |
| C23 | 0.968 | - | C23 | −0.923 | - |
| C24 | 0.952 | - | C24 | −0.926 | - |
| C25 | 0.964 | - | C25 | −0.873 | −0.303 |
| C26 | - | 0.961 | C26 | −0.970 | - |
| C27 | 0.976 | - | C27 | −0.984 | - |
| C28 | - | 0.967 | C28 | −0.984 | - |
| C29 | 0.913 | - | C29 | −0.980 | - |
| C30 | −0.328 | 0.925 | C30 | −0.910 | - |
| C31 | - | 0.634 | C31 | −0.966 | - |
References
- Denatran—Departamento Nacional de Trânsito. Frota de Veículos. 2018. Available online: https://www.denatran.gov.br/estatistica/635-frota-2018 (accessed on 30 June 2018).
- Brito, J.; Rizzo, L.V.; Herckes, P.; Vasconcellos, P.; Caumo, S.E.S.; Fornaro, A.; Ynoue, R.; Artaxo, P.; Andrade, M.F. Physical–chemical characterisation of the particulate matter inside two road tunnels in the São Paulo Metropolitan Area. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2013, 13, 12199–12213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.; Caumo, S.E.S.; Soares, S.; Teinilä, K.; Custódio, D.; Hillamo, R.; Vasconcellos, P.C.; Alves, N.D.O.; Alves, C. Chemical composition of aerosol in São Paulo, Brazil: Influence of the transport of pollutants. Air Qual. Atmosphere Health 2016, 10, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Air Quality Guidelines for Particulate Matter, Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide and Sulfur Dioxide; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005; Available online: http://www.euro.who.int/Document/E87950.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2019).
- Simoneit, B.R.; Sheng, G.; Chen, X.; Fu, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y. Molecular marker study of extractable organic matter in aerosols from urban areas of China. Atmos. Environ. Part A. Gen. Top. 1991, 25, 2111–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, N.Y.M.J.; Bin Abas, M.R.; Rahman, N.A.; Tahir, N.M.; Rushdi, A.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Levels and distributions of organic source tracers in air and roadside dust particles of Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2007, 52, 1485–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoneit, B.R.; Kobayashi, M.; Mochida, M.; Kawamura, K.; Lee, M.; Lim, H.; Turpin, B.J.; Komazaki, Y. Composition and major sources of organic compounds of aerosol particulate matter sampled during the ACE-Asia campaign. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2004, 109, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, F.; He, K.; Liu, X. Characteristics and source identification of fine particulate n-alkanes in Beijing, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 998–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson-Pitts, B.J.; Pitts, J.N. Kinetics and Atmospheric Chemistry. In Chemistry of the Upper and Lower Atmosphere; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 130–178. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, R. Gas-phase tropospheric chemistry of volatile organic compounds: 1. Alkanes and alkenes. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1997, 26, 215–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidleman, T.F.; Billings, W.N.; Foreman, W.T. Vapor-Particle Partitioning of Semivolatile Organic Compounds: Estimates from Field Collections. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1986, 20, 1038–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, C.O.; Ratledge, C. Toxicity of n-Alkanes, n-Alk-1-enes, n-Alkan-1-ols and n-Alkyl-1-bromides towards Yests. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1972, 72, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, I.; Bastian, V.; Becker, K.; Fink, E.; Zabel, F. Reactivity studies of organic substances towards hydroxyl radicals under atmospheric conditions. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 1982, 16, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitts, J.N. Nitration of gaseous polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in simulated and ambient urban atmospheres: A source of mutagenic nitroarenes. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 1987, 21, 2531–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enya, T.; Suzuki, H.; Watanabe, T.; Hirayama, T.; Hisamatsu, Y. 3-Nitrobenzanthrone, a Powerful Bacterial Mutagen and Suspected Human Carcinogen Found in Diesel Exhaust and Airborne Particulates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 2772–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicre, M.; Marty, J.; Saliot, A.; Aparicio, X.; Grimalt, J.O.; Albaiges, J. Aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons in different sized aerosols over the Mediterranean Sea: Occurrence and origin. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 1987, 21, 2247–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Allaban, M.; A Gillies, J.; Gertler, A.W.; Clayton, R.; Proffitt, D. Tailpipe, resuspended road dust, and brake-wear emission factors from on-road vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 5283–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogge, W.F.; Hildemann, L.M.; Mazurek, M.A.; Cass, G.R.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Sources of fine organic aerosol. 3. Road dust, tire debris, and organometallic brake lining dust: Roads as sources and sinks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 1892–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogge, W.F.; Hildemann, L.M.; Mazurek, M.A.; Cass, G.R.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Sources of fine organic aerosol. 2. Noncatalyst and catalyst-equipped automobiles and heavy-duty diesel trucks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 636–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Readman, J.W.; Fillmann, G.; Tolosa, I.; Bartocci, J.; Villeneuve, J.-P.; Catinni, C.; Mee, L.D. Petroleum and PAH contamination of the Black Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 44, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. Estatística Populacional Brasileira. 2017. Available online: https://cidades.ibge.gov.br/brasil/sp/sao-paulo/panorama (accessed on 30 June 2018).
- Vasconcellos, P.; Souza, D.Z.; Magalhães, D.; Da Rocha, G.O. Seasonal Variation of n-Alkanes and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Concentrations in PM10 Samples Collected at Urban Sites of São Paulo State, Brazil. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 222, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, R.L. Hidrocarbonetos Alifáticos (n-alcanos) Associados ao Material Particulado Atmosferico da Estação da Lapa e Regiões no Entorno da Baía de Todos os Santos; Universidade Federal da Bahia: Salvador, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcellos, P.; Zacarias, D.; Pires, M.A.; Pool, C.S.; Carvalho, L.R. Measurements of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in airborne particles from the metropolitan area of São Paulo City, Brazil. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 3009–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caumo, S.; Vicente, A.; Custódio, D.; Alves, C.; Vasconcellos, P. Organic compounds in particulate and gaseous phase collected in the neighbourhood of an industrial complex in São Paulo (Brazil). Air Qual. Atmosphere Health 2017, 11, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Huang, B.; Liu, M.; Bi, X.; Ren, Z.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J. Characterization of PM2.5-bound nitrated and oxygenated PAHs in two industrial sites of South China. Atmos. Res. 2012, 109, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.A. Characterisation of solvent extractable organic constituents in atmospheric particulate matter: An overview. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências 2008, 80, 21–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Gadi, R.; Mandal, T.; Sharma, S. Seasonal variations and source profile of n-alkanes in particulate matter (PM10) at a heavy traffic site, Delhi. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala, R.S.; Smith, J.E. An improved measure of the odd-even predominance in the normal alkanes of sediment extracts and petroleum. Geochem. Et Cosmochim. Acta 1970, 34, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavouras, I.G.; Stratigakis, N.; Stephanou, E.G. Iso- and anteiso-alkanes: Specific tracers of environmental tobacco smoke in indoor and outdoor particle-size distributed urban aerosols. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavouras, I.G.; Lawrence, J.; Koutrakis, P.; Stephanou, E.G.; Oyola, P. Measurement of particulate aliphatic and polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons in Santiago de Chile: Source reconciliation and evaluation of sampling artifacts. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 4977–4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.F.; Kumar, P.; Freitas, E.D.; Ynoue, R.Y.; Martins, J.; Martins, L.D.; Nogueira, T.; Perez-Martinez, P.J.; De Miranda, R.M.; Albuquerque, T.T.D.A.; et al. Air quality in the megacity of São Paulo: Evolution over the last 30 years and future perspectives. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 159, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffney, J.S.; Marley, N.A. Atmospheric chemistry and air pollution. Sci. World J. 2003, 3, 199–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CONAMA Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente. RESOLUÇÃO/conama/N.o 003 de 28 de junho de 1990. Brasil, 1990. Available online: http://www2.mma.gov.br/port/conama/res/res90/res0390.html (accessed on 25 June 2019).
- CETESB. Padrões de Qualidade do Ar. 2018. Available online: https://cetesb.sp.gov.br/ar/padroes-de-qualidade-do-ar/ (accessed on 6 June 2019).
- Alves, C.; Oliveira, C.; Martins, N.C.T.; Mirante, F.; Caseiro, A.; Pio, C.; Matos, M.; Silva, H.; Oliveira, C.; Camões, F. Road tunnel, roadside, and urban background measurements of aliphatic compounds in size-segregated particulate matter. Atmos. Res. 2016, 168, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yu, N.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S.; Ma, L.; Zhao, J.; Lohmann, R. Particulate matter, gaseous and particulate polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in an urban traffic tunnel of China: Emission from on-road vehicles and gas-particle partitioning. Chemosphere 2015, 134, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, J.; Carbone, S.; Dos Santos, D.A.M.; Dominutti, P.; Alves, N.D.O.; Rizzo, L.V.; Artaxo, P. Disentangling vehicular emission impact on urban air pollution using ethanol as a tracer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simoneit, B.R.T.; Cardoso, J.N.; Robinson, N. An assessment of the origin and composition of higher molecular weight organic matter in aerosols over Amazonia. Chemosphere 1990, 21, 1285–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoneit, B.R.T. Organic matter of the troposphere-III. Characterization and sources of petroleum and pyrogenic residues in aerosols over the western united states. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 1984, 18, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcellos, P.C.; Carvalho, L.R.F.; Pool, C.S. Volatile organic compounds inside urban tunnels of São Paulo City, Brazil. J. Br. Chem. Soc. 2005, 16, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Air Quality Guidelines; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, P.A.D.P.; Lopes, W.A.; Carvalho, L.S.; Da Rocha, G.O.; Bahia, N.D.C.; Loyola, J.; Quiterio, S.L.; Escaleira, V.; Arbilla, G.; De Andrade, J.B. Atmospheric concentrations and dry deposition fluxes of particulate trace metals in Salvador, Bahia, Brazil. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 7837–7850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Kawamura, K.; Shooter, D. Wintertime organic aerosols in Christchurch and Auckland, New Zealand: Contributions of residential wood and coal burning and petroleum utilization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 5257–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcellos, P.; Souza, D.Z.; Ávila, S.G.; Araújo, M.P.; Naoto, E.; Nascimento, K.H.; Cavalcante, F.S.; Dos Santos, M.; Smichowski, P.; Behrentz, E.; et al. Comparative study of the atmospheric chemical composition of three South American cities. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 5770–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, A.M.; Sutton, P.A.; Lewis, C.A.; Lewis, A.C.; Scarlett, A.G.; Chau, W.; Widdows, J.; Rowland, S.J. Unresolved Complex Mixtures of Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Thousands of Overlooked Persistent, Bioaccumulative, and Toxic Contaminants in Mussels. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulo, F. Lei Ordinária 316—2001 São Paulo, SP. Legislacao Municipal do Estado de Sao Paulo; 2003. Available online: https://www.al.sp.gov.br/propositura/?id=107180&tipo=1&ano=2001 (accessed on 15 June 2019).
- Masiol, M.; Harrison, R.M. Aircraft engine exhaust emissions and other airport-related contributions to ambient air pollution: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 95, 409–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhao, J.; Xu, H.; Arimoto, R.; Wang, G.; Han, Y.; Shen, Z.; Li, G. n-Alkanes and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in total suspended particulates from the southeastern Tibetan Plateau: Concentrations, seasonal variations, and sources. Sci. Total. Environ. 2014, 470, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Peng, Y.; Bai, Z. Distributions and sources of n-alkanes in PM 2.5 at urban, industrial and coastal sites in Tianjin, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Kawamura, K. Molecular characteristics of urban organic aerosols from Nanjing: A case study of a mega-city in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7430–7438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.L.; Bi, X.H.; Sheng, G.Y.; Tan, J.; Fu, J.M. Seasonal Variation of the Particle Size Distribution of n-Alkanes and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Urban Aerosol of Guangzhou, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 117, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oros, D.R.; Standley, L.J.; Chen, X.; Simoneit, B.R. Epicuticular Wax Compositions of Predominant Conifers of Western North America. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C 1999, 54, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Xie, M.; Shi, L.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Shang, W.; Wang, K.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Chu, G. Alkanes, compound-specific carbon isotope measures and climate variation during the last millennium from varved sediments of Lake Xiaolongwan, northeast China. J. Paleolimnol. 2013, 50, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladji, R.; Yassaa, N.; Balducci, C.; Cecinato, A.; Meklati, B.Y. Annual variation of particulate organic compounds in PM10 in the urban atmosphere of Algiers. Atmos. Res. 2009, 92, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miranda, R.M.; Perez-Martinez, P.J.; Andrade, M.D.F.; Ribeiro, F.N.D. Relationship between black carbon (BC) and heavy traffic in São Paulo, Brazil. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2019, 68, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, M.T.; Parmigiani, M.M.M.; Andrade, M.D.F.; Morawska, L.; Kumar, P. A review of emissions and concentrations of particulate matter in the three major metropolitan areas of Brazil. J. Transp. Health 2017, 4, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministério do Meio Ambiente. Proconve: Programa de Controle de Poluição do ar Por Veículos Automotores; Ministério do Meio Ambiente: Brasilia, Brazil, 2018.
- Bozzetti, C.; El Haddad, I.; Salameh, D.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Fermo, P.; Gonzalez, R.; Minguillon, M.C.; Iinuma, Y.; Poulain, L.; Elser, M.; et al. Organic aerosol source apportionment by offline-AMS over a full year in Marseille. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2017, 17, 8247–8268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Wang, G.; Hu, S.; Han, Q.; Xu, Y.; Gao, Z. Aliphatic alkanes and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in atmospheric PM10 aerosols from Baoji, China: Implications for coal burning. Atmos. Res. 2009, 93, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
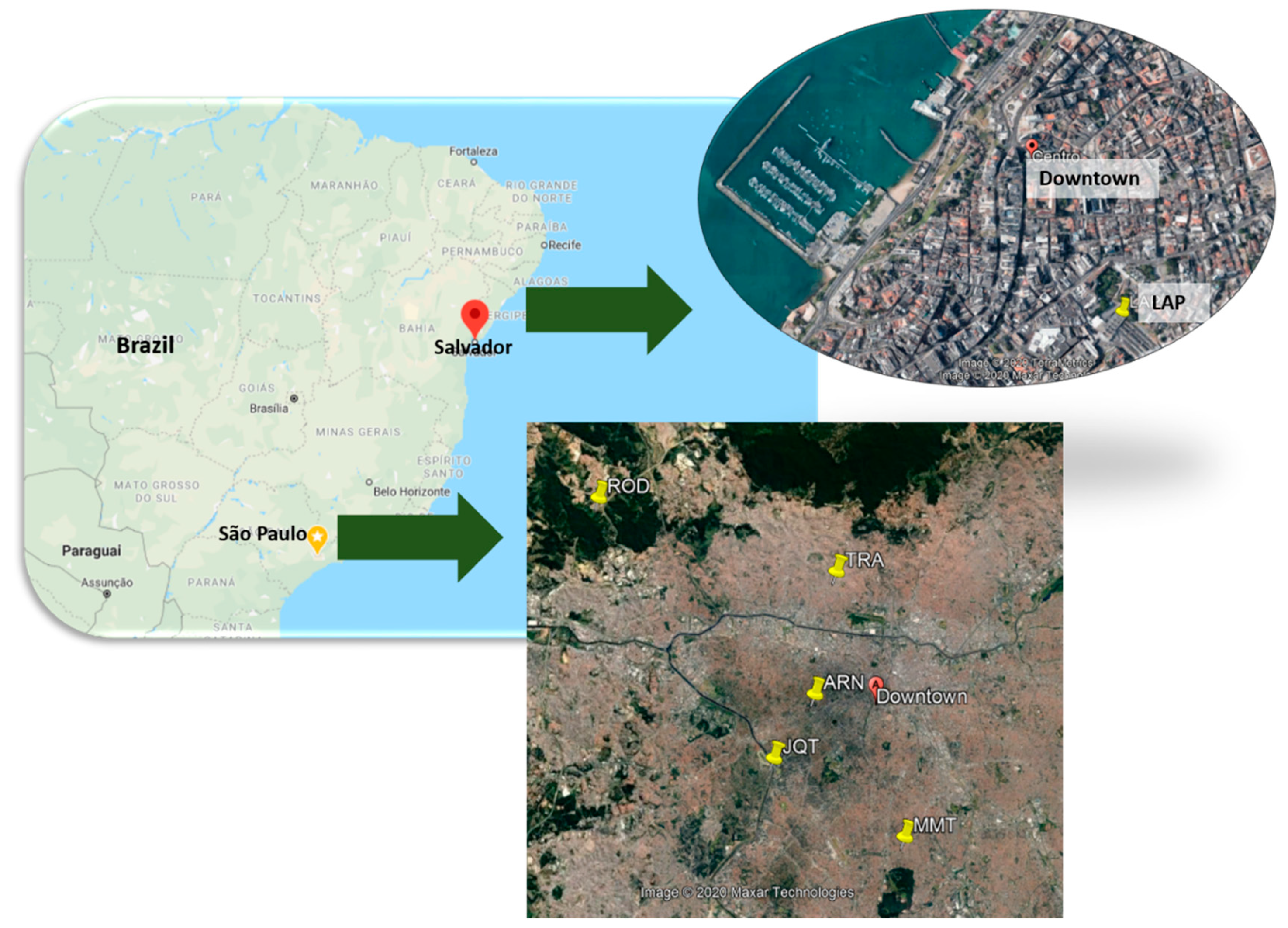
| City | Site | PM Size | N | Sampling Duration (h) | Days of Sampling | Month | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| São Paulo | JQT01 | TSP | 3 | 6 | 2 | August | 2001 |
| MMT | TSP | 2 | 6 | 2 | August | 2001 | |
| JQT11 | PM2.5 | 6 | 6 | 3 | May | 2011 | |
| ROD | PM2.5 | 4 | 6 | 2 | July | 2011 | |
| ARN | PM2.5 | 7 | 24 | 7 | September | 2013 | |
| TRA | PM2.5 | 4 | 24 | 4 | May | 2015 | |
| Salvador | LAP10 | PM10 | 27 | 8 | 9 | April–May | 2010 |
| LAP13 | PM10 | 25 | 8 | 8 | October | 2013 |
| Site | Mean | Min | Max | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LAP10 ** | 141 | 82 | 171 | 37.0 |
| LAP13 ** | 91 | 56 | 127 | 29.0 |
| JQT01 *** | 488 | 419 | 571 | 62.1 |
| MMT *** | 253 | 199 | 308 | 44.5 |
| JQT11 * | 52 | 49 | 59 | 4.2 |
| ROD * | 233 | 202 | 282 | 32.9 |
| TRA * | 92 | 46 | 145 | 40.5 |
| ARN * | 79 | 44 | 124 | 32.7 |
| Site | CPI1 | CPI2 | ACL | %PNA | Cmax |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LAP10 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 27 | 97 | C32 |
| LAP13 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 28 | 97 | C29 |
| JQT01 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 28 | 75 | C21 |
| MMT | 1.0 | 1.0 | 26 | 96 | C24 |
| JQT11 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 29 | 99 | C30 |
| ROD | 0.2 | 0.4 | 28 | 99 | C30 |
| ARN | 1.1 | 1.2 | 28 | 93 | C26 |
| TRA | 0.9 | 1.4 | 28 | 97 | C30 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caumo, S.; Bruns, R.E.; Vasconcellos, P.C. Variation of the Distribution of Atmospheric n-Alkanes Emitted by Different Fuels’ Combustion. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060643
Caumo S, Bruns RE, Vasconcellos PC. Variation of the Distribution of Atmospheric n-Alkanes Emitted by Different Fuels’ Combustion. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(6):643. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060643
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaumo, Sofia, Roy E. Bruns, and Pérola C. Vasconcellos. 2020. "Variation of the Distribution of Atmospheric n-Alkanes Emitted by Different Fuels’ Combustion" Atmosphere 11, no. 6: 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060643
APA StyleCaumo, S., Bruns, R. E., & Vasconcellos, P. C. (2020). Variation of the Distribution of Atmospheric n-Alkanes Emitted by Different Fuels’ Combustion. Atmosphere, 11(6), 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060643





