Exposure and Respiratory Tract Deposition Dose of Equivalent Black Carbon in High Altitudes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Route Characteristics
2.2. Description of Travel Modes
2.3. Instrumentation and Sampling Design
2.4. Estimation of Respiratory Tract Deposition Dose
3. Results and Discussion
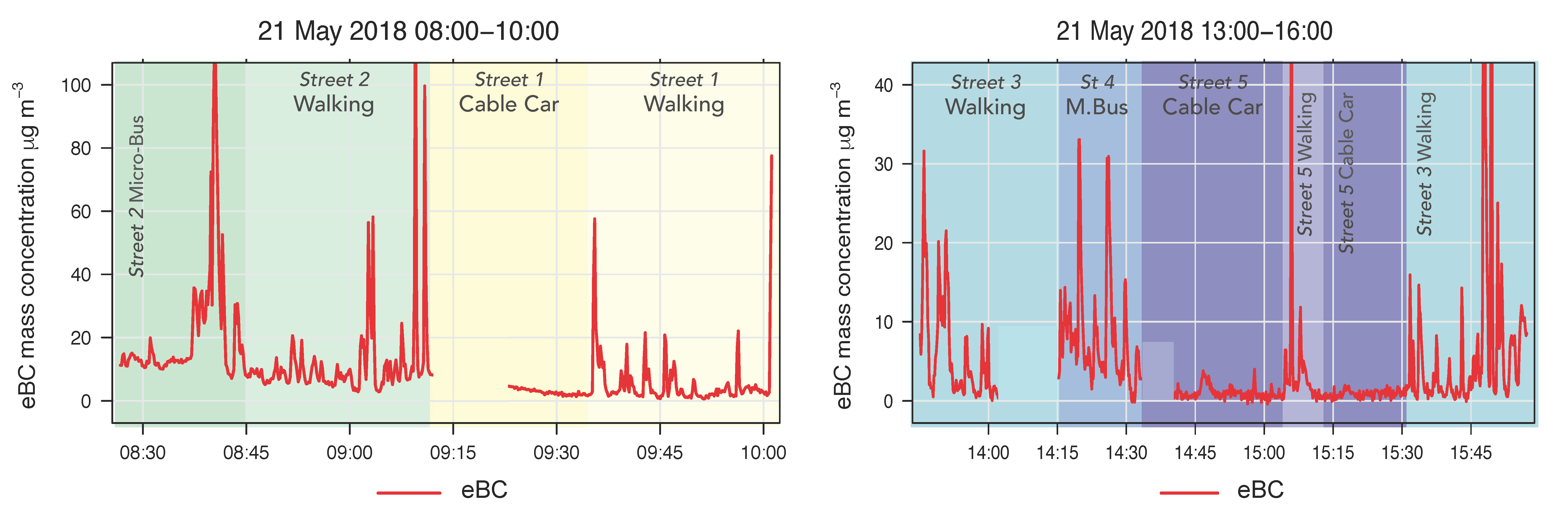
3.1. Equivalent Black Carbon (eBC) Exposure in TMEs
3.2. Potential Respiratory Tract Deposition Dose (RDD) Assessment
3.3. Reduction of Exposure and RDD in Cable Car Ride
4. Summary and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greenbaum, D. HEI Panel on the Health Effects of Traffic-Related Air Pollution. In Traffic-Related Air Pollution: A Critical Review of the Literature on Emissions, Exposure, and Health Effects; HEI Special Report 17. 386; Health Effects Institute: Boston, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Landrigan, P. Air Pollution And Health. Lancet Public Health 2017, 2, e4–e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomis, D.; Grosse, Y.; Lauby-Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Baan, R.; Mattock, H.; Straif, K. The carcinogenicity of outdoor air pollution. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 1262–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Ambient Air Quality Database; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; Available online: http://www9.who.int/entity/airpollution/data/aap_air_quality_database_2018_v9.xlsx (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Froines, J.R.; Zhao, J.; Wang, H.; Yu, S.-Z.; Detels, R. Air pollution and case fatality of SARS in the People’s Republic of China: An ecologic study. Environ. Health 2003, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Nethery, R.C.; Sabath, B.M.; Braun, D.; Dominici, F. Exposure to air pollution and COVID-19 mortality in the United States: A nationwide cross-sectional study. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Rivas, I.; Singh, A.P.; Ganesh, V.J.; Ananya, M.; Frey, H.C. Dynamics of coarse and fine particle exposure in transport microenvironments. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nazelle, A.; Fruin, S.; Westerdahl, D.; Martinez, D.; Ripoll, A.; Kubesch, N.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M. A travel mode comparison of commuters’ exposures to air pollutants in Barcelona. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, I.; Kumar, P.; Hagen-Zanker, A. Exposure to air pollutants during commuting in London: Are there inequalities among different socio-economic groups? Environ. Int. 2017, 101, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dons, E.; Panis, L.I.; Van Poppel, M.; Theunis, J.; Wets, G. Personal exposure to Black Carbon in transport microenvironments. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 55, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, W.; Vijayan, A.; Schulte, N.; Herner, J.D. Commuter exposure to PM2.5, BC, and UFP in six common transport microenvironments in Sacramento, California. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vouitsis, I.; Taimisto, P.; Kelessis, A.; Samaras, Z. Microenvironment particle measurements in Thessaloniki, Greece. Urban Clim. 2014, 10, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lei, X.-N.; Xiu, G.; Gao, C.-Y.; Gao, S.; Qian, N.-S. Personal exposure to black carbon during commuting in peak and off-peak hours in Shanghai. Sci. Total. Environ. 2015, 524, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.D.; Knibbs, L.D. Daily personal exposure to black carbon: A pilot study. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 132, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okokon, E.; Yli-Tuomi, T.; Turunen, A.W.; Taimisto, P.; Pennanen, A.; Vouitsis, I.; Samaras, Z.; Voogt, M.; Keuken, M.; Lanki, T. Particulates and noise exposure during bicycle, bus and car commuting: A study in three European cities. Environ. Res. 2017, 154, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraiwa, M.; Selzle, K.; Pöschl, U. Hazardous components and health effects of atmospheric aerosol particles: Reactive oxygen species, soot, polycyclic aromatic compounds and allergenic proteins. Free Radic. Res. 2012, 46, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madueño, L.; Kecorius, S.; Birmili, W.; Müller, T.; Simpas, J.; Vallar, E.; Galvez, M.C.; Cayetano, M.G.; Wiedensohler, A. Aerosol Particle and Black Carbon Emission Factors of Vehicular Fleet in Manila, Philippines. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Health Effects of Black Carbon. 2012. Available online: http://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0004/162535/e96541.pdf (accessed on 7 May 2020).
- Löndahl, J.; Massling, A.; Pagels, J.; Swietlicki, E.; Vaclavik, E.; Loft, S. Size-Resolved Respiratory-Tract Deposition of Fine and Ultrafine Hydrophobic and Hygroscopic Aerosol Particles During Rest and Exercise. Inhal. Toxicol. 2007, 19, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Exposure Factors Handbook. 2011. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-09/documents/efh-chapter06.pdf (accessed on 7 May 2020).
- Rode, P.; Floater, G.; Thomopoulos, N.; Docherty, J.; Schwinger, P.; Mahendra, A.; Fang, W.; Meyer, G.; Shaheen, S. Accessibility in Cities: Transport and Urban Form; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 239–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocarejo, J.P.; Portilla, I.J.; Velasquez, J.M.; Cruz, M.N.; Pena, A.; Oviedo, D.R. An innovative transit system and its impact on low income users: The case of the Metrocable in Medellín. J. Transp. Geogr. 2014, 39, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insituto Nacional de Estadística. Available online: https://www.ine.gob.bo/ (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Bürger, J. Comparison of Urban Transportation Mmodes in La Paz and Strategies toward a Data-driven, Adaptive Multimodal Intelligent Transport System, Technical Report. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/334429746_Comparison_of_Urban_Transportation_Modes_in_La_Paz_and_Strategies_toward_a_Data-Driven_Adaptive_Multimodal_Intelligent_Transport_System (accessed on 7 May 2020).
- Madueño, L.; Kecorius, S.; Löndahl, J.; Müller, T.; Pfeifer, S.; Haudek, A.; Mardoñez, V.; Wiedensohler, A. A new method to measure real-world respiratory tract deposition of inhaled ambient black carbon. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targino, A.C.; Rodrigues, M.; Krecl, P.; Cipoli, Y.A.; Ribeiro, J.P.M. Commuter exposure to black carbon particles on diesel buses, on bicycles and on foot: A case study in a Brazilian city. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 25, 1132–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londähl, J. Experimental Determination of the Deposition of Aerosol Particles in the Human Respiratory Tract. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Physics, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 27 February 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Betancourt, R.M.; Galvis, B.; Balachandran, S.; Ramos-Bonilla, J.; Sarmiento, O.L.; Gallo-Murcia, S.; Contreras, Y. Exposure to fine particulate, black carbon, and particle number concentration in transportation microenvironments. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 157, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, A.-S.; Georgellis, A.; Andersson, N.; Bedada, G.B.; Bellander, T.; Johansson, C. Personal exposure to black carbon in Stockholm, using different intra-urban transport modes. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 674, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milledge, J.S. The Control of Breathing at High Altitude. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, W.D.; Zeman, K.L.; Jarabek, A.M. Nasal Contribution to Breathing and Fine Particle Deposition in Children Versus Adults. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2007, 71, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foos, B.; Marty, M.; Schwartz, J.; Bennett, W.; Moya, J.; Jarabek, A.M.; Salmon, A.G. Focusing on children’s inhalation dosimetry and health effects for risk assessment: An introduction. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2008, 71, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiuchi, M.; Kirihara, Y.; Fukuoka, Y.; Pontzer, H. Sex differences in respiratory and circulatory cost during hypoxic walking: Potential impact on oxygen saturation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoene, R.B. Limits of human lung function at high altitude. J. Exp. Boil. 2001, 204, 3121–3127. [Google Scholar]
- Lahiri, S.; Kao, F.; Velásquez, T.; Martinez, C.; Pezzia, W. Respiration of man during exercise at high altitude: Highlander vs lowlander. Respir. Physiol. 1970, 8, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, H.B.; Echeverria, R.S.; Alvarez, P.S.; Krupa, S. Air Quality Standards for Particulate Matter (PM) at high altitude cities. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 173, 255–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alas, H.D.C.; Weinhold, K.; Costabile, F.; Di Ianni, A.; Müller, T.; Pfeifer, S.; Di Liberto, L.; Turner, J.R.; Wiedensohler, A. Methodology for high-quality mobile measurement with focus on black carbon and particle mass concentrations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 4697–4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedensohler, A.; Andrade, M.; Weinhold, K.; Müller, T.; Birmili, W.; Velarde, F.; Moreno, I.; Forno, R.; Sanchez, M.; Laj, P.; et al. Black carbon emission and transport mechanisms to the free troposphere at the La Paz/El Alto (Bolivia) metropolitan area based on the Day of Census (2012). Atmos. Environ. 2018, 194, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepeda, M.; Schoufour, J.; Freak-Poli, R.; Koolhaas, C.M.; Dhana, K.; Bramer, W.M.; Franco, O.H. Levels of ambient air pollution according to mode of transport: A systematic review. Lancet Public Health 2017, 2, e23–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kecorius, S.; Madueño, L.; Vallar, E.; Alas, H.; Betito, G.; Birmili, W.; Cambaliza, M.O.; Catipay, G.; Gonzaga-Cayetano, M.; Galvez, M.C.; et al. Aerosol particle mixing state, refractory particle number size distributions and emission factors in a polluted urban environment: Case study of Metro Manila, Philippines. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 170, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, D.J.; De Hoogh, K.; Morris, C.; Gulliver, J. Effects of travel mode on exposures to particulate air pollution. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, R.; Gani, S.; Guttikunda, S.K.; Wilson, D.; Tiwari, G. On-road PM2·5 pollution exposure in multiple transport microenvironments in Delhi. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 123, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazikhani, M.; Feyz, M.E.; Mahian, O.; Sabazadeh, A. Effects of altitude on the soot emission and fuel consumption of a light-duty diesel engine. Transport 2013, 28, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ge, Y.; Yu, L. Combustion and Emission Characteristics of a Heavy-Duty Diesel Engine at Idle at Various Altitudes. SAE Int. J. Engines 2013, 6, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloke, L.; Harris, G.; Latham, S.; Quimby, A.; Smith, E.; Baughan, C. Reducing the Environmental Impact of Driving: A Review of Training and In-Vehicle Technologies; Transport Res. Lab.: Crowthorne, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Batterman, S. Air pollution and health risks due to vehicle traffic. Sci. Total. Environ. 2013, 450, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Fleet. Available online: https://www.globalfleet.com/en/wikifleet/bolivia (accessed on 29 May 2020).
- Panis, L.I.; De Geus, B.; Vandenbulcke, G.; Willems, H.; Degraeuwe, B.; Bleux, N.; Mishra, V.; Thomas, I.; Meeusen, R. Exposure to particulate matter in traffic: A comparison of cyclists and car passengers. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2263–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, T.; Duan, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, W.; Wu, X.; Yu, Y. Research on Inhalation Rate Exposure Factors of Chinese Residents in Environmental Health Risk Assessment; Research of Environmental Sciences 10; Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zuurbier, M.; Hoek, G.; Hazel, P.V.D.; Brunekreef, B. Minute ventilation of cyclists, car and bus passengers: An experimental study. Environ. Health 2009, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
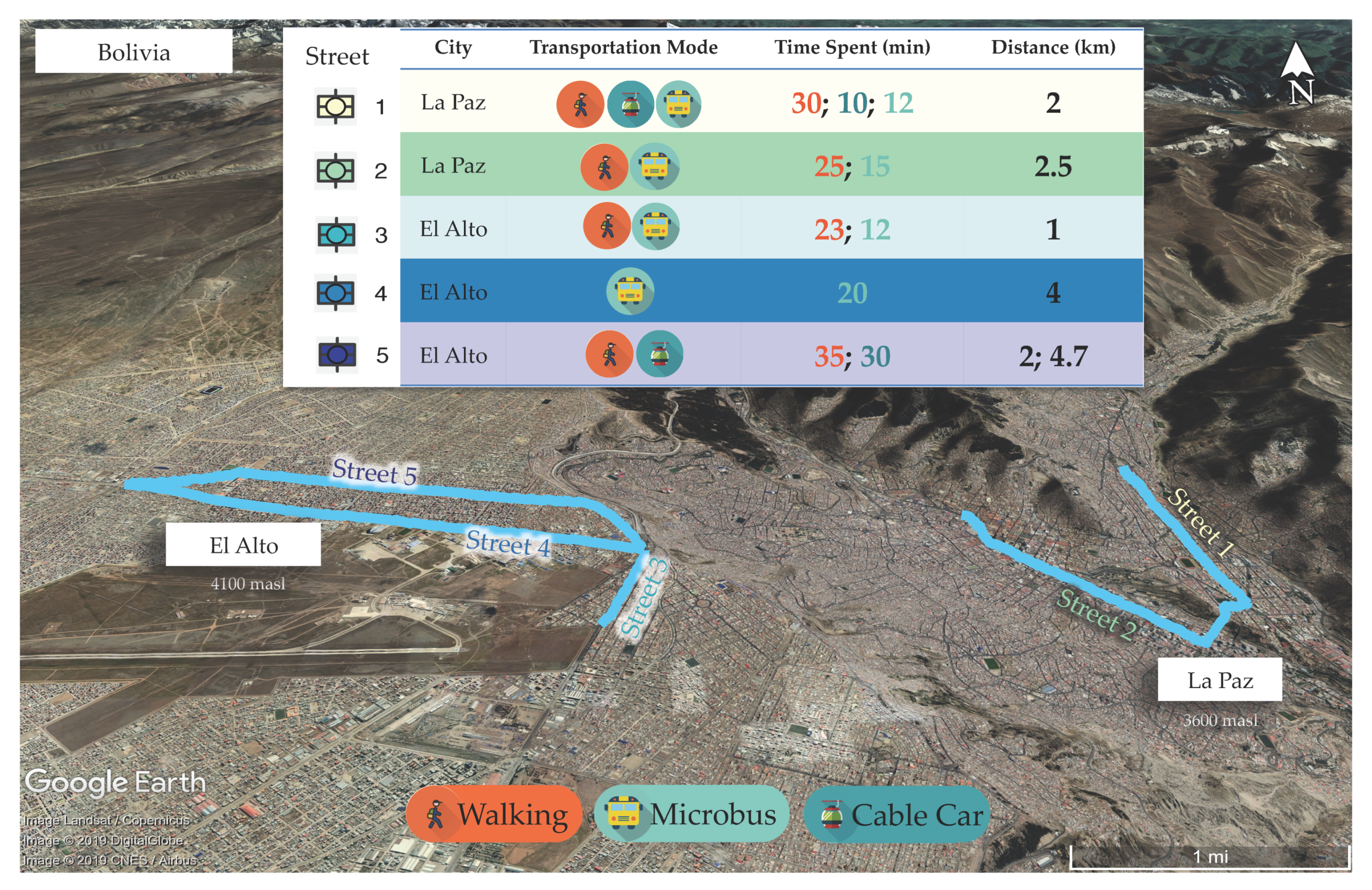


| Segment ID | Street 1 | Street 2 | Street 3 | Street 4 | Street 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| City | LP | LP | EA | EA | EA |
| Street Name | Busch | Arce | 6 de Marzo | Juan Pablo II | 16 de Julio |
| Type | Residential | Commercial | Commercial | Commercial | Residential |
| Lanes | 4 | 4 | 8 | 10 | 4 |
| Travel Mode | W, CC, MB | W, MB | W, MB | MB | W, CC |
| Distance (km) | 2 | 2.5 | 1 | 4 | 2, 4.7 |
| Minute Ventilation (10−2 m3 min−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activity * | Male | Female | |||
| Sitting | 1.39 a | 0.51 b | 1.89 c | 1.04 a | 0.42 b |
| Walking | 2.33 a | 2.92 b | 4.76 c | 1.92 a | 2.29 b |
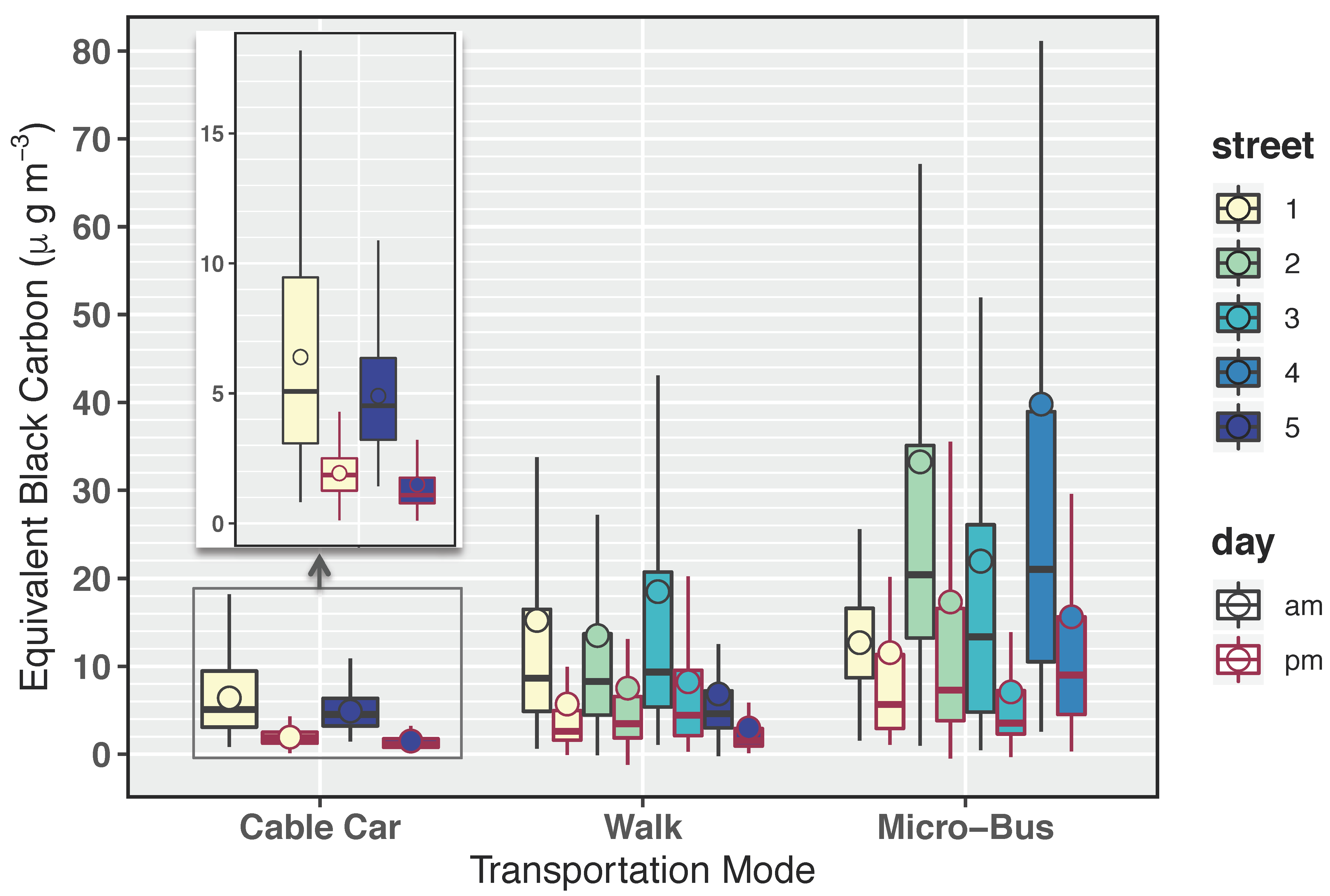
| Mode | Variable | Street 1 | Street 2 | Street 3 | Street 4 | Street 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cable Car | AM | 6.6 (4.2) | - | - | - | 5.1 (2.1) |
| PM | 1.9 (1.3) | - | - | - | 1.6 (1.5) | |
| Overall * | 3.7 (3.1) [2.8] | |||||
| n (eBC, 1 min) | 900 | |||||
| # trips | 62 | |||||
| Kruskal–Wallis test | ** | |||||
| Walk | AM | 15.5 (23.1) | 13.9 (21.8) | 18.9 (39.9) | - | 7.0 (10.7) |
| PM | 5.8 (18.0) | 7.8 (17.4) | 8.3 (11.5) | - | 3.0 (5.1) | |
| Overall * | 10.3 (21.6) [4.9] | |||||
| n (eBC, 1 min) | 4832 | |||||
| # trips | 179 | |||||
| Kruskal–Wallis test | ** | |||||
| W/CC Ratio (dimensionless) | 1.75 | |||||
| Microbus | AM | 11.8 (16.2) | 34.0 (41.3) | 22.4 (25.0) | 40.7 (74.5) | - |
| PM | 12.2 (23.8) | 17.7 (28.8) | 7.3 (12.5) | 15.9 (24.9) | - | |
| Overall * | 24.9 (44) [12.8] | |||||
| n (eBC, 1 min) | 1628 | |||||
| # trips | 104 | |||||
| Kruskal–Wallis test | ** | |||||
| MB/CC Ratio (dimensionless) | 4.6 | |||||
| Potential Respiratory Deposition Dose (μg) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode | Overall * | Street 1 | Street 2 | Street 3 | Street 4 | Street 5 |
| Cable Car | 0.6 (0.5) [0.5] | |||||
| AM | 1.1 (0.7) [0.9] | - | - | - | 0.8 (0.4) [0.8] | |
| PM | 0.3 (0.2) [0.3] | - | - | - | 0.3 (0.2) [0.2] | |
| Walk | 13 (27) [6.3] | |||||
| AM | 20 (29) [11] | 17 (28) [11] | 24 (50) [12] | - | 8.8 (14) [5.9] | |
| PM | 7.4 (23) [3.3] | 10 (21) [4.5] | 11 (15) [5.7] | - | 3.8 (6.4) [2.0] | |
| Microbus | 6.6 (11) [3.3] | |||||
| AM | 3.4 (1.5) [3.5] | 9.0 (11) [5.5] | 6.0 (6.7) [3.6] | 11 (20) [5.7] | - | |
| PM | 3.1 (4.3) [1.5] | 4.7 (7.6) [2.0] | 1.9 (3.3) [1.0] | 4.2 (6.6) [2.4] | - | |
| Year Published | Location | Elevation (masl) | Minute Ventilation | eBC Exposure | Norm. eBC RDD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (10−2 m3 min−1) | (μg m−3) | (μg min−1) | ||||||
| Walk | Bus | Walk | Bus | Walk | Bus | |||
| 2012 | Barcelona, Spain [8] | 12 | 3.41 | 2.01 | 6.3 | 7.6 | 0.22 | 0.16 |
| 2012 | Mol, Belgium [10] | 16 | 4.92 | 1.61 | 3.6 | 6.6 | 0.1 | 0.08 |
| 2014 | Thessaloniki, Greece [12] | 0 | - | 2.01 | - | 5.5 | - | 0.11 |
| 2015 | Shanghai, China [13] | 4 | 1.05 | 0.78 | 5.59 | 7.3 | 0.06 | 0.13 |
| 2017 | Sacramento, California [11] | 9 | - | 1.18 | - | 0.95 | - | 0.01 |
| 2017 | London, UK [9] | 11 | 2.27 | 1.11 | 2.6 | 5.4 | 0.08 | 0.04 |
| 2018 | Londrina, Brazil [26] | 610 | 2.68 | 1.22 | 4.1 | 10.3 | 0.07 | 0.07 |
| 2019 | Stockholm, Sweden [29] | 0 | 1.9 | 1.3 | 1.7 | 2.7 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| 2020 | This Study (La Paz; El Alto) | 3600; 4100 | 4.8 | 1.9 | 10.3 | 24.9 | 0.48 | 0.46 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madueño, L.; Kecorius, S.; Andrade, M.; Wiedensohler, A. Exposure and Respiratory Tract Deposition Dose of Equivalent Black Carbon in High Altitudes. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060598
Madueño L, Kecorius S, Andrade M, Wiedensohler A. Exposure and Respiratory Tract Deposition Dose of Equivalent Black Carbon in High Altitudes. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(6):598. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060598
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadueño, Leizel, Simonas Kecorius, Marcos Andrade, and Alfred Wiedensohler. 2020. "Exposure and Respiratory Tract Deposition Dose of Equivalent Black Carbon in High Altitudes" Atmosphere 11, no. 6: 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060598
APA StyleMadueño, L., Kecorius, S., Andrade, M., & Wiedensohler, A. (2020). Exposure and Respiratory Tract Deposition Dose of Equivalent Black Carbon in High Altitudes. Atmosphere, 11(6), 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060598





