Abstract
Indoor and outdoor ultrafine, accumulation mode, and coarse fractions collected at two preschools (S1 and S2) in Hanoi capital, Vietnam were characterized in terms of mass-size distribution and elemental composition to identify major emission sources. The sampling campaigns were performed simultaneously indoors and outdoors over four consecutive weeks at each school. Indoor average concentrations of CO2 and CO at both schools were below the limit values recommended by American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (1000 ppm for CO2) and World Health Organization (7 mg/m3 for CO). Indoor concentrations of PM2.5 and PM10 at S1 and S2 were strongly influenced by the presence of children and their activities indoors. The indoor average concentrations of PM2.5 and PM10 were 49.4 µg/m3 and 59.7 µg/m3 at S1, while those values at S2 were 7.9 and 10.8 µg/m3, respectively. Mass-size distribution of indoor and outdoor particles presented similar patterns, in which ultrafine particles accounted for around 15–20% wt/wt while fine particles (PM2.5) made up almost 80% wt/wt of PM10. PM2.5–10 did not display regular shapes while smaller factions tended to aggregate to form clusters with fine structures. Oxygen (O) was the most abundant element in all fractions, followed by carbon (C) for indoor and outdoor particles. O accounted for 36.2% (PM0.5–1) to 42.4% wt/wt (PM0.1) of indoor particles, while those figures for C were in the range of 14.5% (for PM0.1) to 18.1% (for PM1–2.5). Apart from O and C, mass proportion of other major and minor elements (Al, Ca, Cr, Fe , K, Mg, Si, Ti) could make up to 50%, whereas trace elements (As, Bi, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, La, Mn, Mo, Ni, Pb, Rb, Sb, Se, Sn, Sr, and Zn) accounted for less than 0.5% of indoor and outdoor airborne particles. There were no significant indoor emission sources of trace and minor elements. Traffic significantly contributed to major and trace elements at S1 and S2.
1. Introduction
Indoor air quality is becoming increasingly important as people spend more and more time indoor for daily activities such as work, leisure activities, sport, and commuting to work in cars and/or public transportation facilities. There has been an increasing research interest in indoor air quality of school environments as children spend a considerable amount of time in their school days indoors where, in certain cases, air is more polluted than outdoor [1,2,3,4]. Moreover, children are more sensitive to atmospheric pollutants than adults, due to their not-fully developed respiratory system and high rates of acute respiratory infections [5]; hence, their exposure to indoor airborne particles can result in negative health impacts. Particles originate from a number of mobile and stationary sources and can be directly emitted (primary emission sources) or formed in the atmosphere by transformation of gaseous components (secondary emission sources) [6,7]. Primary emission sources can be divided into two types, namely, natural and anthropogenic sources. Anthropogenic emissions are linked with human activities such as industrial processes, agricultural activities, fossil fuels and biomass combustion, traffic, and construction activities [6,7]. Generally, the main secondary emission sources of particles include SO2, NOx, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and ammonia, which may be photo-chemically transformed and take part in the formation of particulate matter (PM) [6,7].
Industries such as metallurgy, petro-chemistry, and the cement along with fossil fuels combustion are known to emit fine particles (PM2.5, particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter < 2.5 μm) [8]. Some natural and mechanical processes such as dust storms, sea pray, soil dust resuspension, construction/demolition, non-exhaust vehicle emissions, and industrial fugitives usually emit coarser particles (PM10, particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter < 10 μm) [9].
The health effects of airborne particles (PM) depend strongly on their size, specific surface area, number, and chemical composition, such as their heavy metal contents [10,11]. These potentially toxic elements could be emitted by various sources, such as industries [3,12,13], road traffic [3,4,13,14,15], and biomass combustions [16,17,18]. Fine and ultrafine particles can penetrate deeply into the human respiratory system, and hence may cause more adverse impacts on human health [5,11]. In addition, ultrafine and fine particles are very high in numbers, and have higher surface area than larger particles, which promote them to adsorb, retain, and release toxic substances in the pulmonary system [10,17,18]. Previous studies showed that most of the airborne particles from combustion are composed of chain-aggregated masses of fine carbonaceous spheres, and adverse organic compounds such as polycyclic aromatic hydro-carbons (PAHs) and quinones [5].
In general, school environments do not present typical indoor emission sources of airborne particles such as heating combustion, smoking, and cooking. However, airborne particle concentrations and their elemental contents are strongly influenced by several factors, such as the number of occupants and their indoor activities [1,3,19], ventilation systems [20,21], air exchange rates [19,21,22], indoor furniture, painting and building materials [23,24], outdoor particles’ penetration capacity, and resuspension of deposited particles [19,22].
A number of studies on school indoor air quality (IAQ) have focused on inhalable suspended particles and their chemical composition in school environments [12,13,14,15,25,26,27]. However, research on mass-size distribution of airborne particles and elemental composition of ultrafine, accumulation mode, fine, and coarse particles in school environments is very limited.
The increasingly rapid urbanization and industrialization in Hanoi, Vietnam, has been suspected to induce problems to environments, including air pollution issues. Recently, bad air quality in Hanoi has been reported in different national and regional media. The study on the air quality in Hanoi is still limited, though there have been some studies carried out on roadsides for outdoor air pollutants [28,29]. Potential emission sources of airborne particles and their associated contents in Hanoi could be traffic, construction and demolition activities, and biomass burning in winter. To the best of our knowledge, there is no research on chemical composition of size-resolved airborne particles in school environments in Hanoi, Vietnam.
The main objectives of this study are to identify the sources of airborne particles in classrooms and to determine the influence of the children’s activities to the elemental distribution for different particle size fractions at two preschools in Hanoi, Vietnam, where young children who are among the most sensitive to air pollution spend most of their time indoors.
To do so, the indoor and outdoor concentrations of major, minor, and trace elements were analyzed according to their particle size fractions, ranging from ultrafine to coarse fraction (PM0.1, PM0.5, PM1, PM2.5, PM10, and PM2.5–10). In addition, comfort parameters and CO and CO2 concentrations were simultaneously measured indoors and outdoors to evaluate their atmospheric concentrations’ variability and assist the interpretation of particles’ emission sources.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Sites and School Characteristics
Two preschools were selected in the Hanoi capital, Vietnam (Figure 1). The climate of the region is characterized by a high level of humidity, four seasons around the year. Hanoi is the second largest Vietnamese city by population (8.05 million as of 2019) after Ho Chi Minh City, with a density of up to 40,300 inhabitants/km2 in the center district compared with the average figure of 2398 inhabitants/km2 for the whole city. This is causing traffic congestion in many parts of the city, and consequently, air pollution. The two preschools were selected to match two close types of environments: urban center (school 1 (S1)) and urban periphery (school 2 (S2)). The spatial distance between the two schools is about 4 km (Figure 1). The schools were also selected for the study based upon edifice characteristics such as ventilation system, internal covering including flooring, wall, and ceiling, windows structure, and building age, which are summarized in Table 1.
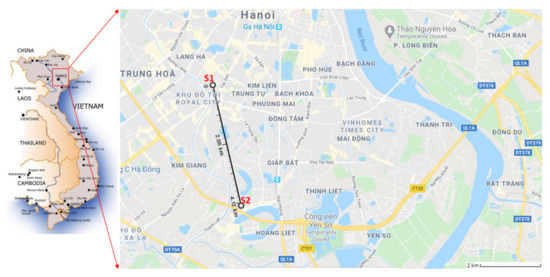
Figure 1.
Location of the two examined preschools in Hanoi, S1 = school 1, S2 = school 2.

Table 1.
List of main characteristics of the monitored schools.
School 1 (S1), built in the 1990s and made of brick, is located in close proximately to a main road conjunction of the city, where there are high traffic density roads, with a lot of vehicles commuting at almost all times of the day. A large gas station is located about 400 meters from the school. School 2 (S2) built in the 2010s, is a three-level brick building situated in a peripheral area of Hanoi, in proximity to the ring road N0 3. There is parking nearby and a gas station at a distance of about 500 meters. Cleaning at the two schools is conducted on a daily basis using cleaning products.
2.2. Measurement Strategy
The 4-week sampling campaigns for each school were divided into two periods: in the presence and absence of children in the classrooms. The occupied periods consisted of teaching hours during five school days, from Monday to Friday. The unoccupied periods included all nights (from 7 p.m. to 6 a.m. of the next day) of the weekdays and weekends to avoid resuspended particles due to occupants’ activities during the class [1]. The teaching hours started at 08:00 and finished at 16:00. The sampling campaigns were simultaneously conducted indoors and outdoors of the two schools. They were conducted successively at each school, from 15 November 2019 to 20 January 2020 under relatively cool and stable meteorological conditions during each campaign. Outdoor average temperatures were 22.5 and 21.3 °C at the two schools. Two identical particle samplers (Nanosampler II, KANOMAX) were deployed to collect different size fractions of airborne particles, which were then subjected to mass concentration, morphology, and chemical composition determination. Comfort parameters such as temperature, relative humidity, CO, and CO2 gases were monitored indoors and outdoors during the campaigns using two identical Qtrak, TSI. All equipment was calibrated prior to being deployed for the sampling campaigns. In addition, information about daily school activities in the studied classrooms (number of pupils present, closing/opening state of doors and windows, cleaning method and products used) were collected by questionnaires. Some chemicals identified among the cleaning products used at S1 and S2 were polyacrylic acid, triethanolamine, ethoxylated alcohol, benzisothiazolinone, methylchloroisothiazolinone, methylisothiazolinone, and other preservatives, dyes, and fragrances, which were not given specific names by producers. Details on sampling strategy were presented in previous work [3].
2.3. Aerosol Sampling, Morphology, and Chemical Analysis
Aerosol samples were simultaneously collected indoors and outdoors on Zefluor filters (Pall Corporation, 0.45 µm porosity) by impaction (for each stage) and filtration (for backup filter) using five-stage cascade impactors, Nanosampler II (Kanomax Japan Inc.) at a constant flow-rate of 40 L/min to collect different particle size fractions, i.e., between 10 and 2.5 µm, between 2.5 and 1 µm, between 1.0 and 0.5 µm, and between 0.5 and 0.1 µm. Teflon filters were selected as they are nonhygroscopic and chemically inert, have low blanks, and therefore, improve the analytical quality of the analyses. To assess concentrations and composition of PM10, PM2.5, PM1, PM0.5, and PM0.1, successive fractions collected on the cascade impactor stages (filter substrates) were summed. The sampling flow-rate was calibrated by a TSI 4040 mass flow-meter before and after each sampling campaign.
In order to examine the impact of the presence of occupants and their activities at school on pollutants’ concentrations, ten indoor and ten outdoor particle samples were collected during occupied periods (during the class) and unoccupied periods (no occupants in the classrooms) at each school. Regarding occupied periods, each sample was collected during 2 school days, corresponding to 16 hours. The same numbers of samples were collected during unoccupied periods at each school: over two nights or 24 hours for school days, and 48 h during weekends (two complete days). In total, 80 airborne particle samples were sampled at the two schools. Volumes of filtered air varied from 38.4 m3 (during occupied periods) to 115 m3 (during unoccupied periods).
The collected airborne particles were kept in clean Petri dishes and stored in a temperature (20 ± 1 °C) and relative humidity (45%–50%) controlled room for 48 h before weighing according to the standard reference method (EN 12341:2014). Each filter was weighed four times before and after exposure with a microbalance (Mettler-Toledo UMT2, Switzerland) with a 0.1 mg reading resolution. The difference in weighed mass and the sampled air volume were used to calculate PM mass concentrations. The samples were then digested at 200 °C in Teflon reactors with a microwave oven, (model Multiwave GO Plus, Anton Paar). The acid digestion mixture (4 mL HNO3 Supra-pure (65%), Merck, 1 mL H2O2 Suprapur (30%), Merck) was optimized to mineralize major, minor, and trace elements [3,30]. The concentrations of Al, Ba, Ca, K, Mg, Fe, and Ti were measured by a ICP-OES iCAP™ 6500, Thermo Scientific, while those of Ag, As, Bi, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, La, Mn, Mo, Ni, Pb, Pd, Pt, Rb, Sb, Se, Sn, Sr, V, and Zn were analyzed by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry ICP-MS (Elan 9000, Perkin Elmer) according to the optimized procedure [3,30].
Particle morphology and composition of PM0.1, PM0.5, PM1, PM2.5, and PM10 were analyzed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) (model TM4000Plus, Hitachi, Japan) coupled with an Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS) (model AztecOn, Oxford Instrument, UK). SEM provides images of a sample by scanning the sample’s surface with a focused beam of electrons. The electrons interact with atoms in the sample, producing various signals that provide information about the surface topography and chemical composition of the sample. The chemical composition is analyzed by an energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy coupled with SEM. High magnification of 10,000x was used in this work. Only elements with a mass proportion larger than 0.5% of analyzed particles can be detected. They included the following elements: Al, Ba, Ca, K, Na, Mg, Fe, Si, Ti, O, C, and S.
2.4. Data Quality Assurance and Validation
Regarding mass concentrations of airborne particles, 10 field and 10 laboratory blank filters were weighted before and after each sampling campaign to estimate the drift and repeatability of the microbalance. The mean uncertainties associated to mass concentration for the different particle fractions were around 6%, and always lower than 15%.
Concerning elemental concentrations, the procedure for quality assurance and quality control was applied according to our previous work [3]. In summary, all the contaminant contents of the laboratory and field filter blanks were respectively below 5% and 12% of their concentrations in the different particle fractions. The Standard Reference Materials (Urban particulate matter—NIST 1648 and Indoor dust—NIST 2584, from National Institute of Standard and Technology, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) were regularly checked to estimate the analytical reproducibility and to validate the whole procedure. Most of the analyzed elements showed very good recovery rates (from 86% to 110%), except for Si, which always presented lower than 29.5% of its mass in these Standard Reference Materials (SRMs). The quality control solutions (ICP multi-elemental standards solution VI of 10 and 100 ppm, Certipur®, Merck) were validated only when the discrepancies between the measured and the standard values were below 5%. Concentration of four elements (Ag, Pd, Pt, and V) were eliminated from the database as they were presented in the particle samples with concentrations below their detection limits (Supplementary Table S1).
Finally, 23 elements (Mg, Al, K, Ca, Ba, Sr, Ti, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Se, Rb, Mo, Cd, Sn, Sb, La, Pb, and Bi) were selected because of their adequate results in terms of quality assurance, quality control, and their concentrations in different particle fractions above the quantification limits.
2.5. Emission Source Analysis
When necessary, a t test was performed in order to check whether data differed significantly from one another. A statistical significance level of 0.05 was used throughout the study. Spearman correlations between elements, CO, CO2, temperature, and relative humidity were applied to all the particulate fractions, including indoor, outdoor PM0.1, PM0.5, PM1, PM2.5, and PM10. Average concentrations of CO, CO2, and the corresponding values of temperature and relative humidity were monitored during the same sampling periods when indoor and outdoor airborne particles were collected.
Enrichment factor (EF) can be used as a first approach for identifying the emission sources of elements. The advantage of using EF is that it is quite simple [9,12,13], while more precise analyses can be achieved by using a combination of other methods, such as factor analysis or receptor models such as Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF), Chemical Mass Balance (CMB)… [9]. EF is calculated according to the following equation:
where (CE/CX)Aerosol is the ratio between concentrations of element E and X (reference element) in the airborne particle sample, and (CE/CX)Crust is the E to X concentration ratio in the average upper continental crust proposed by McLennan [31]. Reference elements could be Al, Fe, La, Ni, or Zn [10,12]. In this work, Al was used for the EF calculation as it presented a very good recovery rate and high content in different particle fractions, and no specific emissions sources of this element near the sampling locations were recorded before, during, and after the campaigns.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Indoor, Outdoor Comfort Parameters, and CO, CO2 Concentrations
Results on indoor, outdoor comfort parameters, and CO, CO2 concentrations are presented in Table 2. It is noted that indoor and outdoor average CO concentrations obtained during the class and when the classrooms were empty at S1 and S2 were clearly lower than the 8 hour and 24 hour guidelines for indoor air (10 mg/m3 or 8732 ppm and 7 mg/m3 or 6113 ppm, respectively) set by the World Health Organization (WHO) [32]. During teaching hours, indoor concentrations of CO at S1 varied from 0.4 to 8.3 ppm, averaging 2.7 ppm, while those values at S2 were in the range of 0.4–5.5 ppm, averaging 1.1 ppm (Table 2). There were no significant differences in indoor and outdoor CO levels at S1 and S2 between the two periods in the presence and absence of children (p > 0.05). This implies that there were no significant indoor emission sources of CO at S1 and S2.

Table 2.
Comfort parameters, CO2, and CO concentration measured indoors and outdoors at the surveyed preschools (n = 80, average ± standard deviation: SD).
Regarding CO2 concentrations, indoor average levels of CO2 obtained during the class at S1 (742 ± 276) and S2 (589 ± 141) were relatively higher than those obtained when the rooms were empty (436 ± 33 for S1 and 427 ± 49 for S2) due to children’s respiration (Table 2). However, there were no significant discrepancies between outdoor CO2 levels obtained during classes and those obtained when the classrooms were vacant for both the schools (p > 0.05). All indoor and outdoor average concentration of CO2 at S1 and S2 were below the recommended values of 1000 ppm set by American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) [33], although there were certain moments where indoor CO2 levels during teaching hours exceeded 1000 ppm (Table 2). Those levels of indoor CO2 were lower than several results of research conducted in classrooms, especially in cold climate countries where doors and windows are frequently closed to avoid the cold [15,34,35].
Comfort parameters in classrooms at S1 and S2 were relatively stable and favorable to academic performance for children. For instance, during classes, indoor levels of temperature and relative humidity at S1 were 24.5 ± 1.8 and 53.1 ± 13.8, while those values at S2 were 25.6 ± 2.3 and 70.7 ± 8.4, respectively (Table 2). Indoor relative humidity was relatively higher at S2 than at S1, which could be attributed to outdoor levels at S2 being higher compared to S1.
3.2. Indoor and Outdoor Mass Concentrations of Size-Resolved Airborne Particles
The indoor and outdoor mass concentrations of ultrafine, fine, and coarse particles are summarized in Table 3. Daily indoor PM10 concentrations obtained during teaching hours at S1 ranged from 10.1 to 117 µg/m3, averaging 59.7 ± 48.9 µg/m3. This was largely higher than during the period when there were no children in the classrooms (16.8 ± 20.2 µg/m3), which fluctuated from 2.9 to 46.4 µg/m3. This suggests that children and their activities at school result in an increase in indoor PM10 concentration. Regarding outdoor, there was no significant discrepancy between the two periods regardless of the presence or absence of children in the classrooms (p > 0.05). For instance, outdoor average concentrations of PM10 collected during class and when the school was vacant were 164 ± 46.6 and 134.6 ± 52.2 µg/m3, respectively (Table 3).

Table 3.
Indoor and outdoor size-resolved airborne particle concentrations at S1 and S2 (n = 10 for each parameter, with a total of 80 samples, average ± SD, in parentheses are min–max values).
Similar trends were observed at S2 where indoor PM10 concentrations varied within the range of 8.7–12.7 µg/m3 during classes and 2.5–10.5 µg/m3 when the classrooms were empty. These observations can be explained by occupants’ physical activities in the classroom (running, playing with toys, movements…) which would contribute to a strong increase in coarse factions. For instance, average indoor concentration of PM2.5–10 fraction sampled during the lesson was 10.5 ± 8.2, ranging from 2.0 to 20.8 µg/m3, whereas those values obtained without children in the classrooms were 1.7 ± 0.8, ranging from 1.0 to 3.0 (Table 3). In contrast, when there were no occupants in the classrooms, the building envelope of S1 and S2 prevented the penetration of the coarse fraction from outdoors owing to their filtration capacity [1,15,19]. Outdoor average concentrations of PM10 for occupied and unoccupied periods at S2 were 226 ± 20.7 µg/m3 and 175 ± 36.6 µg/m3, respectively (Table 3). They largely exceeded the daily limit (50 µg/m3) recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) and were relatively higher than Vietnam 24 h exposure regulations (150 µg/m3) for ambient air. Indoor PM10 concentrations measured during teaching hours slightly surpassed the daily limits (50 µg/m3) set by WHO for indoor air. It is noted that there are no guidelines for indoor air in Vietnam.
Similarly, indoor concentrations of PM2.5 at S1 and S2 were strongly influenced by the presence of children and their activities within the classrooms. Average PM2.5 levels obtained during the lesson at S1 and S2 were 49.4 ± 41.0 µg/m3 and 7.9 ± 1.8 µg/m3, while those values obtained when the rooms were vacant were 15.7 ± 19.0 µg/m3 and 4.2 ± 3.0 µg/m3, respectively (Table 3). Indoor PM10 and PM2.5 at S1 were higher than at S2, which could be explained by the fact that the number of children present in the examined classroom at S1 was almost twice as high compared to the classroom at S2 (30 at S1 versus 17 at S2), while the classroom’s volume was lower than at S2 (60 m3 at S1 versus 90 m3 at S2). Given that S2 was located in close proximity to the ring road N0 3, emissions from both mechanical (road surface abrasion, resuspension of road dusts, brake wear) and thermal processes (exhaust from vehicles) were expected to contribute to higher concentrations of outdoor coarse and fine particles at S2, which will be analyzed in detail in the subsequent section.
Only indoor average concentration of PM2.5 collected in the presence of children at S1 located in Hanoi center largely exceeded the limit value (25 µg/m3 for 24 h exposure) recommended by WHO. However, all the outdoor concentrations of PM2.5 at S1 and S2 were largely higher than the WHO guideline for ambient air, and they also largely exceeded the Vietnam standard (50 µg/m3 for 24 h exposure). The outdoor average concentrations of PM2.5 collected during class at S1 were 107 ± 40.0 and the corresponding value at S2 was 177 ± 20.2, respectively (Table 3). This is in accordance with results on PM2.5 obtained from a monitoring station of United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) located in Hanoi [36]. However, until now, there have been no large-scale campaigns in Hanoi capital to gather a large enough dataset in order to draw conclusions on such phenomena. Interestingly, school situation and number of children and their activities could lead to discrepancies in indoor PM10 and PM2.5 concentrations at S1 and S2, but ultrafine particles seemed not to be influenced by those factors. In fact, indoor average concentrations of PM0.1 in the presence of children at S1 and S2 were 3.1 ± 1.3 µg/m3 and 2.2 ± 0.6 µg/m3 respectively, while those values obtained when there were no children in the classrooms at S1 and S2 were 1.4 ± 1.2 µg/m3 and 1.1 ± 0.6 µg/m3, respectively (Table 3). The differences in indoor and outdoor concentrations of ultrafine particles between S1 and S2 were insignificant (p > 0.05).
PM0.1 (ultrafine particles or particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter < 0.1 µm); PM0.5 (particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter < 0.5 µm); PM1 (particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter < 1 µm); PM2.5 (particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter < 2.5 μm); PM2.5 (particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter < 10 μm); PM2.5-10 (fraction of particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter in the range of 2.5-10 μm).
It should be noted that, although there have been a number of studies on indoor concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 in school environments, only a few studies on mass concentration and composition of ultrafine particles have been performed. Table 4 compares particle mass concentrations at different places in the world. It is noted that indoor concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 seemed not to be impacted by school typology, whereas the latter positively influenced the outdoor levels of PM10 and PM2.5. Indoor concentrations of PM10 in our research were within the concentration range of other work, while concentrations of finer particles (PM1 and PM2.5) in this study were among the highest levels (Table 4). With regard to the outdoor situation, concentrations of PM1, PM2.5, and PM10 in this study were much higher than most other research.

Table 4.
Comparison of indoor and outdoor airborne particle concentrations at various schools in the world (in parentheses are min–max values).
3.3. Particle Mass-Size Distribution
Fine fraction (≤2.5 µm) accounted for the major proportions of indoor and outdoor PM10 mass concentrations, with about 80% of the total mass (Figure 2). In the presence of children and during their activities at school, indoor PM2.5 represented smaller proportions of PM10 compared with the period where the classrooms were empty (75.8% and 82.5% versus 81.4% and 92.0% at S1 and S2, respectively). This could be explained by occupants’ activities contributing mainly to the resuspension of the coarse fraction, as presented previously in this study and in several works published [1,15,19,20,37].
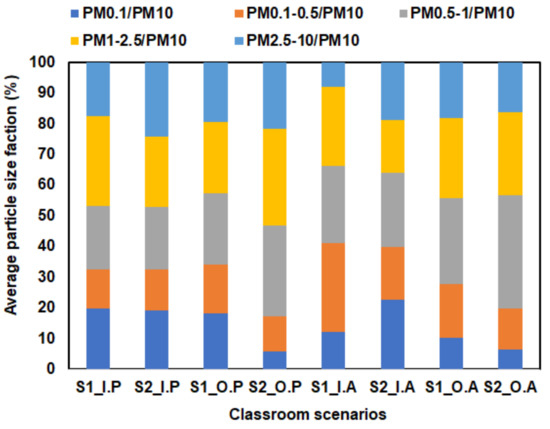
Figure 2.
Mass-size distribution of indoor and outdoor airborne particles (n = 80, I.P and O.P denote Indoor and Outdoor in the Presence of children while I.A and O.A are Indoor and Outdoor in the Absence of children, respectively).
Regarding outdoors, it is noted that there were no significant differences in PM2.5 proportions in PM10 between the two periods. The accumulation mode (0.1–1 µm) accounted for a relatively large percentage of PM10, ranging from 33.4% to 54.2% (Figure 2). The accumulation mode was also impacted by children’s activities in classrooms but in a lesser extent than the case of larger particles. In the presence of children in the classroom, there were no significant differences in percentage of the 0.1–1 µm fraction between the two periods, accounting for around 33% of PM10 at S1 and S2, but they increased to 41.3% at S2 and 54% at S1 for outdoors (Figure 2). Ultrafine particles represented around 15% of PM10 at S1 and 12% at S2. However, mass proportion of these ultrafine particles in PM10 could vary from period to period during the sampling campaigns.
3.4. Morphology and Elemental Analysis
3.4.1. Morphology and Elemental Concentration of Ultrafine, Fine, and Coarse Airborne Particles
SEM images and the corresponding elemental analysis of indoor PM0.1, PM0.1–0.5, PM0.5–1, PM1–2.5, and PM2.5–10 sampled during the unoccupied periods at S1 are presented in Figure 3 and Figure 4. Figure 5 and Figure 6 show SEM images and the corresponding elemental composition of outdoor PM0.1, PM0.1–0.5, PM0.5–1, PM1–2.5, and PM2.5–10 sampled during teaching hours at the same school, respectively. In terms of particle morphology, indoor and outdoor particles collected at S1 presented similar forms for each particulate fraction. Particles within the largest fraction (PM2.5–10) did not have regular forms but most of them displayed the cubic-like shape, while smaller fractions tended to aggregate to form clusters with fine structures. The submicron fractions (PM0.5–1 and PM0.1–0.5) presented the largest population, which were aggregated more tightly, resulting in the formation of blocks of particles with much lower porosity compared to other factions.
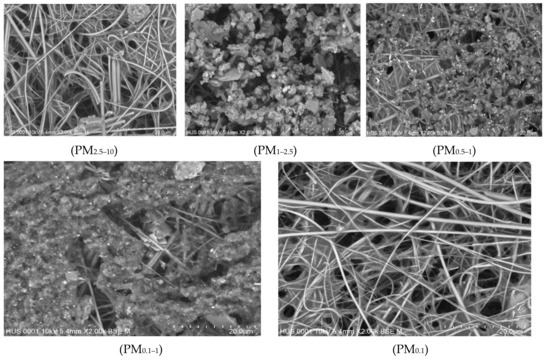
Figure 3.
Scanning electron microscope (SEM) images of indoor airborne particles (PM2.5–10, PM1–2.5, PM0.5–1, PM0.1–1, and PM0.1) collected in absence of children at S1.
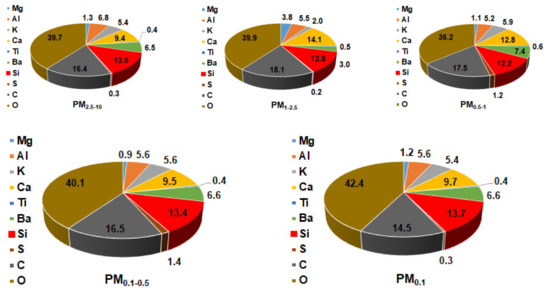
Figure 4.
Elemental composition of indoor PM2.5–10, PM1–2.5, PM0.5–1, PM0.1–1, and PM0.1 collected when the rooms were empty at S1.
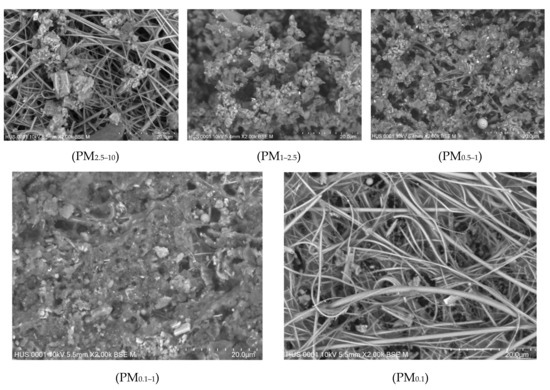
Figure 5.
SEM images of outdoor airborne particles (PM2.5–10, PM1–2.5, PM0.5–1, PM0.1–1, and PM0.1) collected during the class at S1.
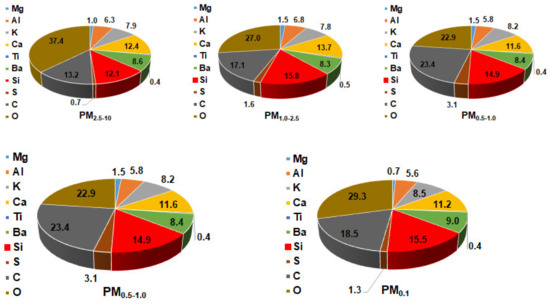
Figure 6.
Elemental composition of outdoor PM2.5–10, PM1–2.5, PM0.5–1, PM0.1–1, and PM0.1 collected during the class at S1.
As for ultrafine particles, they were entangled into the porous structure of the filter matrix to make blocks of particles which looked like additional filters. However, the inner structure of ultrafine particles could not be revealed due to the limit of resolution of the deployed SEM instrument. Regarding elemental composition performed with EDS of these collected particles, it was noted that oxygen was the most abundant element, followed by C and Si. Oxygen accounted for 36.2% to 42.4% for indoor particles and 22.9% to 37.4% for outdoor ones, while those figures for C were in the range of 14.5%–18.1% and 13.2%–24.2%, respectively (Figure 4 and Figure 6). These obtained results suggest that the proportion of elemental carbon in outdoor particles would be more important than indoors.
Regarding major elements, Si and Ca were the most abundant elements, followed by Al. The mass proportion of all the examined elements could make up to 50% of the indoor and outdoor airborne particles (Figure 4 and Figure 6). The distribution of those major elements will be analyzed in detail in the subsequent section. All trace elements presenting proportions below 0.5%, which is the quantification limit of EDS, were not analyzed in this section.
Indoor and outdoor concentrations of major and trace elements sampled during teaching hours and analyzed by ICP methods are presented in Supplementary Table S2. The results obtained when schools were vacant are illustrated in Supplementary Tables S3 and S4. As expected, major elements such as Al, Ba, Ca, Fe, K, Mg, and Ti were the most abundant in indoor and outdoor particles (Supplementary Table S1). In addition, indoor PM10, PM2.5, and PM1 elemental concentrations were clearly higher in the presence of children than during their absence (Supplementary Tables S2–S4), mainly due to more important particle mass concentrations, as presented previously. However, ultrafine particles seemed not to be impacted by children’s activities in the classroom. Similarly, the higher indoor particle mass concentrations at S1 seemed to lead to higher elemental concentrations in indoor particles compared to S2 (Supplementary Table S2) for almost all elements. For instance, average concentrations of Ca and Al in indoor PM10 at S1 were 9157 and 4768 ng/m3, while those values at S2 were much less, averaging 1281 and 574 ng/m3, respectively. On the contrary, larger outdoor mass concentrations of PM2.5 and PM10 collected during the class at S2 compared to S1 resulted in higher levels of most of the associated elemental contents. Outdoor average concentrations of Cu and Zn collected during classes at S2 were 100 and 603 ng/m3, while those values at S1 were 53.3 and 340 ng/m3, respectively (Supplementary Table S2). Some elements (Mg, Mn, Pb) presented higher concentrations at S1 compared to S2, which could be attributed to outdoor temporary emission sources at S1, which was reflected in large variations in the concentrations of these elements.
Compared to other studies conducted in school environments, the concentrations of major elements in this work were relatively higher than those obtained in European schools, whereas trace and minor element contents were generally lower in this work [13,19,25,27]. Indoor concentrations of major elements in PM10 varied from about 65 ng/m3 to more than 9100 ng/m3 in this work compared to a range of 13–4380 ng/m3 reported by Tran et al. [3] in a work conducted in 3 elementary schools at industrial, urban, and rural areas in the north of France, or a range of 4–1494 ng/m3 in Oliveira et al. [15] performed at a preschool in an urban area of Portugal. However, the work of Chithra et al. [38] conducted in a naturally ventilated school in Chanai, India, revealed higher major element contents accounting for about 11 µg/m3, while trace and minor elements represented more than 850 ng/m3.
3.4.2. Elemental Distribution of Ultrafine, Fine and Coarse Particles
Proportions of trace, minor, and major elements in size-resolved indoor and outdoor airborne particles sampled during teaching hours at S1 and S2 are presented in Figure 7 and Supplementary Table S5.
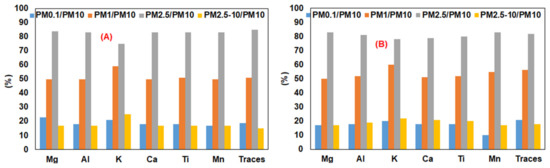
Figure 7.
Average elemental distribution in different indoor (A) and outdoor (B) particulate fractions (%) sampled during the class at S1 (n = 80, average ± SD).
It is shown that major, minor, and trace elements in ultrafine fraction accounted for around 15%–20%, while their concentration in fine particles (PM2.5) made up a range of 75% to 80% of indoor and outdoor PM10 at S1 and S2. Major elements seemed to be slightly more enriched in coarse fraction (PM2.5–10) compared to trace elements. For instance, concentrations of Al, Ba, Ca, K, Mg, Fe, and Ti in PM2.5–10 fraction accounted for proportions ranging from 25% to 50% of their contents in indoor PM10 at S2, while those figures for trace elements (As, Bi, Cd, Cu, La, Mo, Ni, Rb, Sb, Se, Sn, Pb) were within the range of 10% to 25% (Supplementary Table S5). A similar trend was observed with the case of indoor particles at S1 and for outdoor particles at S1 and S2. Indoor activities of occupants seemed not to influence the elemental distribution in indoor particles compared to outdoor ones (Figure 7). Our results were in accordance with reported work [3,16] carried out in school environments.
Major, minor, and trace elements commonly presented unimodal distribution for indoor and outdoor airborne particles at S1 and S2 (Figure 8 and Figure 9, and Supplementary Figure S1), with the dominant peak occurring in the particle diameter range (Dp) = 0.5–1 µm at S2 and 1–2.5 µm at S1. The average accumulative proportions of examined elements indoor and outdoor at S1 and S2 accounted for about 65–90% of their total mass in PM10. The appearance of unimodal distribution for all elements might be associated with the limited resolution of the cascade impactor (only one fraction in coarse particles—PM2.5–10), which probably masked the elemental distribution within the coarse mode. Waheed et al. [41] found that trace elements such as Pb, Cd, Se, Sn, Bi, and Zn presented unimodal distribution in the fine fraction (0.2–1 µm), while some trace, minor, and major elements such as Al, Fe, Ca, Ba, Mg, Sr, Ge, Zr, and U were distributed in unimodal mode in coarse fraction (1–4 µm). Malandrino et al. [42] showed that Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Mo, and Sn were found in the coarse mode (2.7–11 µm), while As, Co, Pb, and V were mainly present in the accumulation mode (<2.7 µm) and Ni and Zn presented several modes spread throughout the size distribution. It is noted that elements could present unimodal, bimodal, or several modes, and their accumulation in different fractions might vary due to discrepancies in emission sources, such as mechanical processes, combustion of fossil fuels/biomass, industry, etc. [9,42,43,44].
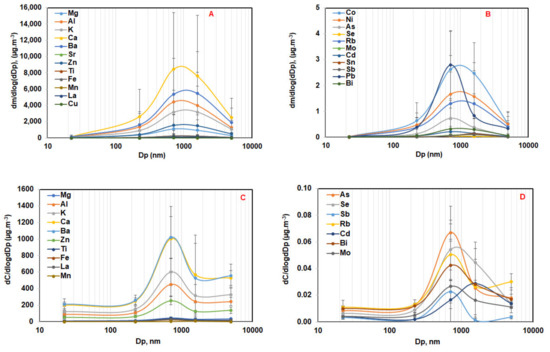
Figure 8.
Average size-resolved elemental distributions of indoor airborne particles sampled during the class at S1 (A,B) and S2 (C,D). n = 80, average ± SD.
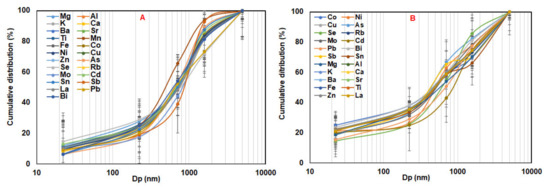
Figure 9.
Cumulative size-resolved elemental distributions of indoor airborne particles sampled during the class at S1 (A) and S2 (B). n = 80, average ± SD.
3.5. Emission Sources of Indoor and Outdoor Airborne Particles
3.5.1. Indoor to Outdoor Ratio of Elements in Size-Resolved Airborne Particles
Indoor to outdoor ratios (I/O ratios) of pollutants are usually used to figure out the presence of indoor emission sources. In this work, I/O ratios of different elements were calculated from their indoor and outdoor corresponding concentrations in PM0.1, PM0.5, PM1, PM2.5, and PM10. The results obtained during teaching hours are presented in Table 5. It was found that I/O ratios for different elements showed similar trends both for S1 and S2. I/O ratios of all examined elements for all fractions were largely below the unity (Table 5), suggesting that indoor emission sources of the examined elements were negligible. This is also confirmed by questionnaires which revealed that classrooms’ floors were cleaned almost every day, all footwear and outerwear were kept outdoors, and children mainly played with plastic and wood toys, along with arts and crafts activities which might emit volatile organic compounds, but no significant sources of metallic elements. It is interesting to note that I/O ratios for all elements were quite low (around 0.1–0.3 and always <0.7). This is due to higher concentrations of corresponding outdoor airborne particles at the two schools, as presented previously, which could lead to the higher elemental contents in outdoor particles, hence higher I/O ratios [3]. A similar trend was observed for samples collected when the classrooms were empty (Supplementary Table S6).

Table 5.
Indoor to outdoor ratios (I/O ratios) of different elements sampled during the class at S1 and S2 (n = 80, average ± SD, in parentheses are min–max values).
3.5.2. Enrichment Factors and Correlation
Enrichment factors (EFs) for different elements were calculated according to Equation (1). There were no significant discrepancies between EFs of indoor and outdoor particles at S1 and S2, while fine particles (PM2.5) represented most of the indoor and outdoor PM10 at the two schools. Consequently, EFs were calculated for indoor PM2.5 collected during teaching hours at S1 and S2. The error bars represent standard deviations of corresponding elements. The results obtained are presented in Figure 10. Elements with EFs < 10 are usually considered as non-enriched and associated with crustal emission sources [44,45], while those with EFs > 10 are considered to be dominated by the emission of anthropogenic sources. EFs in the range of 10–100 suggest moderately enriched elements, while EFs above 100 show significantly enriched elements in examined particles [9,44,46]. The results showed that most of examined elements (Ca, Mg, K, Fe, Mn, Sr, Ti, Rb, Mo, Sn, Se, Pb, Ni, Co, As) were non-enriched and originated from crustal sources, while Cu, Sb, Cd, Bi, and Ba were moderately enriched, and La and Zn were the most enriched by the contribution of anthropogenic emissions. Cd, Cu, Sb, Bi, Ba, and Zn could be associated to the traffic emissions [3,47,48]. Cd, Sb, and Zn could be emitted from incineration of municipal wastes [49]. The enrichment of La in PM2.5 at S1 and S2 could be attributed to thermal processes, such as power plants and the cement industry [50]. Traffic-associated elements such as Cd, Cu, Bi, and Zn [3,47,48] presented EFs values higher at S2 than at S1, confirming that traffic emission at S2 was more important. As presented previously, S2 was exposed directly to two streets and situated in close proximity (about 100 m) to the ring road N0 3, where there was dense traffic, whereas S1 was located a hundred meters from main roads and it was surrounded by several buildings and houses that might prevent traffic-originated airborne particles from penetrating into the indoors at S1.
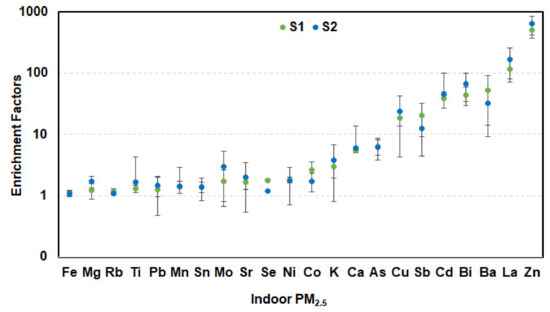
Figure 10.
Enrichment factors of elements in indoor PM2.5 collected during the class at S1 and S2 (n = 10, average ± SD).
The results of Spearman correlation coefficients are presented in Supplementary Table S7. It was observed that variations in temperature and relative humidity were not correlated with elemental contents of indoor and outdoor airborne particles. Similarly, CO2 and CO concentrations did not show good correlations with elemental contents. This suggests that CO was emitted not only from traffic sources but also from other combustion processes. Regarding CO2, although there was a positive correlation between indoor CO2 levels and indoor PM10 and PM2.5 concentrations, this did not guarantee good correlations with elemental concentrations because indoor PM2.5 and PM10 were different from outdoor ones; hence, their metal contents. In addition, outdoor CO2 did not reflect only the traffic emissions, as there were other combustions and processes which emitted CO2. As a result, CO2 was not correlated with indoor and outdoor elements.
Regarding correlations between elements, most of them were strongly correlated with each other (coefficients > 0.7), suggesting common emission sources, especially traffic (Supplementary Table S7). However, some elements were weakly correlated, which was probably linked to other emission sources rather than traffic (exhaust and non-exhaust emissions). For instance, Sb was weakly correlated with Al (0.57), Mn (0.52), Rb (0.39), and Sr (0.58), implying that Al, Mn, Rb, and Sr not only originated from traffic but also from other sources, such as construction works, which occurred in a large number of places in Hanoi in recent years.
4. Conclusions
This work performed at 2 schools of Hanoi, Vietnam, is the first study focusing on elemental composition, morphology, and distribution of indoor and outdoor airborne particles, which provides insight into the context of air quality in Hanoi regarding airborne particle sources and their elemental contents. The results showed that the average concentrations of indoor and outdoor CO and CO2 were below the limit values recommended by WHO and ASHRAE for 24 h exposure. Indoor average concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 were below the limit values recommended by WHO at S2, whereas they exceeded these recommendations at S1. The presence of children and their activities strongly influenced the concentration of fine (PM2.5) and coarse (2.5–10 µm) factions, whereas they did not seem to have significant impacts on ultrafine particles.
Regarding elemental composition and morphology of airborne particles sampled at S1 and S2, it was shown that the coarse fraction (2.5–10 µm) did not present regular shapes, while smaller factions tended to aggregate to form clusters with fine structures. The submicron fractions (PM0.5–1 and PM0.1–0.5) presented the largest population, which were aggregated more tightly. Oxygen (36.2%–42.4%) was the most abundant element, followed by C (14.5%–18.1%) and then Si in indoor and outdoor airborne particles. A mass proportion of major and minor elements could make up 50%, whereas trace elements accounted for less than 0.5% of the indoor and outdoor airborne particles. Elemental distribution of major, minor, and trace elements were mainly presented in fine fraction (<2.5 µm), with around 75%–80% of total mass of PM10, implying great potential health risk associated with fine particles and their elemental composition.
The preliminary results on emission sources revealed the presence of heavy metals inside the two preschools mainly due to the penetration of outdoor sources. Ca, Mg, K, Fe, Mn, Sr, Ti, Rb, Mo, Sn, Se, Pb, Ni, Co, and As originated from crustal sources, while Cu, Sb, Cd, Bi, Ba, La, and Zn were enriched by the contribution of anthropogenic emissions, such as traffic and incineration.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4433/11/5/519/s1: Figure S1: Average size-resolved elemental distribution outdoor airborne particles sampled during teaching hours at S1 (A, B) and S2 (C, D); n = 10, average ± SD. Table S1: Detection, quantification limits, and recovery rates of different elements. Table S2: Elemental concentrations of indoor and outdoor ultrafine, fine, and coarse particles (ng/m3) sampled during teaching hours (n = 80, average ± SD) at S1 and S2. Table S3: Elemental concentrations of indoor and outdoor ultrafine, fine, and coarse particles (ng/m3) sampled in the absence of children at S1 (n = 10, average ± SD). Table S4: Elemental concentrations of indoor and outdoor ultrafine, fine, and coarse particles (ng/m3) sampled in the absence of children at S2 (n = 10, average ± SD). Table S5: Elemental distribution in different indoor and outdoor particulate fractions (%) sampled during teaching hours (n = 80, average ± SD). Table S6: I/O ratios of different elements sampled in the absence of children at S1 and S2 (n = 80, average ± SD, in parentheses are min–max values). Table S7: Correlation between elements, pollutant gases, and comfort parameters (n = 80).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.D.T., P.M.N., and M.B.T.; methodology, T.D.T., M.B.T., and L.Y.A.; software, N.M.H. and M.N.D.; formal analysis, T.D.T., P.M.N., C.V.L., D.T.N., and M.N.D.; investigation, T.D.T., P.M.N., V.M.N., and D.T.P.; writing—original draft preparation, T.D.T., P.M.N., N.M.H., and C.V.L.; writing—review and editing, M.B.T., N.V.N., T.H.L., D.T.N., and D.T.P.; visualization, T.D.T., L.Y.A., T.H.L., D.T.N., and N.V.N.; supervision, M.B.T.; L.Y.A., and N.V.N.; funding acquisition, T.D.T.; project administration, P.M.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is funded by Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under grant number 104.99-2016.67.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the two preschools, S1 and S2, for allowing the measurement campaigns to be conducted indoors and outdoors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tran, D.T.; Alleman, L.Y.; Coddeville, P.; Galloo, J.C. Indoor-outdoor behavior and sources of size-resolved airborne particles in French classrooms. Build. Environ. 2014, 81, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallarés, S.; Gómez, E.T.; Martínez, A.; Jordán, M.M. The relationship between indoor and outdoor levels of PM10 and its chemical composition at schools in a coastal region in Spain. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, D.T.; Alleman, L.Y.; Coddeville, P.; Galloo, J.C. Elemental characterization and source identification of size resolved atmospheric particles in French classrooms. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 54, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofful, L.; Perrino, C. Chemical Composition of Indoor and Outdoor PM2.5 in Three Schools in the City of Rome. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1422–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Health Aspects of Air Pollution Results from the WHO Project: Systematic Review of Health Aspects of Air Pollution in Europe; WHO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2004; pp. 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi, M.; Decesari, S.; Finessi, E.; Giulianelli, L.; Carbone, C.; Fuzzi, S.; O’Dowd, C.D.; Ceburnis, D.; Facchini, M.C. Primary and Secondary Organic Marine Aerosol and Oceanic Biological Activity: Recent Results and New Perspectives for Future Studies. Mar. Aerosol Cloud Clim. Interact. 2010, 310682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okita, T. Formation of Aerosols in the Atmosphere. Phys. Scripta 1988, 31, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez- Camacho, S.; de la Rosa, J.; Sánchez de la Campa, A.M.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; González-Castanedo, Y.; Garcia-Orellana, I.; Nava, S. Ultrafine particle and fine trace metal (As, Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn) pollution episodes induced by industrial emissions in Huelva, SW Spain. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 61, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugamsetty, B.; Wei, H.; Liu, C.-N.; Awasthi, A.; Hsu, S.-C.; Tsai, C.-J.; Roam, G.-D.; Wu, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-F. Source Characterization and Apportionment of PM10, PM2.5 and PM0.1 by Using Positive Matrix Factorization. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 476–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frampton, M.W.; Ghio, A.J.; Samet, J.M.; Carson, J.L.; Carter, J.D.; Devlin, R.B. Effects of aqueous extracts of PM10 filters from the Utah valley on human airway epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 277, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A.; Burnett, R.T.; Thun, M.J.; Calle, E.E.; Krewski, D.; Ito, K.; Thurston, G.D. Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. JAMA 2002, 287, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbengue, S.; Alleman, L.Y.; Flament, P. Size-distributed metallic elements in submicronic and ultrafine atmospheric particles from urban and industrial areas in northern France. Atmos. Res. 2014, 135, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbengue, S.; Alleman, L.Y.; Flament, P. Metal-bearing fine particle sources in a coastal industrialized environment. Atmos. Res. 2017, 183, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, I.; Viana, M.; Moreno, T.; Pandolfi, M.; Amato, F.; Reche, C.; Bouso, L.; Àlvarez-Pedrerol, M.; Alastuey, A.; Sunyer, J.; et al. Child exposure to indoor and outdoor air pollutants in schools in Barcelona, Spain. Environ. Int. 2014, 69, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.; Slezakova, K.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Pereira, M.C.; Morais, S. Assessment of air quality in preschool environments (3–5 years old children) with emphasis on elemental composition of PM10 and PM2.5. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggieri, S.; Longo, V.; Perrino, C.; Canepari, S.; Drago, G.; L’Abbate, L.; Balzan, M.; Cuttitta, G.; Scaccianoce, G.; Minardi, R.; et al. Indoor Air Quality in Schools of a Highly Polluted South Mediterranean Area. Indoor Air 2019, 29, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.; Rivas, I.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Sunyer, J.; Alvarez-Pedrerol, M.; Bouso, L.; Sioutas, C. Indoor/outdoor relationships of quasi-ultrafine, accumulation and coarse mode particles in school environments in Barcelona: Chemical composition and Sources. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 32849–32883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, T.; Alameer, A.; Jaghbeir, O.; Albeitshaweesh, K.; Malkawi, M.; Boor, B.E.; Koivisto, A.J.; Löndahl, J.; Alrifai, O.; Al-Hunaiti, A. Indoor Particle Concentrations, Size Distributions, and Exposures in Middle Eastern Microenvironments. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.T.; Alleman, L.Y.; Coddeville, P.; Galloo, J.C. Indoor particle dynamics in schools: Determination of air exchange rate, size-resolved particle deposition rate and penetration factor in real-life conditions. Indoor Built Environ. 2015, 26, 1335–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, A.C.K. Particle deposition indoors: A review. Indoor Air 2002, 12, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazaroff, W.W. Indoor particle dynamics. Indoor Air 2004, 14, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatcher, T.L.; Layton, D.W. Deposition, resuspension and penetration of particles within a residence. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 1487–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babich, F.; Demanega, I.; Avella, F.; Belleri, A. Low Polluting Building Materials and Ventilation for Good Air Quality in Residential Buildings: A Cost–Benefit Study. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolkoff, P.; Wilkins, C.K.; Clausen, P.A.; Nielsen, G.D. Organic compounds in office environments: Sensory irritation, odor, measurements and the role of reactive chemistry. Indoor Air 2006, 16, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, P.; Bellander, T.; Sällsten, G.; Bomand, J. Indoor and outdoor concentrations of PM2.5 trace elements at homes, preschools and schools in Stockholm, Sweden. J. Environ. Monit. 2007, 9, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Morawska, L.; He, C.; Gilbert, D. Impact of ventilation scenario on air exchange rates and on indoor particle number concentrations in an air conditioned classroom. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromme, H.; Diemer, J.; Dietrich, S.; Cyrys, J.; Heinrich, J.; Lang, W.; Kiranoglu, M.; Twardella, D. Chemical and morphological properties of particulate matter (PM10, PM2.5) in school classrooms and outdoor air. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 597–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.; Huynh, H.V.; Nguyen, T.K.O. Traffic emission inventory for estimation of air quality and climate co-benefits of faster vehicle technology intrusion in Hanoi, Vietnam. Carbon Manag. 2015, 6, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.Q.T.; Nguyen, T.K.O. Roadside BTEX and other gaseous air pollutants in relation to emission sources. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 7685–7697. [Google Scholar]
- Lamaison, L.; Alleman, L.Y.; Robache, A.; Galloo, J.C. Quantification of trace metalloids and metals in airborne particles applying dynamic reaction cell inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Appl. Spectrosc. 2009, 63, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLennan, S.M. Relationships between the trace element composition of sedimentary rocks and upper continental crust. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2001, 2, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Indoor Air Quality: Selected Pollutants; WHO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2010; pp. 86–96. [Google Scholar]
- ANSI/ASHRAE. Standard: 62.1–2013. In Ventilation for Acceptable Indoor Air Quality; American Society of Heating Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2013; pp. 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z.; Deng, W.; Tenorio, R. Investigation of Indoor Air Quality and the Identification of Influential Factors at Primary Schools in the North of China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainka, A.; Zajusz-Zubek, E. Indoor Air Quality in Urban and Rural Preschools in Upper Silesia, Poland: Particulate Matter and Carbon Dioxide. Int. J. Environ. Res. Publ. Health. 2015, 12, 7697–7711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Real-Time Network. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/airnow/index.cfm?action=airnow.global_summary#Vietnam$Hanoi (accessed on 27 February 2020).
- Braniš, M.; Řezáčová, P.; Domasová, M. The effect of outdoor air and indoor human activity on mass concentrations of PM10, PM2.5, and PM1 in a classroom. Environ. Res. 2005, 99, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chithra, V.S.; Madanayak, S.N.S. Source Identification of Indoor Particulate Matter and Health Risk Assessment in School Children. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2018, 22, 04018002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.; Nunes, T.; Silva, J.; Duarte, M. Comfort Parameters and Particulate Matter (PM10 and PM2.5) in School Classrooms and Outdoor Air. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 1521–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovelli, S.; Cattaneo, A.; Nuzzi, C.P.; Spinazzè, A.; Piazza, S.; Carrer, P.; Cavallo, D.M. Airborne Particulate Matter in School Classrooms of Northern Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Publ. Health 2014, 11, 1398–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waheed, A.; Li, X.; Tan, M.; Bao, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y. Size Distribution and Sources of Trace Metals in Ultrafine/Fine/Coarse Airborne Particles in the Atmosphere of Shanghai. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malandrino, M.; Casazza, M.; Abollino, O.; Minero, C.; Maurino, V. Size resolved metal distribution in the PM matter of the city of Turin (Italy). Chemosphere 2016, 147, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Tan, J.; Wang, S.; Hao, J.; Chai, F. Size distributions and sources of elements in particulate matter at curbside, urban and rural sites in Beijing. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contini, D.; Cesari, D.; Donateo, A.; Chirizzi, D.; Belosi, F. Characterization of PM10 and PM2.5 and their metals content in different typologies of sites in South-Eastern Italy. Atmosphere 2014, 5, 435–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, N.; Pey, J.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; López, J.M.; Viana, M. Partitioning of major and trace components in PM10-PM2.5-PM1 at an urban site in Southern Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1677–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bi, X.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J. Hospital indoor PM10/PM2.5 and associated trace elements in Guangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 366, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Moreno, T.; Vian, M.M.; Castillo, S.; Pey, J.; Rodríguez, S.; Artiñano, B.; Salvador, P.; Sánchez, M.; et al. Spatial and temporal variations in airborne particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5) across Spain 1999–2005. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 3964–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alleman, L.Y.; Lamaison, L.; Perdrix, E.; Robache, A.; Galloo, J.C. PM10 metal concentrations and source identification using positive matrix factorization and wind sectoring in a French industrial zone. Atmos. Res. 2010, 96, 612–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolocka, M.P.; Lake, D.A.; Johnston, M.V.; Wexler, A.S. Size-resolved fine and ultrafine particle composition in Baltimore, Maryland. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, D07S04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, P.; Delgado Saborit, J.M.; Harrison, R.M. A review of chemical and physical characterisation of atmospheric metallic nanoparticles. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).