Low-Cost Air Quality Sensors: One-Year Field Comparative Measurement of Different Gas Sensors and Particle Counters with Reference Monitors at Tušimice Observatory
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Clearly defined sensor application targets;
- Appropriate sensor placement (study design) to monitor the given target;
- Selection of suitable sensor types;
- Initial and continuous verification of sensor measurement quality;
- Sensor data control and processing;
- Appropriate use and interpretation of results.
2. Experimental Methodology
2.1. Study Area and Experimental Design
2.2. Technical Specification of Tested Sensors and Reference (or Equivalent to Reference) Monitors
2.2.1. Cairpol Gas Sensors
2.2.2. Plantower and Alphasense Miniature Particle Counters
2.2.3. Reference Monitors and Other Equivalent Methods
2.2.4. Data Analysis and Data Control
3. Results
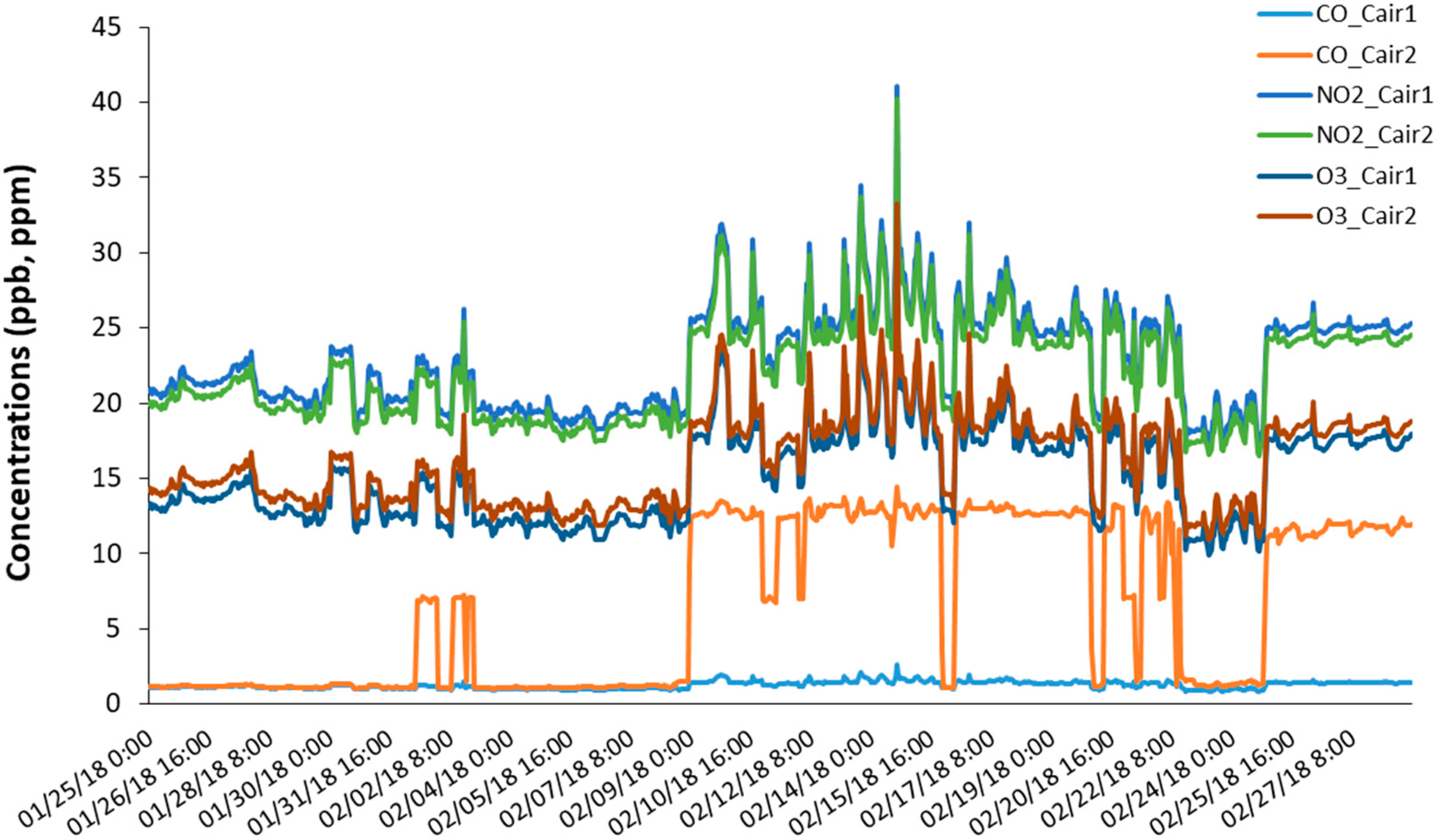
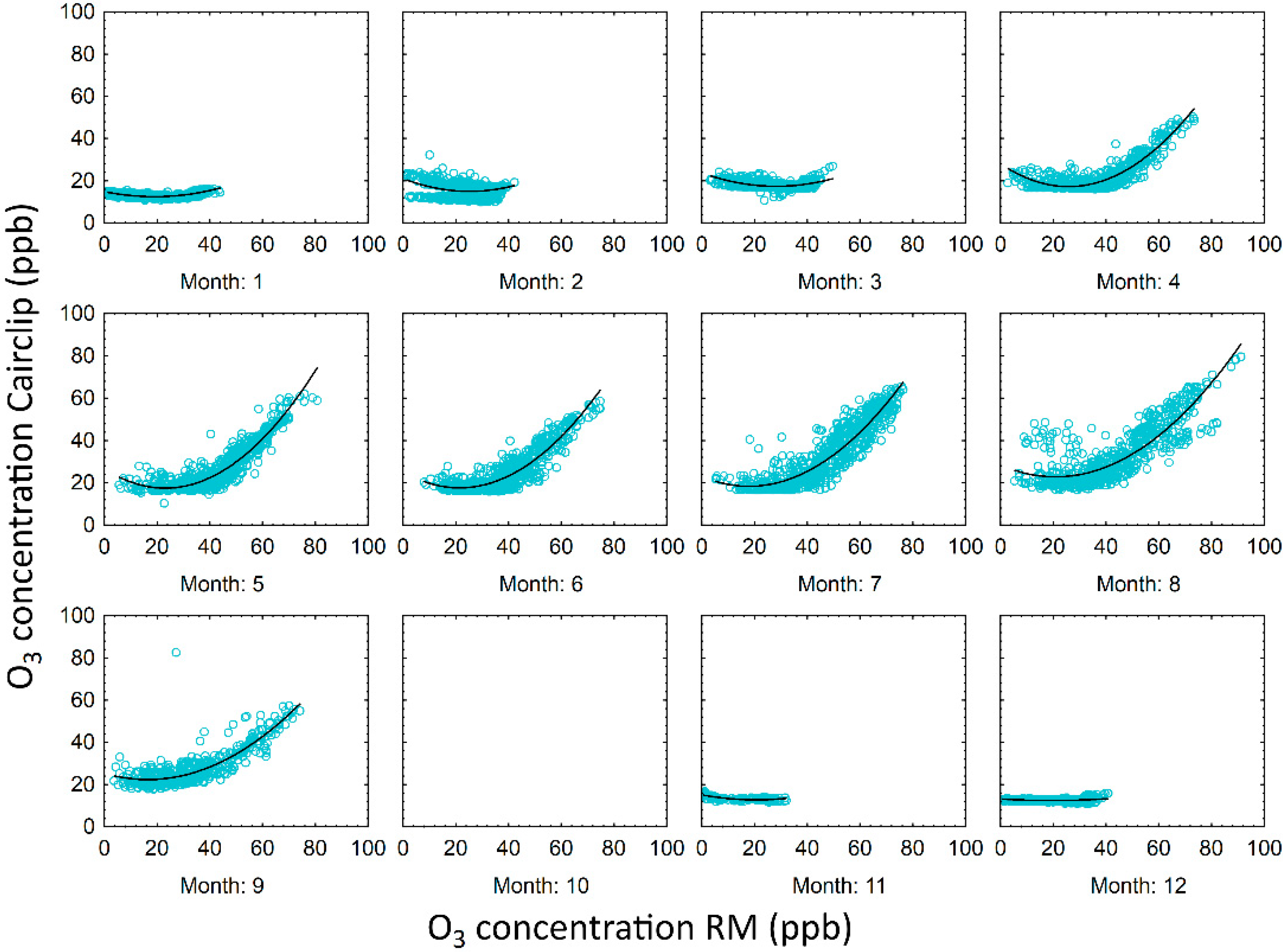
3.1. Cairpol Gas Sensors
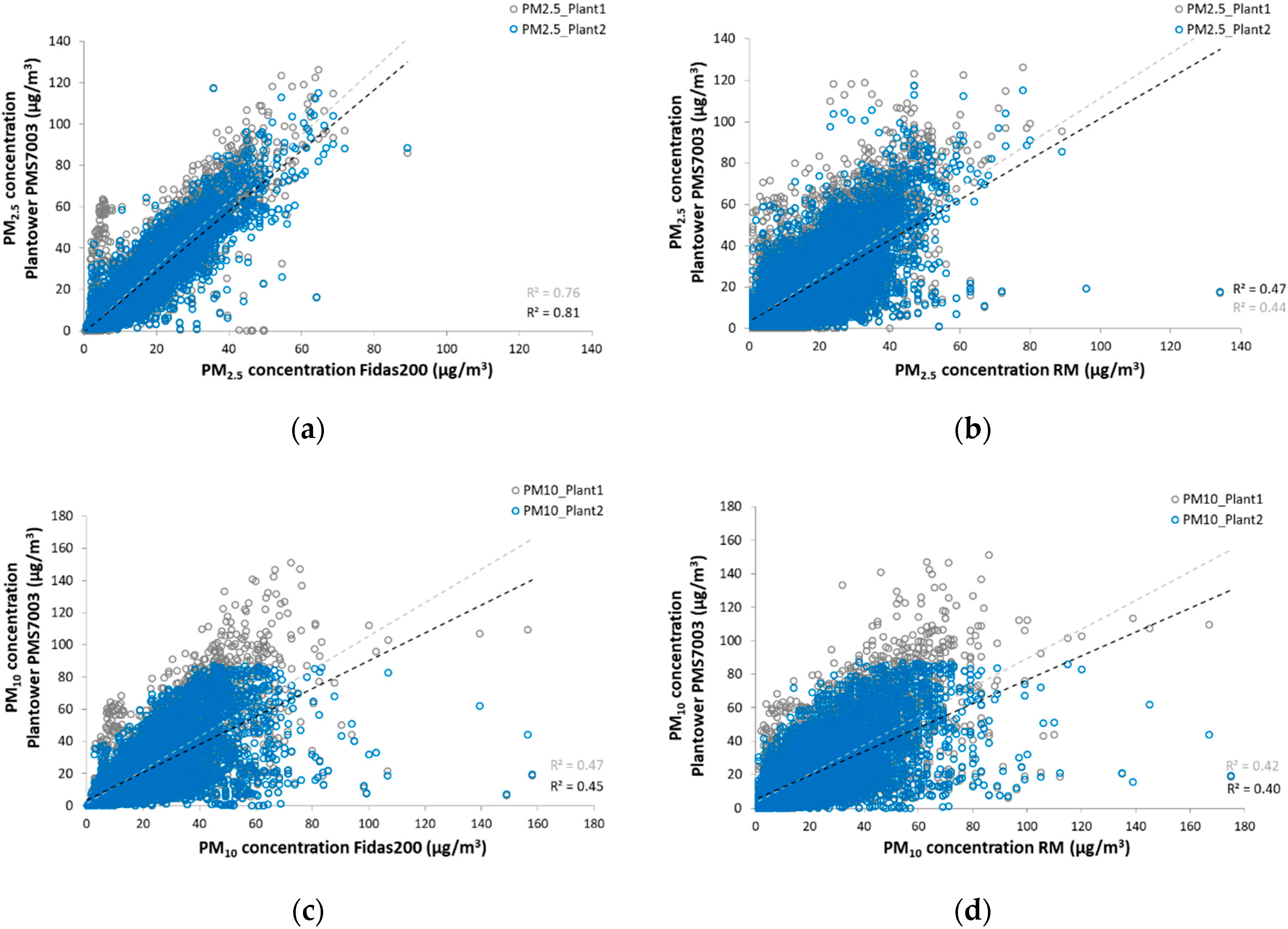
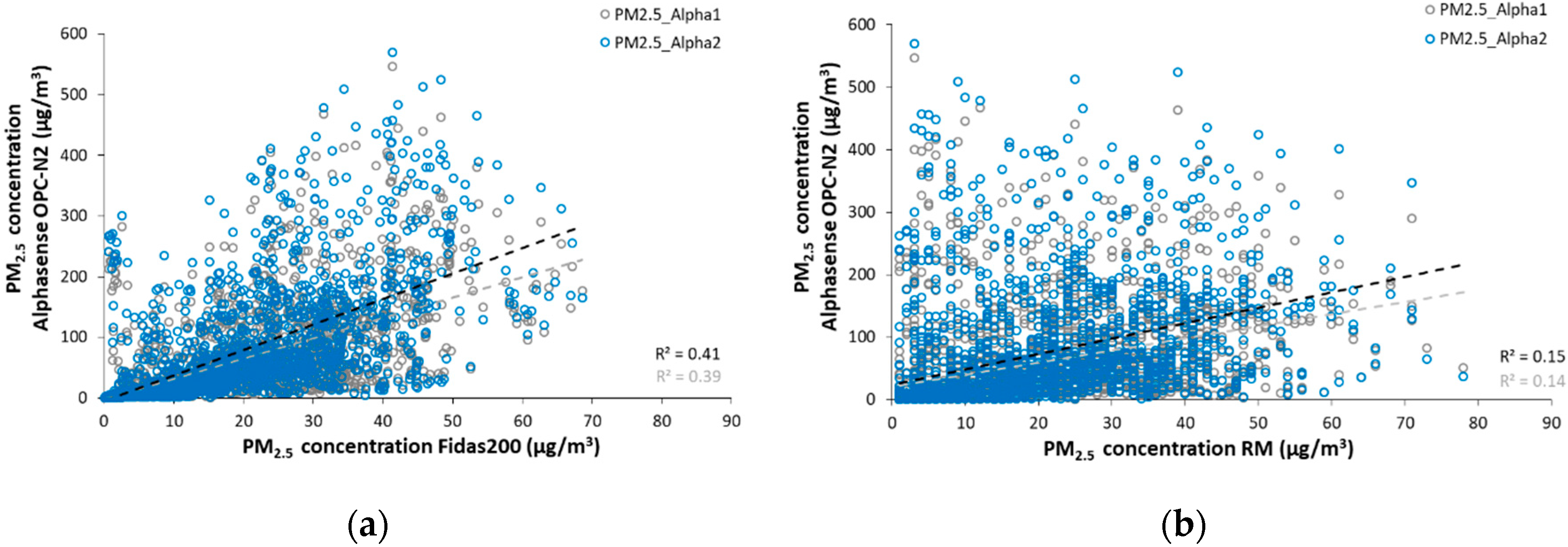
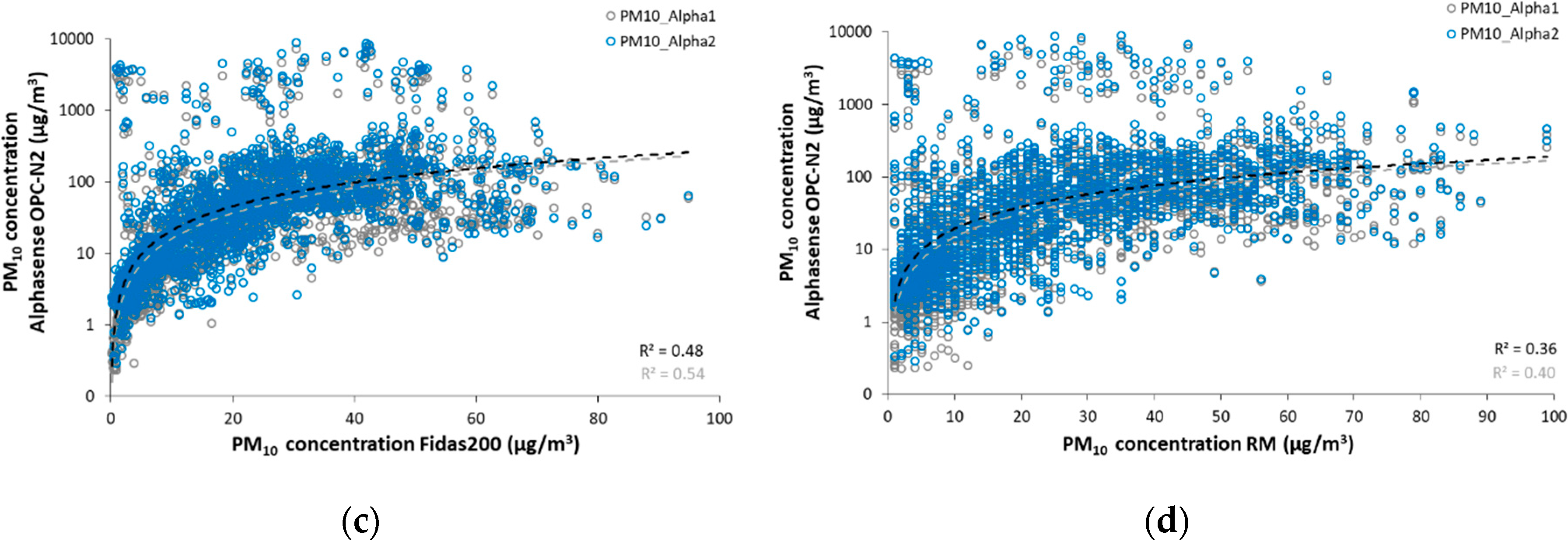
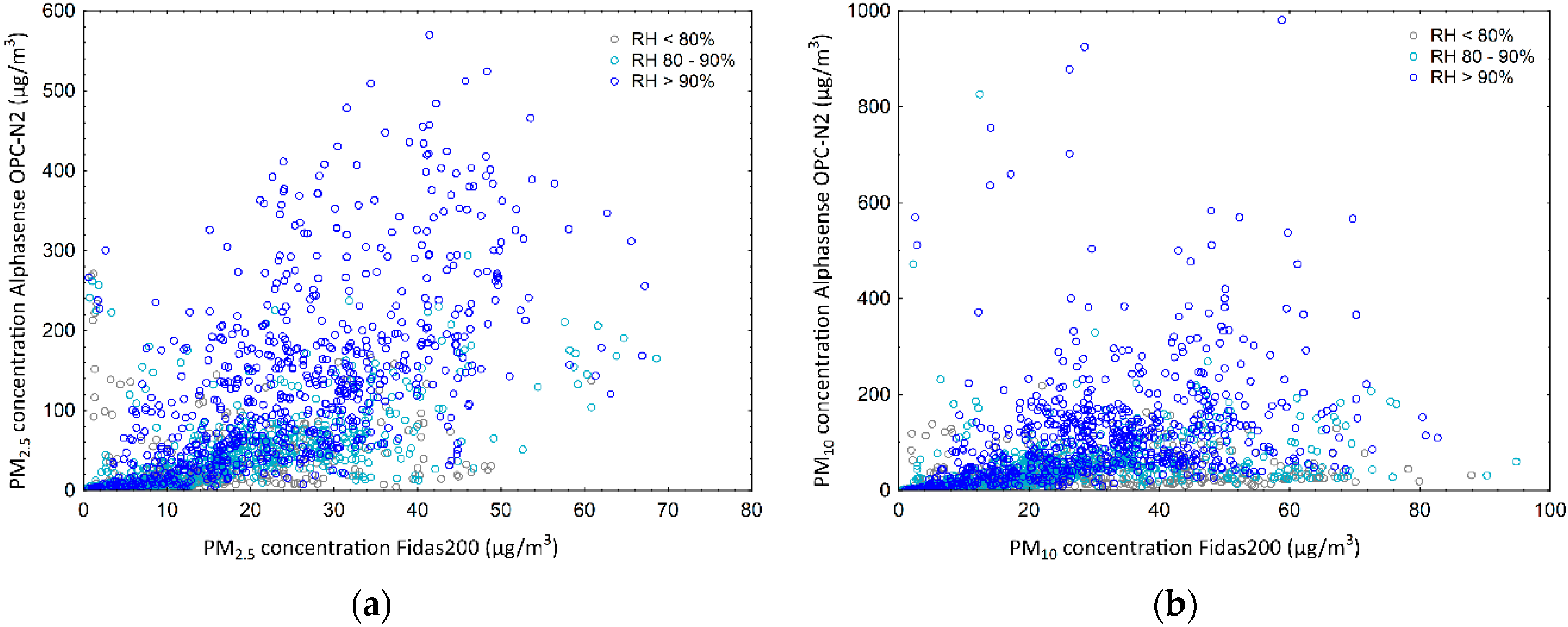
3.2. Plantower and Alphasense Particle Counters
4. Discussion
4.1. Cairpol Gas Sensors
4.2. Plantower and Alphasense Particle Counters
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, P.; Morawska, L.; Martani, C.; Biskos, G.; Neophytou, M.; Di Sabatino, S.; Bell, M.; Norford, L.; Britter, R. The rise of low-cost sensing for managing air pollution in cities. Environ. Int. 2015, 75, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKercher, G.R.; Salmond, J.A.; Vanos, J.K. Characteristics and applications of small, portable gaseous air pollution monitors. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Languille, B.; Gros, V.; Bonnaire, N.; Pommier, C.; Honoré, C.; Debert, C.; Gauvin, L.; Srairi, S.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Chaix, B.; et al. A methodology for the characterization of portable sensors for air quality measure with the goal of deployment in citizen science. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier-Oxandale, A.; Feenstra, B.; Papapostolou, V.; Zhang, H.; Kuang, M.; Boghossian, B.D.; Polidori, A. Field and laboratory performance evaluations of 28 gas-phase air quality sensors by the AQ-SPEC program. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 220, 117092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerboles, M. European Committee for Standardization: CEN/TC 264/WG 42—Ambient Air—Air Quality Sensors. Available online: https://standards.cen.eu/dyn/www/f?p=204:22:0::::FSP_ORG_ID,FSP_LANG_ID:2012773,25&cs=13EA71B95E446E4F77D5EEB632F4BF317 (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- Feenstra, B.; Papapostolou, V.; Hasheminassab, S.; Zhang, H.; Der Boghossian, B.; Cocker, D.; Polidori, A. Performance evaluation of twelve low-cost PM2.5 sensors at an ambient air monitoring site. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 216, 116946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelle, L.; Gerboles, M.; Villani, M.G.; Aleixandre, M.; Bonavitacola, F. Field calibration of a cluster of low-cost available sensors for air quality monitoring. Part A: Ozone and nitrogen dioxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 215, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelle, L.; Gerboles, M.; Villani, M.G.; Aleixandre, M.; Bonavitacola, F. Field calibration of a cluster of low-cost commercially available sensors for air quality monitoring. Part B: NO, CO and CO2. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 238, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego, C.; Costa, A.M.; Ginja, J.; Amorim, M.; Coutinho, M.; Karatzas, K.; Sioumis, T.; Katsifarakis, N.; Konstantinidis, K.; De Vito, S.; et al. Assessment of air quality microsensors versus reference methods: The EuNetAir joint exercise. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 147, 246–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castell, N.; Dauge, F.R.; Schneider, P.; Vogt, M.; Lerner, U.; Fishbain, B.; Broday, D.; Bartonova, A. Can commercial low-cost sensor platforms contribute to air quality monitoring and exposure estimates? Environ. Int. 2017, 99, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, M.I.; Popoola, O.A.M.; Stewart, G.B.; Landshoff, P.; Calleja, M.; Hayes, M.; Baldovi, J.J.; McLeod, M.W.; Hodgson, T.F.; Dicks, J.; et al. The use of electrochemical sensors for monitoring urban air quality in low-cost, high-density networks. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 70, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Ning, Z.; Ye, S.; Sun, L.; Yang, F.; Wong, K.C.; Westerdahl, D.; Louie, P.K.K. Impact analysis of temperature and humidity conditions on electrochemical sensor response in ambient air quality monitoring. Sensors 2018, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauerová, P.; Novák, Z.; Rychlík, Š.; Keder, J. Small air quality sensors: In vivo testing of electrochemical Cairpol sensors in comparison to reference measurement. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2018, 230, 343–354. [Google Scholar]
- Crilley, L.R.; Shaw, M.; Pound, R.; Kramer, L.J.; Price, R.; Young, S.; Lewis, A.C.; Pope, F.D. Evaluation of a low-cost optical particle counter (Alphasense OPC-N2) for ambient air monitoring. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoest, V.; Van Osei, F.B.; Stein, A.; Hoek, G. Calibration of low-cost NO2 sensors in an urban air quality network. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 210, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulot, F.M.J.; Johnston, S.J.; Basford, P.J.; Easton, N.H.C.; Apetroaie-Cristea, M.; Foster, G.L.; Morris, A.K.R.; Cox, S.J.; Loxham, M. Long-term field comparison of multiple low-cost particulate matter sensors in an outdoor urban environment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauerová, P.; Keder, J. Hodnocení Testovacího Měření Různých Typů Malých Senzorů Kvality Ovzduší na Observatoři Tušimice: Cairclip (Cairpol, FR), PMS7003 (Plantower, CHN); Czech Hydrometeorological Institute: Prague, Czech Republic, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg, S.; Williams, R.; Hagler, G.S.W.; Rickard, J.; Brown, R.; Garver, D.; Harshfield, G.; Stauffer, P.; Mattson, E.; Judge, R.; et al. Long-term evaluation of air sensor technology under ambient conditions in Denver, Colorado. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 4605–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairpol. Technical Datasheet Cairsens O3/NO2; Cairpol Environment S.A.: Poissy, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cairpol. Technical Datasheet Cairsens NO2; Cairpol Environment S.A.: Poissy, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Spinelle, L.; Gerboles, M.; Aleixandre, M. Report of Laboratory and in-Situ in itu Validation of Micro-Sensor Sensor for Monitoring Ambient air Pollution. O12: CairClip O3/NO2 of Cairpol (F); Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, W.; Hagler, G.; Williams, R.; Sharpe, R.; Brown, R.; Garver, D.; Judge, R.; Caudill, M.; Rickard, J.; Davis, M.; et al. Community Air Sensor Network (CAIRSENSE) project: Evaluation of low-cost sensor performance in a suburban environment in the southeastern United States. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 5281–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notario, A.; Bravo, I.; Adame, J.A.; Díaz-de-Mera, Y.; Aranda, A.; Rodríguez, A.; Rodríguez, D. Behaviour and variability of local and regional oxidant levels (OX = O3 + NO2) measured in a polluted area in central-southern of Iberian Peninsula. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairpol. Technical Datasheet Cairsens SO2; Cairpol Environment S.A.: Poissy, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cairpol. Technical Datasheet Cairsens CO; Cairpol Environment S.A.: Poissy, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, Z.; Haoxin, Z. Digital Universal Particle Concentration Sensor: PMS7003 Series Data Manual; Plantower: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Alphasense. Alphasense User Manual OPC-N2 Optical Particle Counter; Sensor Technology House: Essex, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Teledyne API. Available online: http://www.teledyne-api.com/ (accessed on 5 March 2018).
- Environment, SA. Available online: http://www.environnement-sa.com/ (accessed on 14 January 2019).
- Palas, Fidas200. Available online: https://www.palas.de/en/product/fidas200 (accessed on 20 November 2018).
- Smolík, P.; Rychlík, Š. Validační Zpráva Pro Metodu T 22 AA-005; Czech Hydrometeorological Institute: Prague, Czech Republic, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fishbain, B.; Lerner, U.; Castell, N.; Cole-Hunter, T.; Popoola, O.; Broday, D.M.; Martinez Iniguez, T.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; Jovasevic-Stojanovic, M.; Topalovic, D.; et al. An evaluation tool kit of air quality micro-sensing units. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zoest, V.M.; Stein, A.; Hoek, G. Outlier Detection in Urban Air Quality Sensor Networks. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissert, L.F.; Alberti, K.; Miskell, G.; Pattison, W.; Salmond, J.A.; Henshaw, G.; Williams, D.E. Low-cost sensors and microscale land use regression: Data fusion to resolve air quality variations with high spatial and temporal resolution. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 213, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, A.L.; Griswold, W.G.; RS, A.; Johnston, J.E.; Herting, M.M.; Thorson, J.; Collier-Oxandale, A.; Hannigan, M. Low-Cost Air Quality Monitoring Tools: From Research to Practice (A Workshop Summary). Sensors 2017, 17, 2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clements, A.L.; Reece, S.; Conner, T.; Williams, R. Observed data quality concerns involving low-cost air sensors. Atmos. Environ. X 2019, 3, 100034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.C.; Von Schneidemesser, E.; Peltier, R.E. Low-Cost Sensors for the Measurement of Atmospheric Composition: Overview of Topic and Future Applications; WMO-No.121.; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, T.; Bergin, M.H.; Johnson, K.K.; Tripathi, S.N.; Shirodkar, S.; Landis, M.S.; Sutaria, R.; Carlson, D.E. Field evaluation of low-cost particulate matter sensors in high-and low-concentration environments. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 4823–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gas Sensor Type | Measurement Range | Limit of Detection | Uncertainty | Interference Effect | Temperature Effect on Zero Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cairclip SO2 (ppb) | 0–1000 | 50 | <25% | NO2, O3: ~−125% H2S: ~5% CO, H2: <1% | Not detected |
| Cairclip NO2 (ppb) | 0–250 | 20 | <30% | Cl2: ~80% sulfur compounds: negative interference O3: ~80% | ±50 ppb |
| Cairclip O3 (ppb, also O3/NO2 ppb) | 0–250 | 20 | <30% | Cl2: ~80% sulfur compounds: negative interference | ±50 ppb |
| Cairclip CO (ppm) | 0–20 | 0.05 | <25% | H2 < 60% Long-term high concentrations of H2S, NOx, SO2 may interfere with the signal | ±1 ppm |
| Particle Counter Type | Measured Fractions | Detection Range (µm) | Measurement Range | Maximum Consistency Error/Coincidence Probability | Standard Volume |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plantower PMS7003 | PM1 | 0.30–10.00 | 0–500 (µg/m3) | ±10% at conc. 100–500 μg/m3 ±10 μg/m3 at conc. 0–100 μg/m3 | 0.1 L |
| PM2.5 | |||||
| PM10 | |||||
| Alphasense OPC-N2 | PM1 | 0.38–17.00 | 0–10,000 (particles/s) | 0.84% at 106 particles/L | 1.2 L |
| PM2.5 | |||||
| PM10 |
| Type of Sensor | Sensor ID | Reference Monitor | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD 1 | Intra-Sensors | Mean ± SD 1 | ||
| 1 | 2 | Correlation (rS) 2 | ||
| Cairclip SO2 (ppb) | 97.68 ± 53.45 | 31.01 ± 30.16 | 0.99 | 1.67 ± 1.69 |
| Cairclip NO2 (ppb) | 30.54 ± 13.63 | 29.61 ± 13.49 | 1.00 | 6.31 ± 4.20 |
| Cairclip O3 (ppb) | 22.53 ± 12.50 | 23.68 ± 12.83 | 1.00 | 32.57 ± 17.42 |
| Cairclip CO (ppm) | 1.81 ± 0.97 | 12.26 ± 7.49 | 0.81 | - 3 |
| Type of Sensor | Sensor ID | Presence 1 (%) | Correlation with RM | Measurement Error 3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rS 2 | MBE | MAE | RMSE | |||
| Cairclip SO2 (ppb) | 1 | 94.8 | 0.02 | −110.11 | 110.11 | 119.89 |
| 2 | 72.6 | 0.00 | −30.35 | 30.52 | 44.46 | |
| Cairclip NO2 (ppb) | 1 | 94.8 | −0.26 | −27.99 | 27.99 | 30.54 |
| 2 | 94.8 | −0.26 | −27.13 | 27.13 | 29.75 | |
| Cairclip O3 (ppb) | 1 | 94.8 | 0.68 | 11.13 | 13.31 | 15.03 |
| 2 | 94.8 | 0.68 | 9.94 | 12.47 | 14.16 | |
| Cairclip CO (ppm) | 1 | 94.8 | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | 94.8 | - | - | - | - | |
| Type of Sensor | Sensor ID | Fidas200 | RM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD 1 | Intra-Sensors Correl. | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD 1 | ||
| 1 | 2 | rS 2 | |||
| PMS7003 PM1 | 15.14 ± 12.37 | 13.38 ± 10.95 | 0.95 | 12.67 ± 10.26 | - 3 |
| PMS7003 PM2.5 | 22.14 ± 19.33 | 20.67 ± 17.17 | 0.96 | 14.63 ± 11.00 | 17.39 ± 12.21 |
| PMS7003 PM10 | 24.34 ± 21.92 | 22.56 ± 18.69 | 0.96 | 22.19 ± 14.76 | 24.46 ± 16.85 |
| OPC-N2 PM1 | 39.59 ± 43.72 | 43.95 ± 47.82 | 0.99 | 15.17 ± 12.53 | - 3 |
| OPC-N2 PM2.5 | 56.86 ± 72.36 | 67.87 ± 85.24 | 0.99 | 17.05 ± 13.72 | 17.93 ± 14.25 |
| OPC-N2 PM10 | 149.40 ± 536.43 | 196.00 ± 661.98 | 0.99 | 22.63 ± 17.39 | 25.14 ± 19.56 |
| Type of Sensor | Sensor ID | Presence 1 (%) | Correlation with Fidas200 1, RM 2 | Measurement Error | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rS 2 | rS 3 | MBE 4 | MAE 4 | RMSE 4 | MBE 5 | MAE 5 | RMSE 5 | |||
| PMS7003 PM1 | 1 | 93.3 | 0.88 | - | −2.70 | 4.08 | 6.86 | - | - | - |
| 2 | 94.9 | 0.91 | - | −1.08 | 3.24 | 4.74 | - | - | - | |
| PMS7003 PM2.5 | 1 | 94.8 | 0.87 | 0.63 | −7.94 | 8.92 | 13.53 | −4.93 | 10.61 | 14.99 |
| 2 | 93.0 | 0.90 | 0.66 | −6.08 | 7.13 | 10.58 | −3.07 | 9.10 | 12.56 | |
| PMS7003 PM10 | 1 | 95.9 | 0.70 | 0.62 | −2.51 | 11.05 | 15.93 | −0.31 | 12.05 | 16.63 |
| 2 | 95.9 | 0.73 | 0.63 | −0.82 | 9.70 | 13.82 | 1.39 | 11.01 | 15.16 | |
| OPC-N2 PM1 | 1 | 86.5 | 0.85 | - | −26.27 | 27.52 | 45.43 | - | - | - |
| 2 | 78.3 | 0.83 | - | −28.91 | 30.47 | 50.51 | - | - | - | |
| OPC-N2 PM2.5 | 1 | 86.5 | 0.83 | 0.66 | −43.27 | 44.59 | 81.71 | −42.68 | 46.07 | 84.58 |
| 2 | 78.3 | 0.81 | 0.63 | −51.38 | 52.97 | 97.64 | −50.79 | 54.30 | 100.52 | |
| OPC-N2 PM10 | 1 | 86.5 | 0.77 | 0.68 | −140.12 | 143.56 | 620.93 | −137.11 | 142.96 | 621.47 |
| 2 | 78.3 | 0.75 | 0.66 | −174.61 | 178.06 | 766.85 | −171.60 | 177.21 | 767.39 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bauerová, P.; Šindelářová, A.; Rychlík, Š.; Novák, Z.; Keder, J. Low-Cost Air Quality Sensors: One-Year Field Comparative Measurement of Different Gas Sensors and Particle Counters with Reference Monitors at Tušimice Observatory. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050492
Bauerová P, Šindelářová A, Rychlík Š, Novák Z, Keder J. Low-Cost Air Quality Sensors: One-Year Field Comparative Measurement of Different Gas Sensors and Particle Counters with Reference Monitors at Tušimice Observatory. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(5):492. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050492
Chicago/Turabian StyleBauerová, Petra, Adriana Šindelářová, Štěpán Rychlík, Zbyněk Novák, and Josef Keder. 2020. "Low-Cost Air Quality Sensors: One-Year Field Comparative Measurement of Different Gas Sensors and Particle Counters with Reference Monitors at Tušimice Observatory" Atmosphere 11, no. 5: 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050492
APA StyleBauerová, P., Šindelářová, A., Rychlík, Š., Novák, Z., & Keder, J. (2020). Low-Cost Air Quality Sensors: One-Year Field Comparative Measurement of Different Gas Sensors and Particle Counters with Reference Monitors at Tušimice Observatory. Atmosphere, 11(5), 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050492





