Sniffin’ Sticks and Olfactometer-Based Odor Thresholds for n-Butanol: Correspondence and Validity for Indoor Air Scenarios
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Participants
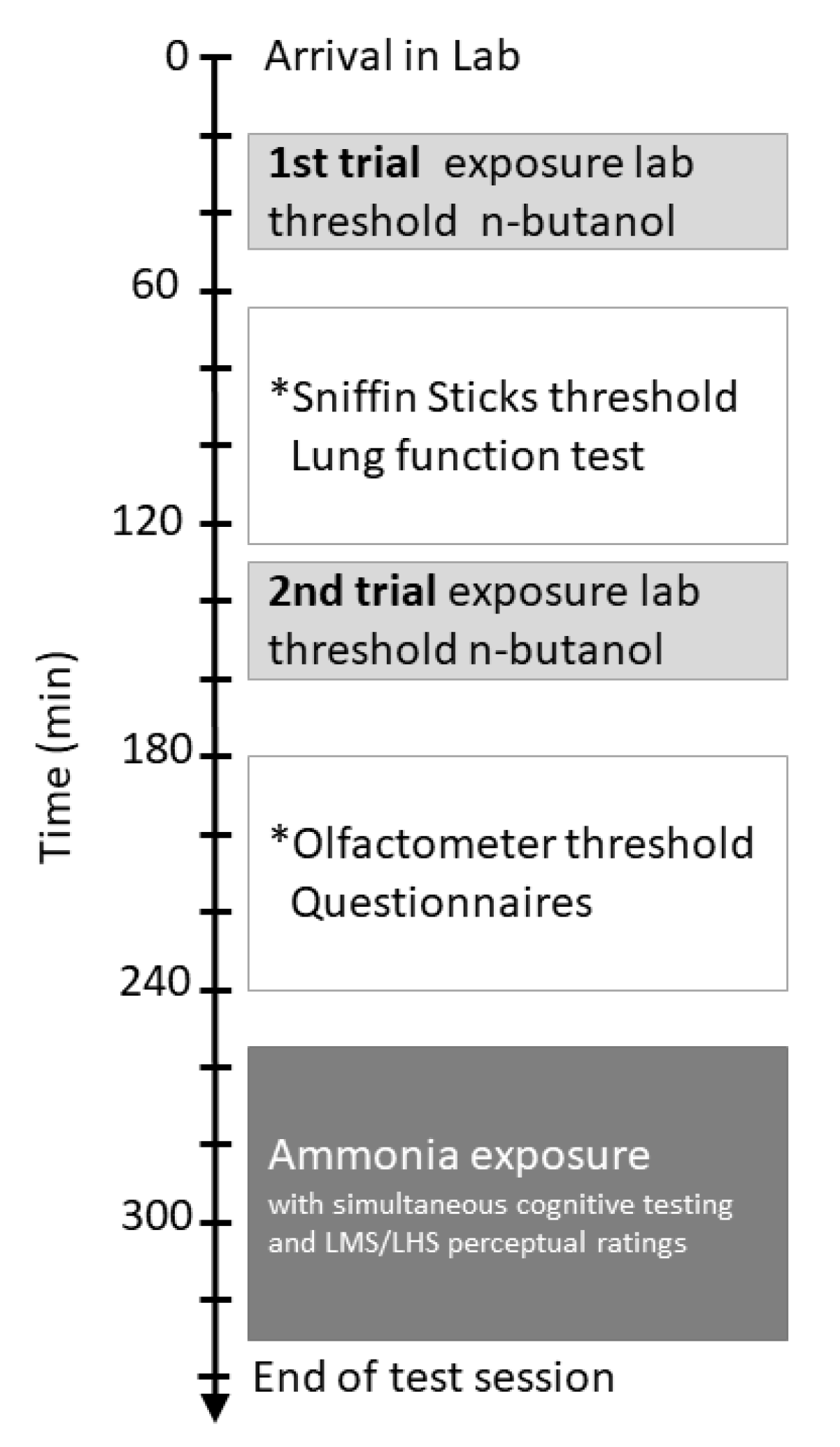
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Materials
2.3.1. Sniffin’ Sticks-Based Threshold for n-Butanol
2.3.2. Olfactometer-Based Threshold for n-Butanol
2.3.3. Exposure Lab-Based Threshold for n-Butanol
2.3.4. Experimental Ammonia Exposure
2.3.5. Air Monitoring in the Exposure Lab
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Results of the Psychometric Threshold Assessments
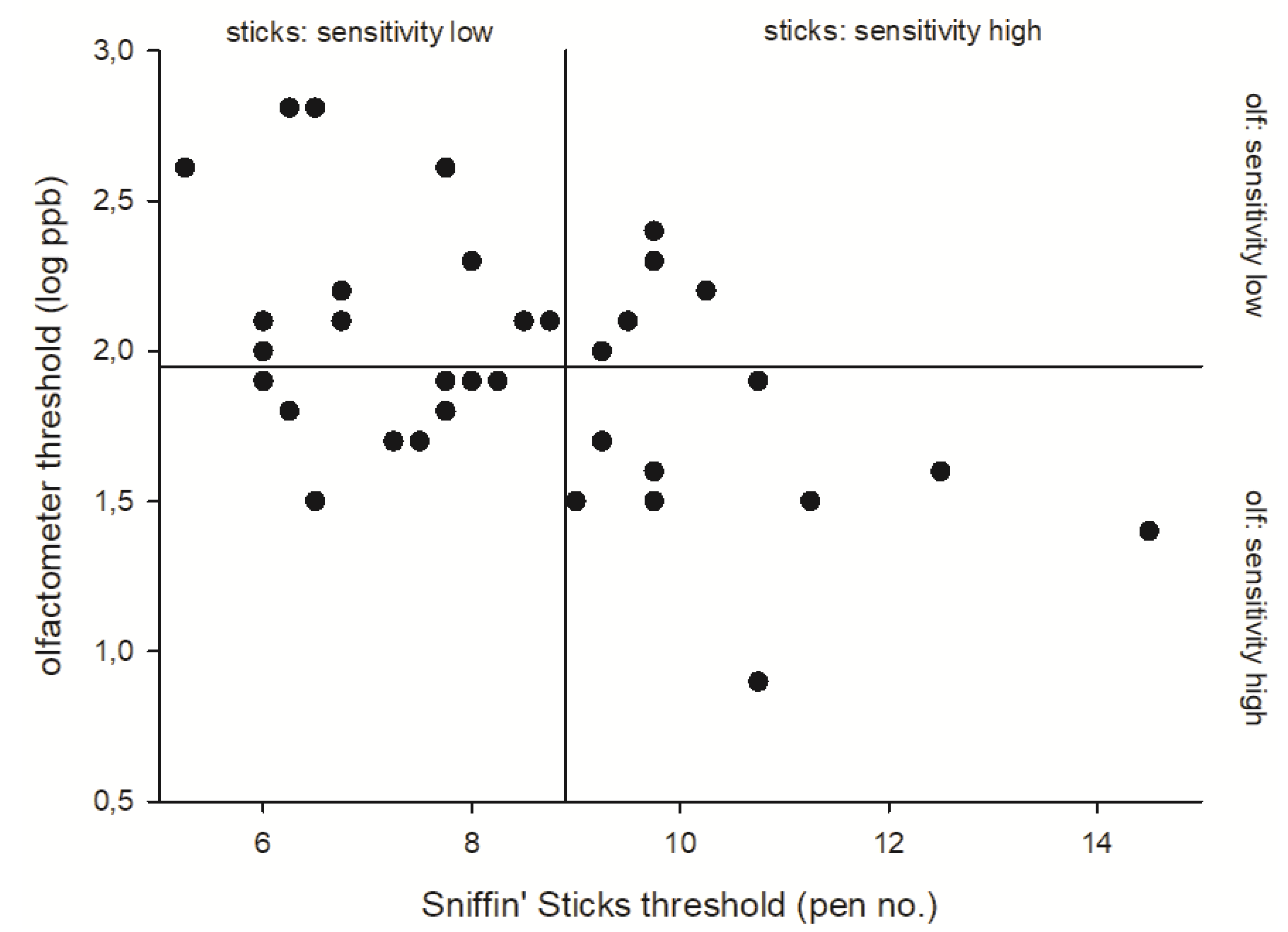
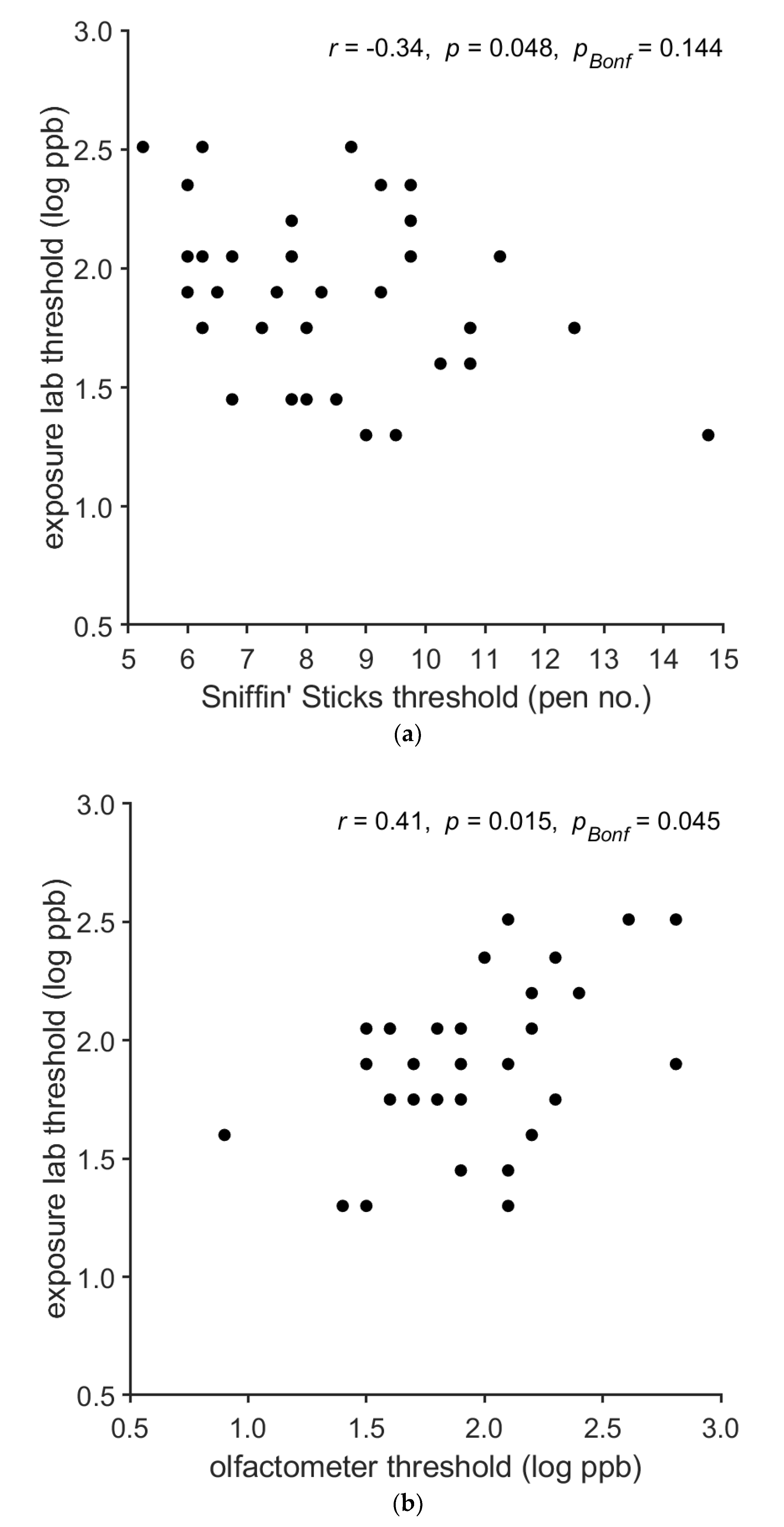
3.2. Results of the between-Method Correlations for n-Butanol Thresholds
3.3. Results of the Modulation of Odor Effects by n-Butanol Thresholds
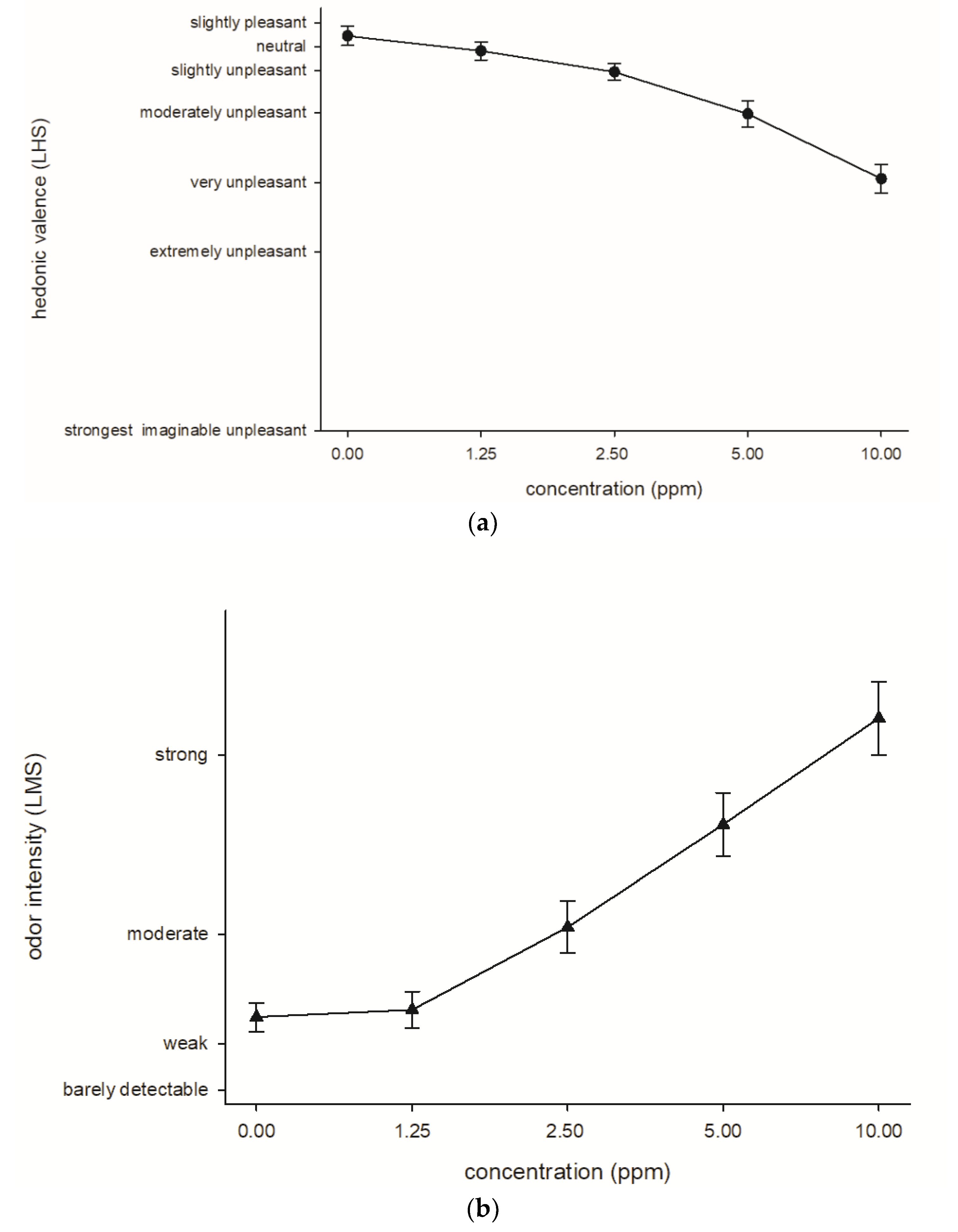
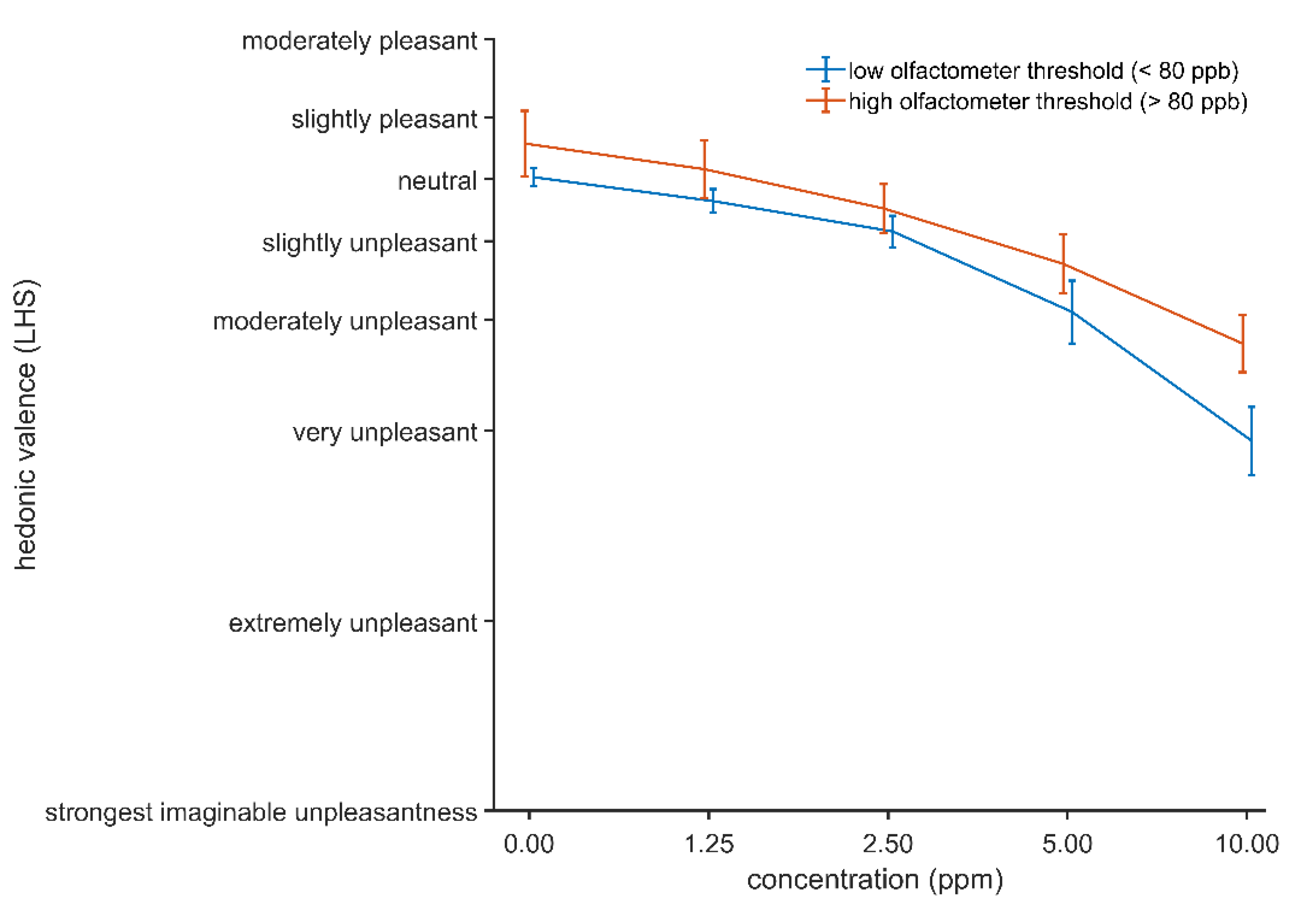
3.3.1. Chemosensory Perceptions
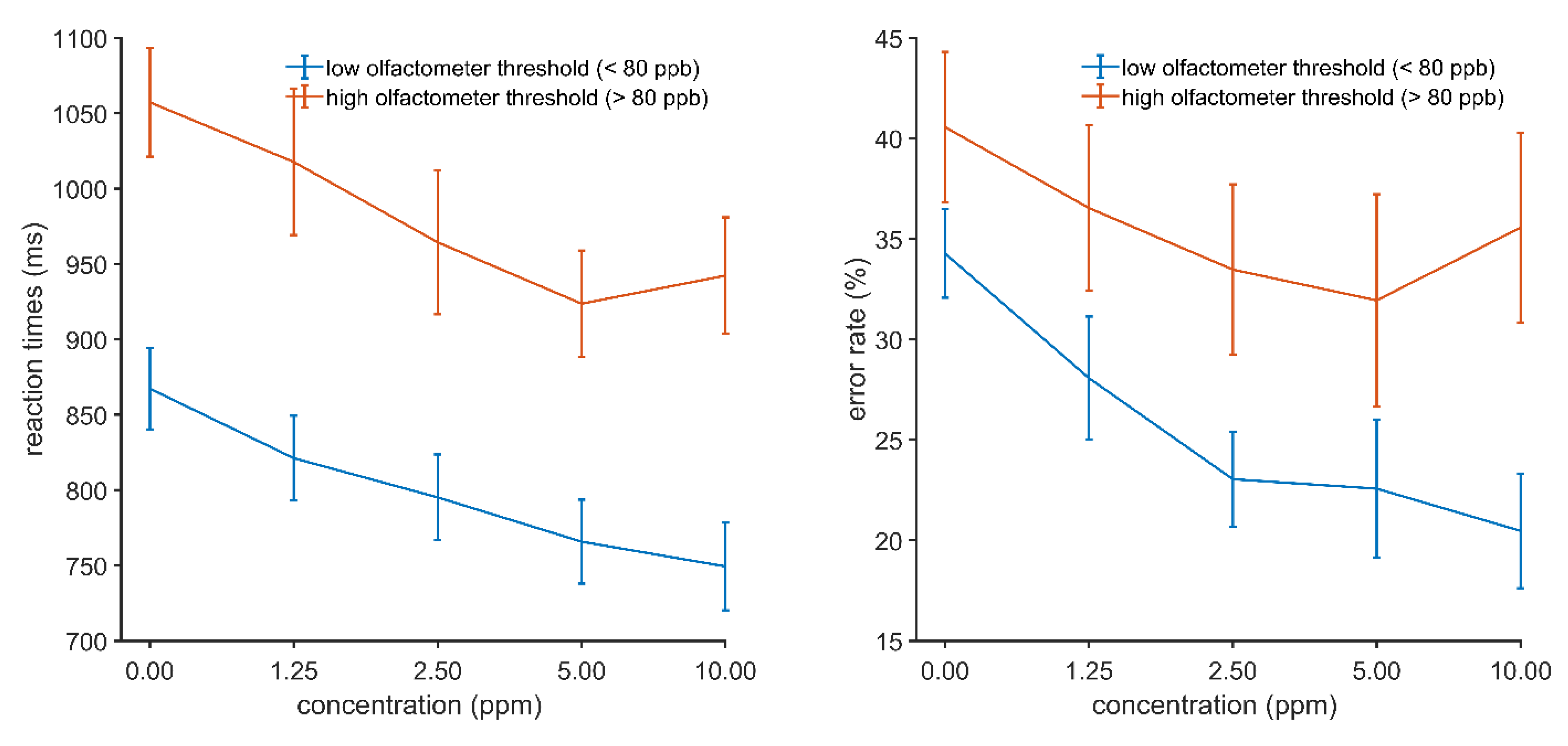
3.3.2. Odor Effects on Behavioral Task Performance
4. Discussion
5. Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hummel, T.; Kobal, G.; Gudziol, H.; Mackay-Sim, A. Normative data for the “Sniffin’ Sticks” including tests of odor identification, odor discrimination, and olfactory thresholds: An upgrade based on a group of more than 3000 subjects. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2007, 264, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannebeck, D. Olfactometers according to EN 13725. In Springer Handbook of Odor; Buettner, A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 545–552. [Google Scholar]
- Bekanntmachung des Umweltbundesamtes. Richtwerte für 1-Butanol in der Innenraumluft. Bundesgesundh. Gesundh. Gesundh. 2014, 57, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barczak, R.; Sowka, I.; Nych, A.; Sketowicz, M.; Zwozdiak, P. Application of the standard sniffin’ sticks method to the determination odor inspectors’ olfactory sensitivity in Poland. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2010, 23, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feilberg, A.; Hansen, M.J.; Pontoppidan, O.; Oxbol, A.; Jonassen, K. Relevance of n-butanol as a reference gas for odorants and complex odors. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 1751–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummel, T.; Sekinger, B.; Wolf, S.R.; Pauli, E.; Kobal, G. ‘Sniffin’ sticks’: Olfactory performance assessed by the combined testing of odor identification, odor discrimination and olfactory threshold. Chem. Senses 1997, 22, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DIN EN 13725. Air Quality—Determination of Odour Concentration by Dynamic Olfactometry; German Version Beuth: Berlin, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucker, K.; Both, R.; Bischoff, M.; Guski, R.; Winneke, G. Odor frequency and odor annoyance. Part I: Assessment of frequency, intensity and hedonic tone of environmental odors in the field. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2008, 81, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.E.; Jinks, A.L.; Stevenson, R.J. A comparison of sniff bottle staircase and olfactometer-based threshold tests. Behav. Res. Methods 2013, 45, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärnekull, S.C.; Jonsson, F.U.; Larsson, M.; Olofsson, J.K. Affected by smells? Environmental chemical responsivity predicts odor perception. Chem. Senses 2011, 36, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacharra, M.; Schäper, M.; Kleinbeck, S.; Blaszkewicz, M.; van Thriel, C. Olfactory acuity and automatic associations to odor words modulate adverse effects of ammonia. Chem. Percept 2016, 9, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacharra, M.; Kleinbeck, S.; Schäper, M.; Blaszkewicz, M.; van Thriel, C. Multidimensional assessment of self-reported chemical intolerance and its impact on chemosensory effects during ammonia exposure. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2016, 89, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacharra, M.; Schäper, M.; Kleinbeck, S.; Blaszkewicz, M.; Wolf, O.T.; van Thriel, C. Stress lowers the detection threshold for foul-smelling 2-mercaptoethanol. Stress 2015, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.G. Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, J.; Anzinger, A.; Kopietz, R.; Schopf, V.; Kleemann, A.M.; Pollatos, O.; Wiesmann, M. Test-retest reliability of the olfactory detection threshold test of the Sniffin’ sticks. Chem. Senses 2008, 33, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haehner, A.; Mayer, A.M.; Landis, B.N.; Pournaras, I.; Lill, K.; Gudziol, V.; Hummel, T. High test-retest reliability of the extended version of the “Sniffin’ Sticks” test. Chem. Senses 2009, 34, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmerich, W. StatistikGuru: Poweranalyse für Korrelationen. Available online: https://statistikguru.de/rechner/poweranalyse-korrelation.html (accessed on 25 April 2020).
- Nordin, S.; Millqvist, E.; Löwhagen, O.; Bende, M. A short Chemical Sensitivity Scale for assessment of airway sensory hyperreactivity. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2004, 77, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, D.; Clark, L.A.; Tellegen, A. Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: The PANAS scales. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1988, 54, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GOLD Guidelines. Diagnosis of Disease of Chronic Airway Limitation: Asthma, COPD and Asthma-COPD Overlap Syndrome (ACOS). Available online: http://goldcopd.org/asthma-copd-asthma-copd-overlap-syndrome (accessed on 26 March 2020).
- Kirchner, W.K. Age differences in short-term retention of rapidly changing information. J. Exp. Psychol. 1958, 55, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonnell, L.; Falkenstein, M. Does the error negativity reflect the degree of response conflict? Brain Res. 2006, 1095, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, B.A.; Dalton, P.; Cowart, B.; Shaffer, G.; Rankin, K.; Higgins, J. Evaluating the ‘Labeled Magnitude Scale’ for measuring sensations of taste and smell. Chem. Senses 1996, 21, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Wood, A.; Green, B.G. Derivation and evaluation of a labeled hedonic scale. Chem. Senses 2009, 34, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normative Data for the Sniffin’ Sticks (University Hospital Carl Gustav Carus Dresden). Available online: https://www.uniklinikum-dresden.de/de/das-klinikum/kliniken-polikliniken-institute/hno/forschung/interdisziplinaeres-zentrum-fuer-riechen-und-schmecken/downloads/SDI_Normwerte_2015.pdf (accessed on 6 May 2020).
- Oleszkiewicz, A.; Schriever, V.A.; Croy, I.; Hahner, A.; Hummel, T. Updated Sniffin’ Sticks normative data based on an extended sample of 9139 subjects. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 276, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinbeck, S.; Schäper, M.; Juran, S.A.; Kiesswetter, E.; Blaszkewicz, M.; Golka, K.; Zimmermann, A.; Brüning, T.; van Thriel, C. Odor Thresholds and breathing changes of human volunteers as consequences of sulphur dioxide exposure considering individual factors. Saf. Health Work 2011, 2, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeets, M.A.; Bulsing, P.J.; van Rooden, S.; Steinmann, R.; de Ru, J.A.; Ogink, N.W.; van Thriel, C.; Dalton, P.H. Odor and irritation thresholds for ammonia: A comparison between static and dynamic olfactometry. Chem. Senses 2007, 32, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacharra, M.; Kleinbeck, S.; Schäper, M.; Juran, S.A.; Hey, K.; Blaszkewicz, M.; Lehmann, M.L.; Golka, K.; van Thriel, C. Interindividual differences in chemosensory perception: Toward a better understanding of perceptual ratings during chemical exposures. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2016, 79, 1026–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG). List of MAK and BAT Values; WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIST/SEMATECH e-Handbook of Statistical Methods. Available online: https://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/prc/section1/prc16.htm (accessed on 6 May 2020).
- Hedner, M.; Larsson, M.; Arnold, N.; Zucco, G.M.; Hummel, T. Cognitive factors in odor detection, odor discrimination, and odor identification tasks. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2010, 32, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bax, C.; Sironi, S.; Capelli, L. How can odors be measured? An overview of methods and their applications. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, P.; Uliaque, B.; Canellas, E.; Escudero, A.; Nerin, C. Identification and quantification of odorous compounds from adhesives used in food packaging materials by headspace solid phase extraction and headspace solid phase microextraction coupled to gas chromatography-olfactometry-mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 745, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.; Ringsdorf, A. Human odour thresholds are tuned to atmospheric chemical lifetimes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond B Biol. Sci. 2020, 375, 20190274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cometto-Muniz, J.E.; Cain, W.S. Nasal pungency, odor, and eye irritation thresholds for homologous acetates. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1991, 39, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, W.S.; Lee, N.S.; Wise, P.M.; Schmidt, R.; Ahn, B.H.; Cometto-Muniz, J.E.; Abraham, M.H. Chemesthesis from volatile organic compounds: Psychophysical and neural responses. Physiol. Behav. 2006, 88, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Thriel, C.; Schäper, M.; Kiesswetter, E.; Kleinbeck, S.; Juran, S.; Blaszkewicz, M.; Fricke, H.H.; Altmann, L.; Berresheim, H.; Brüning, T. From chemosensory thresholds to whole body exposures-experimental approaches evaluating chemosensory effects of chemicals. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2006, 79, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, Y. Measurement of odor threshold by triangle odor bag method. Odor Meas. Rev. 2003, 118, 118–127. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, R.M.; Luk, C.-H.; Flinker, A.; Aggarwal, A.; Lapid, H.; Haddad, R.; Sobel, N. Predicting odor pleasantness from odorant structure: Pleasantness as a reflection of the physical world. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 10015–10023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN EN 13725. Stationary Source Emissions—Determination of Odour Concentration by Dynamic Olfactometry and Odour Emission Rate from Stationary Sources, German and English version prEN 13725:2019; Beuth: Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Thriel, C.; Kiesswetter, E.; Schäper, M.; Blaszkewicz, M.; Golka, K.; Juran, S.; Kleinbeck, S.; Seeber, A. From neurotoxic to chemosensory effects: New insights on acute solvent neurotoxicity exemplified by acute effects of 2-ethylhexanol. Neurotoxicology 2007, 28, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Subject Characteristics | Total Sample |
|---|---|
| Men/Women (n) | 12/23 |
| Age (mean (SD)) | 23.8 (3.1) |
| CSS-SHR (mean (SEM)) | 31.8 (1.3) |
| Negative affectivity (mean (SEM)) | 14.0 (0.7) |
| FEV1 (mean (min-max)) | 96.4% (84.8–111.1%) |
| Subject Characteristics | Total Sample | Sniffin’ Sticks Threshold | Olfactometer Threshold | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <9 | ≥9 | >80 ppb | ≤80 ppb | ||
| Men/Women (n) | 12/23 | 7/14 | 5/9 | 6/10 | 6/13 |
| Sniffin’ Sticks T No. pen (median (IQR)) | 8.0 (6.5–9.8) | 6.8 (6.3–8.0) | 9.8 * (9.3–10.8) | 8.0 (6.5–9.1) | 8.3 (7.3–10.8) |
| Olfactometer T ppb (median (IQR)) | 80 (50–160) | 101 (64–160) | 45.2 * (32–127) | 160 (127–228) | 50.4 * (32–80) |
| Exposure lab T ppb (median (IQR)) | 80 (40–113) | 80 (57–113) | 68.3 (40–113) | 136.6 (48–226) | 80 (40–113) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pacharra, M.; Kleinbeck, S.; Schäper, M.; Hucke, C.I.; van Thriel, C. Sniffin’ Sticks and Olfactometer-Based Odor Thresholds for n-Butanol: Correspondence and Validity for Indoor Air Scenarios. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050472
Pacharra M, Kleinbeck S, Schäper M, Hucke CI, van Thriel C. Sniffin’ Sticks and Olfactometer-Based Odor Thresholds for n-Butanol: Correspondence and Validity for Indoor Air Scenarios. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(5):472. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050472
Chicago/Turabian StylePacharra, Marlene, Stefan Kleinbeck, Michael Schäper, Christine I. Hucke, and Christoph van Thriel. 2020. "Sniffin’ Sticks and Olfactometer-Based Odor Thresholds for n-Butanol: Correspondence and Validity for Indoor Air Scenarios" Atmosphere 11, no. 5: 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050472
APA StylePacharra, M., Kleinbeck, S., Schäper, M., Hucke, C. I., & van Thriel, C. (2020). Sniffin’ Sticks and Olfactometer-Based Odor Thresholds for n-Butanol: Correspondence and Validity for Indoor Air Scenarios. Atmosphere, 11(5), 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050472





