Directional Extreme Value Models in Wave Energy Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Directional Extreme Value Model
2.1. Parameter Estimation
2.2. Design Values for Directional Extreme model
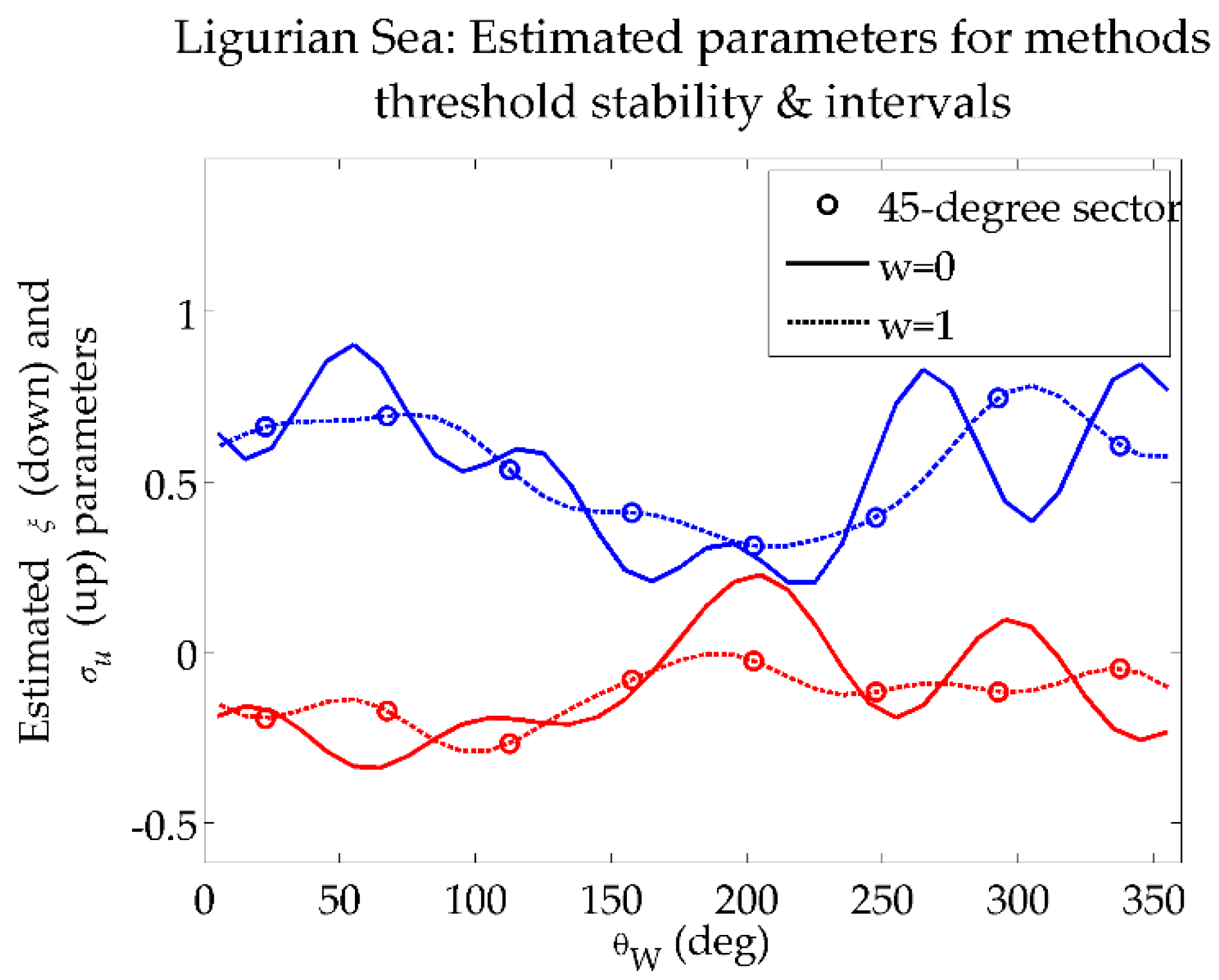
2.3. Methods for Threshold Selection
2.3.1. Mean Excess Plot
2.3.2. Threshold Stability Plot
2.3.3. Percentiles
2.4. Methods for Declustering
- Define clusters of observations in case of consecutive exceedances based on an empirical criterion or parametric models (e.g., Markov chain models, Bartlett-Lewis process).
- Identify the highest value in each cluster, called declustered peaks.
- Assume the declustered peaks are independent and fit GP distribution to these peaks.
2.4.1. Runs Declustering Method
2.4.2. Intervals Declustering Method
2.4.3. Declustering Algorithm (DeCA)
3. Uncertainty Quantification
- Step 1: Estimate the unknown parameters of the GP distribution (as functions of ) from the initial sample using the ML method described above.
- Step 2: Create (random) samples , , by random resampling with replacement from the initial sample and obtain the estimates .
- Step 3: Repeat step 2 for a large number . The minimum number of bootstrap sample for the calculation of reliable confidence intervals is 1000, as is suggested by various studies that address modelling of extremes of environmental parameters; see, for example, Kysely [76], Panagoulia, et al. [77] and Soukissian and Tsalis [78].
- Step 4: Estimate the two constants of BCA bootstrap method, and for each unknown parameter. Then estimate the lower and upper limits , and , , respectively.
4. Description of Wave Data
5. Numerical Results
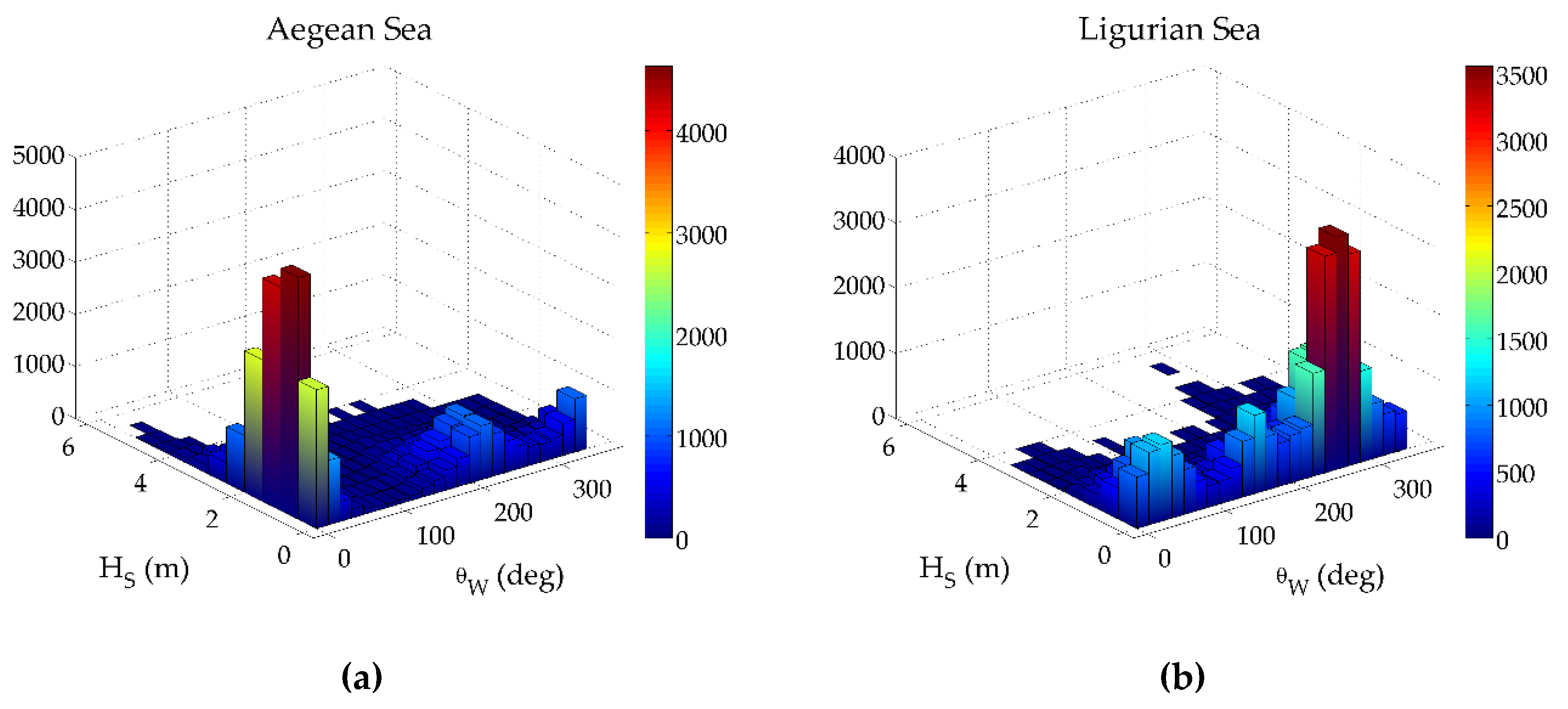
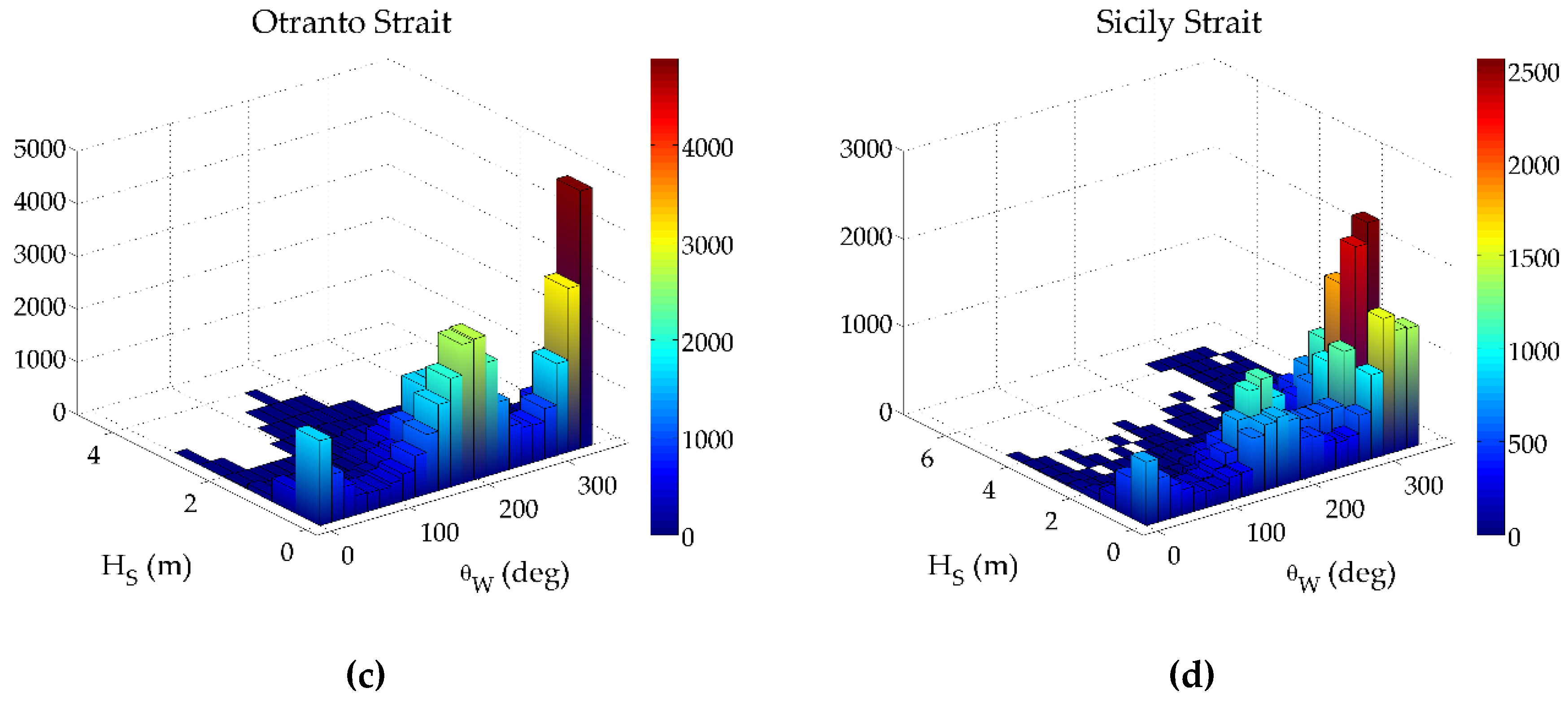
5.1. Preliminary Results
5.2. Final Results
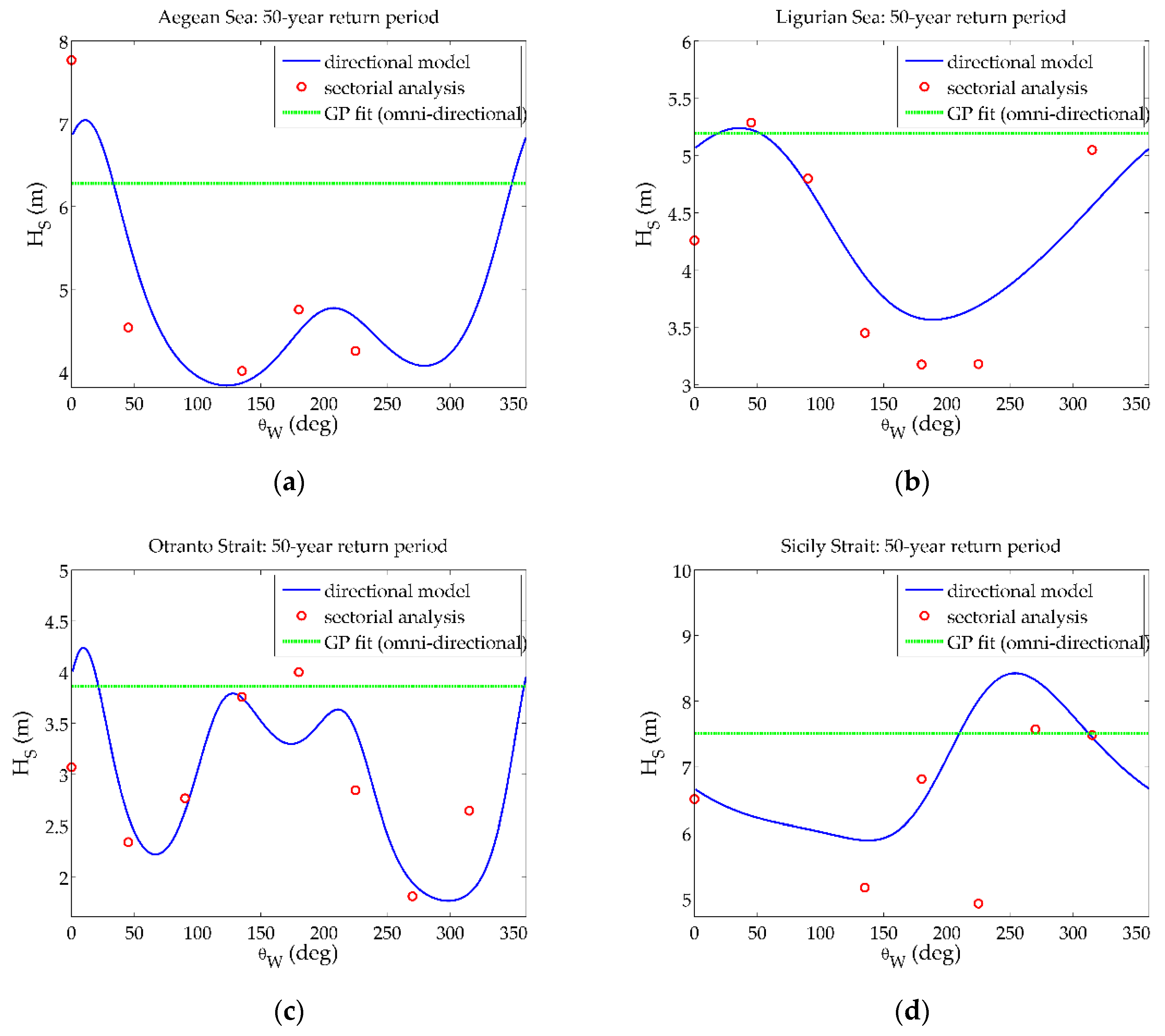
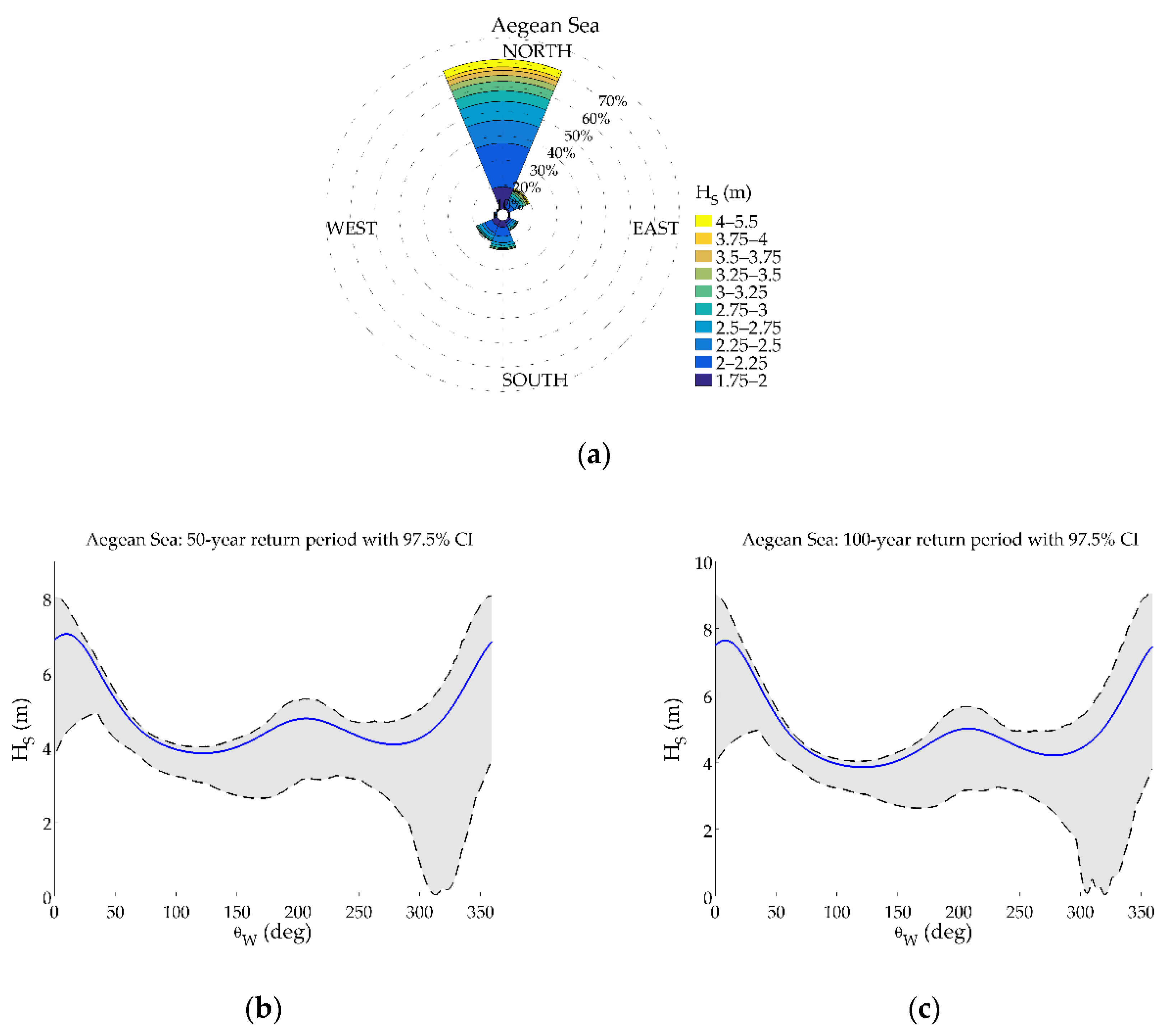
- For Aegean Sea, the dominant sector for extreme wave heights is the northern one, probably attributed to the Etesian winds, which gives extreme values up to 7 m at this sector and lower values characterize the rest directional sectors (e.g., for the sector the value is 4.3 m in the mean) as regards the 50-year return period. Furthermore, the low values of the lower bound of the 97.5% confidence intervals in the north-western sector can be justified by the lack of data obtained from the implementation of the specific combination of methods.
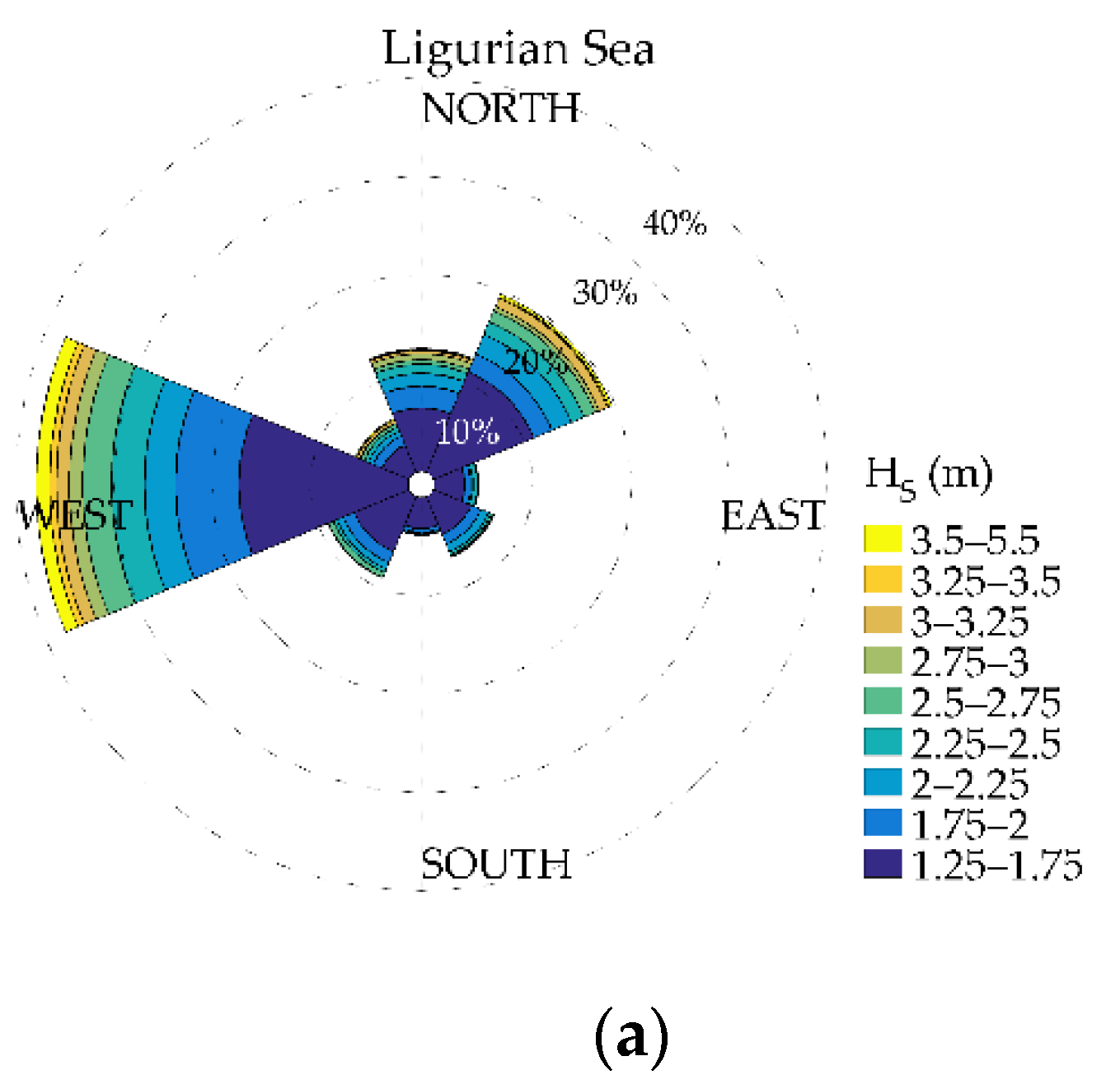
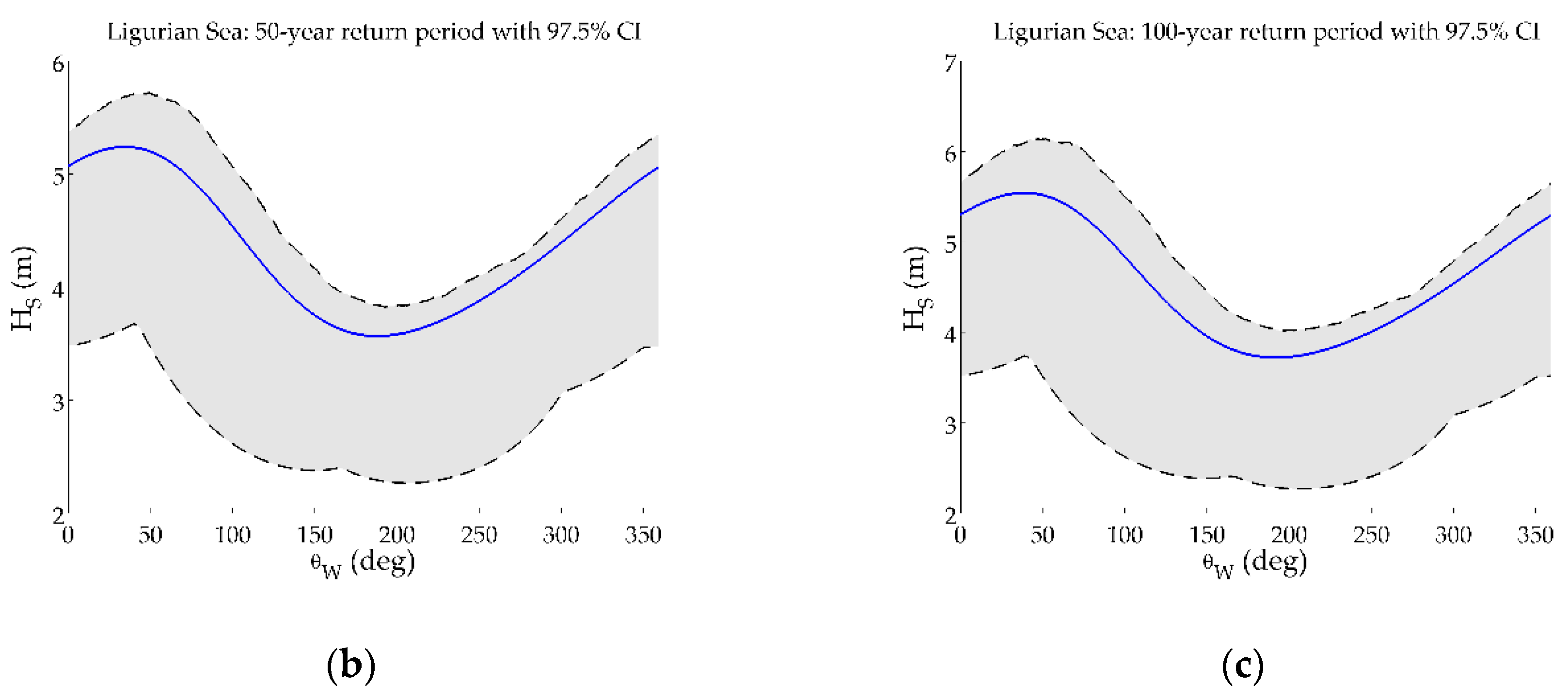
- For Ligurian Sea, the north-eastern sector is characterized by high values of (5.4 m for the 50-year return period), even though it is the second dominant directional sector for , while the southern sector, with the least amount of extreme data, provides the lowest values (3.6 m).
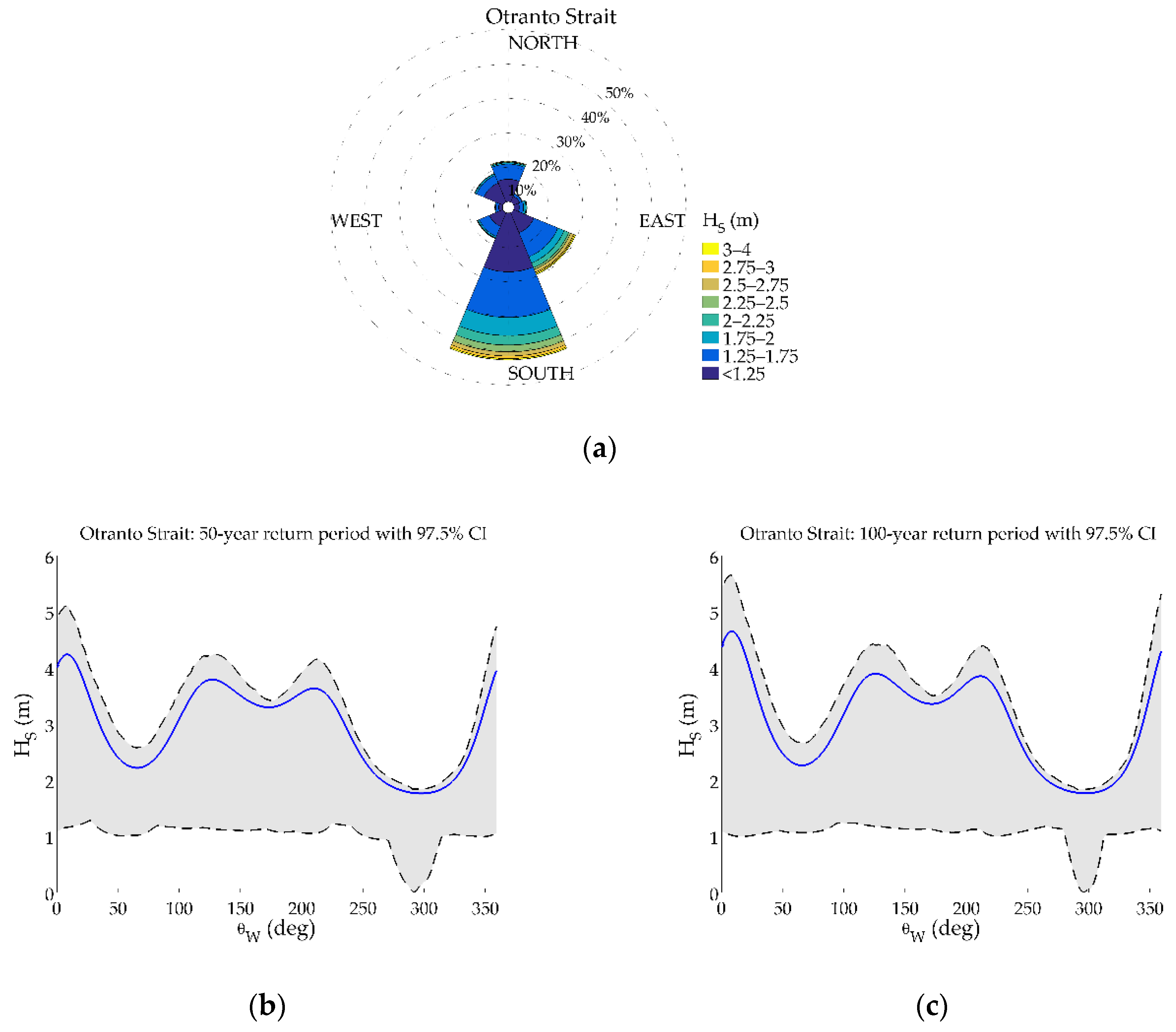
- For Otranto Strait, the two dominant wave directions (in the south and south-eastern sectors) are translated in two consecutive peaks in the design value graphs, while the two concave forms (in the north-eastern and western sectors) correspond to the sectors with the minimum amount of extreme data. Let note that the form of the lower bounds differs from the design value.
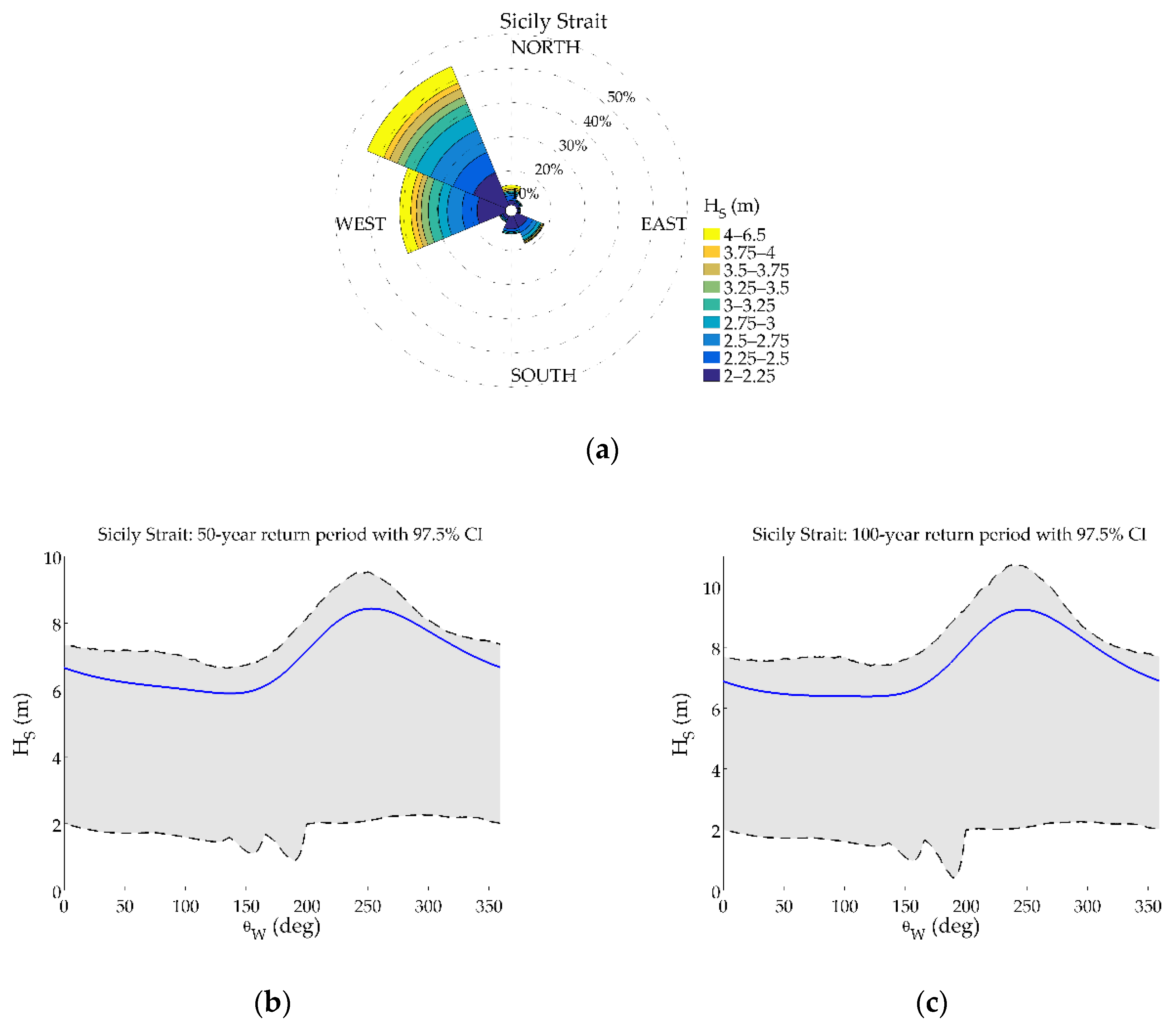
- For Sicily Strait, the location with the most intense sea states according to the analyzed hindcast wave data, the second dominant directional sector for (i.e., the western) is characterized by the highest design values (8.4 m for the 50-year return period) and the lowest values are observed for the south-eastern sector (5.9 m for the 50-year return period). The largest difference between the lower bounds of the confidence interval and the design value is close to 6.3 m for the 50-year return period encountered in the south-western sector.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naess, A. Statistical extrapolation of extreme value data based on the peaks over threshold method. J. Offshore Mech. Arct. 1998, 120, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caires, S.; Sterl, A. 100-year return value estimates for ocean wind speed and significant wave height from the ERA-40 data. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 1032–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukissian, T.H.; Kalantzi, G. Extreme value analysis methods used for wave prediction. In Proceedings of the 16th International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 28 May–2 June 2006; pp. 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Caires, S. A Comparative Simulation Study of the Annual Maxima and the Peaks-over-Threshold Methods; Technical report, SBW-Belastingen: Subproject “Statistics”. Deltares Report 1200264-002; Deltares: Delft, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.J. The POT Model Described by the Generalized Pareto Distribution with Poisson Arrival Rate. J. Hydrol. 1991, 129, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, S. An Introduction to Statistical Modeling of Extreme Values, 1st ed.; Springer: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leadbetter, M.R.; Lindgren, G.; Rootzen, H. Extremes and Related Properties of Random Sequences and Processes, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Balkema, A.A.; de Haan, L. Residual Life Time at Great Age. Ann. Probab. 1974, 2, 792–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickands, J. Statistical inference using extreme order statistics. Ann. Stat. 1975, 3, 119–131. [Google Scholar]
- Vanmontfort, M.A.J.; Witter, J.V. Testing Exponentiality against Generalized Pareto Distribution. J. Hydrol. 1985, 78, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosbjerg, D.; Madsen, H.; Rasmussen, P.F. Prediction in Partial Duration Series with Generalized Pareto-distributed Exceedances. Water Resour. Res. 1992, 28, 3001–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, R.M.; Mcmahon, T.A.; Chiew, F.H.S. Floodflow Frequency Model Selection in Australia. J. Hydrol. 1993, 146, 421–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, R.W.; Parlange, M.B.; Naveau, P. Statistics of extremes in hydrology. Adv. Water Resour. 2002, 25, 1287–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prudhomme, C.; Jakob, D.; Svensson, C. Uncertainty and climate change impact on the flood regime of small UK catchments. J. Hydrol. 2003, 277, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimshaw, S.D. Computing Maximum-Likelihood-Estimates for the Generalized Pareto Distribution. Technometrics 1993, 35, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosking, J.R.M.; Wallis, J.R. Parameter and Quantile Estimation for the Generalized Pareto Distribution. Technometrics 1987, 29, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, J.A.; Landwehr, J.M.; Matalas, N.C.; Wallis, J.R. Probability Weighted Moments - Definition and Relation to Parameters of Several Distributions Expressable in Inverse Form. Water Resour. Res. 1979, 15, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharram, S.H.; Gosain, A.K.; Kapoor, P.N. A Comparative-Study for the Estimators of the Generalized Pareto Distribution. J. Hydrol. 1993, 150, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, E.; Hadi, A.S. Fitting the generalized Pareto distribution to data. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1997, 92, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, M.E.; Cabras, S. A default Bayesian procedure for the generalized Pareto distribution. J. Stat. Plan. Infer. 2007, 137, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudez, P.D.; Kotz, S. Parameter estimation of the generalized Pareto distribution-Part II. J. Stat. Plan. Infer. 2010, 140, 1374–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarrott, C.; MacDonald, A. A Review of Extreme Value Threshold Estimation and Uncertainty Quantification. Revstat.-Stat. J. 2012, 10, 33–60. [Google Scholar]
- Langousis, A.; Mamalakis, A.; Puliga, M.; Deidda, R. Threshold detection for the generalized Pareto distribution: Review of representative methods and application to the NOAA NCDC daily rainfall database. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 2659–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drees, H.; de Haan, L.; Resnick, S.I. How to make a Hill plot. Ann. Statist. 2000, 28, 254–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choulakian, V.; Stephens, M.A. Goodness-of-fit tests for the generalized Pareto distribution. Technometrics 2001, 43, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northrop, P.J.; Coleman, C.L. Improved threshold diagnostic plots for extreme value analyses. Extremes 2014, 17, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABS. Guide for Load and Resistance Factor Design (LRFD) Criteria for Offshore Structures; American Bureau of Shipping: Houston, TX, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- DNV. Recommended Practice DNV-RP-C205: Environmental Conditions and Environmental Loads; Det Norske Veritas AS: Oslo, Norway, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Soukissian, T.H. Probabilistic modeling of directional and linear characteristics of wind and sea states. Ocean. Eng. 2014, 91, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Arwade, S.R.; Myers, A.T.; Valamanesh, V.; Pang, W.C. Effect of wind and wave directionality on the structural performance of non-operational offshore wind turbines supported by jackets during hurricanes. Wind Energy 2017, 20, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukissian, T.H.; Karathanasi, F.E. On the selection of bivariate parametric models for wind data. Appl. Energy 2017, 188, 280–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriarty, W.W.; Templeton, J.I. On the Estimation of Extreme Wind Gusts by Direction Sector. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1983, 13, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, S.G.; Walshaw, D. Directional Modeling of Extreme Wind Speeds. J. R. Stat. Soc. C-App. 1994, 43, 139–157. [Google Scholar]
- Simiu, E.; Hendrickson, E.M.; Nolan, W.A.; Olkin, I.; Spiegelman, C.H. Multivariate Distributions of Directional Wind Speeds. J. Struct. Eng.-Asce 1985, 111, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solari, S.; Losada, M.A. Simulation of non-stationary wind speed and direction time series. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2016, 149, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folgueras, P.; Solari, S.; Losada, M.A. The selection of directional sectors for the analysis of extreme wind speed. Nat. Hazard. Earth Sys. 2019, 19, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.E.; Tawn, J.A. Statistics for extreme sea currents. J. R. Stat. Soc. C-App. 1997, 46, 183–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewans, K.C.; Jonathan, P. The effect of directionality on extreme wave design criteria. In Proceedings of the 9th International Workshop on Wave Hindcasting and Forecasting, Victoria, BC, Canada, 24–29 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ewans, K.; Jonathan, P. The effect of directionality on Northern North Sea extreme wave design criteria. J. Offshore Mech. Arct. Eng. 2008, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonathan, P.; Ewans, K. The effect of directionality on extreme wave design criteria. Ocean. Eng. 2007, 34, 1977–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonathan, P.; Ewans, K.; Forristall, G. Statistical estimation of extreme ocean environments: The requirement for modelling directionality and other covariate effects. Ocean. Eng. 2008, 35, 1211–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forristall, G.Z. On the use of directional wave criteria. J. Waterw. Port. Coast. 2004, 130, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukissian, T.H.; Kalantzi, G.D. A new method for applying r-Largest maxima model for design sea-state prediction. Int. J. Offshore Polar 2009, 19, 176–182. [Google Scholar]
- Reiss, R.-D.; Thomas, M. Statistical Analysis of Extreme Ealues, with Application to Insurance, Finance, Hydrology and Other Fields, 3rd ed.; Birkhäuser Verlag: Basel, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Davison, A.C.; Smith, R.L. Models for Exceedances over High Thresholds. J. R. Stat. Soc. B Met. 1990, 52, 393–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, W.; Weller, J. Mean residual life. In Statistics and Related Topics; Csorgo, M., Dawson, D.A., Rao, J.N.K., Saleh, A.K.M.E., Eds.; Norrh-Holland Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1981; pp. 169–184. [Google Scholar]
- Hogg, R.V.; Klugman, S.A. Loss Distributions; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Begueria, S. Uncertainties in partial duration series modelling of extremes related to the choice of the threshold value. J. Hydrol. 2005, 303, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Arcilla, A.; Aguar, J.G.; Egozcue, J.J.; Ortego, M.I.; Galiatsatou, P.; Prinos, P. Extremes from scarce data: The role of Bayesian and scaling techniques in reducing uncertainty. J. Hydraul. Res. 2008, 46, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumouchel, W.H. Estimating the stable index-alpha in order to measure tail thickness - a critique. Ann. Stat. 1983, 11, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastoe, E.F.; Tawn, J.A. Modelling the distribution of the cluster maxima of exceedances of subasymptotic thresholds. Biometrika 2012, 99, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabemann, I.; Weisse, R. Climate change impact on extreme wave conditions in the North Sea: An ensemble study. Ocean. Dynam. 2008, 58, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arns, A.; Wahl, T.; Haigh, I.D.; Jensen, J.; Pattiaratchi, C. Estimating extreme water level probabilities: A comparison of the direct methods and recommendations for best practise. Coast. Eng. 2013, 81, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo-Posada, P.J.; Eagleson, P.S. Identification of Independent Rainstorms. J. Hydrol. 1982, 55, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, M. Coastal Storim Definition. In Coastal Storms: Processes and Impacts; Ciavola, P., Coco, G., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2017; p. 288. [Google Scholar]
- Davenport, A.G. Note on the distribution of the largest value of a random function with application to gust loading. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. 1964, 28, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.L.; Weissman, I. Estimating the extremal index. J. R. Stat. Soc. B Met. 1994, 56, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, I.D.; Bowers, J.; Mould, G. Estimating return period wave heights and wind speeds using a seasonal point process model. Coast. Eng. 1997, 31, 305–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawcett, L.; Walshaw, D. Improved estimation for temporally clustered extremes. Environmetrics 2007, 18, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapelonis, Z.G.; Gavriliadis, P.N.; Athanassoulis, G.A. Extreme value analysis of dynamical wave climate projections in the Mediterranean Sea. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 66, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerma, A.N.; Bulteau, T.; Lecacheux, S.; Idier, D. Spatial variability of extreme wave height along the Atlantic and channel French coast. Ocean. Eng. 2015, 97, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samayam, S.; Laface, V.; Annamalaisamy, S.S.; Arena, F.; Vallam, S.; Gavrilovich, P.V. Assessment of reliability of extreme wave height prediction models. Nat. Hazard. Earth Sys. 2017, 17, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, V.M.; Haigh, I.D.; Wahl, T. Spatial and temporal clustering analysis of extreme wave events around the UK coastline. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, C.A.T.; Segers, J. Inference for clusters of extreme values. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 2003, 65, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M. Heuristic tools for the estimation of the extremal index: A comparison of methods. Revstat.-Stat. J. 2018, 16, 115–136. [Google Scholar]
- Moloney, N.R.; Faranda, D.; Sato, Y. An overview of the extremal index. Chaos 2019, 29, 022101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acero, F.J.; Garcia, J.A.; Gallego, M.C. Peaks-over-threshold study of trends in extreme rainfall over the Iberian Peninsula. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 1089–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebrian, A.C.; Abaurrea, J. Drought analysis based on a marked cluster Poisson model. J. Hydrometeorol. 2006, 7, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della-Marta, P.M.; Mathis, H.; Frei, C.; Liniger, M.A.; Kleinn, J.; Appenzeller, C. The return period of wind storms over Europe. Int. J. Climatol. 2009, 29, 437–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukissian, T.H.; Arapi, P.M. The effect of declustering in the r-largest maxima model for the estimation of Hs -design values. Open Ocean. Eng. J. 2011, 4, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, B. Bootstrap methods - another look at the jackknife. Ann. Stat. 1979, 7, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajvidi, N. Confidence intervals and accuracy estimation for heavy-tailed Generalized Pareto distributions. Extremes 2003, 6, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, S.; Simiu, E. Estimating uncertainty in the extreme value analysis of data generated by a hurricane simulation model. J. Eng. Mech.-Asce 2003, 129, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, B. Better bootstrap confidence intervals. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1987, 82, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, B.; Tibshirani, R.J. An Introduction to the Bootstrap; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; p. 456. [Google Scholar]
- Kysely, J. A Cautionary Note on the Use of Nonparametric Bootstrap for Estimating Uncertainties in Extreme-Value Models. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2008, 47, 3236–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagoulia, D.; Economou, P.; Caroni, C. Stationary and nonstationary generalized extreme value modelling of extreme precipitation over a mountainous area under climate change. Environmetrics 2014, 25, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukissian, T.H.; Tsalis, C. Effects of parameter estimation method and sample size in metocean design conditions. Ocean. Eng. 2018, 169, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besio, G.; Mentaschi, L.; Mazzino, A. Wave energy resource assessment in the Mediterranean Sea on the basis of a 35-year hindcast. Energy 2016, 94, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, G.; Barani, S.; Scafidi, D.; Capello, M.; Cutroneo, L.; Vagge, G.; Besio, G. Near real-time monitoring of significant sea wave height through microseism recordings: An application in the Ligurian Sea (Italy). Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2018, 165, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, N.I. Statistical Analysis of Circular Data, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993; p. 294. [Google Scholar]
- Mudersbach, C.; Wahl, T.; Haigh, I.D.; Jensen, J. Trends in high sea levels of German North Sea gauges compared to regional mean sea level changes. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 65, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penalba, M.; Ulazia, A.; Ibarra-Berastegui, G.; Ringwood, J.; Saenz, J. Wave energy resource variation off the west coast of Ireland and its impact on realistic wave energy converters’ power absorption. Appl. Energy 2018, 224, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
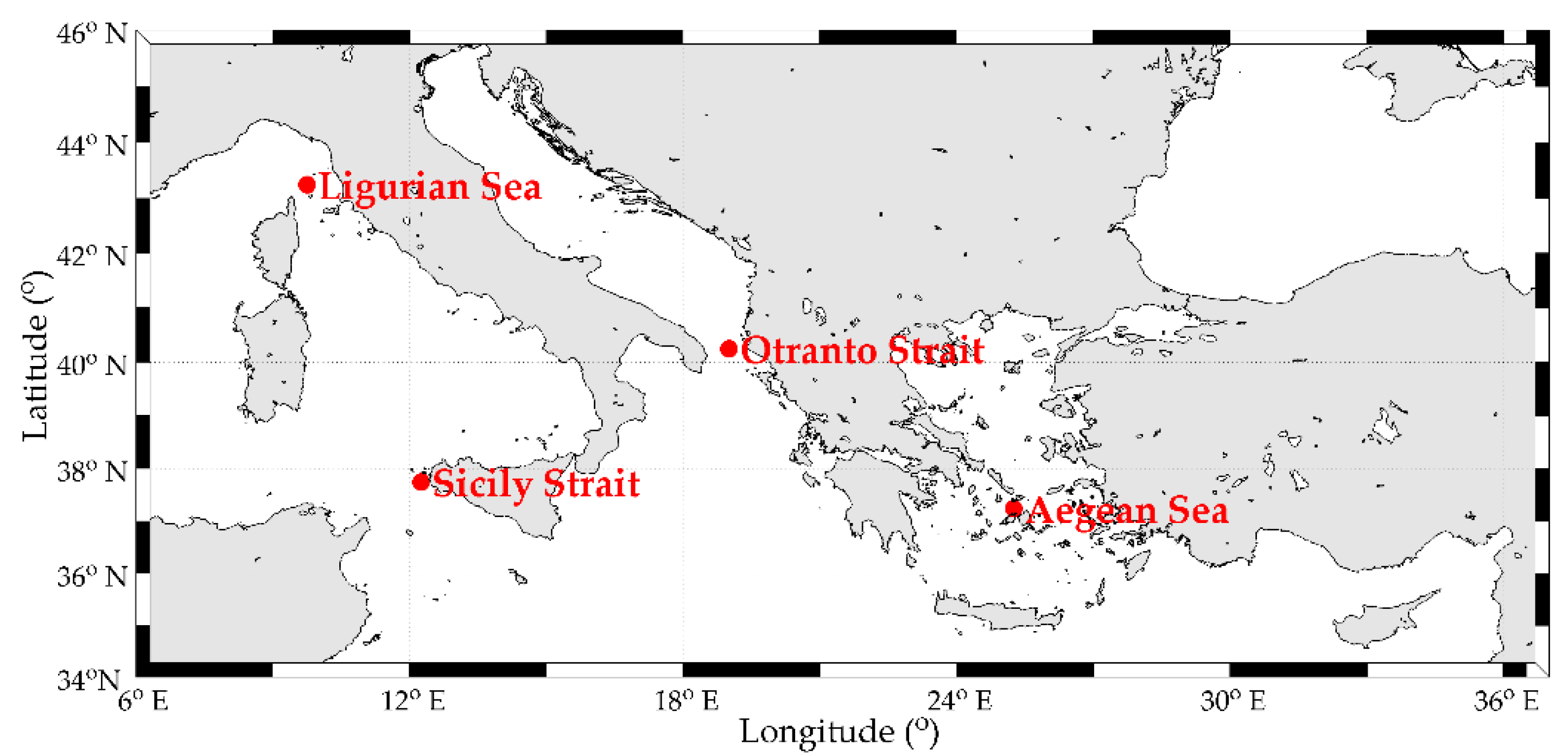
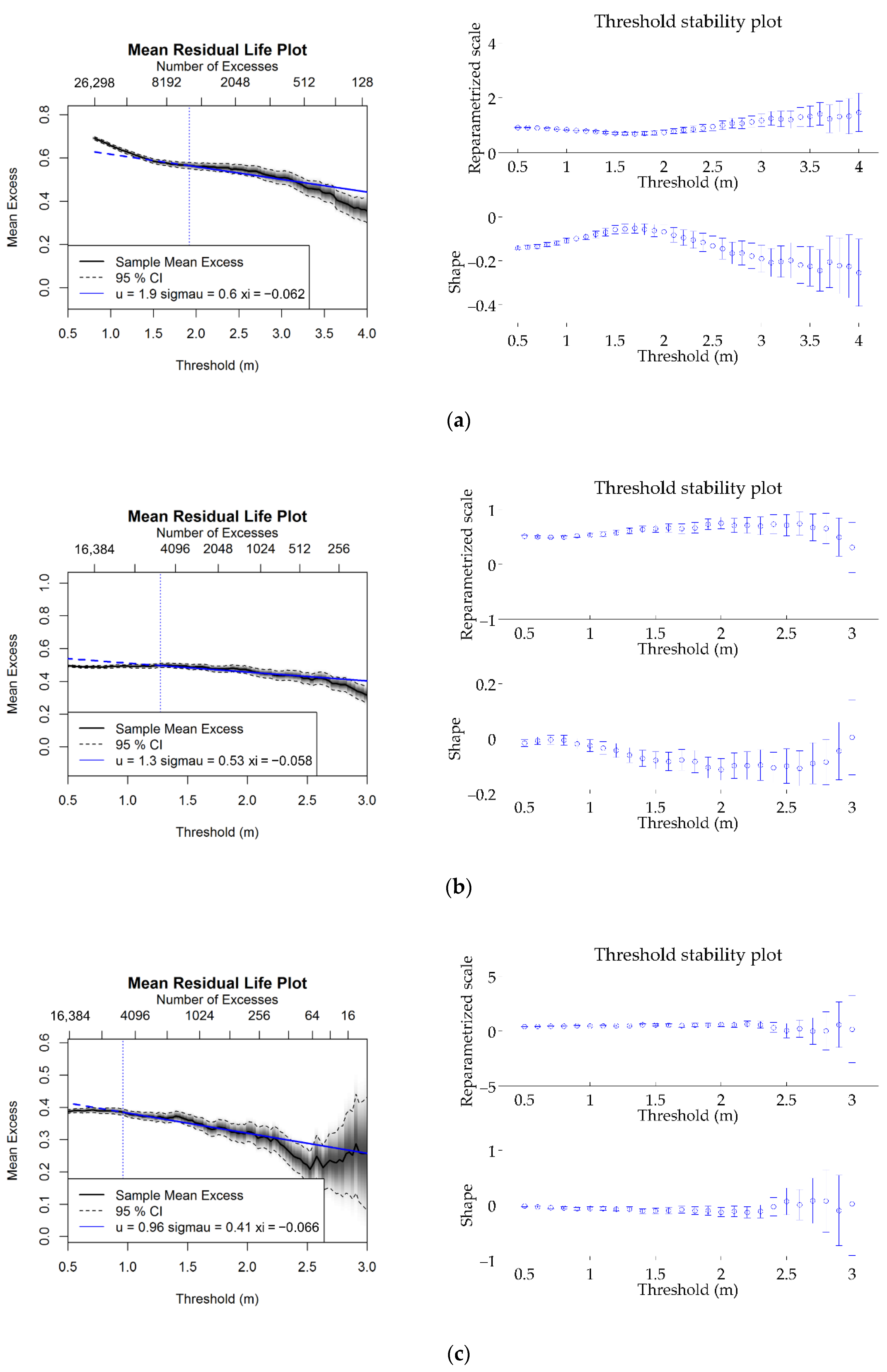
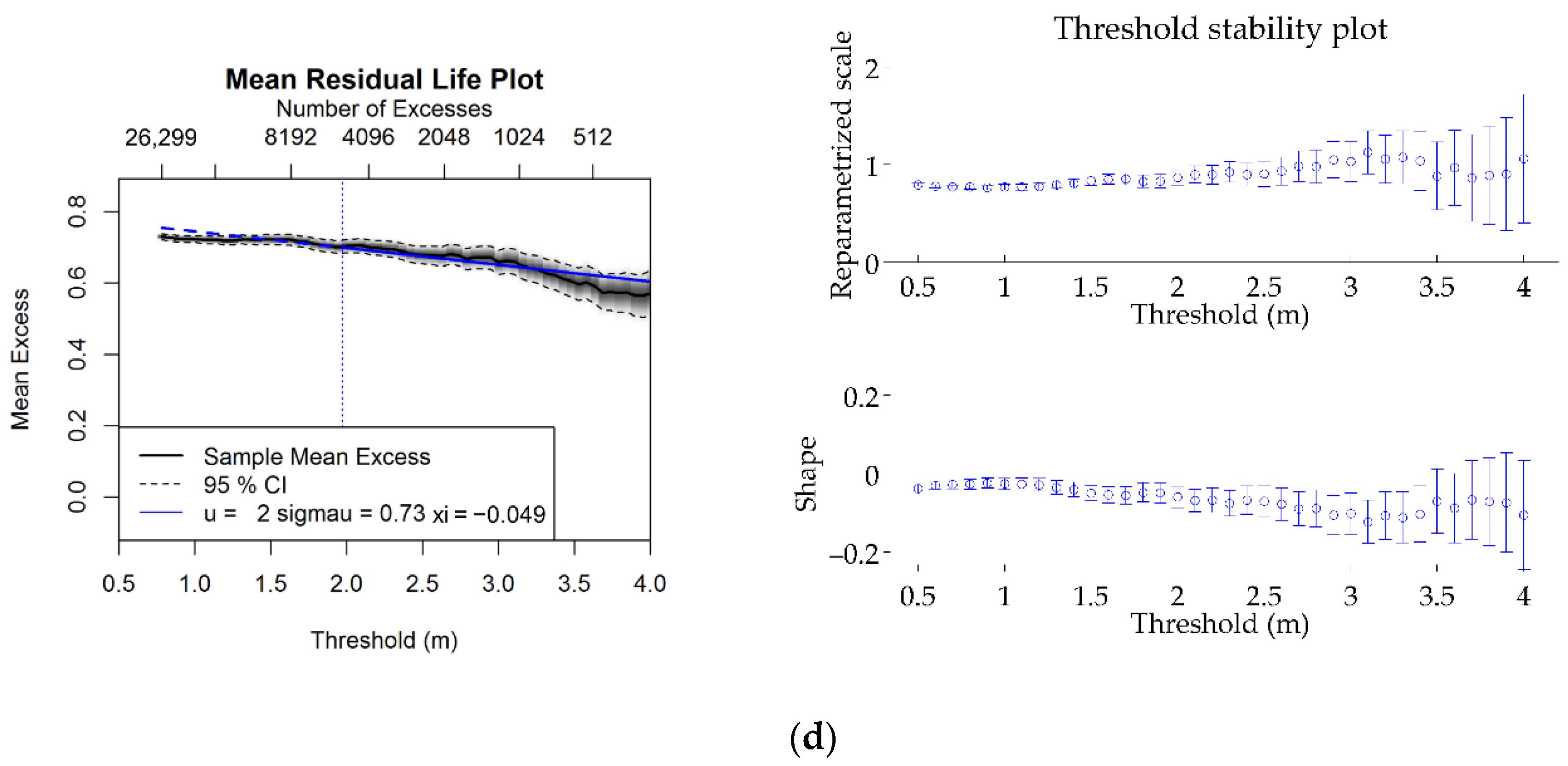
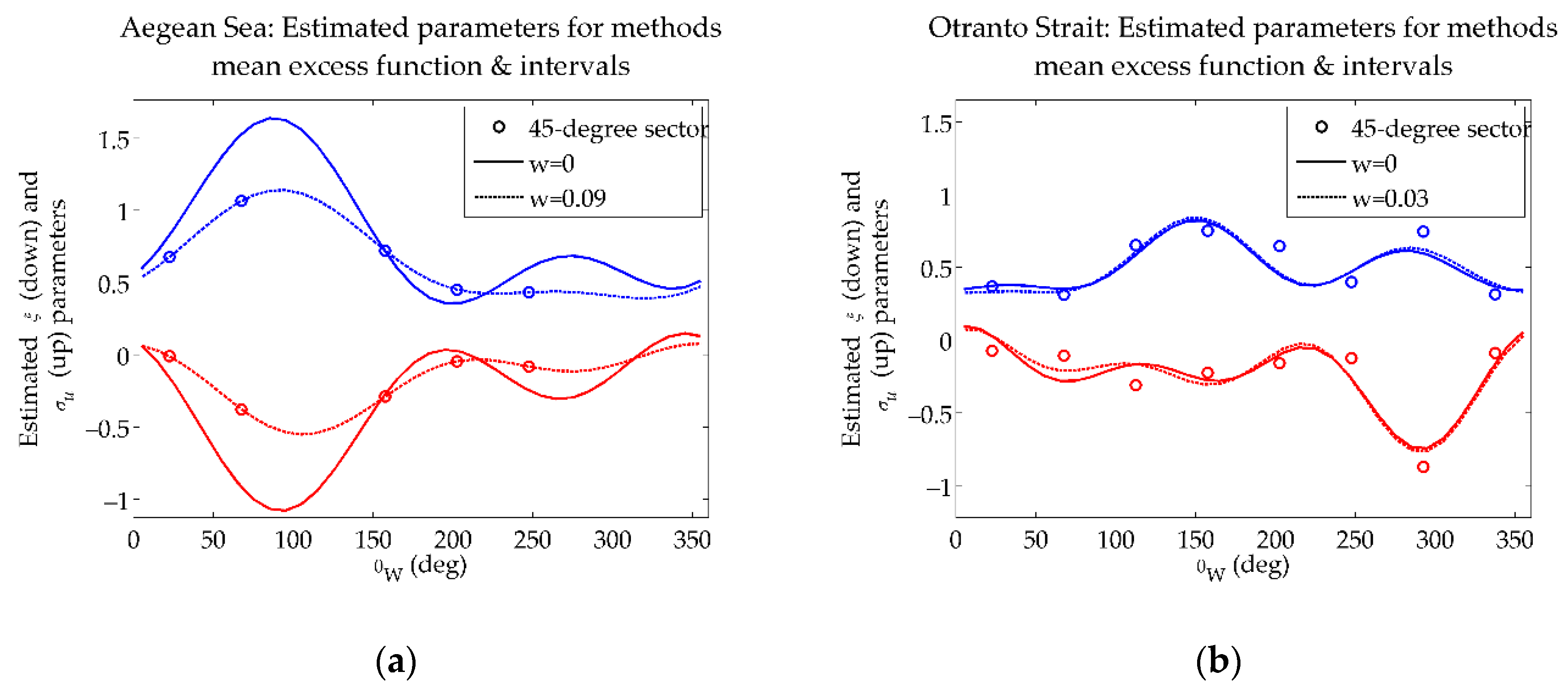
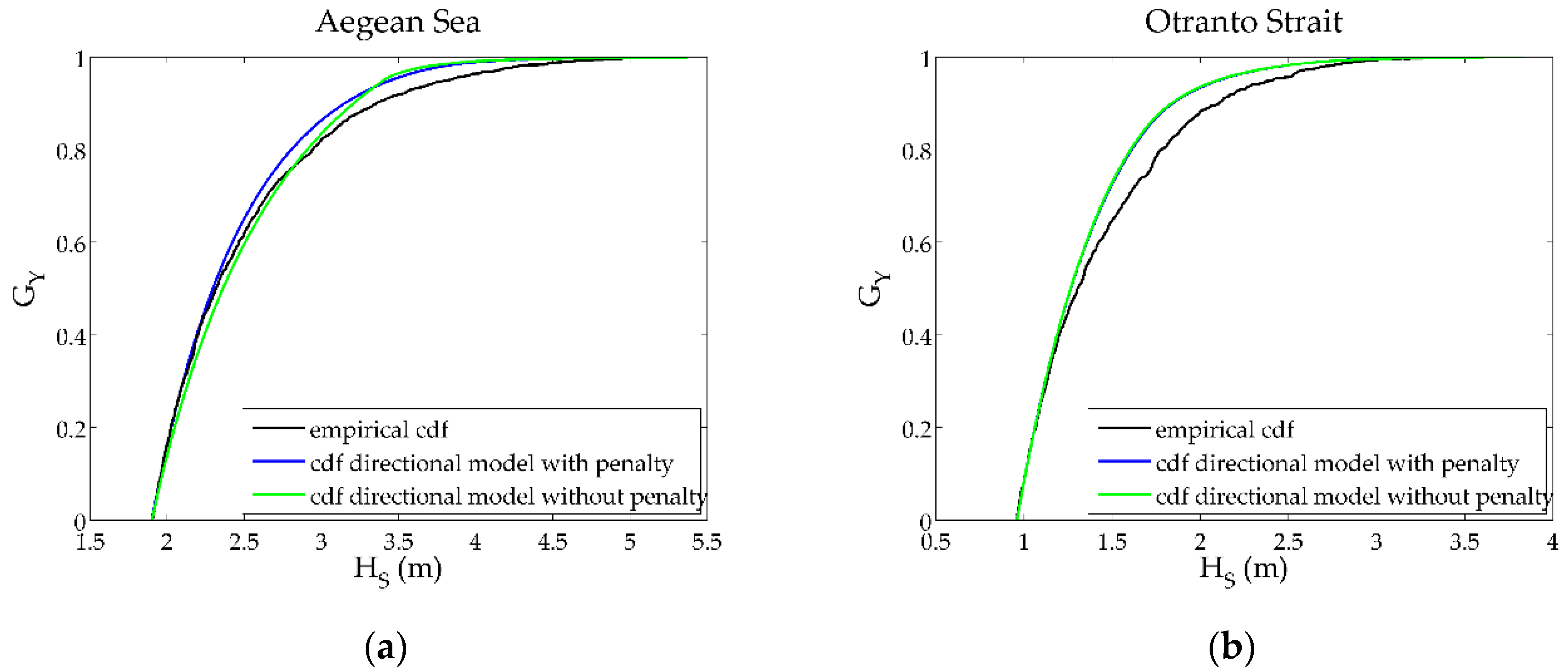
| Area | Latitude, Longitude (°) | Period | Sample Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aegean Sea | 37.75° N, 25.25° E | 1979–2014 | 52,596 |
| Ligurian Sea | 43.25° N, 9.75° E | ||
| Otranto Strait | 40.25° N, 19.00° E | ||
| Sicily Strait | 37.75° N, 12.25° E |
| Locations | (m) | (m) | (m) | (m) | (m) | (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aegean Sea | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 5.4 | 0.7 | 69.5 | 1.3 | 5.3 |
| Ligurian Sea | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 5.4 | 0.5 | 80 | 1.8 | 7.6 |
| Otranto Strait | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 3.8 | 0.4 | 85.5 | 1.9 | 7.7 |
| Sicily Strait | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 6.4 | 0.7 | 74.4 | 1.7 | 7.1 |
| Locations | (rad) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aegean Sea | 353.47 | 0.42 | 0.58 | 1.08 | 0.38 | 0.51 |
| Ligurian Sea | 272.26 | 0.31 | 0.69 | 1.18 | −0.18 | 0.22 |
| Otranto Strait | 240.07 | 0.17 | 0.83 | 1.29 | −0.29 | −0.32 |
| Sicily Strait | 287.50 | 0.39 | 0.61 | 1.11 | 0.28 | 0.20 |
| Threshold Selection Method | Aegean Sea | Ligurian Sea | Otranto Strait | Sicily Strait |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95th percentile | 2.32 | 1.62 | 1.24 | 2.47 |
| Mean excess function | 1.90 | 1.30 | 0.96 | 2.00 |
| Threshold stability | 2.10 | 1.50 | 1.00 | 2.10 |
| DeCA | 2.61 | 1.89 | 1.25 | 2.66 |
| Threshold Selection Method | Declustering Method | Aegean Sea | Ligurian Sea | Otranto Strait | Sicily Strait |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95th percentile | Runs | 323 | 340 | 297 | 288 |
| Intervals | 671 | 830 | 782 | 669 | |
| Mean excess function | Runs | 383 | 374 | 326 | 328 |
| Intervals | 1234 | 1303 | 1229 | 1064 | |
| Threshold stability | Runs | 365 | 359 | 325 | 322 |
| Intervals | 939 | 991 | 1165 | 963 | |
| DeCA | DeCA | 197 | 285 | 308 | 233 |
| Threshold Selection Method | Declustering Method | Aegean Sea | Ligurian Sea | Otranto Strait | Sicily Strait |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95th percentile | Runs | 1 (0.20) | 3 (0.24) | 1 (0.13) | 1 (0.06) |
| Intervals | 1 (0.03) | 3 (0.18) | 1 (0.12) | 1 (0.01) | |
| Mean excess function | Runs | 1 (0.31) | 2 (0.42) | 1 (0.22) | 1 (0.10) |
| Intervals | 2 (0.09) | 1 (0.17) | 3 (0.03) | 1 (0.02) | |
| Threshold stability | Runs | 1 (0.17) | 3 (0.42) | 1 (0.17) | 1 (0.29) |
| Intervals | 1 (0.02) | 1 (0.30) | 1 (0.03) | 3 (0.03) | |
| DeCA | DeCA | 1 (0.20) | 3 (0.24) | 1 (0.13) | 1 (0.06) |
| Parameter | Estimate | Bootstrap 97.5% CIs |
|---|---|---|
| −0.17 | [−0.59, −0.04] | |
| 0.10 | [−0.31, 0.20] | |
| −0.20 | [−0.54, −0.06] | |
| 0.14 | [−0.09, 0.22] | |
| 0.06 | [−0.46, 0.32] | |
| 0.66 | [0.36, 0.79] | |
| −0.02 | [−0.28, 0.10] | |
| 0.35 | [−0.16, 0.52] | |
| −0.13 | [−0.42, −0.05] | |
| 0.00 | [−0.64, 0.18] |
| Parameter | Estimate | Bootstrap 97.5% CIs |
|---|---|---|
| −0.07 | [−0.29, −0.02] | |
| −0.02 | [−0.20, 0.05] | |
| 0.07 | [−0.17, 0.16] | |
| 0.54 | [0.46, 0.57] | |
| 0.16 | [0.01, 0.21] | |
| −0.08 | [−0.20, −0.01] |
| Parameter | Estimate | Bootstrap 97.5% CIs |
|---|---|---|
| −0.24 | [−0.87, −0.11] | |
| 0.00 | [−0.31, 0.09] | |
| 0.15 | [−0.44, 0.31] | |
| 0.16 | [−0.64, 0.28] | |
| 0.16 | [−0.24, 0.30] | |
| 0.15 | [−0.43, 0.32] | |
| −0.07 | [−0.26, 0.00] | |
| 0.51 | [0.23, 0.54] | |
| −0.14 | [−0.35, −0.09] | |
| 0.00 | [−0.20, 0.10] | |
| −0.01 | [−0.23, 0.07] | |
| −0.15 | [−0.33, −0.06] | |
| −0.03 | [−0.27, 0.05] | |
| 0.09 | [−0.08, 0.15] |
| Parameter | Estimate | Bootstrap 97.5% CIs |
|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | [−0.52, 0.08] | |
| −0.16 | [−1.05, −0.04] | |
| −0.02 | [−0.71, 0.13] | |
| 0.71 | [0.27, 0.76] | |
| 0.37 | [−0.45, 0.47] | |
| −0.09 | [−0.96, 0.01] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karathanasi, F.; Soukissian, T.; Belibassakis, K. Directional Extreme Value Models in Wave Energy Applications. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11030274
Karathanasi F, Soukissian T, Belibassakis K. Directional Extreme Value Models in Wave Energy Applications. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(3):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11030274
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarathanasi, Flora, Takvor Soukissian, and Kostas Belibassakis. 2020. "Directional Extreme Value Models in Wave Energy Applications" Atmosphere 11, no. 3: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11030274
APA StyleKarathanasi, F., Soukissian, T., & Belibassakis, K. (2020). Directional Extreme Value Models in Wave Energy Applications. Atmosphere, 11(3), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11030274







