Fog Droplet Size Distribution and the Interaction between Fog Droplets and Fine Particles during Dense Fog in Tianjin, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
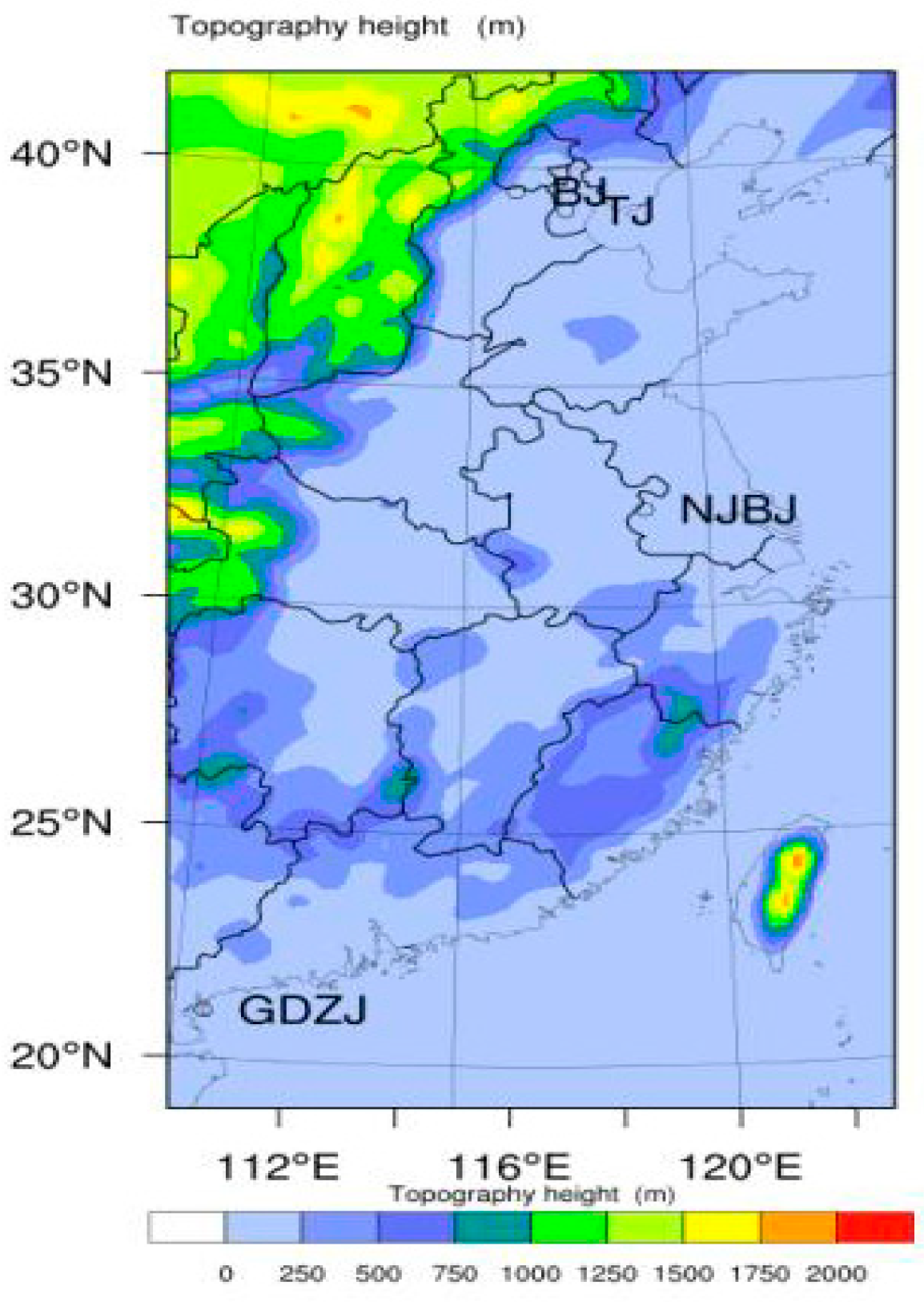
2. Measurement and Data Processing
3. Characteristics of Fog Droplet Size Distribution and Fine Particle
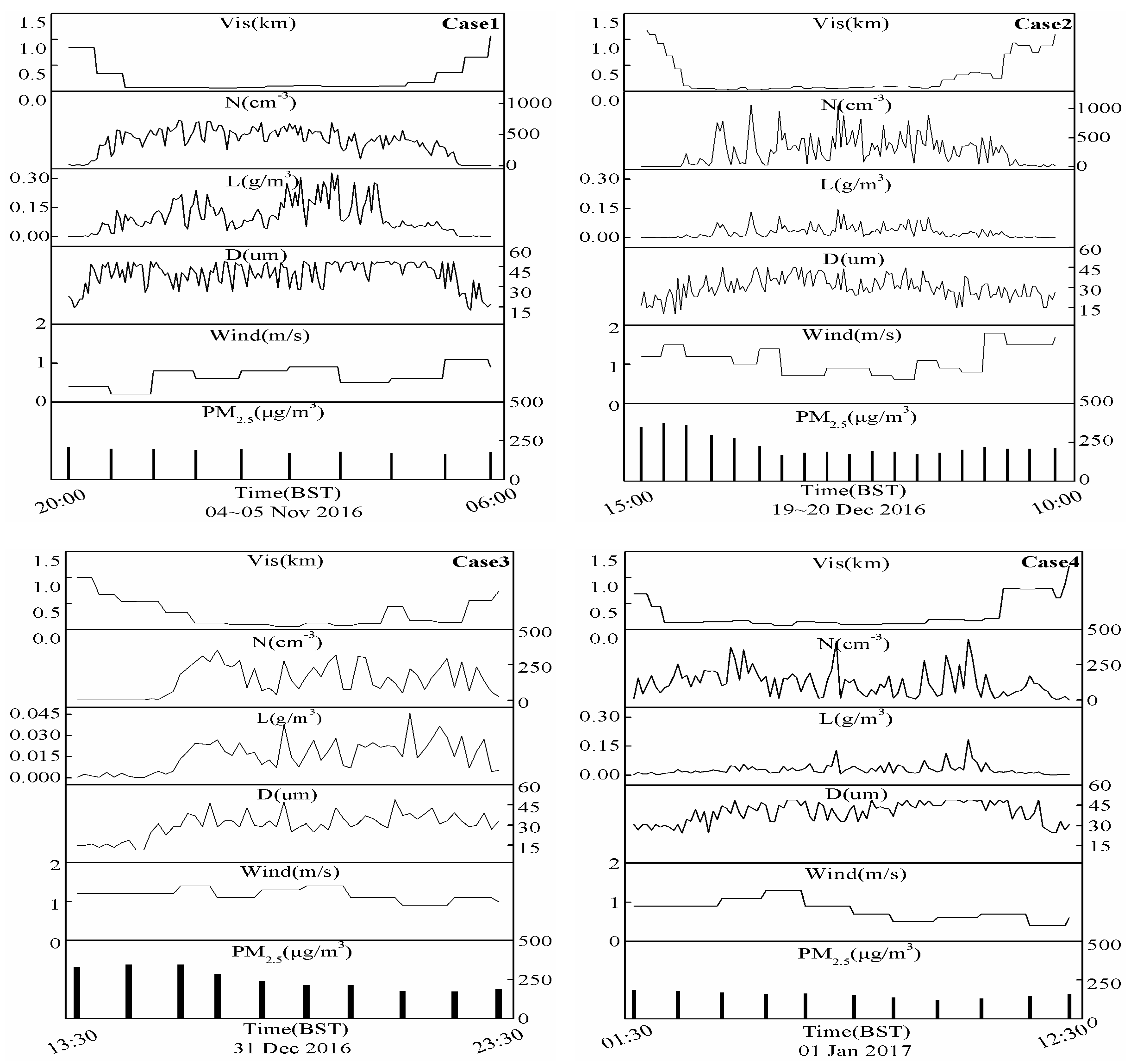
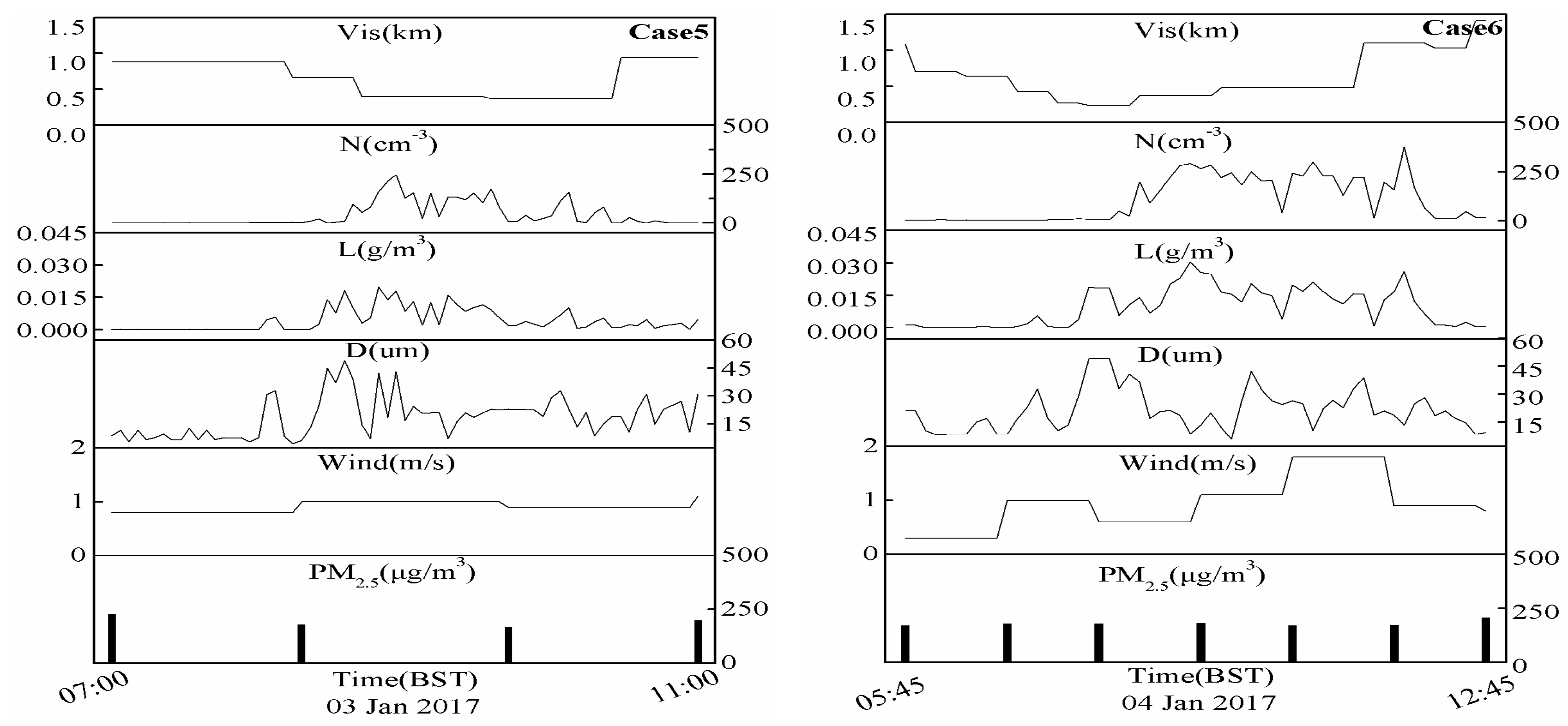
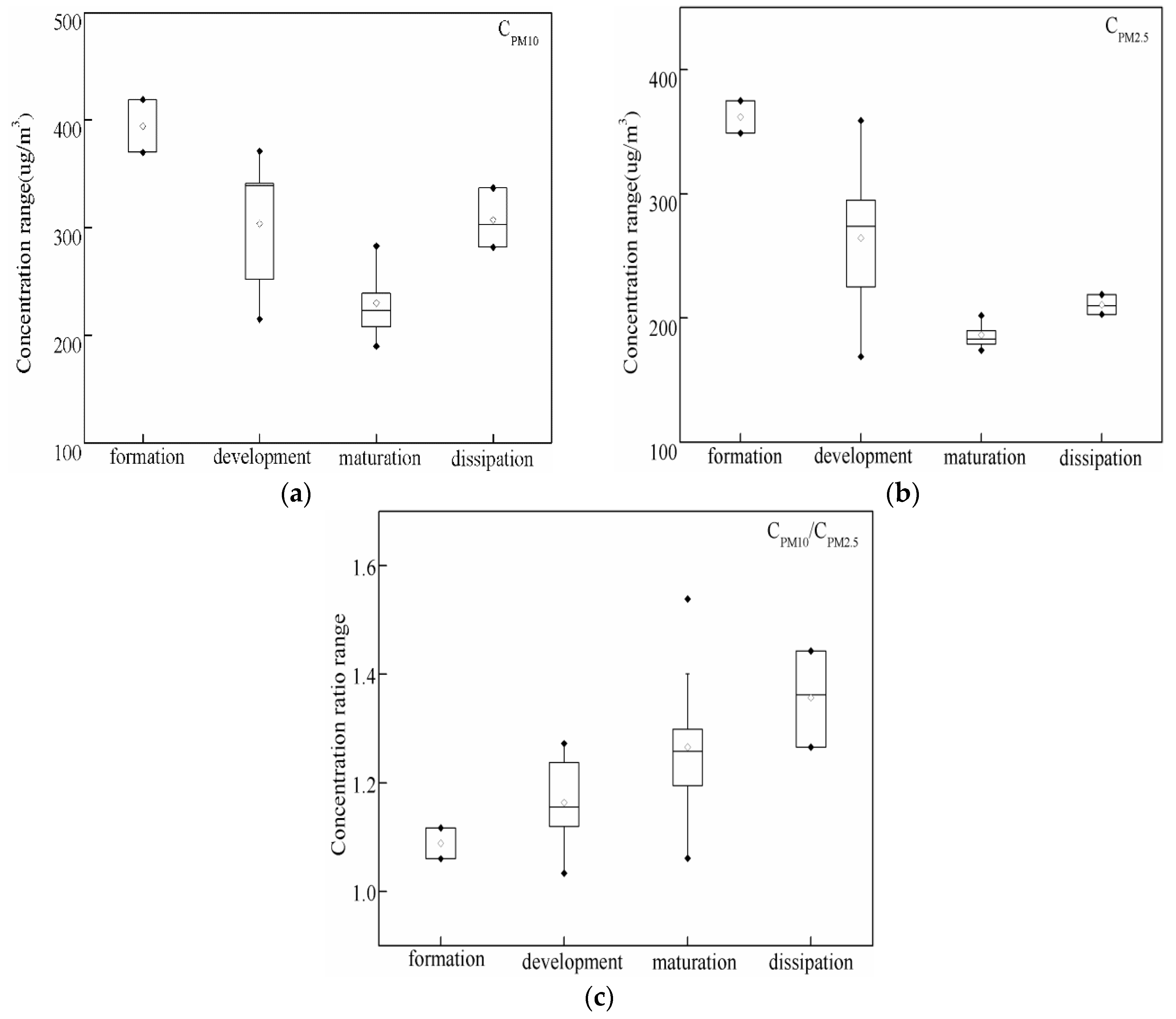
3.1. Evolution Characteristics of the Fog Droplet Size Distribution and Fine Particle
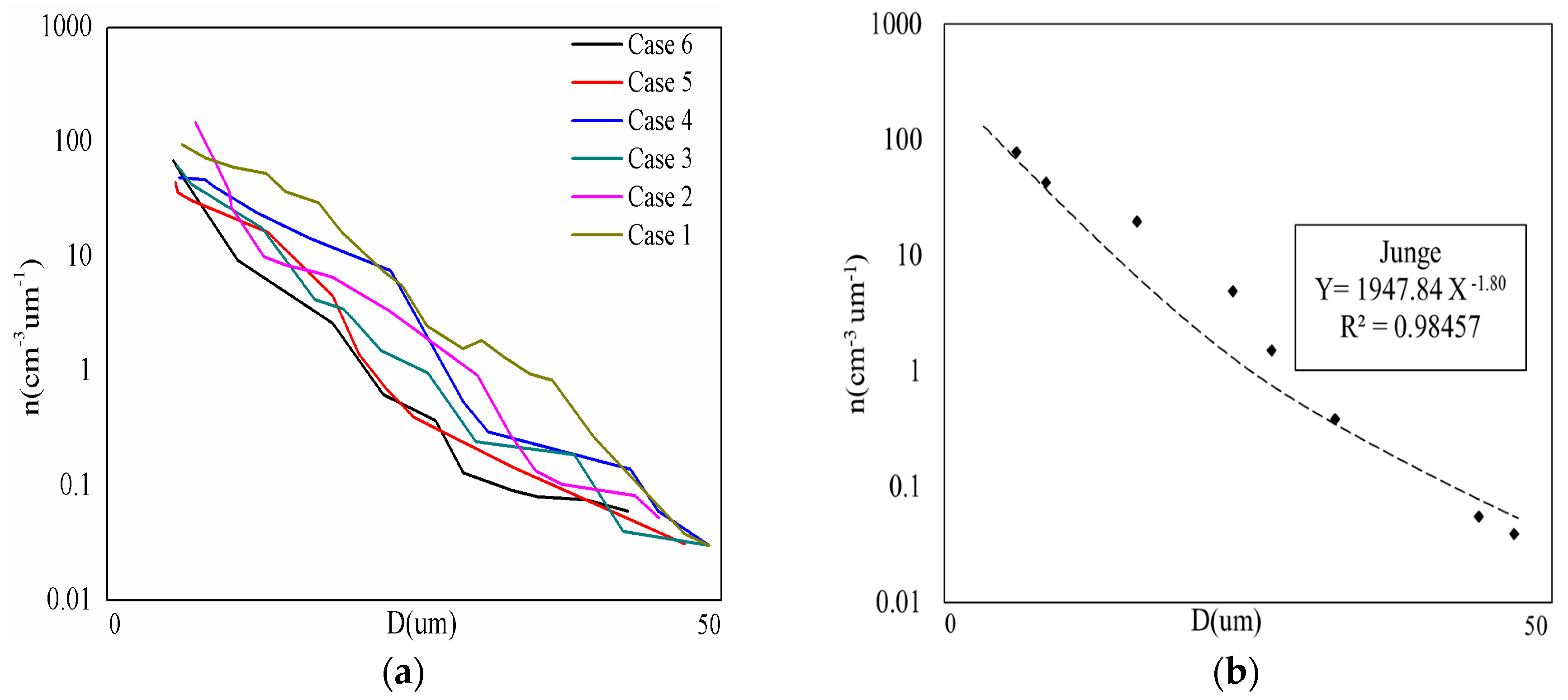
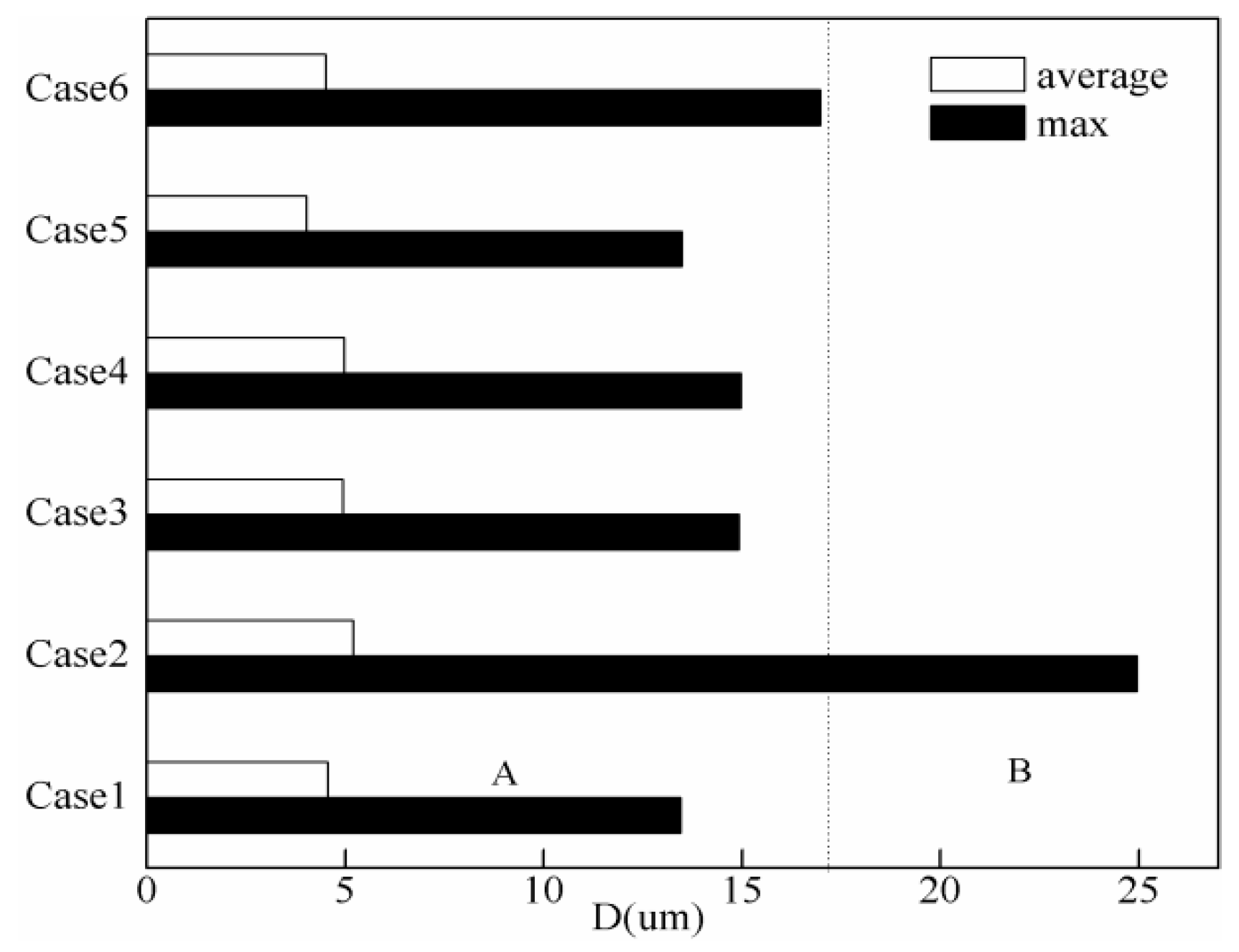
3.2. Statistical Characteristics of the Fog Droplet Size Distribution
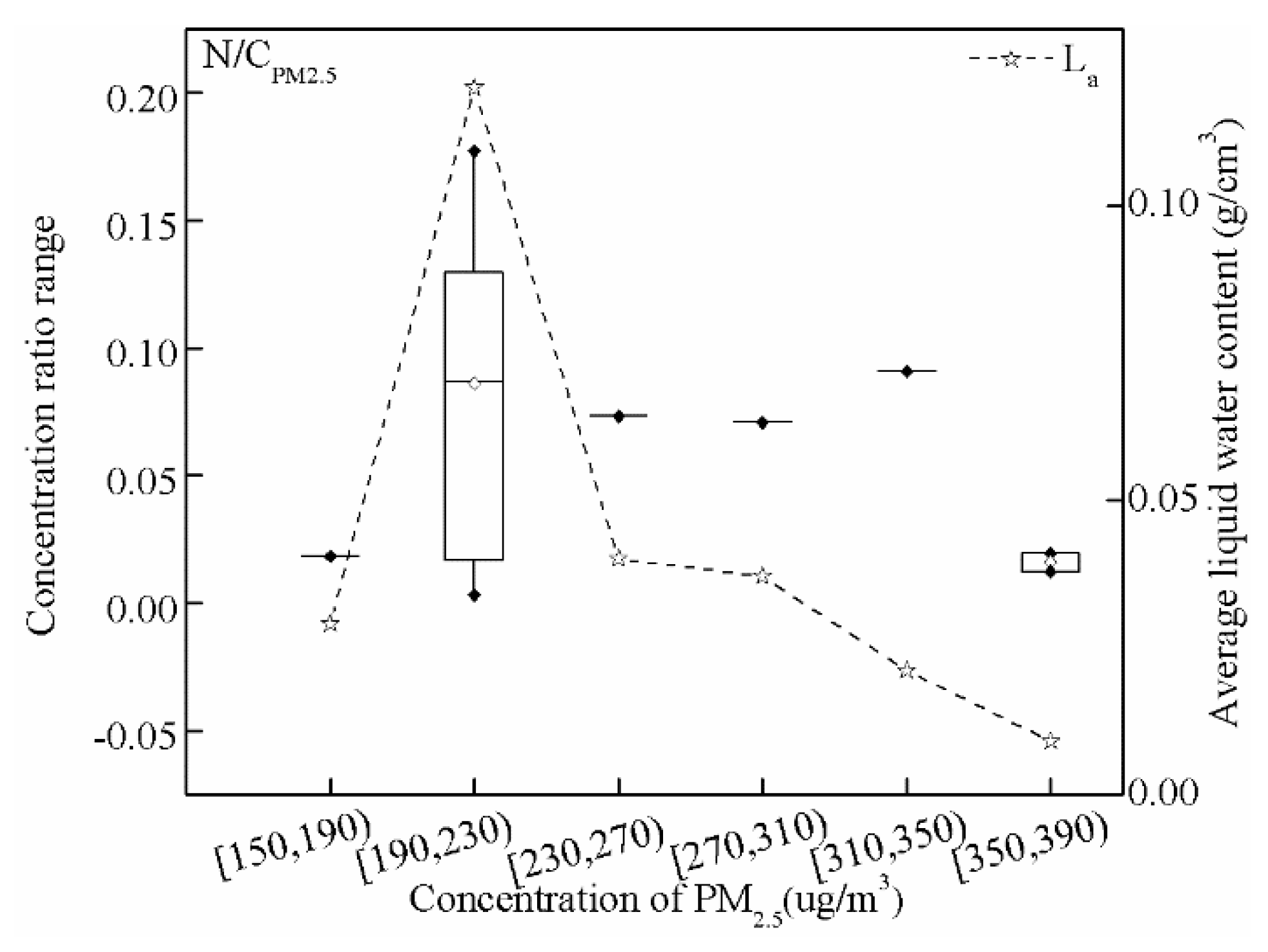
3.3. Interaction between Fog Droplets and Atmospheric Fine Particles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kulkarni, R.; Jenamani, R.K.; Pithani, P.; Konwar, M.; Nigam, N.; Ghude, S.D. Loss to aviation economy due to winter fog in New Delhi during the winter of 2011–2016. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thies, B.; Egli, S.; Bendix, J. The Influence of Drop Size Distributions on the Relationship between Liquid Water Content and Radar Reflectivity in Radiation Fogs. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeffelin, M.; Bergot, T.; Elias, T.; Tardif, R.; Carrer, D.; Chazette, P.; Colomb, M.; Drobinski, P.; Dupont, E.; Dupont, L.; et al. PARISFOG: Shedding new light on fog physical processes. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 767–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, B.A.; Kunkel, B.A. A numerical model of warm fog dissipation by hygroscopic particle seeding. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1970, 9, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gultepe, I.; Fernando, H.J.S.; Pardyjak, E.R.; Hoch, S.W.; Silver, Z.; Creegan, E.; Leo, L.S.; Pu, Z.; Wekker, S.F.J.; Hang, C. An Overview of the MATERHORN Fog Project: Observations and Predictability. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2016, 173, 2983–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Daum, P.H.; Yum, S.S.; Liu, Y.; Senum, G.I.; Lu, M.-L.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Jonsson, H. Observations of marine stratocumulus microphysics and implications for processes controlling droplet spectra: Results from the Marine Stratus/Stratocumulus Experiment. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D18210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, H.E. Microstructure of a radiation fog. J. Atmos. Sci. 1981, 38, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J. Radiation Fog. Part I: Observations of Stability and Drop Size Distributions. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2011, 139, 167–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, D.; Bergot, T.; Khlifi, M.E. Numerical study of a coastal fog event over Casablanca, Morocco. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 141, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, D. A preliminary impact study of wind on assimilation and forecast systems into the one-dimensional fog forecasting model COBEL-ISBA over Morocco. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gultepe, I.; Milbrandt, J.A. Microphysical Observations and Mesoscale Model Simulation of a Warm Fog Case during FRAM Project. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2007, 164, 1161–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, J.; Shen, S.; Liu, S.; Lu, W. Evolution of liquid water content in a sea fog controlled by a high-pressure pattern. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2010, 16, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Lu, C.; Yu, H.; Zhao, L.; Lü, J. Fog research in China: An overview. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 27, 639–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petters, M.D.; Kreidenweis, S.M. A single parameter representation of hygroscopic growth and cloud condensation nucleus activity. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 1961–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhar, M.K.; Yasmin, N.; Chishtie, F.; Shahid, I. Temporal variability and characterization of aerosols across the Pakistan Region during the winter fog periods. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.; Wang, Z.M.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, Y. Roles of relative humidity in aerosol pollution aggravation over Central China during wintertime. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolaki, S.; Haeffelin, M.; Lac, C.; Dupont, J.C.; Elias, T.; Masson, V. Influence of aerosols on the life cycle of a radiation fog event. A numerical and observational study. Atmos. Res. 2015, 151, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, T.; Haeffelin, M.; Drobinski, P.; Gomes, L.; Rangognio, J.; Bergot, T.; Chazette, P.; Raut, J.-C.; Colomb, M. Particulate contribution to extinction of visible radiation: Pollution, haze, and fog. Atmos. Res. 2009, 92, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, J.; Zhang, Q.; He, H.; Liu, J.; Huang, M.; Jin, H. Analysis of the formation of fog and haze in North China Plain (NCP). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 8205–8214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimadera, H.; Kondo, A.; Kaga, A.; Shrestha, K.L.; Inoue, Y. Contribution of transboundary air pollution to ionic concentrations in fog in the Kinki Region of Japan. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5894–5907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aikawa, M.; Hiraki, T.; Suzuki, M.; Tamaki, M.; Kasahara, M. Separate chemical characterizations of fog water, aerosol, and gas before, during, and after fog events near an industrialized area in Japan. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 1950–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahey, K.M.; Pandis, S.N.; Collett, J.L.; Herckes, P. The influence of size-dependent droplet composition on pollutant processing by fogs. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 4561–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.J.; Guo, X.L.; Fang, C.G.; Zhu, S.C. Observation analysis on characteristics of formation, evolution and transition of a long-lasting severe fog and haze episode in North China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Feng, Y.; Yao, Q.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M. Characteristics and formation mechanism of a winter haze–fog episode in Tianjin, China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 98, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Wu, B.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z. Impact of water vapor transfer on a Circum-Bohai-Sea heavy fog: Observation and numerical simulation. Atmos. Res. 2019, 229, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wu, B.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Cai, X.; Song, Y. Characteristics of the atmospheric boundary layer and its relation with PM2.5 during haze episodes in winter in the North China Plain. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yang, J.; Niu, S.; Li, Z. On the evolution and structure of a radiation fog event in Nanjing. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 28, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, F.; Ge, X.; Yang, M.; Xia, J.; Liu, G.; Li, F. Chemical and Light Extinction Characteristics of Atmospheric Aerosols in Suburban Nanjing, China. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Niu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, F.; Zhao, L.; Lü, J. An observation study of sea fog in the coastal area of South China Sea. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 38, 694–702, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagler, G.S.W.; Bergin, M.H.; Salmon, L.G.; Yu, J.Z.; Wan, E.C.H.; Zheng, M.; Zeng, L.M.; Kiang, C.S.; Zhang, Y.H.; Lau, A.K.H.; et al. Source areas and chemical composition of fine particulate matter in the Pearl River Delta region of China. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 3802–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Tie, X.; Li, C.; Ying, Z.; Kai-Hon Lau, A.; Huang, J.; Deng, X.; Bi, X. An extremely low visibility event over the Guangzhou region: A case study. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6568–6577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, J.; Tie, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, D. Characteristics of heavy aerosol pollution during the 2012–2013 winter in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 88, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberger, J.L.; Gasko, M. Comparing Location Estimators: Trimmed Means, Medians, and Trimean. Understanding Robust and Exploratory Data Analysis; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 297–336. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/285809421_Comparing_location_estimators_Trimmed_means_medians_and_trimean (accessed on 4 March 2020).
- Grade of Fog Forecast GB/T 27964–2011. 2011. Available online: http://c.gb688.cn/bzgk/gb/showGb?type=online&hcno=F0E92BAD8204180AA7AB052A3FD73B70 (accessed on 4 March 2020). (In Chinese).
- Niu, S.J.; Liu, D.Y.; Zhao, L.J.; Lu, C.S.; Lü, J.J.; Yang, J. Summary of a 4-Year Fog Field Study in Northern Nanjing, Part 2: Fog Microphysics. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2011, 169, 1137–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, J.W. A Numerical Model of the Formation of Droplet Spectra in Advection Fogs at Sea and Its Applicability to Fogs off Nova Scotia. J. Atmos. Sci. 1978, 35, 1522–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dabek-Zlotorzynska, E.; Dann, T.F.; Kalyani Martinelango, P.; Celo, V.; Brook, J.R.; Mathieu, D.; Ding, L.; Austin, C.C. Canadian National Air Pollution Surveillance (NAPS) PM2.5 speciation program: Methodology and PM2.5 chemical composition for the years 2003–2008. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikari, S.; Kundan, L.S.; Akira, K.; Akikazu, K.; YOSHIO, I. Fog simulation using a mesoscale model in and around the Yodo River Basin, Japan. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Tang, J.; Huang, J.; Mao, J.T.; Zhou, X.J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, F.Z.; Zhou, H.G. The measurement of aerosol optical properties at a rural site in Northern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 2229–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, D.S.; Tripathi, S.N.; Gupta, T. Chemical and microphysical properties of the aerosol during foggy and nonfoggy episodes: A relationship between organic and inorganic content of the aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2012, 12, 14483–14524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Gupta, T. Chemical Characterization and Source Apportionment of Submicron (PM1) Aerosol in Kanpur Region, India. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2010, 10, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, C.G.; Stuefer, M.; Heymsfield, A.J.; Kim, C.K. The microphysical properties of ice fog measured in urban environments of Interior Alaska. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 11136–11147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, M.A. Physical, chemical, and ultraviolet radiative characteristics of aerosol in central Alaska. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, R.G. The Relationship between visibility and liquid water content in fog. J. Atmos. Sci. 1971, 28, 1183–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Han, S.; Bian, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Tie, X.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Yao, Q. Effect of Aerosols on Visibility and Radiation in Spring 2009 in Tianjin, China. Aerosol. Air. Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachorro, V.E.; De Frutos, A.M.; Gonzalez, M.J. Analysis of the relationships between Junge size distribution and Angstrom a turbidity parameters from spectral measurements of atmospheric aerosol extinction. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1993, 27, 1585–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomfield, P.; Royle, J.A.; Steinberg, L.J.; Yang, Q. Accounting for meteorological effects in measuring urban ozone levels and trends. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 3067–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, J.G. Relationship between fog condensation nuclei and fog microstructure. J. Atmos. Sci. 1980, 37, 1854–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Laj, P.; Fuzzi, S.; Lazzari, A.; Ricci, L.; Orsi, G.; Berner, A.; Dusek, U.; Schell, D.; Guenther, A.; Wendisch, M.; et al. The size dependent composition of fog droplets. Contrib. Atmos. Phys. 1998, 71, 115–130. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/etdeweb/biblio/613361 (accessed on 4 March 2020).
- Izhar, S.; Gupta, T.; Panday, A.K. Scavenging efficiency of water soluble inorganic and organic aerosols by fog droplets in the Indo Gangetic Plain. Atmos. Res. 2019, 235, 104767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Instrument | Manufacturer | Model | Time Resolution | Measured Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fog monitor | DMT, US | FM-120 | 1 s | N, L, D, size distribution |
| Forward scatter visibility meter | Belfort, US | MODEL6000 | 1 min | Vis |
| Ambient particulate monitor | Thermo, US | TEOM (RP1405D) | 1 h | CPM2.5, CPM10 |
| Automatic weather station | Huayun Sounding, China | DZZ5 | 5 min | Wind, T, P, RH |
| Case | Date | Dr/Drma (h) | Nmax/Na (particles/cm3) | Lmax/La (g/m3) | Dmax (µm) | Visma (m) | Classification of Fog | CPM2.5max (μg/m3) | CPM2.5min (μg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 04~05 Nov 2016 | 10/8 | 737/363 | 0.332/0.105 | 48 | 107~60 | Dense | 210 | 164 |
| 2 | 19~20 Dec 2016 | 19/10.5 | 1070/596 | 0.145/0.041 | 45 | 100~30 | Strong dense | 375 | 169 |
| 3 | 31 Dec 2016 | 10/3.5 | 356/172 | 0.046/0.018 | 49 | 120~70 | Dense | 346 | 173 |
| 4 | 01 Jan 2017 | 11/7.5 | 431/141 | 0.183/0.035 | 48 | 200~80 | Dense | 188 | 121 |
| 5 | 03 Jan 2017 | 4/0.5 | 247/102 | 0.020/0.010 | 49 | 400~370 | Dense | 230 | 167 |
| 6 | 04 Jan 2017 | 7/2.5 | 374/142 | 0.031/0.013 | 42 | 480~240 | Dense | 207 | 171 |
| Observation Site | Na (particles/cm3) | La (g/m3) | Dmax (µm) | Average Spectrum | Main Chemical Composition of Fog Water | Concentrations of Aerosols | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tianjin, China | 253 | 0.037 | 47 | Junge | Sulfate > particulate organic matter > elemental carbon > nitrate [45] | CPM2.5max 188–375 μg/m3, CPM2.5min 121–173 μg/m3 | 2016 (This research) |
| Nanjing, China [27,28] | 380 | 0.04 | 47 | Junge | Nitrate > Sulfate | 166 ± 96 μg/m3 | 2007 |
| Kanpur, India [40,41] | 400 | - | - | Junge | Nitrate > Sulfate > Crustal elements | CPM1 199 μg/m3 | 2012 |
| Baoding, China [23] | 350–500 | 0.001–0.01 | 50 | - | Sulfate | NPM2.5 104 particles/cm3 | 2011 |
| Yodogawa Basin, Japan [20,38] | - | 0.112 | - | - | Nitrate > Sulfate Ca2+, Na+, Mg2+ | - | 2005 |
| Fairbanks, Alaska, USA [42,43] | 68 | - | 60 | Generalized gamma | Sulfur > Crustal compounds Ca2+, Na+, K+ | 0.3 < D < 0.5µm 10 particles/cm3 | 2012 |
| Zhanjiang Coast of Guangzhou, China [29,30,31] | 231 | 0.114 | 50 | Generalized gamma | Sulfate > Nitrate > Ammonium Na+, Cl− | CPM2.5 100–200 μg/m3 | 2011 |
| West coast of Casablanca, Morocco [9] | - | - | - | Generalized gamma | - | - | 2008 |
| Nova Scotia, Canada [36,37] | 78 | 0.092 | - | Generalized gamma | Sulfate> Nitrate > Organic matter Na+, Cl− | CPM2.5 10 μg/m3 | 1975 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Wu, B.; Wang, Z.; Hao, T. Fog Droplet Size Distribution and the Interaction between Fog Droplets and Fine Particles during Dense Fog in Tianjin, China. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11030258
Liu Q, Wu B, Wang Z, Hao T. Fog Droplet Size Distribution and the Interaction between Fog Droplets and Fine Particles during Dense Fog in Tianjin, China. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(3):258. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11030258
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qing, Bingui Wu, Zhaoyu Wang, and Tianyi Hao. 2020. "Fog Droplet Size Distribution and the Interaction between Fog Droplets and Fine Particles during Dense Fog in Tianjin, China" Atmosphere 11, no. 3: 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11030258
APA StyleLiu, Q., Wu, B., Wang, Z., & Hao, T. (2020). Fog Droplet Size Distribution and the Interaction between Fog Droplets and Fine Particles during Dense Fog in Tianjin, China. Atmosphere, 11(3), 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11030258




