Abstract
Air pollution shows a generally decreasing trend from the north to the south in China since 2013 (GB3095-2012, the current standard for monitoring). However, an opposite observation was recorded in 2017, especially in winter. In this study, we collected monitoring data of six air pollutants in 2016 and 2017, from a northern city (Beijing) and a southern city (Nanjing) for comparison. As air pollution was highly dependent upon meteorological conditions, we further analyzed their relationships to explain this abnormal phenomenon. Seasonal averaged PM2.5, PM10, SO2, CO, and NO2 were negatively correlated with wind scale (WS) while 8-h O3 exhibited an opposite relationship. Relative humidity (RH) has opposite effects on the concentrations of different pollutants in Beijing and Nanjing. The 8-h O3 showed the closest positive correlation with temperature (T), which is due to its formation mechanism. In Beijing, decreased RH, together with more wind from northwest in winter, resulted in an improved air quality in 2017. In Nanjing, WS, RH, T, and wind direction fluctuated within a narrow range in each season, leading to relatively stable pollutant concentrations. These results suggest that meteorological conditions are important factors to evaluate the air quality and implement control measures.
1. Introduction
Over the past decades, China has achieved great progress in social and economic areas and has attracted worldwide attention. Due to this rapid development, however, China has been experiencing severe air pollution problems, which in turn threatens the sustainable development [1,2,3]. Air pollutants pose timely issues and potential risks to human health and ecosystem. It has been widely demonstrated that exposure to polluted air could increase the morbidity of many illnesses and induce premature mortality [4,5]. For example, Rohde and Muller [6] estimated that ambient air pollution caused 1.6 million premature deaths over China in 2014.
Air pollution in China has raised great concern from the government, the public, and scientists [7]. The most stringent regulation “Air Pollution Prevention Action Plan” was enacted on September 10, 2013 and implemented on 1 January 2015. Since 2013, the real-time monitoring of six air pollutants, i.e., particles with an aerodynamic diameter equal to or less than 2.5 µm (PM2.5), particles with an aerodynamic diameter equal to or less than 10 µm (PM10), sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and ozone (O3), have been conducted and corresponding data were released to the public in major Chinese cities. Although the total concentrations of these air pollutants decreased significantly in recent years, unfortunately, the pollution levels in most Chinese cities still exceed the standards recommended by the World Health Organization [8]. According to the monitoring data, air quality in northern China is poorer than that in southern China (Bulletin of the Ministry of Ecology and Environment, http://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/zghjzkgb/lnzghjzkgb/index.shtml). This could be partially explained by the winter heating and unfavorable dispersion conditions in northern cities. Interestingly, in the year 2017, particularly in winter, visible and detectable improvement in air quality was recorded in the northern city Beijing, even better than that in many southern cities. However, to our knowledge, there is no case study focused on this abnormal phenomenon as well as the underlying mechanisms.
Air pollution is affected by multiple factors, including pollutant emissions, meteorological conditions, terrain, pollutant transport, and transformation [9,10,11]. Previous studies revealed that both pollutant emissions and meteorological conditions dominated pollutant concentration trends [12,13]. Beside emission control, favorable meteorological conditions have significant impacts on air quality by determining dispersion conditions and thus atmospheric environmental capacity [14]. Local and regional meteorology (e.g., wind speed and wind direction) are responsible for the spatial and temporal distribution of air pollutants [15]. Furthermore, weather conditions (e.g., temperature and relative humidity) also play an important role in chemical reactions, and then change the reacted pollutant concentrations [16]. He et al. [17] reported that more than 70% of the daily concentration variation over China could be explained by the meteorological conditions. However, there is still a knowledge gap between meteorological parameters and their impacts on concentrations of air pollutants in a specific region.
Therefore, the aim of the present study was to clarify the interactions between meteorological factors and ambient air quality, and unfold the reasons why Beijing had increased “blue skies” in 2017. We first collected the concentrations of six criteria air pollutants in 2016 and 2017, from Beijing and the southern city Nanjing [18]. In comparison, Nanjing is a major city in the well-developed Yangtze River Delta in Southern China, which is also experiencing serious air pollution [19,20]. Simultaneously we investigated the meteorological data (including temperature, relative humidity, wind scale, and wind direction), and then explored the relationship between air pollution and these parameters. Our results can provide a better understanding of the mechanisms that lead to or reduce pollution, and enhance the accuracy of air pollution forecast under various meteorological conditions.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Cities
Beijing (39°90′ N, 116°40′ E) and Nanjing (32°07′ N, 118°78′ E) were selected in this study (Figure 1). Beijing, the capital of China, is located in the northern part of North China Plain (NCP) and is surrounded by the Taihang and the Yanshan mountains to the northeast, northwest, and southwest sides. Nanjing is the provincial capital of Jiangsu and one of the major cities in the Yangtze River Delta (YRD), South China. Both NCP and YRD have suffered from severe air pollution problems in recent years. Beijing and Nanjing are representative cities in these two regions, respectively, due to their high population density and well developed economies [21]. However, the meteorological conditions in these two cities are dramatically different. Beijing has a typical monsoon-influenced climate, characterized by hot, humid summer and cold, dry, and windy winter [22]. Spring and fall in Beijing could be affected by sandstorms from the Mongolian Gobi Desert [23]. Differently, Nanjing is located in the subtropical humid climate area, with moist summer and winter. Therefore, the different climatic conditions of these two cities could provide typical examples for studying the relationships between atmospheric pollutants and meteorological parameters in China.
Figure 1.
Sampling sites in Beijing and Nanjing on Google maps.
2.2. Data
Hourly concentrations of air pollutants including PM2.5, PM10, SO2, CO, NO2, and O3 in Beijing and Nanjing from March 2016 to February 2018 were collected from http://www.cnemc.cn/. Meteorological parameters, including temperature (T), relative humidity (RH), wind direction, and wind scale (WS) were also acquired during the same period from the website of the China Meteorological Data Sharing Service System Administration (http://data.cma.cn/site/index.html). A sanity check was conducted on the initial data to delete any problematic data points. Valid hourly average parameters were then averaged using data from nine national air quality monitoring sites in Nanjing (i.e., Pukou, Xianlin University Town, Maigao Bridge, Ruijin Road, Shanxi Road, Caochang Gate, Olympic Sports Center, Zhonghua Gate, Xuanwu Lake). As for Beijing, there were 21 national air quality monitoring sites in different districts (i.e., Dingling background station, Dingling, Changping, Huairou, Shijingshan City, Ancient City, Shunyi, Chaoyang Olympic Sports Center, Olympic Sports Center, West Park Officials, Park Officials, Haidian, Haidian Wanliu, Dongcheng, East 4th Ring Road, Chaoyang Agricultural Exhibition Hall, Agricultural Exhibition Hall, West Wanshou Nishinomiya, Wanshou Nishinomiya, East Temple of Heaven, Temple of Heaven). Daily average meteorological parameters and pollutant concentrations were calculated only when there were more than 16 h of valid data within that day. The daily O3 concentrations were calculated by averaging the maximum concentrations of 8-h (8-h O3). Four seasons were defined as the following categories: spring (March to May), summer (June to August), fall (September to November), and winter (December to February). Pearson correlation analyses were then conducted between each meteorological parameter (T, RH, and WS) and pollutant concentration for each season in each city whereby we used routines of the software MATLAB. Besides, we screened out the heavily polluted days (when the ambient air quality index was more than 150), determined their wind direction as the one with the highest frequency, and calculated the cumulative contribution ratios of each wind direction. Eight wind directions were categorized in this study: N (337.5–22.5°), NE (22.5–67.5°), E (67.5–112.5°), SE (112.5–157.5°), S (157.5–202.5°), SW (202.5–247.5°), W (247.5–292.5°), NW (292.5–337.5°).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Data Overview
Figure 2 shows the annual mean concentrations of PM2.5, PM10, SO2, CO, NO2, and 8-h O3 in Beijing and Nanjing during the study period. For all six air pollutants (except 8-h O3 in Beijing and NO2 in Nanjing), downward trends were observed in their annual averaged concentrations, indicating the positive effects of China’s National Air Pollution Control Action Plan since 2013. However, air pollution needs to be controlled continuously, as evidenced by the frequent occurrence of polluted days in both Beijing and Nanjing. For example, the annual averaged PM2.5 concentrations in 2017 were 49.6 μg m−3 (Beijing) and 43.3 μg m−3 (Nanjing), respectively, far exceeding the Chinese Ambient Air Quality Standards (CAAQS: 15 μg m−3 for Grade I and 35 μg m−3 for Grade II). Similarly, the annual average concentrations of PM10 in 2017 were also higher than the CAAQS Grade II (70 μg m−3). Further, the daily average concentrations of PM2.5 and PM10 in 2017 still often exceeded the 24 h standards (Beijing: 69 days and 25 days, Nanjing: 45 days and 28 days, respectively) (Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6). As for the gaseous species, their concentrations in Nanjing were generally higher than those in Beijing, especially in 2017. This result was quite different from that reported in previous studies, which may be partially explained by the policy factors [24]. Policies of emission reduction (e.g., replacing coal supply with gas supply, upgrading of industrial structure) were implemented more effectively in Beijing than Nanjing these years [25,26]. Generally, SO2 and CO concentrations in both Beijing and Nanjing met the Grade II annual or daily standards of CAAQS. The annual averaged NO2 concentration in Beijing was higher than that in Nanjing in 2016, while contrasting results were observed in 2017. Nanjing had higher 8-h O3 concentrations than Beijing, which was in compliance with their latitudinal distribution. It should be noted that the concentrations of 8-h O3 in both cities have not been decreased markedly, and thus more attention should be paid to the control of O3 and the risks of population exposure to O3.
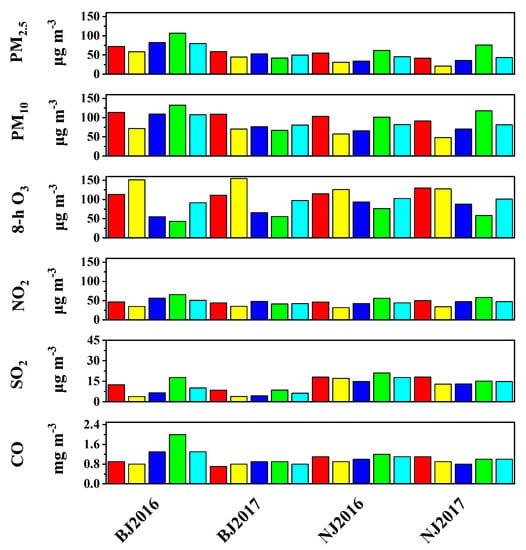
Figure 2.
Seasonal and annual average concentrations of six criteria air pollutants in different cities and years. Red, yellow, dark blue, green, and light blue represent spring, summer, fall, winter, and annual values, respectively.
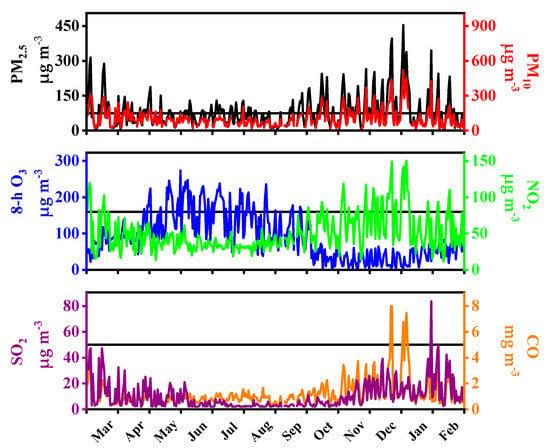
Figure 3.
Daily average concentrations of PM2.5, PM10, CO, NO2, SO2, and 8-h O3 in Beijing in 2016. The horizontal black lines represent the Grade II daily standards of Chinese Ambient Air Quality Standards (CAAQS) for PM2.5, PM10, NO2, and 8-h O3, the Grade I daily standards of CAAQS for SO2 and CO.
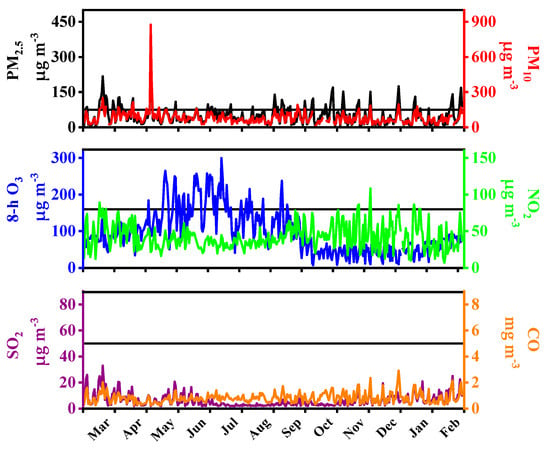
Figure 4.
Daily average concentrations of PM2.5, PM10, CO, NO2, SO2, and 8-h O3 in Beijing in 2017. The horizontal black lines represent the Grade II daily standards of Chinese Ambient Air Quality Standards (CAAQS) for PM2.5, PM10, NO2, and 8-h O3, the Grade I daily standards of CAAQS for SO2 and CO.
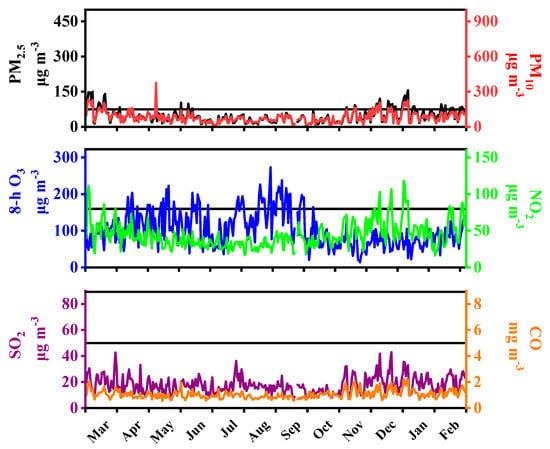
Figure 5.
Daily average concentrations of PM2.5, PM10, CO, NO2, SO2, and 8-h O3 in Nanjing in 2016. The horizontal black lines represent the Grade II daily standards of Chinese Ambient Air Quality Standards (CAAQS) for PM2.5, PM10, NO2, and 8-h O3, the Grade I daily standards of CAAQS for SO2 and CO.
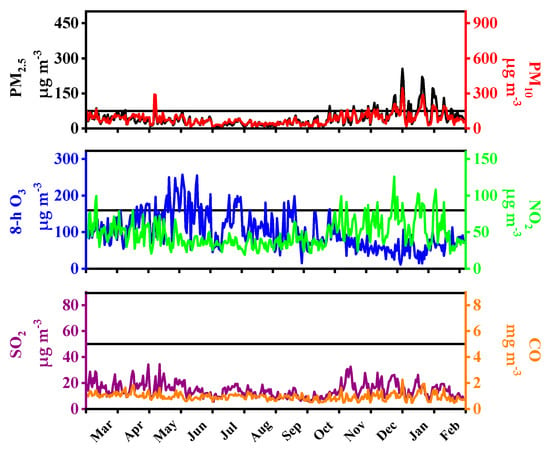
Figure 6.
Daily average concentrations of PM2.5, PM10, CO, NO2, SO2, and 8-h O3 in Nanjing in 2017. The horizontal black lines represent the Grade II daily standards of Chinese Ambient Air Quality Standards (CAAQS) for PM2.5, PM10, NO2, and 8-h O3, the Grade I daily standards of CAAQS for SO2 and CO.
Meteorological condition is an important factor affecting the distribution of air pollutants. Figure 7 shows the statistical average of meteorological parameters including temperature (T), relative humidity (RH), and wind scale (WS). The southern city Nanjing is warmer than Beijing, with the annual average temperature 16.9 vs. 13.6 °C in 2016 and 18.0 vs. 13.5 °C in 2017. Nanjing also had higher annual RH than Beijing, especially in winter. Besides, the annual average WS was higher in Nanjing, which may be related to thunderstorms and typhoons. Our results are consistent with those of Zhang et al. [27] who found that Beijing had the lowest annual average wind speed, although its daily maximum wind speed was the highest among three megacities in China.
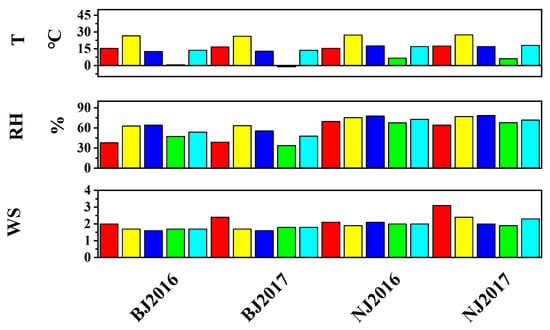
Figure 7.
Seasonal and annual average measurements of ambient temperature (T, °C), relative humidity (RH, %), and surface wind scale (WS) in different cities and years. Red, yellow, dark blue, green, and light blue represent spring, summer, fall, winter, and annual values, respectively.
3.2. Hourly Variations of Pollutants in Two Cities
In this study, the annual mean concentrations of each hour within a daily cycle were analyzed to explore the characteristics of diurnal variation in six air pollutants (Figure 8). PM10 concentrations exhibited two peaks in both Beijing and Nanjing. PM10 reached its first peak value in the morning, in accordance with the morning rush hours as well as the peaks of NO2 and CO, indicating that primary emissions make an important contribution during this period. After that, the concentrations of PM10 decreased, fell to the trough value in the afternoon, and then peaked again during the evening rush hours. It should be noted that the peak/trough time occurred a little later in Nanjing than that in Beijing, which corresponds to the different life/work schedules between these two cities (i.e., people that live in North China, generally wake up earlier and have an earlier bedtime than those in a southern city). PM2.5 revealed a trend similar to, but less obvious than, that of PM10, especially at the rush hours, indicating the greater contributions of vehicle emissions to PM10 pollution. Besides, the bimodal patterns of PM10 and PM2.5 were opposite to the changes of boundary layer height [28]. These results collectively indicate that both atmospheric boundary layer height and anthropogenic emissions greatly affect the concentrations of air pollutants.
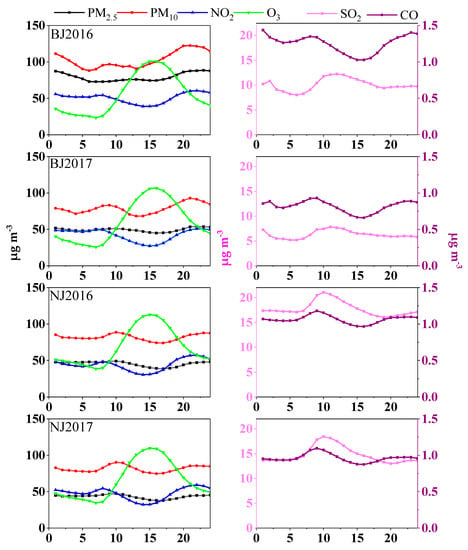
Figure 8.
Diurnal variation of six criteria air pollutants in different cities and years.
SO2 concentrations showed a unimodal pattern in Nanjing: the peak value appeared at around 10:00 am, mainly because of the increased emissions and the unfavorable diffusion conditions. In the evening (1:00–2:00 am), due to the diesel vehicle emissions, high SO2 concentrations were consistent with high levels of PM10, PM2.5, NO2, and CO in Beijing. As CO can be adopted as an indicator of boundary layer height (i.e., an increase in CO indicates a decrease in boundary layer height [29]), unfavorable diffusion conditions also resulted in high concentrations of these pollutants shortly after midnight. Diurnal variation of CO also exerted a double-peak curve, implying that automobile exhaust was the main source of CO [30]. Further, the hourly average concentrations of CO were higher in Beijing than those in Nanjing in 2016, while contrasting results were recorded in the year 2017. Such differences could be ascribed, at least partially, to the traffic control measures enforced in Beijing. The diurnal changes of NO2 were similar to those of CO, implying their same source from vehicle emissions [31]. Apart from diffusion conditions, the reduced NO2 in the afternoon could be explained by the enhanced solar radiation for photolysis [32]. Different from other pollutants, O3 concentrations showed a trough value at around 7:00–8:00 am. With increasing temperature and solar radiation in the afternoon, an obvious photochemical reaction occurred (i.e., NOx + volatile organic compounds (VOCs) + hv → O3 [33]), as evidenced by the sharply increased O3 concentrations accompanied by the decreased NO2 and CO concentrations.
3.3. Seasonal Variations of Air Pollutants and Meteorological Parameters
As air pollutants and meteorological conditions varied greatly in different temporal scales, Figure 2 and Figure 7 also show the seasonal variations of all pollutants and meteorological parameters. Generally, the concentrations of PM2.5 peaked in winter, followed by spring or fall, and summer, successively. In Beijing, this may be related to the coal-burning central heating, leading to more PM2.5 emissions in winter. Further, temperature inversion layers led to a reduced exchange between the atmospheric boundary layer and the free troposphere, and seasonal changes in vertical temperature gradient also accounted for the observed winter pollution. Besides, rainy weather in summer is conductive to scavenging the air pollutants [34]. In 2017, however, PM2.5 concentrations decreased significantly in Beijing in every season, especially in winter, with much lower average PM2.5 concentrations (42.0 μg m−3) than those in other seasons. Therefore, marked improvement in air quality in Beijing has been recorded, and the public had witnessed many clear and blue sky days during that period. PM10 had similar downward changes as PM2.5 in Beijing in the year of 2017, while its highest concentrations often appeared in spring or winter. Similarly, NO2 and SO2 concentrations in Beijing and Nanjing were often highest in spring or winter, while lowest in summer. In contrast, the highest 8-h O3 concentrations occurred in summer (except in NJ2017), followed by spring, fall, and winter, which has lower solar radiation and is unfavorable for O3 production [35]. In both cities, average CO concentrations in all seasons were comparable.
As expected, T, RH, and WS also showed remarkable seasonal variations. Average temperatures of Nanjing in all seasons were higher than those in Beijing. In both cities, the values of T peaked in summer, followed by spring, fall, and winter (except NJ2016), although the differences among seasons were smaller in Nanjing, especially between spring and fall. In Beijing, summer and fall had higher average RH than spring and winter. The lowest RH value was recorded in the winter of 2017 (33.7%). Significantly higher levels of RH were observed in Nanjing in all seasons, with narrow ranges (64.0%–78.4%). Identically, Beijing had lower seasonal average WS, which was higher in spring and winter and lower in summer and fall. In Nanjing, WS was very close among all seasons except in the spring of 2017. Seasonal distributions of wind direction in Beijing and Nanjing were analyzed (data not shown). In Beijing, southwest and northeast winds were prevalent in 2016, although north wind was frequent in winter with large wind speed. Southwest wind dominated wind direction in the spring, summer, and winter of 2017, while northeast wind dominated in fall. It should be noted that northwest wind occurred frequently in the winter of 2017. Since there are few anthropogenic emissions upwind of Beijing, clean wind from northwestern diluted the pollutants from industrial areas in southwest and northeast, resulting in reduced air pollutants. In Nanjing, the wind was mostly from east in each season. North wind was slightly more frequent in fall and winter, which could transport pollutants from many large chemical plants located to the north of Nanjing. Besides, north wind near surface was not strong enough to blow the pollutants away [36].
3.4. Correlation between Air Pollutants and Meteorological Factors
To better understand the relationship between pollutants (PM2.5, PM10, SO2, CO, NO2, and 8-h O3) and meteorological factors (T, RH, and WS), regression analyses were conducted across different seasons to calculate their correlation coefficients (Figure 9). In both Beijing and Nanjing, concentrations of most air pollutants (except 8-h O3) were negatively correlated with WS in all seasons, with a few exceptions in summer. WS determines horizontal transportation distance per unit time. Air pollutants began to accumulate under the stagnant weather conditions. The higher the WS, the more effective in pollutant removal. Generally, gaseous pollutants are more likely to be diluted or reacted than particulate pollutants [37], and thus stronger correlations exist between WS and gaseous pollutants than those between WS and PM2.5/PM10. Han et al. [38] also found that wind speed was the most important meteorological factor affecting pollutant distribution. For the secondary pollutant O3, however, the dilution of particulate pollutants by wind could increase solar radiation, and then facilitate O3 formation [39]. As a result, 8-h O3 concentrations had a positive relation with WS.
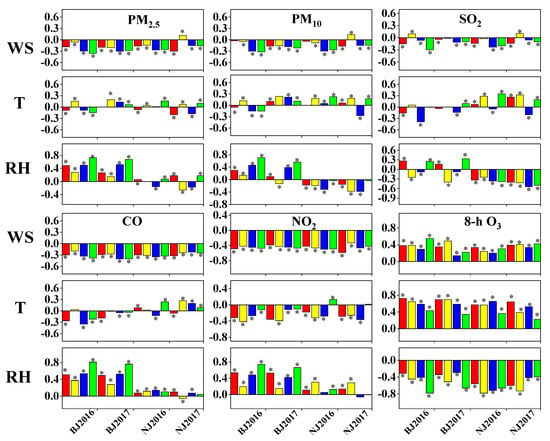
Figure 9.
Correlations between six criteria air pollutants and meteorological factors: surface wind scale (WS), ambient temperature (T), and relative humidity (RH). Red, yellow, blue, and green represent spring, summer, fall, and winter, respectively. * indicates the significant level at 95%.
The relationships between air pollutants and RH were complicated. In Beijing, PM2.5, PM10, SO2, CO, and NO2 concentrations were positively correlated with RH in most cases, especially in winter. Under high humidity conditions, aerosols can absorb more semi-volatile species for growth, thus leading to an increase in PM concentrations [40]. In addition, high RH favors the formation of temperature inversion, which makes the atmospheric stratification stable and hinders the vertical diffusion of pollutants [41]. However, in high RH seasons in Beijing (e.g., summer) or moist Nanjing, PM2.5, PM10, and soluble SO2 (with high Henry constant 1.64 bar [42]) had negative correlations with RH, which could be partially explained by the wet scavenging effects [43]. Although we did not collect rainfall data, the association of high RH with precipitation has been demonstrated in southern China, which can facilitate pollutant deposition [44]. The concentrations of 8-h O3 were negatively correlated with RH in all seasons in both cities. Cloud cover was positively correlated with relative humidity, thus high RH always reduces the UV light intensity, which drives the O3 concentrations and the surface air temperature [45]. As expected, 8-h O3 had the strongest positive correlation with T, which was due to the important role of temperature in O3 formation [46]. In contrast, NO2 values were negatively correlated with T, which was due to the transformation of NO2 to O3 and the vertical dispersion under high temperature conditions [47]. Only weak correlations were observed between T and other air pollutants.
In general, PM2.5, PM10, SO2, CO, and NO2 had a higher correlation with WS and RH, while 8-h O3 was more closely related to T and RH. Such relationships are consistent with those of Wagner [48] who found that WS affected primary pollutants (PM2.5, PM10, SO2, CO, and NO2) but T influenced secondary pollutant O3. In Beijing, although PM2.5, PM10, SO2, CO, and NO2 concentrations decreased significantly from the year 2016 to 2017, seasonal average WS showed only a slight increase, indicating the limited role of WS in the air quality improvement in 2017. Nevertheless, RH was lower in the fall and winter of 2017 than that in 2016, which might contribute greatly to the downward trend in these five pollutants on a yearly basis. In the case of 8-h O3, decreased RH in fall and winter, together with increased T in spring and fall, resulted in increased 8-h O3 concentrations in the year 2017 in Beijing. In Nanjing, WS, RH, and T fluctuated between 2016 and 2017 in the same season, with relatively narrow ranges, leading to relatively stable concentrations of PM2.5, PM10, SO2, CO, NO2, and 8-h O3 in 2017.
3.5. Contribution of Wind Directions to Heavily Polluted Days
Apart from WS, T, and RH, wind directions are thought to affect air quality greatly. We further analyzed the contributions of wind directions in heavily polluted days (i.e., the heavily polluted days of each wind direction divided by the total heavily polluted days in Beijing or Nanjing each year, Figure 10). In 2016, southwest and northeast winds contributed the majority of the heavily polluted days in Beijing, followed by east wind. The contributions of wind directions in 2017 were generally different, with an obviously increased proportion of southwest wind. Such patterns could be explained by regional transport. Baoding, Shijiazhuang, and Handan, the major industrial cities in North China, are located to the southwest of Beijing. There are also many heavy industrial cities located to the northeast of Beijing, such as Shenyang, Anshan, and Fushun. Wind from these directions transports pollutants and worsens the air quality of Beijing. These results are consistent with the findings of Ma et al. [49] and Zhang et al. [50]. In addition, Beijing is located on the northern edge of the North China Plain, surrounded by mountains on three sides. When southwest or northeast wind dominated, the diffusion and dilution of pollutants would be hindered, which might be another reason why these wind directions deteriorate air pollution in Beijing. In Nanjing, heavy air pollution was most closely related to east wind, followed by southwest wind, northwest wind, and north wind. A series of cities including Suzhou, Changzhou, Wuxi, and Zhenjiang constitute the industrial center of the Yangtze River Delta, located to the east and southeast of Nanjing. Besides, there are a few large petrochemical plants in the north of Nanjing. These results collectively indicate the importance of regional transport in pollutant concentrations.
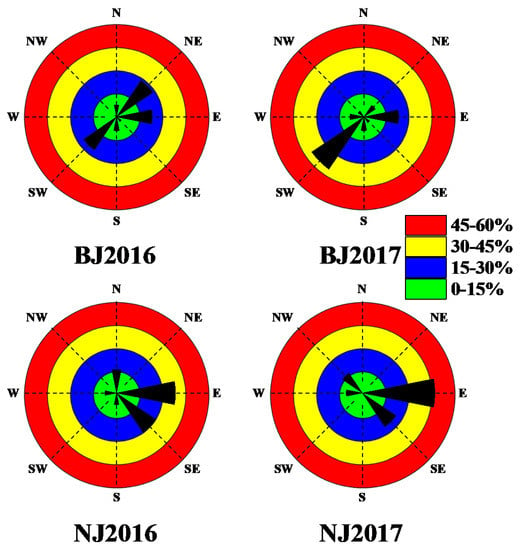
Figure 10.
Distributions of heavily polluted days (when the ambient air quality index was more than 150) according to their respective wind directions.
4. Conclusions
This paper comparatively analyzed the temporal characteristics of air pollutants from March, 2016 to February, 2018, in a northern (Beijing) and a southern (Nanjing) city in China. Generally, there were downward trends in the annual mean concentrations of PM2.5, PM10, SO2, CO, and NO2, implying the effective implementation of emission reduction targets. Conversely, the concentrations of 8-h O3 exerted a stable or even upward trend, and thus more attention should be paid to the exposure of humans to O3 in these cities.
As expected, Beijing experienced more severe air pollution problems than Nanjing in 2016, which may be associated with the winter heating and unfavorable dispersion conditions in northern cities. However, in 2017, the concentrations of most air pollutants were lower in Beijing than those in Nanjing. Therefore, meteorological data during the same period were collected to explore their relationship with air pollutants. Our results reveal that PM2.5, PM10, SO2, CO, and NO2 are generally correlated with WS and RH, while 8-h O3 is correlated to T and anti-correlated to RH. A slight increase in seasonal average WS, marked decrease in RH, as well as the more frequent northwest wind in winter, resulted in an improved air quality in BJ2017. In contrast, WS, RH, T, and wind direction remained relatively constant between 2016 and 2017 in the same season, leading to relatively stable concentrations of PM2.5, PM10, SO2, CO, NO2, and 8-h O3 in NJ2017. Our results suggest that meteorological conditions play an important role in ambient air pollution, which should be considered in decision-making processes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Y.W.; methodology: H.Z.; software: H.Y. and J.G.; Validation: Y.Y. and Y.W.; formal analysis: H.Z. and Y.Y.; Investigation: H.Z. and X.G.; resources: M.W., H.Y., J.G., and R.L.; data curation: M.W., H.Y., J.G., and R.L.; writing-original draft preparation: Y.W.; writing-review and editing: Y.W. and X.G.; supervision: X.G.; project administration: X.G.; funding acquisition: X.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D program of China (grant number 2018YFC0213802), Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 21976093, 21777073, 41601090, and 41877337), and the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for College Students in Jiangsu Province (grant number 201810300095X).
Conflicts of Interest
None.
References
- Lyu, W.; Li, Y.; Guan, D.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z. Driving forces of Chinese primary air pollution emissions: An index decomposition analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 133, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Peng, H.; Temulun, T.; Liu, L.-Q.; Mao, J.; Lu, Z.-N.; Chen, H. How harmful is air pollution to economic development? New evidence from PM2.5 concentrations of Chinese cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 743–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Wu, L.; Xie, Y.; He, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, T.; Lin, Y.; Jin, T.; Wang, A.; Liu, Y.; et al. Air pollution in China: Status and spatiotemporal variations. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Zhou, L.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, T.; Guo, Y.; Wellenius, G.A.; Bassig, B.A.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Zheng, X. Short-term effects of air pollution on daily mortality and years of life lost in Nanjing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maji, K.J.; Dikshit, A.K.; Arora, M.; Deshpande, A. Estimating premature mortality attributable to PM2.5 exposure and benefit of air pollution control policies in China for 2020. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohde, R.A.; Muller, R.A. Air Pollution in China: Mapping of Concentrations and Sources. PLoS. ONE 2015, 10, e0135749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, H.D. Environment and Health in China: Challenges and Opportunities. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, A530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, B.; Reddington, C.L.; Arnold, S.R.; Spracklen, D.V. Substantial changes in air pollution across China during 2015–2017. Environ Res. Lett. 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-C.; Klemeš, J.J.; Dong, X.; Fan, W.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Varbanov, P.; Reviews, S.E. Air pollution terrain nexus: A review considering energy generation and consumption. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2019, 105, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cheng, S.; Yao, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J. Multiple perspectives for modeling regional PM2.5 transport across cities in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region during haze episodes. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 212, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; He, W.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, J.; Wu, X.; Wu, W.; Li, X.; Yin, C. Influence of Low Impact Development practices on urban diffuse pollutant transport process at catchment scale. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 213, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Ma, J.; Shen, G.; Shen, H.; Zhu, X.; Yun, X.; Meng, W.; Cheng, H.; Liu, J.; Li, B.; et al. Distinguishing Emission-Associated Ambient Air PM2.5 Concentrations and Meteorological Factor-Induced Fluctuations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10416–10425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Nie, D.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Shi, Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Chen, M.; Ge, X.; et al. Evaluation of particulate matter deposition in the human respiratory tract during winter in Nanjing using size and chemically resolved ambient measurements. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2019, 12, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Cheng, T.; Gu, X.; Shi, S.; Wang, W.; Wu, Y.; Bao, F. Contribution of meteorological factors to particulate pollution during winters in Beijing. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Song, H.; Zhai, S.; Lu, S.; Kong, Y.; Xia, H.; Zhao, H. Particulate matter pollution in Chinese cities: Areal-temporal variations and their relationships with meteorological conditions (2015–2017). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, Z.; Cui, L.; Fu, H.; Zhang, L.; Kong, L.; Chen, W.; Chen, J. Air pollution characteristics in China during 2015-2016: Spatiotemporal variations and key meteorological factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 902–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Gong, S.; Yu, Y.; Yu, L.; Wu, L.; Mao, H.; Song, C.; Zhao, S.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; et al. Air pollution characteristics and their relation to meteorological conditions during 2014–2015 in major Chinese cities. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Chang, W.; Yang, Y. Climatic effects of air pollutants over china: A review. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 32, 115–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, S.; Zhao, Q.; Shen, G.; Wu, H. Seasonal variation of urban carbonaceous aerosols in a typical city Nanjing in Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 106, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Yu, X.; Zhu, B.; Kumar, K.R.; Li, M.; Li, L. Characterization and source apportionment of black carbon aerosol in the Nanjing Jiangbei New Area based on two years of measurements from Aethalometer. J. Aerosol Sci. 2020, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Jiao, L.; Yuan, M.; Dong, T.; Zhang, B.; Du, C. How does urban population density decline over time? An exponential model for Chinese cities with international comparisons. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 183, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Wang, X.; Hao, P.; Dong, L. Study on the microclimatic characteristics and human comfort of park plant communities in summer. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parungo, F.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, D.; Harris, J. Gobi dust storms and the Great Green Wall. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1994, 21, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, G.; He, K. Rapid transition in winter aerosol composition in Beijing from 2014 to 2017: Response to clean air actions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11485–11499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Tong, D.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Hong, C.; Geng, G.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Qi, J.; et al. Trends in China’s anthropogenic emissions since 2010 as the consequence of clean air actions. Atmos. Chem Phys. 2018, 18, 14095–14111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, T.; Ma, X.; Jia, H.; Tian, R.; Chang, Y.; Cao, F.; Zhang, Y. Aerosol chemical component: Simulations with WRF-Chem and comparison with observations in Nanjing. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Ying, Q.; Hu, X.M. Relationships between meteorological parameters and criteria air pollutants in three megacities in China. Environ. Res. 2015, 140, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Xu, J.; Tie, X.; Mao, X.; Gao, W.; Chang, L. Long-term measurements of planetary boundary layer height and interactions with PM2.5 in Shanghai, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Hu, M.; Deng, Z.; Xiao, R.; Kondo, Y.; Takegawa, N.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhang, Y.J. The characteristics and origins of carbonaceous aerosol at a rural site of PRD in summer of 2006. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 1811–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wang, T.; Simpson, I.J.; Blake, D.R.; Yu, X.M.; Kwok, Y.H.; Li, Y.S. Source contributions to ambient VOCs and CO at a rural site in eastern China. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 4551–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltic, P.; Weilenmann, M. NO2/NO emissions of gasoline passenger cars and light-duty trucks with Euro-2 emission standard. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 5207–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Bian, H.; Feng, Y.; Liu, A.; Li, X.; Zeng, F.; Zhang, X. Analysis of the Relationship between O3, NO and NO2 in Tianjin, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2011, 11, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillman, S. Some theoretical results concerning O3-NOx-VOC chemistry and NOx-VOC indicators. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.-M.; Lee, Y.-R.; Kim, D.; Jeong, M.-J.; Stockwell, W.R.; Kundu, P.K.; Oh, S.-M.; Shin, D.-B.; Lee, S.-J. New indices for wet scavenging of air pollutants (O3, CO, NO2, SO2, and PM10) by summertime rain. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 82, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, C.; Palm, M.; Vigouroux, C.; Notholt, J.; Hu, Q.; Jones, N.; Wang, W.; Su, W.; Zhang, W.; et al. Ozone seasonal evolution and photochemical production regime in the polluted troposphere in eastern China derived from high-resolution Fourier transform spectrometry (FTS) observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14569–14583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Li, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Tang, G.; Tao, J. Spatial oscillation of the particle pollution in eastern China during winter: Implications for regional air quality and climate. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 144, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, C.A.; Mukerjee, S.; Gonzales, M.; Rodes, C.E.; Lawless, P.A.; Natarajan, S.; Myers, E.A.; Norris, G.A.; Smith, L.; Ière, M.; et al. Ozoeasurement of fine and ultrafine particulate matter, criteria pollutants and meteorological conditions in urban El Paso, Texas. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 37, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Meshesha, D.T.; Li, L.; Zheng, M. Meteorological and urban landscape factors on severe air pollution in Beijing. J. Air Waste Manag. 2015, 65, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banta, R.M.; Senff, C.J.; Alvarez, R.J.; Langford, A.O.; Parrish, D.D.; Trainer, M.K.; Darby, L.S.; Michael Hardesty, R.; Lambeth, B.; Andrew Neuman, J. Dependence of daily peak O3 concentrations near Houston, Texas on environmental factors: Wind speed, temperature, and boundary-layer depth. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, B.; Cui, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, R.; Zhang, L.; Fu, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Qiong, A. Observations of atmospheric pollutants at Lhasa during 2014-2015: Pollution status and the influence of meteorological factors. J. Environ. Sci. (China) 2018, 63, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ji, Z.; Kang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Lee, S.Y. Spatiotemporal variations of air pollutants in western China and their relationship to meteorological factors and emission sources. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.L.; Dixon, J.K.; Maginn, E.J.; Brennecke, J. Measurement of SO2 solubility in ionic liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2006, 110, 15059–15062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, W.; Altwicker, E.; Asman, W. Numerical simulation of wet scavenging of air pollutants. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1990, 24, 2485–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.M.; Tai, A.P.K.; Mickley, L.J.; Moch, J.M.; Donkelaar, A.; Shen, L.; Martin, R.V. Synoptic meteorological modes of variability for fine particulate matter (PM2.5) air quality in major metropolitan regions of China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 6733–6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walcek, C.J. Cloud cover and its relationship to relative humidity during a springtime midlatitude cyclone. Mon. Weather Rev. 1994, 122, 1021–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brion, J.; Chakir, A.; Daumont, D.; Malicet, J.; Parisse, C. High-resolution laboratory absorption cross section of O3. Temperature effect. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1993, 213, 610–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Situ, S.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Sha, C.; Zhouc, L.; Wu, L.; Wu, L.; Ye, L.; Li, C. The synergetic control of NO2 and O3 concentrations in a manufacturing city of southern China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 201, 402–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, E.J.E.M. Impacts on air pollution in urban areas. Environ. Manag. 1994, 18, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Xia, Y.; Liu, X.; Tian, P.; Han, Z.; Xia, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Roles of regional transport and heterogeneous reactions in the PM2.5 increase during winter haze episodes in Beijing. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, X.; Zhao, T.; Gong, S.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Luo, L.; Gui, K.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Y.; et al. A modelling study of the terrain effects on haze pollution in the Sichuan Basin. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 196, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).