Quantifying the Independent Influences of Land Cover and Humidity on Microscale Urban Air Temperature Variation in Hot Summer: Methods of Path Analysis and Genetic SVR
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
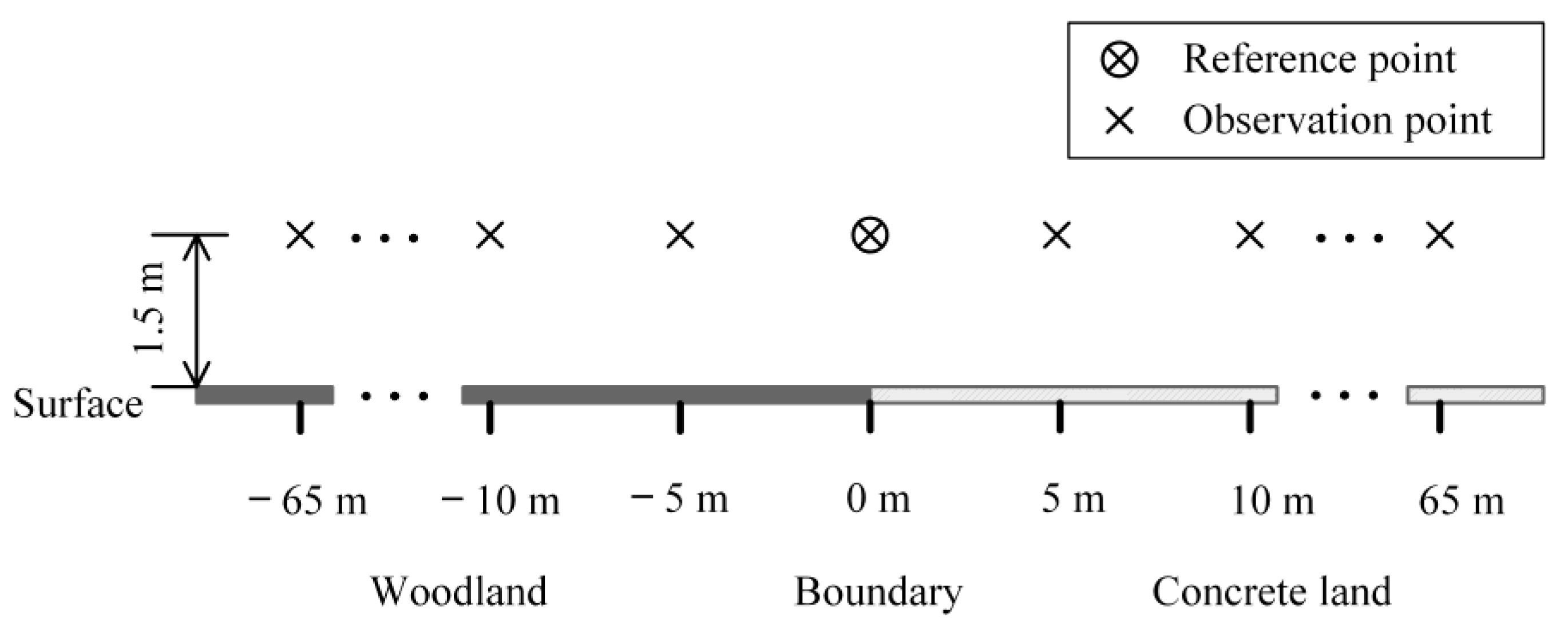
2.1. Field Measurements
2.2. Parameter Derivation and Variable Definition
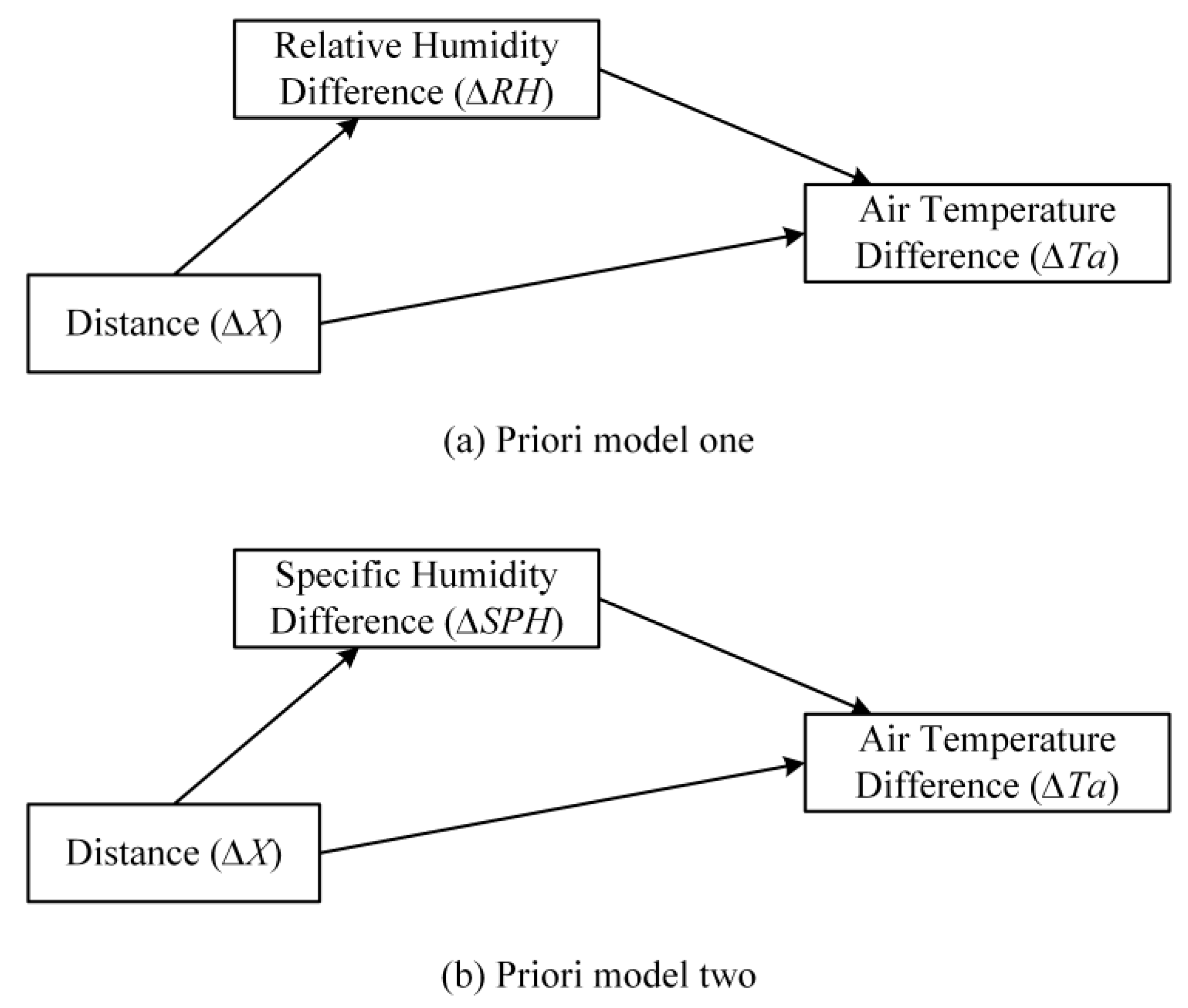
2.3. Path Analysis
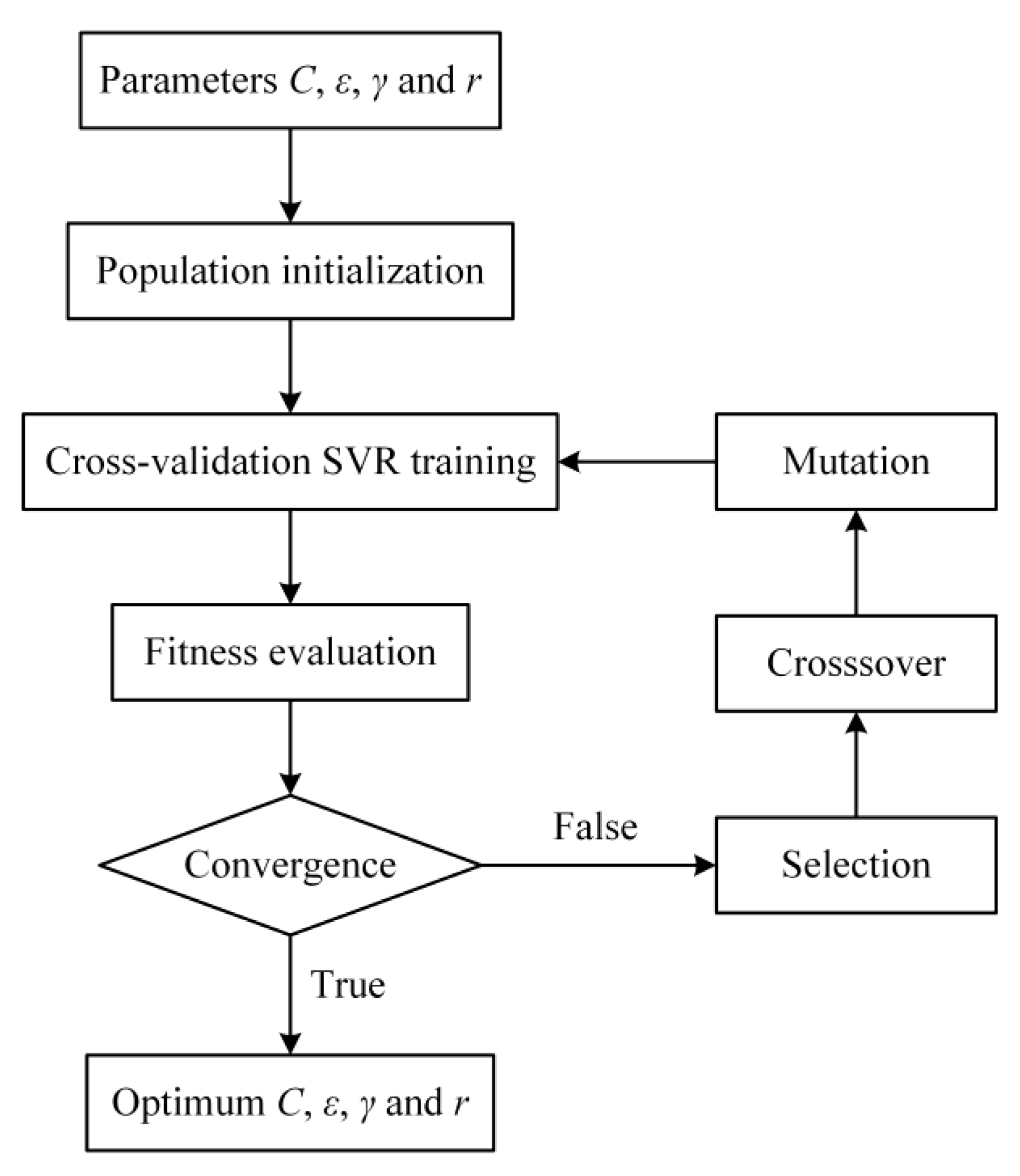
2.4. Genetic Support Vector Regression
2.4.1. Support Vector Regression
2.4.2. Genetic Algorithm to Optimize SVR Parameters
3. Results and Discussion
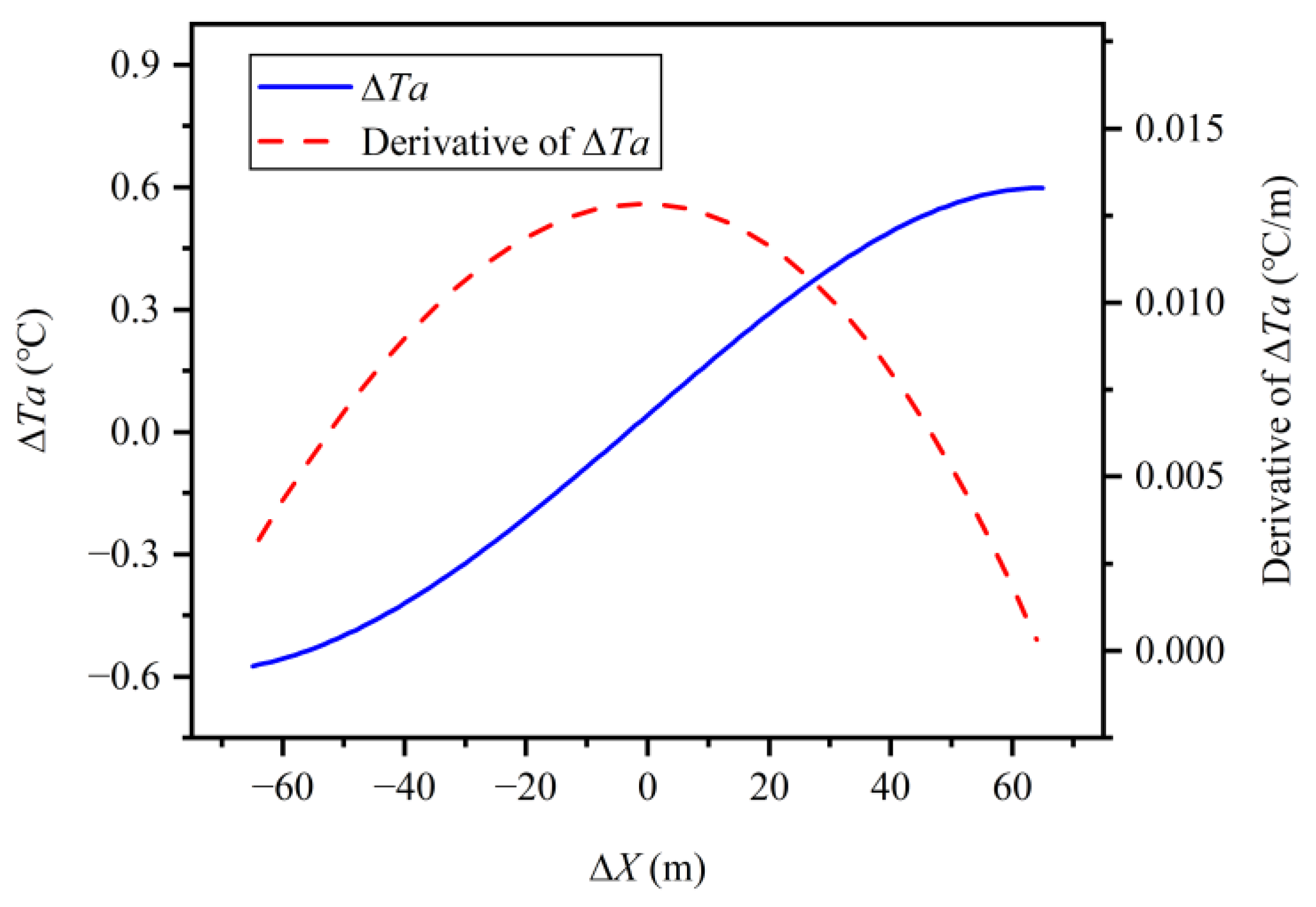
3.1. Distributions of ∆Ta and ∆RH of the Two Land Covers
3.2. Effects of Variables on ∆Ta in Priori Models
3.3. Independent Contributions of ∆X and ∆RH
3.4. Implication for High Air Temperature Mitigation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crutzen, P.J. New Directions: The growing urban heat and pollution “island” effect–Impact on chemistry and climate. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3539–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, D.J.; Winner, D.A. Effect of climate change on air quality. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.G.; Bell, M.L. Weather-Related Mortality How Heat, Cold, and Heat Waves Affect Mortality in the United States. Epidemiology 2009, 20, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ippoliti, D.; Michelozzi, P.; Marino, C.; de’Donato, F.; Menne, B.; Katsouyanni, K.; Kirchmayer, U.; Analitis, A.; Medina-Ramon, M.; Paldy, A.; et al. The impact of heat waves on mortality in 9 European cities: Results from the EuroHEAT project. Environ. Health 2010, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.W.; Mengersen, K.; Wang, X.Y.; Ye, X.F.; Guo, Y.M.; Pan, X.C.; Tong, S.L. Daily average temperature and mortality among the elderly: A meta-analysis and systematic review of epidemiological evidence. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2012, 56, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liu, H.Z.; Ou, C.Q.; Lin, G.Z.; Ding, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Shen, J.C.; Chen, P.Y. Impact of Heat Wave in 2005 on Mortality in Guangzhou, China. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2013, 26, 647–654. [Google Scholar]
- Mazdiyasni, O.; AghaKouchak, A.; Davis, S.J.; Madadgar, S.; Mehran, A.; Ragno, E.; Sadegh, M.; Sengupta, A.; Ghosh, S.; Dhanya, C.T.; et al. Increasing probability of mortality during Indian heat waves. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritze, T. The Effect of Heat and Cold Waves on the Mortality of Persons with Dementia in Germany. Sustainability 2020, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Park, C.; Lee, W.; Pehlivan, N.; Choi, M.; Jang, J.; Kim, H. Heatwave-Related Mortality Risk and the Risk-Based Definition of Heat Wave in South Korea: A Nationwide Time-Series Study for 2011–2017. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlegel, I.; Muthers, S.; Mucke, H.G.; Matzarakis, A. Comparison of Respiratory and Ischemic Heart Mortalities and their Relationship to the Thermal Environment. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oerlemans, J. Quantifying global warming from the retreat of glaciers. Science 1994, 264, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karl, T.R.; Trenberth, K.E. Modern global climate change. Science 2003, 302, 1719–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meehl, G.A.; Tebaldi, C. More intense, more frequent, and longer lasting heat waves in the 21st century. Science 2004, 305, 994–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, S.E.; Alexander, L.V.; Nairn, J.R. Increasing frequency, intensity and duration of observed global heatwaves and warm spells. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, J.P.; Diaz, F.J.A.; Garcia, J.A.G. Analysis of Extreme Temperature Events over the Iberian Peninsula during the 21st Century Using Dynamic Climate Projections Chosen Using Max-Stable Processes. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Zhou, N.F.; Chen, S.F. The Record-Breaking High Temperature over Europe in June of 2019. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaghmanesh, M.; Beecham, S.; Brien, C.J. Developing resilient green roofs in a dry climate. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.; Sato, M.; Ruedy, R.; Lacis, A.; Oinas, V. Global warming in the twenty-first century: An alternative scenario. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 9875–9880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, A.M.; Wu, G.X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.M. New proofs of the recent climate warming over the Tibetan Plateau as a result of the increasing greenhouse gases emissions. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 1396–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Cai, M. Impact of urbanization and land-use change on climate. Nature 2003, 423, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.J.; Yu, Y.; Yu, L.J.; Yin, C.M.; Liu, N.; Zhao, S.P.; Chen, X. Effect of soil texture and hydraulic parameters on WRF simulations in summer in east China. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2016, 17, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnfield, A.J. Two decades of urban climate research: A review of turbulence, exchanges of energy and water, and the urban heat island. Int. J. Climatol. 2003, 23, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arribas, A.; Gallardo, C.; Gaertner, M.A.; Castro, M. Sensitivity of the Iberian Peninsula climate to a land degradation. Clim. Dyn. 2003, 20, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, V. Urban surface modeling and the meso-scale impact of cities. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2006, 84, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielke, R.A. Land use and climate change. Science 2005, 310, 1625–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirmeyer, P.A.; Niyogi, D.; de Noblet-Ducoudre, N.; Dickinson, R.E.; Snyder, P.K. Impacts of land use change on climate. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 1905–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luck, G.W.; Smallbone, L.T.; O’Brien, R. Socio-Economics and Vegetation Change in Urban Ecosystems: Patterns in Space and Time. Ecosystems 2009, 12, 604–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowler, D.E.; Buyung-Ali, L.; Knight, T.M.; Pullin, A.S. Urban greening to cool towns and cities: A systematic review of the empirical evidence. Landsc. Urban Plann. 2010, 97, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deilami, K.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Liu, Y. Urban heat island effect: A systematic review of spatio-temporal factors, data, methods, and mitigation measures. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 67, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani-Beni, M.; Zhang, B.; Xie, G.D.; Xu, J. Impact of urban park’s tree, grass and waterbody on microclimate in hot summer days: A case study of Olympic Park in Beijing, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 32, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meili, N.; Manoli, G.; Burlando, P.; Bou-Zeid, E.; Chow, W.T.L.; Coutts, A.M.; Daly, E.; Nice, K.A.; Roth, M.; Tapper, N.J.; et al. An urban ecohydrological model to quantify the effect of vegetation on urban climate and hydrology (UT&C v1.0). Geosci. Model Dev. 2020, 13, 335–362. [Google Scholar]
- Myrup, L.O. A Numerical Model of the Urban Heat Island. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1969, 8, 908–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulpiani, G.; Di Giuseppe, E.; Di Perna, C.; D’Orazio, M.; Zinzi, M. Thermal comfort improvement in urban spaces with water spray systems: Field measurements and survey. Build. Environ. 2019, 156, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazeri, H.; Toparlar, Y.; Blocken, B.; Hensen, J.L.M. Simulating the cooling effects of water spray systems in urban landscapes: A computational fluid dynamics study in Rotterdam, The Netherlands. Landsc. Urban Plann. 2017, 159, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Li, X.F.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Z.Q. Modeling the influence of fountain on urban microclimate. Build. Simul. 2015, 8, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahed, J.; Kinab, E.; Ginestet, S.; Adolphe, L. Impact of urban heat island mitigation measures on microclimate and pedestrian comfort in a dense urban district of Lebanon. Sust. Cities Soc. 2020, 61, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Ulpiani, G. Water mist spray for outdoor cooling: A systematic review of technologies, methods and impacts. Appl. Energy 2019, 254, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.H.; Hou, M.T.; Jia, G.S.; Zhao, C.L.; Zhen, X.J.; Xu, Y.H. Comparison of surface and canopy urban heat islands within megacities of eastern China. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 156, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.J.; Feng, Z.L.; Liao, H.X.; Huang, B.; Peng, S.L.; Zhou, T. Spatial-temporal pattern of, and driving forces for, urban heat island in China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, F.W. On the Computation of Saturation Vapor Pressure. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1967, 6, 203–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomarken, A.J.; Waller, N.G. Structural equation modeling: Strengths, limitations, and misconceptions. Ann. Rev. Clin. Psych. 2005, 1, 31–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosseel, Y. lavaan: An R Package for Structural Equation Modeling. J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 48, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Lin, C.J. LIBSVM: A Library for Support Vector Machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2011, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.T.; Zhan, Z.C.; Long, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.C.; Yao, L. Comparative Study of SVM Methods Combined with Voxel Selection for Object Category Classification on fMRI Data. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamouris, M.; Ding, L.; Fiorito, F.; Oldfield, P.; Osmond, P.; Paolini, R.; Prasad, D.; Synnefa, A. Passive and active cooling for the outdoor built environment–Analysis and assessment of the cooling potential of mitigation technologies using performance data from 220 large scale projects. Sol. Energy 2017, 154, 14–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnham, C.; Nakao, M.; Nishioka, M.; Nabeshima, M.; Mizuno, T. Study of mist-cooling for semi-enclosed spaces in Osaka, Japan. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnham, C.; Emura, K.; Mizuno, T. Evaluation of cooling effects: Outdoor water mist fan. Build. Res. Inf. 2015, 43, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Ye, D.F.; Zhao, H.Z.; Liang, T.; Lin, Z.F.; Yin, H.; Yang, Y. The research and application of spray cooling technology in Shanghai Expo. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2011, 31, 3726–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Cai, J.; Lin, Z.F.; Zhang, Q.R.; Cui, Y.Z. Solving model of temperature and humidity profiles in spray cooling zone. Build. Environ. 2017, 123, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


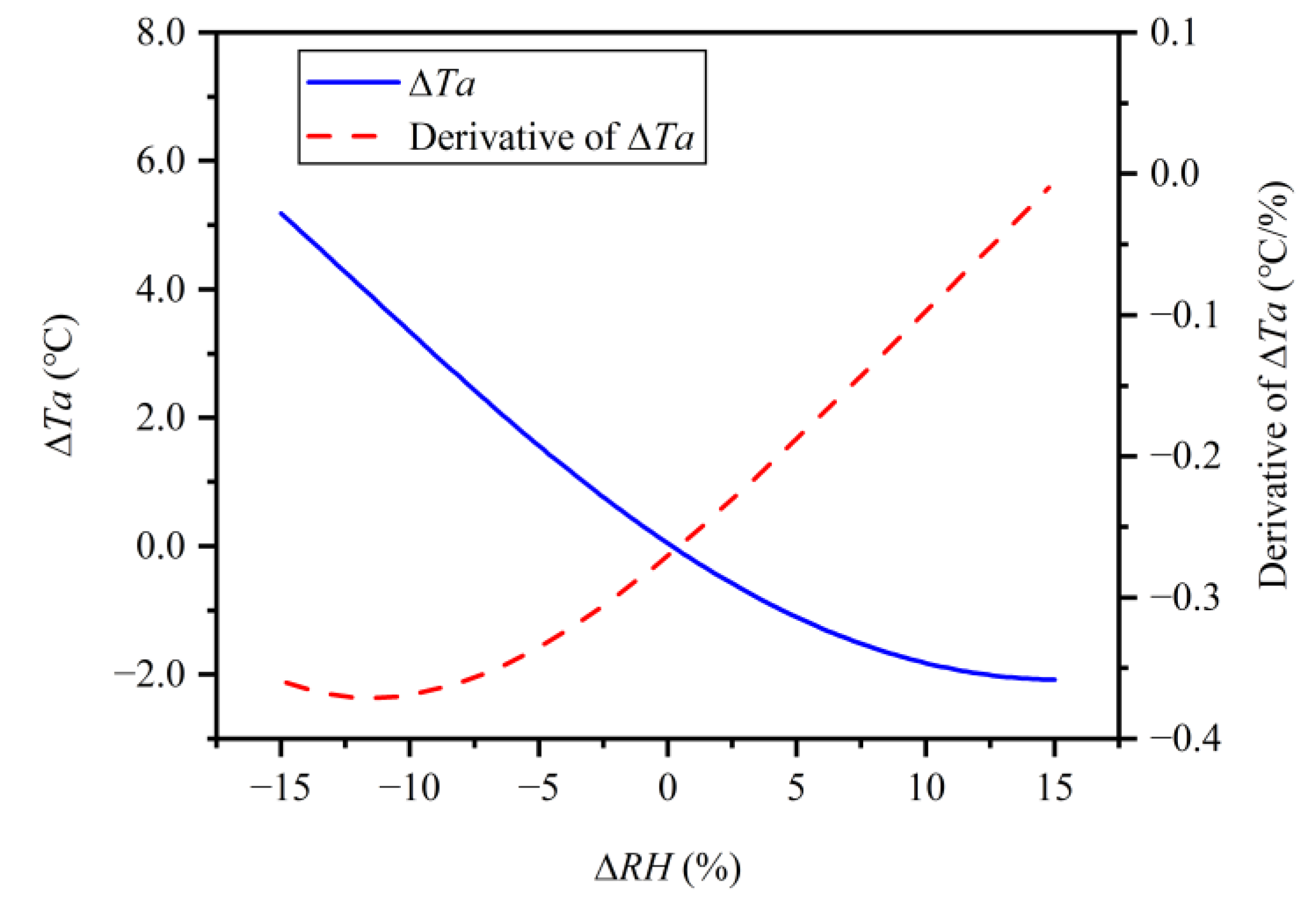
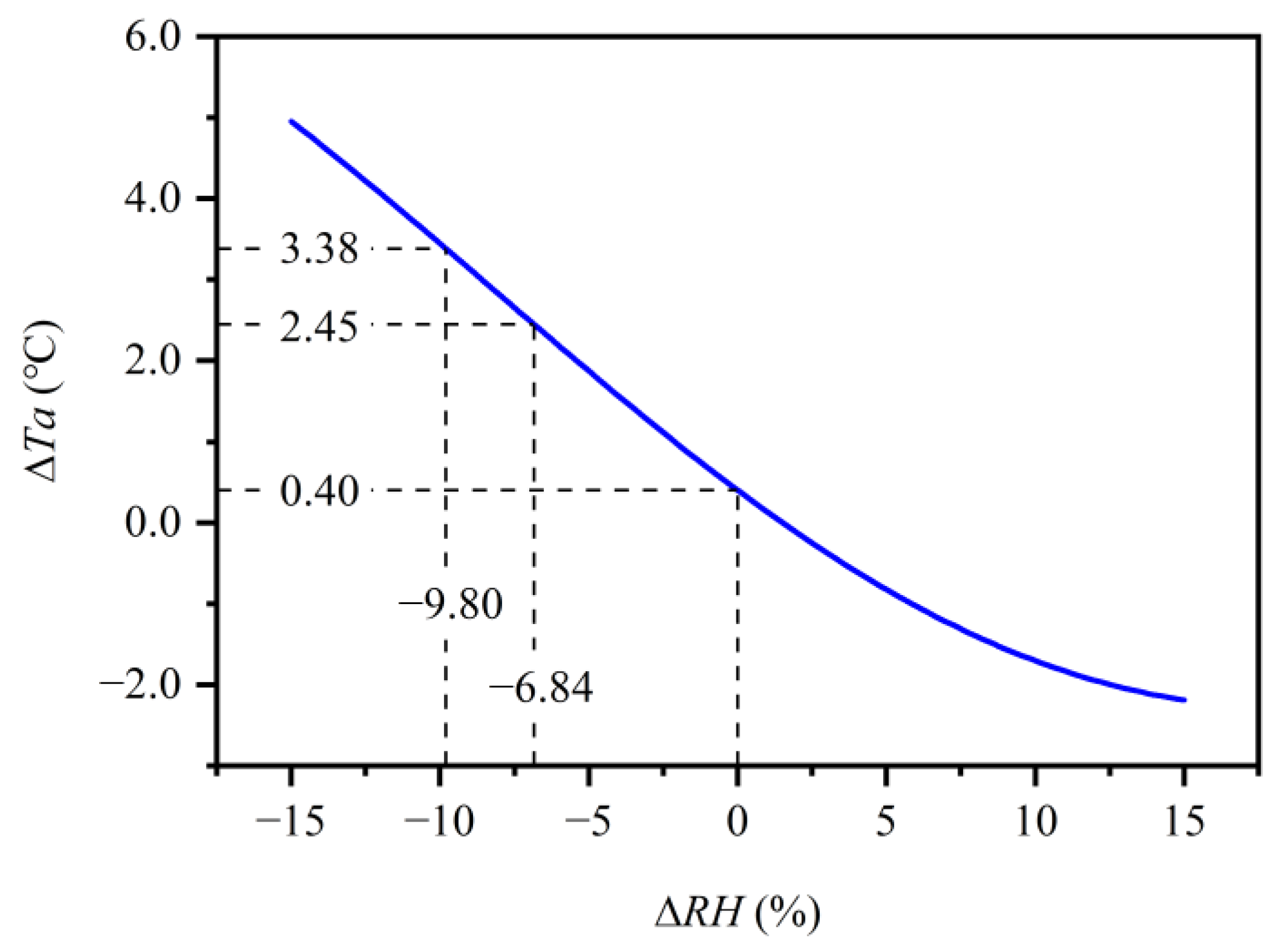
| Variable | Chi-Square | DF | Prob (> Chi-Square) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air Temperature Difference (∆Ta) | 94.13 | 1 | 0.0000 |
| Relative Humidity Difference (∆RH) | 83.26 | 1 | 0.0000 |
| Response Variable | Path | Standardized Path Coefficient | t-Statistic | Prob (> |t|) | R-Square |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air Temperature Difference (∆Ta) | ∆Ta ← ∆X 1 | 0.143 | 4.181 | 0.000 | 0.870 |
| ∆Ta ← ∆RH | −0.822 | −21.415 | 0.000 | ||
| Relative Humidity Difference (∆RH) | ∆RH ← ∆X | −0.740 | −12.741 | 0.000 | 0.547 |
| Response Variable | Path | Standardized Path Coefficient | t-Statistic | Prob (> |t|) | R-Square |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air Temperature Difference (∆Ta) | ∆Ta ← ∆X | 0.709 | 13.025 | 0.000 | 0.574 |
| ∆Ta ← ∆SPH | −0.109 | −1.764 | 0.040 | ||
| Specific Humidity Difference (∆SPH) | ∆SPH ← ∆X | −0.387 | −4.776 | 0.000 | 0.150 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, W.; Wang, N.; Xin, A.; Liu, L.; Hou, J.; Zhang, Y. Quantifying the Independent Influences of Land Cover and Humidity on Microscale Urban Air Temperature Variation in Hot Summer: Methods of Path Analysis and Genetic SVR. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121377
Shi W, Wang N, Xin A, Liu L, Hou J, Zhang Y. Quantifying the Independent Influences of Land Cover and Humidity on Microscale Urban Air Temperature Variation in Hot Summer: Methods of Path Analysis and Genetic SVR. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(12):1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121377
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Weifang, Nan Wang, Aixuan Xin, Linglan Liu, Jiaqi Hou, and Yirui Zhang. 2020. "Quantifying the Independent Influences of Land Cover and Humidity on Microscale Urban Air Temperature Variation in Hot Summer: Methods of Path Analysis and Genetic SVR" Atmosphere 11, no. 12: 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121377
APA StyleShi, W., Wang, N., Xin, A., Liu, L., Hou, J., & Zhang, Y. (2020). Quantifying the Independent Influences of Land Cover and Humidity on Microscale Urban Air Temperature Variation in Hot Summer: Methods of Path Analysis and Genetic SVR. Atmosphere, 11(12), 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121377




