The Lagged Effect of Anthropogenic Aerosol on East Asian Precipitation during the Summer Monsoon Season
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
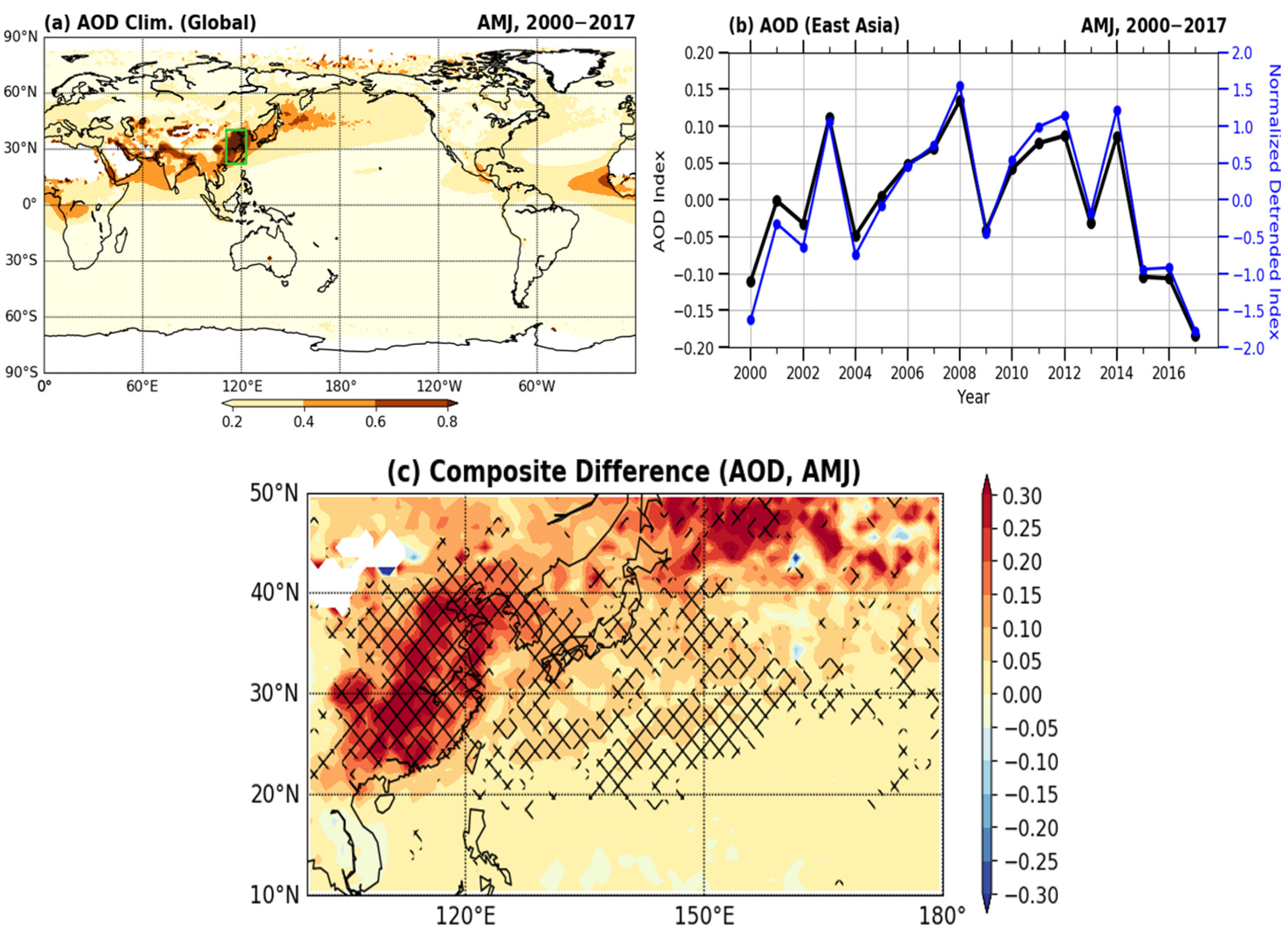
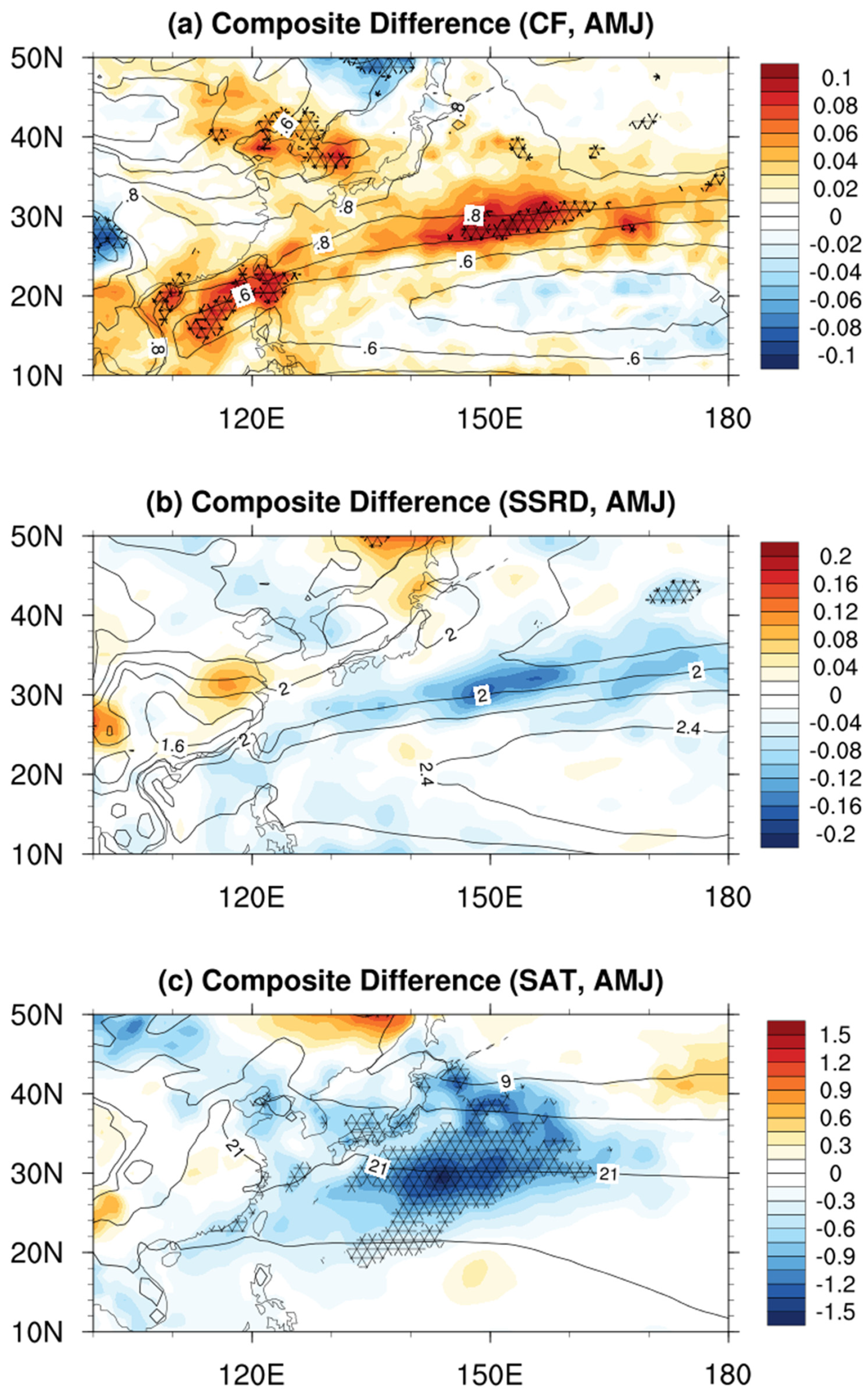
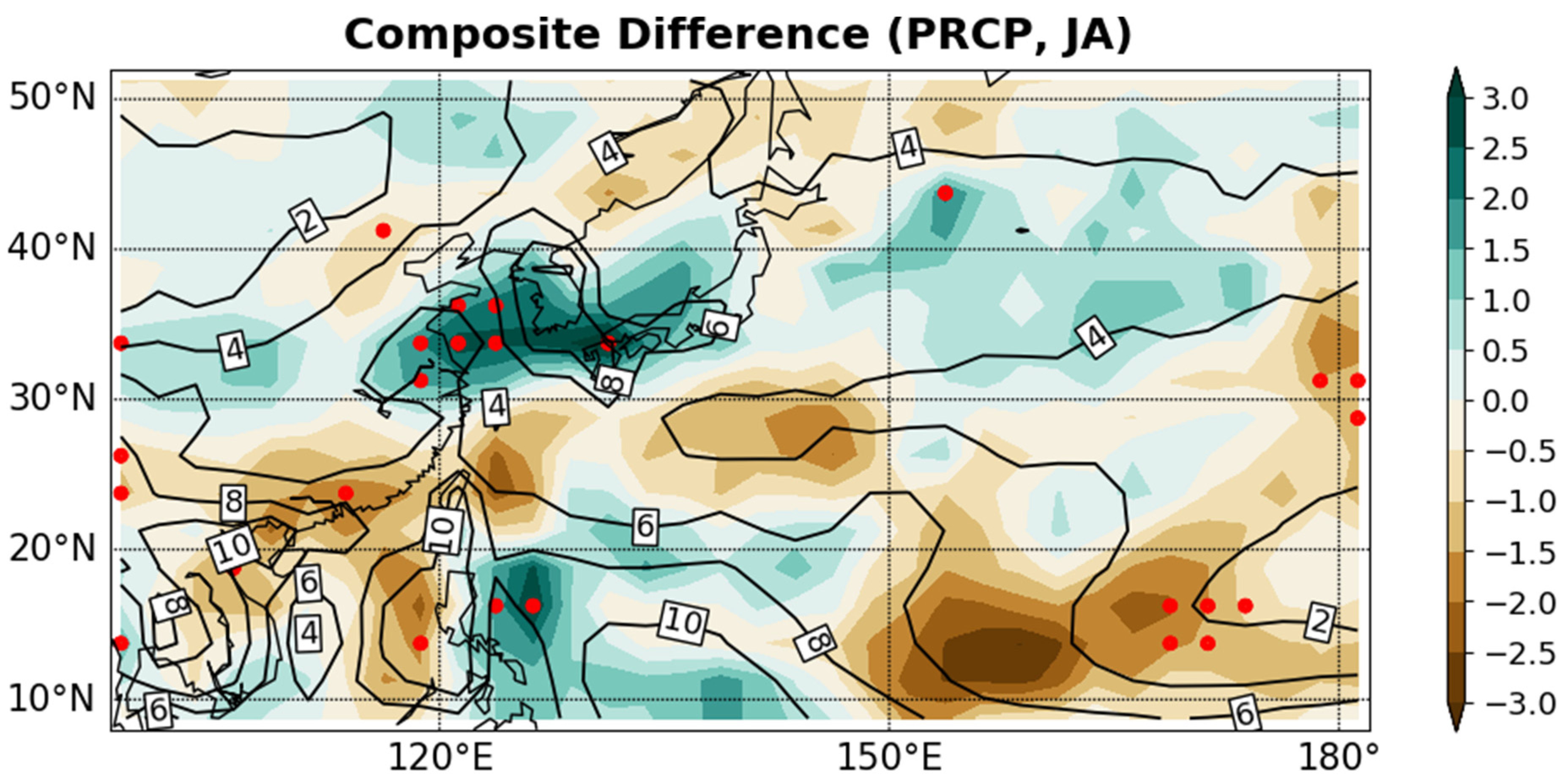
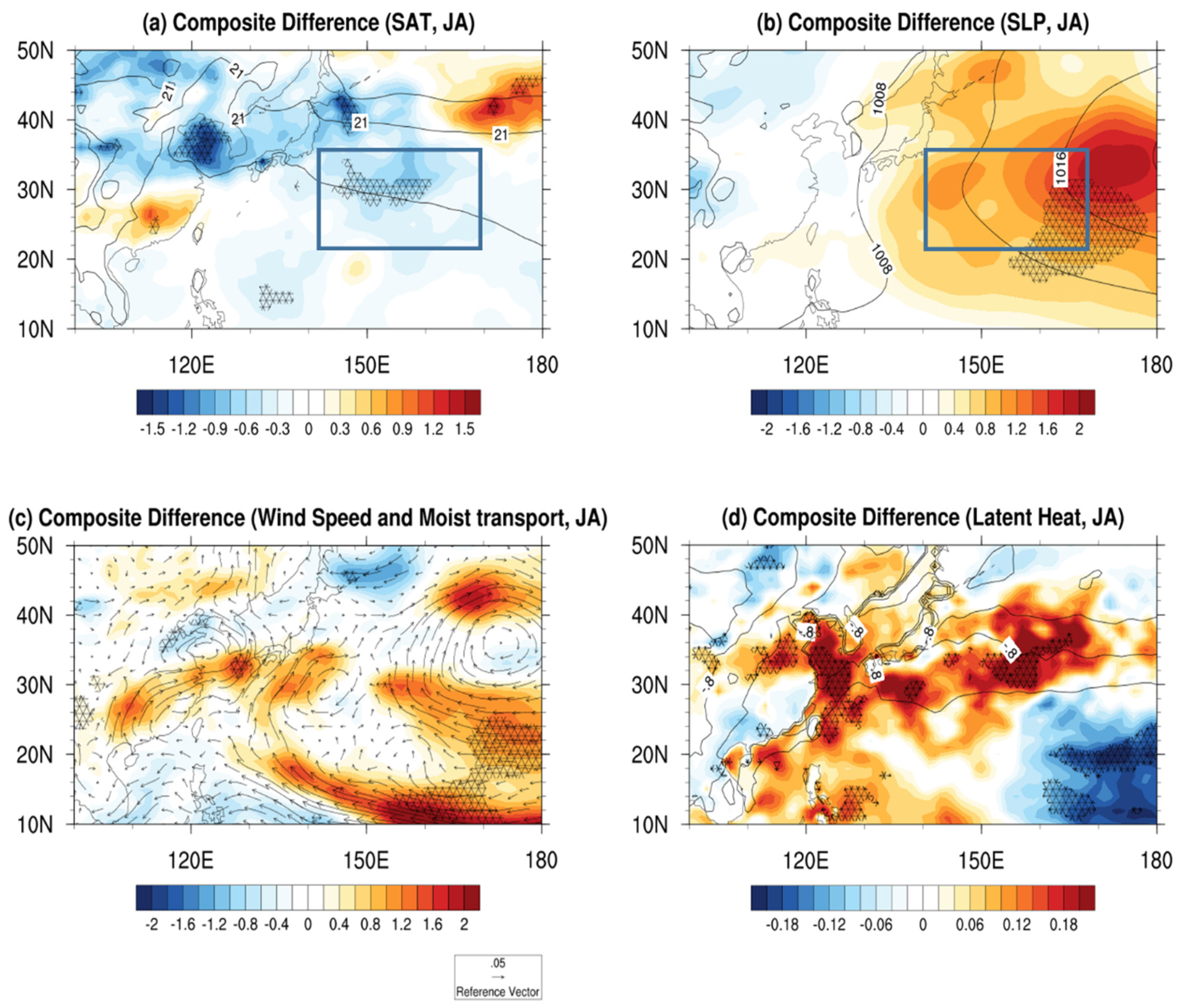
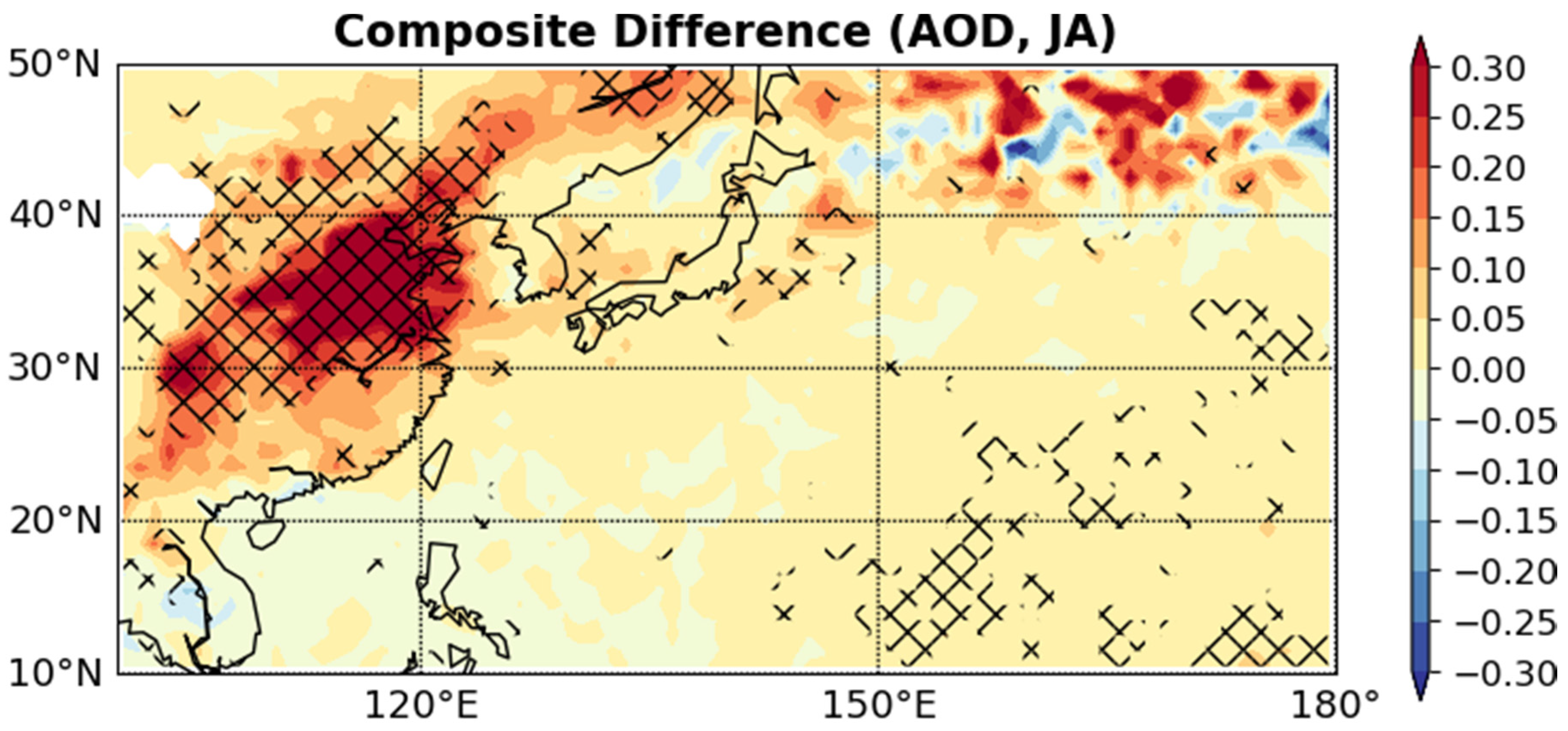
3. Results
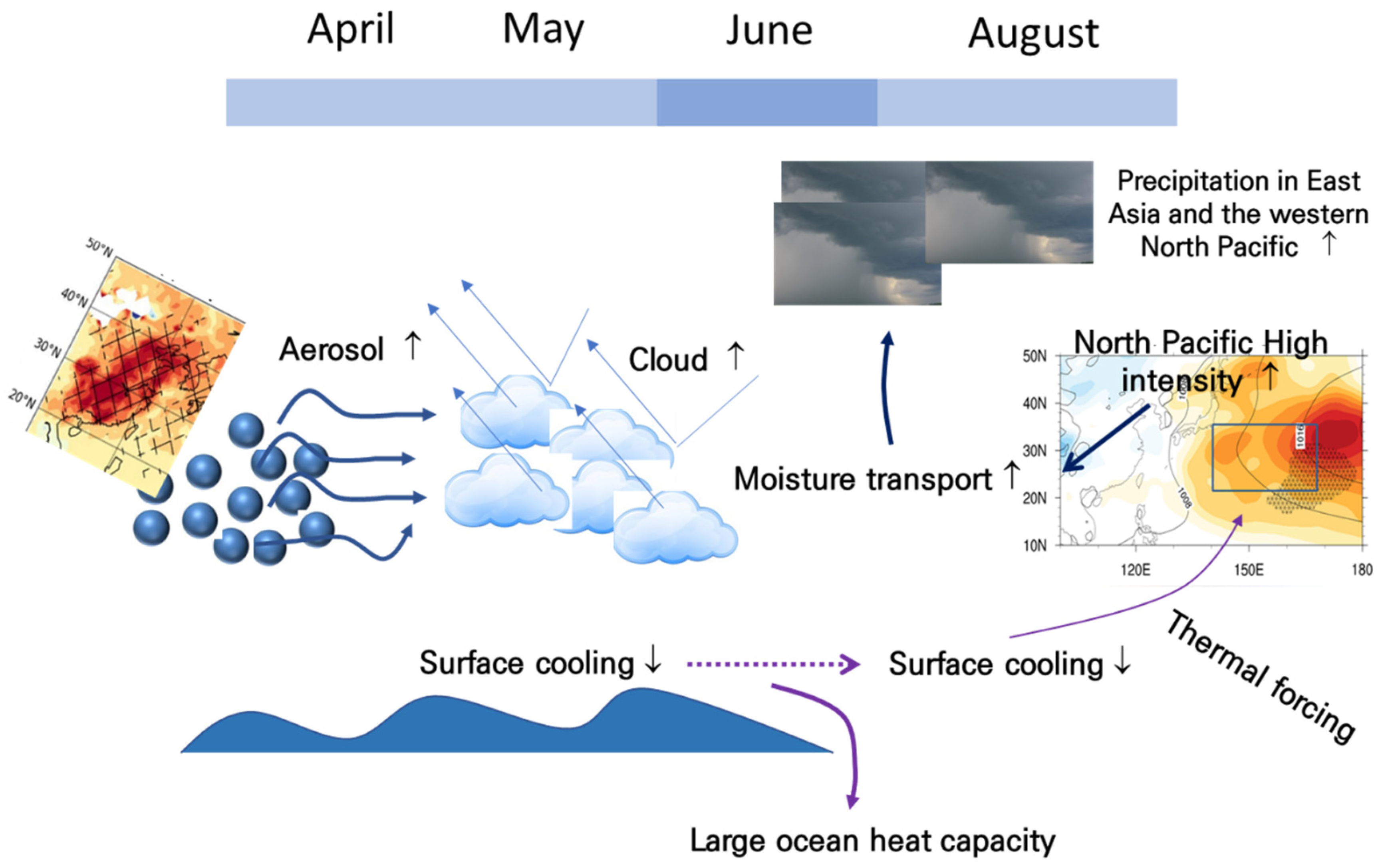
4. Summary and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; Lau, W.M.; Ramanathan, V.; Wu, G.; Ding, Y.; Manoj, M.; Liu, J.; Qian, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, T. Aerosol and monsoon climate interactions over Asia. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 866–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.-H.; Tsay, S.-C.; Maring, H.B.; Yen, M.-C.; Sheu, G.-R.; Wang, S.-H.; Chi, K.H.; Chuang, M.-T.; Ou-Yang, C.-F.; Fu, J.S. An overview of regional experiments on biomass burning aerosols and related pollutants in Southeast Asia: From BASE-ASIA and the Dongsha Experiment to 7-SEAS. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 78, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolli, S.; Khor, W.Y.; Matjafri, M.Z.; Lim, H.S. Monsoon season quantitative assessment of biomass burning clear-sky aerosol radiative effect at surface by ground-based lidar observations in Pulau Pinang, Malaysia in 2014. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Yoon, S.C.; Ramanathan, V.; Shi, G.Y.; Takemura, T.; Higurashi, A.; Takamura, T.; Aoki, K.; Sohn, B.J.; Kim, S.W. Overview of the Atmospheric Brown Cloud East Asian Regional Experiment 2005 and a study of the aerosol direct radiative forcing in east Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, R.J.; Schwartz, S.; Hales, J.; Cess, R.D.; Coakley, J.J.; Hansen, J.; Hofmann, D. Climate forcing by anthropogenic aerosols. Science 1992, 255, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.K. The aerosol-monsoon climate system of Asia: A new paradigm. J. Meteorol. Res. 2016, 30, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Savijärvi, H. The effect of aerosols on long wave radiation and global warming. Atmos. Res. 2014, 135, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Allen, R.; Sherwood, S. Aerosol-cloud semi-direct effect and land-sea temperature contrast in a GCM. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Lee, W.S. Dynamic feedbacks of troposphere aerosols on marine low cloud during boreal spring. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.; Rosenfeld, D. Aerosol–cloud–precipitation interactions. Part 1. The nature and sources of cloud-active aerosols. Earth. Sci. Rev. 2008, 89, 13–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, K.; Lee, L.; Reddington, C.; Pringle, K.; Rap, A.; Forster, P.; Mann, G.; Spracklen, D.; Woodhouse, M.; Regayre, L. Large contribution of natural aerosols to uncertainty in indirect forcing. Nature 2013, 503, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Lohmann, U.; Raga, G.B.; O’dowd, C.D.; Kulmala, M.; Fuzzi, S.; Reissell, A.; Andreae, M.O. Flood or drought: How do aerosols affect precipitation? Science 2008, 321, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twomey, S. The influence of pollution on the shortwave albedo of clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 1977, 34, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, B.A. Aerosols, cloud microphysics, and fractional cloudiness. Science 1989, 245, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S.; Donner, L.J.; Phillips, V.T.; Ming, Y. The dependence of aerosol effects on clouds and precipitation on cloud-system organization, shear and stability. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoesly, R.M.; Smith, S.J.; Feng, L.; Klimont, Z.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Pitkanen, T.; Seibert, J.J.; Vu, L.; Andres, R.J.; Bolt, R.M. Historical (1750–2014) anthropogenic emissions of reactive gases and aerosols from the Community Emission Data System (CEDS). Geosci. Model. Dev. 2018, 11, 369–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, T.; Akimoto, H.; Kurokawa, J.-i.; Horii, N.; Yamaji, K.; Yan, X.; Hayasaka, T. An Asian emission inventory of anthropogenic emission sources for the period 1980–2020. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streets, D.G.; Wu, Y.; Chin, M. Two-decadal aerosol trends as a likely explanation of the global dimming/brightening transition. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Niu, T.; Zhang, X.; Gong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J. Atmospheric aerosol compositions in China: Spatial/temporal variability, chemical signature, regional haze distribution and comparisons with global aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 779–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, J.H.; Su, H. Atmospheric responses to the redistribution of anthropogenic aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 9625–9641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streets, D.G.; Yu, C.; Wu, Y.; Chin, M.; Zhao, Z.; Hayasaka, T.; Shi, G. Aerosol trends over China, 1980–2000. Atmos. Res. 2008, 88, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Jiang, J.H.; Gu, Y.; Diner, D.; Worden, J.; Liou, K.-N.; Su, H.; Xing, J.; Garay, M.; Huang, L. Decadal-scale trends in regional aerosol particle properties and their linkage to emission changes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 054021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-S.; Ho, C.-H.; Kim, J.; Gong, D.-Y.; Park, R.J. The impact of aerosols on the summer rainfall frequency in China. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 1802–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Yeh, S.W.; Park, R.J. Effects of sulfate aerosol forcing on East Asian summer monsoon for 1985–2010. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhuang, B.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Xie, M.; Yin, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, C.; Zhu, J.; Ji, L. The interactions between anthropogenic aerosols and the East Asian summer monsoon using RegCCMS. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 5602–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y. Distinct effects of anthropogenic aerosols on the East Asian summer monsoon between multidecadal strong and weak monsoon stages. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 7026–7040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.I.; Park, R.J.; Yeh, S.W. Dissimilar effects of two El Nino types on PM2.5 concentrations in East Asia. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Bi, X.; Qian, Y. Direct radiative forcing and regional climatic effects of anthropogenic aerosols over East Asia: A regional coupled climate-chemistry/aerosol model study. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, AAC 7-1–AAC 7-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Highwood, E.; Shaffrey, L.; Turner, A. The effect of regional changes in anthropogenic aerosols on rainfall of the East Asian Summer Monsoon. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 1521–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Giorgi, F. Regional climatic effects of anthropogenic aerosols? The case of Southwestern China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 3521–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Zhou, T.; Qian, Y. Responses of East Asian summer monsoon to natural and anthropogenic forcings in the 17 latest CMIP5 models. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Li, W.; Li, L.; Zhang, F. “North drying and south wetting” summer precipitation trend over China and its potential linkage with aerosol loading. Atmos. Res. 2013, 125, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y. Inter-decadal variation of the summer precipitation in East China and its association with decreasing Asian summer monsoon. Part I: Observed evidences. Int. J. Climatol. 2008, 28, 1139–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, S.; Hansen, J.; Nazarenko, L.; Luo, Y. Climate effects of black carbon aerosols in China and India. Science 2002, 297, 2250–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q. Abrupt change of the mid-summer climate in central east China by the influence of atmospheric pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 5029–5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bi, L.; Jia, X.; Yi, B.; Lin, X.; Zhang, F. Impact of dust shortwave absorbability on the East Asian summer monsoon. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL089585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Wang, Z. Responses of the East Asian summer monsoon to aerosol forcing in CMIP5 models: The role of upper-tropospheric temperature change. Int. J. Climatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Yang, J.; Bao, Q.; Wang, W.-C. Intraseasonal responses of the East Asia summer rainfall to anthropogenic aerosol climate forcing. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Guo, P.; Wang, Z. A modeling study of the effects of direct radiative forcing due to carbonaceous aerosol on the climate in East Asia. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 26, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Lin, Z.; Lu, R.; Lian, Y. Circulation anomalies associated with interannual variation of early-and late-summer precipitation in Northeast China. Sci. China Earth. Sci. 2011, 54, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Zhou, T.; Wu, Z. Distinct principal modes of early and late summer rainfall anomalies in East Asia. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 3864–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Zhou, T. Seasonality and three-dimensional structure of interdecadal change in the East Asian monsoon. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 5344–5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Kaufman, Y.; Tanré, D.; Mattoo, S.; Chu, D.; Martins, J.V.; Li, R.-R.; Ichoku, C.; Levy, R.; Kleidman, R. The MODIS aerosol algorithm, products, and validation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 947–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanre, D.; Buis, J.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.; Nakajima, T. AERONET—A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martonchik, J.V.; Diner, D.J.; Kahn, R.A.; Ackerman, T.P.; Verstraete, M.M.; Pinty, B.; Gordon, H.R. Techniques for the retrieval of aerosol properties over land and ocean using multiangle imaging. IEEE. Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1212–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.; Hsu, N.; Bettenhausen, C.; Jeong, M.; Holben, B.; Zhang, J. Global and regional evaluation of over-land spectral aerosol optical depth retrievals from SeaWiFS. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shao, T.; Hua, S.; Zhu, Q.; Luo, R. Association of anthropogenic aerosols with subtropical drought in East Asia. Int. J. Climatol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, N.; Venkataraman, C.; Muduchuru, K.; Ghosh, S.; Mondal, A. Disentangling sea-surface temperature and anthropogenic aerosol influences on recent trends in South Asian monsoon rainfall. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 2287–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Arkin, P.; Chang, A.; Ferraro, R.; Gruber, A.; Janowiak, J.; McNab, A.; Rudolf, B.; Schneider, U. The global precipitation climatology project (GPCP) combined precipitation dataset. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, D.P. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzer, A.; De Meij, A.; Yoon, J.; Tost, H.; Georgoulias, A.; Astitha, M. AOD trends during 2001–2010 from observations and model simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 5521–5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, D.; Ouyang, X.; Zhang, X. Variability of satellite-based total aerosols and the relationship with emission, meteorology and landscape in North China during 2000–2016. Environ. Earth. Sci. 2018, 77, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.M. Long Temporal Analysis of 3-km MODIS Aerosol Product Over East China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 2478–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.-P.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Wu, Y.-R.; Zhaxi, Y.; Che, H.-Z.; La, B.; Wang, W.; Li, X.-W. Spatio-temporal variation trends of satellite-based aerosol optical depth in China during 1980–2008. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6802–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin-Tai, L.; Da, P.; Rui-Xiong, Z. Trend and interannual variability of Chinese air pollution since 2000 in association with socioeconomic development: A brief overview. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2013, 6, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Saravanan, R. Asian pollution climatically modulates mid-latitude cyclones following hierarchical modelling and observational analysis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uematsu, M.; Yoshikawa, A.; Muraki, H.; Arao, K.; Uno, I. Transport of mineral and anthropogenic aerosols during a Kosa event over East Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, T.; Uno, I.; Nakajima, T.; Higurashi, A.; Sano, I. Modeling study of long-range transport of Asian dust and anthropogenic aerosols from East Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 11-1–11-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, J.I.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Koren, I.; Li, R.R. Aerosol-cloud interaction-misclassification of MODIS clouds in heavy aerosol. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Koren, I.; Remer, L.A.; Rosenfeld, D.; Rudich, Y. The effect of smoke, dust, and pollution aerosol on shallow cloud development over the Atlantic Ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11207–11212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, U.; Feichter, J. Global indirect aerosol effects: A review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 715–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, R.; Ghan, S.J.; Lin, Y.; Hu, J.; Pan, B.; Levy, M.; Jiang, J.H.; Molina, M.J. Assessing the effects of anthropogenic aerosols on Pacific storm track using a multiscale global climate model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6894–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Woodley, W.L.; Khain, A.; Cotton, W.R.; Carrió, G.; Ginis, I.; Golden, J.H. Aerosol effects on microstructure and intensity of tropical cyclones. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 987–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R. Getting to the critical nucleus of aerosol formation. Science 2010, 328, 1366–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, G.; Fan, J.; Wu, D.L.; Molina, M.J. Intensification of Pacific storm track linked to Asian pollution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5295–5299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, H.J.; Kim, M.K.; Kwon, W.T. Observed short-and long-term changes in summer precipitation over South Korea and their links to large-scale circulation anomalies. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 972–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Zhang, P.; Chen, L.; Xu, N. Integrated analysis of dust transport and budget in a severe Asian dust event. Aerosol. Air. Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 2390–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhao, T.; Boiyo, R.; Chen, S.; Lu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y. Vertical structures of dust aerosols over East Asia based on CALIPSO retrievals. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Mu, J.; Yang, M.; Yu, X. Reexamining the Mechanisms of East Asian Summer Monsoon Changes in Response to Non–East Asian Anthropogenic Aerosol Forcing. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 2929–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-J.; Jeong, Y.-C.; Yeh, S.-W. The Lagged Effect of Anthropogenic Aerosol on East Asian Precipitation during the Summer Monsoon Season. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121356
Lee S-J, Jeong Y-C, Yeh S-W. The Lagged Effect of Anthropogenic Aerosol on East Asian Precipitation during the Summer Monsoon Season. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(12):1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121356
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Su-Jung, Yong-Cheol Jeong, and Sang-Wook Yeh. 2020. "The Lagged Effect of Anthropogenic Aerosol on East Asian Precipitation during the Summer Monsoon Season" Atmosphere 11, no. 12: 1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121356
APA StyleLee, S.-J., Jeong, Y.-C., & Yeh, S.-W. (2020). The Lagged Effect of Anthropogenic Aerosol on East Asian Precipitation during the Summer Monsoon Season. Atmosphere, 11(12), 1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121356




