Effectiveness and Eco-Costs of Air Cleaners in Terms of Improving Fungal Air Pollution in Dwellings Located in Southern Poland—A Preliminary Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Sampling Sites
2.2. Sampling and Analysis Methods
2.3. Statistical Analysis
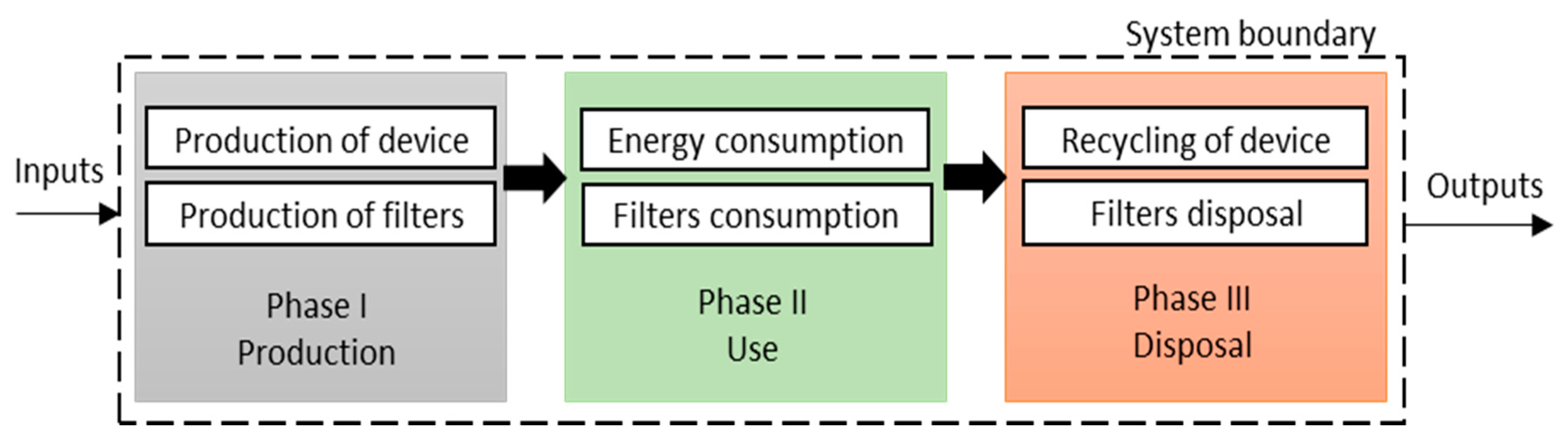
2.4. LCA Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Concentration of Culturable Fungal Aerosol and the Effectiveness of ACLs
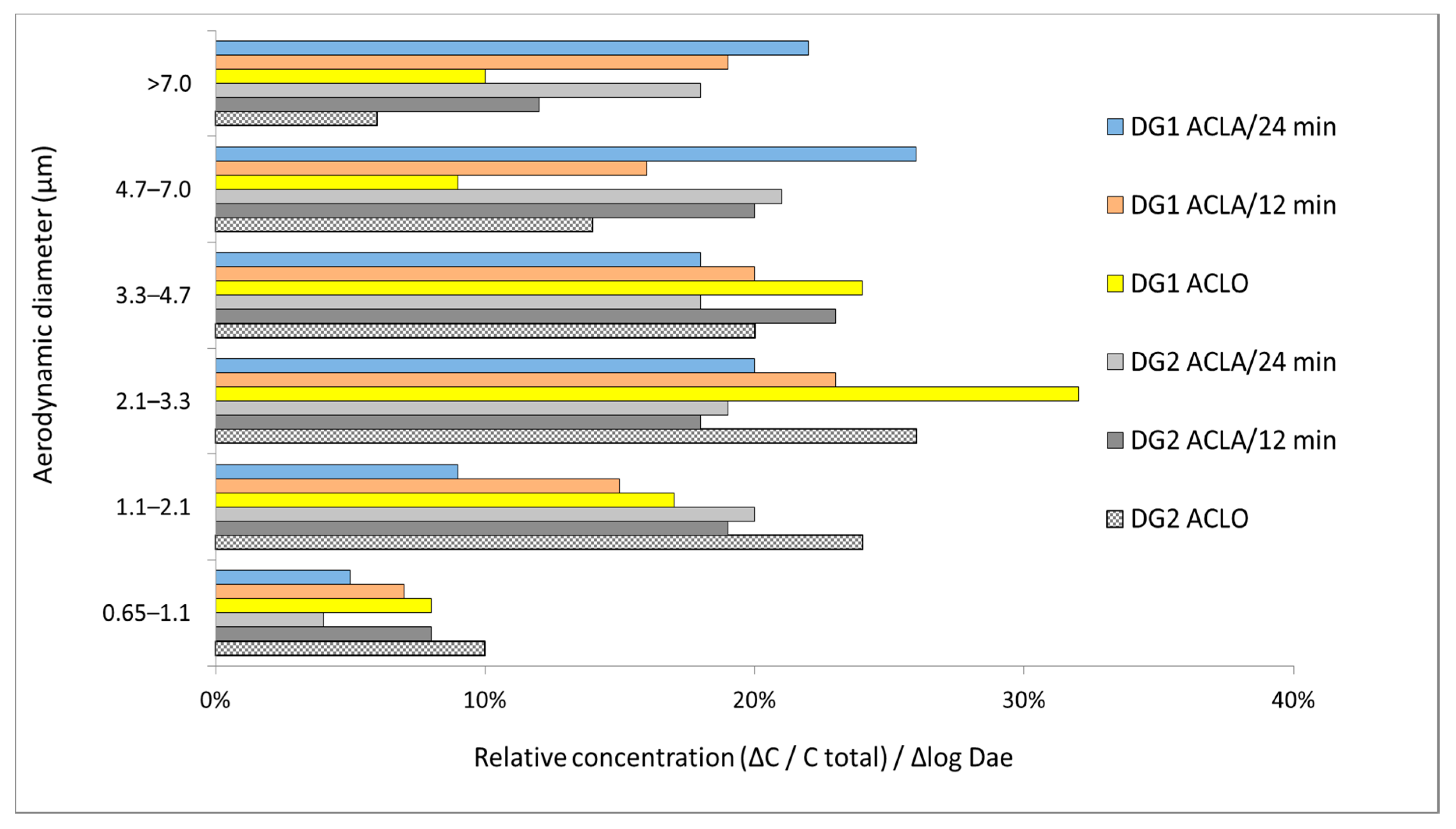
3.2. The Size Distribution of Fungal Aerosol and the Effectiveness of ACLs
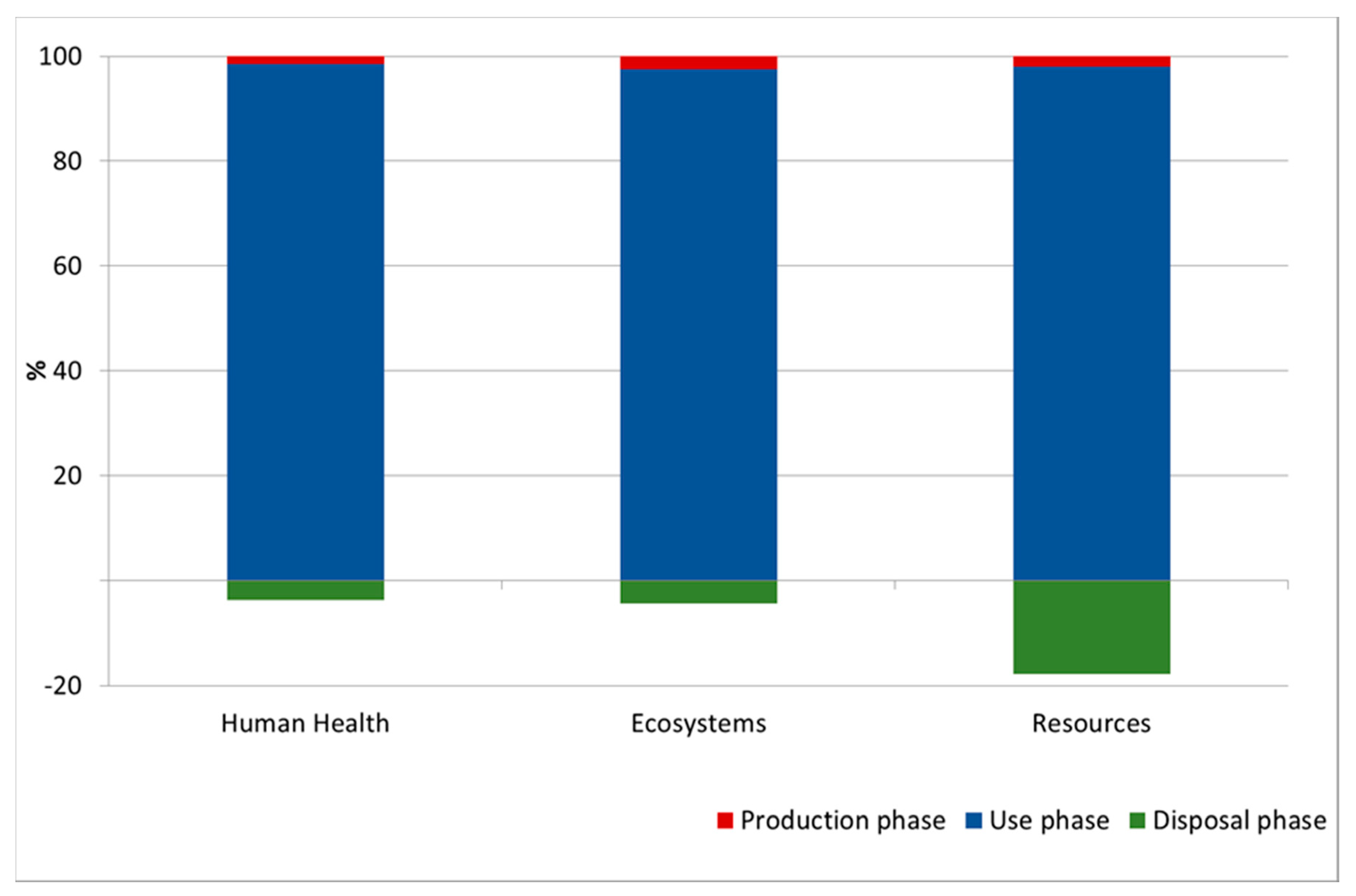
3.3. LCA—The Ecological Cost of Emission Reduction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saini, J.; Dutta, M.; Marques, G. A comprehensive review on indoor air quality monitoring systems for enhanced public health. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2020, 30, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simoni, M.; Jaakkola, M.S.; Carrozzi, L.; Baldacci, S.; Di Pede, F.; Viegi, G. Indoor air pollution and respiratory health in the elderly. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 21, 15S–20S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cincinelli, A.; Martellini, T.; Cincinelli, A.; Martellini, T. Indoor Air Quality and Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kelly, F.J.; Fussell, J.C. Improving indoor air quality, health and performance within environments where people live, travel, learn and work. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 200, 90–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Feng, Q.; Cai, H.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, K.; Li, F.; Liu, S.; Li, X. Towards locating time-varying indoor particle sources: Development of two multi-robot olfaction methods based on whale optimization algorithm. Build. Environ. 2019, 166, 106413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, M.; Hoek, G.; Smit, H.A.; De Jongste, J.C.; Gerritsen, J.; Postma, D.S.; Kerkhof, M.; Brunekreef, B. Air pollution and development of asthma, allergy and infections in a birth cohort. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 29, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; Hospodsky, D.; Yamamoto, N.; Nazaroff, W.W.; Peccia, J. Size-resolved emission rates of airborne bacteria and fungi in an occupied classroom. Indoor Air 2012, 22, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Leuken, J.P.G.; Swart, A.N.; Droogers, P.; Van Pul, A.; Heederik, D.; Havelaar, A.H. Climate change effects on airborne pathogenic bioaerosol concentrations: A scenario analysis. Aerobiologia 2016, 32, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fröhlich-Nowoisky, J.; Kampf, C.J.; Weber, B.; Huffman, J.A.; Pöhlker, C.; Andreae, M.O.; Lang-Yona, N.; Burrows, S.M.; Gunthe, S.S.; Elbert, W.; et al. Bioaerosols in the Earth system: Climate, health, and ecosystem interactions. Atmos. Res. 2016, 182, 346–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reinmuth-Selzle, K.; Kampf, C.J.; Lucas, K.; Lang-Yona, N.; Fröhlich-Nowoisky, J.; Shiraiwa, M.; Lakey, P.S.J.; Lai, S.; Liu, F.; Kunert, A.T.; et al. Air Pollution and Climate Change Effects on Allergies in the Anthropocene: Abundance, Interaction, and Modification of Allergens and Adjuvants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4119–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samake, A.; Uzu, G.; Martins, J.M.F.; Calas, A.; Vince, E.; Parat, S.; Jaffrezo, J.L. The unexpected role of bioaerosols in the Oxidative Potential of PM. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kabir, E.; Jahan, S.A. Airborne bioaerosols and their impact on human health. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 67, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliabadi, A.A.; Rogak, S.N.; Bartlett, K.H.; Green, S.I. Preventing Airborne Disease Transmission: Review of Methods for Ventilation Design in Health Care Facilities. Adv. Prev. Med. 2011, 2011, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kildesø, J.; Würtz, H.; Nielsen, K.F.; Kruse, P.; Wilkins, K.; Thrane, U.; Gravesen, S.; Nielsen, P.A.; Schneider, T. Determination of fungal spore release from wet building materials. Indoor Air 2003, 13, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.-W.; Yang, C.S. Fungal Contamination as a Major Contributor to Sick Building Syndrome. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 55, 31–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.; Baron, P.; Willeke, K. Aerosol Measurement: Principles, Techniques, and Applications, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shelton, B.G.; Kirkland, K.H.; Flanders, W.D.; Morris, G.K. Profiles of airborne fungi in buildings and outdoor environments in the United States. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 1743–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO. Guidelines for Indoor Air Quality: Dampness and Mould; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2009; ISBN 7989289041683. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, B.; Lal, H.; Srivastava, A. Review of bioaerosols in indoor environment with special reference to sampling, analysis and control mechanisms. Environ. Int. 2015, 85, 254–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.D.; Lacey, R.E.; Pak, H.; Fearing, A.; Ramos, G.; Baig, T.; Smith, B.; Koustova, A. Assays and enumeration of bioaerosols-traditional approaches to modern practices. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 611–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siersted, H.C.; Gravesen, S. Extrinsic allergic alveolitis after exposure to the yeast Rhodotorula rubra. Allergy 1993, 48, 298–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman, M.; Lacasse, Y.; Pardo, A.; Cormier, Y. Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Caused by Fungi. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2010, 7, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Hwang, G.B.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, B.U. Generation characteristics of fungal spore and fragment bioaerosols by airflow control over fungal cultures. J. Aerosol Sci. 2010, 41, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, M.F.; Almouqatea, S. Assessment of airborne bacteria and fungi in an indoor and outdoor environment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 7, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.J.; Ma, S.Y.; Cao, G.Q.; Meng, C.; He, B.J. Distribution characteristics, growth, reproduction andtransmission modes and control strategies for microbial contamination in HVAC systems: A literature review. Energy Build. 2018, 177, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, W.; Li, H. Investigation of dust loading and culturable microorganisms of HVAC systems in 24 office buildings in Beijing. Energy Build. 2015, 103, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.-C.; Park, H.-K.; Tetteh, A.O.; Zheng, D.; Ouellette, N.T.; Nadeau, K.C.; Hildemann, L.M. Mixing and sink effects of air purifiers on indoor PM2.5 concentrations: A pilot study of eight residential homes in Fresno, California. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gunschera, J.; Markewitz, D.; Bansen, B.; Salthammer, T.; Ding, H. Portable photocatalytic air cleaners: efficiencies and by-product generation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 7482–7493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Cho, B.-B.; Anusha, J.R.; Sim, J.Y.; Raj, C.J.; Yu, K.-H. Assessment of air purifier on efficient removal of airborne bacteria, Staphylococcus epidermidis, using single-chamber method. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaughnessy, R.J.; Sextro, R.G. What Is an Effective Portable Air Cleaning Device? A Review. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2006, 3, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiner, S. Not all HEPA filters are the same. Power Eng. 2017, 121, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C. Aerosol Filtration Application Using Fibrous Media—An Industrial Perspective. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterman, S.; Du, L.; Mentz, G.; Mukherjee, B.; Parker, E.; Godwin, C.; Chin, J.-Y.; O’Toole, A.; Robins, T.; Rowe, Z.; et al. Particulate matter concentrations in residences: An intervention study evaluating stand-alone filters and air conditioners. Indoor Air 2012, 22, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wheeler, A.J.; Gibson, M.D.; MacNeill, M.; Ward, T.J.; Wallace, L.A.; Kuchta, J.; Seaboyer, M.; Dabek-Zlotorzynska, E.; Guernsey, J.R.; Stieb, D.M. Impacts of Air Cleaners on Indoor Air Quality in Residences Impacted by Wood Smoke. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12157–12163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisk, W.J. Health benefits of particle filtration. Indoor Air 2013, 23, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morishita, M.; Thompson, K.C.; Brook, R.D. Understanding Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Diseases: Is It Preventable? Curr. Cardiovasc. Risk Rep. 2015, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onmek, N.; Kongcharoen, J.; Singtong, A.; Penjumrus, A.; Junnoo, S. Environmental Factors and Ventilation Affect Concentrations of Microorganisms in Hospital Wards of Southern Thailand. J. Environ. Public Health 2020, 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xiong, Y.; Kang, T.; Xiang, Z.; Qin, C. Bacterial community analysis of floor dust and HEPA filters in air purifiers used in office rooms in ILAS, Beijing. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-J.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, H.J.; Yoon, J.S.; Lee, M.J.; Choi, K.-S.; Sung, U.-D.; Park, W.-T.; Lee, J.; Jeon, J.; et al. Highly Efficient, Flexible, and Recyclable Air Filters Using Polyimide Films with Patterned Thru-Holes Fabricated by Ion Milling. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nevalainen, A.; Willeke, K.; Liebhaber, F.; Pastuszka, J.S.; Burge, H.; Henningson, E. Bioaerosol sampling. In Aerosol Measurement: Principles, Techniques and Applications; Willeke, K., Baron, P., Eds.; Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 471–492. [Google Scholar]
- Brągoszewska, E.; Bogacka, M.; Pikoń, K. Efficiency and Eco-Costs of Air Purifiers in Terms of Improving Microbiological Indoor Air Quality in Dwellings—A Case Study. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brągoszewska, E.; Biedroń, I. Indoor Air Quality and Potential Health Risk Impacts of Exposure to Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria in an Office Rooms in Southern Poland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- PN-EN 12322 In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Devices. Culture Media for Microbiology. Performance Criteria for Culture Media. 2005. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/growth/single-market/european-standards/harmonised-standards/iv-diagnostic-medical-devices_en (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- ISO 11133 Microbiology of Food, Animal Feed and Water—Preparation, Production, Storage and Performance Testing of Culture Media. 2014. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/53610.html (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Principles and Framework; ISO 14040; International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- Bogacka, M.; Pikoń, K. Best Practice In Environmental Impact Evaluation Based On Lca—Methodologies Review. In Proceedings of the 14th International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference-SGEM, Albena, Bulgaria, 17–26 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pikoń, K.; Bogacka, M. Local Specificity in Environmental Impact Assessment—End-Point Local Evaluation Indicators. In Proceedings of the 14th International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference-SGEM, Albena, Bulgaria, 17–26 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gayer, A.; Mucha, D.; Adamkiewicz, Ł.; Badyda, A. Children exposure to PM2.5 in kindergarten classrooms equipped with air purifiers—A pilot study. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Fire and Environmental Safety Engineering (FESE 2018), Lviv, Ukraine, 7–8 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto, K.; Kawakami, Y. Effectiveness of Airborne Fungi Removal by using a HEPA Air Purifier Fan in Houses. Biocontrol Sci. 2018, 23, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, B.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C. Air purifiers: A supplementary measure to remove airborne SARS-CoV-2. Build. Environ. 2020, 177, 106918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellier, R. Aerosol transmission of influenza A virus: A review of new studies. J. R. Soc. Interface 2009, 6, S783–S790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lacey, J.; Dutkiewicz, J. Bioaerosols and occupational lung disease. J. Aerosol Sci. 1994, 25, 1371–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, M.; Ensor, D.; Sparks, L. Airborne particle sizes and sources found in indoor air. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1992, 26, 2149–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine. Damp Indoor Spaces and Health; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; ISBN 10-0-309-09193-4. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Directive 2012/19/EU of 4 July 2012 on Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE). Off. J. Eur. Union 2012, 55, 38–71. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/ (accessed on 14 November 2020).

| Parameters and Basic Description of DG1 and DG2 | Dwelling 1 (DG1) | Dwelling 2 (DG2) |
|---|---|---|
| Home localization | close the city center | close the city center |
| Building built-in | 1990s | 1980s |
| Equipment | table, chairs, sofa | table, chairs, sofa, |
| 2 armchairs | ||
| Ventilation system | natural | natural |
| Volume, m3 | 64 | 62 |
| Number of occupants | 4 (2 adults and 2 children) | 4 (2 adults and 2 children) |
| Number of animals | - | 2 dogs |
| Floor covered with | PVC and carpet | PVC and carpet |
| Indoor temperature, °C | 22.5 +/− 5.1 | 20.5 +/− 4.4 |
| Indoor relative humidity, % | 41. +/− 8.1 | 48.2 +/− 3.9 |
| Outdoor temperature, °C | 29.1 +/− 4.2 | 28.6 +/− 3.3 |
| Outdoor relative humidity, % | 39.1 +/− 7.4 | 44.2 +/− 8.9 |
| Location | Average Concentration CFU·m−3 +/−SD | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|
| DG1 ACLA/12 min | 373 +/− 101 | 21 | 410 |
| DG2 ACLA/12 min | 419 +/−124 | 14 | 544 |
| DG1 ACLA/24 min | 306 +/−92 | 18 | 404 |
| DG2 ACLA/24 min | 338 +/−86 | 4 | 419 |
| DG1 ACLO | 474 +/−134 | 14 | 522 |
| DG2 ACLO | 582 +/−141 | 7 | 640 |
| LCA | Product/Service | Assumption | Unit | Chosen Ecoinvent Database |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase I Production | Production of the device | 1 | piece | Air filter, decentralized unit, 180–250 m3/h {RER}| production | Alloc Def, U |
| Production of the carbon filter | 1 | piece | Included in device production | |
| Production of the HEPA filter | 1 | piece | Included in device production | |
| Phase II Use | Electricity consumption | 85.5 | kWh/year | Electricity, low voltage {PL}| market for | Alloc Def, U |
| Filter changes | 1 | piece/year | Not included (for the first year the original filter is used) | |
| Phase III Disposal | Recycling of plastic | 2 | kg | _42 Recycling of plastics basic, EU27 |
| Recycling of metal | 1 | kg | _60 Recycling of metals basic, n.e.c., EU27 | |
| Disposal of filters | 1 | kg | Not included (lack of database) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brągoszewska, E.; Bogacka, M.; Pikoń, K. Effectiveness and Eco-Costs of Air Cleaners in Terms of Improving Fungal Air Pollution in Dwellings Located in Southern Poland—A Preliminary Study. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111255
Brągoszewska E, Bogacka M, Pikoń K. Effectiveness and Eco-Costs of Air Cleaners in Terms of Improving Fungal Air Pollution in Dwellings Located in Southern Poland—A Preliminary Study. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(11):1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111255
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrągoszewska, Ewa, Magdalena Bogacka, and Krzysztof Pikoń. 2020. "Effectiveness and Eco-Costs of Air Cleaners in Terms of Improving Fungal Air Pollution in Dwellings Located in Southern Poland—A Preliminary Study" Atmosphere 11, no. 11: 1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111255
APA StyleBrągoszewska, E., Bogacka, M., & Pikoń, K. (2020). Effectiveness and Eco-Costs of Air Cleaners in Terms of Improving Fungal Air Pollution in Dwellings Located in Southern Poland—A Preliminary Study. Atmosphere, 11(11), 1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111255







