Statistically Downscaled CMIP6 Projections Show Stronger Warming for Germany
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
3. Data
4. Results
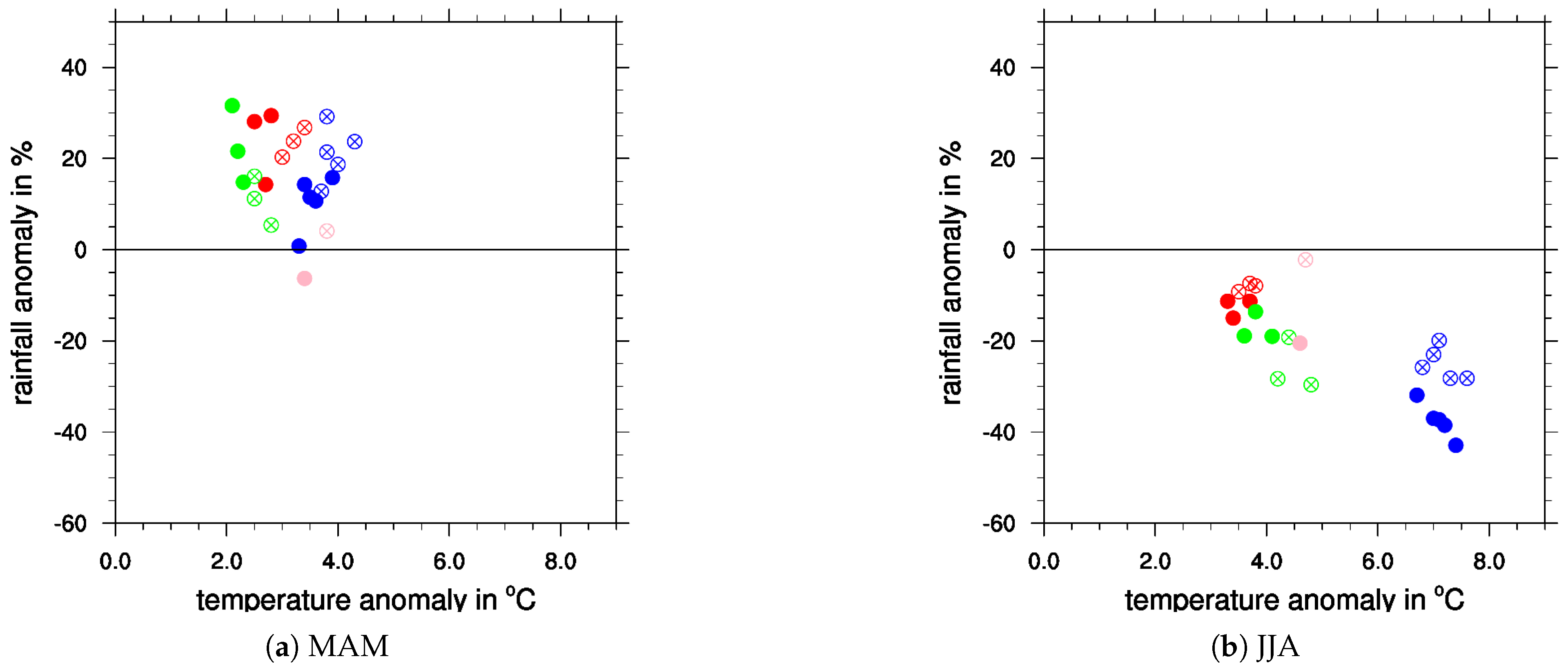
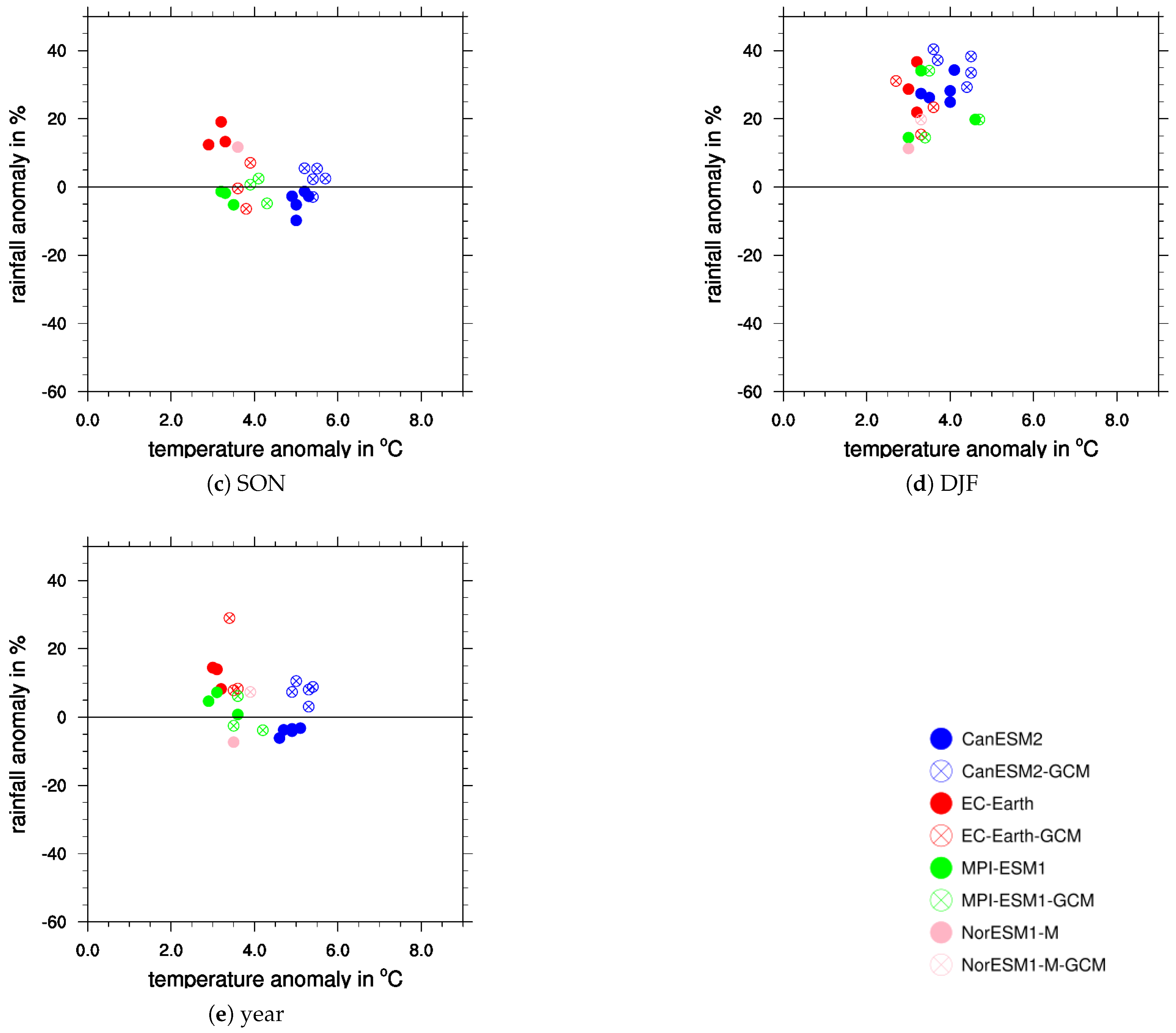
4.1. Comparing Global and Regional Change Signals
4.2. Comparing Regional CMIP5 and CMIP6 Signals
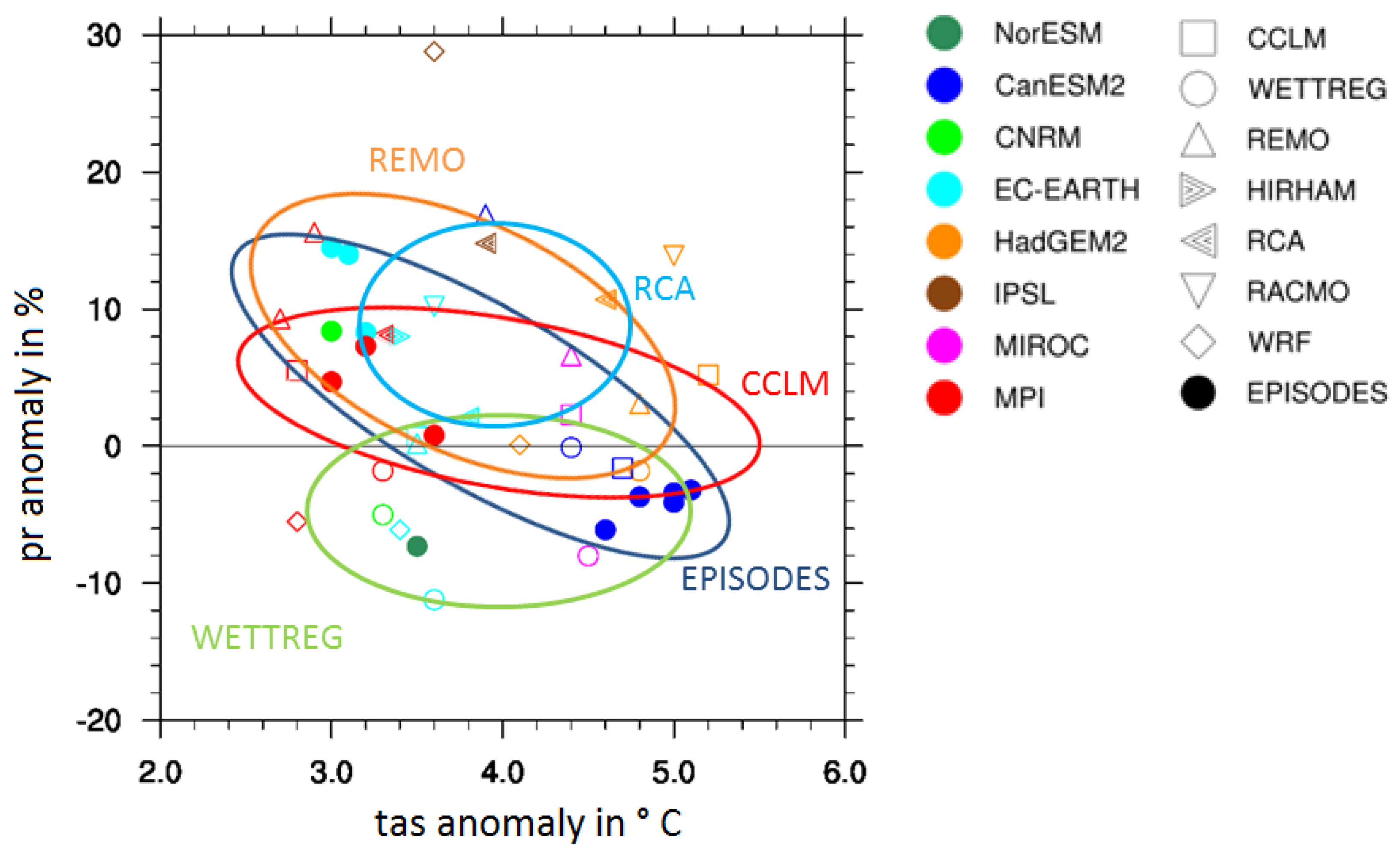
4.3. Internal Model-Chain Variability
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Additional Figures
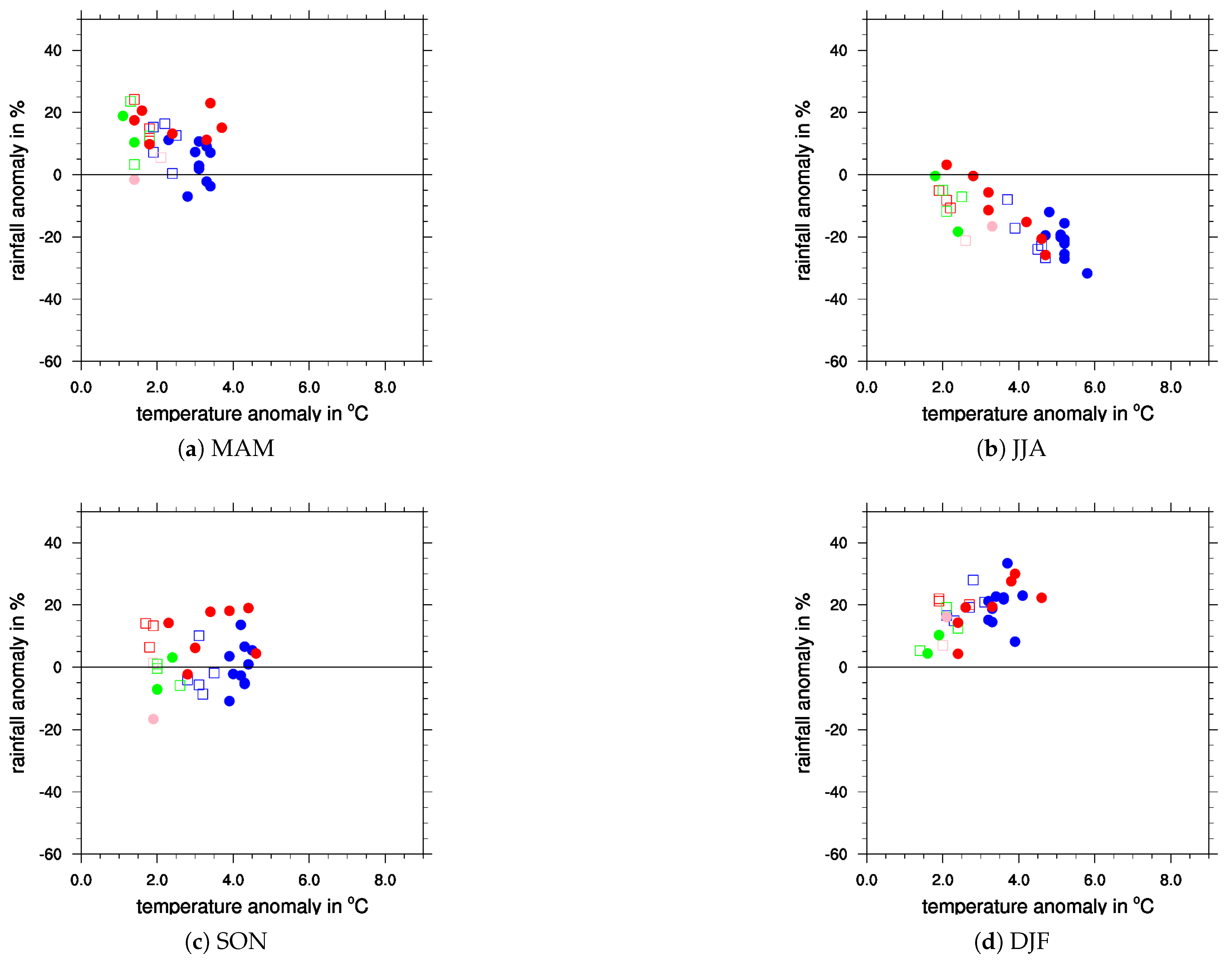

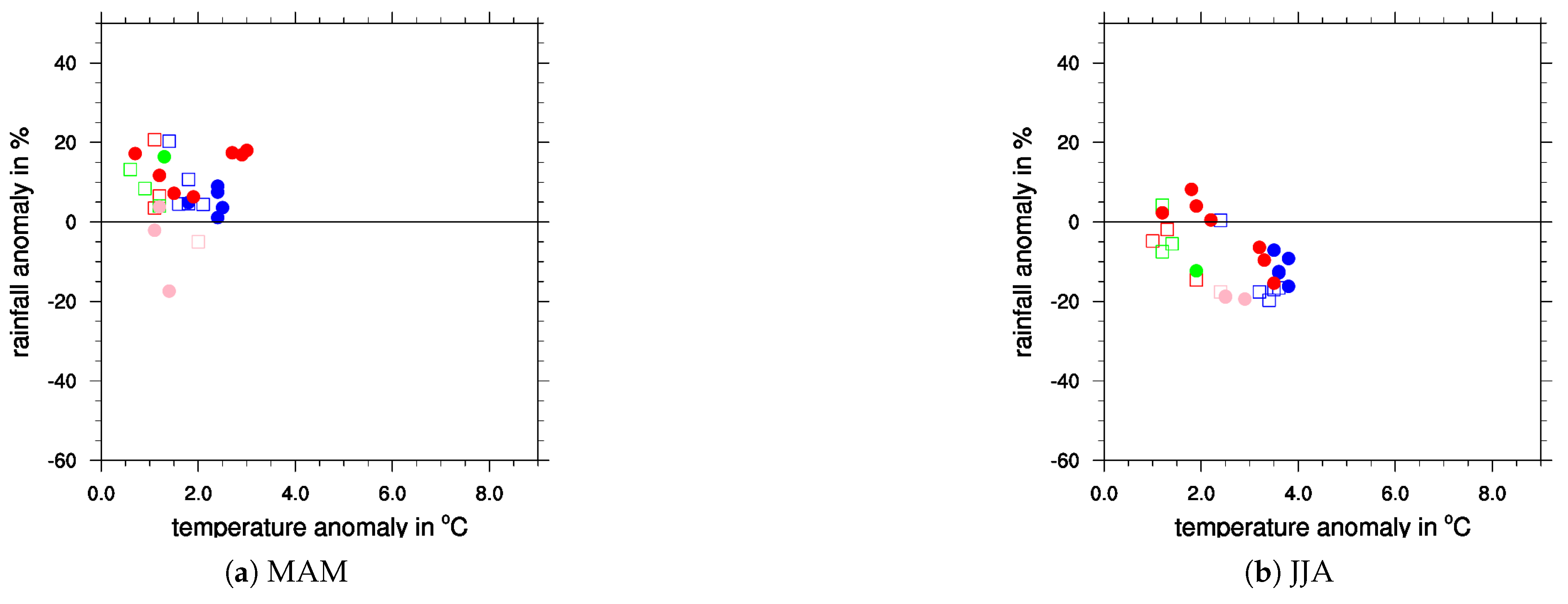
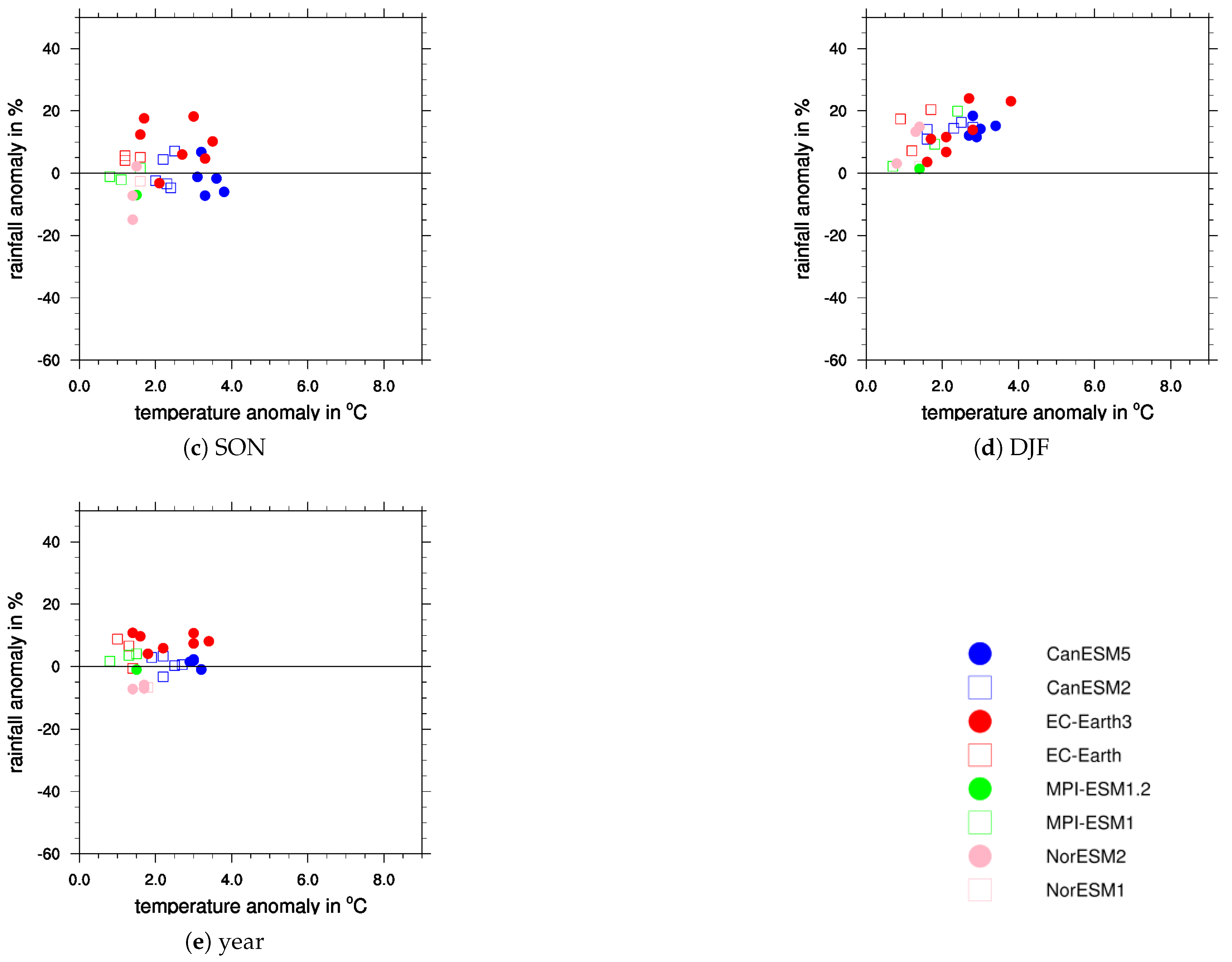
References
- Edwards, P. A Vast Machine—Computer Models, Climate Data, and the Politics of Global Warming; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Von Storch, H. Climate models and modeling: An editorial essay. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2010, 1, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, P. Constructing climate knowledge with computer models. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2010, 1, 565–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, P. History of climate modeling. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2011, 2, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.E.; Stouffer, R.J.; Meehl, G.A. An Overview of CMIP5 and the Experiment Design. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2012, 93, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, B.C.; Kriegler, E.; Riahi, K.; Ebi, K.L.; Hallegatte, S.; Carter, T.R.; Mathur, R.; van Vuuren, D.P. A new scenario framework for Climate Change Research: Scenario matrix architecture. Clim. Chang. 2014, 122, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The CMIP6 landscape. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2019, 9, 727. [CrossRef]
- Flynn, C.M.; Mauritsen, T. On the Climate Sensitivity and Historical Warming Evolution in Recent Coupled Model Ensembles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2020, 2020, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CarbonBrief. CMIP6: The Next Generation of Climate Models Explained. 1999. Available online: https://www.carbonbrief.org/cmip6-the-next-generation-of-climate-models-explained (accessed on 16 November 2020).
- Zelinka, M.D.; Myers, T.A.; McCoy, D.T.; Po-Chedley, S.; Caldwell, P.M.; Ceppi, P.; Klein, S.A.; Taylor, K.E. Causes of Higher Climate Sensitivity in CMIP6 Models. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehl, G.A.; Senior, C.A.; Eyring, V.; Flato, G.; Lamarque, J.F.; Stouffer, R.J.; Taylor, K.E.; Schlund, M. Context for interpreting equilibrium climate sensitivity and transient climate response from the CMIP6 Earth system models. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6. Available online: https://advances.sciencemag.org/content/6/26/eaba1981.full.pdf (accessed on 16 November 2020). [CrossRef]
- Boé, J.; Somot, S.; Corre, L.; Nabat, P. Large discrepancies in summer climate change over Europe as projected by global and regional climate models: Causes and consequences. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 54, 2981–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørland, S.L.; Schär, C.; Lüthi, D.; Kjellström, E. Bias patterns and climate change signals in GCM-RCM model chains. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 074017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreienkamp, F.; Paxian, A.; Früh, B.; Lorenz, P.; Matulla, C. Evaluation of the empirical–statistical downscaling method EPISODES. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 991–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, D.; Petersen, J.; Eggert, B.; Alias, A.; Christensen, O.B.; Bouwer, L.; Braun, A.; Colette, A.; Déqué, M.; Georgievski, G.; et al. EURO-CORDEX: New high-resolution climate change projections for European impact research. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2013, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübener, H.; Bülow, K.; Fooken, C.; Früh, B.; Hoffmann, P.; Höpp, S.; Keuler, K.; Menz, C.; Mohr, V.; Radtke, K.; et al. ReKliEs-De Endbericht; Technical Report. Hessisches Landesamt für Naturschutz, Umwelt und Geologie: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2018. Available online: https://cera-www.dkrz.de/WDCC/ui/cerasearch/entry?acronym=ReKliEs-De_Ergebnisbericht (accessed on 16 November 2020).
- Wyser, K.; Kjellström, E.; Koenigk, T.; Martins, H.; Döscher, R. Warmer climate projections in EC-Earth3-Veg: The role of changes in the greenhouse gas concentrations from CMIP5 to CMIP6. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 054020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauritsen, T.; Roeckner, E. Tuning the MPI-ESM1.2 Global Climate Model to Improve the Match With Instrumental Record Warming by Lowering Its Climate Sensitivity. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2020, 12, e2019MS002037. Available online: https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1029/2019MS002037 (accessed on 16 November 2020). [CrossRef]
- Rauthe, M.; Steiner, H.; Riediger, U.; Mazurkiewicz, A.; Gratzki, A. A Central European precipitation climatology? Part I: Generation and validation of a high-resolution gridded daily data set (HYRAS). Meteorol. Z. 2013, 22, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frick, C.; Steiner, H.; Mazurkiewicz, A.; Riediger, U.; Rauthe, M.; Reich, T.; Gratzki, A. Central European high-resolution gridded daily data sets (HYRAS): Mean temperature and relative humidity. Meteorol. Z. 2014, 23, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyring, V.; Bony, S.; Meehl, G.A.; Senior, C.A.; Stevens, B.; Stouffer, R.J.; Taylor, K.E. Overview of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) experimental design and organization. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 1937–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinquini, L.; Crichton, D.; Mattmann, C.; Harney, J.; Shipman, G.; Wang, F.; Ananthakrishnan, R.; Miller, N.; Denvil, S.; Morgan, M.; et al. The Earth System Grid Federation: An open infrastructure for access to distributed geospatial data. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2014, 36, 400–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swart, N.C.; Cole, J.N.; Kharin, V.V.; Lazare, M.; Scinocca, J.F.; Gillett, N.P.; Anstey, J.; Arora, V.; Christian, J.R.; Jiao, Y.; et al. CCCma CanESM5 model output prepared for CMIP6 CMIP historical. Earth Syst. Grid Fed. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swart, N.C.; Cole, J.N.; Kharin, V.V.; Lazare, M.; Scinocca, J.F.; Gillett, N.P.; Anstey, J.; Arora, V.; Christian, J.R.; Jiao, Y.; et al. CCCma CanESM5 Model Output Prepared for CMIP6 ScenarioMIP ssp245. 2019. Available online: https://cera-www.dkrz.de/WDCC/ui/cerasearch/cmip6?input=CMIP6.ScenarioMIP.CCCma.CanESM5.ssp245 (accessed on 16 November 2020).
- Swart, N.C.; Cole, J.N.; Kharin, V.V.; Lazare, M.; Scinocca, J.F.; Gillett, N.P.; Anstey, J.; Arora, V.; Christian, J.R.; Jiao, Y.; et al. CCCma CanESM5 Model Output Prepared for CMIP6 ScenarioMIP ssp585. 2019. Available online: https://cera-www.dkrz.de/WDCC/ui/cerasearch/cmip6?input=CMIP6.ScenarioMIP.CCCma.CanESM5.ssp585 (accessed on 16 November 2020).
- Hazeleger, W.; Guemas, V.; Wouters, B.; Corti, S.; Andreu-Burillo, I.; Doblas-Reyes, F.J.; Wyser, K.; Caian, M. Multiyear climate predictions using two initialization strategies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doescher, R. The EC-Earth3 earth system model for the climate model intercomparison project 6. Manuscr. Prep. 2020; Unpublished work. [Google Scholar]
- EC-Earth Consortium (EC-Earth). EC-Earth-Consortium EC-Earth3 Model Output Prepared for CMIP6 CMIP Historical. 2019. Available online: https://cera-www.dkrz.de/WDCC/ui/cerasearch/cmip6?input=CMIP6.CMIP.EC-Earth-Consortium.EC-Earth3.historical (accessed on 16 November 2020).
- EC-Earth Consortium (EC-Earth). EC-Earth-Consortium EC-Earth3 Model Output Prepared for CMIP6 ScenarioMIP ssp245. 2019. Available online: https://cera-www.dkrz.de/WDCC/ui/cerasearch/cmip6?input=CMIP6.ScenarioMIP.EC-Earth-Consortium.EC-Earth3.ssp245 (accessed on 16 November 2020).
- EC-Earth Consortium (EC-Earth). EC-Earth-Consortium EC-Earth3 Model Output Prepared for CMIP6 ScenarioMIP ssp585. 2019. Available online: https://cera-www.dkrz.de/WDCC/ui/cerasearch/cmip6?input=CMIP6.ScenarioMIP.EC-Earth-Consortium.EC-Earth3.ssp585 (accessed on 16 November 2020).
- Wieners, K.H.; Giorgetta, M.; Jungclaus, J.; Reick, C.; Esch, M.; Bittner, M.; Legutke, S.; Schupfner, M.; Wachsmann, F.; Gayler, V.; et al. MPI-M MPI-ESM1.2-LR Model Output Prepared for CMIP6 CMIP Historical. 2019. Available online: https://cera-www.dkrz.de/WDCC/ui/cerasearch/cmip6?input=CMIP6.CMIP.MPI-M.MPI-ESM1-2-LR.historical (accessed on 16 November 2020).
- Wieners, K.H.; Giorgetta, M.; Jungclaus, J.; Reick, C.; Esch, M.; Bittner, M.; Gayler, V.; Haak, H.; de Vrese, P.; Raddatz, T.; et al. MPI-M MPI-ESM1.2-LR Model Output Prepared for CMIP6 ScenarioMIP ssp245. 2019. Available online: https://cera-www.dkrz.de/WDCC/ui/cerasearch/cmip6?input=CMIP6.ScenarioMIP.MPI-M.MPI-ESM1-2-LR.ssp245 (accessed on 16 November 2020).
- Wieners, K.H.; Giorgetta, M.; Jungclaus, J.; Reick, C.; Esch, M.; Bittner, M.; Gayler, V.; Haak, H.; de Vrese, P.; Raddatz, T.; et al. MPI-M MPI-ESM1.2-LR Model Output Prepared for CMIP6 ScenarioMIP ssp585. 2019. Available online: https://cera-www.dkrz.de/WDCC/ui/cerasearch/cmip6?input=CMIP6.ScenarioMIP.MPI-M.MPI-ESM1-2-LR.ssp585 (accessed on 16 November 2020).
- Seland, Ø.; Bentsen, M.; Oliviè, D.J.L.; Toniazzo, T.; Gjermundsen, A.; Graff, L.S.; Debernard, J.B.; Gupta, A.K.; He, Y.; Kirkevåg, A.; et al. NCC NorESM2-LM Model Output Prepared for CMIP6 CMIP Historical. 2019. Available online: https://cera-www.dkrz.de/WDCC/ui/cerasearch/cmip6?input=CMIP6.CMIP.NCC.NorESM2-LM.historical (accessed on 16 November 2020).
- Seland, Ø.; Bentsen, M.; Oliviè, D.J.L.; Toniazzo, T.; Gjermundsen, A.; Graff, L.S.; Debernard, J.B.; Gupta, A.K.; He, Y.; Kirkevåg, A.; et al. NCC NorESM2-LM Model Output Prepared for CMIP6 ScenarioMIP ssp245. 2019. Available online: https://cera-www.dkrz.de/WDCC/ui/cerasearch/cmip6?input=CMIP6.ScenarioMIP.NCC.NorESM2-LM.ssp245 (accessed on 16 November 2020).
- Bentsen, M.; Oliviè, D.J.L.; Seland, Ø.; Toniazzo, T.; Gjermundsen, A.; Graff, L.S.; Debernard, J.B.; Gupta, A.K.; He, Y.; Kirkevåg, A.; et al. NCC NorESM2-MM Model Output Prepared for CMIP6 ScenarioMIP ssp585. 2019. Available online: https://cera-www.dkrz.de/WDCC/ui/cerasearch/cmip6?input=CMIP6.ScenarioMIP.NCC.NorESM2-MM.ssp585 (accessed on 16 November 2020).
- Uwe, S. Climate Data Operators (CDO) User Guide; Technical Report; DKRZ: Hamburg, Germany, 2019; p. 222. Available online: https://code.mpimet.mpg.de/projects/cdo/embedded/cdo.pdf (accessed on 17 November 2020).
- Zhu, J.; Poulsen, C.J.; Otto-Bliesner, B.L. High climate sensitivity in CMIP6 model not supported by paleoclimate. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2020, 10, 378–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, P.M.; Maycock, A.C.; McKenna, C.M.; Smith, C.J. Latest climate models confirm need for urgent mitigation. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2020, 10, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Technical Report; Intergovernmental Panel On Climate Change: Cambridge, UK, 2013; p. 1535. Available online: http://www.climatechange2013.org/images/report/WG1AR5_ALL_FINAL.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2014).
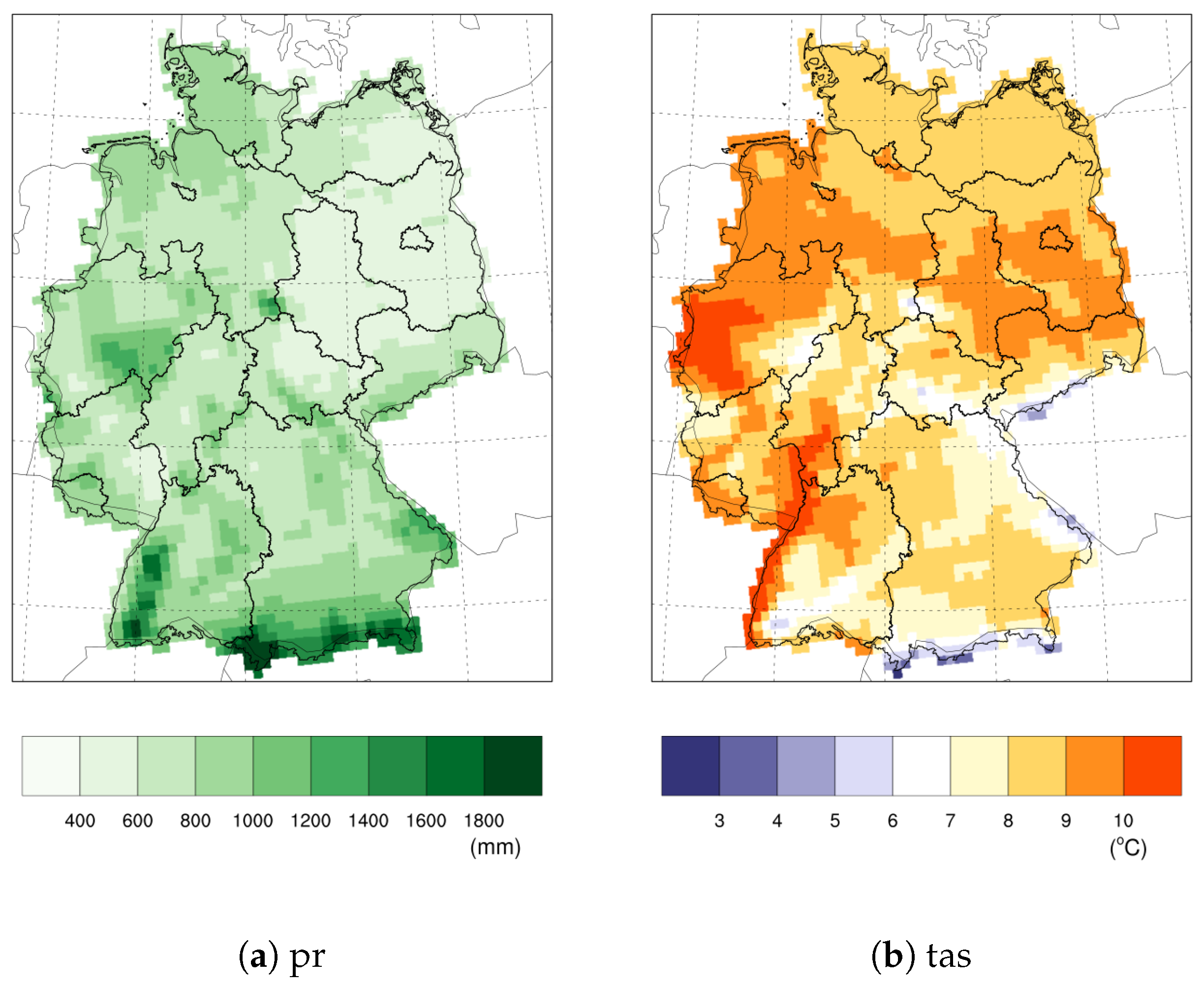
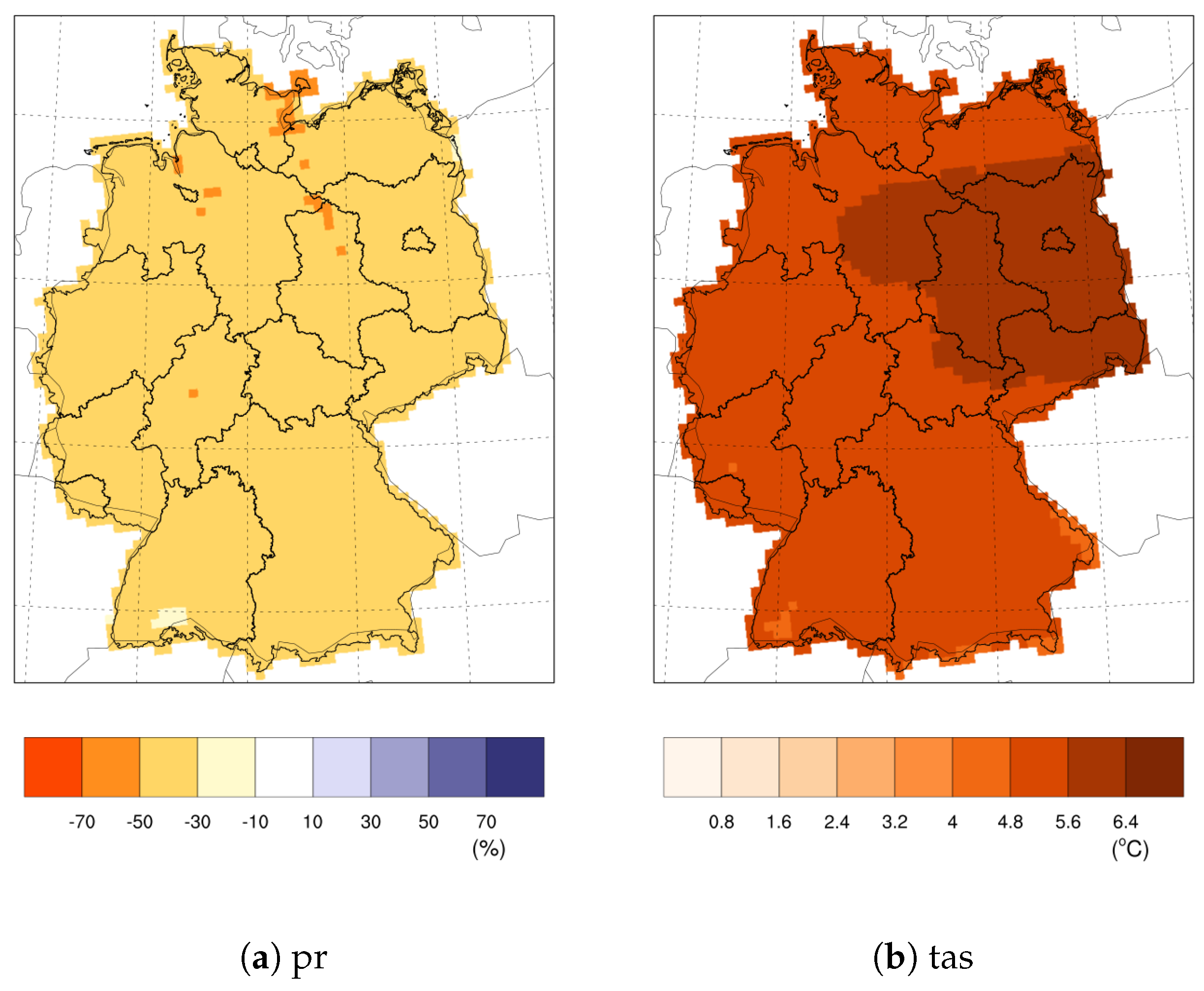
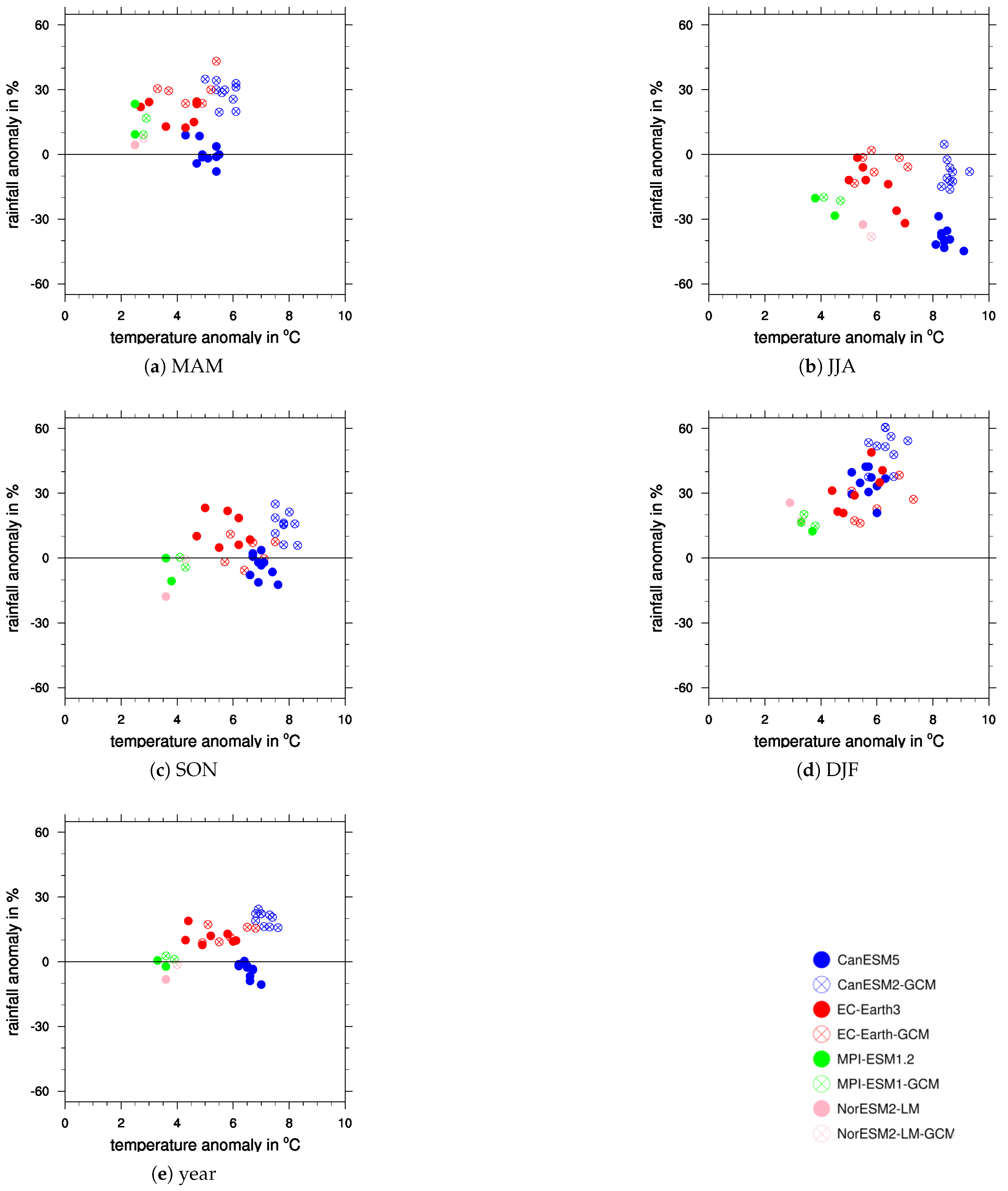
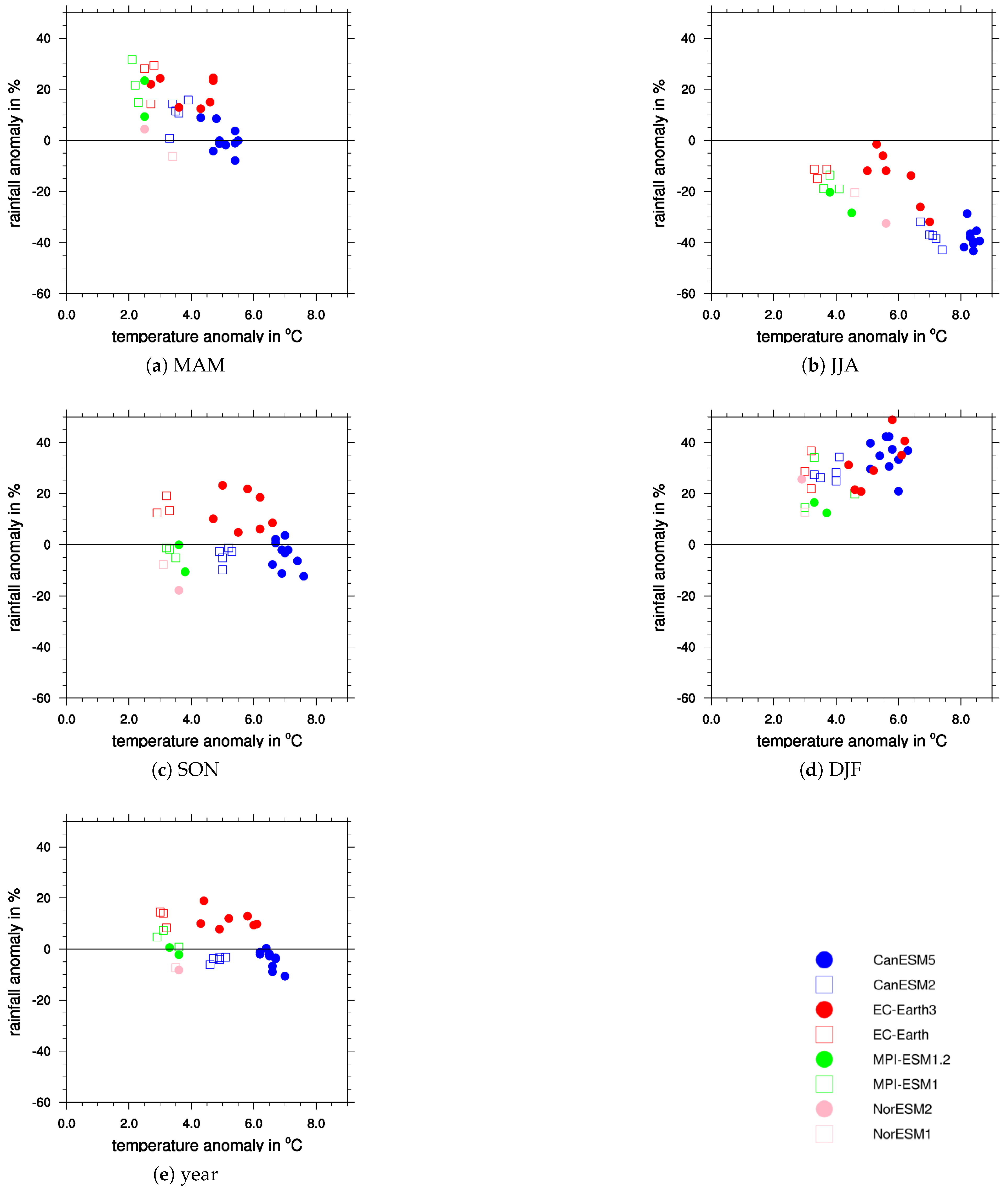
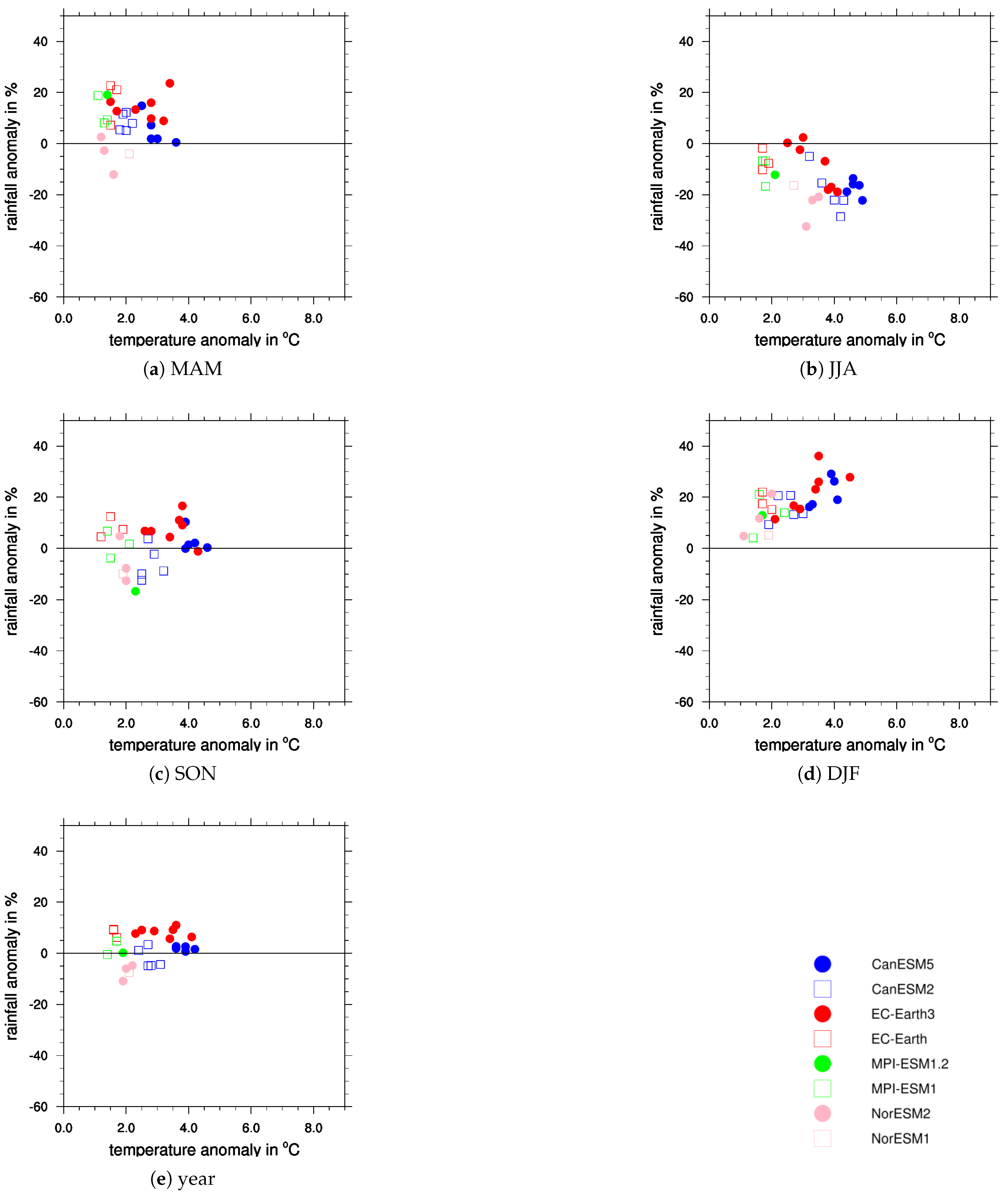
| Model | Reasons for Change in ECS since CMIP5 |
|---|---|
| MPI-ESM1.2 | Tuned with cloud parameters to be the same as CMIP5. Pretuned version had ECS = 7 caused by a positive low-cloud feedback in the tropics. |
| EC-Earth3 | Early indications of the role of cloud-aerosol interactions. |
| CanESM5 | Large increase since CMIP5 model (3.7–5.6)—at least half seems to be related to cloud feedback increase. |
| NorESM2-LM | Small decrease since CMIP5 model (2.9–2.5), which is not yet understood. |
| CMIP5 | CMIP6 | |
|---|---|---|
| CanESM | CanESM2 (r1 to r5) | CanESM5 [23,24,25] (r1 to r10) |
| EC-EARTH | EC-EARTH [26] (r2, r9, r12) | EC-EARTH3-veg [27,28,29,30] (r1, r4, r6, r9, r11, r13, r15) |
| MPI-ESM | MPI-ESM-LR (r1 to r3) | MPI-ESM1-2-HR [31,32,33] (r1 and r2) |
| NorESM | NCC-NorESM1-M (r1) | NorESM2-LM [34,35,36] (r1 to r3) |
| CMIP6 SSP5-8.5 | tas (Change in °C) | pr (Change in %) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2071–2100 | MAM | JJA | SON | DJF | year | MAM | JJA | SON | DJF | year |
| CanESM | −0.6 | −0.2 | −0.8 | −0.6 | −0.6 | −28 | −30 | −19 | −18 | −24 |
| EC-EARTH | −0.5 | −0.1 | −0.8 | −0.7 | −0.5 | −11 | −10 | 10 | 10 | −2 |
| MPI-ESM | −0.4 | −0.3 | −0.5 | −0.1 | −0.3 | 3 | −4 | −3 | −3 | −3 |
| NorESM | −0.3 | −0.3 | −0.7 | −0.4 | −0.4 | −3 | 6 | −17 | 9 | −7 |
| CMIP5 RCP8.5 | tas (Change in °C) | pr (Change in %) | ||||||||
| 2071–2100 | MAM | JJA | SON | DJF | year | MAM | JJA | SON | DJF | year |
| CanESM | −0.4 | −0.1 | −0.4 | −0.4 | −0.3 | −11 | −13 | −7 | −8 | −12 |
| EC-EARTH | −0.5 | −0.2 | −0.6 | −0.1 | −0.4 | 0 | −4 | 15 | 6 | −3 |
| MPI-ESM | −0.4 | −0.6 | −0.8 | −0.2 | −0.6 | 12 | 9 | −2 | 0 | 4 |
| NorESM | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 10 | 19 | 20 | 9 | 15 |
| SSP5-8.5/RCP8.5 | tas (Change in °C) | pr (Change in %) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2041–2070 | MAM | JJA | SON | DJF | year | MAM | JJA | SON | DJF | year |
| CanESM | 0.9 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 1.0 | −7 | −2 | 2 | 0 | −1 |
| EC-EARTH | 0.8 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.1 | 1.3 | −1 | −3 | 0 | −2 | −1 |
| MPI-ESM | −0.3 | −0.1 | 0.0 | −0.2 | −0.1 | 2 | −1 | 0 | −5 | −1 |
| NorESM | −0.7 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | −7 | 5 | −18 | 9 | −4 |
| SSP5-8.5/RCP8.5 | tas (Change in °C) | pr (Change in %) | ||||||||
| 2071–2100 | MAM | JJA | SON | DJF | year | MAM | JJA | SON | DJF | year |
| CanESM | 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 1.7 | −10 | −1 | 0 | 7 | 0 |
| EC-EARTH | 1.3 | 2.5 | 2.6 | 2.2 | 2.1 | −5 | −2 | −2 | 3 | −1 |
| MPI-ESM | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.4 | −0.1 | 0.3 | −6 | −7 | −3 | −8 | −5 |
| NorESM | −0.9 | 1.0 | 0.5 | −0.1 | 0.1 | 11 | −12 | −10 | 13 | −1 |
| SSP2-4.5/RCP4.5 | tas (Change in °C) | pr (Change in %) | ||||||||
| 2041–2070 | MAM | JJA | SON | DJF | year | MAM | JJA | SON | DJF | year |
| CanESM | 0.6 | 0.4 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 0.8 | −4 | 3 | −2 | 0 | 0 |
| EC-EARTH | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 3 | 5 | 4 | −2 | 3 |
| MPI-ESM | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.3 | −0.2 | 0.3 | 8 | −9 | −6 | −9 | −4 |
| NorESM | −0.8 | 0.2 | −0.2 | −0.2 | −0.2 | 0 | −1 | −4 | 8 | 0 |
| SSP2-4.5/RCP4.5 | tas (Change in °C) | pr (Change in %) | ||||||||
| 2071–2100 | MAM | JJA | SON | DJF | year | MAM | JJA | SON | DJF | year |
| CanESM | 1.0 | 0.8 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 1.1 | −3 | 1 | 9 | 0 | 4 |
| EC-EARTH | 1.0 | 1.6 | 2.0 | 1.4 | 1.6 | −3 | −2 | 0 | −2 | 0 |
| MPI-ESM | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.6 | -0.1 | 0.3 | 7 | −2 | −18 | −9 | −3 |
| NorESM | −0.7 | 0.6 | 0.0 | −0.3 | −0.1 | 0 | −9 | 5 | 8 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kreienkamp, F.; Lorenz, P.; Geiger, T. Statistically Downscaled CMIP6 Projections Show Stronger Warming for Germany. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111245
Kreienkamp F, Lorenz P, Geiger T. Statistically Downscaled CMIP6 Projections Show Stronger Warming for Germany. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(11):1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111245
Chicago/Turabian StyleKreienkamp, Frank, Philip Lorenz, and Tobias Geiger. 2020. "Statistically Downscaled CMIP6 Projections Show Stronger Warming for Germany" Atmosphere 11, no. 11: 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111245
APA StyleKreienkamp, F., Lorenz, P., & Geiger, T. (2020). Statistically Downscaled CMIP6 Projections Show Stronger Warming for Germany. Atmosphere, 11(11), 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111245





