Multilevel Validation of Doppler Wind Lidar by the 325 m Meteorological Tower in the Planetary Boundary Layer of Beijing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment and Methodology
2.1. Observation Site and Instruments
2.2. Retrieval Methods and Data Processing
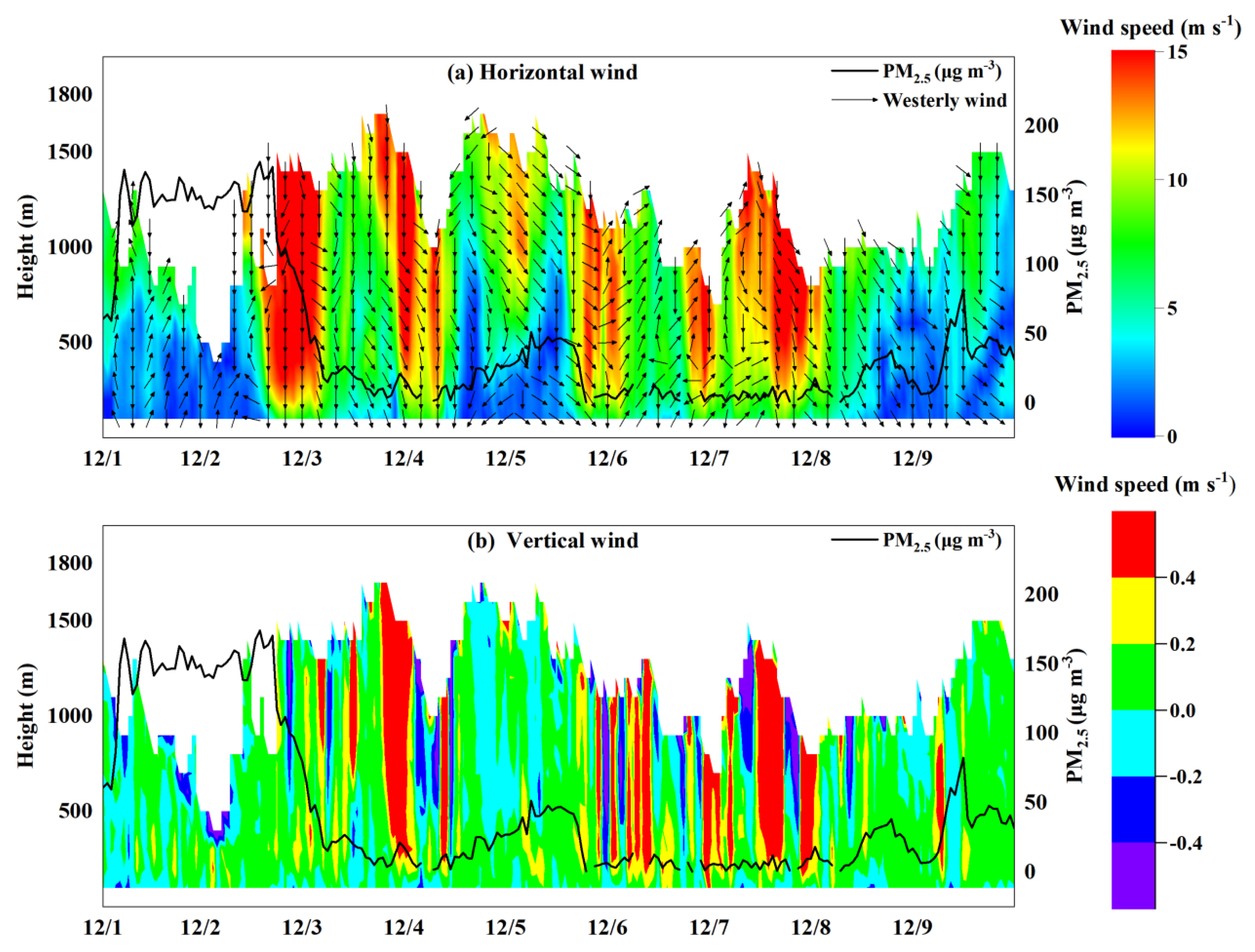
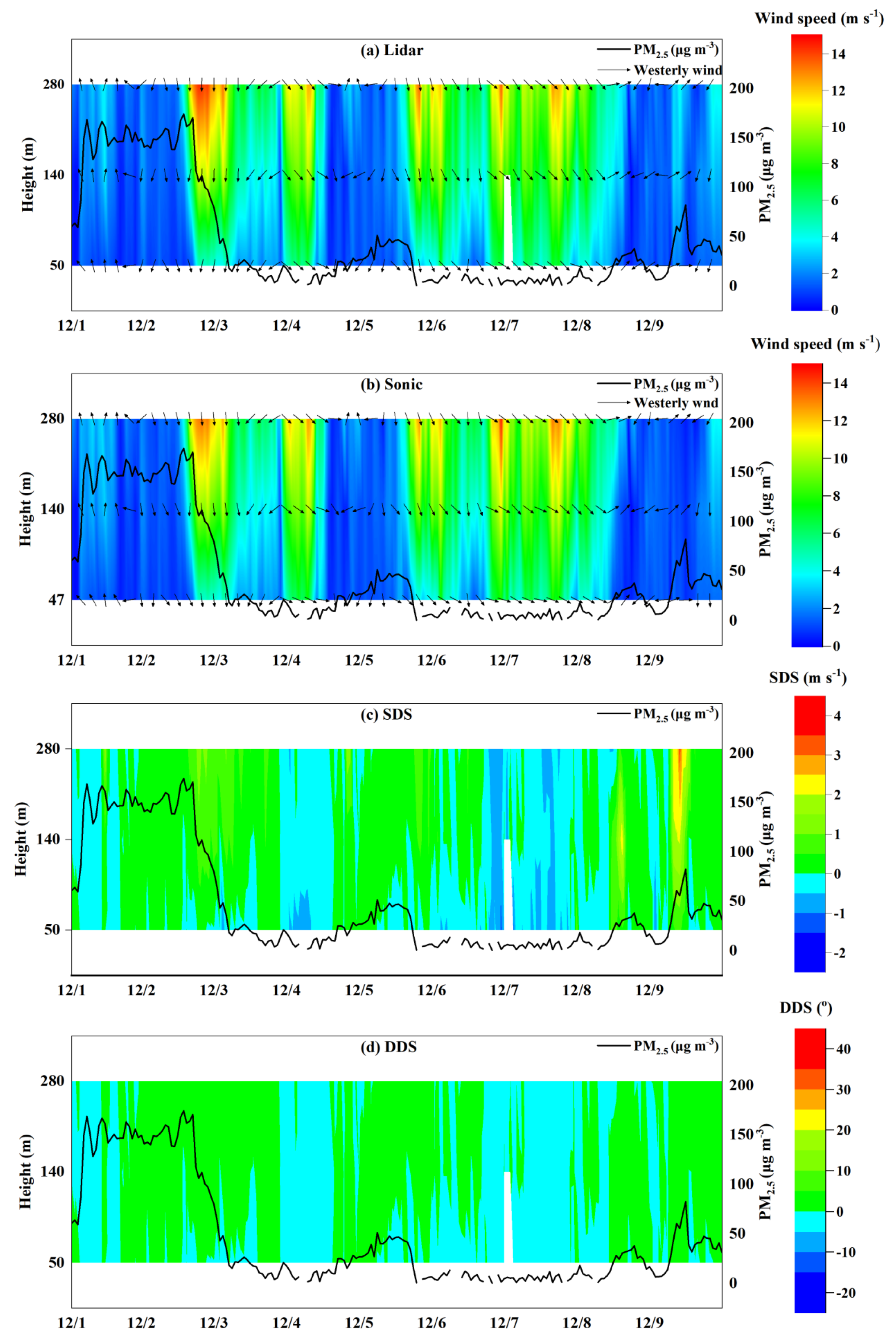
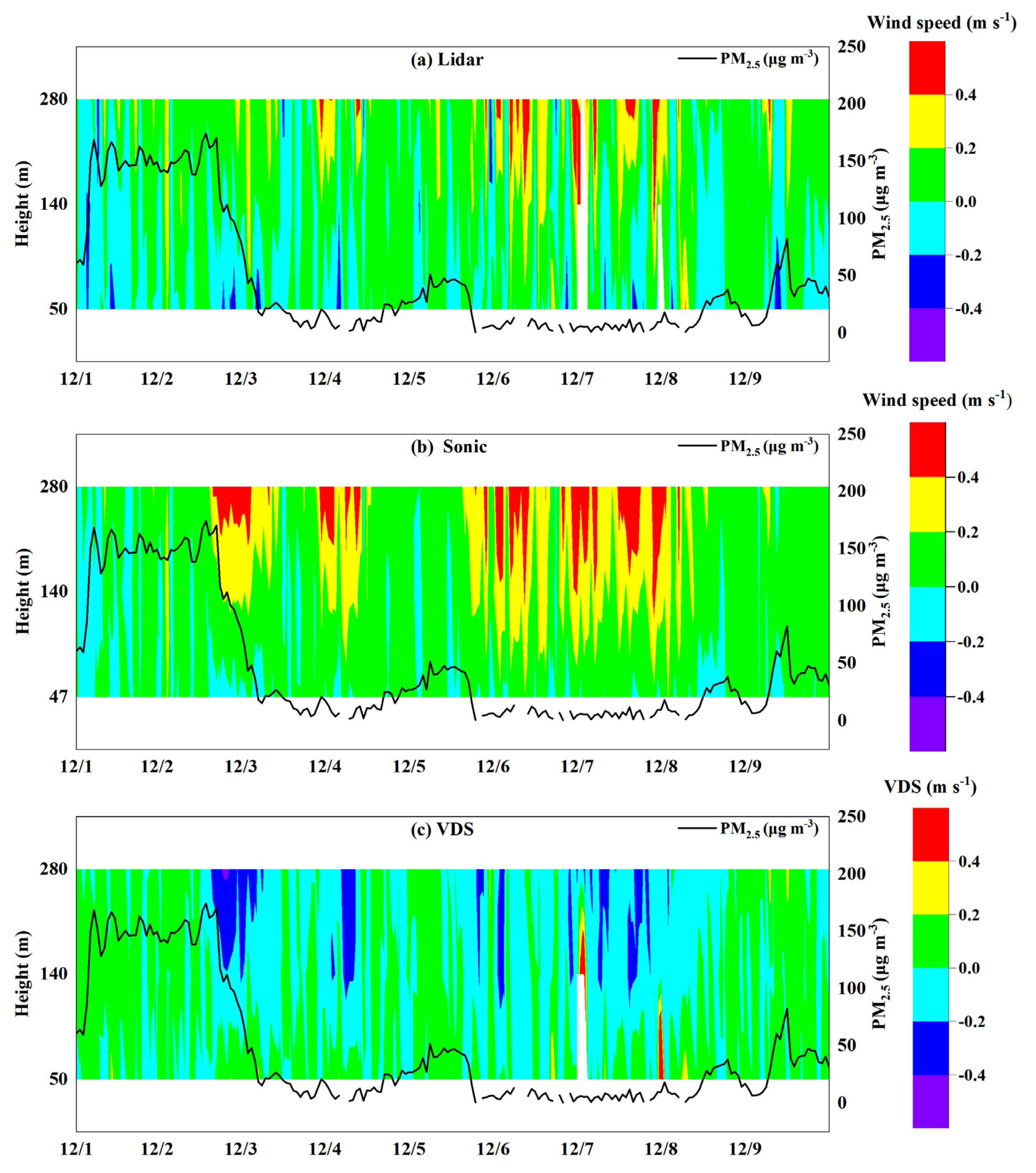
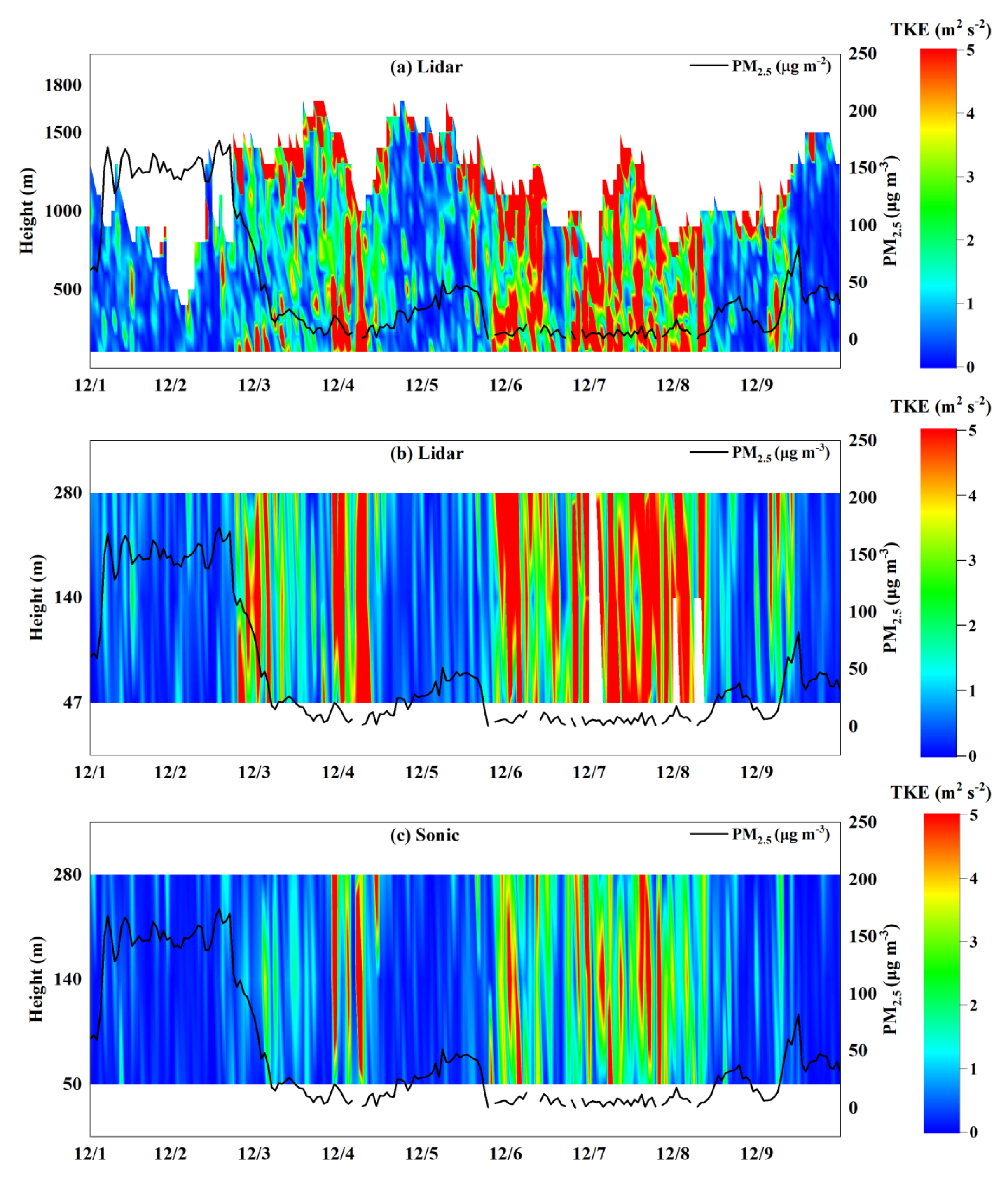
3. The General Situation during Pollution Episodes over Beijing
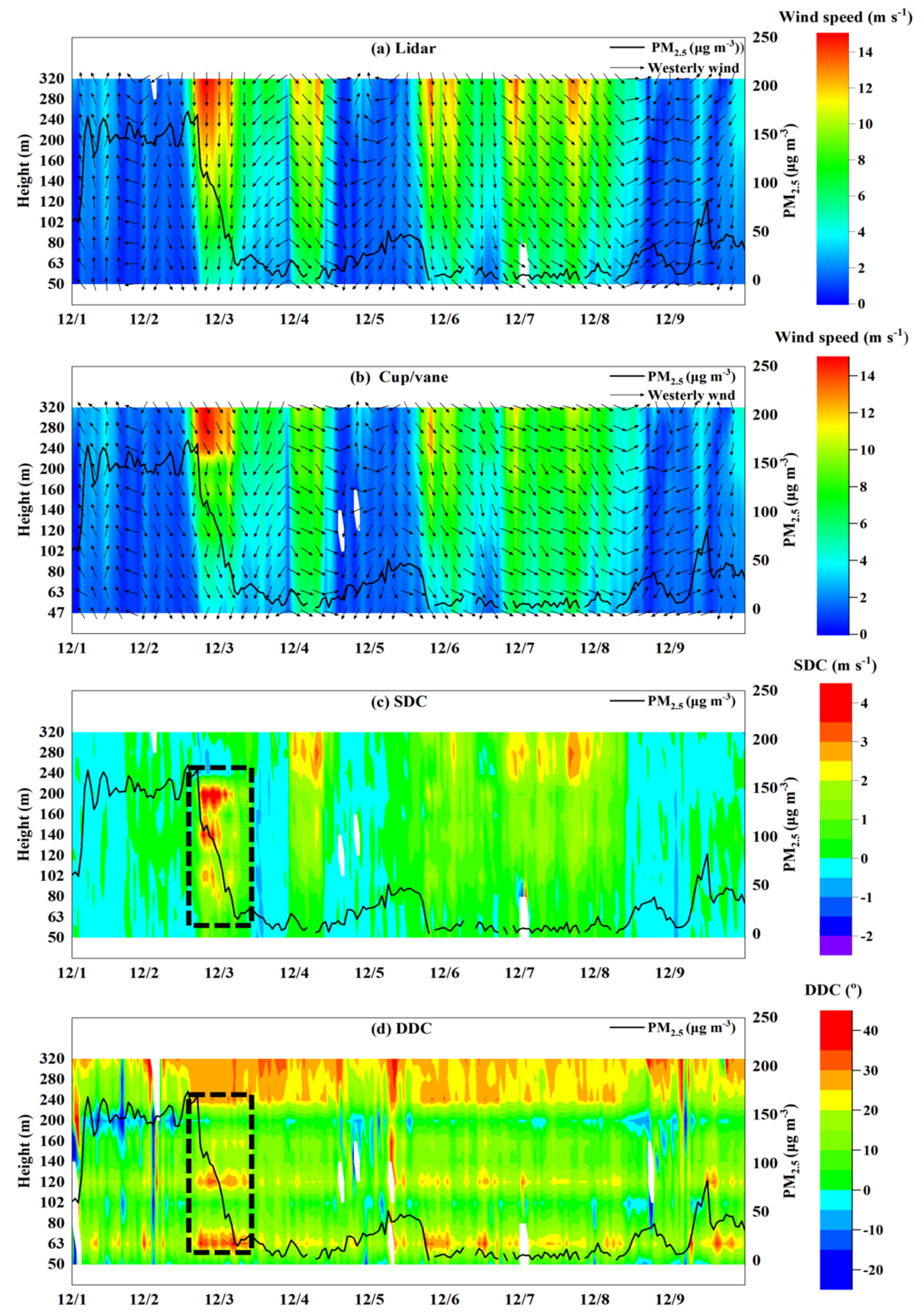
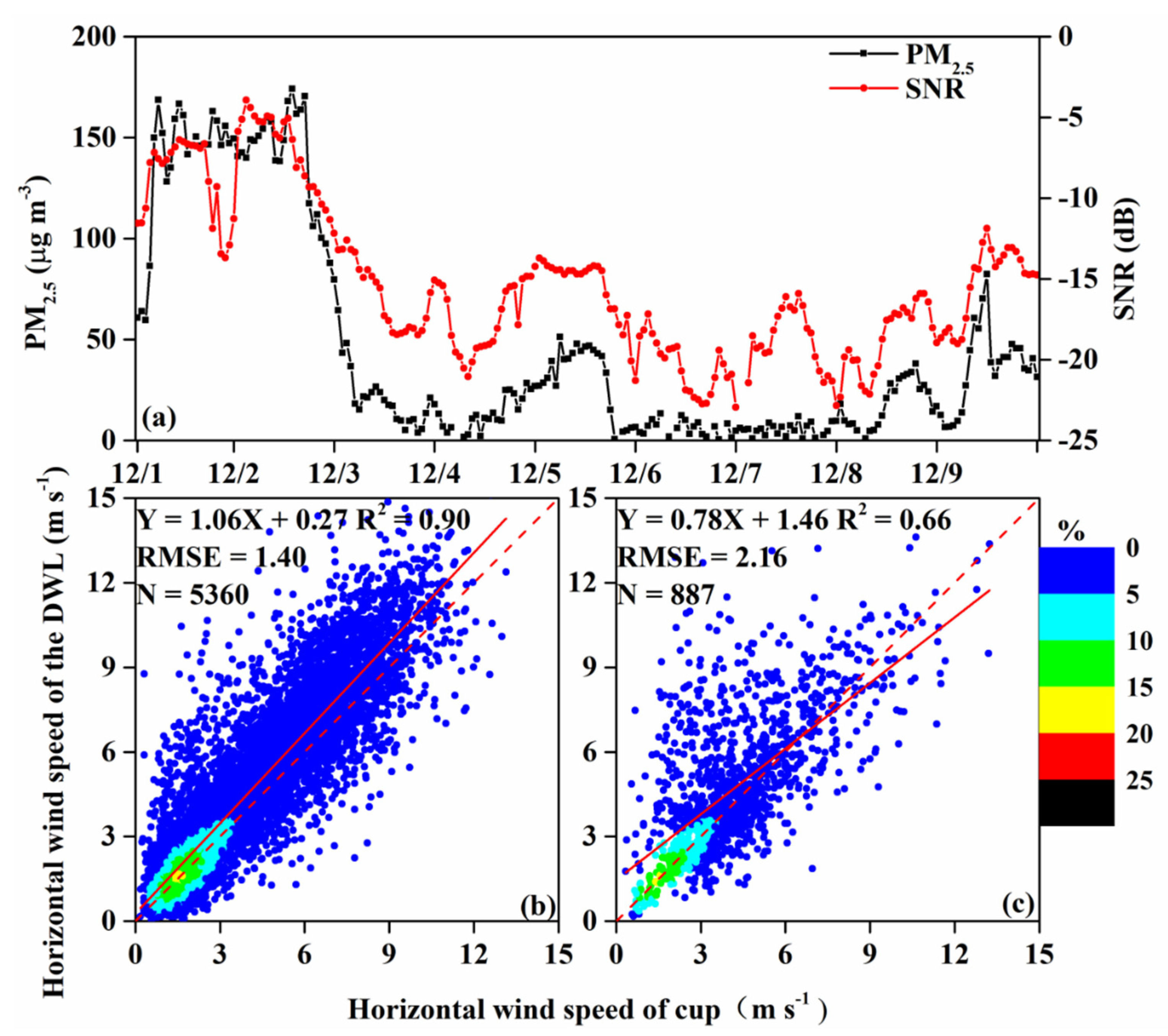
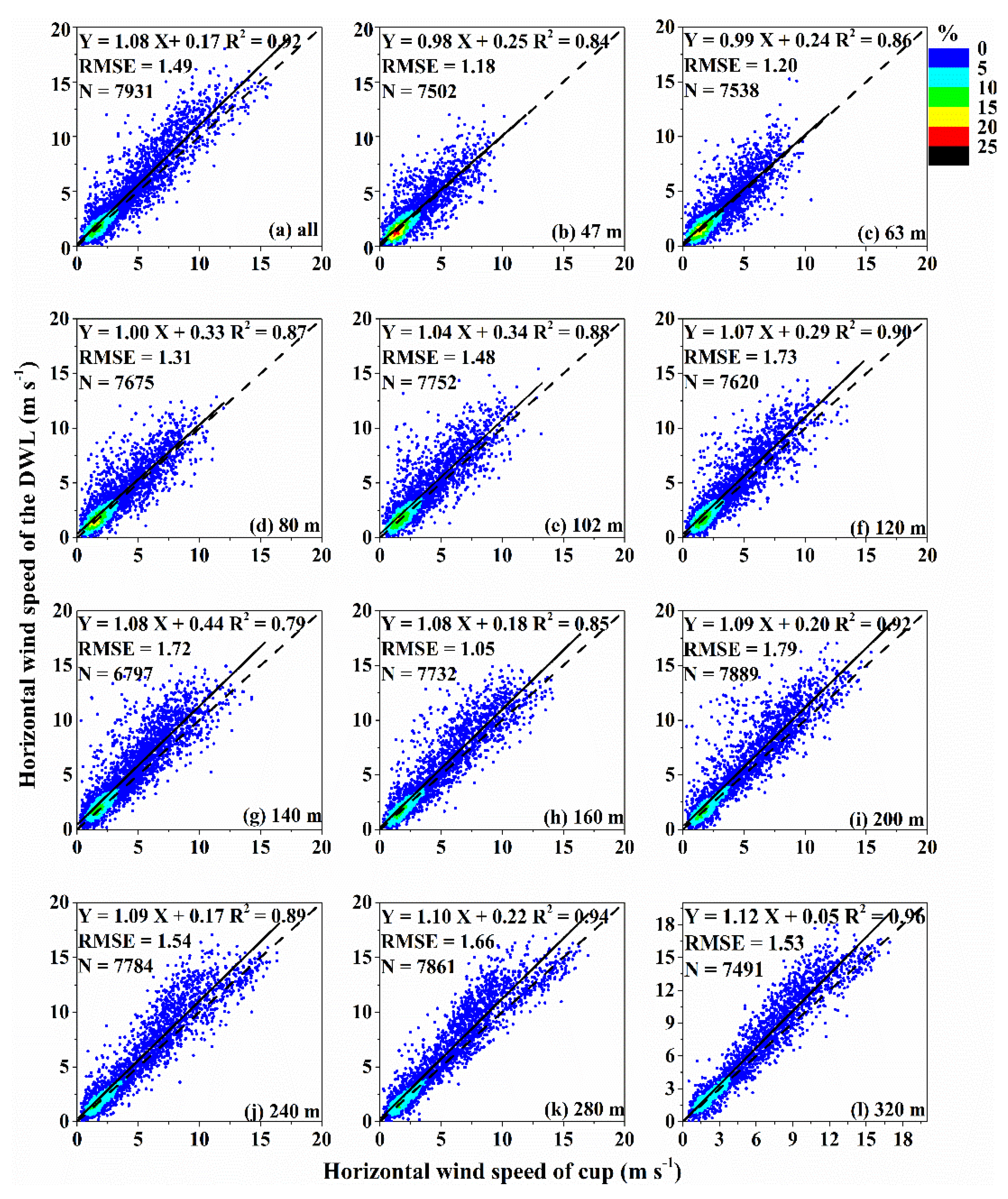
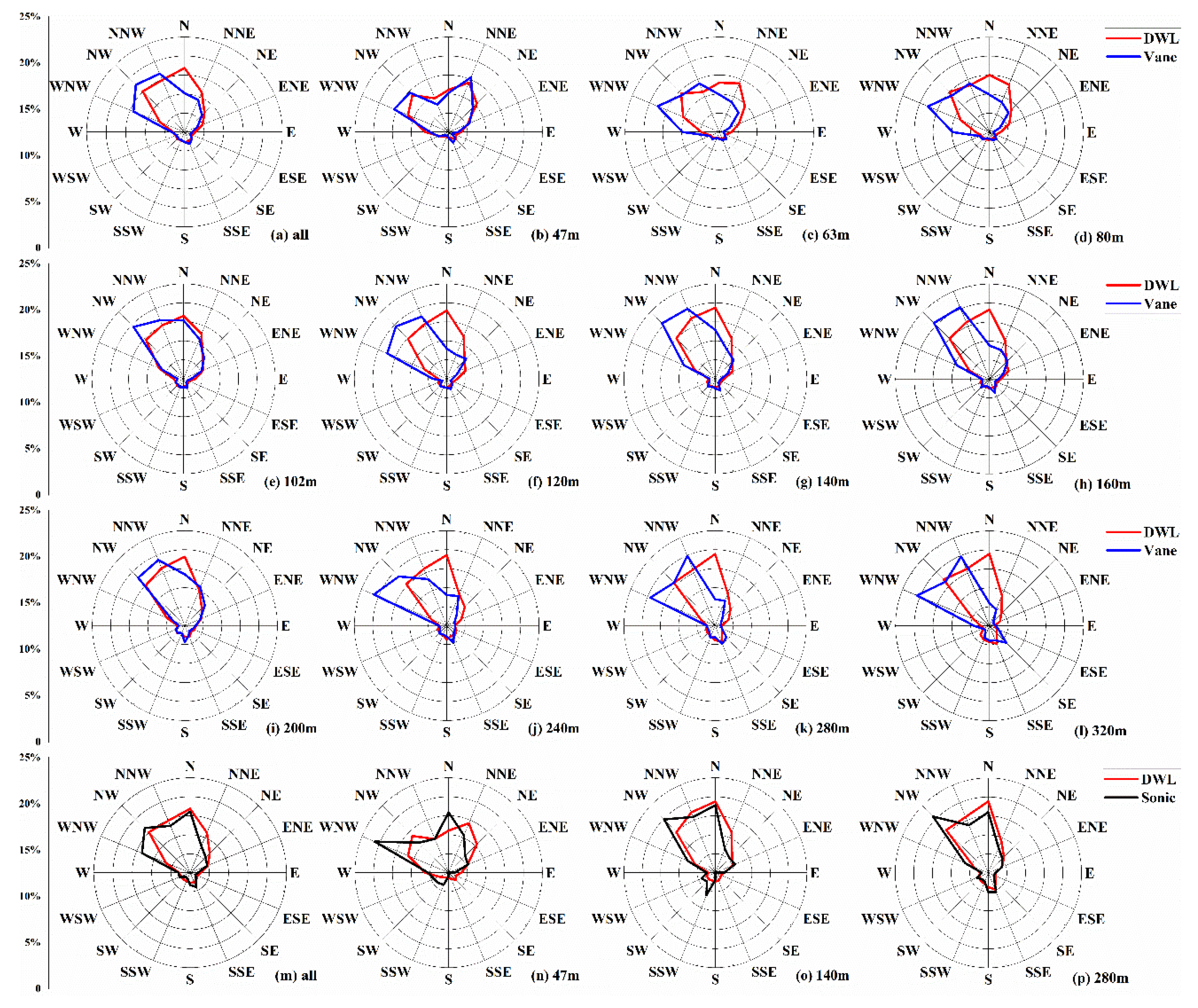
4. Horizontal Wind Validation of the DWL by a Cup Anemometer and Wind Vane
5. Three-Dimensional Wind Validation of the DWL by a Sonic Wind Anemometer
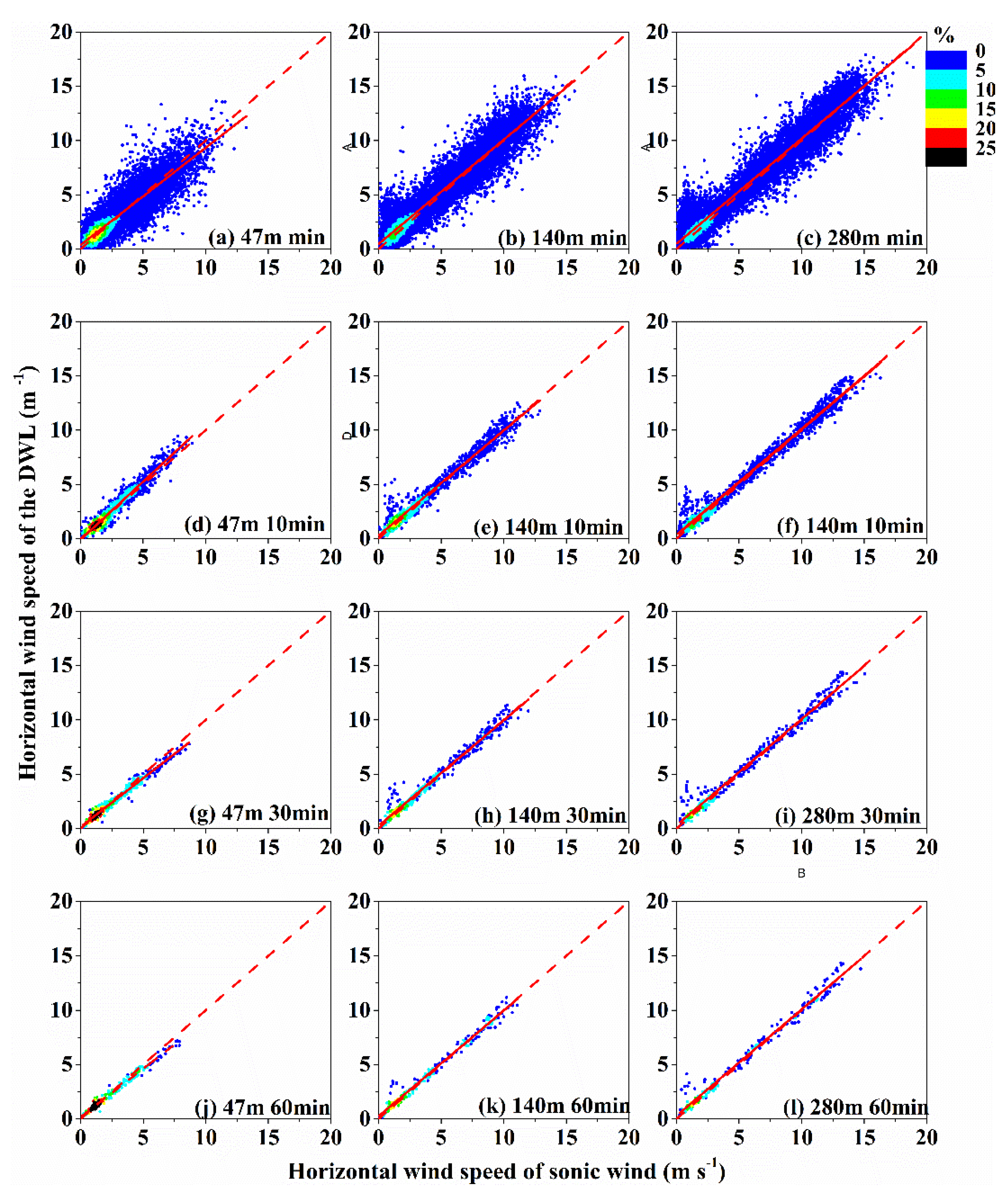
5.1. Horizontal Wind Validation of the DWL by a Sonic Wind Anemometer
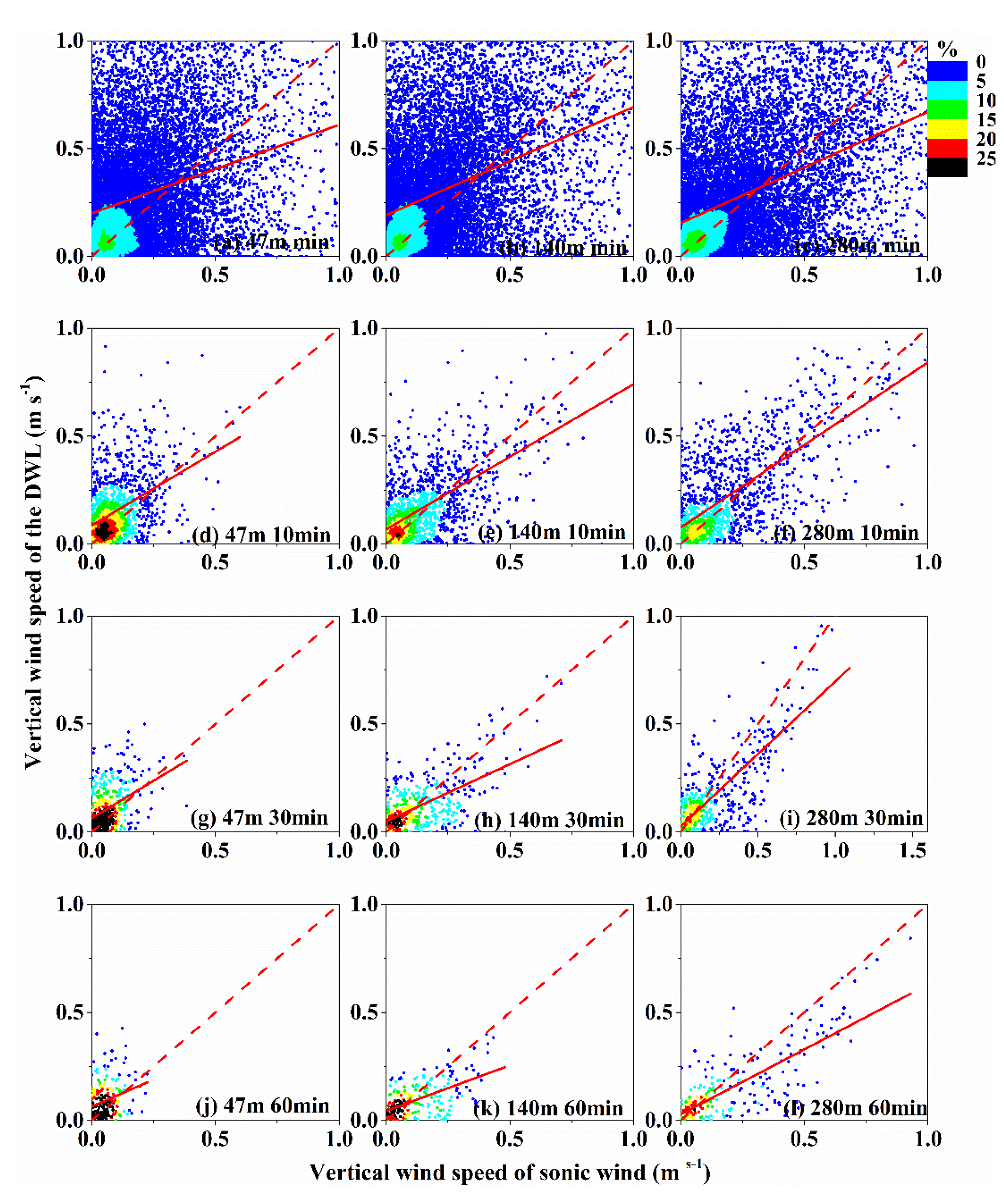
5.2. Vertical Wind Validation of the DWL by a Sonic Wind Anemometer
5.3. TKE Validation of the DWL by a Sonic Wind Anemometer
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gresham, C.A.; Williams, T.M.; Lipscomb, D.J. Hurricane Hugo Wind Damage to Southeastern U.S. Coastal Forest Tree Species. Biotropica 1991, 23, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogwijk, M.; Vries, B.D.; Turkenburg, W. Assessment of the global and regional geographical, technical and economic potential of onshore wind energy. Energy Econ. 2004, 27, 889–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.G.; Annamalai, H. Climate change and the South Asian summer monsoon. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novan, K. Valuing the Wind: Renewable Energy Policies and Air Pollution Avoided. Am. Econ. J. Econ. Policy 2015, 7, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañadillas, B.; Westerhellweg, A. Testing the performance of a ground-based wind LiDAR system: One-year inter-comparison at the offshore platform FINO1. Dewi Mag. 2011, 38, 58–74. [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich, K.; Lundquist, J.K.; Aitken, M.; Kalina, E.A.; Marshell, R.F. Stability and Turbulence in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer: A Comparison of Remote Sensing and Tower Observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundquist, J.K.; Churchfield, M.J.; Lee, S.; Clifton, A. Quantifying error of lidar and sodar Doppler beam swinging measurements of wind turbine wakes using computational fluid dynamics. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 907–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haefele, A.; Ruffieux, D. Validation of the 1290 MHz wind profiler at Payerne, Switzerland, using radiosonde GPS wind measurements. Meteorol. Appl. 2015, 22, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathe, A.; Mann, J. A review of turbulence measurements using ground-based wind lidars. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 7, 3147–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.F.; Klein, P.M.; Wharton, S.; Sathe, A.; Bonin, T.A.; Chilson, P.B.; Muschinski, A. Evaluation of three lidar scanning strategies for turbulence measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist, J.K.; Wilczak, J.M.; Ashton, R.; Bianco, L.; Brewer, W.A.; Choukulkar, A.; Clifton, A.; Debnath, M.Q.; Delgado, R.; Friedrich, K.; et al. Assessing State-of-the-Art Capabilities for Probing the Atmospheric Boundary Layer: The XPIA Field Campaign. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 2, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumer, V.M.; Reuder, J.; Furevik, B.R. A Comparison of LiDAR and Radiosonde Wind Measurements. Energy Procedia 2014, 53, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Päschke, E.; Leinweber, R.; Lehmanu, V. An one-year comparison of 482 MHz radar wind profiler, RS92-SGP Radiosonde and 1.5 μm Doppler Lidar wind measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss 2014, 7, 11439–11479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissmann, M.; Busen, R.; Dörnbrack, A.; Rahm, S.; Reitebuch, O. Targeted Observations with an Airborne Wind Lidar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2005, 22, 1706–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achtert, P.; Brooks, I.M.; Brooks, B.J.; Moat, B.I.; Prytherch, J.; Persson, P.O.G.; Tjernström, M. Measurement of wind profiles by motion-stabilised ship-borne Doppler lidar. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 4993–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.K.; Yao, X. Air pollution in mega cities in China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, H.D.; Chen, R.J.; Tong, S.L. Ambient air pollution, climate change, and population health in China. Environ. Int. 2012, 42, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.F.; Cao, J.J.; Han, Y.M.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.J.; Gong, S.L.; Yu, Y.; Yu, L.J.; Wu, L.; Mao, H.J.; Song, C.B.; Zhao, S.P.; Lin, H.L.; Li, X.Y.; et al. Air pollution characteristics and their relation to meteorological conditions during 2014-2015 in major Chinese cities. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jiboori, M.H.; Hu, F. Surface Roughness around a 325-m Meteorological Tower and Its Effect on Urban Turbulence. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 22, 595–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.D.; Xin, J.Y.; Gong, C.S.; Quan, J.N.; Liu, G.J.; Zhao, W.P.; Wang, Y.S.; Liu, Z.; Song, T. The formation mechanism of air pollution episodes in Beijing city: Insights into the measured feedback between aerosol radiative forcing and the atmospheric boundary layer stability. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.M.; Zhang, Q.H.; Ji, D.S.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.W.; Wang, P.; Ding, L.; Jiang, G.B. Levels and Vertical Distributions of PCBs, PBDEs, and OCPs in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer: Observation from the Beijing 325-m Meteorological Tower. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1030–1035. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.S.; Zhi, L.; Hu, F. Boundary layer wind structure from observations on a 325 m tower. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2010, 98, 818–832. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, S.F.; Jiang, R.B.; Qie, X.S.; Wang, D.F.; Sun, Z.L.; Liu, M.Y. Characteristics of upward lightning on the Beijing 325 m meteorology tower and corresponding thunderstorm conditions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 12093–12095. [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey, K.; Quelet, P.T.; Choukulkar, A.; Wilczak, J.M.; Wolfe, D.E.; Oncley, S.P.; Brewer, W.A.; Debnath, M.; Ashton, R.; Jungo, G.V.; et al. Identification of tower-wake distortions using sonic anemometer and lidar measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 393–407. [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa, J. A revaluation of the Kansas mast influence on measurements of stress and cup anemometer overspeeding. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1980, 18, 411–430. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, T. Dynamic Response of a Cup Anemometer. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1987, 4, 281–287. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, D.B. Comparison of Three Methods for Calculating the Standard Deviation of the Wind Direction. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1987, 25, 703. [Google Scholar]
- Yamartino, R.J. A Comparison of Several “Single-Pass” Estimators of the Standard Deviation of Wind Direction. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1987, 23, 1372–1377. [Google Scholar]
- Wilczak, J.M.; Oncley, S.P.; Stage, S.A. Sonic anemometer tilt correction algorithms. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2001, 99, 127–150. [Google Scholar]
- Kumer, V.M.; Reuder, J.; Dorninger, M.; Zauner, R.; Grubišić, V. Turbulent kinetic energy estimates from profiling wind LiDAR measurements and their potential for wind energy applications. Renew. Energy 2016, 99, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, J.; Tie, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, D.L. Characteristics of heavy aerosol pollution during the 2012–2013 winter in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 88, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, B.; Zhang, J.K.; Yu, Y.C.; Wang, Y.S. Characteristics of aerosol size distributions and chemical compositions during wintertime pollution episodes in Beijing. Atmos. Res. 2015, 168, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsom, R.K.; Brewer, W.A.; Wilczak, J.M.; Wolfe, D.E.; Oncley, S.P.; Lundquist, J.K. Validating precision estimates in horizontal wind measurements from a Doppler lidar. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathe, A.; Mann, J.; Vasiljevic, N.; Lea, G. A six-beam method to measure turbulence statistics using ground-based wind lidars. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratto, G.; Maronna, R.; Berri, G. Analysis of Wind Roses Using Hierarchical Cluster and Multidimensional Scaling Analysis at La Plata, Argentina. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2010, 137, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, R.P. Geomagnetic field variations. Space Sci. Rev. 1976, 18, 413–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonin, T.A.; Newman, J.F.; Klein, P.M.; Chilson, P.B.; Wharton, S. Improvement of vertical velocity statistics measured by a Doppler lidar through comparison with sonic anemometer observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 5833–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browninga, K.A.; Wexler, R. The Determination of Kinematic Properties of a Wind Field Using Doppler Radar. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1968, 7, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.; Cariou, J.P.; Courtney, M.S.; Parmentier, R.; Mikkelsen, T.; Wagner, R.; Lindelöw, P.; Sj¨oholm, M.; Enevoldsen, K. Comparison of 3D turbulence measurements using three staring wind lidars and a sonic anemometer. Meteorol. Ztschrift 2009, 18, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathe, A.; Mann, J.; Gottschall, J.; Courtney, M.S. Can Wind Lidars Measure Turbulence? J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2011, 28, 853–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Hocut, C.M.; Hoch, S.W.; Creegan, E.; Fernando, H.J.S.; Whiteman, C.D.; Felton, M.; Huynh, G. Triple doppler wind lidar observations during the mountain terrain atmospheric modeling and observations field campaign. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 02615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuertes, F.C.; Iungo, G.V.; Porté-Agel, F. 3D turbulence measurements using three synchronous wind lidars: Validation against sonic anemometry. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
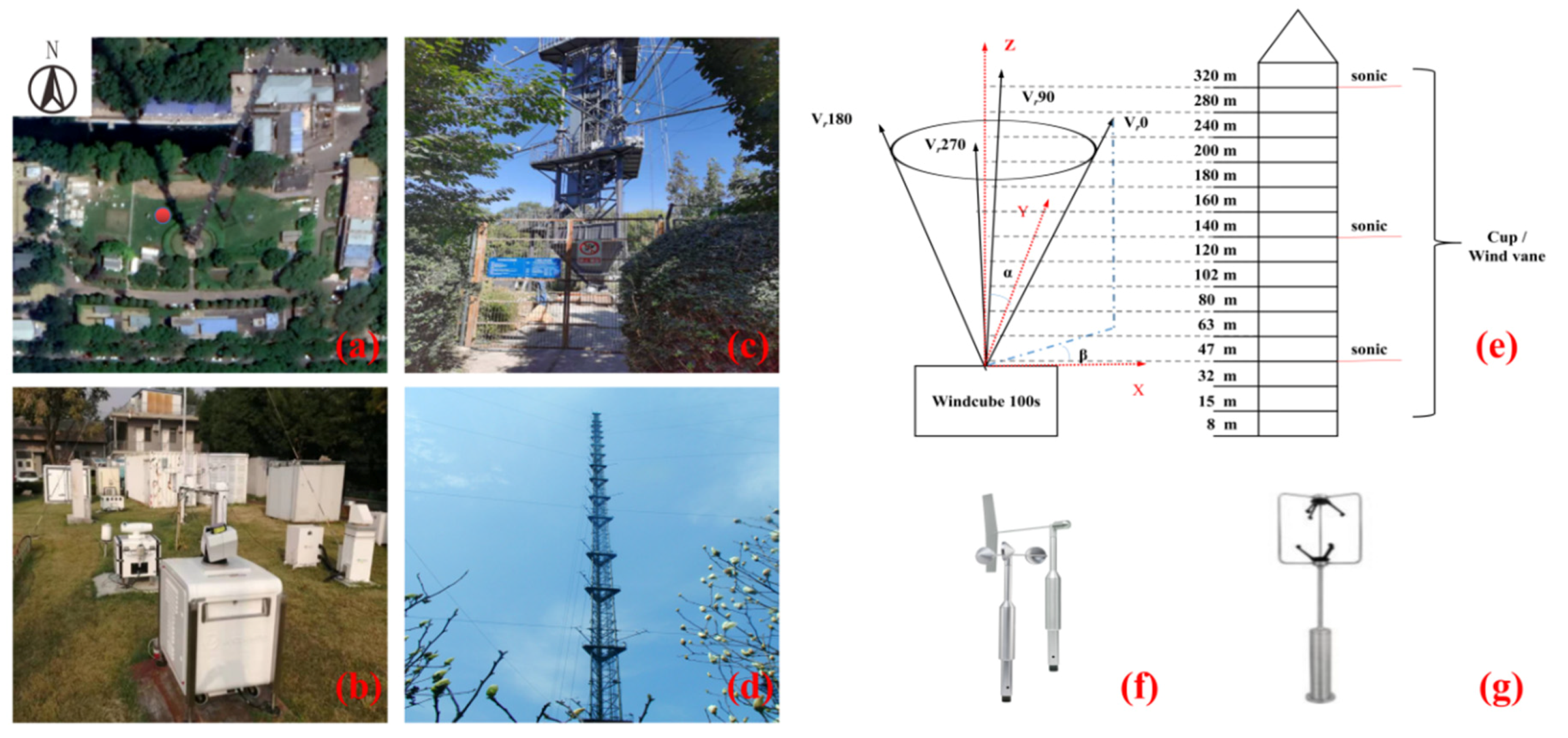
| Parameters | Doppler Wind Lidar | Cup Anemometer | Wind Vane | Sonic Wind Anemometer | PM2.5 Sampler |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instrument | Windcube 100s * | MetOne 010C | MetOne 020C | Windmaster-pro * | RP1400 |
| Resolution | 0.01 m s−1/ 0.1° | 0.1 m s−1 | 0.1° | 0.01 m s−1/ 0.1° | 0.01 μg m−3 |
| Accuracy | ±0.5 m s−1/ ±1° | ±0.07 m s−1 | ±3° | ±12 m s−1 | ±1.5 μg m−3 h−1 |
| Range | 0–60 m s−1/ 0–360° | 0–60 m s−1 | 0–360° | 0–45 m s−1/ 0–359° | 0–5 μg m−3 |
| level | 50 (47), 63, 80, 102, 120, 140, 160, 200, 240, 280, 320 m AGLs | 50 (47), 140, 280 m AGLs | 8 m AGLs | ||
| Horizontal DWL vs. Sonic Wind Anemometer | Vertical DWL vs. Sonic Wind Anemometer | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H (m) | Slope | Offset | R2 | N | RMSE | Slope | Offset | R2 | N | RMSE |
| 47–1 min | 0.9 | 0.38 | 0.9 | 7683 | 0.99 | 0.41 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 6794 | 0.37 |
| 140–1 min | 0.96 | 0.46 | 0.95 | 7861 | 1.1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 6769 | 0.37 |
| 280–1 min | 0.97 | 0.46 | 0.97 | 7935 | 1.11 | 0.52 | 0.15 | 0.46 | 6632 | 0.31 |
| 47–10 min | 1.07 | −0.08 | 0.97 | 762 | 1.11 | 0.68 | 0.09 | 0.43 | 794 | 0.46 |
| 140–10 min | 0.97 | 0.29 | 0.98 | 785 | 0.58 | 0.67 | 0.07 | 0.63 | 773 | 0.46 |
| 280–10 min | 0.98 | 0.34 | 0.98 | 787 | 0.67 | 0.76 | 0.08 | 0.75 | 762 | 0.2 |
| 47–30 min | 0.9 | 0.17 | 0.98 | 260 | 0.36 | 0.69 | 0.06 | 0.41 | 264 | 0.12 |
| 140–30 min | 0.97 | 0.25 | 0.99 | 263 | 0.49 | 0.69 | 0.06 | 0.59 | 264 | 0.14 |
| 280–30 min | 0.98 | 0.31 | 0.99 | 264 | 0.61 | 0.67 | 0.02 | 0.77 | 264 | 0.17 |
| 47–60 min | 0.89 | 0.18 | 0.99 | 132 | 0.58 | 0.5 | 0.06 | 0.48 | 132 | 0.12 |
| 140–60 min | 0.97 | 0.24 | 0.99 | 132 | 0.45 | 0.42 | 0.04 | 0.57 | 132 | 0.13 |
| 280–60 min | 0.98 | 0.29 | 0.99 | 132 | 0.58 | 0.6 | 0.03 | 0.77 | 132 | 0.13 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, L.; Xin, J.; Zuo, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, X.; Ma, Y.; Jia, D.; Wu, F. Multilevel Validation of Doppler Wind Lidar by the 325 m Meteorological Tower in the Planetary Boundary Layer of Beijing. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101051
Dai L, Xin J, Zuo H, Ma Y, Zhang L, Wu X, Ma Y, Jia D, Wu F. Multilevel Validation of Doppler Wind Lidar by the 325 m Meteorological Tower in the Planetary Boundary Layer of Beijing. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(10):1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101051
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Lindong, Jinyuan Xin, Hongchao Zuo, Yongxiang Ma, Lei Zhang, Xinrui Wu, Yongjing Ma, Danjie Jia, and Fangkun Wu. 2020. "Multilevel Validation of Doppler Wind Lidar by the 325 m Meteorological Tower in the Planetary Boundary Layer of Beijing" Atmosphere 11, no. 10: 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101051
APA StyleDai, L., Xin, J., Zuo, H., Ma, Y., Zhang, L., Wu, X., Ma, Y., Jia, D., & Wu, F. (2020). Multilevel Validation of Doppler Wind Lidar by the 325 m Meteorological Tower in the Planetary Boundary Layer of Beijing. Atmosphere, 11(10), 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101051






