Impacts of the Tropical Pacific–Indian Ocean Associated Mode on Madden–Julian Oscillation over the Maritime Continent in Boreal Winter
Abstract
1. Introduction
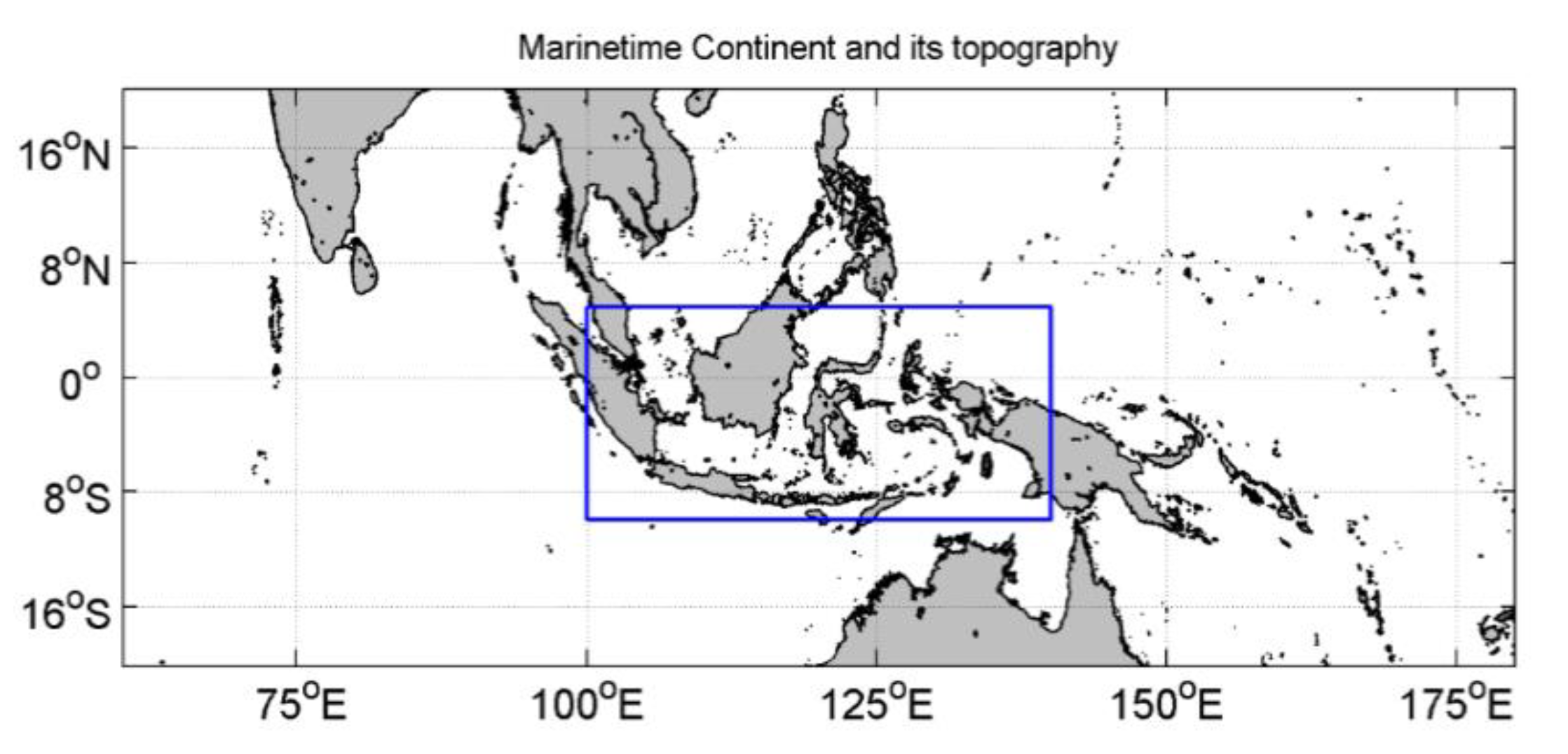
2. Data and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Differences of Madden–Julian Oscillation (MJO) Intensity over the Maritime Continent (MC) between Positive and Negative Phases of Pacific–Indian Ocean Associated Mode (PIOAM)
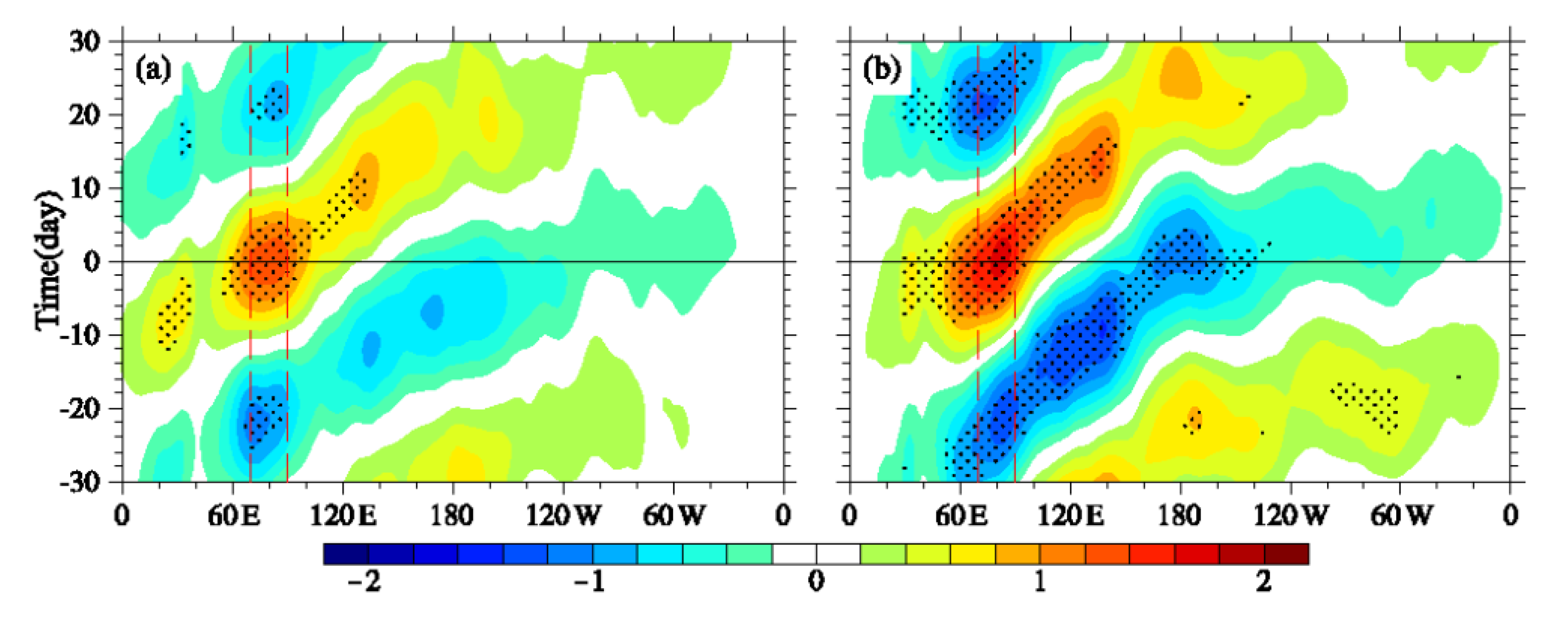
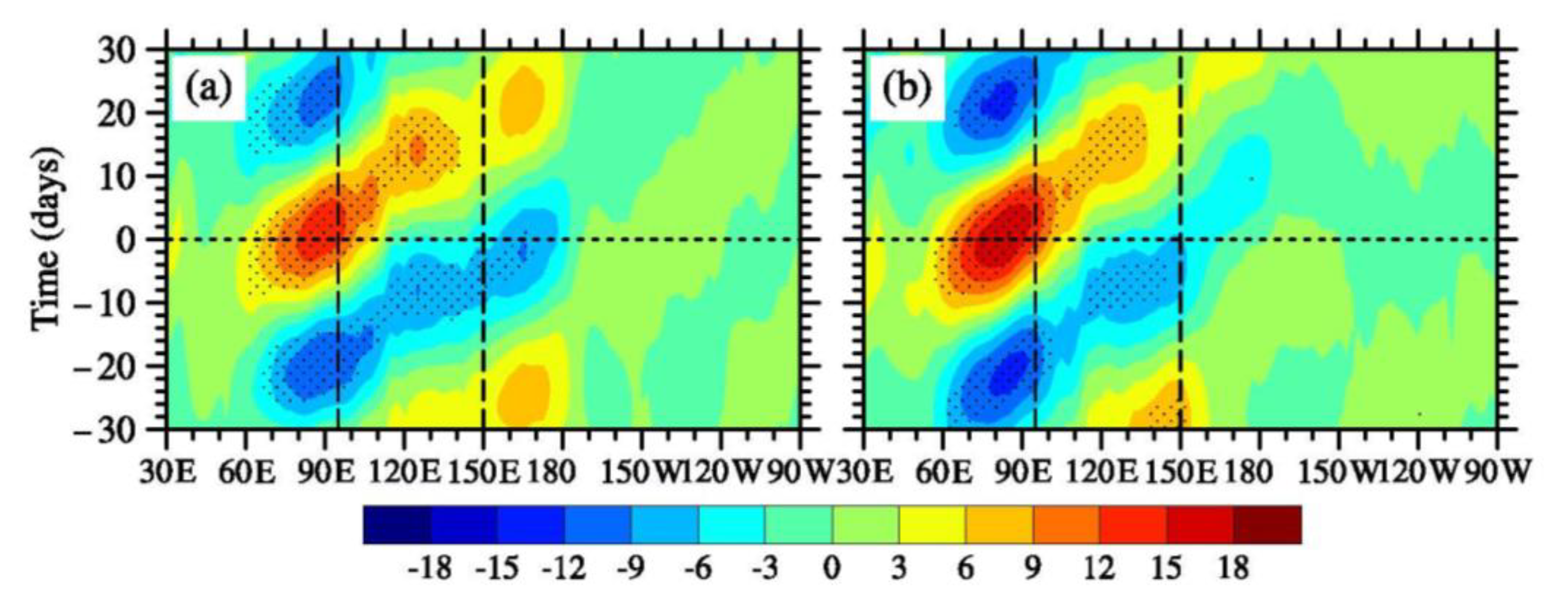
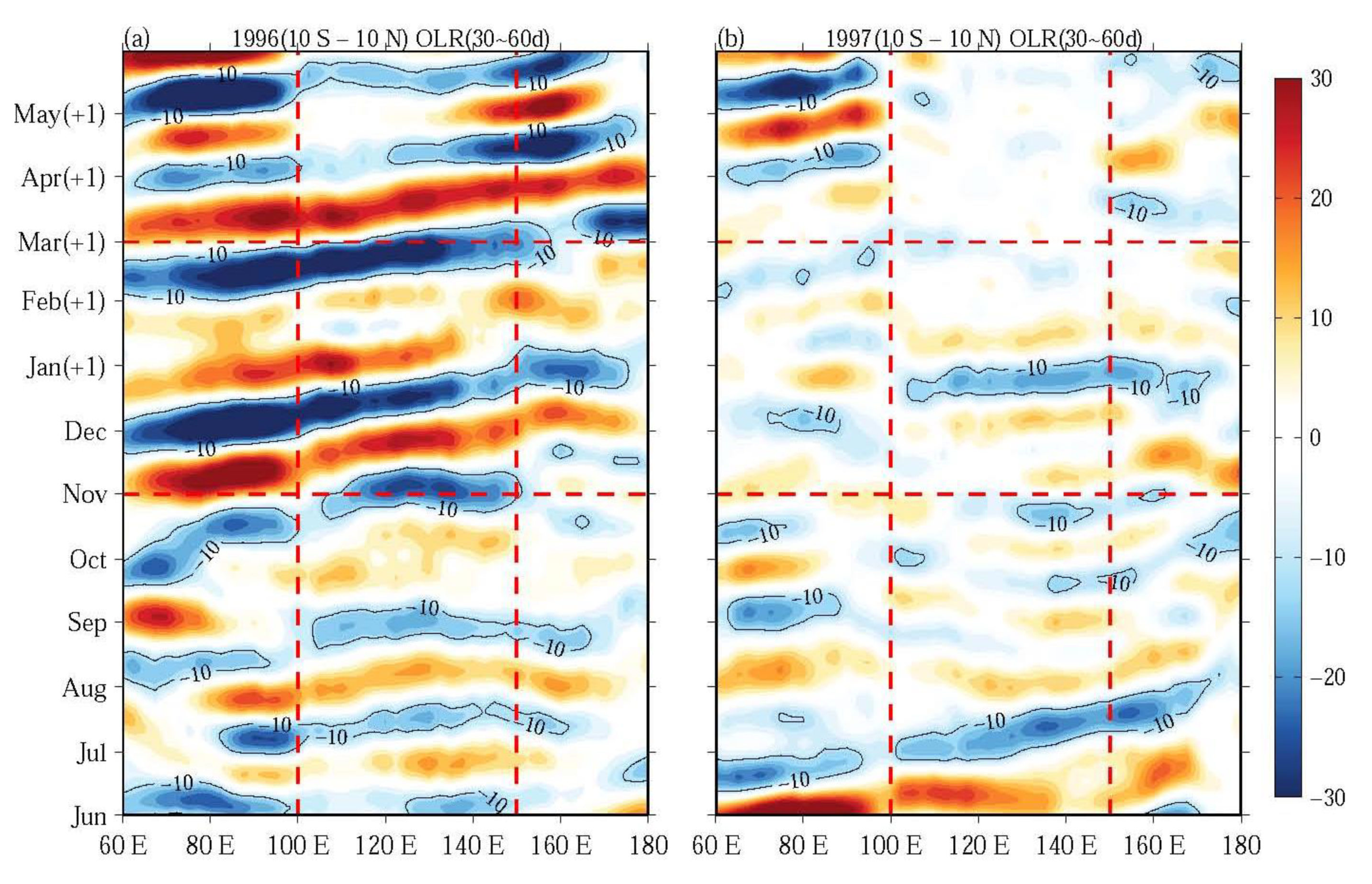
3.2. Differences of the Eastward Propagation of MJO between Positive and Negative Phases of PIOAM
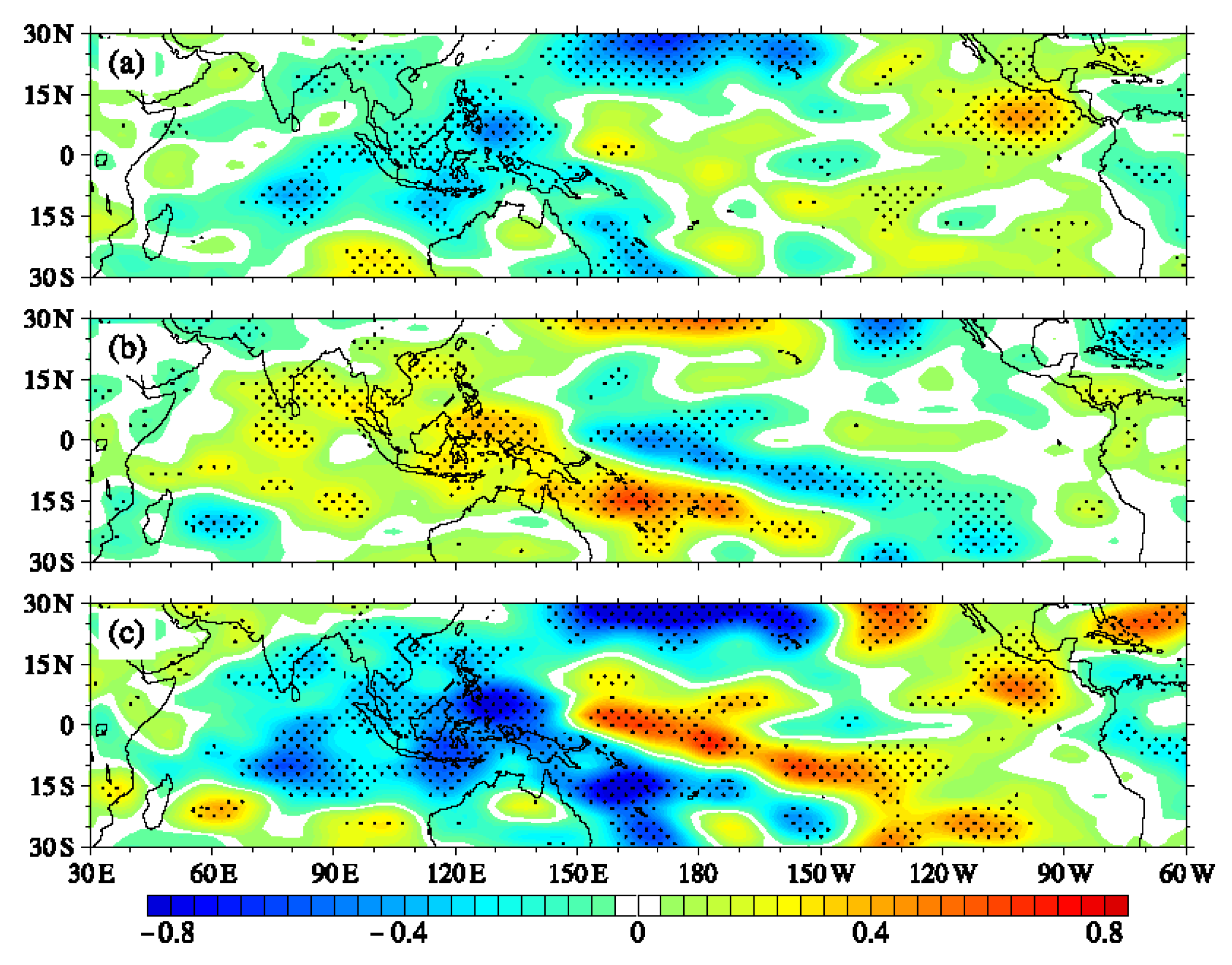
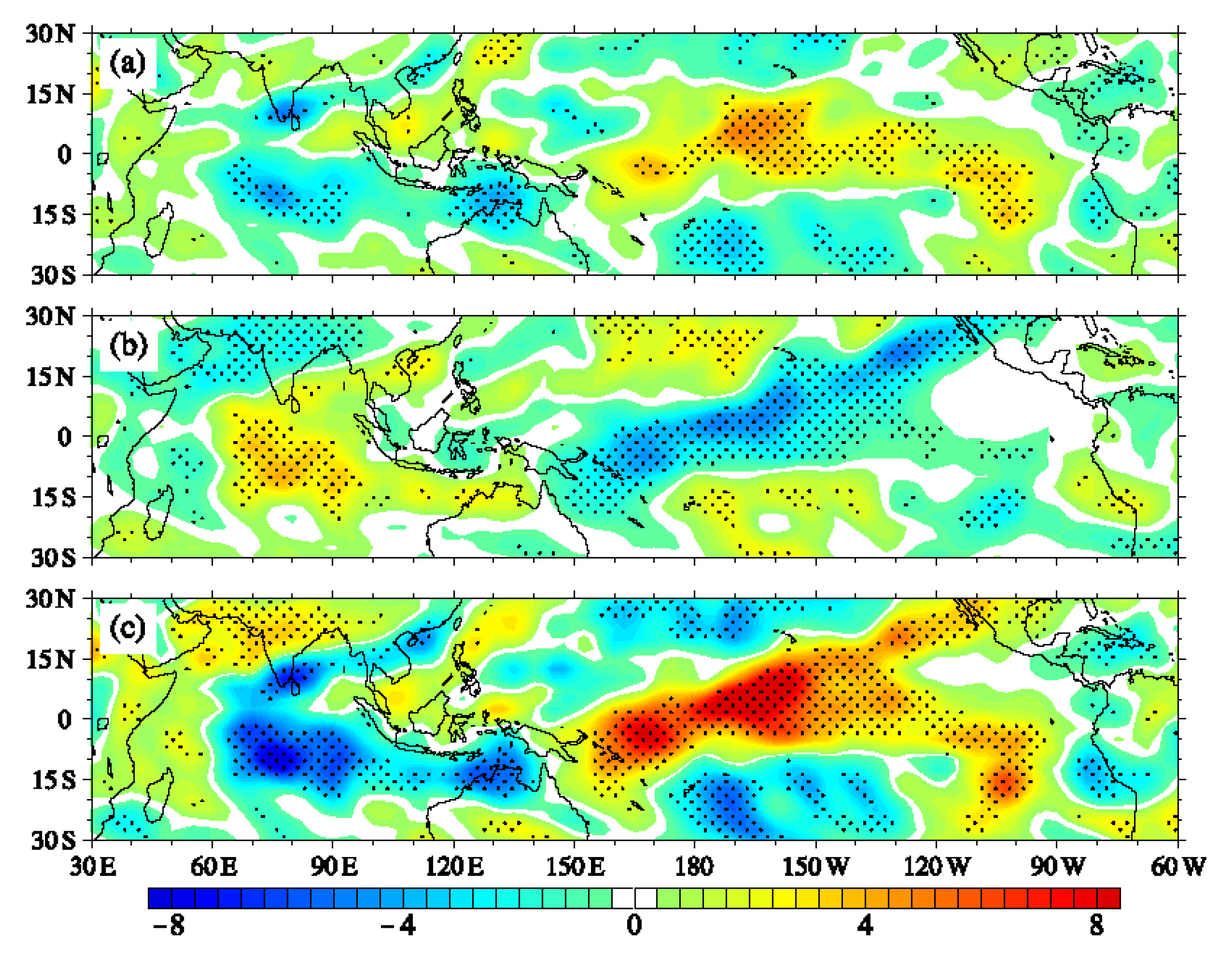
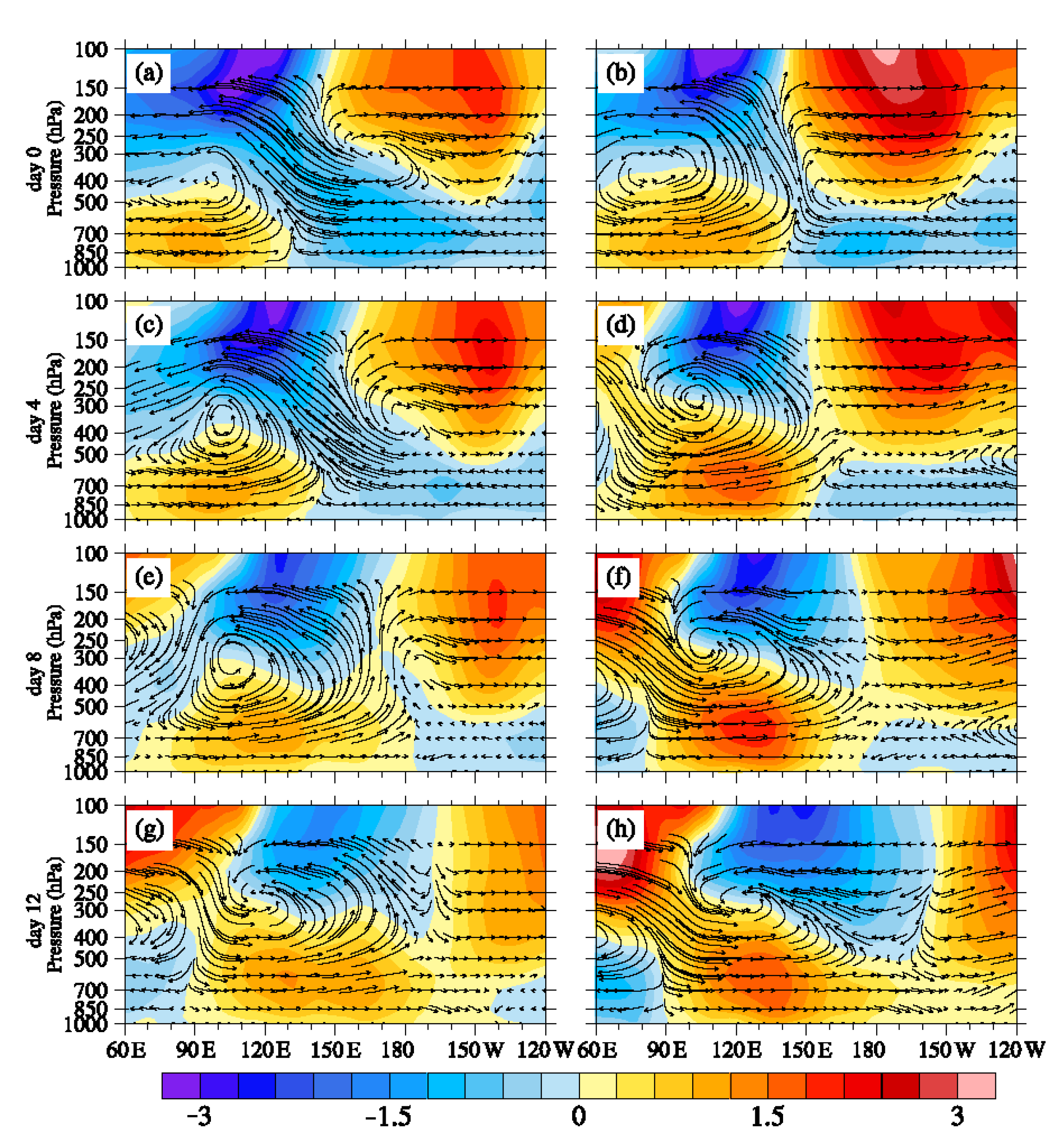
3.3. Differences of the MJO Structure over the Maritime Continent between Positive and Negative Phases of PIOAM
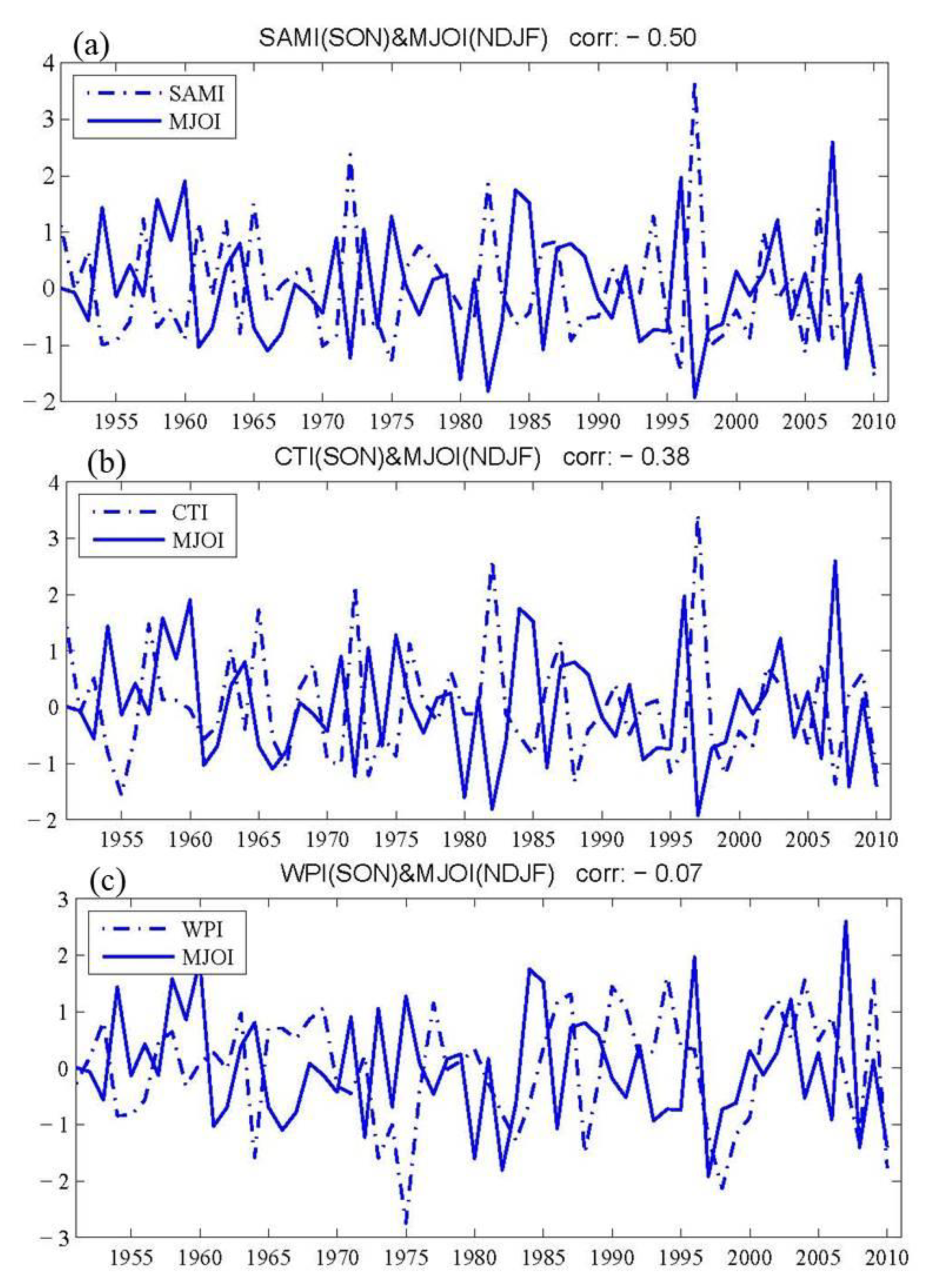
3.4. Causes for the Different Characteristics in Positive and Negative Phases of PIOAM
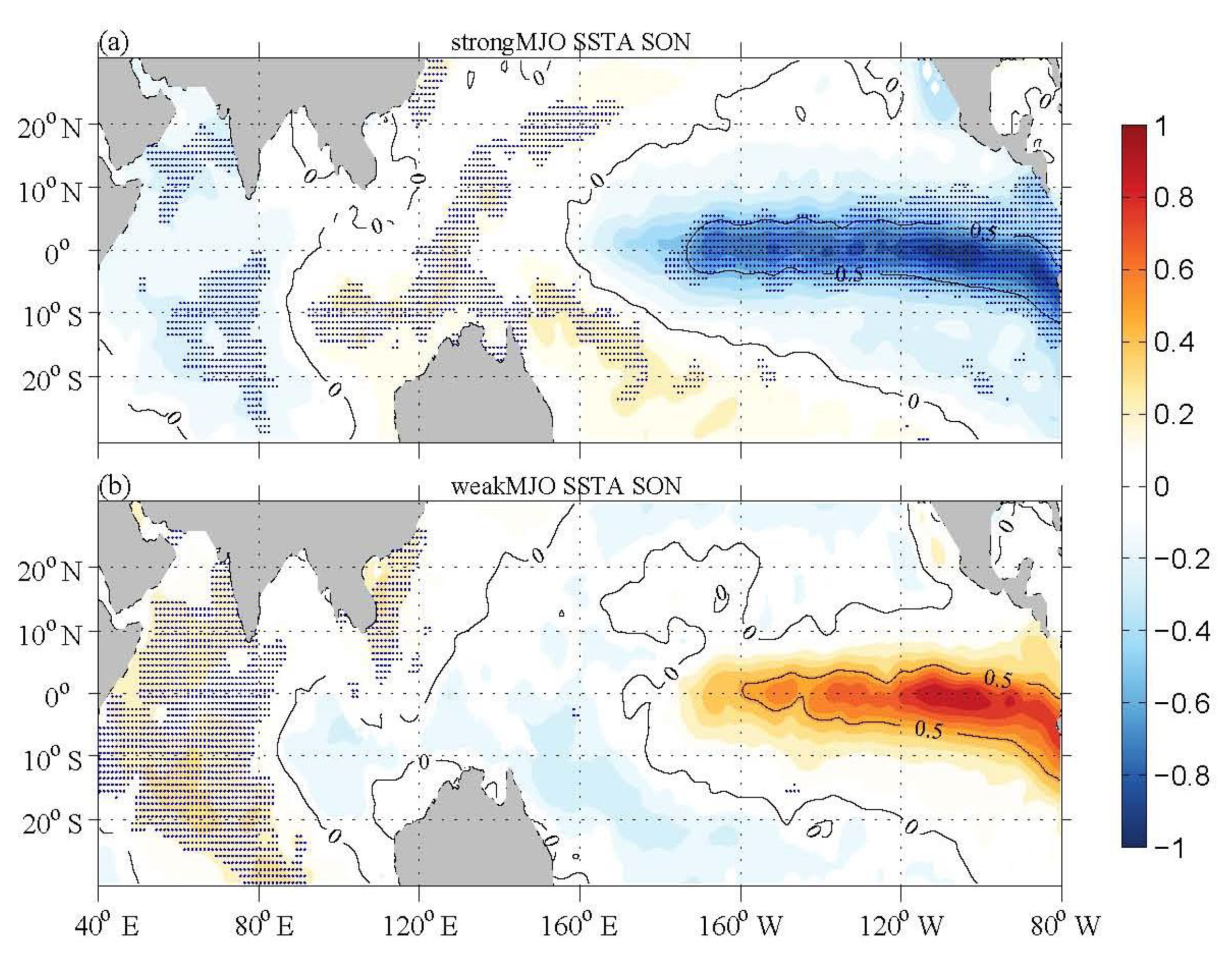
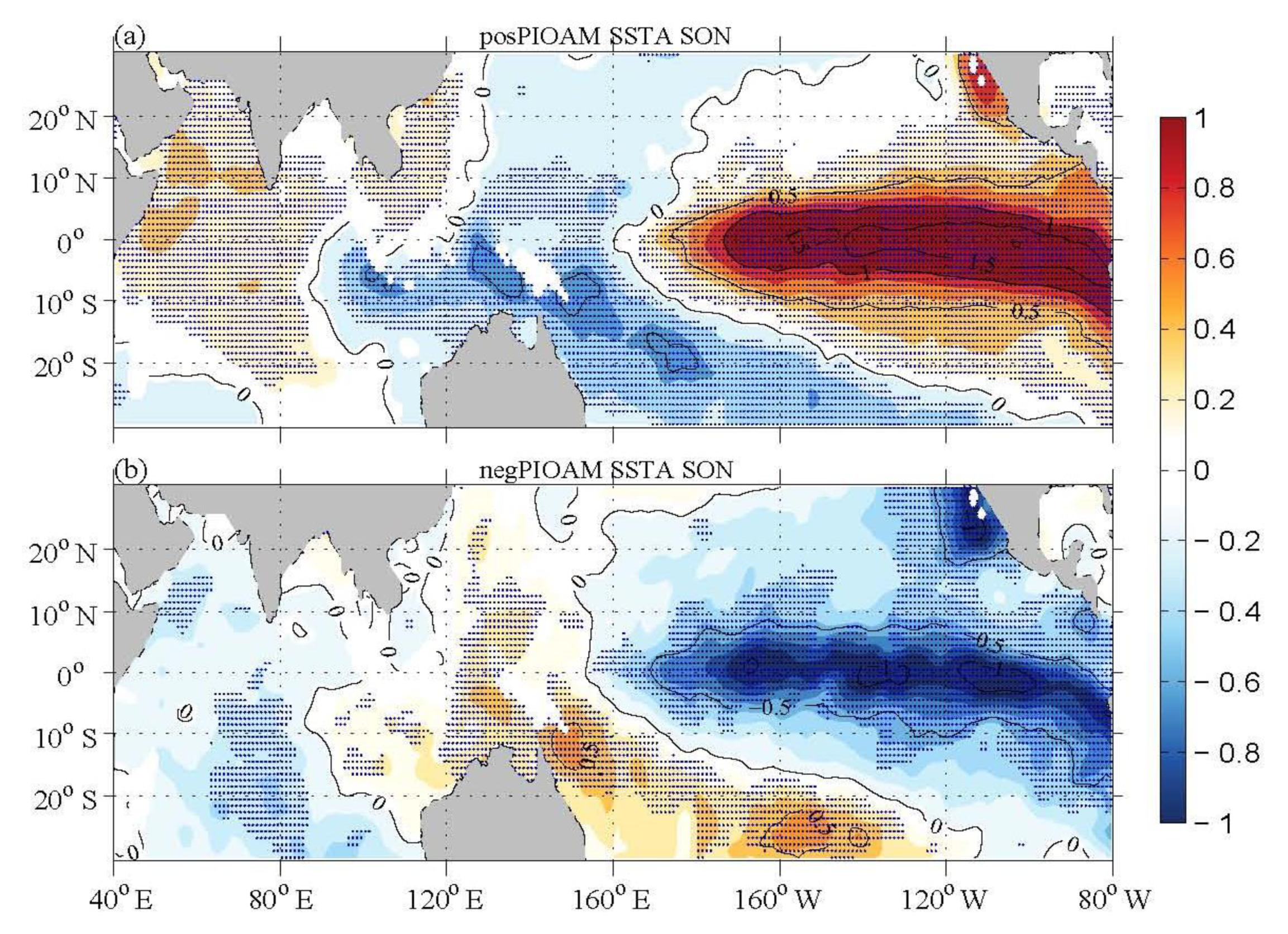
3.4.1. Abnormal Distribution of SST
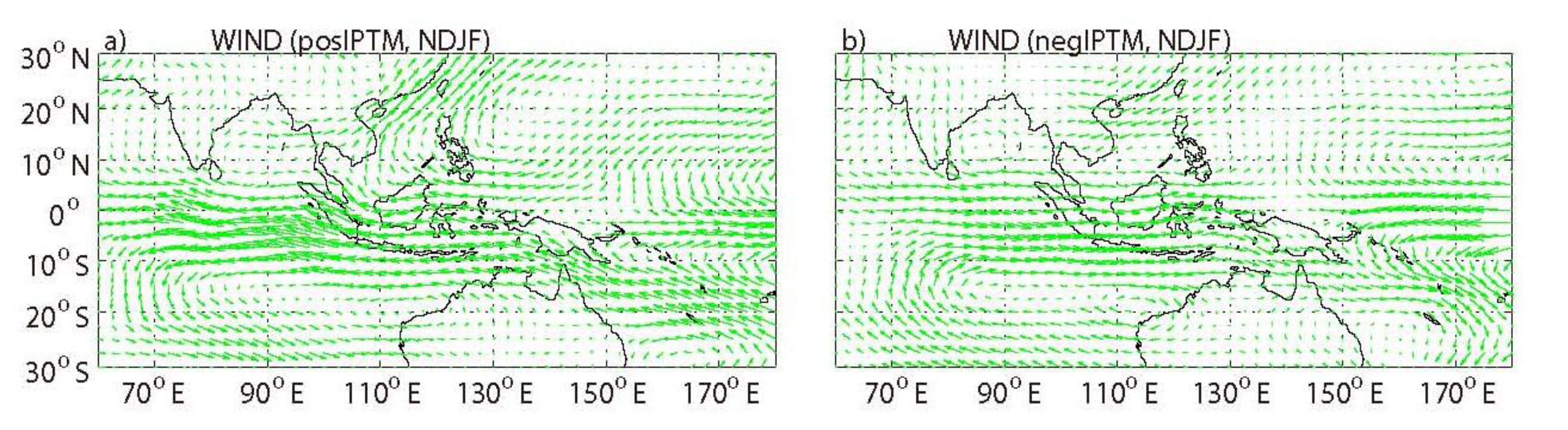
3.4.2. Abnormal Distribution of Horizontal Wind Field
4. Conclusions and Discussions
- (1)
- MC–MJO possesses prominent seasonally “phase-locked” features, which means that the MJO is strongest in the boreal winter and weakest in the boreal summer. MC–MJO also exhibits significant interannual and interdecadal variations.
- (2)
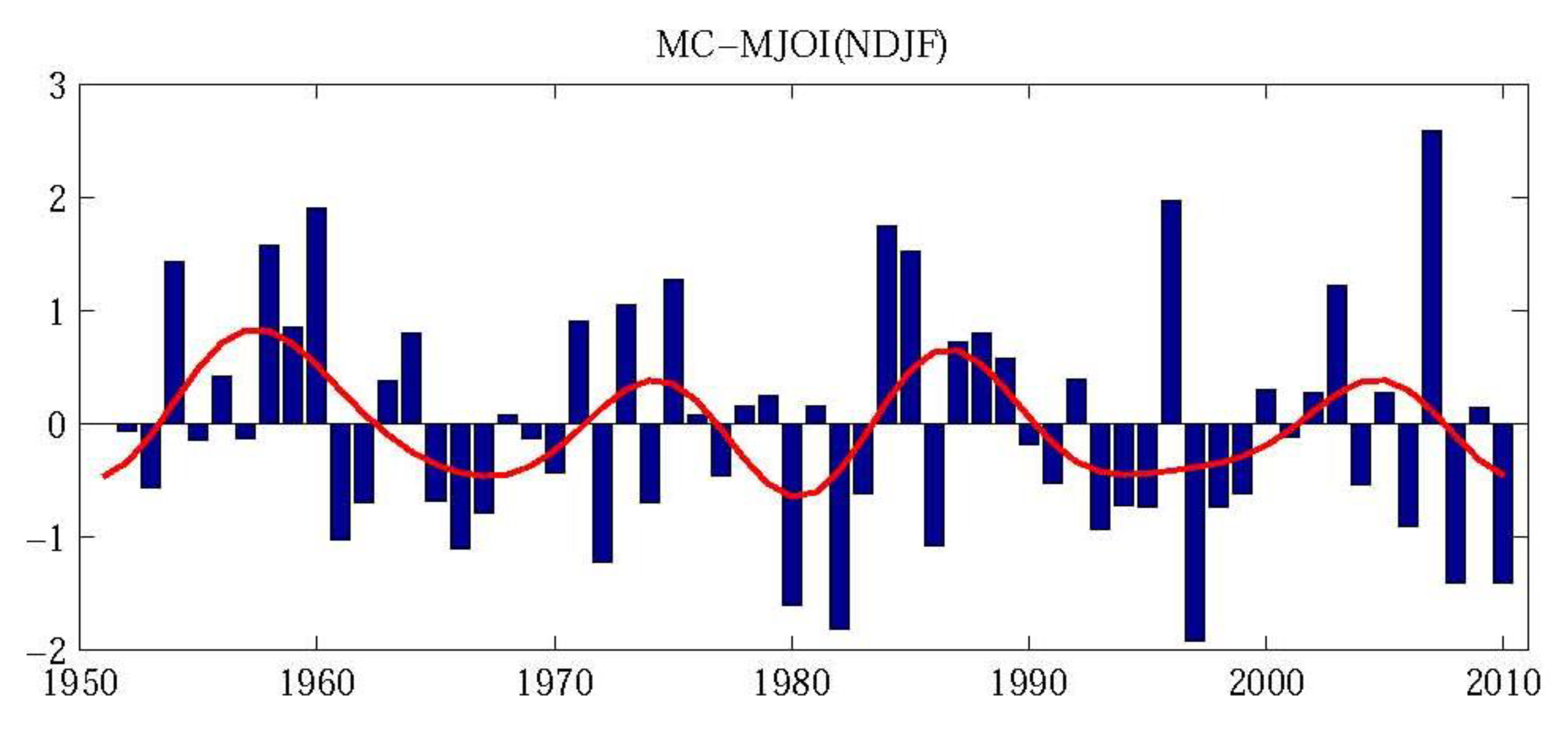
- In winter (November to February in the following year), the interannual variation of the MC–MJO kinetic energy has more significant correlations with PIOAM than both types of ENSO (especially the Central Pacific ENSO). When the positive (negative) PIOAM anomaly in autumn is stronger (weaker), the MJO kinetic energy over the MC region in winter is lower (higher). However, the MC–MJO convection in winter has no such close association with the PIOAM.
- (3)
- The positive and negative PIOAM have different influences on the propagation of the MC–MJO. During the positive phase of the PIOAM, the MJO kinetic energy in winter usually fails to move across the Maritime Continent and arrives into the western Pacific, while during the negative phase of the PIOAM, the MJO kinetic energy over the MC region can propagate to the equatorial western Pacific without significant reduction. In contrast, the preliminary statistical results reveal that the MJO convection during the positive PIOAM phase tends to move across the Maritime Continent and arrive in the equatorial western Pacific more easily than in the negative PIOAM phase, which is not consistent with the propagation of the MC–MJO kinetic energy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chao, J.P.; Yuan, S.Y. Concerted development of atmosphere-ocean interaction events in the tropical Indian Ocean and Pacific Ocean. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2002, 22, 247–252. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.Y.; Mu, M.Q.; Pan, J. Indian Ocean temperature dipole and SSTA in the equatorial Pacific Ocean. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2002, 47, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, H.; Xie, S.P.; Mccreary, J.P.; Murtugudde, R. Impact of Indian Ocean sea surface temperature on developing El Niño. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 302–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, R.H. A study on relationship between ENSO and tropical Indian Ocean temperature. Acta Meteorlogica Sin. 2008, 66, 120–124. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, J.; Chen, L.; Li, C. The preliminary research of Pacific-Indian Ocean sea surface temperature anomaly mode and the definition of its index. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2004, 20, 617–624. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Li, C. Effect of the Tropical Pacific-Indian Ocean Temperature Anomaly Mode on the South Asia High. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 29, 99–110. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Li, C. The preliminary research of equatorial Pcacific-Indian Ocean temperature anomaly mode and subsurface ocean temperature anomalies. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2009, 31, 24–33. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, C.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, G. Tropical Pacific-Indian Ocean thermocline temperature associated anomaly mode and its evolvement. Chin. J. Geophys. 2013, 56, 3270–3284. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Xia, F.; Chen, X.; Shu, X.; Yang, M.; Li, L.; Wang, D. The interannual cycle features of the tropical Pacific-Indian Ocean associated mode and its mechanisms. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 99, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, C. The tropical Pacific-Indian Ocean associated mode simulated by LICOM2.0. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 34, 1426–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Li, X.; Shi, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J. The Pacific-Indian Ocean associated mode in CMIP5 models. Ocean Sci. 2020, 16, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Jia, X.; Li, C. The tropical Pacific-Indian Ocean temperature anomaly mode and its effect. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 2878–2884. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, X.; Yang, H.; Pan, J.; Li, G. Tropical Pacific-Indian Ocean associated mode and its climatic impacts. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 42, 505–523. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Madden, R.A.; Julian, P.R. Detection of a 40-50 day oscillation in the zonal wind in the tropical Pacific. J. Atmos. Sci. 1971, 28, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, R.A.; Julian, P.R. Description of global-scale circulation cells in the tropics with a 40–50 day period. J. Atmos. Sci. 1972, 29, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhou, Y. Relationship between Intraseasonal Oscillation in the tropical atmosphere and ENSO. Acta Geophys. Sin. 1994, 37, 17–26. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q. Strong/weak summer monsoon activity over the South China Sea and atmospheric intraseasonal oscillation. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 18, 1146–1160. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, J.D.; Matthews, A.J.; Haroly, D.J. The modulation of tropical cyclone activity in Australian region by the Madden-Julian Oscillation. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 129, 2970–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, A.; Meinke, H.; Power, B.; Maia, A.; Wheeler, M.C.; White, N.; Stone, R.C.; Ribbe, J. Near-global impact of the Madden-Julian Oscillation on rainfall. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L09704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.N.; Wang, B.Z.; Zeng, C.Q. Impacts of the Madden–Julian oscillation on summer rainfall in Southeast China. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Li, C.; Tan, Y.; Guan, Z.-J. The impacts of the MJO (Madden–Julian Oscillation) on spring rainfall in East China. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2011, 27, 814–822. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lv, J.; Ju, J.; Ren, J.; Gan, W. The influence of the Madden-Julian oscillation activity anomalies on Yunnan’s extreme drought of 2009–2010. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2012, 55, 98–112. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C. Madden–Julian Oscillation: Bridging weather and climate. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1849–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ling, J.; Song, J.; Pan, J.; Tian, H.; Chen, X. Research progress in China on the tropical atmospheric intraseasonal oscillation. J. Meteorol. Res. 2014, 28, 671–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, K.C.; Jones, C.; Paegle, J.N. Pan America. Intraseasonal Variability of the Atmosphere-Ocean Climate System, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; 641p. [Google Scholar]
- Recalde-Coronel, G.C.; Zaitchik, B.; Pan, W.K. Madden-Julian oscillation influence on sub-seasonal rainfall variability on the west of South America. Clim. Dym. 2020, 54, 2167–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, E.D.; Hartmann, D.L. Modulation of hurricane activity in the Gulf of Mexico by the Madden-Julian Oscillation. Science 2000, 287, 2002–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhou, W. Modulation of western North Pacific tropical cyclone activities by the ISO. Part 1: Genesis and intensity. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 2904–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Bhatla, R. Modulation of active-break spell of Indian summer monsoon by Madden Julian Oscillation. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 128, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.M.; Chan, P.H. The 40–50 day oscillation and the El Niño/Southern Oscillation: A new perspective. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1986, 67, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendon, H.H.M.C.; Wheeler, C. Zhang: Seasonal dependence of the MJO–ENSO relationship. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, C.; Tan, Y. The influence of El Niño on MJO over the equatorial pacific. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2015, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.H.; Weng, C.-H.; Wu, C.-H. Contrasting characteristics between the northward and eastward propagation of the intraseasonal oscillation during the boreal summer. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 727–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Smith, I. Numerical simulation of the tropical intraseasonal oscillation and the effect of warm SSTS. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 1995, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kessler, W.S. EOF representations of the Madden-Julian Oscillation and its connection with ENSO. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 3055–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.Y.; Lau, N.C. Modulation of the Madden--Julian Oscillation by ENSO: Inferences from observations and GCM simulations. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2005, 83, 727–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, B.; Matthews, A.J. Observed changes in the lifetime and amplitude of the Madden-Julian Oscillation associated with interannual ENSO sea surface temperature anomalies. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 2659–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gushchina, D.; Dewitte, B. Intraseasonal tropical atmospheric variability associated with the two flavors of El Niño. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 3669–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, C.; Ling, J. Different MJO activities between EP El Niño and CP El Niño. Sci. Sin. Terrae 2015, 45, 318–334. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Ling, J.; Li, C. Evolution of the Madden–Julian Oscillation in two types of El Niño. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 1919–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Chen, Z.; Wen, Z.; Lu, R. Impacts of two types of El Niño on the MJO during boreal winter. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 33, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, E.A.; Gordon, A.L.; Kim, D. Observations of the Madden Julian oscillation during indian ocean dipole events. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 2588–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, C. Possible influences of the tropical Indian Ocean dipole on the eastward propagation of MJO. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2014, 20, 173–180. [Google Scholar]
- Benedict, J.J.; Pritchard, M.S.; Collins, W.D. Sensitivity of MJO propagation to a robust positive Indian Ocean dipole event in the superparameterized CAM. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2015, 7, 1901–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiki, A.; Nagura, M.; Hasegawa, T. Seasonal onset of the Madden–Julian oscillation and its relation to the southeastern Indian Ocean cooling. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 93, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.; Coauthors, P. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebmann, B.; Smith, C.A. Description of a Complete (Interpolated) Outgoing Longwave Radiation Dataset. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 1275–1277. [Google Scholar]
- Rayner, N.A.; Parker, D.E.; Horton, E.B.; Folland, C.K.; Alexander, L.V.; Rowell, D.P.; Kent, E.C.; Kaplan, A. Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchon, C.E. Lanczos filtering in one and two dimensions. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1979, 18, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.L.; Jin, F.F. Niño indices for two types of ENSO. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L04704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X. Numerical Simulation of the Intraseasonal Oscillation. Ph.D. Thesis, Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2006. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Li, C. New progress in the study of atmospheric Intraseasonal Oscillation. Adv. Nat. Sci. 2004, 14, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Yin, M.; Chen, X.; Yang, M.; Xia, F.; Li, L.; Chen, G.; Yu, P.; Zhang, C. Impacts of the Tropical Pacific–Indian Ocean Associated Mode on Madden–Julian Oscillation over the Maritime Continent in Boreal Winter. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101049
Li X, Yin M, Chen X, Yang M, Xia F, Li L, Chen G, Yu P, Zhang C. Impacts of the Tropical Pacific–Indian Ocean Associated Mode on Madden–Julian Oscillation over the Maritime Continent in Boreal Winter. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(10):1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101049
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xin, Ming Yin, Xiong Chen, Minghao Yang, Fei Xia, Lifeng Li, Guangchao Chen, Peilong Yu, and Chao Zhang. 2020. "Impacts of the Tropical Pacific–Indian Ocean Associated Mode on Madden–Julian Oscillation over the Maritime Continent in Boreal Winter" Atmosphere 11, no. 10: 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101049
APA StyleLi, X., Yin, M., Chen, X., Yang, M., Xia, F., Li, L., Chen, G., Yu, P., & Zhang, C. (2020). Impacts of the Tropical Pacific–Indian Ocean Associated Mode on Madden–Julian Oscillation over the Maritime Continent in Boreal Winter. Atmosphere, 11(10), 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101049




