Origins and Spatial Distribution of Non-Pure Sulfate Particles (NSPs) in the Stratosphere Detected by the Balloon-Borne Light Optical Aerosols Counter (LOAC)
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Non-Pure Sulfate Particles (NSPs) in the Stratosphere
1.2. Methodologies for NSPs Detection in the Stratosphere
2. Present Approach with Balloon-Borne Aerosol Counters
2.1. Context
2.2. The LOAC Instrument
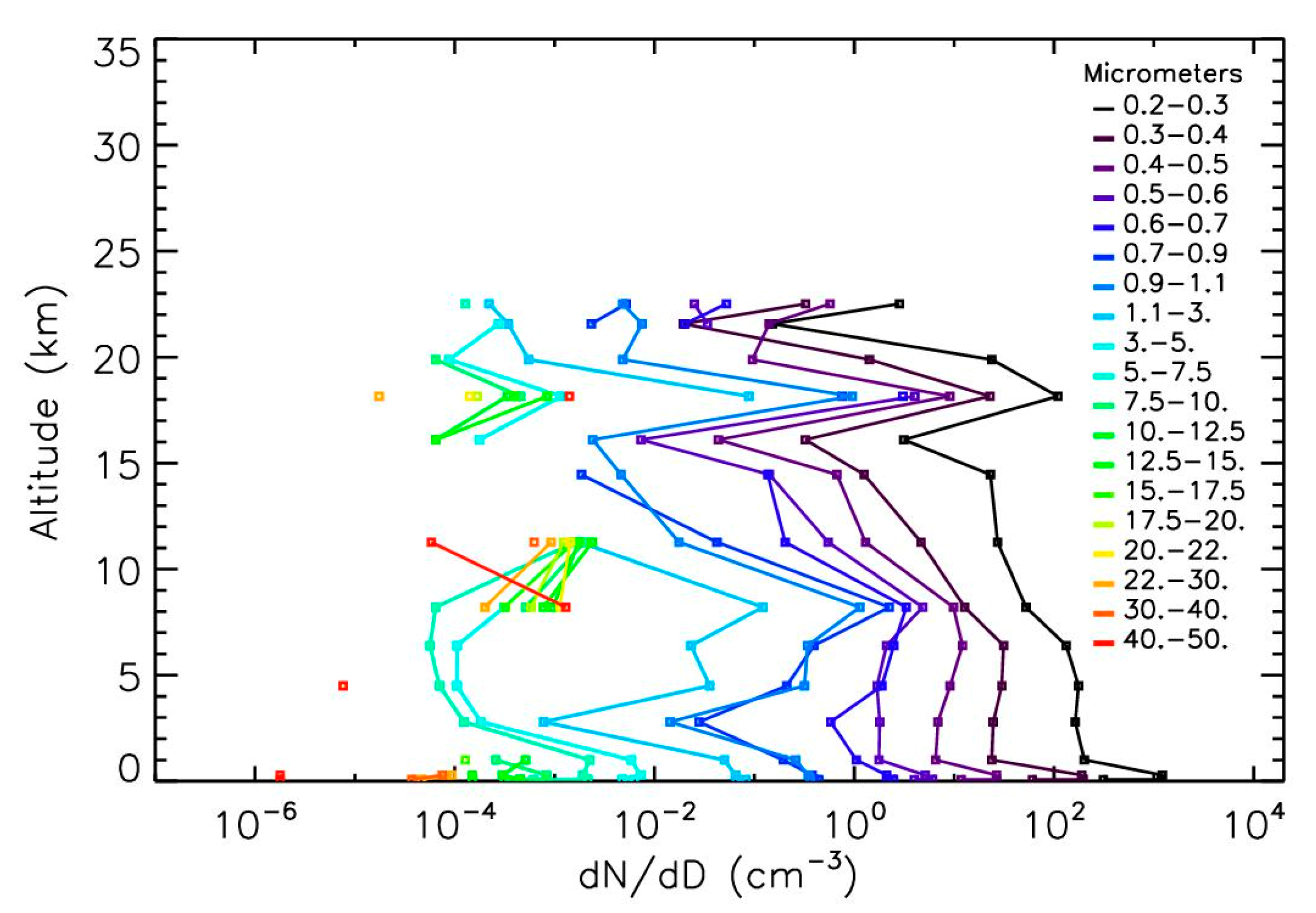
2.3. Vertical Profile of Aerosol Concentrations Obtained with LOAC
2.4. Origin of Stratospheric Concentration Enhancements and Transport Mechanisms
2.5. Background Concentrations for Large NSPs
3. Discussion on the Spatial and Temporal Variability, Size, and Composition of NSPs
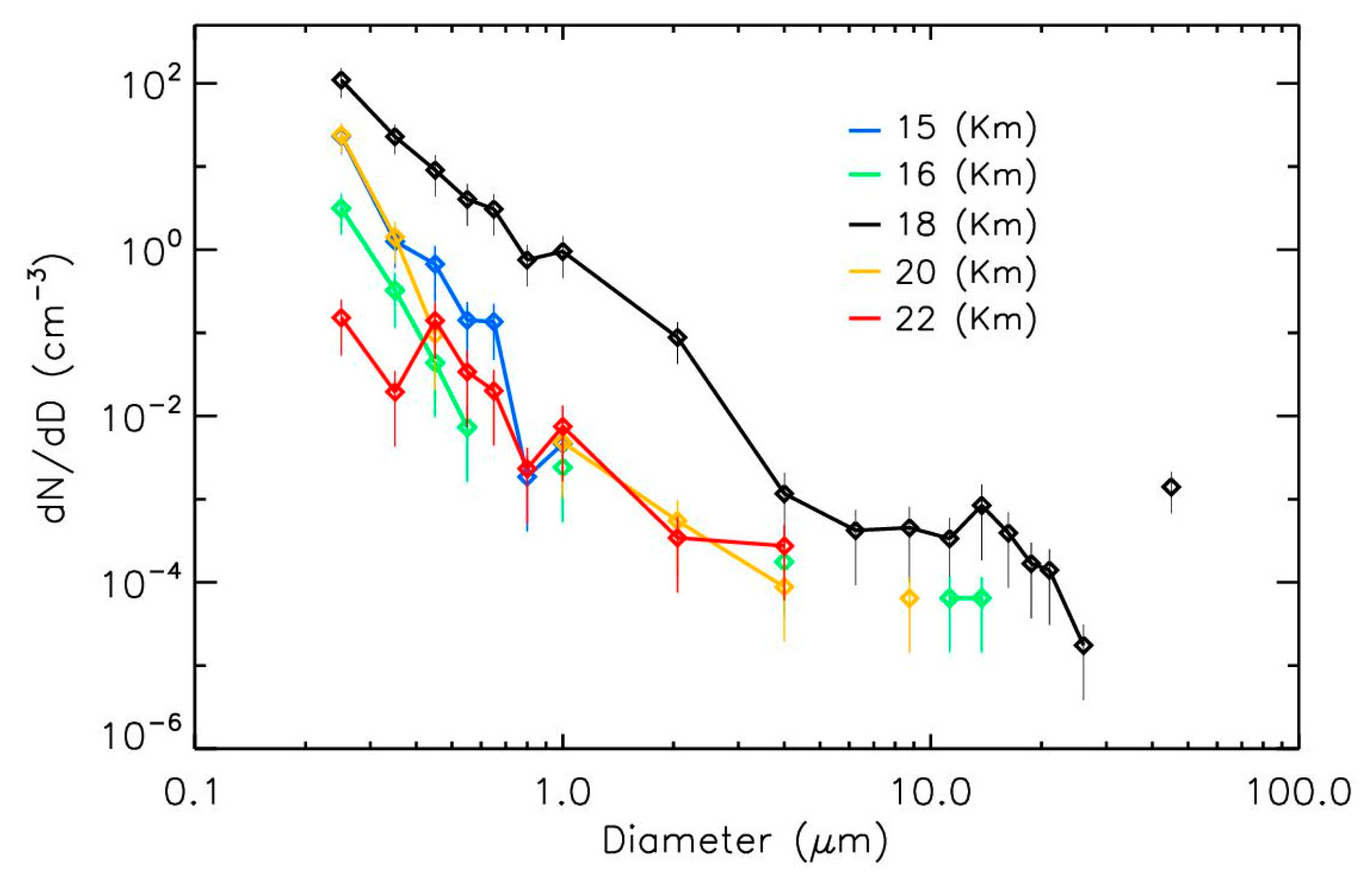
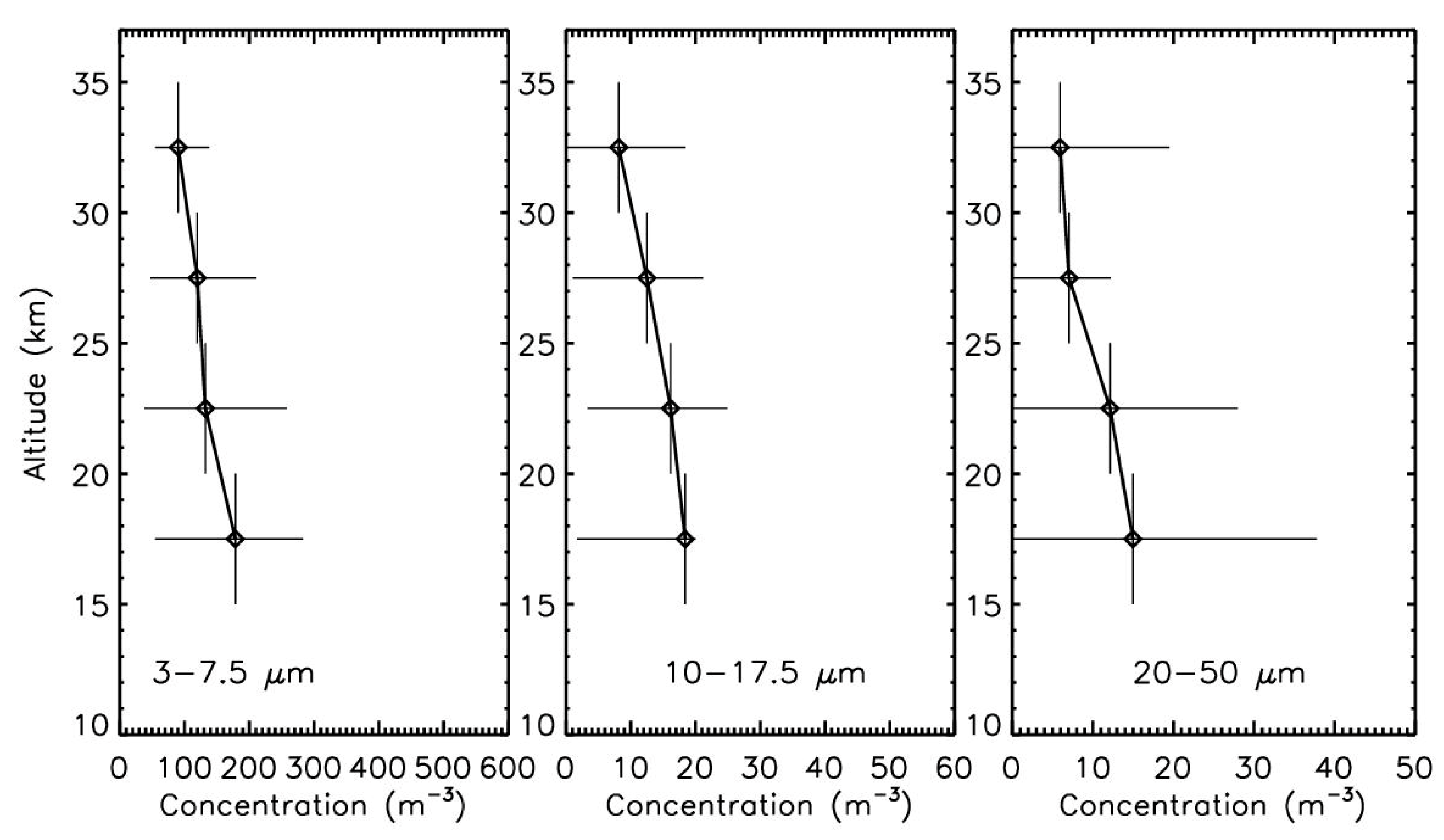
3.1. Vertical Dependence of NSPs
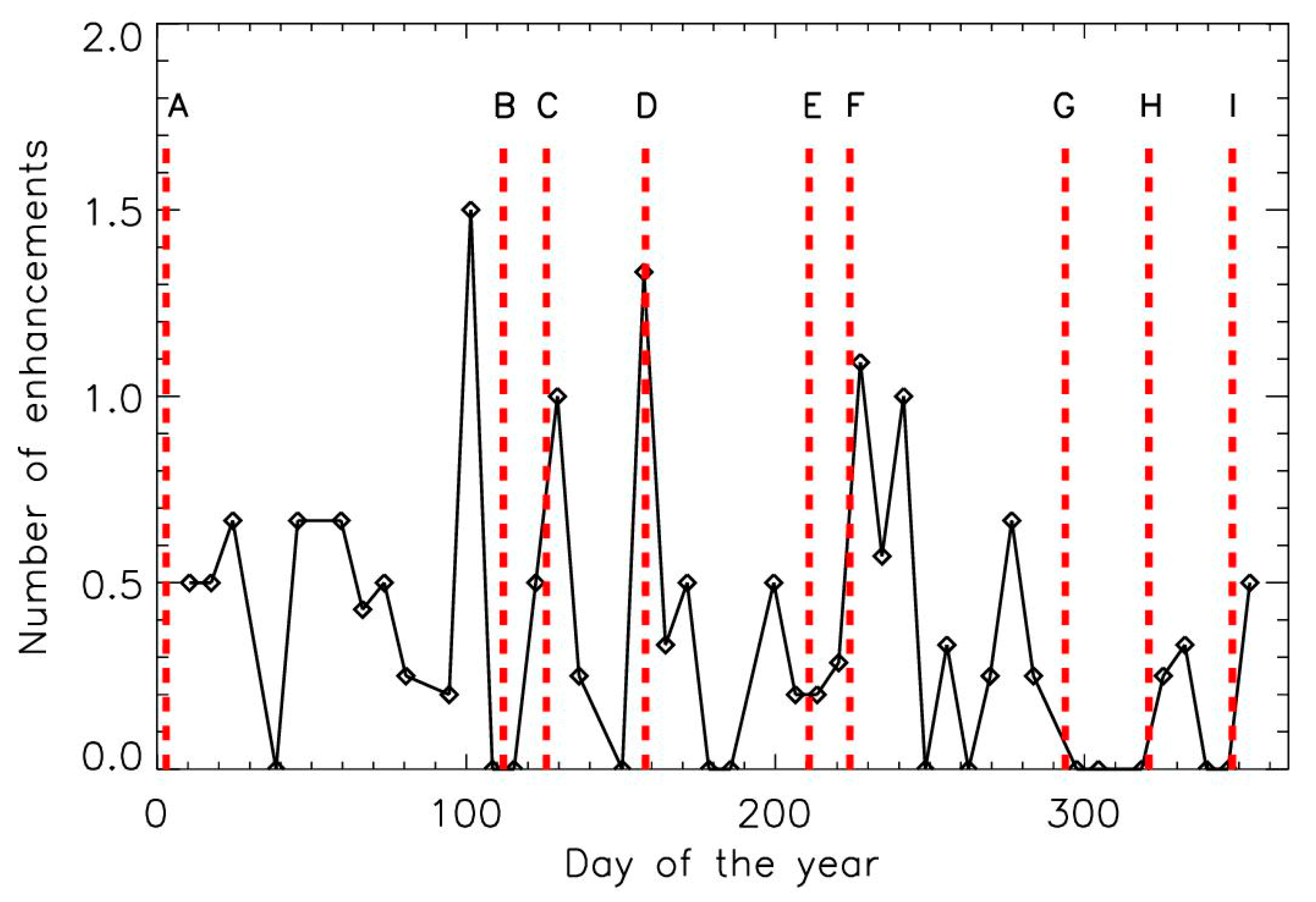
3.2. Sporadic Strong Concentration Enhancements in the Stratospheric Aerosol Content Related to Reported Events
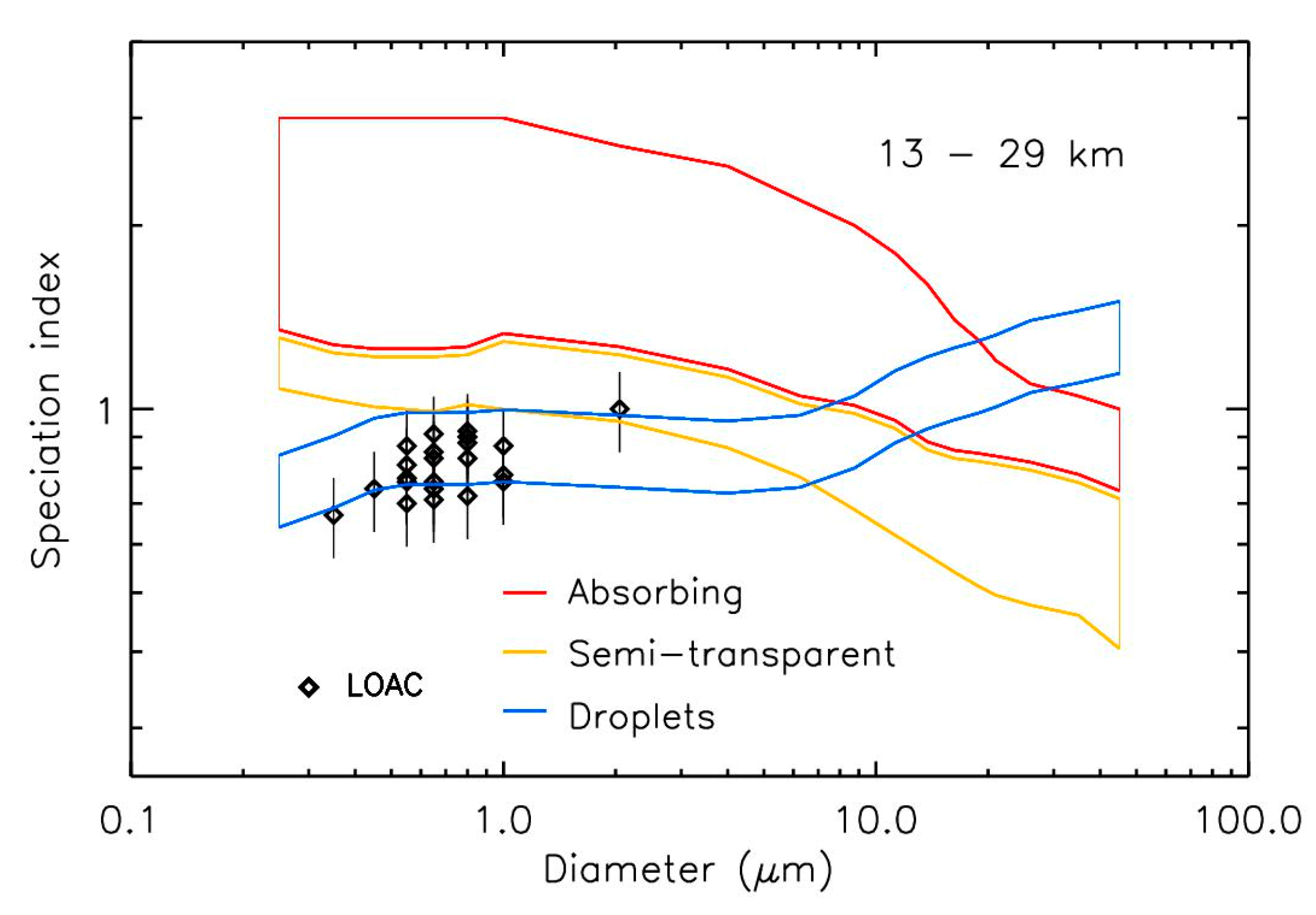
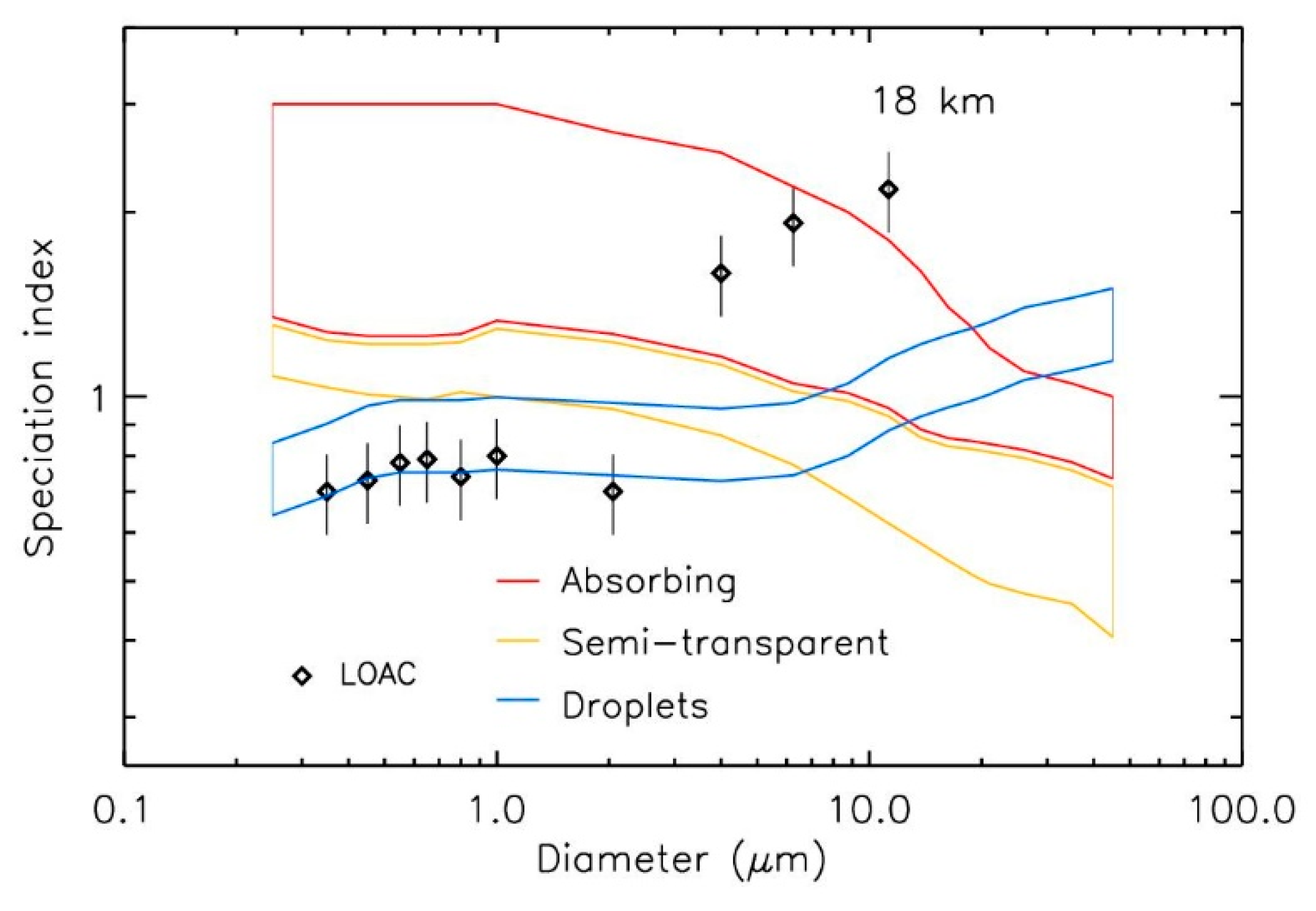
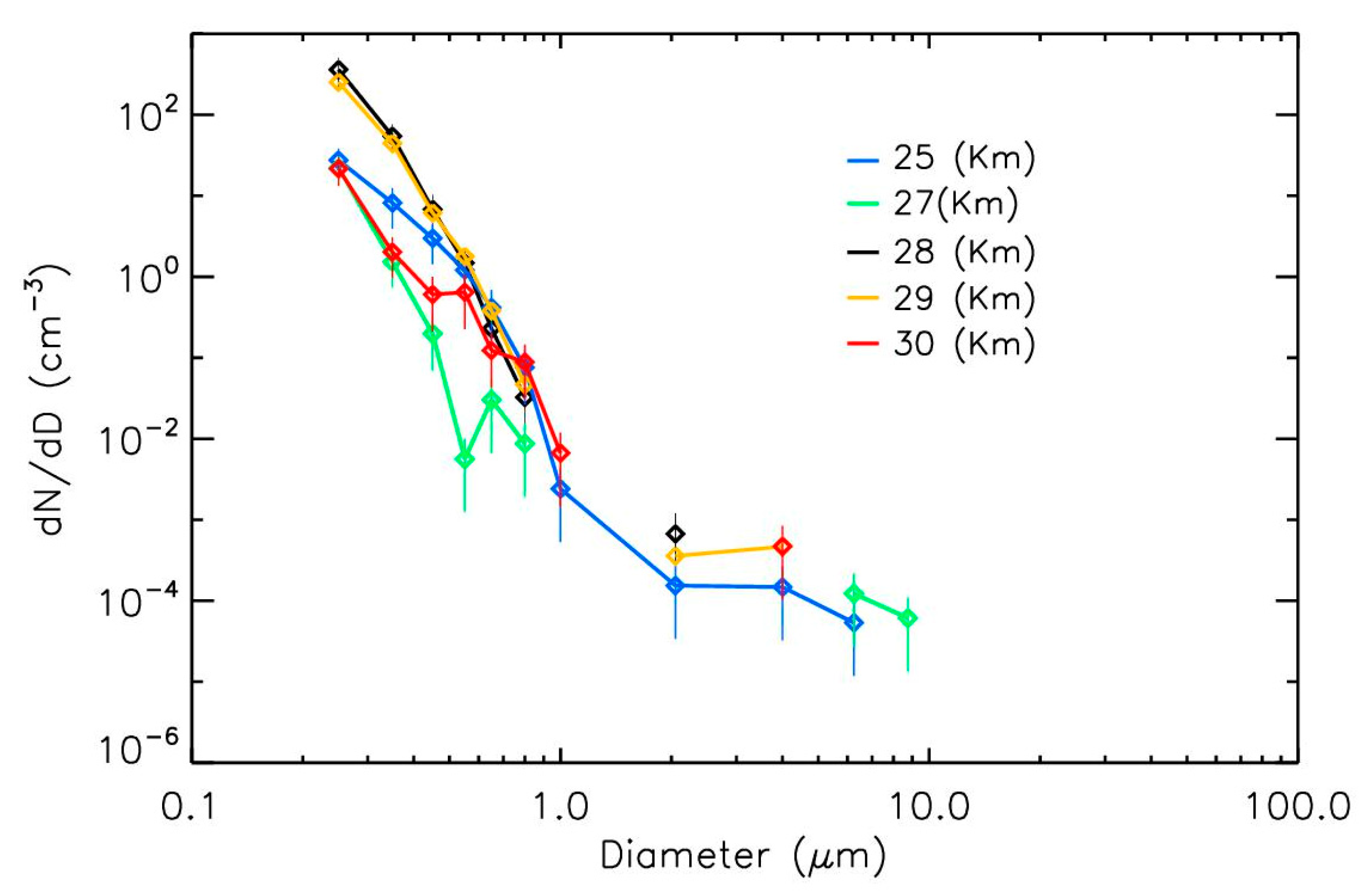
3.3. Size Distribution
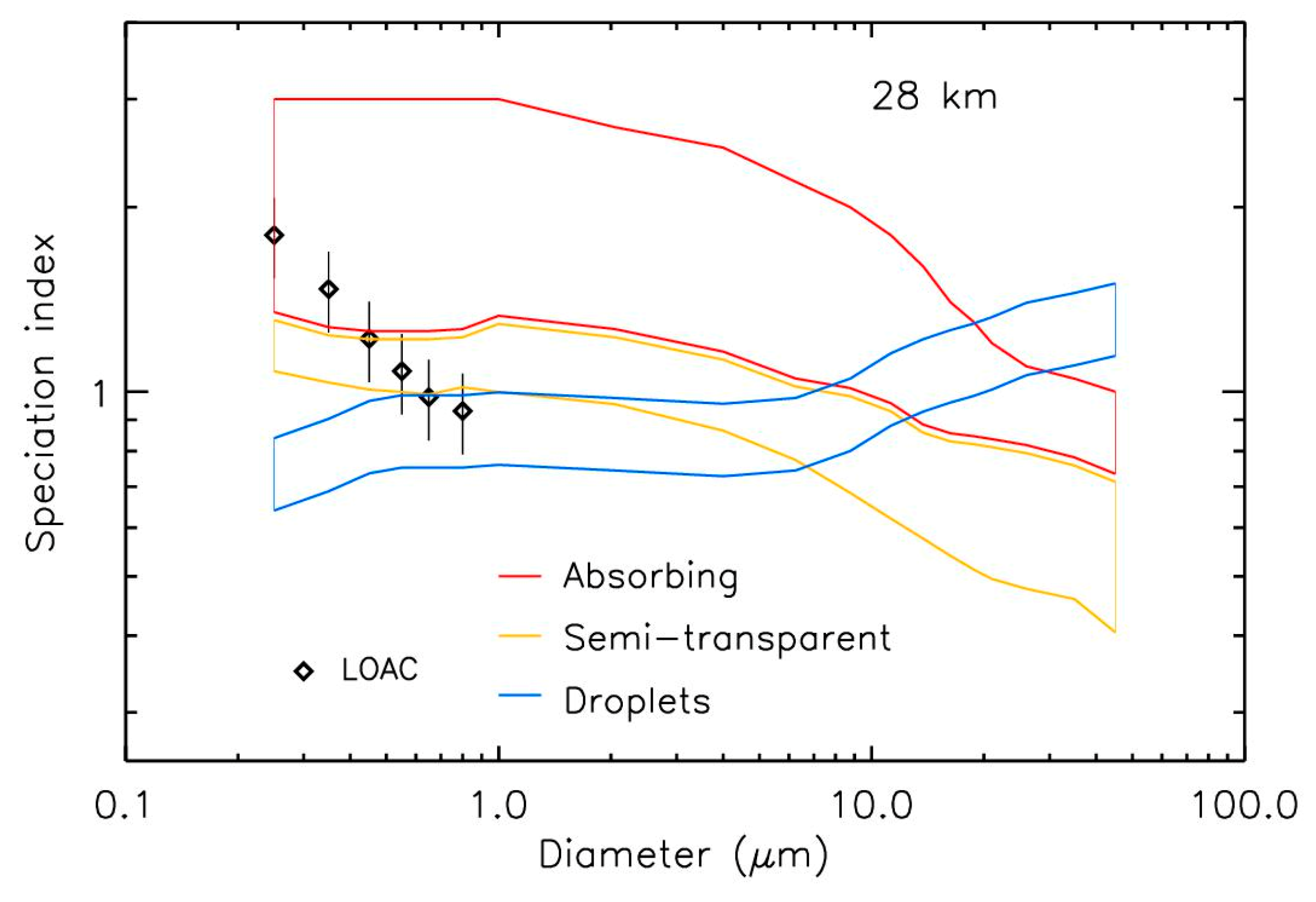
3.4. Particles Chemical Composition
4. Discussion about Possible Sources of NSPs, from Ground to Space
4.1. Context
4.2. Sources from Earth’s Surface
4.3. Production within the Atmosphere
4.4. Dust from Space
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kremser, S.; Thomason, L.W.; von Hobe, M.; Hermann, M.; Deshler, T.; Timmreck, C.; Toohey, M.; Stenke, A.; Schwarz, J.P.; Weigel, R.; et al. Stratospheric aerosol–Observations, processes, and impact on climate. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 278–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, A.; Höpfner, M.; Sinnhuber, B.-M.; Griessbach, S.; Deshler, T.; von Clarmann, T.; Stiller, G. MIPAS observations of volcanic sulfate aerosol and sulfur dioxide in the stratosphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 1217–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, P.B.; Livingston, J.M.; Pueschel, R.F.; Bauman, J.J.; Pollack, J.B.; Brooks, S.L.; Hamill, P.; Thomason, L.W.; Stowe, L.L.; Deshler, T.; et al. Global to microscale evolution of the Pinatubo volcanic aerosol derived from diverse measurements and analyses. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 18745–18763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshler, T.; Hervig, M.E.; Hofmann, D.J.; Rosen, J.M.; Liley, J.B. Thirty years of in situ stratospheric aerosol size distribution measurements from Laramie, Wyoming (41°N) using balloon-borne instruments. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Daniel, J.S.; Nelly, R.R.; Vernier, J.-P.; Dutton, E.G.; Thomason, L.W. The persistently variable “background” stratospheric aerosol layer and global climate change. Science 2011, 333, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jégou, F.; Berthet, G.; Brogniez, C.; Renard, J.-B.; Francois, P.; Haywood, J.M.; Jones, A.; Bourgeois, Q.; Lurton, T.; Auriol, F.; et al. Daugeron Stratospheric aerosols from the Sarychev volcano eruption in the 2009 Arctic summer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 6533–6552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bègue, N.; Vignelles, D.; Berthet, G.; Portafaix, T.; Payen, G.; Jégou, F.; Benchérif, H.; Jumelet, J.; Vernier, J.-P.; Lurton, T.; et al. Long-range transport of stratospheric aerosols in the Southern hemisphere following the 2015 Calbuco eruption. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 15019–15036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernier, J.-P.; Thomason, L.W.; Pommereau, J.-P.; Bourassa, A.; Pelon, J.; Garnier, A.; Hauchecorne, A.; Blanot, L.; Trepte, C.; Degenstein, D.; et al. Major influence of tropical volcanic eruptions on the stratospheric aerosol layer during the last decade. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L12807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshler, T.; Richard Anderson-Sprecher, R.; Jäger, H.; Barnes, J.; Hofmann, D.J.; Clemesha, B.; Simonich, D.; Osborn, M.; Grainger, R.G.; Godin-Beekmann, S. Trends in the nonvolcanic component of stratospheric aerosol over the period 1971–2004. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D01201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgardner, D.; Kok, G.; Raga, G. Warming of the Arctic lower stratosphere by light absorbing particles. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L06117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtius, J.; Weigel, R.; Vossing, H.-J.; Wernli, H.; Werner, A.; Volk, C.M.; Konopka, P.; Krebsbach, M.; Schiller, C.; Roiger, A.; et al. Observations of meteoric material and implications for aerosol nucleation in the winter Arctic lower stratosphere derived from in situ particle measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 3053–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.M.; Cziczo, D.J.; Hudson, P.K.; Thomson, D.S. Carbonaceous material in aerosol particles in the lower stratosphere and tropopause region. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D04203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, J.-B.; Brogniez, C.; Berthet, G.; Bourgeois, Q.; Gaubicher, B.; Chartier, M.; Balois, J.-Y.; Verwaerde, C.; Auriol, F.; Francois, P.; et al. Vertical distribution of the different types of aerosols in the stratosphere, detection of solid particles and analysis of their spatial variability. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D21303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, M.; Weigel, R.; Kandel, K.; Günther, G.; Molleker, S.; Groob, J.-U.; Vogel, B.; Weinbruch, S.; Borrmann, S. Chemical analysis of refractory stratospheric aerosol particles collected within the arctic vortex and inside polar stratospheric clouds. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 8405–8421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütze, K.; Wilson, J.C.; Weinbruch, S.; Benker, N.; Ebert, M.; Günther, G.; Weigel, R.; Borrmann, S. Sub-micrometer refractory carbonaceous particles in the polar stratosphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 12475–12493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padma Kumari, B.; Trigo-Rodriguez, J.M.; Londhe, A.L.; Jadhav, D.B.; Trimbake, H.K. Optical observations of meteoric dust in the middle stratosphere during Leonid activity in recent years 2001–2003 over India. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L16807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padma Kumari, B.; Kulkarni, H.; Jadhav, D.B.; Londhe, A.L.; Trimbake, H.K. Exploring Atmospheric aerosols by twilight photometry. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2008, 25, 1600–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klekociuk, A.; Brown, P.G.; Pack, D.W.; ReVelle, D.O.; Edwards, W.N.; Spalding, R.E.; Tagliaferri, E.; Yoo, B.B.; Zagari, J. Meteoritic dust from the atmospheric disintegration of a large meteoroid. Nature 2005, 436, 1132–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerding, M.; Baumgarten, G.; Blum, U.; Thayer, J.P.; Fricke, K.-H.; Neuber, R.; Fiedler, J. Observation of an unusual mid-stratospheric aerosol layer in the Arctic: Possible sources and implication for polar vortex dynamics. Ann. Geophys. 2003, 21, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Siebert, J.; Timmis, C.; Vaughan, G.; Fricke, K.H. A strange cloud in the Arctic summer stratosphere 1998 above Esrange (68°N.), Sweden. Ann. Geophys. 2000, 18, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaykin, S.M.; Godin-Beekmann, S.; Hauchecorne, A.; Pelon, J.; Ravetta, F.; Keckhut, P. Stratospheric smoke with unprecedentedly high backscatter observed by lidars above southern France. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 1639–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haarig, M.; Ansmann, A.; Baars, H.; Jimenez, C.; Veselovskii, I.; Engelmann, R.; Althausen, D. Depolarization and lidar ratios at 355, 532, and 1064 nm and microphysical properties of aged tropospheric and stratospheric Canadian wildfire smoke. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 11847–11861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baars, H.; Ansmann, A.; Ohneiser, K.; Haarig, M.; Engelmann, R.; Althausen, D.; Hanssen, I.; Gausa, M.; Pietruczuk, A.; Szkop, A.; et al. The unprecedented 2017–2018 stratospheric smoke event: Decay phase and aerosol properties observed with the EARLINET. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 15183–15198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, B.; Del Guasta, M.; Kolenda, J.; Morandi, M.; Rairoux, P.; Stefanutti, L.; Wolf, J.P.; Wöste, L. Stratospheric aerosol size distributions from multispectral lidar measurements at Sodankylä during EASOE. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1994, 21, 1311–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miffre, A.; Anselmo, C.; Geffroy, S.; Fréjafon, E.; Rairoux, P. Lidar remote sensing of laser-induced incandescence on light absorbing particles in the atmosphere. Opt. Exp. 2015, 23, 2347–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.D.; Chittenden, D.M., II. Chemical composition of particles of d <0.20 mm in the lower stratospheric aerosol, Spring. J. Arkans. Acad. Sci. 2002, 56, 153–156. [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee, D.E. Cosmic dust: Collection and research. Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1985, 13, 147–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, J.L.; Zolensky, M.E. Collection and Curation of Interplanetary Dust Particles Recovered from the Stratosphere by NASA. In Analysis of Interplanetary Dust; Zolensky, M., Wilson, T., Rietmeijer, F., Flynn, G., Eds.; American Institute of Physics: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 245–253. [Google Scholar]
- Pueschel, R.F.; Black, D.F.; Snetsinger, K.G.; Hansen AD, A.; Verma, S.; Kato, K. Black carbon (soot) in the lower stratosphere and upper troposphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1992, 19, 1659–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, D.F.; Kato, K. Latitudinal distribution of black carbon soot in the upper troposphere and the lower stratosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 7195–7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pueschel, R.F.; Boering, K.A.; Verma, S.; Howard, S.D.; Ferry, G.V.; Goodman, J.; Allen, D.A.; Hamil, P. Soot aerosol in the lower stratosphere: Pole-to-pole variability and contributions by aircraft. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 13113–13118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strawa, A.W.; Drdla, K.; Ferry, G.V.; Verma, S.; Pueschel, R.F.; Yasuda, M.; Salawitch, R.J.; Gao, R.S.; Howard, S.D.; Bui, P.T.; et al. Carbonaceous aerosol (soot) measured in the lower stratosphere during POLARIS and its role in stratospheric photochemistry. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 26753–26766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, J.-B.; Ovarlez, J.; Berthet, G.; Fussen, D.; Vanhellemont, F.; Brogniez, C.; Hadamcik, E.; Chartier, M.; Ovarlez, H. Optical and physical properties of stratospheric aerosols from balloon measurements in the visible and near-infrared domains. III. Presence of aerosols in the middle stratosphere. App. Opt. 2005, 44, 4086–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eidhammer, T.; Montague, D.C.; Deshler, T. Determination of index of refraction and size of supermicrometer particles from light scattering measurements at two angles. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D16206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.P.; Gao, R.S.; Fahey, D.W.; Thomson, D.S.; Watts, L.A.; Wilson, J.C.; Reeves, J.M.; Darbeheshti, M.; Baumgardner, D.G.; Kok, G.L.; et al. Single-particle measurements of mid-latitude black carbon and light-scattering aerosols from the boundary layer to the lower stratosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D16207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigel, R.; Volk, C.M.; Kandler, K.; Hösen, E.; Günther, G.; Vogel, B.; Grooß, J.-U.; Khaykin, S.; Belyaev, G.V.; Borrmann, S. Enhancements of the refractory submicron aerosol fraction in the Arctic polar vortex: Feature or exception? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 12319–12342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.M.; Thomson, D.S.; Mahoney, M.J. In situ measurements of organics, meteoritic material, mercury, and other elements in aerosols at 5 to 19 km. Science 1998, 282, 1664–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, H.-J.; Drdla, K.; Stohl, A.; Pfister, L.; Loewenstein, M.; Lopez, J.P.; Hudson, P.K.; Murphy, D.M.; Cziczo, D.J.; Fromm, M.; et al. In situ observations of mid-latitude forest fire plumes deep in the stratosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L11101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.M.; Froyd, K.D.; Schwarz, J.P.; Wilson, J.C. Observation of the chemical composition of stratospheric aerosol particles. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 140, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, J.-B.; Berthet, G.; Robert, C.; Chartier, M.; Pirre, M.; Brogniez, C.; Herman, M.; Verwaerde, C.; Balois, J.-Y.; Ovarlez, J.; et al. Optical and physical properties of stratospheric aerosols from balloon measurements in the visible and near-infrared domains: Comparison of extinction, reflectance, polarization and counting measurements. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 7540–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthet, G.; Renard, J.-B.; Catoire, V.; Chartier, M.; Robert, C.; Huret, N.; Coquelet, F.; Bourgeois, Q. Remote sensing measurements in the polar vortex: Comparison to in situ observations and implications for the simultaneous retrievals and analysis of the NO2 and OClO species. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D21310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthet, G.; Renard, J.-B.; Brogniez, C.; Robert, C.; Chartier, M.; Pirre, M. Optical and physical properties of stratospheric aerosols from balloon measurements in the visible and near-infrared domains: Analysis of aerosol extinction spectra from the AMON and SALOMON balloonborne spectrometers. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 7522–7539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishchenko, M.I.; Hovenier, J.W.; Mackowski, D.W. Single scattering by a small volume element. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2004, 21, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, J.-B.; Tripathi, S.N.; Michael, M.; Rawal, A.; Berthet, G.; Fullekrug, M.; Harrison, R.G.; Robert, C.; Tagger, M.; Gaubicher, B. In situ detection of electrified aerosols in the upper troposphere and stratosphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 11187–11194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füllekrug, M.; Diver, D.; Pinçon, J.-L.; Phelps AD, R.; Bourdon, A.; Helling, C.; Blanc, E.; Honary, F.; Harrison, R.G.; Sauvaud, J.-A.; et al. Energetic Charged Particles Above Thunderclouds. Surv. Geophys. 2013, 34, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, J.P., Jr.; Stephens, J.R.; Berg, W.W.; Cahill, T.A.; Onaka, T.; Nakada, Y.; Arnold, J.R.; Fong, N.; Sperry, P.D. Collection of microparticles at high balloon altitudes in the stratosphere. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1990, 98, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciucci, A.; Palumbo, P.; Brunetto, R.; Della Corte, V.; De Angelis, S.; Rotundi, A.; Rietmeijer, F.J.M.; Zona, E.; Colangeli, L.; Esposito, F.; et al. DUSTER (Dust in the Upper Stratosphere Tracking Experiment and Retrieval) preliminary analysis. Mem. Soc. Astron. Ital. 2008, 75, 282–287. [Google Scholar]
- Della Corte, V.; Rietmeijer, F.J.M.; Rotundi, A.; Ferrari, M.; Palumbo, P. Meteoric CaO and carbon smoke particles collected in the upper stratosphere from an unanticipated source. Tellus B 2013, 65, 20174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bingen, C.; Fussen, D.; Vanhellemont, F. A global climatology of stratospheric aerosol size distribution parameters derived from SAGE II data over the period 1984-2000: Reference data. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D06202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, F.; Fussen, D.; Mateshvili, N.; Tétard, C.; Bingen, C.; Dekemper, E.; Loodts, N.; Kyrölä, E.; Sofieva, V.; Tamminen, J.; et al. Optical extinction by upper tropospheric/ stratospheric aerosols and clouds: GOMOS observations for the period 2002. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 7997–8009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, V.; Renard, J.-B.; Hauchecorne, A.; Bekki, S.; Berthet, G. A new climatology of aerosols in the middle and upper stratosphere by alternative analysis of GOMOS observations during 2002. Intern. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 4986–5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, L.W.; Ernest, N.; Millán, L.; Rieger, L.; Bourassa, A.; Vernier, J.-P.; Manney, G.; Luo, B.; Arfeuille, F.; Peter, T. A global space-based stratospheric aerosol climatology 1979–2016. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 469–492. [Google Scholar]
- Bourassa, A.E.; Rieger, L.A.; Lloyd, N.D.; Degenstein, D.A. Odin-OSIRIS stratospheric aerosol data product and SAGE III intercomparison. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromm, M.; Servranckx, R. Transport of forest fire smoke above the tropopause by supercell convection. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromm, M.; Tupper, A.; Rosenfeld, D.; Servranckx, R.; McRae, R. Violent pyro-convective storm devastates Australia’s capital and pollutes the stratosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L05815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemeier, U.; Timmreck, C.; Graf, H.-F.; Kinne, S.; Rast, S.; Self, S. Initial fate of fine ash and sulfur from large volcanic eruption. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 9043–9057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorkavyi, N.; Rault, D.F.; Newman, P.A.; da Silva, A.M.; Dudorov, A.E. New stratospheric dust belt due to the Chelyabinsk bolide. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 4728–4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, L.A.; Bourassa, A.E.; Degenstein, D.A. Odin-OSIRIS detection of the Chelyabinsk meteor. Atmos. Meas. Technol. 2014, 7, 777–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neely, R.R.; English, J.M.; Toon, O.B.; Solomon, S.; Mills, M.; Thayer, J.P. Implications of extinction due to meteoritic smoke in the upper stratosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L24808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeois, Q.; Ekman AM, L.; Renard, J.-B.; Krejci, R.; Devasthale, A.; Bender, A.-M.; Riipinen, I.; Berthet, G.; Tackett, J.L. How much of the global aerosol optical depth is found in the bondary layer and free troposphere? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 7709–7720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernier, J.P.; Pommereau, J.-P.; Garnier, A.; Pelon, J.; Larsen, N.; Nielsen, J.; Christensen, T.; Cairo, F.; Thomason, L.W.; Leblanc, T.; et al. Tropical stratospheric aerosol layer from CALIPSO lidar observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D00H10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernier, J.P.; Fairlie, T.D.; Deshler, T.; Natarajan, M.; Knepp, T.; Foster, K.; Wienhold, F.G.; Bedka, K.M.; Thomason, L.W.; Trepte, C. In situ and space observations of the Kelud volcanic plume: The persistence of ash in the lower stratosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 11104–11118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govardhan, G.; Krishnakumari Satheesh, S.; Nanjundiah, R.; Krishna Moorthy, K.; Suresh Babu, S. Possible climatic implications of high-altitude black carbon emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 9623–9644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernier, J.-P.; Fairlie, T.D.; Deshler, T.; Venkat Ratnam, M.; Gadhavi, H.; Kumar, B.S.; Natarajan, M.; Pandit, A.K.; Akhil Raj, S.T.; Hemanth Kumar, A.; et al. BATAL: The Balloon Measurement Campaigns of the Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2018, 99, 955–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandeville, J.-C. Study of Cosmic Dust Particles on Board LDEF and MIR Space Station. In Origin and Evolution of Interplanetary Dust; Levasseur-Regourd, A.-C., Hasegawa, H., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Alphen aan den Rijn, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Love, S.; Brownlee, D. A direct measurement of the terrestrial mass accretion rate of cosmic dust. Science 1993, 262, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalashnikova, O.; Horanyi, M.; Thomas, G.E.; Toon, O.B. Meteoric smoke production in the atmosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 3293–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, L.A.; Bourassa, A.E.; Degenstein, D.A. Stratospheric aerosol particle size information in Odin-OSIRIS limb scatter spectra. Atmos. Meas. Technol. 2014, 7, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovilakam, M.; Deshler, T. On the accuracy of stratospheric aerosol extinction derived from in situ size distribution measurements and surface area density derived from remote SAGE II and HALOE extinction measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 8426–8447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, J.-B.; Berthet, G.; Salazar, V.; Catoire, V.; Tagger, M.; Gaubicher, B.; Robert, C. In situ detection of aerosol layers in the middle stratosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L20803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.S.; Telg, H.; McLaughlin, R.J.; Ciciora, S.J.; Watts, L.A.; Richardson, M.S.; Schwarz, J.P.; Perring, A.E.; Thornberry, T.D.; Rollins, A.W.; et al. A light-weight, high-sensitivity particle spectrometer for PM2.5 aerosol measurements. Aeros. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessberger, E.K.; Stephan, T.; Rost, D.; Arndt, P.; Maetz, M.; Stadermann, F.J.; Brownlee, D.E.; Bradley, J.P.; Kurat, G. Properties of Interplanetary Dust: Information from Collected Samples. In Interplanetary Dust; Grün, E., Gustafson, B.A.S., Dermott, S.F., Fechtig, H., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 253–294. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, J.-B.; Dulac, F.; Berthet, G.; Lurton, T.; Vignelles, D.; Jégou, F.; Tonnelier, T.; Jeannot, M.; Couté, B.; Akiki, R.; et al. LOAC, a light aerosols counter for ground-based and balloon measurements of the size distribution and of the main nature of atmospheric particles, Principle of measurements and instrument evaluation. Atmos. Meas. Technol. 2016, 9, 1721–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, J.-B.; Dulac, F.; Durand, P.; Bourgeois, Q.; Denjean, C.; Vignelles, D.; Couté, B.; Jeannot, M.; Verdier, N.; Mallet, M. In situ measurements of desert dust particles above the western Mediterranean Sea with the balloon-borne Light Optical Aerosol Counter/sizer (LOAC) during the ChArMEx campaign of summer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 3677–3699. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, O.; Volten, H.; de Haan, J.F.; Vassen, W.; Hovenier, J.W. Experimental determination of scattering matrices of randomly oriented fly ash and clay particles at 442 and 633 nm. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 22833–22844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurton, T.; Renard, J.-B.; Vignelles, D.; Jeannot, M.; Akiki, R.; Mineau, J.-L.; Tonnelier, T. Light scattering at small angles by atmospheric irregular particles: Modelling and laboratory measurements. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques. Atmos. Meas. Technol. 2014, 7, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, J.-B.; Dulac, F.; Berthet, G.; Lurton, T.; Vignelles, D.; Jégou, F.; Tonnelier, T.; Jeannot, M.; Couté, B.; Akiki, R.; et al. LOAC, a light aerosols counter for ground-based and balloon measurements of the size distribution and of the main nature of atmospheric particles, First results from balloon and unmanned aerial vehicle flights. Atmos. Meas. Technol. 2016, 9, 3673–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenniskens, P. Meteor Showers and their Parent Comets; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Rohatschek, H. Levitation of stratospheric and mesospheric aerosols by gravito-photophoresis. J. Aerosol Sci. 1996, 27, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pueschel, R.F.; Verma, S.; Rohatschek, H.; Ferry, G.V.; Boiadjieva, N.; Howard, S.D.; Strawa, A.W. Vertical transport of anthropogenic soot aerosol into the middle atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 3727–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheremisin, A.A.; Shnipov, I.S.; Horvath, H.; Rohatschek, H. The global picture of aerosol layers formation in the stratosphere and in the mesosphere under the influence of gravito-photophoretic and magneto-photophoretic forces. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D19204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheremisin, A.A.; Vassilyev, Y.V.; Horvath, H. Gravito- photophoresis and aerosol stratification in the atmosphere. J. Aerosol Sci. 2005, 36, 1277–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansmann, A.; Baars, H.; Chudnovsky, A.; Mattis, I.; Veselovskii, I.; Haarig, M.; Seifert, P.; Engelmann, R.; Wandinger, U. Extreme levels of Canadian wildfire smoke in the stratosphere over central Europe on 21–22 August. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 11831–11845. [Google Scholar]
- Kloss, C.; Berthet, G.; Sellitto, P.; Ploeger, F.; Bucci, S.; Khaykin, S.; Jégou, F.; Taha, G.; Thomason, L.; Barret, B.; et al. Transport of the 2017 Canadian wildfire plume to the tropics and global stratosphere via the Asian monsoon circulation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 13547–13567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beresnev, S.; Vasiljeva, M.; Suetin, D. Predictions and detection of the “accommodation” forces on Janus particles subjected to directed radiation in a rarefied gas. Vacuum 2012, 86, 1663–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryazin, V.I.; Beresnev, S.A. Influence of vertical wind on stratospheric aerosol transport. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2011, 110, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beresnev, S.A.; Vasil’eva, M.S.; Gryazin, V.I.; Kochneva, L.B. Photophoresis of fractal-like soot aggregates: Microphysical model, comparison with experiment, and possible atmospheric manifestations. Atmos. Ocea. Opt. 2017, 30, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chane-Ming, F.; Vignelles, D.; Jegou, F.; Berthet, G.; Renard, J.-B.; Gheusi, F.; Kuleshov, Y. Gravity-wave effects on tracer gases and stratospheric aerosol concentrations during the 2013 ChArMEx campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 8023–8042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, K.; Chung, S.H.; Friedrich, H.; Buseck, P.R. Fractal parameters of individual soot particles determined using electron tomography: Implications for optical properties. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D14202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardeen, C.G.; Toon, O.B.; Jensen, E.J.; Marsh, D.R.; Harvey, V.L. Numerical simulation of the three-dimensional distribution of meteoric dust in the mesosphere and upper stratosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D17202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plane, J.M.C. Atmospheric chemistry of meteoric metals. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 4963–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plane, J.M.C. Cosmic dust in the earth’s atmosphere. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 6507–6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plane, J.M.C.; Flynn, G.J.; Määttänen, A.; Moores, J.E.; Poppe, A.R.; Carrillo-Sanchez, J.D.; Listowsky, C. Impacts of cosmic dust on planetary atmospheres and surfaces. Space Sci. Rev. 2018, 214, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, M.; Strellnikova, I.; Gumbel, J. Meteoric smoke particles: Evidence from rocket and radar techniques. Adv. Space Res. 2007, 40, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bound, T.C.; Bergstrom, R.W. Light absorption by carbonaceous particles: An investigative review. Aeros. Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 27–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, D.A.; Campbell, J.R.; Hyer, E.J.; Fromm, M.D.; Kablick, G.P., III; Cossuth, J.H.; DeLand, M.T. Wildfire-driven thunderstorms cause a volcano-like stratospheric injection of smoke. Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 1, 2397–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, M.N.; Whitefield, P.D.; Hagen, D.E.; Hopkins, A.R. In situ measurement of the aerosol size distribution in stratospheric solid rocket motor exhaust plumes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateshvili, N.; Mateshvili, G.; Mateshvili, I.; Gheondjian, L.; Avsajanishvili, O. Vertical distribution of dust particles in the Earth’s atmosphere during the 1998 Leonids. Meteorit. B Planet. Sci. 1999, 34, 969–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownlee, D.E. Microparticle Studies by Sampling Techniques. In Cosmic Dust; McDonnell, J., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1978; pp. 295–336. [Google Scholar]
- Hunten, D.M.; Turco, R.P.; Toon, O.B. Smoke and dust particles of meteoric origin in the mesosphere and stratosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 1980, 37, 1342–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandford, S.A.; Engrand, C.; Rotundi, A. Organic Matter in Cosmic Dust. Elements 2016, 12, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietmeijer, F.J.M. Interplanetary dust particles. Rev. Miner. 1998, 36, 1–96. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, K.L.; Blanford, G.E.; Keller, L.P.; Klöck, W.; McKay, D. Carbon abundance and silicate mineralogy of anhydrous interplanetary dust particles. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 1551–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, G.J.; Wirick, S.; Keller, L.P. Organic grain coatings in primitive interplanetary dust particles. Earth Plan. Sp. 2013, 65, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Koschny, D.; Soja, R.; Engrand, C.; Flynn, G.; Lasue, J.; Levasseur-Regourd, A.C.; Malaspina, D.; Nakamura, T.; Poppe, A.R.; Sterken, V.J.; et al. Interplanetary dust, meteoroids, meteors and meteorites. Space Sci. Rev. 2019, 215, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, H.A.; Bradley, J.P.; Dai, Z.R.; Chi, M.; Kearsley, A.T.; Burchell, M.J.; Browning, N.D.; Molster, F. Comparison of comet 81P/Wild 2 dust with interplanetary dust from comets. Science 2008, 319, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levasseur-Regourd, A.C.; Agarwal, J.; Cottin, H.; Engrand, C.; Flynn, G.; Fulle, M.; Gombosi, T.; Langevin, Y.; Lasue, J.; Mannel, T.; et al. Cometary dust. Space Sci. Rev. 2018, 214, 64–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannel, T.; Bentley, M.S.; Boakes, P.; Jeszenszky, H.; Ehrenfreund, P.; Engrand, C.; Koeberl, C.; Levasseur-Regourd, A.C.; Romstedt, J.; Schmied, R.; et al. Dust of comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko collected by Rosetta/ MIDAS: Classification and extension to the nanometer scale. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 630, A26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engrand, C.; Maurette, M. Carbonaceous micrometeorites from Antarctica. Meteor. Planet. Sci. 1998, 33, 565–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Noguchi, T.; Ozono, Y.; Osawa, T.; Nagao, K. Mineralogy of ultracarbonaceous large micrometeorites. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2005, 40, 5046. [Google Scholar]
- Dartois, E.; Engrand, C.; Duprat, J.; Godard, M.; Charon, E.; Delauche, L.; Sandt, C.; Borondics, F. Dome C ultracarbonaceous Antarctic micrometeorites. Infrared and raman fingerprints? Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 609, A65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damoah, R.; Spichtinger, N.; Servranckx, R.; Fromm, M.; Eloranta, E.W.; Razenkov, I.A.; James, P.; Shulski, M.; Forster, C.; Stohl, A. A case study of pyro-convection using transport model and remote sensing data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Laat, A.T.J.; Stein Zweers, D.C.; Boers, R.; Tuinder, O.N.E. A solar escalator: Observational evidence of the self-lifting of smoke and aerosols by absorption of solar radiation in the February 2009 Australian Black Saturday plume. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D04204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromm, M.; Bevilacqua, R.; Servranckx, R.; Rosen, J.; Thayer, J.P.; Herman, J.; Larko, D. Pyro-cumulonimbus injection of smoke to the stratosphere: Observations and impact of a super blowup in northwestern Canada on 3–4 August. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D08205. [Google Scholar]
- Brunamonti, S.; Jorge, T.; Oelsner, P.; Hanumanthu, S.; Singh, B.B.; Kumar, K.R.; Sonbawne, S.; Meier, S.; Singh, D.; Wienhold, F.G.; et al. Balloon-borne measurements of temperature, water vapor, ozone and aerosol backscatter on the southern slopes of the Himalayas during StratoClim 2016. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 15937–15957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Toon, O.B.; Neely, R.R.; Martinsson, B.G.; Brenninkmeijer, C.A. Composition and physical properties of the Asian tropopause aerosol layer and the North American tropospheric aerosol layer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 2540–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadnavis, S.; Kalita, G.; Ravi Kumar, K.; Gasparini, B.; Frank Li, J.-L. Potential impact of carbonaceous aerosol on the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere (UTLS) and precipitation during Asian summer monsoon in a global model simulation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 11637–11654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaykin, S.M.; Godin-Beekmann, S.; Keckhut, P.; Hauchecorne, A.; Jumelet, J.; Vernier, J.-P.; Bourassa, A.; Degenstein, D.A.; Rieger, L.A.; Bingen, C.; et al. Variability and evolution of the midlatitude stratospheric aerosol budget from 22 years of ground-based lidar and satellite observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 1829–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortov, V.E.; Sultanov, V.G.; Shutov, A.V. Chelyabinsk superbolide explosion in the Earth’s atmosphere: A common phenomenon or unique coincidence? Geochem. Intern. 2013, 51, 549–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulson, S.G.; Wallus, M.K.; Wickramasinghe, N.C. On the dynamics of volatile meteorites. Mont. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 445, 3669–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Antonsen, T.; Havnes, O.; Mann, I. Estimates of the size distribution of Meteoric smoke particles from rocket-borne impact probes. J. Geophys. Res. 2017, 122, 12353–12365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cziczo, D.J.; Murphy, D.M.; Thomson, D.S.; Ross, M.N. Composition of individual particles in the wakes of an Athena II rocket and the space shuttle. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, P.A.; Wilson, J.C.; Ross, M.N.; Brock, C.A.; Sheridan, P.J.; Schoeberl, M.R.; Lait, L.R.; Bui, T.P.; Loewenstein, M.; Podolske, J.R. Chance encounter with a stratospheric kerosene rocket plume from Russia over California. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, A.; Kabbara, H.; Courty, M.-A.; Cha, M.S.; Martinez, J.-M.; Belmonte, T. Synthesis of carbon-metal multi strand nanocomposites by discharges in heptane between two metallic electrodes. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2017, 37, 1069–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courty, M.-A.; Martinez, J.-M. Terrestrial carbonaceous debris tracing atmospheric hypervelocity-shock aeroplasma processes. Proc. Eng. 2015, 103, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.; Massereau-Guilbaud, V.; Géraud-Grenier, I.; Plain, A. CH and CN radical contribution in the particle formation generated in a radio-frequency CH4/N2 plasma. Plasma Process. Polym. 2005, 2, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etiope, G.; Fridriksson, T.; Italiano, F.; Winiwarter, W.; Theloke, J. Natural emissions of methane from geothermal and volcanic sources in Europe. J. Volcano. Geother. Res. 2007, 165, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuev, V.V.; Zueva, N.E.; Koutsenogii, P.K.; Savelyeva, E.S. Volcanogenic nanosized carbon aerosol in the stratosphere. Chem. Sustain. Devel. 2014, 22, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Zuev, V.V.; Zueva, N.E.; Savelyeva, E.S. Temperature and ozone anomalies as indicators of volcanic soot in the stratosphere. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2015, 28, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendricks, J.; Kärcher, B.; Döpelheuer, A.; Feichter, J.; Lohmann, U.; Baumgardner, D. Simulating the global atmospheric black carbon cycle: A revisit to the contribution of aircraft emission. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2004, 4, 2521–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levasseur-Regourd, A.C.; Mann, I.; Dumont, R.; Hanner, M.S. Optical and Thermal Properties of Interplanetary Dust. In Interplanetary Dust; Grün, E., Gustafson, B.A.S., Dermott, S.F., Fechtig, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001; pp. 57–94. [Google Scholar]
- Lasue, J.; Levasseur-Regourd, A.C.; Fray, N.; Cottin, H. Inferring the interplanetary dust properties from remote observations and simulations. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 473, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan-Robinson, M.; May, B. An improved model for the infrared emission from the zodiacal dust cloud: Cometary, asteroidal and interstellar dust. Month. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2013, 429, 2894–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesvornyý, D.; Jenniskens, P.; Levison, H.F.; Bottke, W.F.; Vokrouhlicky, D.; Gounelle, M. Cometary origin of the zodiacal cloud and carbonaceous micrometeorites: Implications for hot debris disks. Astrophys. J. 2010, 713, 816–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermott, S.F.; Nicholson, P.D.; Burns, J.A.; Houck, J.R. On the origin of the IRAS solar system dust bands. Nature 1984, 312, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, M.V.; Hunten, D.M.; Low, F.J. Preliminary analysis of cometary dust trails. Adv. Space Res. 1986, 6, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reach, W.T.; Kelley, M.S.; Sykes, M.V. A survey of debris trails from short-period comets. Icarus 2007, 191, 298–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levasseur, A.C.; Blamont, J.E. Satellite observations of intensity variations of the zodiacal light. Nature 1973, 246, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardyn, A.; Baklouti, D.; Cottin, H.; Fray, N.; Briois, C.; Paquette, J.; Stenzel, O.; Engrand, C.; Fischer, H.; Hornung Isnard, R.; et al. Carbon-rich dust in comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko measured by COSIMA/Rosetta. Month. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2017, 469, S712–S722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herique, A.; Kofman, W.; Beck, P.; Bonal, L.; Buttarazzi, I.; Heggy, E.; Lasue, J.; Levasseur-Regourd, A.C.; Quirico, E.; Zine, S. Cosmochemical implications of CONSERT permittivity characterization of 67P/CG. Month. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2017, 462, S516–S532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merouane, S.; Zaprudin, B.; Stenzel, O.; Langevin, Y.; Altobelli, N.; Della Corte, V.; Fischer, H.; Fulle, M.; Hornung, K.; Silén, J.; et al. Dust particle flux and size distribution in the coma of 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko measured in situ by the COSIMA instrument on board Rosetta. Astron. Atrophys. 2016, 596, A87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, Y.; Hilchenbach, M.; Ligier, N.; Merouane, S.; Hornung, K.; Engrand, C.; Schulz, R.; Kissel, J.; Rynö, J.; Eng, P. Typology of dust particles collected by the COSIMA mass spectrometer in the inner coma of 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko. Icarus 2016, 271, 76–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannel, T.; Bentley, M.S.; Schmied, R.; Jeszenszky, H.; Levasseur-Regourd, A.C.; Romstedt, J.; Torkar, K. Fractal cometary dust: A window into the early Solar System. Month. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2016, 462, S304–S311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Sánchez, J.D.; Nesvorný, D.; Pokorný, P.; Janches, D.; Plane, J.M.C. Sources of cosmic dust in the Earth’s atmosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 11979–11986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadamcik, E.; Renard, J.-B.; Lasue, J.; Levasseur-Regourd, A.C.; Blum, J.; Shraepler, R. Light scattering by low density agglomerates of micron-sized grains with the PROGRA2 experiment. J. Quant. Spectr. Rad. Trans. 2007, 106, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, M.; Renard, J.-B.; Hadamcik, E.; Couté, B.; Gaubicher, B.; Jeannot, M. New studies on scattering properties of different kinds of soot. J. Quant. Spectr. Rad. Trans. 2011, 112, 1766–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pommereau, J.-P.; Dalaudier, F.; Barat, J.; Bertaux, J.-L.; Goutail, F.; Hauchecorne, A. First results of a stratospheric experiment using a montgolfiere infra-rouge (MIR). Adv. Space Res. 1985, 5, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalashnikova, D.A.; Markelova, A.N.; Melkov, V.N.; Simonova, G.V. Isotope composition of pyrogenic carbon of various origins. Chem. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 24, 467–471. [Google Scholar]
- Beresnev, S.A.; Vasiljeva, M.S. Black carbon aerosol in stratosphere. In Proceedings of the SPIE 10833, 24th International Symposium on Atmospheric and Ocean Optics: Atmospheric Physics, Tomsk, Russia, 2–5 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Illingworth, A.J.; Barker, H.W.; Beljaars, A.; Ceccaldi, M.; Chepfer, H.; Clerbaux, N.; Cole, J.; Delanoë, J.; Domenech, C.; Donovan, D.P.; et al. The EarthCARE Satellite: The Next Step Forward in Global Measurements of Clouds, Aerosols, Precipitation, and Radiation. Bull. Am. Meteo. Soc. 2015, 96, 1311–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Nature | Typical Size | Source | Origin | Typical Composition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volcanic ashes | <1 µm | From ground | Natural | Silicates, basaltic, salts |
| Biomass burning | <1 µm | From ground | Natural and anthropogenic | Carbonaceous |
| Pollution | <1 µm | From ground | Anthropogenic | Carbonaceous, minerals, sulfur |
| Polymeric nanocomposites | >1 µm | Produced in the atmosphere | Natural | Carbonaceous |
| Rocket exhaust plume | <5 µm | Produced in the atmosphere | Anthropogenic | Alumina |
| Airplane soot | <1 µm | Produced in the atmosphere | Anthropogenic | Carbonaceous |
| Meteoroid disintegration | All sizes | From space and produced in the atmosphere | Natural | Carbonaceous, metals, silicates |
| Satellite disintegration | All sizes | From space and produced in the atmosphere | Anthropogenic | Various |
| Interplanetary/cometary dust | <1 mm | From space | Natural | Carbonaceous, silicates |
| Enhancement Categories | Number of Events (from 151 Flights) | Mainly NSPs | Mainly Sulfates | Enhancements < 10 Times the Background Content | Enhancements > 10 times the Background Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Presence of particles >2 µm | 30 | 20 | 10 | 10 | 20 |
| Particles <2 µm only | 18 | 12 | 6 | 7 | 11 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Renard, J.-B.; Berthet, G.; Levasseur-Regourd, A.-C.; Beresnev, S.; Miffre, A.; Rairoux, P.; Vignelles, D.; Jégou, F. Origins and Spatial Distribution of Non-Pure Sulfate Particles (NSPs) in the Stratosphere Detected by the Balloon-Borne Light Optical Aerosols Counter (LOAC). Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101031
Renard J-B, Berthet G, Levasseur-Regourd A-C, Beresnev S, Miffre A, Rairoux P, Vignelles D, Jégou F. Origins and Spatial Distribution of Non-Pure Sulfate Particles (NSPs) in the Stratosphere Detected by the Balloon-Borne Light Optical Aerosols Counter (LOAC). Atmosphere. 2020; 11(10):1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101031
Chicago/Turabian StyleRenard, Jean-Baptiste, Gwenaël Berthet, Anny-Chantal Levasseur-Regourd, Sergey Beresnev, Alain Miffre, Patrick Rairoux, Damien Vignelles, and Fabrice Jégou. 2020. "Origins and Spatial Distribution of Non-Pure Sulfate Particles (NSPs) in the Stratosphere Detected by the Balloon-Borne Light Optical Aerosols Counter (LOAC)" Atmosphere 11, no. 10: 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101031
APA StyleRenard, J.-B., Berthet, G., Levasseur-Regourd, A.-C., Beresnev, S., Miffre, A., Rairoux, P., Vignelles, D., & Jégou, F. (2020). Origins and Spatial Distribution of Non-Pure Sulfate Particles (NSPs) in the Stratosphere Detected by the Balloon-Borne Light Optical Aerosols Counter (LOAC). Atmosphere, 11(10), 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101031








