Assessment of Urban CO2 Measurement and Source Attribution in Munich Based on TDLAS-WMS and Trajectory Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Measurement System and Auxiliary Data
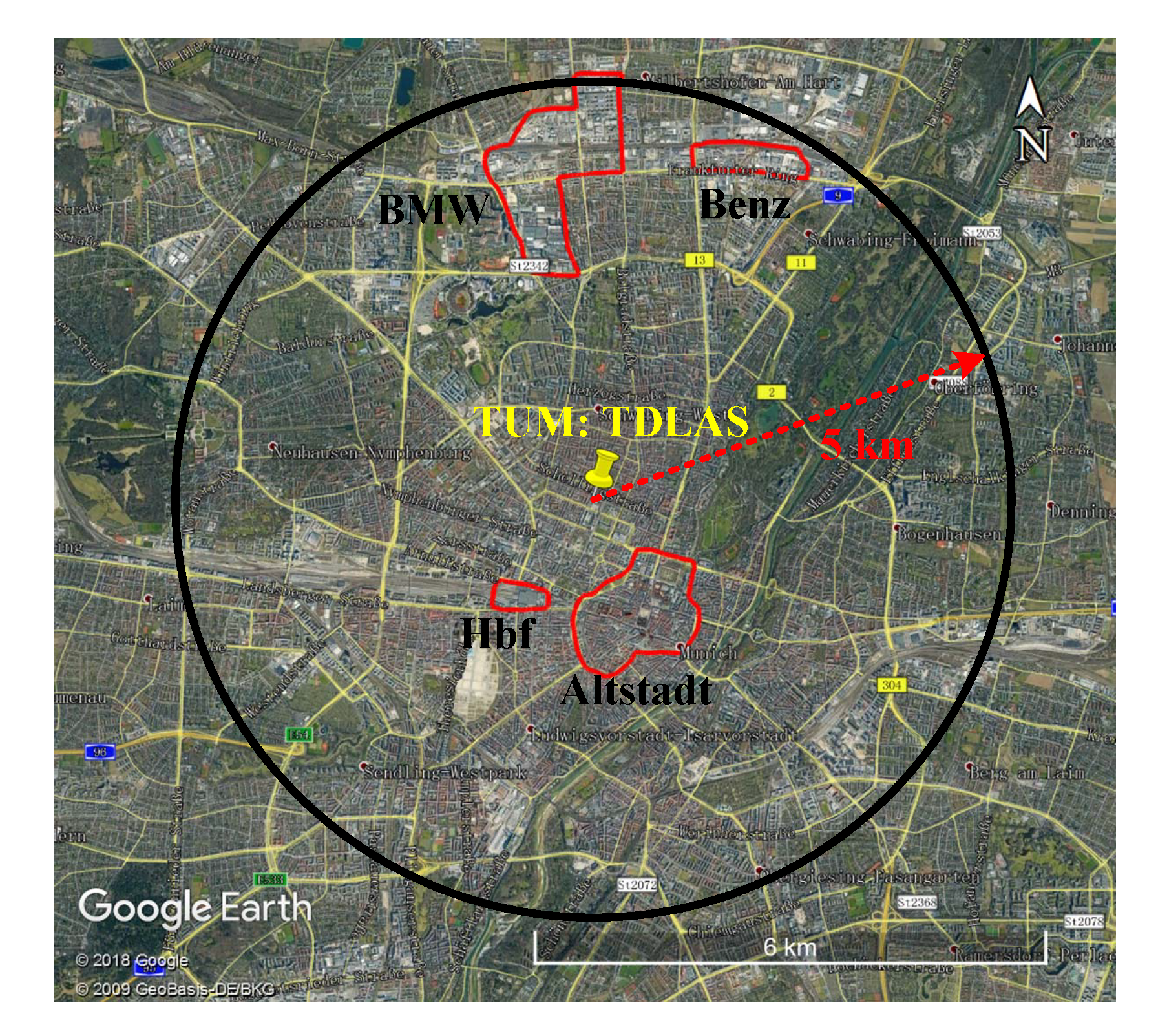
2.1. Measurement Site
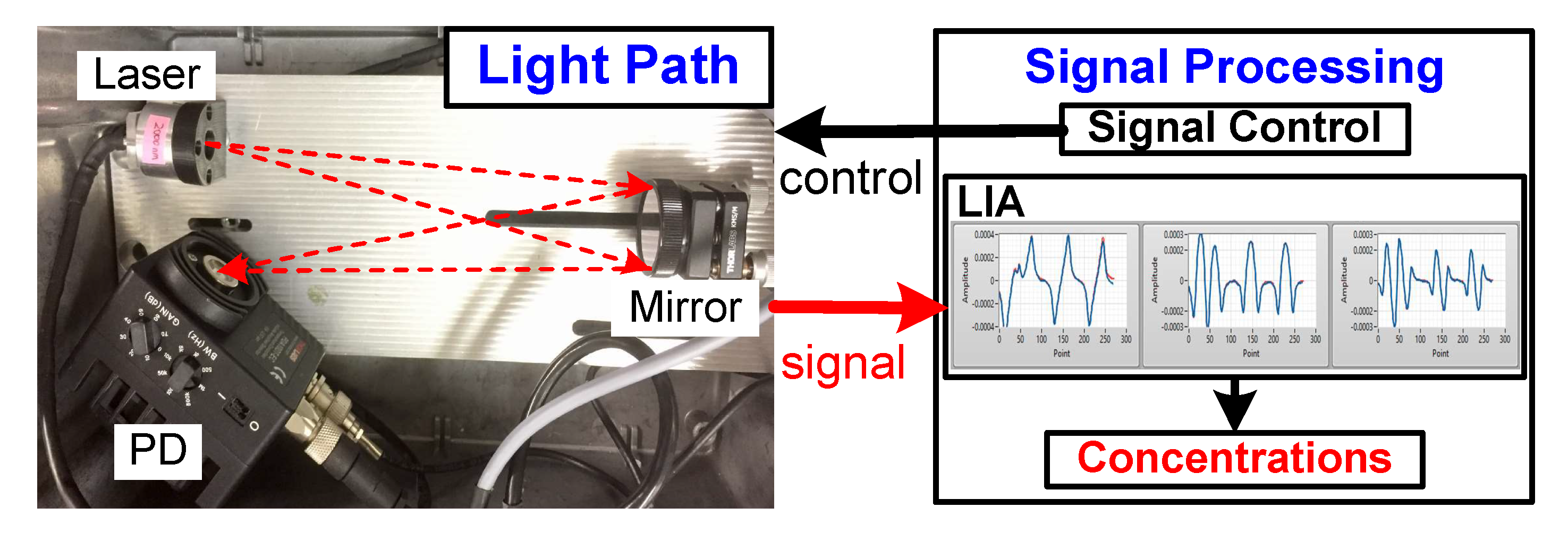
2.2. TDLAS-WMS Sensor
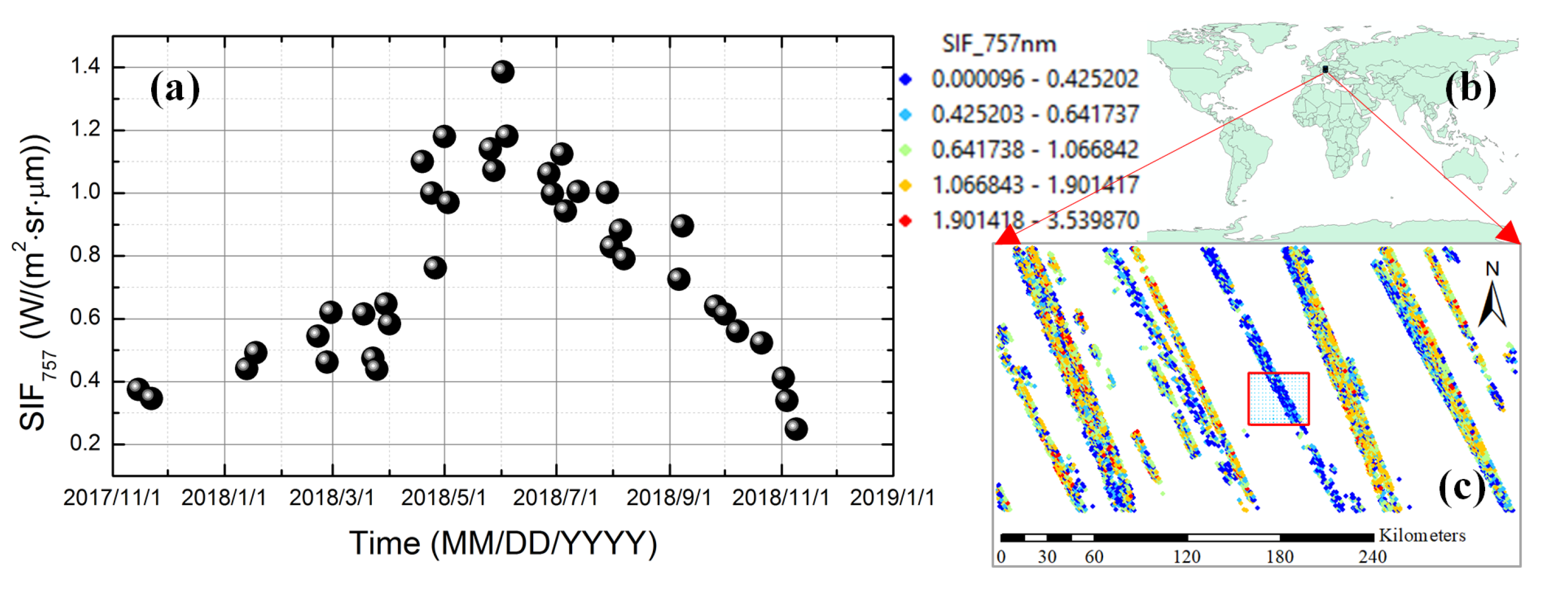
2.3. Auxiliary Data
3. Results and Discussion
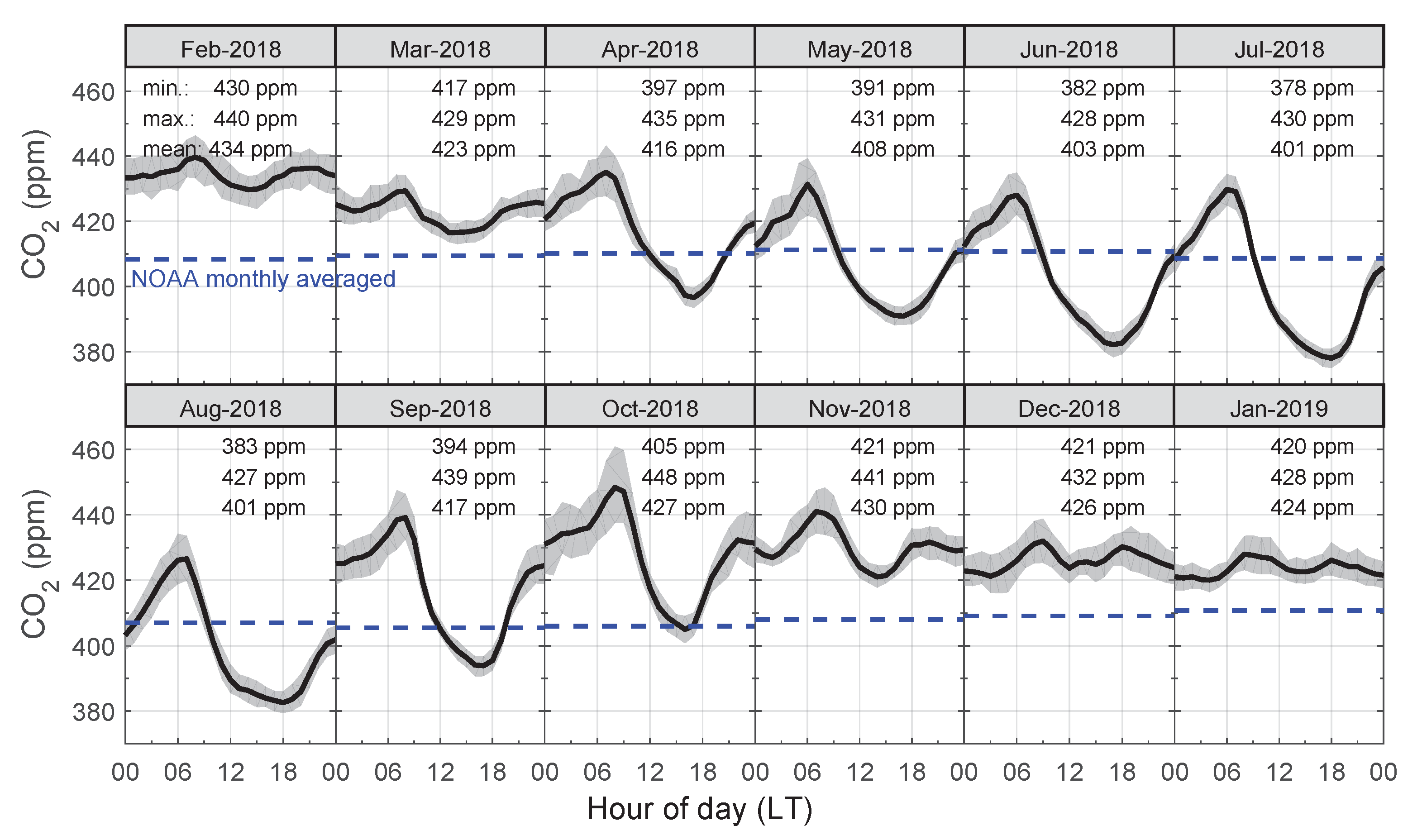
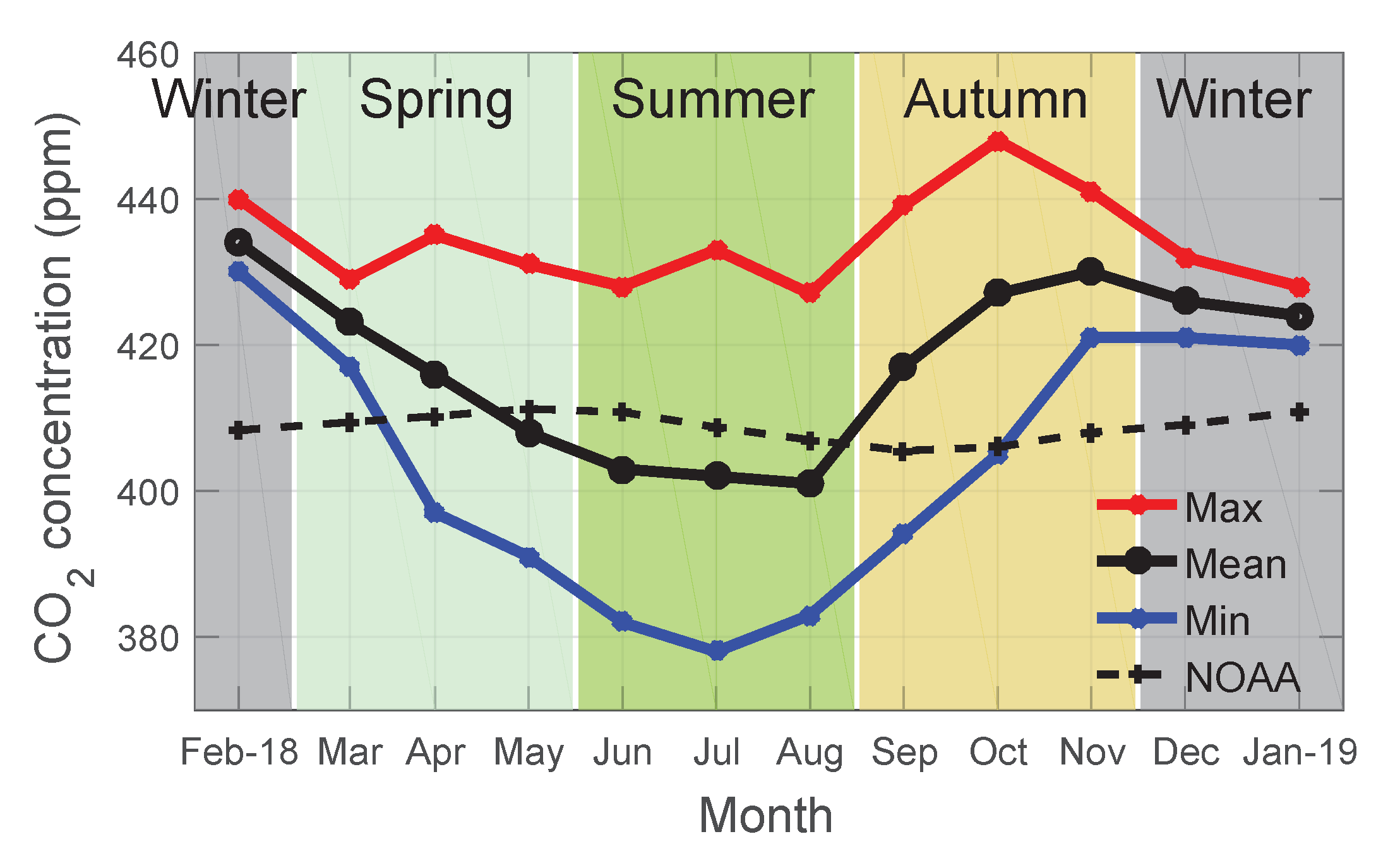
3.1. Diurnal Cycles by Month
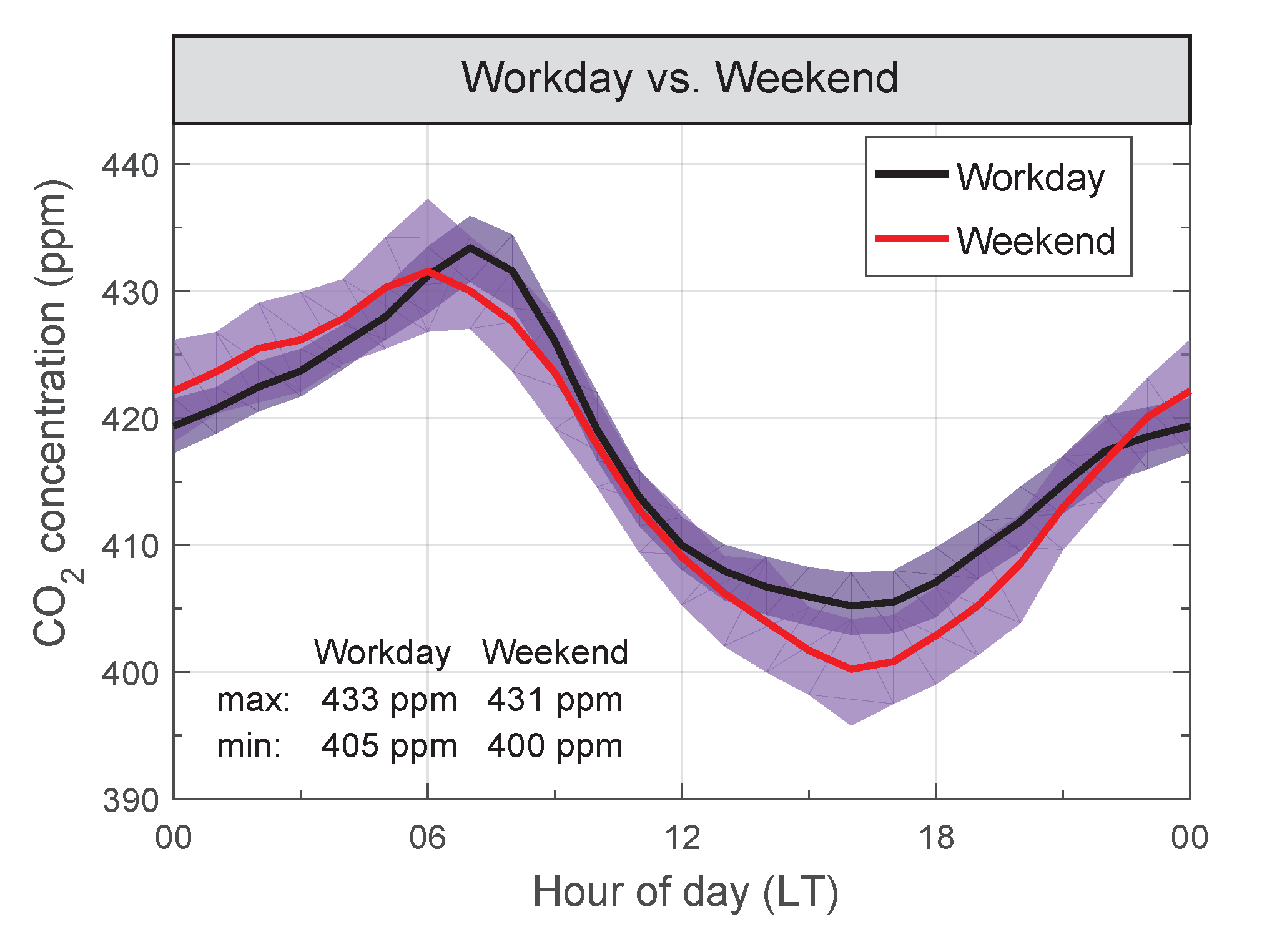
3.2. Diurnal Cycle on Workdays versus Weekends
4. Model Analysis of Winter Data
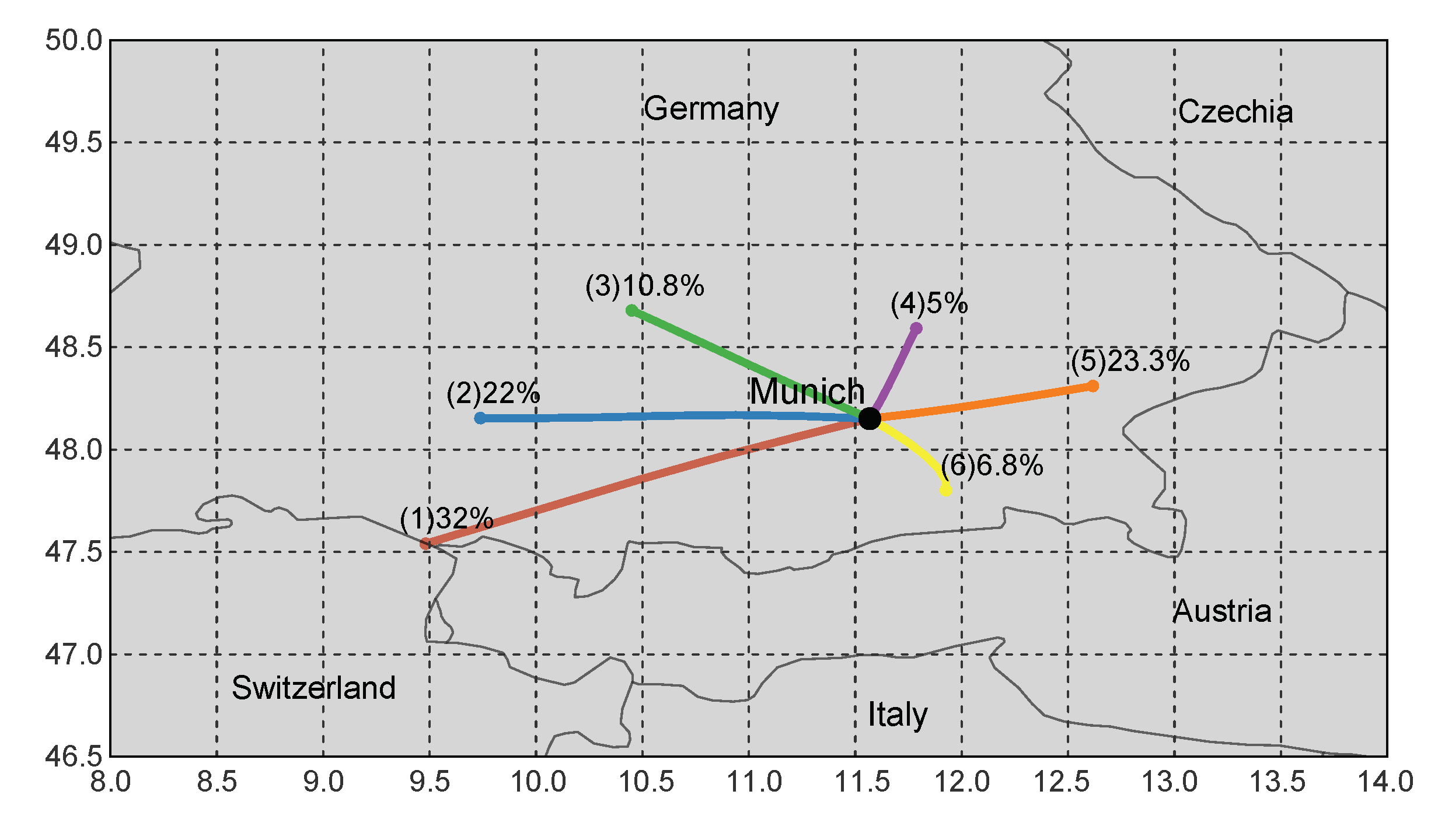
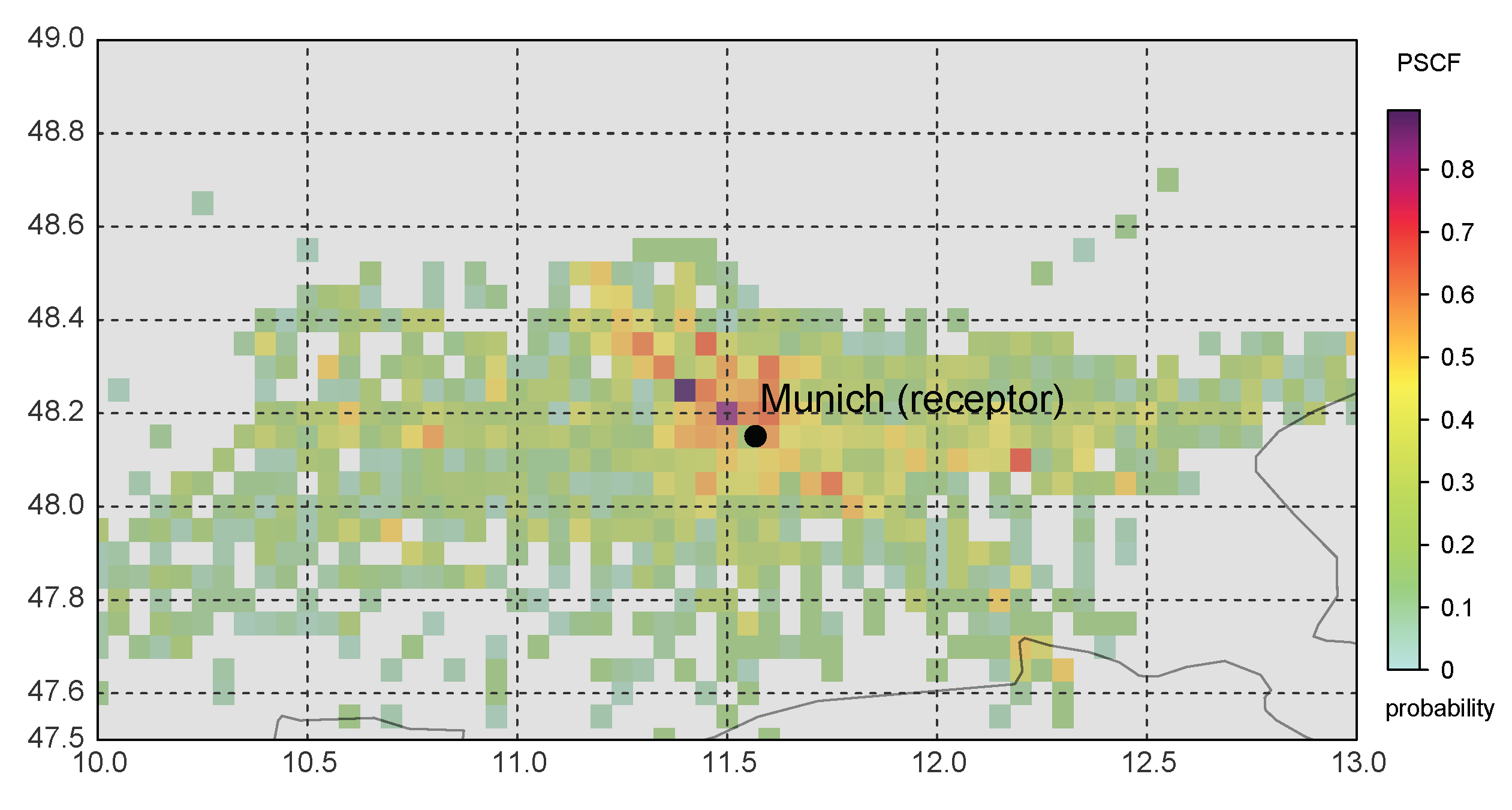
4.1. Trajectory Calculation and Analysis Methods
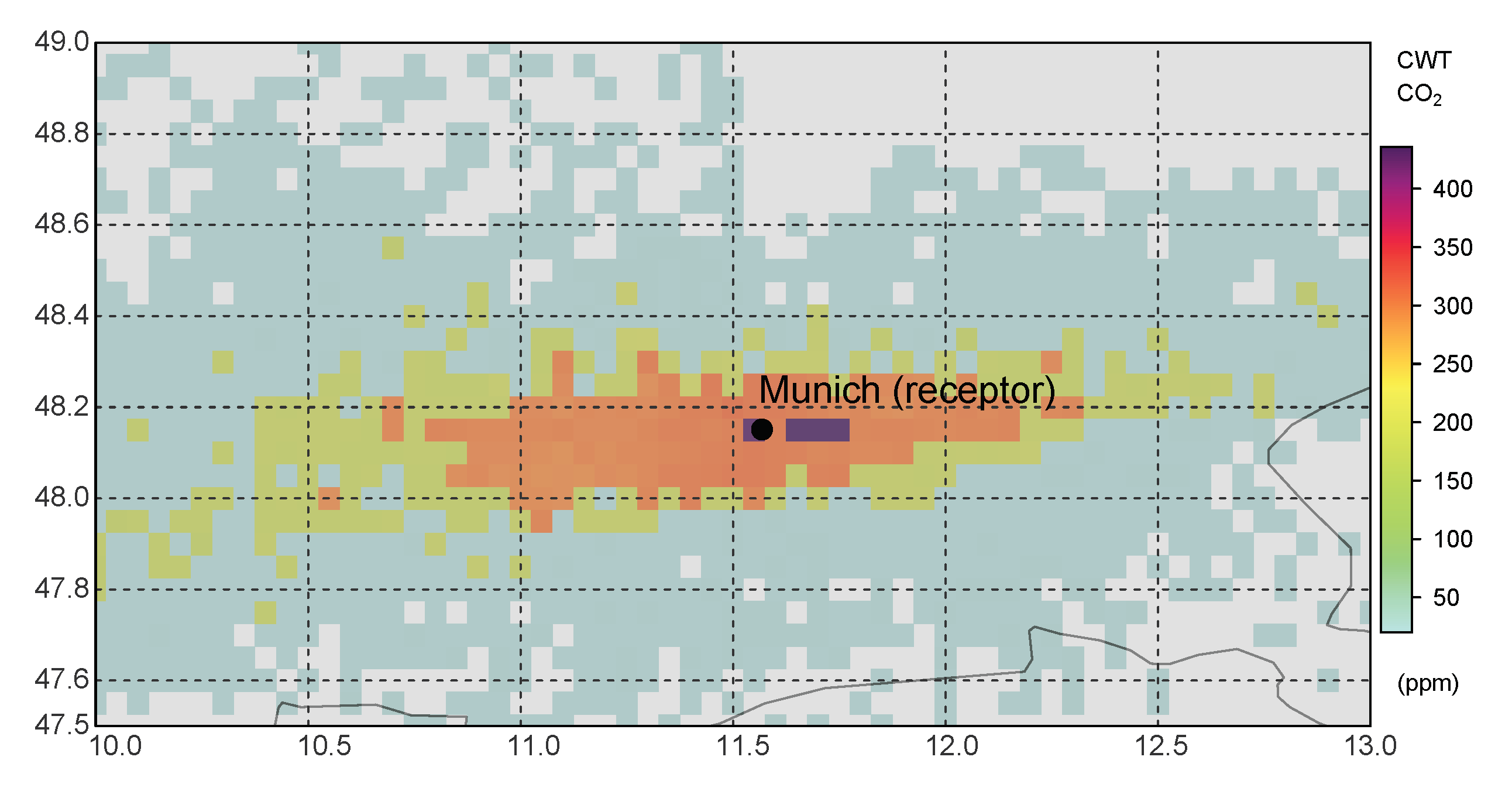
4.2. Analysis of Winter Data
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allen, M.; Barros, V.; Broome, J.; Cramer, W.; Christ, R.; Church, J.; Clarke, L.; Dahe, Q.; Dasgupta, P.; Dubash, N.; et al. IPCC Fifth Assessment Synthesis Report-Climate Change 2014 Synthesis Report; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, I.; Graul, R.; Trivett, N.B. Long-term observations of atmospheric CO2 and carbon isotopes at continental sites in Germany. Tellus B 1995, 47, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazan, L.; Tarniewicz, J.; Ramonet, M.; Laurent, O.; Abbaris, A. Automatic processing of atmospheric CO2 and CH4 mole fractions at the ICOS Atmosphere Thematic Centre. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 4719–4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Ries, L.; Petermeier, H.; Trickl, T.; Leuchner, M.; Couret, C.; Sohmer, R.; Meinhardt, F.; Menzel, A. On the diurnal, weekly, and seasonal cycles and annual trends in atmospheric CO2 at Mount Zugspitze, Germany, during 1981–2016. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 999–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamazaki, T.; Kaneko, Y.; Kuze, A.; Kondo, K. Fourier transform spectrometer for greenhouse gases observing satellite (GOSAT). In Enabling Sensor and Platform Technologies for Spaceborne Remote Sensing; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005; Volume 5659, pp. 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, M.; Moreno, J.; Johannessen, J.A.; Levelt, P.F.; Hanssen, R.F. ESA’s sentinel missions in support of Earth system science. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisp, D.; Pollock, H.R.; Rosenberg, R.; Chapsky, L.; Lee, R.A.; Oyafuso, F.A.; Frankenberg, C.; O’Dell, C.W.; Bruegge, C.J.; Doran, G.B.; et al. The on-orbit performance of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) instrument and its radiometrically calibrated products. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 59–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunch, D.; Toon, G.C.; Blavier, J.F.L.; Washenfelder, R.A.; Notholt, J.; Connor, B.J.; Griffith, D.W.; Sherlock, V.; Wennberg, P.O. The total carbon column observing network. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2011, 369, 2087–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hase, F.; Frey, M.; Blumenstock, T.; Groß, J.; Kiel, M.; Kohlhepp, R.; Mengistu Tsidu, G.; Schäfer, K.; Sha, M.; Orphal, J. Application of portable FTIR spectrometers for detecting greenhouse gas emissions of the major city Berlin. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 3059–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Viatte, C.; Hedelius, J.; Jones, T.; Franklin, J.; Parker, H.; Gottlieb, E.; Wennberg, P.; Dubey, M.; Wofsy, S. Differential column measurements using compact solar-tracking spectrometers. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 8479–8498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, M.; Sha, M.K.; Hase, F.; Kiel, M.; Blumenstock, T.; Harig, R.; Surawicz, G.; Deutscher, N.M.; Shiomi, K.; Franklin, J.E.; et al. Building the COllaborative Carbon Column Observing Network (COCCON): long-term stability and ensemble performance of the EM27/SUN Fourier transform spectrometer. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 1513–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büns, C.; Kuttler, W. Path-integrated measurements of carbon dioxide in the urban canopy layer. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 46, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Fang, Y.; Chen, T.; Li, D.; Kim, J.; Park, M.K.; Park, S.; Kim, K.R. In situ measurement of atmospheric carbon dioxide at Yanbian, China: Estimating its northeast Asian emission regions. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2012, 55, 1742–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röckmann, T.; Eyer, S.; Veen, C.V.d.; Popa, M.E.; Tuzson, B.; Monteil, G.; Houweling, S.; Harris, E.; Brunner, D.; Fischer, H.; et al. In situ observations of the isotopic composition of methane at the Cabauw tall tower site. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 10469–10487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosy, C.; Krampf, K.; Zeeman, M.; Wolf, B.; Junkermann, W.; Schäfer, K.; Emeis, S.; Kunstmann, H. Simultaneous multicopter-based air sampling and sensing of meteorological variables. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 2773–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, K.; Zeeman, M.; Brosy, C.; Münkel, C.; Fersch, B.; Mauder, M.; Emeis, S. Methane distributions and transports in the nocturnal boundary layer at a rural station. In Remote Sensing of Clouds and the Atmosphere XXI; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 10001, p. 1000103. [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda, T.; Yonemura, S.; Tani, A. Comparison of the characteristics of small commercial NDIR CO2 sensor models and development of a portable CO2 measurement device. Sensors 2012, 12, 3641–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lietzke, B.; Vogt, R. Variability of CO2 concentrations and fluxes in and above an urban street canyon. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 74, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueyama, M.; Ando, T. Diurnal, weekly, seasonal, and spatial variabilities in carbon dioxide flux in different urban landscapes in Sakai, Japan. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 14727–14740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Lee, X.; Liu, S.; Hu, N.; Wei, X.; Hu, C.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y. Spatiotemporal variability of the near-surface CO2 concentration across an industrial-urban-rural transect, Nanjing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.; Jacobson, A. Seasonally varying contributions to urban CO2 in the Chicago, Illinois, USA region: Insights from a high-resolution CO2 concentration and δ13C record. Elem. Sci. Anth. 2015, 3, 000052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooijmans, L.M.; Uitslag, N.A.; Zahniser, M.S.; Nelson, D.D.; Montzka, S.A.; Chen, H. Continuous and high-precision atmospheric concentration measurements of COS, CO2, CO and H2O using a quantum cascade laser spectrometer (QCLS). Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 5293–5314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, M.; Emmenegger, L.; Tuzson, B. Compact, circular, and optically stable multipass cell for mobile laser absorption spectroscopy. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 2434–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Bai, Y.; Bi, X.; Li, Y. Self-Calibrated Multiharmonic CO2 Sensor Using VCSEL for Urban In Situ Measurement. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2018, 68, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Chen, J.; Zhao, X.; Ghasemifard, H. VCSEL-Based Atmospheric Trace Gas Sensor Using First Harmonic Detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 4923–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, N.; Toumi, R. Remote sampling of a CO2 point source in an urban setting. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 5287–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, A.; Bostrom, G. Measurements of carbon dioxide in an Oregon metropolitan region. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bréon, F.; Broquet, G.; Puygrenier, V.; Chevallier, F.; Xueref-Remy, I.; Ramonet, M.; Dieudonné, E.; Lopez, M.; Schmidt, M.; Perrussel, O.; et al. An attempt at estimating Paris area CO2 emissions from atmospheric concentration measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 1707–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, W.; Wang, W.; Xu, J. Anthropogenic CO2 emissions from a megacity in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 23157–23169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hangauer, A.; Strzoda, R.; Amann, M.C. VCSEL-based calibration-free carbon monoxide sensor at 2.3 μm with in-line reference cell. Appl. Phys. B 2011, 102, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tuzson, B.; Scheidegger, P.; Looser, H.; Bereiter, B.; Graf, M.; Hundt, M.; Aseev, O.; Maas, D.; Emmenegger, L. Laser driving and data processing concept for mobile trace gas sensing: Design and implementation. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2018, 89, 065107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hangauer, A.; Strzoda, R.; Amann, M.C. Laser spectroscopic oxygen sensor using diffuse reflector based optical cell and advanced signal processing. Appl. Phys. B 2010, 100, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangauer, A.; Chen, J.; Strzoda, R.; Amann, M.C. Multi-harmonic detection in wavelength modulation spectroscopy systems. Appl. Phys. B 2013, 110, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Ding, Y.; Peng, Z.; Du, Y.; Liu, Y. Calibration-free wavelength modulation for gas sensing in tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. B 2014, 117, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.R.; Hess, G. An overview of the HYSPLIT_4 modelling system for trajectories. Aust. Meteorolog. Mag. 1998, 47, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemifard, H.; Yuan, Y.; Luepke, M.; Schunk, C.; Chen, J.; Ries, L.; Leuchner, M.; Menzel, A. Atmospheric CO2 and δ13C Measurements from 2012 to 2014 at the Environmental Research Station Schneefernerhaus, Germany: Technical Corrections, Temporal Variations and Trajectory Clustering. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemifard, H.; Vogel, F.R.; Yuan, Y.; Luepke, M.; Chen, J.; Ries, L.; Leuchner, M.; Schunk, C.; Noreen Vardag, S.; Menzel, A. Pollution Events at the High-AltitudeMountain Site Zugspitze-Schneefernerhaus (2670 m a.s.l.), Germany. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Draxler, R.R. TrajStat: GIS-based software that uses various trajectory statistical analysis methods to identify potential sources from long-term air pollution measurement data. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 938–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Yu, Y.; He, J.; Zhao, S. Integrated modeling of urban–scale pollutant transport: application in a semi–arid urban valley, Northwestern China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2013, 4, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangauer, A.; Chen, J.; Strzoda, R.; Amann, M.C. The frequency modulation response of vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers: experiment and theory. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2011, 17, 1584–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, D. Statistics of atomic frequency standards. Proc. IEEE 1966, 54, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werle, P.; Mücke, R.; Slemr, F. The limits of signal averaging in atmospheric trace-gas monitoring by tunable diode-laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS). Appl. Phys. B 1993, 57, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, R. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology; Springer Science & Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 13. [Google Scholar]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, S.; Jeong, S.; Fischer, M.; Xu, X.; Haman, C.; Lefer, B.; Alvarez, S.; Rappenglueck, B.; Kort, E.; Andrews, A.; et al. Diurnal tracking of anthropogenic CO2 emissions in the Los Angeles basin megacity during spring 2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4359–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankenberg, C.; Butz, A.; Toon, G. Disentangling chlorophyll fluorescence from atmospheric scattering effects in O2 A-band spectra of reflected sun-light. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L03801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankenberg, C.; O’Dell, C.; Berry, J.; Guanter, L.; Joiner, J.; Köhler, P.; Pollock, R.; Taylor, T.E. Prospects for chlorophyll fluorescence remote sensing from the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Super, I.; Dellaert, S.N.; Visschedijk, A.J.; van der Gon, H.A.D. Uncertainty analysis of a European high-resolution emission inventory of CO2 and CO to support inverse modelling and network design. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoning, K.W.; Tans, P.P.; Komhyr, W.D. Atmospheric carbon dioxide at Mauna Loa Observatory: 2. Analysis of the NOAA GMCC data, 1974–1985. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1989, 94, 8549–8565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, R.; Christen, A.; Rotach, M.; Roth, M.; Satyanarayana, A. Temporal dynamics of CO2 fluxes and profiles over a Central European city. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2006, 84, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.Á.; Sánchez, M.L.; Pérez, I.A. Differences between carbon dioxide levels over suburban and rural sites in Northern Spain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munich.Landeshauptstadt. Traffic. Available online: https://www.muenchen.de/rathaus/Stadtverwaltung/Referat-fuer-Stadtplanung-und-Bauordnung/Verkehrsplanung/Verkehrsmodell-VisMuc.html (accessed on 29 December 2019).
- Zhao, X.; Marshall, J.; Hachinger, S.; Gerbig, C.; Frey, M.; Hase, F.; Chen, J. Analysis of total column CO2 and CH4 measurements in Berlin with WRF-GHG. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11279–11302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.; Cohen, M.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull. Am. Meteorolog. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashbaugh, L.L.; Malm, W.C.; Sadeh, W.Z. A residence time probability analysis of sulfur concentrations at Grand Canyon National Park. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 1985, 19, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.K.; Holsen, T.M.; Hopke, P.K. Comparison of hybrid receptor models to locate PCB sources in Chicago. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 545–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabashnikov, V.P.; Chaikovsky, A.P.; Kucsera, T.L.; Metelskaya, N.S. Estimated accuracy of three common trajectory statistical methods. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 5425–5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupu, A.; Maenhaut, W. Application and comparison of two statistical trajectory techniques for identification of source regions of atmospheric aerosol species. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 5607–5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, D.C.; Ropkins, K. openair—An R package for air quality data analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 27, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lan, L.; Ghasemifard, H.; Yuan, Y.; Hachinger, S.; Zhao, X.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Bi, X.; Bai, Y.; Menzel, A.; Chen, J. Assessment of Urban CO2 Measurement and Source Attribution in Munich Based on TDLAS-WMS and Trajectory Analysis. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010058
Lan L, Ghasemifard H, Yuan Y, Hachinger S, Zhao X, Bhattacharjee S, Bi X, Bai Y, Menzel A, Chen J. Assessment of Urban CO2 Measurement and Source Attribution in Munich Based on TDLAS-WMS and Trajectory Analysis. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(1):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010058
Chicago/Turabian StyleLan, Lijuan, Homa Ghasemifard, Ye Yuan, Stephan Hachinger, Xinxu Zhao, Shrutilipi Bhattacharjee, Xiao Bi, Yin Bai, Annette Menzel, and Jia Chen. 2020. "Assessment of Urban CO2 Measurement and Source Attribution in Munich Based on TDLAS-WMS and Trajectory Analysis" Atmosphere 11, no. 1: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010058
APA StyleLan, L., Ghasemifard, H., Yuan, Y., Hachinger, S., Zhao, X., Bhattacharjee, S., Bi, X., Bai, Y., Menzel, A., & Chen, J. (2020). Assessment of Urban CO2 Measurement and Source Attribution in Munich Based on TDLAS-WMS and Trajectory Analysis. Atmosphere, 11(1), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010058






