Analysis of NOx Pollution Characteristics in the Atmospheric Environment in Changchun City
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
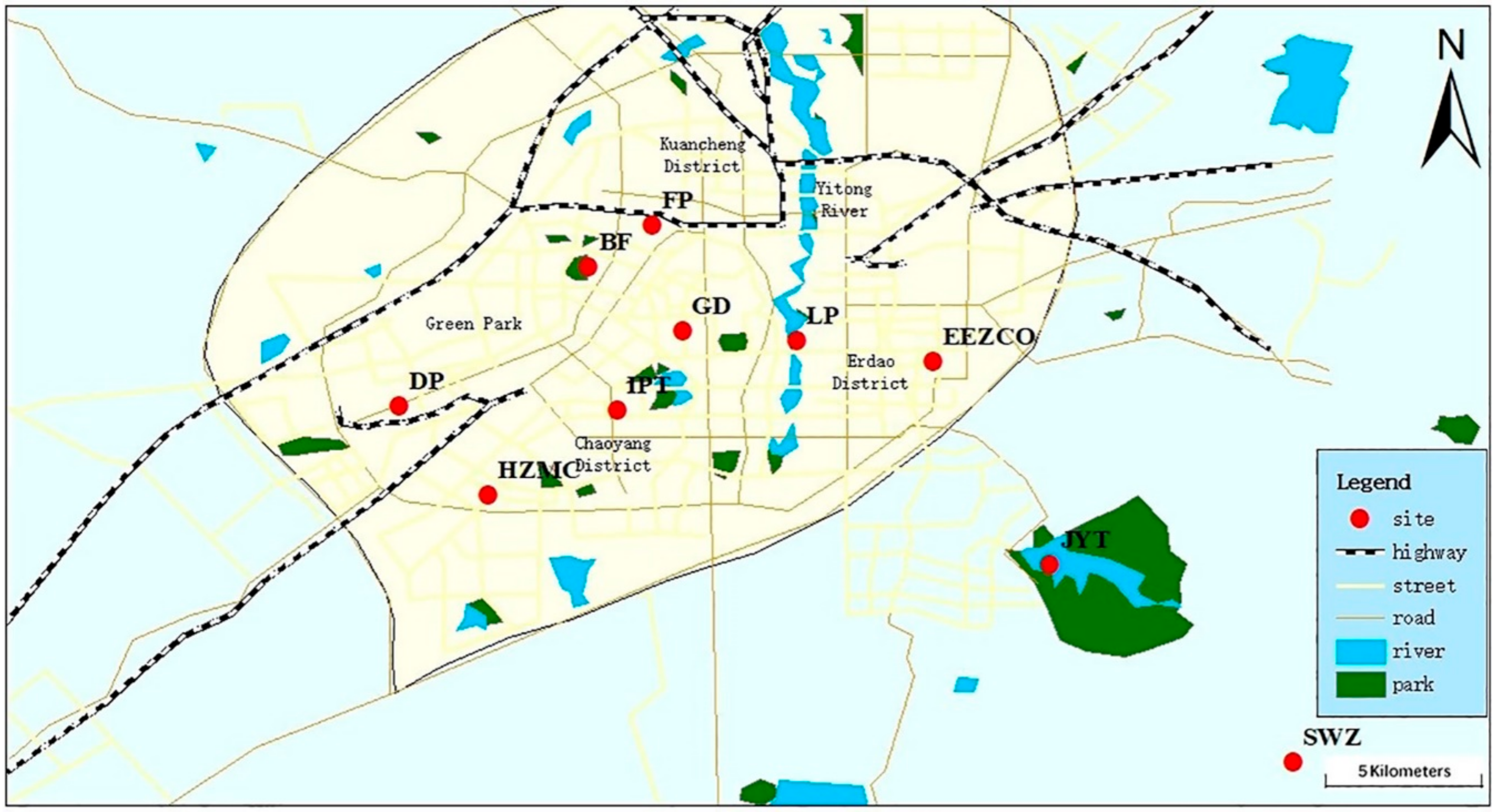
2.1. Research Area and Experimental Design
2.2. Meteorological Factors and Pollutant Information
3. Results
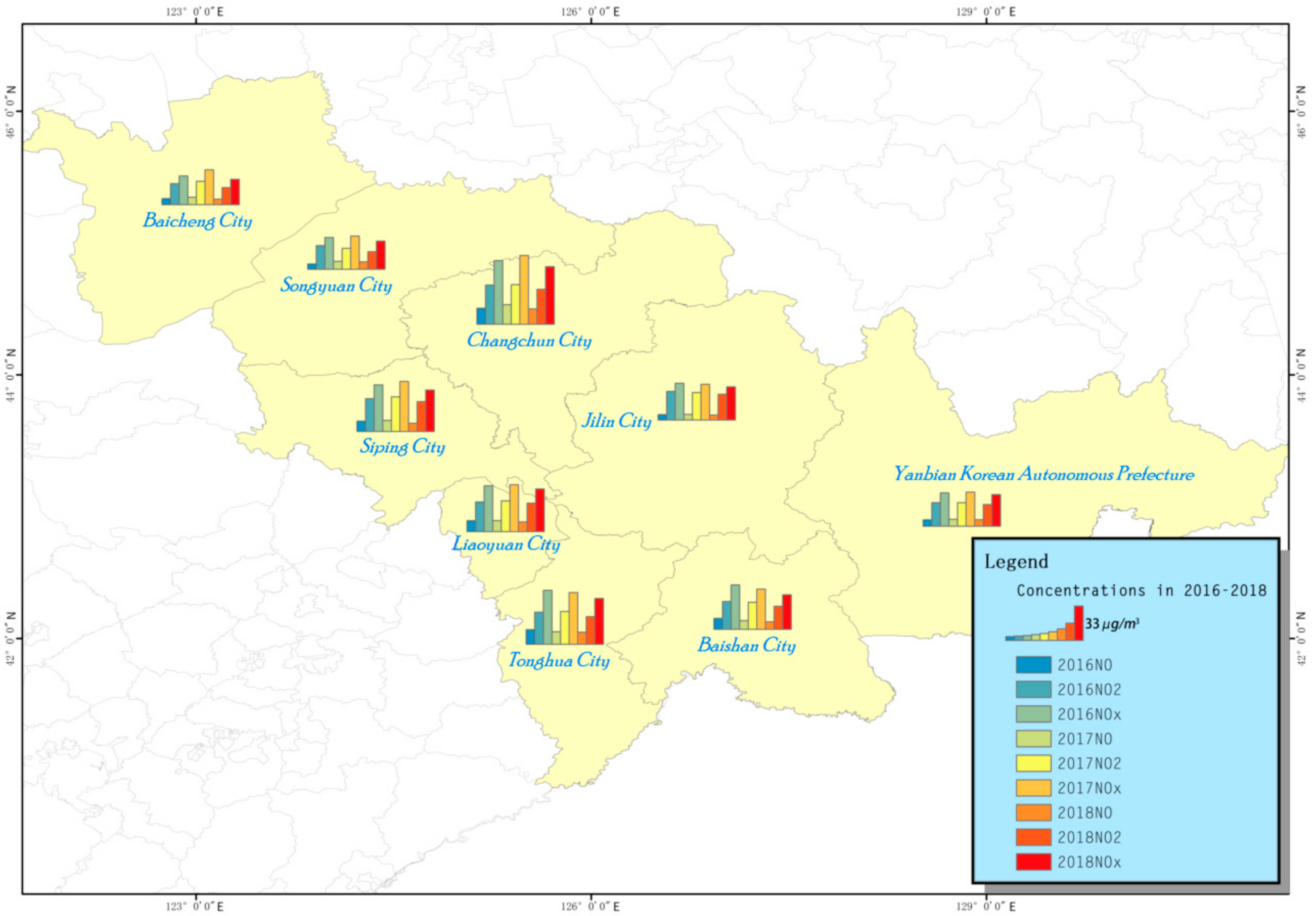
3.1. Analysis of the NOx Pollution Degree in the Whole Province
3.2. Trend Analysis of NOx Pollution in Changchun
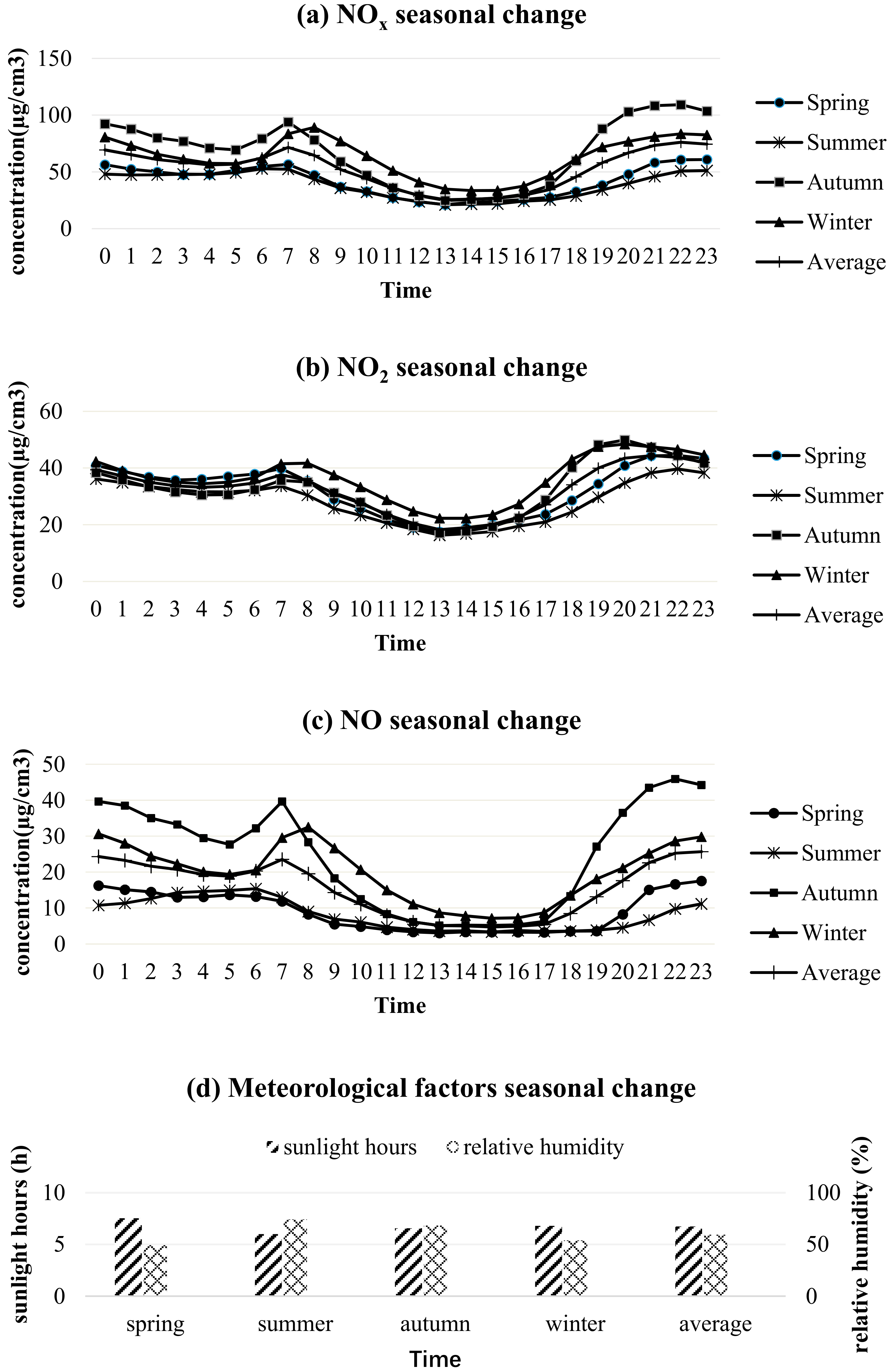
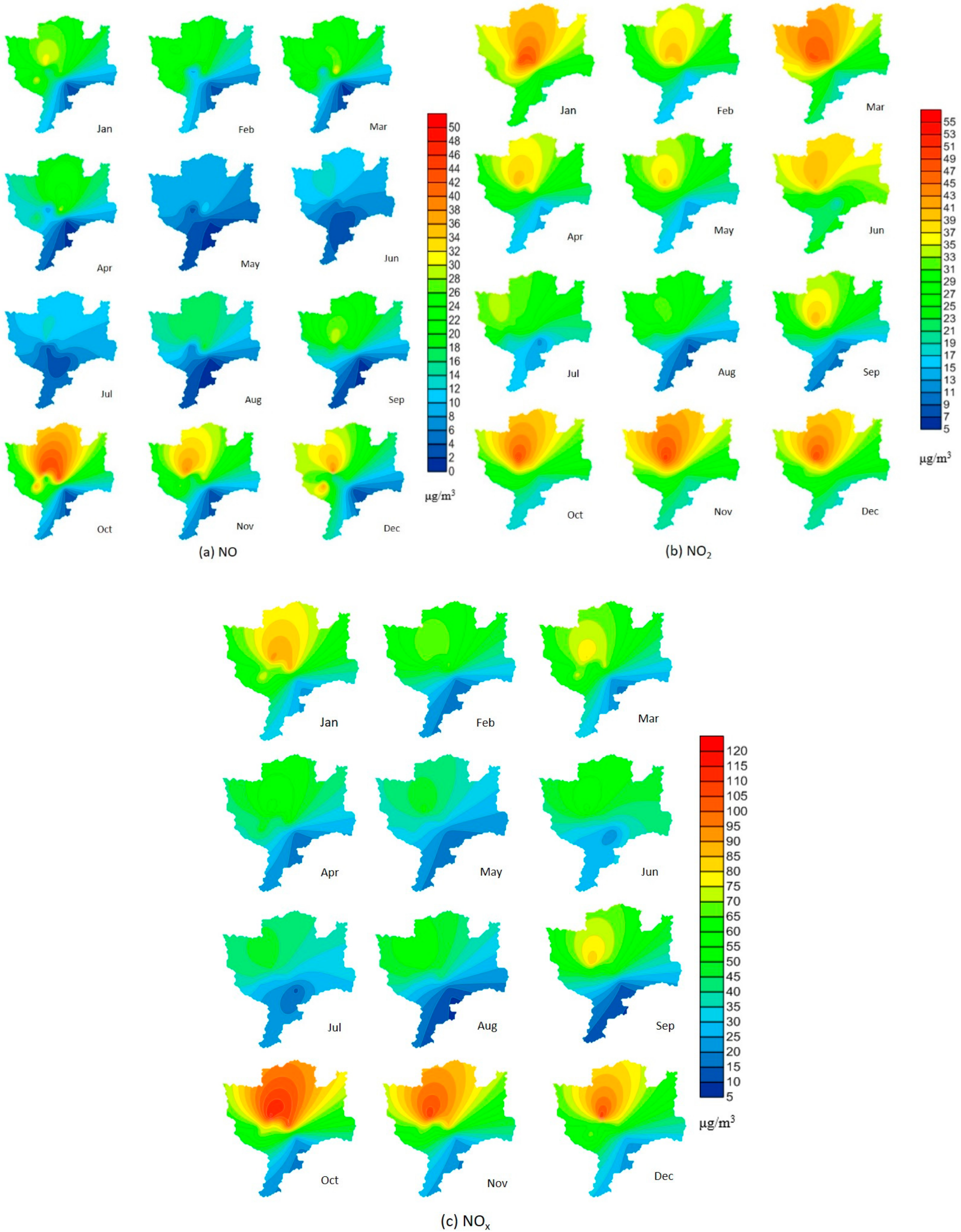
3.2.1. Seasonal Change Analysis
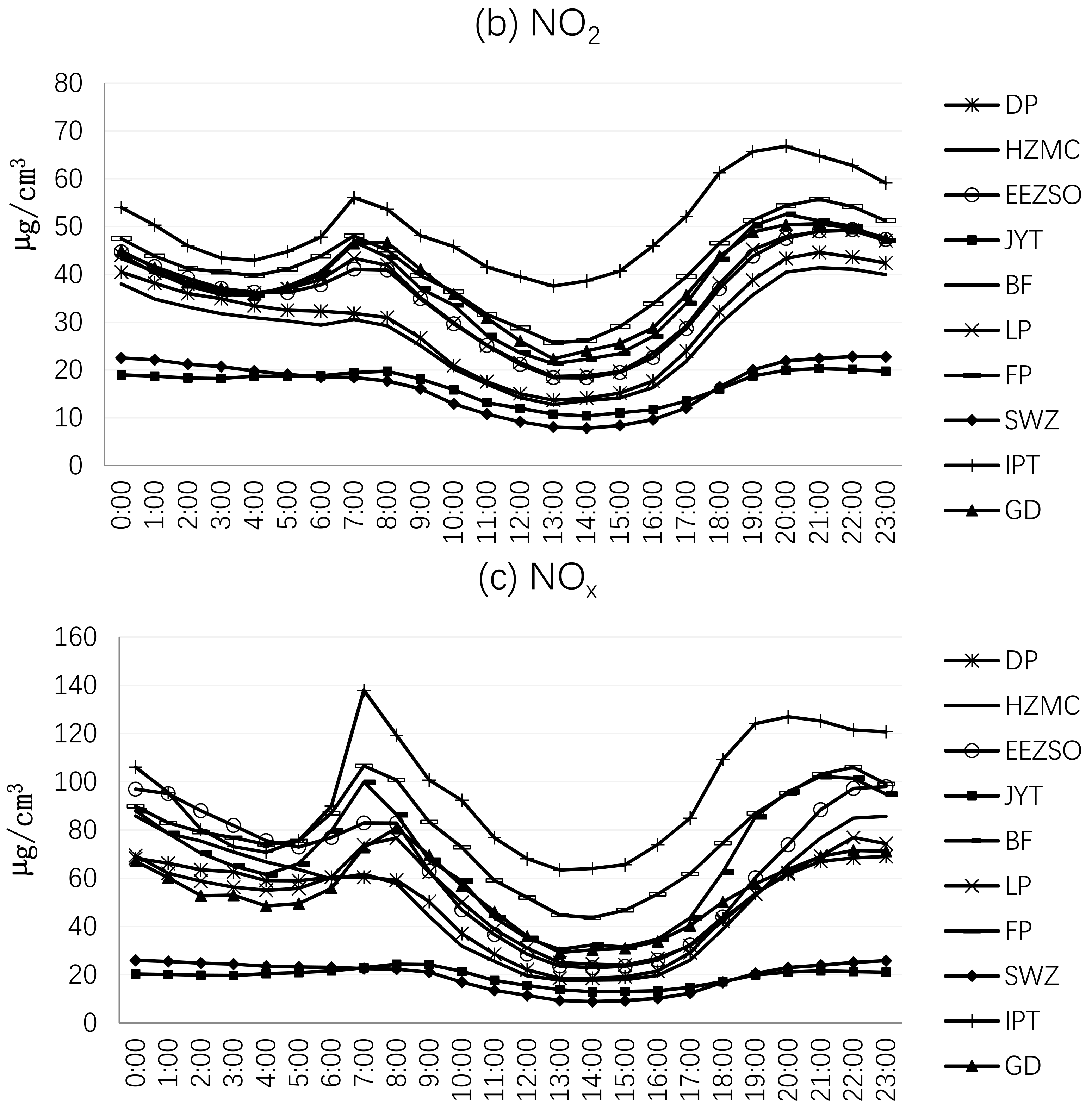
3.2.2. Daily Average Change Analysis
3.2.3. Spatiotemporal Variation
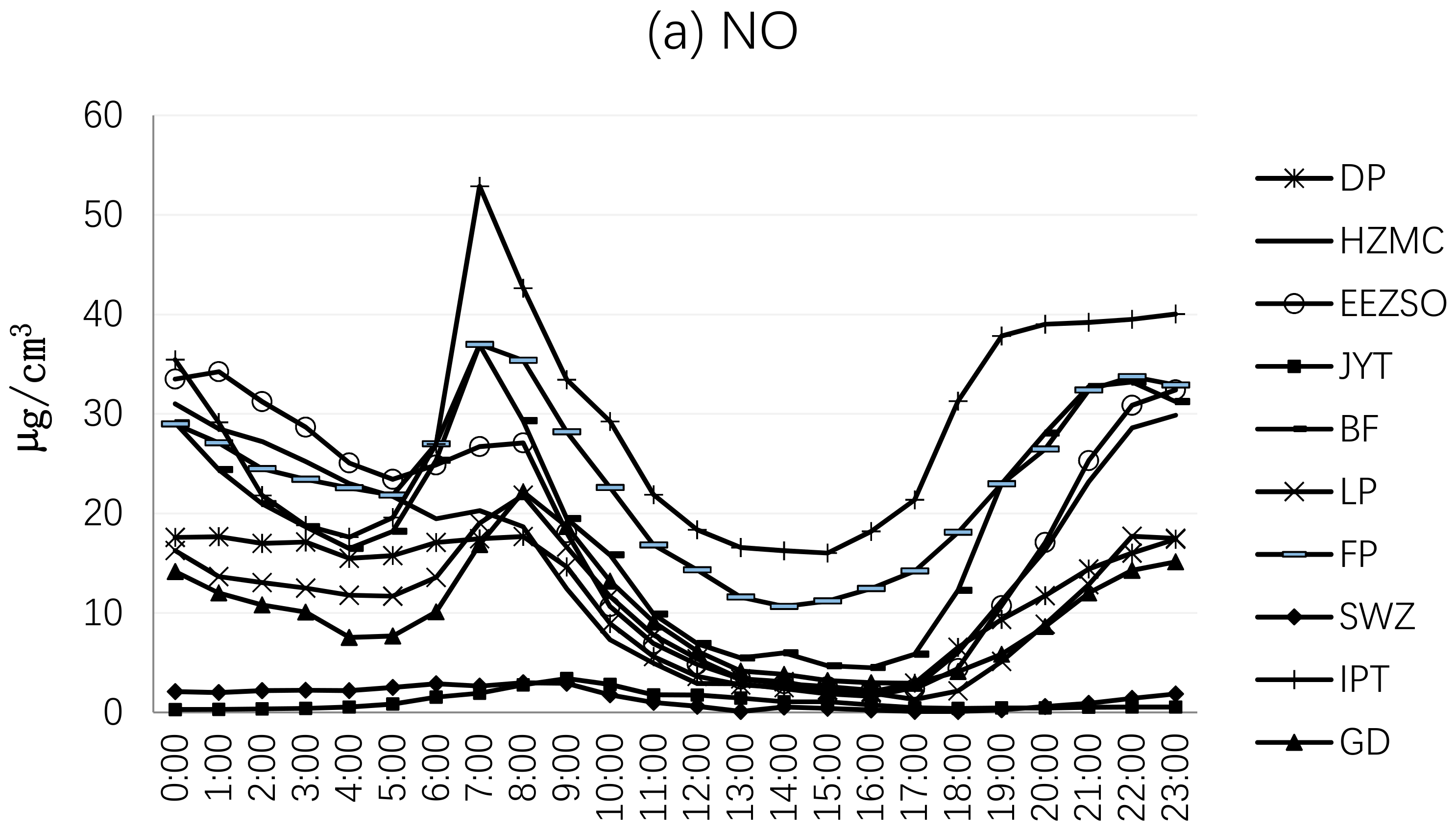
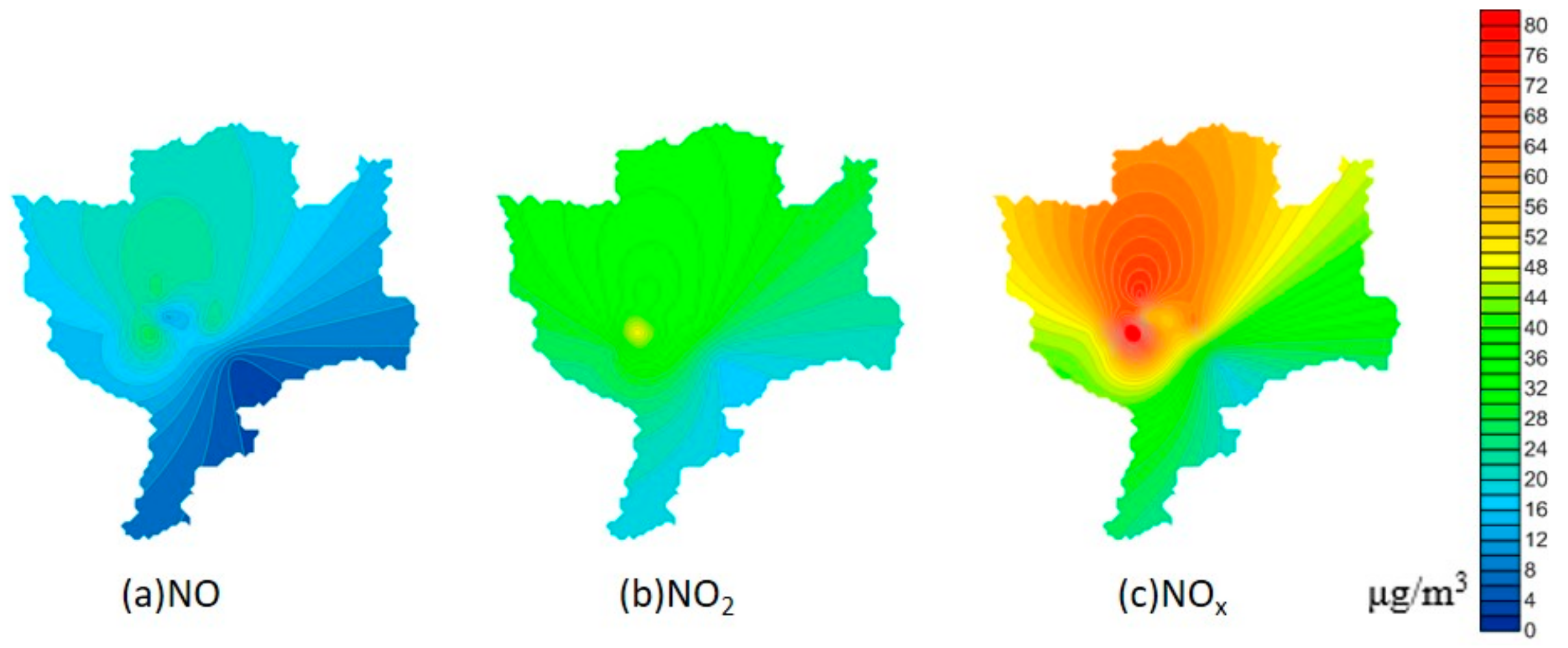
3.2.4. Spatial Variation Analysis
3.2.5. Relationship Between NOx and Meteorological Factors
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G.; He, K. Nox emission trends for China, 1995–2004: The view from the ground and the view from space. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, W.P.; Yin, Y.Q.; Zhang, J.D. Observational study of surface ozone at an urban site in East China. Atmos. Res. 2008, 89, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.M.; Wang, G.C.; Chen, H.B. Analysis of the Variation Characteristics of Atmospheric Ozone Concentration in the Boundary Layer of Beijing Area. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 28, 2615–2619. [Google Scholar]
- Varshney, C.K.; Singh, A.P. Passive samplers for NOx monitoring: A critical review. Environmentalist 2003, 23, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xia, X.H.; Zhao, Y. Heavy metal concentrations in roadside soils and correlation with urban traffic in Beijing, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Wang, S.X.; Xing, J. Analysis of current status and development trend of energy-related nitrogen oxide emissions in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 2470–2479. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Geng, G.N.; Wang, S.W. Satellite remote sensing of changes in NOx emissions over China during 1996–2010. China Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 2857–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.L.; Li, Y.T.; Sun, F. Ground-level NO2 in urban Beijing: Trends, distribution, and effects of emission reduction measures. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.F.; Zhang, W.; Quan, J.N. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of pollutants in the 3500 m high altitude in Beijing area. China Environ. Sci. 2012, 32, 1729–1735. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, K.; Li, S.S.; Zheng, F.B. Spatio-temporal variations in NO2 and PM2.5 over the central plains economic region of China during 2005–2015 based on satellite observations. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 1221–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishanth, T.; Kumar, M.K.S.; Valsaraj, K.T. Variations in surface ozone and NOx at kannur: A tropical, coastal site in India. J. Atmos. Chem. 2012, 69, 101–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.P.; Wang, Y.S.; Hu, B. Study on atmospheric pollution observation of Xianghe River in Beijing during the Beijing Olympic Games. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Cichowicz, R.; Stelegowski, A. Average Hourly Concentrations of Air Contaminants in Selected Urban, Town, and Rural Sites. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 77, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.X.; Zhao, M.; Xing, J. Quantifying the air pollutants emission reduction during the 2008 Olympic games in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 2490–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.F.; Zhu, B.; Wang, Y.S. Vertical gradient observation of O3 and NOx in a photochemical pollution process. J. Environ. Engin. 2010, 4, 411–416. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Gbaguidi, A.; Yan, P.Z. Model elucidating the sources and formation mechanisms of severe haze pollution over northeast mega-city cluster in China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.Q.; Wang, D. Temporal and spatial evolution characteristics and socio-economic drivers of urban air quality in China. Acta Geogr. Sci. 2016, 71, 1357–1371. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, S.; Srivastava, A.K.; Chate, D.M. Impacts of the high loadings of primary and secondary aerosols on light extinction at Delhi during wintertime. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Dahiya, A.; Kumar, N. Investigation into relationships among NO, NO2, NOx, O3, and CO at an urban background site in Delhi, India. Atmos. Res. 2015, 157, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Shen, Z.X.; Chow, J.C. Winter and summer PM2.5 chemical compositions in fourteen Chinese cities. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2012, 62, 1214–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.B.; Wu, L.; Xie, Y.C. Air pollution in China: Status and spatiotemporal variations. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.; Wang, Y.K.; Wu, G. Spatiotemporal characteristics of air pollutants (PM10, PM2.5, SO2, NO2, O3, and CO) in the inland basin city of Chengdu, southwest China. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boersma, K.F.; Jacob, D.J.; Trainic, M. Validation of urban NO2 concentrations and their diurnal and seasonal variations observed from the sciamachy and omi sensors using in situ surface measurements in Israeli cities. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 3867–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionov, D.V.; Timofeyev, Y.M.; Sinyakov, V.P. Ground-based validation of EOS-Aura OMI NO2 vertical column data in the midlatitude mountain ranges of Tien Shan (Kyrgyzstan) and Alps (France). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamsal, L.N.; Martin, R.V.; van Donkelaar, A. Indirect validation of tropospheric nitrogen dioxide retrieved from the omi satellite instrument: Insight into the seasonal variation of nitrogen oxides at northern midlatitudes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.S.; Yu, C.; Chen, L.F. Inter-comparison of model-simulated and satellite-retrieved componential aerosol optical depths in China. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 141, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoder, M.I. Atmospheric conversion of sulfur dioxide to particulate sulfate and nitrogen dioxide to particulate nitrate and gaseous nitric acid in an urban area. Chemosphere 2002, 49, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkin, M.E. Analysis of sources and partitioning of oxidant in the UK—Part 2: Contributions of nitrogen dioxide emissions and background ozone at a kerbside location in London. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 5131–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.Q.; Bian, H.; Feng, Y.C. Analysis of the relationship between O3, NO and NO2 in Tianjin, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2011, 11, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo-Castaneda, D.M.; Teixeira, E.C.; Pereira, F.N. Time-series analysis of surface ozone and nitrogen oxides concentrations in an urban area at Brazil. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2014, 5, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.M.; Harrison, R.M.; Baker, J. The wind speed dependence of the concentrations of airborne particulate matter and NOx. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1682–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Year | COD | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site | DP | HZMC | EEZCO | JYT | BF | LP | FP | SWZ | IPT | GD | |
| 2016 | DP | — | 0.11 | 0.06 | 0.43 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.21 | 0.42 | 0.29 | 0.08 |
| HZMC | 0.11 | 0.37 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.28 | 0.37 | 0.35 | 0.14 | |||
| EEZCO | 0.44 | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.20 | 0.43 | 0.28 | 0.08 | ||||
| JYT | 0.51 | 0.42 | 0.57 | 0.11 | 0.63 | 0.45 | |||||
| BF | 0.13 | 0.10 | 0.50 | 0.18 | 0.10 | ||||||
| LP | 0.21 | 0.41 | 0.29 | 0.06 | |||||||
| FP | 0.56 | 0.09 | 0.17 | ||||||||
| SWZ | 0.62 | 0.44 | |||||||||
| IPT | 0.25 | ||||||||||
| GD | — | ||||||||||
| 2017 | DP | — | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.40 | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0.22 | 0.41 | 0.30 | 0.05 |
| HZMC | 0.06 | 0.46 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.16 | 0.45 | 0.24 | 0.06 | |||
| EEZCO | 0.49 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.48 | 0.21 | 0.10 | ||||
| JYT | 0.52 | 0.43 | 0.56 | 0.13 | 0.62 | 0.43 | |||||
| BF | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.52 | 0.16 | 0.13 | ||||||
| LP | 0.19 | 0.43 | 0.27 | 0.04 | |||||||
| FP | 0.56 | 0.10 | 0.18 | ||||||||
| SWZ | 0.61 | 0.44 | |||||||||
| IPT | 0.27 | ||||||||||
| GD | — | ||||||||||
| 2018 | DP | — | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.44 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 0.22 | 0.46 | 0.32 | 0.08 |
| HZMC | 0.12 | 0.45 | 0.17 | 0.07 | 0.22 | 0.48 | 0.31 | 0.08 | |||
| EEZCO | 0.52 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.54 | 0.22 | 0.09 | ||||
| JYT | 0.55 | 0.46 | 0.59 | 0.16 | 0.66 | 0.47 | |||||
| BF | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.56 | 0.17 | 0.11 | ||||||
| LP | 0.19 | 0.49 | 0.28 | 0.02 | |||||||
| FP | 0.60 | 0.11 | 0.18 | ||||||||
| SWZ | 0.66 | 0.49 | |||||||||
| IPT | 0.27 | ||||||||||
| GD | — | ||||||||||
| NO | NO2 | NOx | O3 | PM2.5 | PM10 | CO | T | WS | P | H | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO | 1 | ||||||||||
| NO2 | 0.591 | 1 | |||||||||
| NOx | 0.963 | 0.779 | 1 | ||||||||
| O3 | −0.43 | −0.161 | −0.402 | 1 | |||||||
| PM2.5 | 0.306 | 0.62 | 0.427 | 0.103 | 1 | ||||||
| PM10 | 0.217 | 0.407 | 0.286 | 0.353 | 0.735 | 1 | |||||
| CO | 0.508 | 0.725 | 0.623 | −0.085 | 0.853 | 0.555 | 1 | ||||
| T | −0.274 | −0.276 | −0.298 | 0.459 | −0.376 | −0.096 | −0.468 | 1 | |||
| WS | −0.402 | −0.336 | −0.42 | 0.528 | 0.059 | 0.336 | −0.109 | 0.169 | 1 | ||
| P | 0.426 | 0.341 | 0.442 | −0.499 | 0.312 | 0.029 | 0.433 | −0.799 | −0.293 | 1 | |
| H | −0.08 | −0.178 | −0.11 | −0.255 | −0.253 | −0.442 | −0.162 | 0.387 | −0.259 | −0.372 | 1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Tan, X.; Fang, C. Analysis of NOx Pollution Characteristics in the Atmospheric Environment in Changchun City. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010030
Wang L, Wang J, Tan X, Fang C. Analysis of NOx Pollution Characteristics in the Atmospheric Environment in Changchun City. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(1):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010030
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lijun, Ju Wang, Xiaodong Tan, and Chunsheng Fang. 2020. "Analysis of NOx Pollution Characteristics in the Atmospheric Environment in Changchun City" Atmosphere 11, no. 1: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010030
APA StyleWang, L., Wang, J., Tan, X., & Fang, C. (2020). Analysis of NOx Pollution Characteristics in the Atmospheric Environment in Changchun City. Atmosphere, 11(1), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010030





