Abstract
In this paper, a review of the Lagrangian stochastic models developed in the last decades for the simulation of the concentration–fluctuation dispersion is presented. The main approaches available in the literature are described and their ability in reproducing the higher order moments of the probability density function is discussed. Then, the Lagrangian approaches for evaluating of the odor annoyance are presented. It is worth to notice that, while Lagrangian stochastic models for mean concentrations are well-known and their ability in correctly reproducing the observation is well assessed, concerning concentration fluctuations the approaches are often new and unknown for most of the scientific community.
1. Introduction
Concerning the study of the atmospheric dispersion, it can be recalled that much research has been devoted to modeling the mean concentration field of non-reactive substances released in the atmospheric boundary layer (ABL), and modeling systems for mean concentration are routinely applied in air quality monitoring activities. Nevertheless, other statistical properties than the mean of scalar quantities (such as concentration) that are advected and mixed by a turbulent velocity field have practical importance in a large number of applications. Some applications require the estimates of second and higher order moments of concentration, and in some cases the knowledge of the full one-time one-point probability density function (pdf) of the concentration is needed. For example, the pdf of concentration may be required in the study of toxic gas effects on humans, the assessment of nuisance due to malodorous materials [1], the flammability of substances [2] and the interaction between turbulence and chemistry. The Lagrangian approach describes the motions of the reactive fluid particles up to a point where the distance between the particles is of the order of the Kolmogorov scale. In most atmospheric flows, this distance is much larger than the molecular scale, where the chemical reactions occur. The dynamic at this scale can be disregarded and, consequently, the dependency on the molecular viscosity and diffusivity neglected [3]. Provided the Reynolds number is large enough (depending on the Schmidt number) we expect that at large enough times Brownian particles will behave like fluid particles and exhibit a Richardson scaling regime followed by diffusive behavior for times larger than the Lagrangian time scale [4]. Lagrangian stochastic models are based on the Langevin equation for the turbulent velocities. This is a stochastic differential equation for a Markovian continuous process. In order to specify the different terms of the equation, it is required to determine two coefficients which should reflect the properties of the turbulent flow. The first one is obtained according to the Kolmogorov’s theory of locally isotropic turbulence in the inertial sub-range and the second one is a solution of the Fokker–Planck equation with a specified pdf of the process, or in other words, the Eulerian pdf of the turbulent velocities [5].
In several countries, odor assessments are based on so-called odor-hours defined by at least 6 min of perceivable odor concentrations in an hour. Modeling odor hours requires the determination of the 90th percentile of the corresponding cumulative frequency distribution. It can be determined by assuming a pdf that is generally completely defined by the concentration fluctuation intensity and the mean concentration [6]. Obtaining an estimation of i requires a more sophisticated approach. Many Lagrangian models have been developed for the second- and higher-order moments of the concentration pdf over the last 10 years. Thomson (1990) [7] and Borgas and Sawford (1994) [8] proposed the two-particle model, Pope (1985) and Cassiani et al. (2005, 2007), Leuzzi et al. (2012) [8,9,10,11,12] the pdf method, while the fluctuating plume model was suggested by Yee et al. (1994), Yee and Wilson (2000), Luhar et al. (2000), Franzese (2003), Mortarini et al. (2009), Ferrero et al. (2013), Bisignano et al. (2014), Marro et al.(2015) [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. Manor (2014) [21] used a Lagrangian particle model to simulate the concentration variance dispersion and Ferrero et al. (2017) [22] suggested a formulation for the variance dissipation time scale to be used in the same model. This parameterization has been used by Oettl and Ferrero (2017) [6] and Ferrero and Oettl (2019) [23] to simulate odor dispersion in field campaigns.
A rigorous Lagrangian approach would require the simultaneous knowledge of position, velocity, and chemical content of all fluid particles in the volume and in the time interval considered, which would be an impossible task. The-two particle approach [7,8,24] gives the variance and covariance of the concentrations in the range of spatial scales of interest.
Several models were presented for the estimation of the moments of concentration in a convective boundary layer (CBL) based on a fluctuating plume approach (e.g., [15,16,17,18,20,25,26]). These models can be easily adapted to simulations in a neutral boundary layer. The fluctuating plume approach has some intrinsic limitations in that it can treat only non-reactive scalars and relies on parameterized in-plume relative concentration fluctuations. A complete theory for relative concentration fluctuations is not available, and experimental measurements are scarce and case specific. As a consequence, to date there is not a solid parameterization for this statistic.
Pope (1994; 2000) and Heinz (2003) [27,28,29] reviewed various closures and modeling techniques for the viscous stresses and pressure gradient terms needed for the modeling of the turbulence velocity pdf. These closures are then used to define a set of Lagrangian stochastic differential equations for the evolution of velocity and position of the fluid particles. The term associated with molecular diffusivity defines the shape of the pdf of concentration. The type of closure used for this term is usually referred to as the micromixing model. A micromixing model describes the evolution of the pdf of concentration using an additional equation for the concentration carried by each particle in the domain. Therefore, the model equations include a set of equations for velocity, position, and concentration of each fluid particle. This separation of the effects of turbulent mixing and molecular processes is typical of a variety of modeling approaches (see, e.g., the short review by [30]).
In this review, we present the main Lagrangian approaches for simulating the higher order moments of the concentration pdf and evaluating of the odor concentration. In Section 2, we introduce the theory of the Lagrangian stochastic models. Section 3 is devoted to Lagrangian models for the concentration fluctuations, while Section 4 presents the Lagrangian method for simulating odor dispersion. Conclusions are summarized in Section 5.
2. Lagrangian Stochastic Models
Lagrangian stochastic models (LSMs) are based on the Langevin equation that describes the temporal evolution of the velocity of pollutant particles in a turbulent field. The solution of the Langevin equation is a continuous stochastic Markov process. In fact, particle position and velocity, in a turbulent flow, can be considered a bivariate Markov process in the range of the turbulent energy spectrum between the Kolmogorov time scale τη (approximately equal to the correlation time of the accelerations) and the Lagrangian time scale TL.
The Langevin equation for the turbulent velocity of a Lagrangian particle can be written as
and is coupled to the equation for the particle position x(t)
where dWj is an incremental Wiener process component, Gaussian distributed with zero mean and variance of
where the notation < > represents an ensemble average.
The term can be derived from the Kolmogorov theory of local isotropy in the inertial sub-range [31]. This theory is based on similarity relations valid in a particular interval of the turbulence spectrum. The energy is transferred from the larger vortices to the smaller ones, until to the smallest scales of the atmospheric turbulence, where it is dissipated by the viscosity. Inside this energetic cascade there is a part of the spectrum where the vortices are sufficiently small so that they are not affected by the anisotropy induced from the larger vortices and are not dissipated as heat. This part of the turbulent spectrum is called the inertial sub-range. This interval coincides with the interval of temporal scales in which the turbulent velocities can be considered a Markov process.
Defining the structure function of the Lagrangian velocities, in one dimension, as
then, if τη ≤ dt ≤ TL, the following relationship can be considered [31]:
where ε is the mean rate of turbulent kinetic energy dissipation and C0 is a universal constant.
Substituting dui(t) as given by the Langevin equation in (Equation (1)), averaging and considering only the terms of the order of dt, leads to
and
A Eulerian description of a continuous Markov process is available through the Fokker–Planck equation. If the position and turbulent velocity can be considered a continuous stochastic Markov process, the Fokker–Planck equation can be used to calculate the coefficient a of the Langevin equation for any given pdf [32].
where is the Lagrangian pdf of the particles.
In the stationary case, does not depend on time and the Fokker–Planck equation reduces to
where is given by Equation (7).
Following Thomson (1987) [5], it can be stated that an LSM satisfies the well-mixed condition (if the particles are initially well-mixed in the fluid, they will remain so), if is equal to the Eulerian atmospheric pdf. This is a necessary and sufficient condition. In other words, all moments of must equal the measured or parameterized moments.
In one dimension, the Fokker–Planck equation can be solved and the term calculated, for a given pdf, as [5]
where
and
In addition, [33].
LSMs usually are one-dimensional models solving one or two and, in some cases, three Langevin equations, one for each Cartesian direction. The extension to a fully three-dimensional model was dealt with by [8,34,35]. It can be demonstrated that a unique solution for the Fokker–Planck equation, in the three-dimensional case, exists only for homogeneous, isotropic turbulence [8]. The non-uniqueness of the solution is related to the first term on the right side of Equation (9), as this equation can be satisfied by any vector obtained through adding a rotational vector, in space, to [36].
The theory of this section is applicable to one-particle models, and these have been widely tested and applied to many different situations characterized by non-homogeneous turbulence and different stability conditions. However, it should be stressed that a one-particle model is only able to describe the absolute dispersion and to predict the mean concentration fields. To simulate the concentration fluctuations, other developments of this model or different approaches should be applied (see Section 3). However, the model described in this chapter and the related theory is the base for these developments.
3. Observations and Lagrangian Modeling of Concentration Fluctuation
3.1. Experimental Results
In the past, numerous field and wind-tunnel experiments have been carried out concerning concentration fluctuations. The focus of the studies has been mostly the intensity of concentration fluctuations, I, but often the shape of the normalized probability density function (pdf) has been analyzed, too. It should be stated that this review has been limited to field campaigns, as laboratory experiments are limited in the sense that the full range of large-scale eddies in the atmosphere and very stable atmospheric stratifications cannot be properly modeled.
Hanna (1984) [37] reported that only a few field campaigns were available at the beginning of the 1980s due to the difficulties involved in obtaining and interpreting the data at that time. The earliest experiment quoted by Hanna (1984) [37] was undertaken by Ramsdell and Hinds (1971) [38], who observed concentration fluctuations from 10 to 20 min duration releases of 85Kr from a point source 1 m above ground level. Averaging time was 39 s and arcs of samplers were located at downwind distances of 200 and 800 m. They observed that the intensity of concentration fluctuations increased from about 1.5 on the plume axis to about 3.0 towards the edges under stable and slightly unstable atmospheric conditions.
Investigations by Jones (1981) [39] revealed an increase in very close (<10 m) to a ground-level release of ionized air from a point source with a diameter of 0.01 m. At slightly larger distances (>10 m) the intensity of concentration fluctuations decreased. More than a decade later Mole and Jones (1994) [40] repeated similar ground-level tracer releases using again ionized air, but used improved technology. The field campaign covered convective as well as stable atmospheric conditions. Regarding the intensity no clear trend with downwind distance was evident from their data. The authors assumed that the samplers were located at around the maximum of the intensity, and covered only a small range of distances from the source, therefore, no trend was visible due to the specific experimental layout. Furthermore, higher values were found during unstable conditions.
Lewellen and Sykes (1986) [41], by analyzing LIDAR data gathered from plumes originating from tall (200 m) power-plant stacks, found to be lowest (from 0.2 to 4) in the center of the plume, with increasing values in the edges of the plume, therefore confirming the early results of Ramsdell and Hinds (1971) [38]. Moreover, their data supported the usage of a clipped normal distribution for the concentration pdf. One of the main drawbacks of this study yet was the low sampling frequency available at that time.
Quite a different experimental set up was used by Mylne and Mason (1991) [42] half a decade later. Tracer was released close to the surface and sampled with a temporal resolution of 0.1 s at distances between 50 m and 1000 m. In contrast to the field experiments described in Mylne and Mason (1991) [41], no data was available for stable atmospheric conditions. In accordance with previous works, a minimum of the concentration-fluctuations intensity on the plume centerline and an increase towards the edges was reported. In the alongwind direction on the plume centerline was found to decrease rapidly, though, it approached a near-constant, non-zero value at longer range. The concentration pdf has been shown to be generally well described by the clipped normal form as was also the case in the study of Lewellen and Sykes (1986) [41]. Mylne (1992) [43] reported that concentration-fluctuation observations (i.e., intensity, pdf) in stable conditions are qualitatively similar to those in near-neutral or slightly unstable conditions, but that there are some significant quantitative differences regarding the time scales, which are much larger due to the effect of horizontal meandering of plumes. Peak-to-mean (p/m) concentrations were also found to be significantly higher in stable conditions (>10) than in near-neutral or convective conditions.
A large range of the p/m ratio from 4 to 99 was also found by Lung et al. (2002) [44] analyzing nine field experiments performed in flat terrain using 85Kr released from a ground-level point source in near-neutral and convective conditions. Furthermore, they established a reasonable linear relationship between p/m and , whereby the largest observed values for were around 30. While Lung et al. (2002) [44] reported also increasing towards the edge of the plumes and decreasing values at larger distances, in contrary to the studies mentioned previously, they concluded that the Gamma- and Weibull pdfs provided a better fit to the data than did a log-normal distribution.
Earlier Lung et al. (2002) [13] by studying data gathered from fast-response concentration measurements in the surroundings of a point-source release near the ground, stated that the concentration pdf depends on crosswind and downwind location. Close to the source, in the meander-dominated regime of plume development, an exponential shape fits observations best, while farther downwind, where meandering and internal fluctuations contribute almost equally, the pdf on the plume axis is bimodal. Further away from the source, in the turbulent-diffusive regime, where internal fluctuations become dominant, the pdf assessed at plume centerline becomes unimodal again. The data of Yee et al. (1994) [13] supported also strongly that the intensity of concentration fluctuations exhibits a minimum (~0.6–3.0) at the plume centerline axis, and increases towards the edges of the plume in horizontal crosswind direction (~10–30).
The Joint Urban 2003 (JU03) experiment conducted in downtown Oklahoma City is still the most comprehensive study of concentration fluctuations in an urban setting. Naturally, clear plume shapes as can be found in flat terrain without obstacles and homogenous land-use cannot be expected in built-up areas. Therefore, the focus of the study published by Finn et al. (2010) [45] was on possible differences in plume dispersion between day and nighttime conditions. However, when classified by fluctuation intensity , few differences were evident between daytime and nighttime pdfs. The log-normal pdf provided the overall best fit to their data compared to the exponential or clipped-normal pdfs. In agreement with other field experiments performed in less complex environments, a decrease of was observed with increasing distance to the tracer release.
Figure 1 shows an example of observed concentration signals from selected 120 Hz gas analyzers, used in the JU03 experiment (IOP 188, release 5, a continuous release. Courtesy of the U.S. Defense Threat Reduction Agency). The left panel illustrates the locations of the source (black pentagon) and the gas analyzers (green circles), where the wind direction is around 200°, so the selected four analyzers are close to the plume axis. At the right pane, the corresponding concentration signals are plotted, each normalized by its time average. For all four time series it can be observed that the peaks are considerably higher than the mean value (unity). One can also notice, that the concentration time series measured closer to the source are characterized by larger gaps of zero concentration, referred to as ‘intermittency’, which reflects the existence of time intervals when the whole plume lies outside of the detector’s measuring volume.
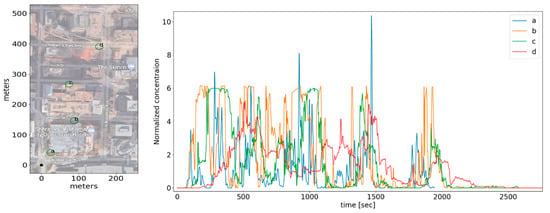
Figure 1.
Concentration signals observed in JU03 field campaign (IOP 188, release 5). The left panel shows the continuous source (black pentagon), and four selected fast gas analyzers (green circles, labeled a, b, c and d), coordinates are given in meters with the source at the origin. The right panel presents the corresponding concentration signals.
More recently, NOAA [46,47] carried out extensive tracer experiments (Sagebrush I, II) in flat and homogenous terrain in 2013 (convective with low wind speeds, and near-neutral with higher wind speeds) and in 2016 (low-wind speeds, convective to stable conditions). In 2013, observed unconditional (including zeros) intensities ranged between 1.4 and 17.6, and in 2016 between 0.6 and 16, while unconditional p/m ratios were found in the range 5.1 to 19.9.
Though the experimental data discussed was gathered under varying environmental conditions (e.g., meteorology, land cover), different measurement equipment (e.g., analyzers, tracers) and methods (e.g., sampling frequencies and duration, source geometries), one may identify at least two common features that could serve as benchmarks for testing dispersion models for concentration fluctuations and odors: (i) With increasing distance the intensity of concentration fluctuations is found to decrease in practically all experiments regardless the environmental conditions and experimental set-up. A few data sets indicated that there might be an increase in the intensity very close to point sources, and at least one study indicated that the intensity is not approaching zero even at large distances. (ii) Intensities evaluated along horizontal cross-sections of plumes show usually a minimum at the plume centerline and increasing values towards the edges. Having said this, no universal shape of the concentration pdf could be found so far, as it seems to depend on the sampling location, but probably could also be locally influenced.
3.2. Two-Particle Model
The two-particle approach is probably the pioneering one for modeling concentration second order statistics within the framework of a Lagrangian stochastic model [48]. The approach essentially stems from the Bayesian probability distributions, relating source distributions and receptor concentration statistics. The ensemble-averaged concentration, can be written as
with the source rate . is the conditional probability distribution for a particle released from at time to arrive to the detector location at time . In practice, this probability distribution is calculated by the Langevin equations, Equations (1) and (2). Equivalently, the simultaneous two-point concentration covariance is
where here, is the two-particle conditional probability distribution for two particles released at two different times from two different points, to arrive simultaneously to the points . For the limit we have the second moment of the concentration
with the aid of Equation (13), the concentration variance is determined by
A pair of particles, at locations at some time , which are carried by a turbulent flow moves with correlated velocities. The velocities are correlated because mutual eddies, with typical dimensions greater than will affect the positions of the two particles. The correlation is determined by the structure function describing spatial correlation in the flow. The two-particle probability function should hence take into account the dependence of the velocity correlation of the two particles, upon their mutual separation, and for nonhomogeneous flows, also upon their absolute locations.
It is insightful to consider two limits of Equation (15). The first, far-field limit applies when separation between the particles exceeds the turbulent mixing length scale, and thus the turbulent velocities of the two particles are no longer correlated. For that limit, the two-particle probability can be approximated as the multiplication of two independent single-particle probabilities.
Equation (17), substituted in Equation (15), leads to , and thus, the concentration variance is zero. This limit is a proper description of plumes with sizes extending well beyond the turbulent length scales, which indeed exhibit very low concentration fluctuations intensity.
On the other hand, when particles are close enough to each other, such that their mutual separation is less than the Kolmogorov scale, , which corresponds to the length scale of the smallest eddies, the near field limit is considered. By neglecting separation of particles by means of molecular diffusion, one can write
which, substituted into Equation (15), gives an upper bound for the concentration second moment and consequently, for the concentration fluctuations intensity [24].
It is important to mention, that the computational application of Equation (15) for the calculation of the concentration variance is not as straight-forward as the usual calculation of average concentrations using Equation (13). The straight-forward approach of utilizing Equation (15) within the framework of a Lagrangian stochastic model (LSM) would imply releasing multiple particle pairs from a localized source and monitoring events where two of the particles comprising a pair simultaneously visit the same control volume. Unfortunately, these events are extremely rare in comparison to a single-particle simulation. This issue will be addressed in the following review of different particle pair models.
The first LSM models that accounted for inter-particle correlation took into consideration only correlation resulting from common initial conditions of simultaneously-emitted particles from a point source. Such a model is Frank Gifford’s “random force model” [49]. Although simple and straight forward to implement, this approach fails to completely describe relative dispersion because the rate of separation growth does not depend on the separation.
Separation dependence of the dynamics was first introduced into a LSM model by [24] Durbin (1980) and later by some other authors (e.g., [50]). These models independently describe the dynamics of the pair center of mass, and the pair separation .
A typical set of equations of motion is
where are independent turbulent velocities for a single uncorrelated particle, and the functions are designed to rescale and such that the velocity fluctuations separating the particles will scale like . Durbin [24] has solved the equations for an infinite area source (one dimensional), where the dynamics is simulated backwards from the point of interest towards the source in order to reduce the number of particles needed.
Kaplan and Dinar (1991) [51] realized that the above approach does not comply with the so called “two to one” condition. This condition demands that
i.e., each of the single particles comprising a pair will exhibit, by itself, a single-particle statistics. They hence proposed an alternative approach in which instead of rescaling the uncorrelated velocity fluctuations, the correlation between particles is taken into account by generating stochastic velocity accelerations from a joint pdf which depends on the pair separation.
Another theoretical contribution for the subject came with the introduction of the “well-mixed condition” for particle pairs [7]. This condition demands that the probability distribution function , describing the state of an ensemble of particle pairs at time , should tend to a physically reasonable steady-state distribution which conforms with the single and two-point statistics of the turbulence. Thomson solved the resulting model numerically by expressing as
where if the probability for the pair’s center of mass, and is the probability of the pair’s inter-separation. For homogenous turbulence, is a function of only and thus can be numerically evaluated independently of . This enables the calculation of Equation (13) with a number of particles equivalent to regular average concentration calculations. As noted by Thomson, the suggested model does not fulfill the ‘two to one’ criteria. Yet, his numerical experiments show that practically, this discrepancy shows only minor importance.
In spite of the advancement in the development of the particle pair approach, it has not attained operational maturity. This is attributed to a few shortcomings. First, the usage of any of the advanced particle pair methods demands knowledge of the structure function tensor. While for homogeneous or infinite boundary layer flows this is plausible, this is not the case for more complex flows encountered in actual environmental applications, such as complex topography or canopy flows. Secondly, as explained above, a computational implementation with a feasible number of particles is not straight forward, especially in complex three-dimensional heterogeneous flows. Nevertheless, as will be shown in the following, the work on particle pair models paved the way to more practical models.
3.3. Fluctuating Plume Model
As seen in the previous section, the dynamics of a pair of particles in a turbulent flow is different from the dynamics of a single particle. Richardson (1926) [52] showed that the shape of a cloud of contaminant is affected and changed only by eddies with a lengthscale comparable to the cloud instantaneous dimension, while larger vortices would just advect the cloud. Following Richardson (1926) [52] and Gifford (1959) [53] assumed that the absolute dispersion could be divided in a meandering part, related to the movement of the plume barycentre, and a relative diffusion part, related to the internal mixing inside the plume. In Gifford’s (1959) [53] fluctuating plume model concentration fluctuations were produced by the instantaneous bodily movements of the plume, while internal fluctuations were not considered. In two-particle models this would be equivalent to two particles with a very small initial separation that would likely tend to move as a single particle. Therefore, Gifford’s (1959) [53] model is expected to perform well close to the source. However, as the plume (or the two particles) is swept around by the turbulent eddies it would also change shape and the changes in the concentration fluctuations would depend on eddies with sizes comparable to the plume instantaneous dimension or smaller. Yee and Wilson (2000) [14] took into account the effect of in-plume fluctuations assuming a functional form (a gamma function) for the pdf concentration relative to the plume barycenter. Luhar et al. (2000) [15] proposed a LSM for simulating the centroid vertical position and thus going beyond the vertical homogeneity and Gaussian pdf of turbulence assumed by both Gifford (1959) [53] and Yee and Wilson (2000) [14]. Following Luhar et al. (2000) [15], Franzese (2003) [16] developed a fluctuating plume model in which the Lagrangian equations governing the centroid motions are evaluated filtering out the energy fluctuations whose wavelengths are larger than the cloud instantaneous dimensions using a low-pass filter. After the barycenter pdf is evaluated by the LSM, the absolute concentration field is evaluated assuming horizontal homgeneous turbulence and then parameterizing the relative concentration pdf, i.e., parameterizing the plume dispersion relative to the instantaneous plume centroid. Both models of Luhar et al. (2000) [15] and Franzese (2003) [16] were specifically developed for a convective boundary layer. Mortarini et al. (2009) [17] extended their approach to dispersion in a simulated plant canopy. The model presented here is the one presented in Mortarini et al. (2009) [17].
In a fixed reference frame, the concetration moments are defined as
where c is the instantaneous concentration and is the instantaneous spatial pdf of the concentration. Gifford’s (1959) [53] assumption consists of writing the concentration pdf as
is the pdf of the plume centroid, , at a distant x from the source, while represents the concentration pdf relative to . Hence, is conditional to the centroid location, it is the concentration pdf in the frame of reference moving with the plume barycentre. Since
it follows that
where represent the concentration moments at a distance x from the source. Equation (25) summarizes the fluctuating plume models: it states that at any distance x from the source the absolute concentration field can be evaluated by integrating the concentration field relative to the plume centroid over the pdf of the centroid position The evaluation of the absolute concentration field requires the separate determination of and . It is worth noticing that Equation (25) states that, in principle, the fluctuating plume model can evaluate all the moments of the concentration distribution and not only the first two as the two-particle models.
Assuming that the plume meandering on the crosswind direction is independent on the meandering on the vertical direction, can be factorized as
If horizontal homogeneity is assumed, the barycenter pdf in the crosswind direction, is Gaussian [14,53]. To take into account the vertical inhomogeneities of the velocity field, the pdf of the vertical centroid position, can be evaluated using the following stochastic differential equations
where is the vertical velocity of the centroid, represents the deterministic acceleration, b is the diffusion coefficient and are the increments of a Wiener process, with zero mean and variance equal to dt.
The term in Equation (25) needs to be parameterized using a Gamma pdf for the concentration relative to the plume barycentre. However, its parameterization is quite complex and its details are outside the scopes of the present manuscript. For further information we refer our reader to [15,16,17,18].
3.4. Pdf Micro-Mixing Model
In a LSM, the trajectory associated with every single particle is equivalent to an independent realization of a single marked molecule in a turbulent flow. It therefore follows, that a large enough set of simulated trajectories connecting any arbitrarily chosen two points and , represent all the different possibilities of getting from to .
If a point particle emitted at point represents an air parcel with some known pdf of a physical property (concentration, temperature, etc.), which is altered during its travel to , and if this property is influenced by the processes the parcel experiences along its trajectory, then calculating the different optional trajectories from to will enable determining the pdf of the physical property at . This is, in a nutshell, the idea behind pdf models implemented by LSM [54].
Specifically, for concentration fluctuations, the physical process which changes the concentration of an air parcel along its trajectory is the turbulent mixing with its environment [10,55]. As mixing acts to reduce concentration fluctuations, it is natural to model the process as a first order tend towards the local mean concentration value with some time constant. This approach, termed ‘interaction by exchange with the mean’ (IEM) involves an additional equation to the set of LSM Equations (1) and (2)
where is the particle concentration, is the local mean concentration, and a time scale which represents the local rate of mixing which needs to be parameterized (see Section 3.7).
In practice, applying the model demands the computational domain to be densely populated with particles throughout the simulation. All particles are initialized with , and in the course of the simulation, all particles passing through the source are assigned a prescribed concentration. The simulation is run until statistical convergence is attained. The concentration pdf at any given location is evaluated by the different individual concentration values associated with the different particles visiting the location immediate control volume along the simulation. Higher order statistics are directly derived from the pdf.
The IEM method has been applied for various applications [9,56] which also include concentration fluctuations in rural and urban environments [57]. However, a few shortcomings have been reported. A basic requirement of a mixing model is that it will not influence the mean concentration. The IEM violates this, creating spurious fluctuations of the average concentration, especially in the vicinity of strong mean concentration gradients. As explained by Sawford (2004) [55], this is caused because on the average, particles moving down a concentration gradient will carry greater concentration than particles moving in the up-gradient direction. Mixing both populations towards the mean, as done in IEM wrongly reduces the flux, altering the average concentration. Additionally, Sawford (2004) [55] has reported that IEM does not model plume meandering, and therefore underestimates concentration variance in near and mid field, where the concentration fluctuations are dominated by plume meandering.
As a remedy to the above shortcomings, the interaction by exchange with conditional mean (IECM) extension was suggested, which is different from IEM in the representation of mixing. The concentration equation applied in IECM is
where is the conditional mean concentration, i.e., the mean concentration where only particles possessing the same velocity as the current particle are considered. Limiting mixing to particles with the same velocity is reasonable, because actual mixing an air parcel mixes with its immediate surrounding fluid, which have similar instantaneous velocity. Sawford (2004) [55] also shows that IECM models correctly evaluate the concentration flux, and as a result, the concentration fluctuations near the source are properly recovered.
A considerable downside of the IECM approach, stopping it from attaining operational maturity is its computational difficulty of implementation. Obtaining statistical convergence for every different velocity at every spatial location involves the usage of a very large number of particles. This has led some authors to seek ways of accelerating the model. Cassiani et al. (2005) [10] used a dynamical grid, expanding with time to contain a dispersing plume. Nesting, as well as particle splitting and merging algorithms were also applied (Cassiani et al., 2007) [11]. Postma et al. (2011) [58] performed the calculation following two steps, a first one to calculate on an Eulerian grid, and a second one with particles interacting with the concentration averages, emitted sequentially instead of simultaneously.
3.5. Volumetric Particle Approach
Another step of single-particle mixing models towards practical applications was made with the introduction of the volumetric particle approach (VPA). Differing from pdf methods which demand a computational domain fully populated with particles, VPA enables the calculation of the concentration second moment with particles ejected from the source only, so the computational requirements remain modest and comparable with classical average concentration calculations.
The VPA method has been suggested independently by Cassiani (2013) [59] and by Kaplan (2014) [60]. While the former developed the method as an extension of the IEM\IECM methods, the latter has presented the method as stemming from the two-particle probability formulation. It is insightful to present both directions of reasoning.
Cassiani (2013) [59] has introduced a volume (hence the method’s name) associated with each particle, where is the particle mass, which is conserved, and is the particle concentration which is governed, like in IEM, by Equation (28). The average concentration in a grid cell labeled with volume is
Recognizing the term as the probability that particle will be associated with concentration , the second moment of the concentration can be written as
The implementation of Equation (31) is straight forward. Alongside with the calculation of average concentration at site using Equation (30), the second moment at the site is determined using Equation (31). Finally, values are updated, and movement of the particles according to the LSM equations of motions take part.
Kaplan’s [60] starting point is the relation between the two-particles probability function and the concentration second moment, Equation (15), here written for an instantenous source gives
In order to express Equation (32) in terms of the easily evaluated , instead of , the equation is rearranged to obtain
where the term in the inner integral is recognized as the conditional probability of a particle released from at , to arrive at at time , subject to the condition that another particle, simultaneously released from , also reaches at time .
Next, we define
as the concentration attributed to particles reaching at time , simultaneously with particles released from . Equation (33) is now written as
To model , the far field limit of the two-particles probability function, Equation (17), is used. For large distances from the source, , and . is hence modeled as tending towards the local average concentration with some time constant . The equations of motions and the implementation is exactly as done by Cassiani (2013) [59], only that the particle-associated concentration that emerges at Cassiani (2013) [59] as a result of the particle-associated volume, is interpreted by Kaplan (2014) [60] in terms of which is related to two particle statistics.
It is worth noting that the two interpretations are complementary, and also shed light on the physical meaning of the particle-associated volume introduced by Cassiani (2013) [59]. Let us consider the limit of a point source. Keeping each particle mass constant implies that . is defined as the concentration associated with events where particles visit simulataneously with their pair counterparts. If we regard as an intantenous puff volume, is it clear why the smaller gets (thus enlarging ), the more probable it is for two particles to reach simulataneously.
The VPA model has been successfully evaluated against wind tunnel experimental data of dispersion in a neutral boundary layer [59,60], canopy turbulence [59] and decaying grid turbulence [60]. It has also been used for environmental analysis involving reacting pollutants [61].
Unlike the IEM\IECM models, the VPA model cannot be used directly to calculate concentration moments higher than the second moment. However, the first two moments fully define a gamma distribution function, which describe the distribution of instantenous concentrations for a wide scale of ranges [62,63]. This agrees with observed scaling relations between the first two moments and higher moments [19]. Marro et al. (2018) [64] took advantage of these results and proposed a so-called VPΓ model, which utilizes the VPA model for the calculation of the two first moments and estimates the third and fourth moment using the gamma function hypothesis. The model was successfully compared against the IECM approach which directly yields the whole concentration pdf distribution.
3.6. Parameterizations
In many problems related to the tracer dispersion in a turbulent flow, the cross-covariance term between the concentration fluctuations has to be modeled or parameterized. This is the case, for example, for the chemical reaction simulation on a time scale lower than the typical equilibrium scale. The covariance of two compounds participating to the reaction should be accounted for [65]. The contribution of this term is often referred as ‘segregation’ coefficient α, that is
where primes indicate the concentration fluctuations of the chemical compounds A and B. To calculate this quantity the second order moments of the concentration distribution are necessary. As already discussed herein, single-particle LSM, which account for independent particle trajectories, cannot provide higher order moments. In order to overcome this shortcoming Alessandrini and Ferrero (2009, 2010, 2011) [66,67,68] adopted a simple parameterization based on wind tunnel data. It is worth noting that many chemical models do not account for the segregation term, considering the chemical reactions as occurring always in equilibrium conditions. This hypothesis is valid only when large time and space scales are considered, but not in short term simulations, where the segregation effect, due to the turbulence mixing, cannot be neglected as shown in Alessandrini et al. (2012) [69].
Because the term is generally negative, considering only the product of the mean values and neglecting the segregation results in an overestimation of the covariance.
Consequently the reaction proceeds too fast. In other words, turbulent mixing at smaller scales is not accounted for unless the term is considered. Alessandrini and Ferrero (2009) [66] proposed a proper parameterization for the segregation coefficient, which was obtained by performing a best fit of the experimental data of Brown and Bilger (1998) [70]
where x is the downwind distance, xs is the stoichiometric distance, which is the axial centerline location where the initial concentration of the reactant A emitted by the source was diluted to the initial background concentration of B (which remains constant outside the plume) and ND the Damköhler number, which represents the ratio between the time scales of turbulence and chemical reaction.
As a matter of fact, if the time scale of any chemical process is large compared with the time scale of the turbulence, i.e., for a very low Damköhler number the turbulent concentration fluctuations are damped and hence do not contribute to the reaction rate. Nevertheless, in many cases, in which the scales are small, as in urban pollution and near the source, the effect of the segregation cannot be neglected [65], thus in the single-particle stochastic model the segregation coefficient should be parameterized in some way. Aguirre et al. (2006) [71] introduced a parameterization which depends on the local gradient of concentration and the diffusion coefficient. However, in practical applications, the calculation of the local gradient at each time step would be very time consuming. Vilá-Guerau de Arellano et al. (2004) [72] introduced the moments method, which involves a closure problem.
3.7. Virtual Variance Sources
The approach of virtual variance sources (VVS), suggested by Manor (2014) [21], is based on the steady state governing equation for the concentration variance
where is the average concentration, is a fluctuation, and are, respectively, the -th components of the mean and turbulent velocities, and is the kinematic viscosity. The first two terms on the left are the advection and turbulent diffusion terms, which have a complete analogue in the equation of passive scalar dynamics. The next term is a production term, which, after applying the K-gradient hypothesis can be written as
The fourth term is a dissipation term, which expresses the smoothing of spatio-temporal heterogeneities by molecular viscosity. This term is commonly modeled by a first order decay, i.e.,
where is a dissipation time scale (see Section 3.8).
In practice, the average concentration field, is calculated first. Then, a source term is determined and used to release particles representing concentration variance. These particles are governed by the same advection\diffusion dynamics as the ‘ordinary’ particles used to model the average concentration, only that they are designed to decay according to Equation (41). The spatial distribution of essentially dictates a very large number of variance sources, which may pose a considerable computationally load. However, as verified by Manor (2014) [21], for a localized source, a small fraction (about 3%) of the potential sources are enough to produce almost all (97%) of the total effect. Thus, only these sources are identified and used.
The VVS approach was tested by Manor (2014) [21] against the JU2003 database. Ferrero et al. (2017) [22] used the approach with an improved parameterization for and compared their results to wind tunnel observations by Fackrell and Robins (1982) [73].
Oettl and Ferrero (2017) [6] used a simplified version of Equations (40) and (41), neglecting the advection and the turbulent diffusion terms (see also Section 4.3). For steady state conditions this results in a simple expression relating the average concentration to the concentration variance
Being strictly algebraic, Equation (42) can be usefully applied regardless of the specific dispersion model.
3.8. Variance Dissipation Time Scale
Differently from the mean concentrations, the concentration fluctuations are not conserved along the flow. Hence the dissipation of variance should be modeled. In analogy with the Eulerian Equation (41), the concentration variance dissipation, to be introduced in the Lagrangian equation in order to determine the decrease of the concentration variance at each timestep, can be evaluated through the dissipation time scale, td.
In the LSM the variance dissipation is accounted for at each time step using the equation
The determination of this time scale is the key point in simulating the concentration variance dispersion. A first attempt to predict was made by Lewellen (1977) [74] who calculated this parameter through the plume standard deviations. However, Sykes et al. (1984) [75] observed that the variance dissipation is controlled by eddies with length scales of the order of the plume size. They also suggested that, while the outer scale becomes rapidly independent of the source, as also shown by Fackrell and Robins (1982) [73], the total concentration variance depends on the inner scale λc. As a matter of fact, the plume can be divided into inner and outer scales. The outer scale corresponds to the scale over which the plume meanders and the inner scale is the relative spread of the plume. As a consequence, Sykes et al. (1984) [75] prescribed an inner scale from which they determined the dissipation time scale . In particular they showed, as also stated by Sawford (1982) [76], that λc should be initially proportional to the time t and then to t3/2. However, in these works, the time scale is obtained from both the length scale and a velocity scale, and the velocity scale actually depends on the length scale. Galperin (1986) [77] showed that the dissipation time scale grows linearly with time, and, if we consider the dissipation time scale as the life-time of the fluctuations, it should be smaller close to the source where the intense mixing causes rapid development and dissipation of the fluctuations. Proportionality between and the Lagrangian integral time scale was proposed by Bèguier et al. (1978) [78] and Warhaft and Lumley (1978) [79], and used by Andronopoulos et al. (2002) [80] and Milliez and Carissimo (2008) [81]. A similar relationship can be found in Yee et al. (2009) [63]. A proportionality coefficient equal to 22 was suggested by Manor (2014) [21]. It is worth to notice that Manor (2014) [21] parameterized as proportional to the local vertical Lagrangian time scale at a particle position. Ferrero et al. (2017) [22] proposed the following function for the dissipation time scale td
where is the value of the vertical component of the Lagrangian time scale at the source height, t* = zi/U (zi is the boundary-layer depth and U is the freestream velocity), α1, α2 are constants, ds is the source diameter, and hs is the source height. Since it has been demonstrated [22] that the observed concentration-variance dispersion by Fackrell and Robins (1982) [73] depend on both source size and height, a dependency on these two parameters was introduced in the parameterization for . As t → 0 (i.e., for times just after emission) Equation (44) becomes a constant that depends on the Lagrangian time scale and the ratio between source diameter and height. As a matter of fact, the dimension of the plume close to the source is of the order of the source size and the eddies that can dissipate the concentration variance should have the same size. The second term in Equation (44) is needed to avoid that at t = 0 and hence that , while in contrast the fluctuations are larger close to the source. Naturally, the mean concentration field has the largest gradient near the source and, as a consequence, concentration fluctuations are highest there. Subsequently the dissipation time scale becomes proportional to the dispersion time.
It can be noted that the parameterization is similar to the expression derived in the Appendix of Sykes et al. (1984) [75], except for the fact that the source-size ratio has a 1/3 power rather than 2/3. An observation of Equation (44) indicates that initially, for , the fluctuation variance rapidly decreases along the particle trajectory, while for longer times, and as a consequence of being dependent on t, dissipation ceases when This is reasonable as the fluctuations become smaller. It is worth noting that the source of the concentration variance depends on the gradient of the mean concentration. For this reason, the largest source terms will be found close to a point source, where the gradients of the mean concentration are higher.
4. Odor Dispersion
The use of general-purpose steady state Gaussian models for predicting odor exposure levels around the vicinity of an industrial site has been considered an accepted practice for many countries around the world for a long time. This practice has been questioned lately in several countries in Europe (e.g., Germany, Italy, Austria, Switzerland) due to the widely known shortcomings of steady-state plume models to accurately assess dispersion under a range of ‘complex’ conditions (e.g., topography; coastal flows, calm and stable conditions; cold flows; heterogeneous land usage). In such circumstances, there is a real danger that odor impact risk can be either under- or overestimated, which has a substantial influence on the development of pragmatic, cost efficient odor mitigation management. Moreover, odor nuisance is known to be closely linked to short-term odor-concentration peaks, as these may reach levels well above the recognition threshold causing immediate annoyance. Short-term concentration peaks of the order of a few seconds (i.e., a single breath) require models for the concentration fluctuation as outlined in the previous chapters. In the following, a brief review about models for assessing odor impact, which are currently in use for regulatory purposes in different countries, is given.
4.1. Fluctuating Plume Models
In order to assess odor impact knowledge about concentration fluctuations are needed. Thus, only Lagrangian models able to provide these quantities should be selected. As we have seen in Section 3.3, Lagrangian fluctuating plume models (FPMs) can satisfy this requirement. Ferrero et al. (2013) [18] showed how FPMs can simulate a chemically reactive plume. However, up to now no Lagrangian FPM has been used for regulatory purposes to predict odor concentrations. On the contrary, Gaussian FPMs have been tested and used for this purpose (see for instance [82,83]) already.
4.2. Lagrangian Stochastic Particle Models
LSM have been used to calculate direction-dependent separation distances to avoid odor annoyance by Piringer et al. 2016 [84]. The relevant short-term peak odor concentrations are calculated with a stability-dependent peak-to-mean algorithm. It was found that the Lagrangian model used by the authors better reproduces the physical processes and generally calculates larger separation distances compared to the Gaussian model applied in their study. For worst-case calculations, necessary when environmental impact assessment studies are carried out, the use of a Lagrangian model is therefore to be preferred.
The peak-to-mean concept, also explained in Piringer et al. (2014) [85], is based on a relationship by Smith (1973) [86], where the peak-to-mean factor is given by
with the mean concentration Cm calculated for an integration time of tm (1800 s) and the peak concentration Cp for an integration time of tp (5 s). The exponent ‘a’ depends on atmospheric stability. Generally, Equation (45) gives relatively large values of . Following Mylne (1992) [42], it is assumed that, due to turbulent mixing, the peak- to-mean factor is reduced with increasing distance from the source. The peak-to-mean factor in Equation (45) is modified by an exponential decaying function of the quantity T/tL, where T = x/u is the time of travel with distance x and the mean wind speed u, and tL is a measure of the Lagrangian time scale [42].
Having said this, Janicke and Janicke (2004) [87] suggested using a constant factor for the peak-to-mean ratio. In their work, they did not only consider the concentrations fluctuations themselves, but took into account the probability of qualified panel members to recognize a certain type of odor dependent on its concentration. This is expressed in the definition of the so-called “odor hour” in the German guideline VDI 3788 (2015) [88] by the following function
whereby is the probability density function of odor concentrations at some observational point for an hourly interval. An odor hour is defined by , i.e., in 10% of the time odor will be detected by the qualified panelists. Janicke and Janicke (2004) [87] and Oettl et al. (2018) [89] demonstrated that for an assumed log-normal distribution for
and > 1 an almost constant peak-to-mean ratio of about 4 is obtained, practically independent on the shape of . In Equation (47) erf is the error function, c the odor concentration, the odor concentration detected by 50% of qualified panel members, and a scale parameter. The value of can be determined by means of dynamic olfactometry. Oettl et al. (2018) [89] analyzed more than 1000 datasets covering a wide range of odor types, and found a median for of around 0.6. In this case, the shape of becomes important and needs to be taken into account in odor assessments.
A second example of the application of a LSM for odor dispersion was recently proposed by Ferrero and Oettl (2019) [23]. This approach can be defined as fully Lagrangian since both mean and variance concentrations are simulated through particle trajectories. In their work, the authors propose and evaluate a one-particle LSM for the assessment of the concentration-fluctuation variance, which, by providing the fluctuation intensity, can be used to predict odor hours. The concentration variance in the Lagrangian particle model evolves according to the same Langevin equation used for the simulation of the turbulent dispersion, which provides the mean concentration field. As already outlined in Section 3.7, the main challenge is to provide a suitable parameterization for the concentration-variance dissipation time scale. From the mean concentration and the variance concentration fields, it is possible to calculate the fluctuation intensity that is the ratio between the concentration standard deviation and the mean concentration. The fluctuation intensity, introduced in the concentration pdf, allows analytically calculating the 90th percentile which is the key parameter needed to assess an odor hour.
4.3. Hybrid Lagrangian-Eulerian (Enrico)
Oettl and Ferrero (2017) [Error! Reference source not found.] suggested a hybrid approach in which the mean concentration is calculated with a LSM, while the concentration variance is estimated on an Eulerian grid neglecting the advection and diffusion terms in the time-dependent governing equation for the concentration variance
One of the main advantages of using Equation (48) is that it can be computed in post-processing mode, and thus, is independent on the dispersion model applied for calculating the mean concentration field. The variance dissipation is currently computed by using the relationship . For more discussion on proper parameterizations, the reader is referred to Section 3.8. The simulated concentration variances are used in combination with a slightly modified two-parameter Weibull pdf to get the 90th percentile of the cumulative frequency distribution of odor-concentration fluctuations, which is required for computing an odor hour. Figure 2 displays modeled concentration-fluctuation intensities using Equation (48). Though, Equation (48) represents a strongly simplified version of the governing equation for the concentration variance, some important features evident from observations (see Section 3.1) are captured: First, towards the edge of the plume the intensities are increasing, and second, after a slight increase close to the source, intensities are slowly decreasing with distance to the source along the plume centerline.
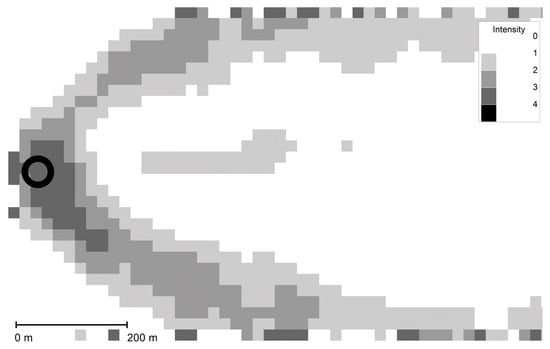
Figure 2.
Modeled intensities of concentration fluctuations using Equation (48) near a point source indicated by the circle, and a wind direction from the left.
4.4. Puff Model (Enrico)
A different Lagrangian approach is the Puff model, in which, differently from the particle models, the plume is composed by different puffs, which follow the mean wind and are dispersed independently. Using the more known and diffused puff model, CALPUFF [90], considered in US EPA guideline an alternative to the Gaussian model able to provide a more effective way of simulating complex conditions, Murguia et al. (2014) [91] evaluate how predictions with different meteorological input data type compare for odor assessment purposes for a complex study site, and whether the use of any of the meteorological data sets offers any advantage in gaining a better understanding of odor exposure and impact risk. The area where the maximum hourly average ground level concentration is greater than 3 ouE/m3 for more than 2% of the hours in the year. It defines the maximum extent at which the CALPUFF model predicts there is reasonable cause of odor annoyance. The 3 ouE/m3 98 percentile is the applicable odor impact criteria. De Melo et al. [92] compared AERMOD and CALPUFF with wind tunnel data simulating odor dispersion around a pig farm building complex. The results show that concentrations predicted by AERMOD are, in general, higher than those predicted by CALPUFF, especially regarding the maximum mean concentrations observed in the near field. Ranzato et al. [93] assessed the olfactory nuisance caused by an anaerobic treatment plant for municipal solid waste by means of two alternative techniques: the field inspection procedure and the atmospheric dispersion model CALPUFF.
5. Conclusions
The paper reviewed open questions and challenges posed by modeling of processes controlling the advection and diffusion of concentration fluctuation through a Lagrangian approach, as well as odor dispersion. In contrast to the mean concentration dispersion, the fluctuation dispersion Lagrangian models are still at the research stage, although the number of works on this matter is large and the range of different methods is very rich. Our capability of monitoring and predicting odor dispersion still suffer from significant limitations and in spite of the number of interesting works, it deserves more in-depth investigations.
Author Contributions
All the authors contribute in writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Schauberger, G.; Piringer, M.; Knauder, W.; Petz, E. Odour emissions from a waste treatment plant using an inverse dispersion technique. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilderman, T.; Hrudey, S.; Wilson, D. A model for effective toxic load from fluctuating gas concentrations. J. Hazard. Mater. 1999, 64, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crone, G.C.; Dinar, N.; van Dop, H.; Verver, G.H.L. A Lagrangian approach for modelling turbulent transport and chemistry. Atmosp. Environ. 1999, 33, 4919–4934. [Google Scholar]
- Sawford, B.L.; Pinton, J.-F. A Lagrangian view of turbulent dispersion and mixing. In Ten Chapters in Turbulence; Davidson, P.A., Kaneda, Y., Sreenivasan, K.R., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; Chapter 4; pp. 131–175. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, D.J. Criteria for the selection of stochastic models of particle trajectories in turbulent flows. J. Fluid Mech. 1987, 180, 529–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oettl, D.; Ferrero, E. A simple model to assess odour hours for regulatory purposes. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 155, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, D.J. A stochastic model for the motion of particle pairs in isotropic high-Reynolds-number turbulence, and its application to the problem of concentration variance. J. Fluid Mech. 1990, 210, 113–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgas, M.S.; Sawford, B.L. A family of stochastic models for two-particle dispersion in isotropic homogeneous stationary turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 1994, 289, 69–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, S.B. PDF methods for turbulent reactive flows. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1985, 11, 119–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassiani, M.; Franzese, P.; Giostra, U. A pdf micromixing model of dispersion for atmospheric flow. Part I: Development of the model, application to homogeneous turbulence and to neutral boundary layer. Atmosp. Environ. 2005, 39, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassiani, M.; Radicchi, A.; Albertson, J.D.; Giostra, U. An efficient algorithm for scalar pdf modelling in incompressible turbulent flow; numerical analysis with evaluation of IEM and IECM micro-mixing models. J. Comp. Phys. 2007, 223, 519–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuzzi, G.; Amicarelli, A.; Monti, P.; Thomson, D. A 3D lagrangian micromixing dispersion model LAGFLUM and its validation with a wind tunnel experiment. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 54, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, E.; Chan, R.; Kosteniuk, P.R.; Chandler, G.M.; Biltoft, C.A.; Bowers, J.F. Experimental Measurements of Concentration Fluctuations and Scales in a Dispersing Plume in the Atmospheric Surface Layer Obtained Using a Very Fast Response Concentration Detector. J. Appl. Met. 1994, 33, 996–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, E.; Wilson, D.J. A comparison of the detailed structure in dispersing tracer plumes measured in grid-generated turbulence with a meandering plume model incorporating internal fluctuations. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2000, 94, 253–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhar, A.; Hibberd, M.; Borgas, M. A skewed meandering-plume model for concentration statistics in the convective boundary layer. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 3599–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzese, P. Lagrangian stochastic modeling of a fluctuating plume in the convective boundary layer. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 1691–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortarini, L.; Franzese, P.; Ferrero, E. A fluctuating plume model for concentration fluctuations in a plant canopy. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, E.; Mortarini, L.; Alessandrini, S.; Lacagnina, C. Application of a Bivariate Gamma Distribution for a Chemically Reacting Plume in the Atmosphere. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2013, 147, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisignano, A.; Mortarini, L.; Ferrero, E.; Alessandrini, S. Analytical offline approach for concentration fluctuations and higher order concentration moments. Int. J. Environ. Poll. 2014, 55, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marro, M.; Nironi, C.; Salizzoni, P.; Soulhac, L. Dispersion of a passive scalar from a point source in a turbulent boundary layer. part ii: Analytical modelling. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2015, 156, 447–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manor, A. A stochastic single particle Lagrangian model for the concentration fluctuation in a plume dispersing inside an urban canopy. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2014, 150, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, E.; Mortarini, L.; Purghè, F. A simple parameterization for the concentration variance dissipation in a Lagrangian single-particle model. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2017, 163, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, E.; Oettl, D. An evaluation of a Lagrangian stochastic model for the assessment of odours. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 206, 237–246. [Google Scholar]
- Durbin, P.A. A stochastic model of two-particle dispersion and concentration fluctuations in homogeneous turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 1980, 100, 279–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassiani, M.; Giostra, U. A simple and fast model to compute concentration moments in a convective boundary layer. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 4717–4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, E.; Mortarini, L.; Alessandrini, S.; Lacagnina, C. A fluctuating plume model for pollutants dispersion with chemical reactions. Int. J. Environ. Poll. 2012, 48, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, S.B. Lagrangian pdf methods for turbulent flows. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1994, 26, 23–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, S.B. Turbulent Flows; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; 806p. [Google Scholar]
- Heinz, S. Statistical Mechanics of Turbulent Flows; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; 214p. [Google Scholar]
- Kernstein, A.L. Linear-eddy modelling of turbulent transport. Part. 6 Microstructure of diffusive scalar mixing fields. J. Fluid. Mech. 1991, 231, 361–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monin, A.S.; Yaglom, A.M. Statistical Fluid Mechanics: Mechanics of Turbulence; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1975; Volume 2, 874p. [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner, C.W. Handbook of Stochastic Methods; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Hinze, J.O. Turbulence; Mc Graw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1975; 790p. [Google Scholar]
- Sawford, B.L.; Guest, F.M. Uniqueness and universality of Lagrangian stochastic models of turbulent dispersion. In Proceedings of the 8th Symposium on Turbulence and Diffusion, San Diego, CA, USA, 25–29 April 1988; pp. 96–99. [Google Scholar]
- Sawford, B.L. Reynolds number effects in Lagrangian stochastic models of turbulent dispersion. Phys. Fluids 1991, A3, 1577–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawford, B.L. Recent developments in the Lagrangian stochastic theory of turbulent dispersion. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1993, 62, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, S.R. Concentration fluctuations in a smoke plume. Atmos. Environ. 1984, 18, 1091–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsdell, J.V.; Hinds, W.T. Concentration fluctuations and peak-to-mean concentration ratios in plumes from a ground-level continuous point source. Atmos. Environ. 1971, 5, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.D. Statistics of concentration fluctuations in short range atmospheric diffusion. In Mathematical Modeling of Turbulent Diffusion in the Environment; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1981; pp. 277–300. [Google Scholar]
- Mole, N.; Jones, C.D. Concentration fluctuation data from dispersion experiments carried out in stable and unstable conditions. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1994, 67, 41–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewellen, W.S.; Sykes, R.I. Analysis of concentration fluctuations from Lidar observations of atmospheric plumes. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 1986, 25, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylne, K.R.; Mason, P.J. Concentration fluctuation measurements in a dispersing plume at a range of up to 1000m. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1991, 117, 177–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylne, K.R. Concentration fluctuation measurements in a plume dispersing in a stable surface layer. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1992, 60, 15–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung, T.; Müller, H.J.; Gläser, M.; Möller, B. Measurements and Modelling of Full-Scale Concentration Fluctuations. Agrartech. Forsch. 2002, 8, E5–E15. [Google Scholar]
- Finn, D.; Clawson, K.L.; Carter, R.G.; Rich, J.D.; Biltoft, C.; Leach, M. Analysis of Urban Atmosphere Plume Concentration Fluctuations. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2010, 136, 431–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, D.; Clawson, K.L.; Eckman, R.M.; Carter, R.G.; Rich, J.D.; Strong, T.W.; Beard, S.A.; Reese, B.R.; Davis, D.; Liu, H.; et al. Project Sagebrush Phase 1. NOAA Technical Memorandum OAR ARL-268; 2015; 362p. Available online: https://www.arl.noaa.gov/documents/reports/ARL-TM-268.pdf (accessed on 8 July 2015).
- Finn, D.; Carter, R.G.; Eckman, R.M.; Rich, J.D.; Gao, Z.; Liu, H. Plume Dispersion in Low-Wind-Speed Conditions During Project Sagebrusch Phase 2, with Emphasis on Concentration Variability. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2018, 169, 67–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawford, B.L. Turbulent relative dispersion. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2001, 33, 289–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gifford, F.A. Horizontal diffusion in the atmosphere: A Lagrangian-dynamical theory. Atmosp. Environ. 1982, 16, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapountzis, H.; Sawford, B.L.; Hunt, J.C.R.; Britter, R.E. Structure of the temperature field downwind of a line source in grid turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 1986, 165, 401–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, H.; Dinar, N. A three-dimensional model for calculating the concentration distribution in inhomogeneous turbulence. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1993, 62, 217–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, L.F. Atmospheric diffusion shown on a distance neighbour graph. Proc. Roy. Soc. 1926, 110, 709–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gifford, F. Statistical properties of a fluctuating plume dispersion model. Adv. Geophys. 1959, 6, 117–137. [Google Scholar]
- Pope, S.B. Turbulent Flows; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sawford, B.L. Micro-mixing modelling of scalar fluctuations for plumes in homogeneous turbulence. Flowturb. Comb. 2004, 72, 133–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopazo, C.; Valiño, L.; Fueyo, N. Statistical description of the turbulent mixing of scalar fields. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 1997, 11, 2975–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, N.S.; Tomlin, A.S. A Lagrangian stochastic model for predicting concentration fluctuations in urban areas. Atmosp. Environ. 2007, 41, 8114–8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postma, J.V.; Wilson, J.D.; Yee, E. Comparing two implementations of a micromixing model. Part I: Wall shear-layer flow. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2011, 140, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassiani, M. The volumetric particle approach for concentration fluctuations and chemical reactions in Lagrangian particle and particle-grid models. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2013, 146, 207–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, H. An estimation of a passive scalar variances using a one-particle Lagrangian transport and diffusion model. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2014, 393, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, H.; Olry, C.; Moussafir, J.; Oldrini, O.; Mahe, F.; Albergel, A. Chemical reactions at street scale using a Lagrangian particle dispersion model. Int. J. Environ. Poll. 2014, 55, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Villermaux, E.; Duplat, J. Mixing as an aggregation process. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 184501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, E.; Wang, B.C.; Lien, F.S. Probabilistic model for concentration fluctuations in compact-source plumes in an urban environment. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2009, 130, 169–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marro, M.; Salizzoni, P.; Soulhac, L.; Cassiani, M. Dispersion of a Passive Scalar Fluctuating Plume in a Turbulent Boundary Layer. Part III: Stochastic Modelling. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2018, 167, 349–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garmory, A.; Richardson, E.S.; Mastorakos, E. Micromixing effects in a reacting plume by the stochastic fields method. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 1078–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandrini, S.; Ferrero, E. A hybrid lagrangian–eulerian particle model for reacting pollutant dispersion in non-homogeneous non-isotropic turbulence. Phys. A 2009, 388, 1375–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandrini, S.; Ferrero, E. An application of a Lagrangian particle model with chemical reactions to power plant pollution dispersion in complex terrain. In Air Pollution Modeling and its Application XX; Steyn, D.G., Rao, S.T., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 361–366. [Google Scholar]
- Alessandrini, S.; Ferrero, E. A Lagrangian particle model with chemical reactions: Application in real atmosphere. Int. J. Environ. Poll. 2011, 47, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandrini, S.; Balanzino, A.; Ferrero, E.; Riva, M. Lagrangian modelling evaluation of the NOx pollution reduction due to electric vehicles introduction. Int. J. Environ. Poll. 2012, 50, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.J.; Bilger, R.W. Experiments on a reacting plume–1. Conventional concentration statistics. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 611–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, C.; Vinkovic, I.; Simoens, S. A subgrid Lagrangian model for turbulent passive and reactive scalar dispersion. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2006, 27, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilá-Guerau de Arellano, J.; Dosio, A.; Vinuesa, J.-F.; Holtslag, A.A.M.; Galmarini, S. The dispersion of chemically reactive species in the atmospheric boundary layer. Meteor. Atmos. Phys. 2004, 87, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewellen, W.S. Use of invariant modelling. In Handbook of Turbulence; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1977; Volume 180. [Google Scholar]
- Sykes, R.I.; Lewellen, W.S.; Parker, S.E. A turbulent-transport model for concentration fluctuations and fluxes. J. Fluid Mech. 1984, 139, 193–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fackrell, J.E.; Robins, A.G. Concentration fluctuations and fluxes in plumes from point sources in a turbulent boundary. J. Fluid Mech. 1982, 117, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawford, B.L. Comparison of some different approximations in the statistical theory of relative dispersion. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1982, 108, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galperin, B. A modified turbulence energy model for diffusion from elevated and ground point sources in neutral boundary layer. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1986, 37, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bèguier, C.; Dekeyser, I. Launder BE Ratio of scalar and velocity dissipation time scales in shear flow turbulence. Phys. Fluids 1978, 21, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warhaft, Z.; Lumley, J.L. An experimental study of the decay of temperature fluctuations in grid-generated turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 1978, 88, 659–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andronopoulos, S.; Grigoriadis, D.; Robins, A.; Venetsanos, A.; Rafailidis, S.; Bartzis, J.G. Three-dimensional modeling of concentration fluctuations in complicated geometry. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2002, 1, 415–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliez, M.; Carissimo, B. Computational fluid dynamical modeling of concentration fluctuations in an idealized urban area. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2008, 127, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourado, H.; Santos, J.M.; Reis Junior, N.C.; Mavroidis, I. Development of a fluctuating plume model for odour dispersion around buildings. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 89, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussio, P.; Gnyp, A.W.; Henshaw, P.F. A fluctuating plume dispersion model for the prediction of odour-impact frequencies from continuous stationary sources. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 2955–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piringer, M.; Knauder, W.; Petz, E.; Schauberger, G. Factors influencing separation distances against odour annoyance calculated by Gaussian and Lagrangian dispersion models. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 140, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piringer, M.; Knauder, W.; Petz, E.; Schauberger, G. Use of ultrasonic anemometer data to derive local odour related peak-to-mean concentration ratios. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2014, 40, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.E. Recommended Guide for the Prediction of the Dispersion of Airborne Effluents; ASME: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Janicke, L.; Janicke, U.; Ahrens, D.; Hartmann, U.; Müller, W.J. Development of the odour dispersion model AUSTAL2000G in Germany. Environ. Odour Manag. Vdi-Ber. 2004, 1850, 411–417. [Google Scholar]
- VDI 3788-1, Environmental meteorology—Dispersion of odorants in the atmosphere—Fundamentals. Available online: https://www.vdi.de/richtlinien/details/vdi-3788-blatt-1-umweltmeteorologie-ausbreitung-von-geruchsstoffen-in-der-atmosphaere-grundlagen (accessed on 29 November 2019).
- Oettl, D.; Kropsch, M.; Mandl, M. Odour assessment in the vicinity of a pig-fatting farm using field inspections (EN 16841-1) and dispersion modelling. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 181, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scire, J.; Strimaitis, D.; Yamartino, R. A User’s Guide for the CALPUFF Dispersion Model; Earth Tech. Inc.: Concord, MA, USA, 2000; pp. 1–521. [Google Scholar]
- Murguia, W.; Pagans, E.; Barclay, J.; Scire, J. Case study: A comparison of predicted odour exposure levels in Barcelona using CALPUFF lite, CALPUFF NoObs and CALPUFF hybrid model. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2014, 40, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- De Melo, A.M.; Santos, J.M.; Mavroidis, I.; Reis, N.C., Jr. Modelling of odour dispersion around a pig farm building complex using AERMOD and CALPUFF. Comparison with wind tunnel results. Build. Environ. 2012, 56, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranzato, L.; Barausse, A.; Mantovani, A.; Pittarello, A.; Benzo, M.; Palmeri, L. A comparison of methods for the assessment of odor impacts on air quality: Field inspection (VDI 3940) and the air dispersion model CALPUFF. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 61, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).