Spatial Distributions and Sources of Inorganic Chlorine in PM2.5 across China in Winter
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Chemical Analysis
2.2. Model of Positive Matrix Factorization
3. Results and Discussions
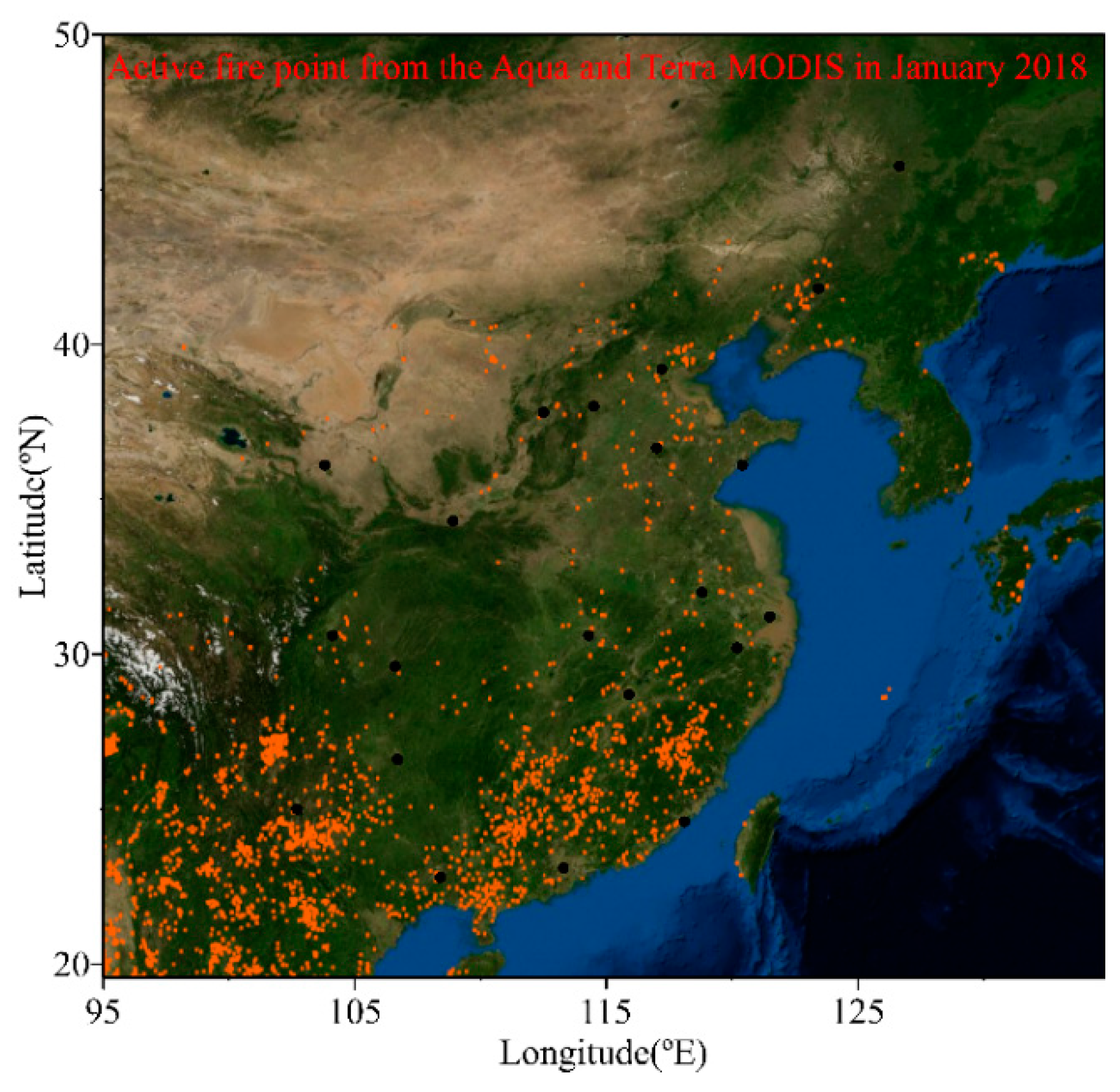
3.1. Spatial Distributions of Cl−, , K+ and Na+ in PM2.5
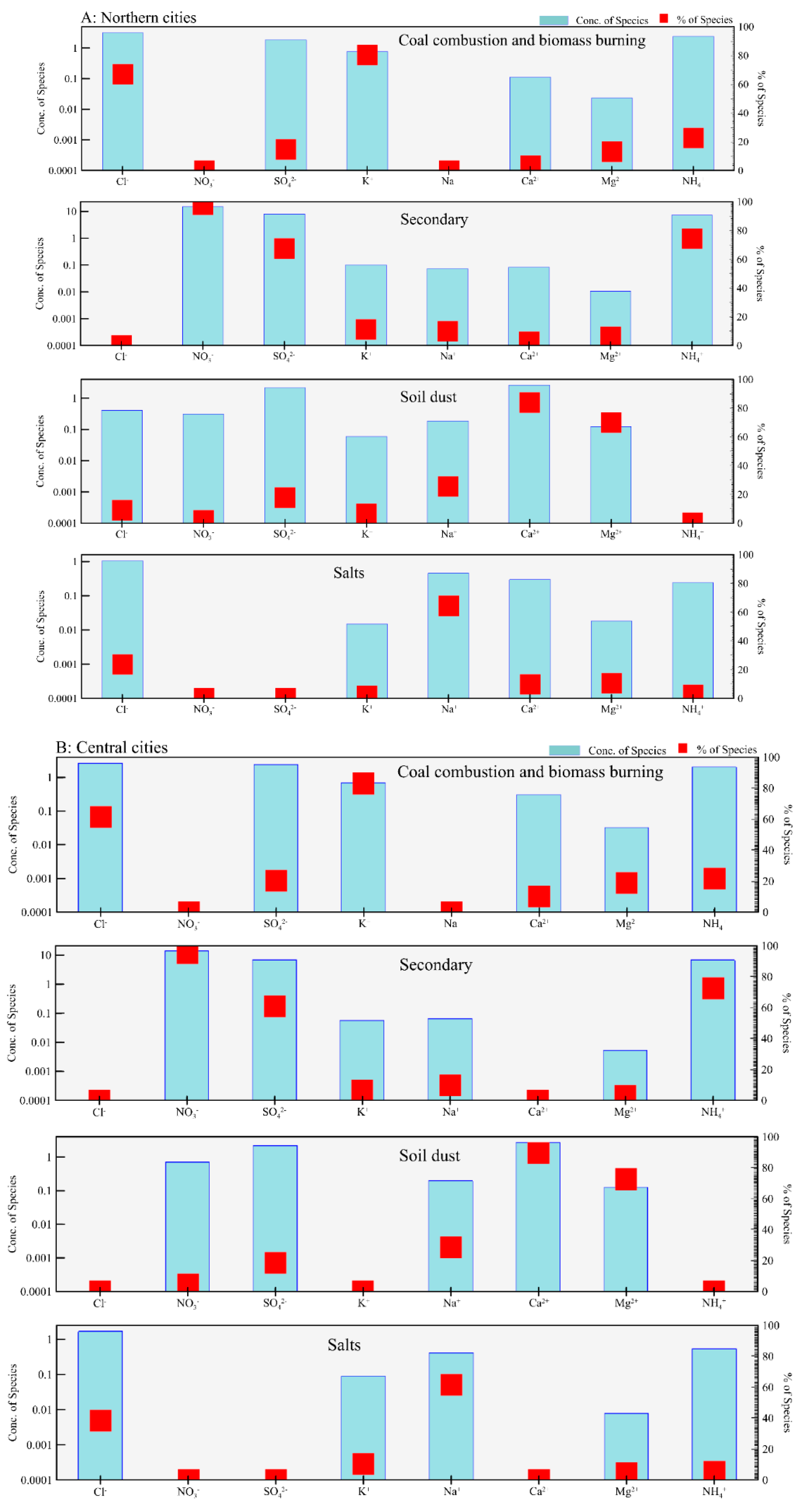
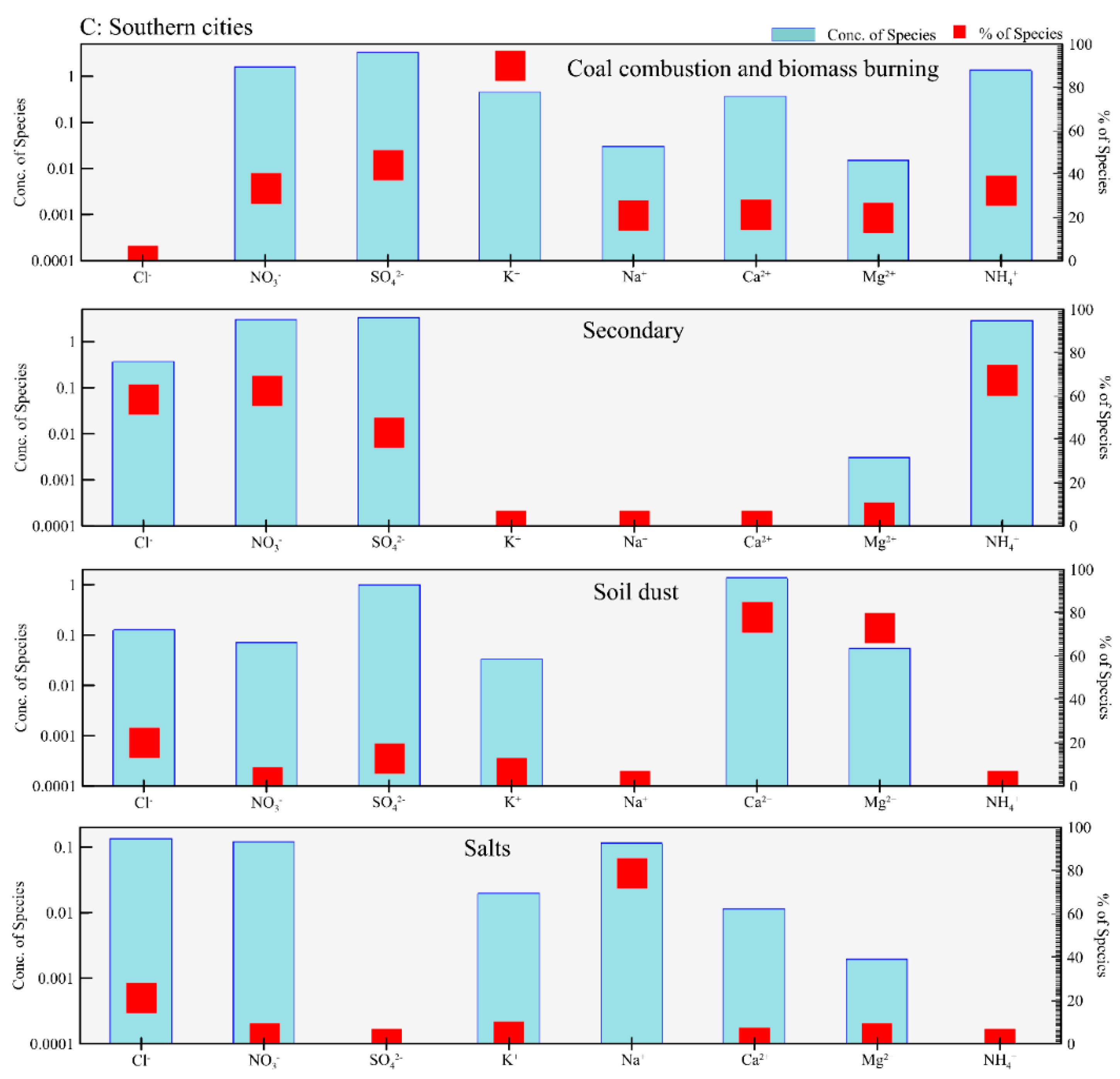
3.2. Source Apportionment of Cl− in PM2.5
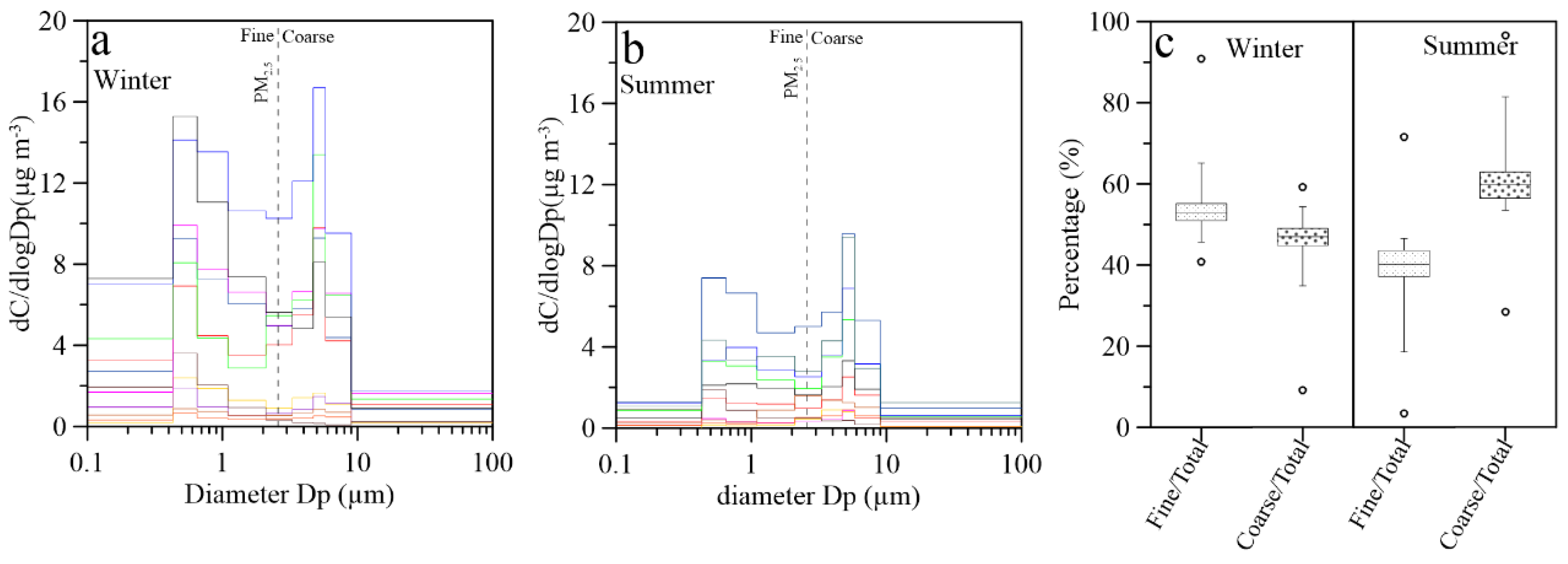
3.3. Size Distributions of Aerosol Cl−: A Review
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hönninger, G.; Platt, U. Observations of BrO and its vertical distribution during surface ozone depletion at Alert. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 2481–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, G.; Gantt, B.; Schwede, D.; Foley, K.; Mathur, R.; Saiz-Lopez, A. Impact of Enhanced Ozone Deposition and Halogen Chemistry on Tropospheric Ozone over the Northern Hemisphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 9203–9211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, W.R.; Von Glasow, R.; Riedel, K.; Anderson, P.; Ariya, P.; Bottenheim, J.; Burrows, J.; Carpenter, L.J.; Fries, U.; Goodsite, M.E.; et al. Halogens and their role in polar boundary-layer ozone depletion. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 4375–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiz-Lopez, A.; Von Glasow, R. Reactive halogen chemistry in the troposphere. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 6448–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherwen, T.; Schmidt, J.A.; Evans, M.J.; Carpenter, L.J.; Großmann, K.; Eastham, S.D.; Jacob, D.J.; Dix, B.; Koenig, T.K.; Sinreich, R.; et al. Global impacts of tropospheric halogens (Cl, Br, I) on oxidants and composition in GEOS-Chem. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 12239–12271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, A.T.; Goldberger, L.; Jahl, L.; Thornton, J.; Sullivan, R.C. Production of N2O5 and ClNO2 through Nocturnal Processing of Biomass-Burning Aerosol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, S.; Savarino, J.; Frey, M.M.; Yan, N.; Bekki, S.; Bottenheim, J.W.; Martins, J.M.F. Tracing the Origin and Fate of NOx in the Arctic Atmosphere Using Stable Isotopes in Nitrate. Science 2008, 322, 730–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altieri, K.E.; Hastings, M.G.; Gobel, A.R.; Peters, A.J.; Sigman, D.M. Isotopic composition of rainwater nitrate at Bermuda: The influence of air mass source and chemistry in the marine boundary layer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 11304–11316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keene, W.C.; Savoie, D.L. The pH of deliquesced sea-salt aerosol in polluted marine air. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 2181–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Glasow, R.; Sander, R. Variation of sea salt aerosol pH with relative humidity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gao, Y. Acidic species and chloride depletion in coarse aerosol particles in the US east coast. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 407, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskins, J.D.; Jaeglé, L.; Shah, V.; Lee, B.H.; Lopez-Hilfiker, F.D.; Campuzano-Jost, P.; Schroder, J.C.; Day, D.A.; Guo, H.; Sullivan, A.P.; et al. Wintertime Gas-Particle Partitioning and Speciation of Inorganic Chlorine in the Lower Troposphere Over the Northeast United States and Coastal Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 12897–12916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasakawa, M.; Uematsu, M. Relative contribution of chemical composition to acidification of sea fog (stratus) over the northern North Pacific and its marginal seas. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Yao, X.H.; Gao, H.W.; Hsu, S.C.; Li, J.W.; Kao, S.J. Nitrogen speciation in various types of aerosols in spring over the northwestern Pacific Ocean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, C.; Spivack, A.J.; Wahlen, M.; Pszenny, A.A.P. Chlorine isotopic composition of marine aerosols: Implications for the release of reactive chlorine and HCl cycling rates. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 3831–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, G.; Wassenaar, L.I. The stable isotopic composition (37Cl/35Cl) of dissolved chloride in rainwater. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keene, W.C.; Khalil, M.A.K.; Erickson, D.J.; McCulloch, A.; Graedel, T.E.; Lobert, J.M.; Aucott, M.L.; Gong, S.L.; Harper, D.B.; Kleiman, G.; et al. Composite global emissions of reactive chlorine from anthropogenic and natural sources: Reactive Chlorine Emissions Inventory. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1999, 104, 8429–8440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Jing, J.; Tao, J.; Hsu, S.-C.; Wang, G.; Cao, J.; Lee, C.S.L.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y. Chemical characterization and source apportionment of PM2.5 in Beijing: Seasonal perspective. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 7053–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, T.J.; Yokelson, R.J.; Cárdenas, B.; Molina, L.T.; Engling, G.; Hsu, S.-C. Trace gas and particle emissions from domestic and industrial biofuel use and garbage burning in central Mexico. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 565–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wu, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, R.; Lin, H.; Zhang, X.; Kao, S.-J. Origins of aerosol nitrate in Beijing during late winter through spring. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seuzaret, C.; Gong, S.L.; Erickson, D.J.; Keene, W.C. A general circulation model based calculation of HCl and ClNO2 production from sea salt dechlorination: Reactive Chlorine Emissions Inventory. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1999, 104, 8347–8372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobert, J.M.; Yevich, R.; Keene, W.C.; Logan, J.A. Global chlorine emissions from biomass burning: Reactive Chlorine Emissions Inventory. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1999, 104, 8373–8389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liss, P.S.; Johnson, M.T. Ocean-Atmosphere Interactions of Gases and Particles; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA; Dordrecht, Netherlands; London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhuang, G.; Yuan, H.; Rahn, K.A.; Wang, Z.; An, Z. Aerosol Particles from Dried Salt-Lakes and Saline Soils Carried on Dust Storms over Beijing. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2009, 20, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmelle, P.; Stix, J.; Bourque, C.P.-A.; Baxter, P.J.; Garcia-Alvarez, J.; Barquero, J. Dry Deposition and Heavy Acid Loading in the Vicinity of Masaya Volcano, a Major Sulfur and Chlorine Source in Nicaragua. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1289–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, M.A.; Spivack, A.J. The Stable-Chlorine Isotope Compositions of Natural and Anthropogenic Materials. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 2004, 55, 231–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yuan, H.; Zhuang, G.; Hao, Z. Long-term monitoring and source apportionment of PM2.5/PM10 in Beijing, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 1323–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galon-Negru, A.G.; Olariu, R.I.; Arsene, C. Chemical characteristics of size-resolved atmospheric aerosols in Iasi, north-eastern Romania: Nitrogen-containing inorganic compounds control aerosol chemistry in the area. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 5879–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsene, C.; Olariu, R.I.; Zarmpas, P.; Kanakidou, M.; Mihalopoulos, N. Ion composition of coarse and fine particles in Iasi, north-eastern Romania: Implications for aerosols chemistry in the area. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 906–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokelson, R.J.; Burling, I.R.; Urbanski, S.P.; Atlas, E.L.; Adachi, K.; Buseck, P.R.; Wiedinmyer, C.; Akagi, S.K.; Toohey, D.W.; Wold, C.E.; et al. Trace gas and particle emissions from open biomass burning in Mexico. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 6787–6808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Engling, G.; He, K.-B.; Duan, F.-K.; Ma, Y.-L.; Du, Z.-Y.; Liu, J.-M.; Zheng, M.; Weber, R.J. Biomass burning contribution to Beijing aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 7765–7781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cheng, M.; Ji, D.; Liu, Z.; Hu, B.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y. Characterization of submicron particles during biomass burning and coal combustion periods in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Wang, F. Aerosol characterization over the North China Plain: Haze life cycle and biomass burning impacts in summer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 2508–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duce, R.A.; Laroche, J.; Altieri, K.; Arrigo, K.R.; Baker, A.R.; Capone, D.G.; Cornell, S.; Dentener, F.; Galloway, J.; Ganeshram, R.S.; et al. Impacts of Atmospheric Anthropogenic Nitrogen on the Open Ocean. Science 2008, 320, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.-W.; Lee, K.; Najjar, R.G.; Jeong, H.-D.; Jeong, H.J. Increasing N Abundance in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean Due to Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition. Science 2011, 334, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, W.; Tang, A.; Shen, J.; Cui, Z.; Vitousek, P.; Erisman, J.W.; Goulding, K.; Christie, P.; et al. Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China. Nature 2013, 494, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elser, J.J.; Andersen, T.; Baron, J.S.; Bergström, A.-K.; Jansson, M.; Kyle, M.; Nydick, K.R.; Steger, L.; Hessen, D.O. Shifts in Lake N:P Stoichiometry and Nutrient Limitation Driven by Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition. Science 2009, 326, 835–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovett, G.M.; Likens, G.E.; Buso, D.C.; Driscoll, C.T.; Bailey, S.W. The biogeochemistry of chlorine at Hubbard brook, New Hampshire, USA. Biogeochemistry 2005, 72, 191–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalá, F.J.; Custodio, E.; Alcala, F. Atmospheric chloride deposition in continental Spain. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 3636–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orehova, T.; Vasileva, T. Evaluation of the atmospheric chloride deposition in the Danube hydrological zone of Bulgaria. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, P.; Crosbie, R. Mapping the spatial distribution of chloride deposition across Australia. J. Hydrol. 2018, 561, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubzova, M.; Krivy, V.; Kreislova, K. Influence of Chloride Deposition on Corrosion Products. Procedia Eng. 2017, 192, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Fuente, D.; Díaz, I.; Alcántara, J.; Chico, B.; Simancas, J.; Llorente, I.; García-Delgado, A.; Jiménez, J.A.; Adeva, P.; Morcillo, M. Corrosion mechanisms of mild steel in chloride-rich atmospheres. Mater. Corros. 2016, 67, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, F. Corrosion of low carbon steel in atmospheric environments of different chloride content. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Han, E.; Ke, W. Introduction to atmospheric corrosion research in China. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2007, 8, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.-C.; Gong, G.-C.; Shiah, F.-K.; Hung, C.-C.; Kao, S.-J.; Zhang, R.; Chen, W.-N.; Chen, C.-C.; Chou, C.C.-K.; Lin, Y.-C.; et al. Sources, solubility, and acid processing of aerosol iron and phosphorous over the South China Sea: East Asian dust and pollution outflows vs. Southeast Asian biomass burning. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2014, 14, 21433–21472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, G.; Duvall, R. Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) 5.0 Fundamentals & User Guide; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Zhou, L.; Kim, E.; Hopke, P.K.; Stanier, C.; Pandis, S. Mining airborne particulate size distribution data by positive matrix factorization. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sheesley, R.J.; Schauer, J.J.; Lewandowski, M.; Jaoui, M.; Offenberg, J.H.; Kleindienst, T.E.; Edney, E.O. Source apportionment of primary and secondary organic aerosols using positive matrix factorization (PMF) of molecular markers. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5567–5574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Wu, J.; Yu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, L.; Di, Y. Seasonal variations and size distributions of water-soluble ions in atmospheric aerosols in Beijing, 2012. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 34, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.-J.; Shen, Z.-X.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Lee, S.-C.; Tie, X.-X.; Ho, K.-F.; Wang, G.-H.; Han, Y.-M. Winter and summer PM2.5 chemical compositions in fourteen Chinese cities. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2012, 62, 1214–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.-F.; Cao, J.-J.; Han, Y.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, M.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Tang, G.; Hu, B.; et al. The heaviest particulate air-pollution episodes occurred in northern China in January, 2013: Insights gained from observation. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira-Filho, M.; Pedrotti, J.J.; Fornaro, A. Water-soluble ions species of size-resolved aerosols: Implications for the atmospheric acidity in São Paulo megacity, Brazil. Atmos. Res. 2016, 181, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhao, J.; Ling, Z.; Hong, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, M.; Wei, X. Modeling the impact of chlorine emissions from coal combustion and prescribed waste incineration on tropospheric ozone formation in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 2709–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, T.; Xia, M.; Gao, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, N.; Gao, Y.; Lee, S.; Wang, X.; Xue, L.; et al. Abundance and origin of fine particulate chloride in continental China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, G.; Zhou, B.; Cheng, C.; Cao, J.; Shen, Z.; An, Z. Chemical composition and size distribution of wintertime aerosols in the atmosphere of Mt. Hua in central China. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Cao, J.; Ho, K.; He, Y. Chemical characterization of aerosol collected at Mt. Yulong in wintertime on the southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Res. 2012, 107, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-N.; Wang, Y.-S.; Wen, T.-X.; Yang, Y.-J.; Li, W. Observation and analysis on water-soluble inorganic chemical compositions of atmospheric aerosol in Gongga Mountain. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2009, 30, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.-N.; Wang, Y.-S.; Wen, T.-X.; Dai, G.-H. Seasonal variation of water-soluble ions in PM2.5 at Changbai Mountain. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2014, 35, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Yu, X.; Fang, X.; Wu, F.; Li, X. A study of aerosol at regional background stations and baseline station. Q. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1996, 7, 396–405. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, S.C.; Liu, S.C.; Huang, Y.T.; Chou, C.C.K.; Lung, S.C.C.; Liu, T.H.; Tu, J.Y.; Tsai, F. Long-range southeastward transport of asian biosmoke pollution: Signature detected by aerosol potassium in northern taiwan-article no. d14301. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.J.; Lee, Y.; Orsini, D.A.; Maxwell-Meier, K.; Thornton, D.C.; Bandy, A.R.; Clarke, A.D.; Sachse, G.W.; Fuelberg, H.E.; Kiley, C.M.; et al. Characteristics and influence of biosmoke on the fine-particle ionic composition measured in Asian outflow during the Transport and Chemical Evolution Over the Pacific (TRACE-P) experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2003, 108, 8816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldman, J.; Lioy, P.; Zelenka, M.; Jing, L.; Lin, Y.; He, Q.; Qian, Z.; Chapman, R.; Wilson, W. Wintertime measurements of aerosol acidity and trace elements in Wuhan, a city in central China. Atmos. Environ. Part B Urban Atmos. 1991, 25, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, P.; Guo, J.; Han, J.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, M. Role of chlorine in ultrafine particulate matter formation during the combustion of a blend of high-Cl coal and low-Cl coal. Fuel 2016, 184, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Kong, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, W.; Wu, J.; Zheng, M.; Zheng, S.; Yang, G.; Wu, F. Emission inventory of water soluble ions in fine particles from residential coal burning in China and implication for emission reduction. China Environ. Sci. 2017, 37, 3708–3721. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chester, R. Marine Geochemistry; Cambridge Univercity Press: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.; Sun, J.; Cao, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Lei, Y.; Gao, J.; Huang, R.-J.; Liu, S.; Huang, Y.; et al. Chemical profiles of urban fugitive dust PM 2.5 samples in Northern Chinese cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantara, S.; Thepnuan, D.; Wiriya, W.; Prawan, S.; Tsai, Y.I. Emissions of pollutant gases, fine particulate matters and their significant tracers from biomass burning in an open-system combustion chamber. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lei, Y.; Huang, Y.; Niu, X.; Xu, H.; Cao, J.; Ho, S.S.H.; et al. Characterization of PM2.5 source profiles from typical biomass burning of maize straw, wheat straw, wood branch, and their processed products (briquette and charcoal) in China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 205, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Zhang, X.; Gong, S.; Zheng, F. Investigation on emission factors of particulate matter and gaseous pollutants from crop residue burning. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Ju, Y.; Wang, G.; Alvarado, E.C.; Yang, X.; Ma, Y.; Liu, A. Inorganic chemical composition of PM2.5 emissions from the combustion of six main tree species in subtropical China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 189, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Bi, X.; Song, W.; Li, T.; Liu, B.; Ding, J.; Xu, J.; Song, C.; Yang, N.; Schulze, B.C.; et al. Residential coal combustion as a source of primary sulfate in Xi’an, China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 196, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y. Research on Layer Burning Industrial Boiler PM2.5 Emissions Characteristics. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 2012. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Huang, C.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Lou, S.; Qiao, L.; Wang, H. Chemical Composition Characteristics of PM2. 5 Emitted by Medium and Small Capacity Coal-fired Boilers in the Yangtze River Delta Region. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 1493–1501. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Bi, X.; Zhang, G.; Huang, B.; Lin, Q.; Wang, X.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J. The chemical composition and stable carbon isotope characteristics of particulate matter from the residential honeycomb coal briquettes combustion. Geochimica 2014, 43, 640–646. [Google Scholar]
- Oris, C.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yu, C. Forms of potassium and chlorine from oxy-fuel co-combustion of lignite coal and corn stover. Carbon Resour. Convers. 2019, 2, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, F.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J. Characterization of water-soluble inorganic ions in size-segregated aerosols in coastal city, Xiamen. Atmos. Res. 2011, 99, 546–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tong, L.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, H.; He, M.; Dai, X.; Zheng, J.; Xiao, H. Seasonal variation and size distributions of water-soluble inorganic ions and carbonaceous aerosols at a coastal site in Ningbo, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, L.; Ji, D.; Wen, T.; Pan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y. Characterization of the size-segregated water-soluble inorganic ions in the Jing-Jin-Ji urban agglomeration: Spatial/temporal variability, size distribution and sources. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, B.; Shen, L.; Xu, H.; An, J.; Xue, G.; Cao, J. Water-soluble ions in atmospheric aerosols measured in five sites in the Yangtze River Delta, China: Size-fractionated, seasonal variations and sources. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 123, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Hu, B.; Wen, T.; Xin, J.; Li, X.; Wang, Y. Size-resolved aerosol water-soluble ions during the summer and winter seasons in Beijing: Formation mechanisms of secondary inorganic aerosols. Chemosphere 2017, 183, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wen, T.; Ji, D.; Wang, Y. Seasonal variation and secondary formation of size-segregated aerosol water-soluble inorganic ions during pollution episodes in Beijing. Atmos. Res. 2016, 168, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Yan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Liu, J.; Di, Y.; Du, Z.; Wu, D. Seasonal variations and size distributions of water-soluble ions of atmospheric particulate matter at Shigatse, Tibetan Plateau. Chemosphere 2016, 145, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wen, T.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y. Chemical composition and size distribution of airborne particulate matters in Beijing during the 2008 Olympics. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 50, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.-C.; Liu, S.C.; Kao, S.-J.; Jeng, W.-L.; Huang, Y.-T.; Tseng, C.-M.; Tsai, F.; Tu, J.-Y.; Yang, Y. Water-soluble species in the marine aerosol from the northern South China Sea: High chloride depletion related to air pollution. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.H.; Huang, Y.; Tao, J.; Ren, Y.Q.; Wu, F.; Cheng, C.L.; Meng, J.J.; Li, J.J.; Cheng, Y.T.; Cao, J.J.; et al. Evolution of aerosol chemistry in Xi’an, inland China during the dust storm period of 2013—Part 1: Sources, chemical forms and formation mechanisms of nitrate and sulfate. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 11571–11585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.B.; Flensborg, J.P.; Shoulaifar, T.K.; Sárossy, Z.; Hansen, B.B.; Egsgaard, H.; DeMartini, N.; Jensen, P.A.; Glarborg, P.; Dam-Johansen, K. Release of Chlorine and Sulfur during Biomass Torrefaction and Pyrolysis. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 3738–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayton, D.C.; Belle-Oudry, D.; Nordin, A. Effect of Coal Minerals on Chlorine and Alkali Metals Released during Biomass/Coal Cofiring. Energy Fuels 1999, 13, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.H.; Liang, L.W.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, Z.B. Dynamic analysis of PM2.5 spatial-temporal characteristics in China. Resour. Sci. 2017, 39, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Liu, J.; Froyd, K.D.; Roberts, J.M.; Veres, P.R.; Hayes, P.L.; Jimenez, J.L.; Nenes, A.; Weber, R.J. Fine particle pH and gas–particle phase partitioning of inorganic species in Pasadena, California, during the 2010 CalNex campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5703–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
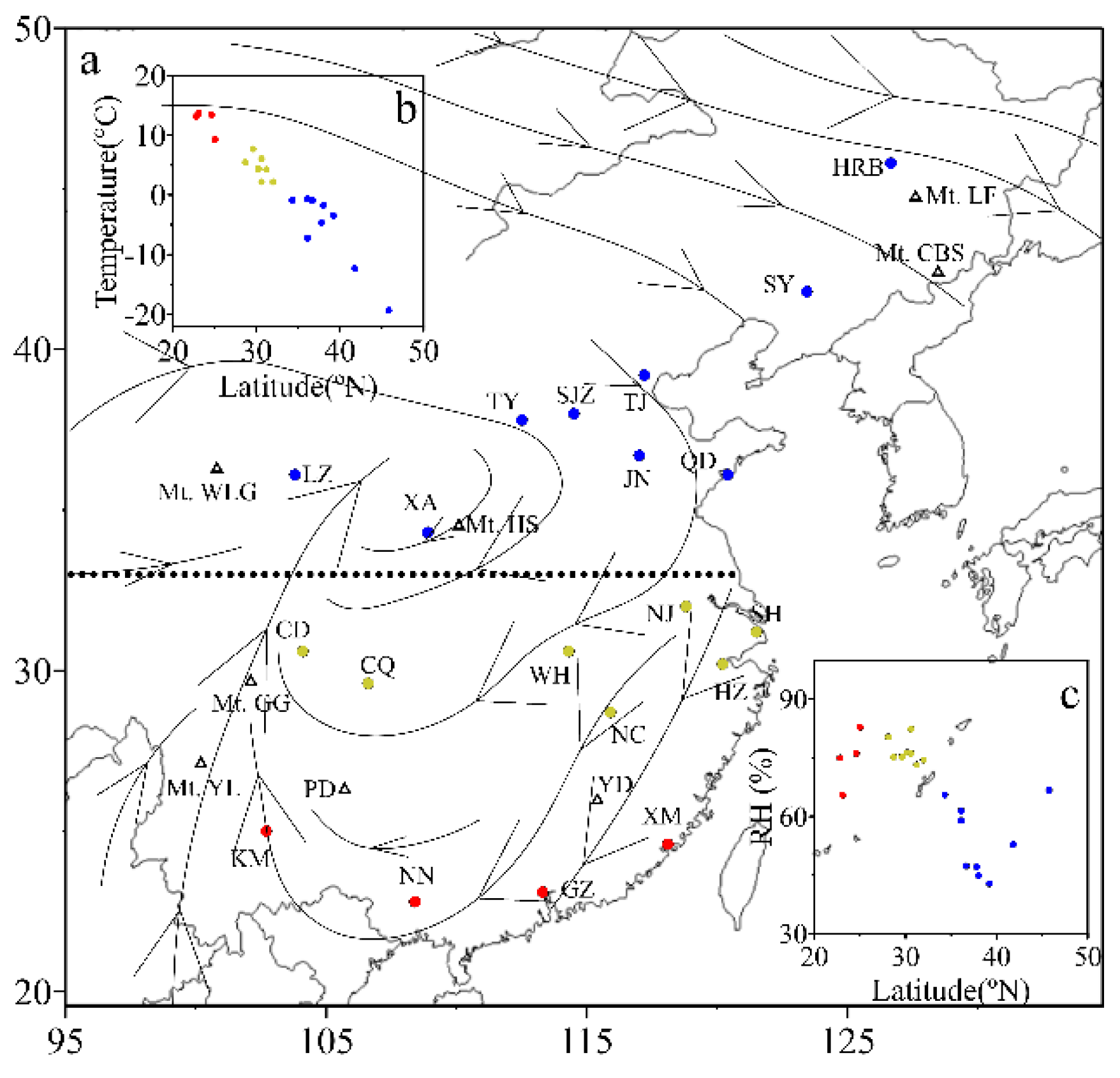
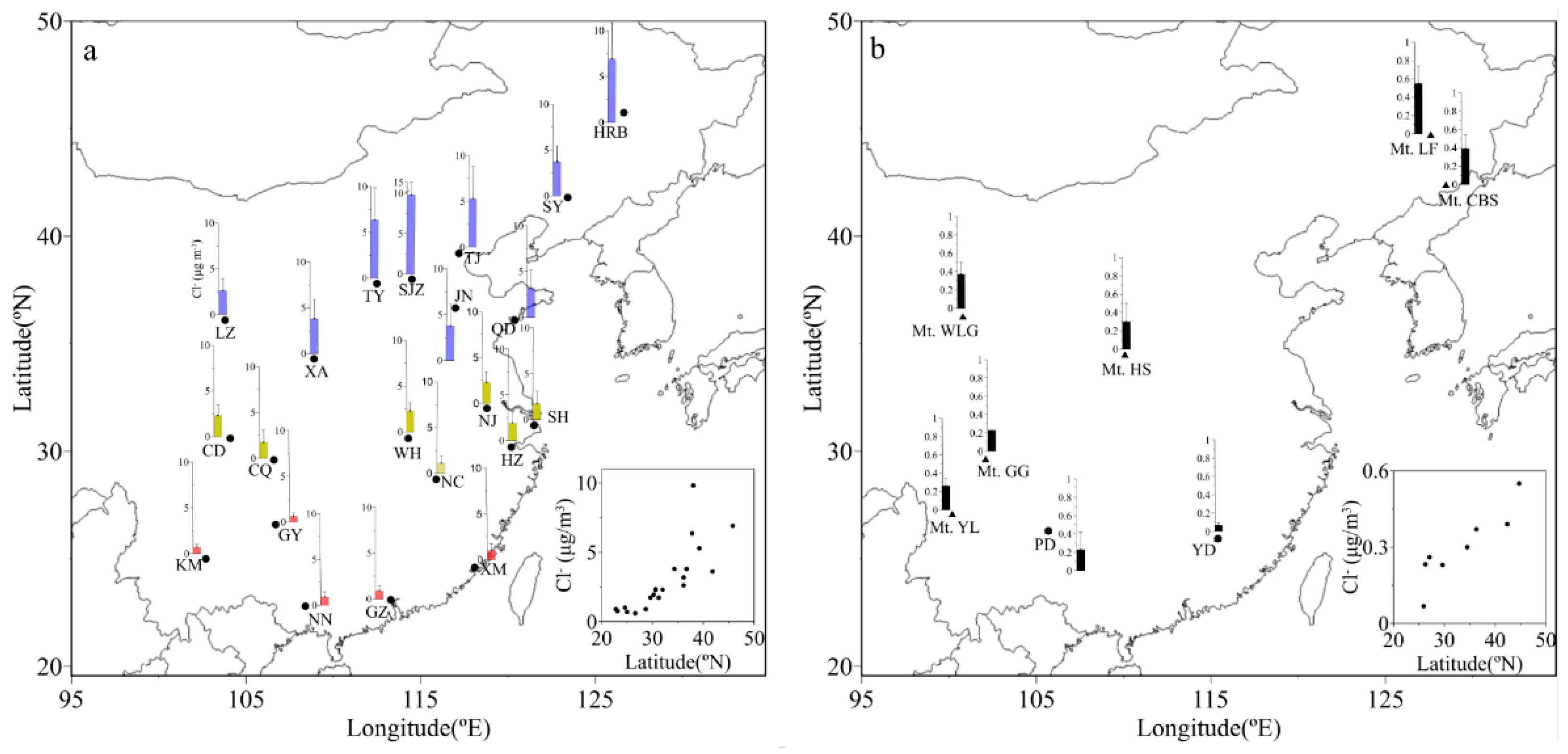
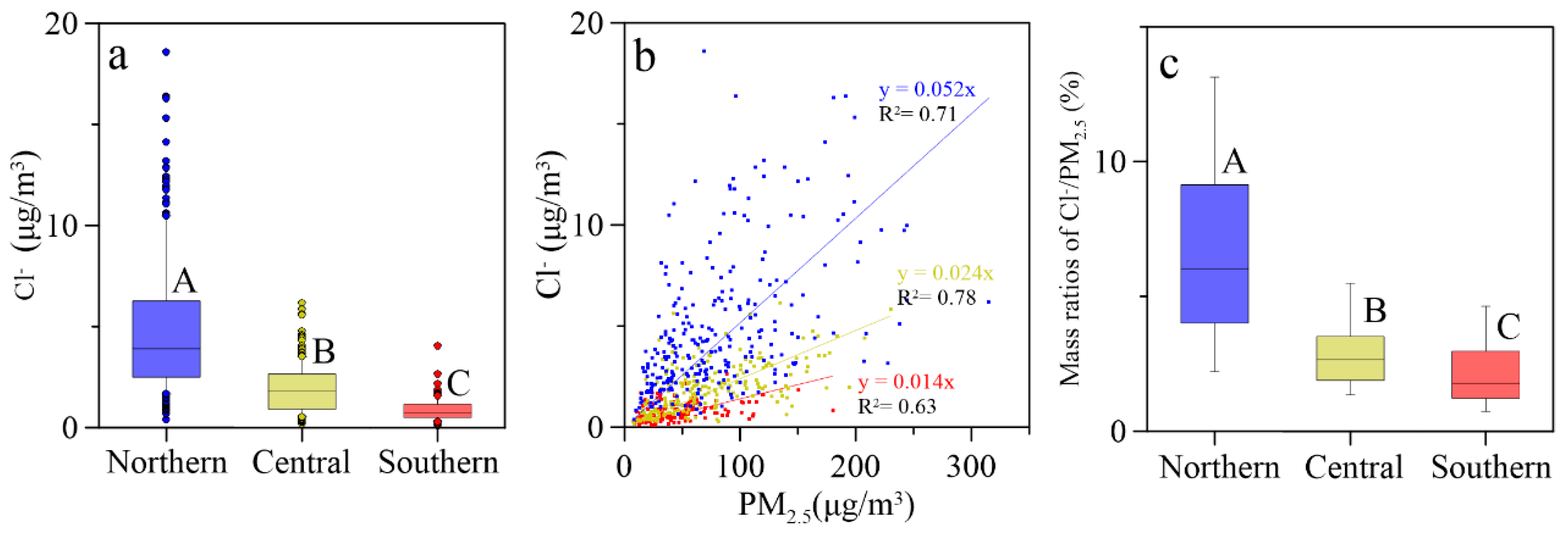
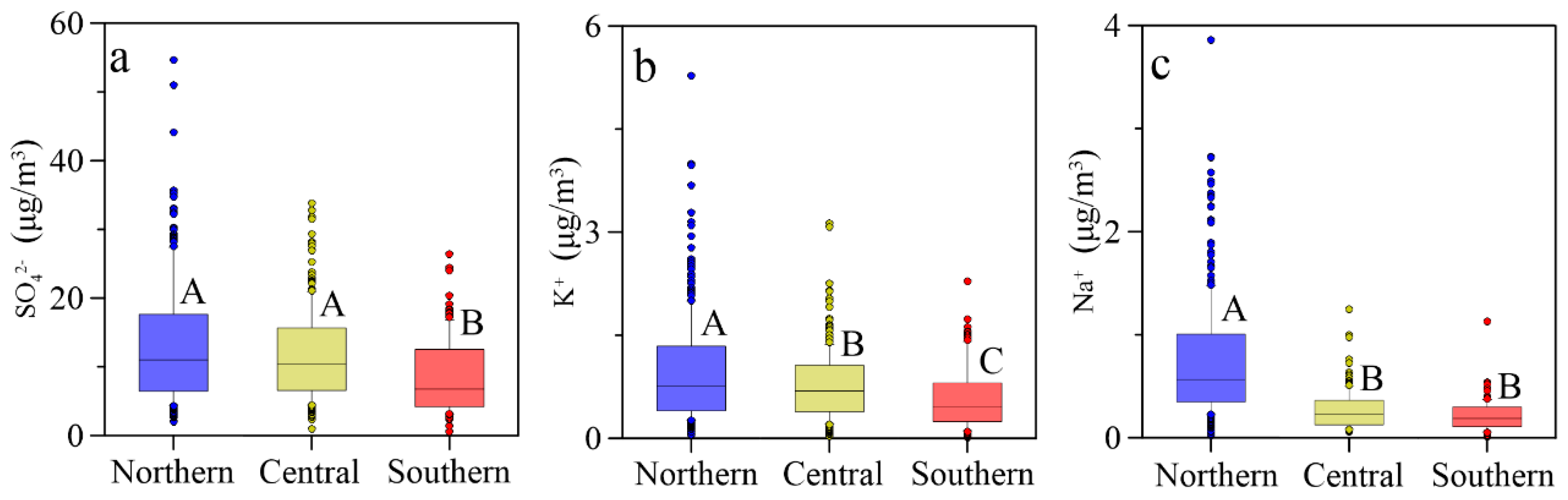

| Locations | Min | Max | Median | Mean 1 | Mean 2 | Mean 3 | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harbin (HRB) | 1.15 | 18.6 | 6.77 | 6.91 | 5.78 | 6.65 | 3.94 |
| Shenyang (SY) | 1.00 | 7.24 | 3.57 | 3.73 | 3.34 | 3.72 | 1.69 |
| Tianjin (TJ) | 0.39 | 16.4 | 4.30 | 5.29 | 4.19 | 5.24 | 3.53 |
| Shijiazhuang (SJZ) | 1.29 | 26.7 | 9.46 | 9.81 | 8.44 | 9.7 | 5.20 |
| Taiyuan (TY) | 1.21 | 12.4 | 5.98 | 6.37 | 5.38 | 6.3 | 3.48 |
| Ji’nan (JN) | 0.84 | 10.44 | 3.12 | 3.79 | 3.21 | 3.64 | 2.36 |
| Qingdao (QD) | 0.99 | 9.77 | 2.65 | 3.18 | 2.74 | 3.17 | 1.95 |
| Xi’an (XA) | 1.08 | 10.5 | 3.18 | 3.80 | 3.34 | 3.74 | 2.14 |
| Lanzhou (LZ) | 0.67 | 5.23 | 2.73 | 2.62 | 2.27 | 2.61 | 1.30 |
| Shanghai (SH) | 0.17 | 5.61 | 1.30 | 1.73 | 1.29 | 1.73 | 1.41 |
| Nanjing (NJ) | 0.69 | 5.83 | 2.11 | 2.30 | 2.05 | 2.29 | 1.14 |
| Hangzhou (HZ) | 0.42 | 4.75 | 1.91 | 1.94 | 1.55 | 1.92 | 1.24 |
| Nanchang (NC) | 0.27 | 3.37 | 0.95 | 1.13 | 0.90 | 1.05 | 0.79 |
| Wuhan (WH) | 0.28 | 4.60 | 2.12 | 2.27 | 2.07 | 2.13 | 0.88 |
| Chongqing (CQ) | 0.32 | 6.14 | 1.56 | 1.73 | 1.28 | 1.72 | 1.34 |
| Chengdu (CD) | 0.42 | 4.52 | 2.39 | 2.32 | 1.96 | 2.32 | 1.17 |
| Kunming (KM) | 0.26 | 1.55 | 0.63 | 0.69 | 0.63 | 0.69 | 0.31 |
| Nanning (NN) | 0.24 | 2.63 | 0.78 | 0.90 | 0.76 | 0.90 | 0.54 |
| Guangzhou (GZ) | 0.11 | 1.83 | 0.66 | 0.76 | 0.59 | 0.76 | 0.52 |
| Xiamen (XM) | 0.13 | 4.02 | 0.93 | 1.01 | 0.83 | 1.01 | 0.70 |
| Locations | Types | Min | Max | Mean | SD | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yudu (YD) | PM2.5 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.02 | This study |
| Puding (PD) | PM2.5 | 0.03 | 0.61 | 0.23 | 0.19 | This study |
| Mt. Hua (HS) | PM10 | 0.3 | 0.2 | [59] | ||
| Mt. Yulong (YL) | TSP | 0.13 | 0.46 | 0.26 | 0.08 | [60] |
| Mt. Gongga (GG) | PM2.5 | 0.03 | 0.52 | 0.17 | - | [61] |
| Mt. Gongga (GG) | PM10 | 0.05 | 1.13 | 0.26 | - | [61] |
| Mt. changbai (CBS) | PM2.5 | - | - | 0.39 | 0.15 | [62] |
| Mt. Longfeng (LF) | TSP | - | - | 0.55 | 0.19 | [63] |
| Mt. Waliguan (WLG) | TSP | - | - | 0.37 | 0.13 | [63] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, L.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Xiao, H.-Y.; Xiao, H.-W.; Zheng, N.-J.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Xie, Y.-J.; Liu, C. Spatial Distributions and Sources of Inorganic Chlorine in PM2.5 across China in Winter. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090505
Luo L, Zhang Y-Y, Xiao H-Y, Xiao H-W, Zheng N-J, Zhang Z-Y, Xie Y-J, Liu C. Spatial Distributions and Sources of Inorganic Chlorine in PM2.5 across China in Winter. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(9):505. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090505
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Li, Yong-Yun Zhang, Hua-Yun Xiao, Hong-Wei Xiao, Neng-Jian Zheng, Zhong-Yi Zhang, Ya-Jun Xie, and Cheng Liu. 2019. "Spatial Distributions and Sources of Inorganic Chlorine in PM2.5 across China in Winter" Atmosphere 10, no. 9: 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090505
APA StyleLuo, L., Zhang, Y.-Y., Xiao, H.-Y., Xiao, H.-W., Zheng, N.-J., Zhang, Z.-Y., Xie, Y.-J., & Liu, C. (2019). Spatial Distributions and Sources of Inorganic Chlorine in PM2.5 across China in Winter. Atmosphere, 10(9), 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090505





