Possible Impacts of Snow Darkening Effects on the Hydrological Cycle over Western Eurasia and East Asia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
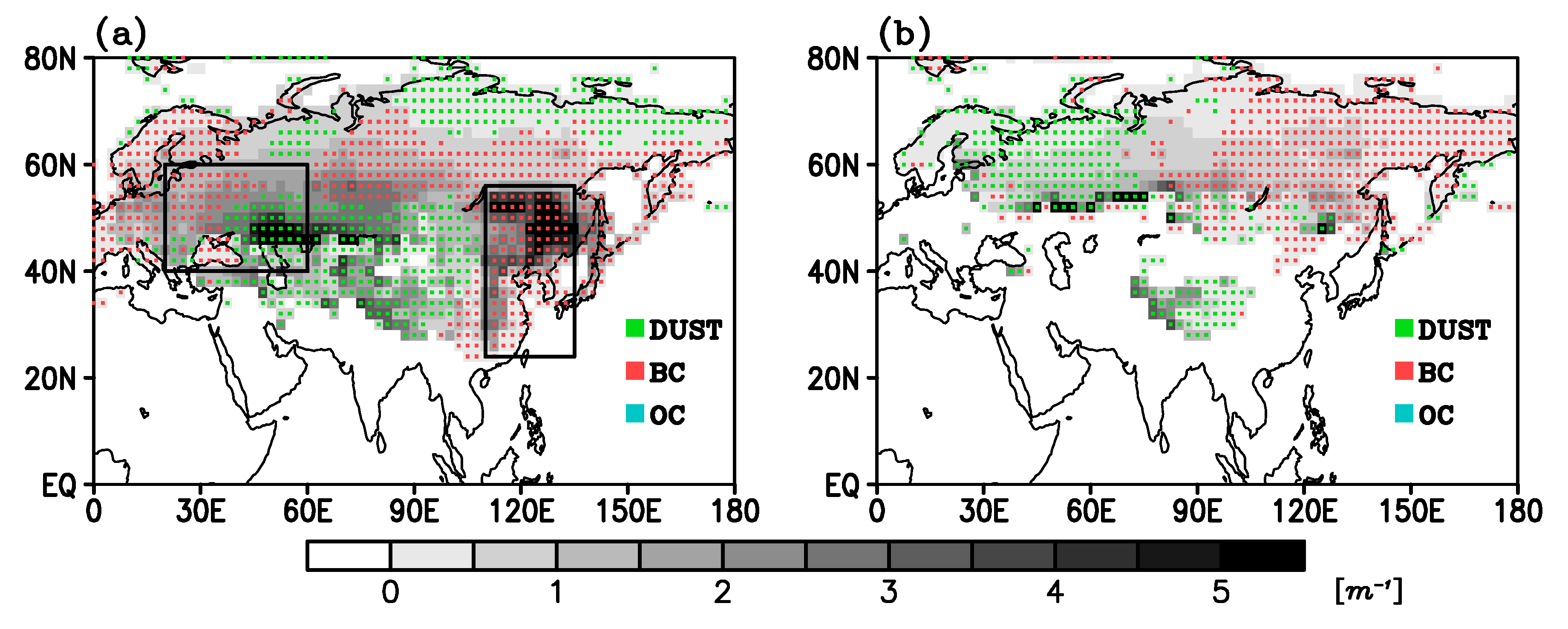
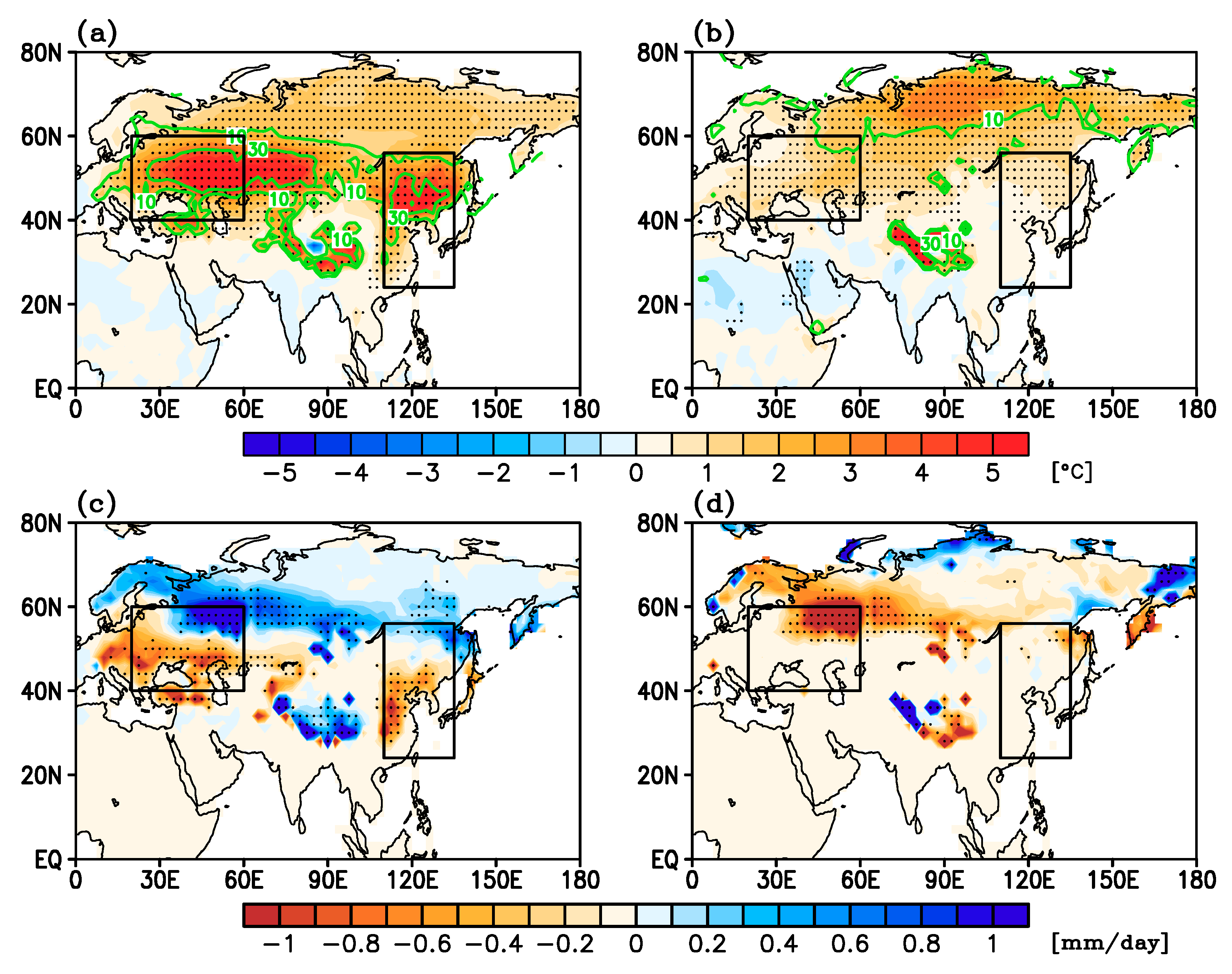
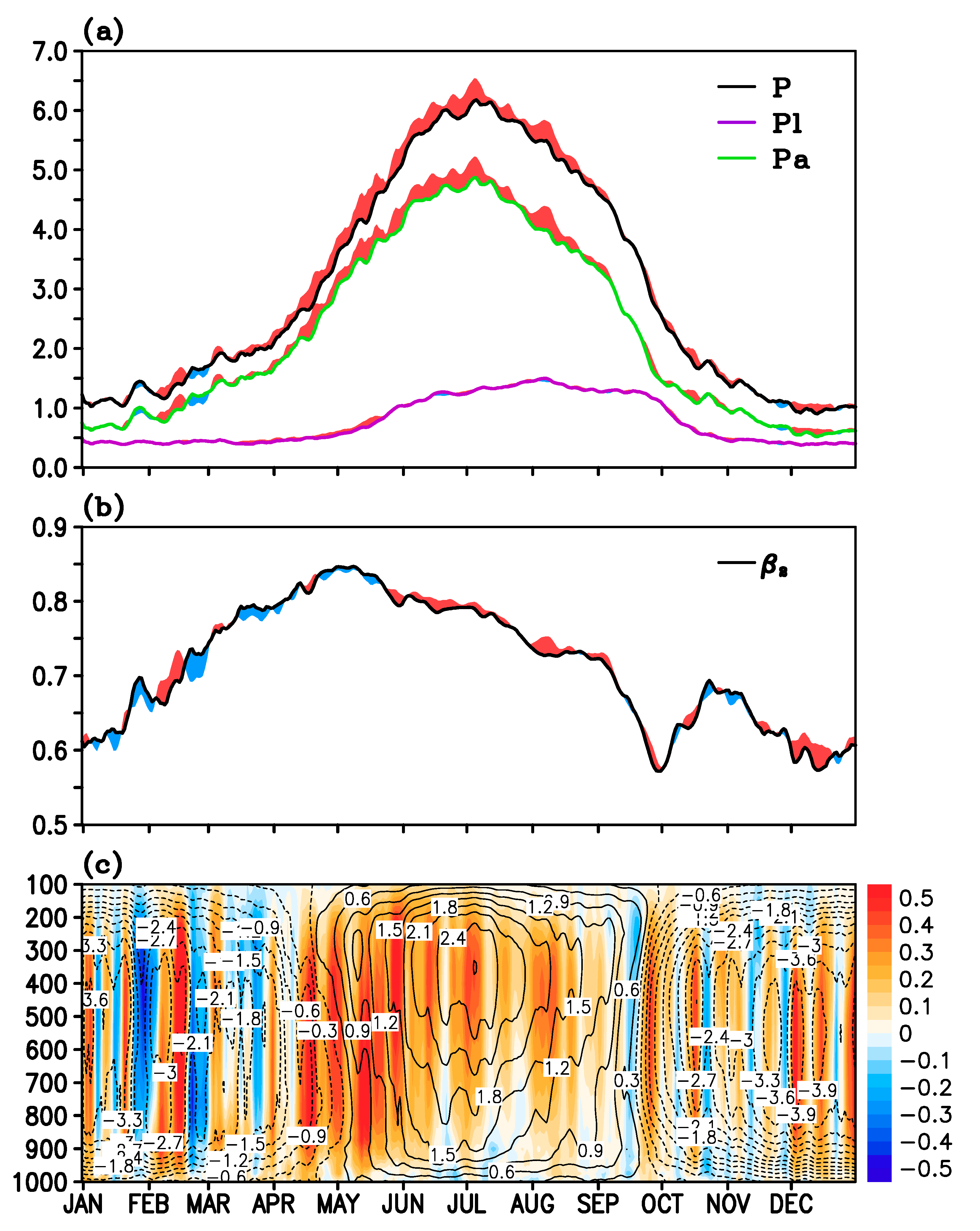
3.1. Forcing and Responses by SDE
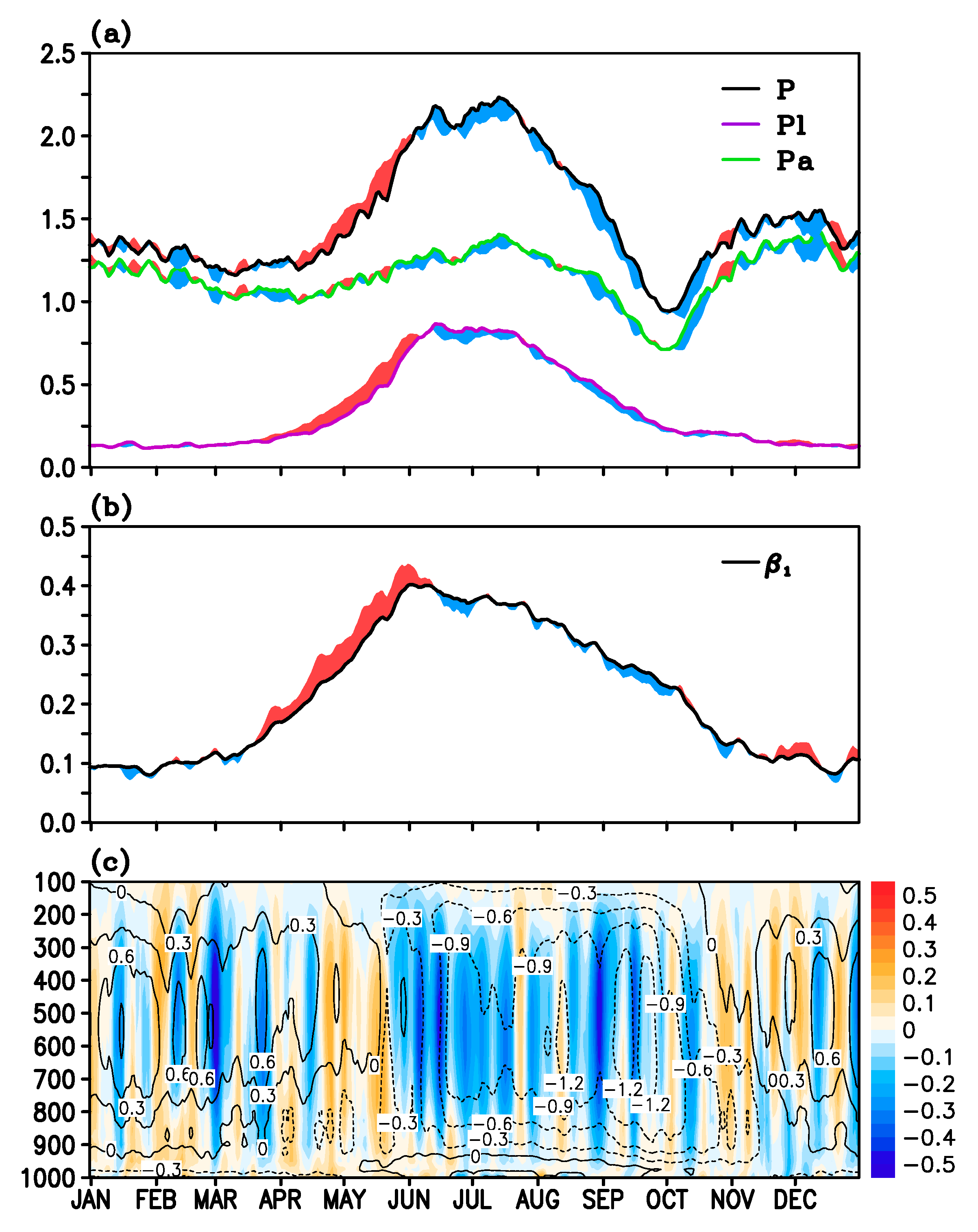
3.2. Changes in Western Eurasia (
3.3. Changes in East Asia (
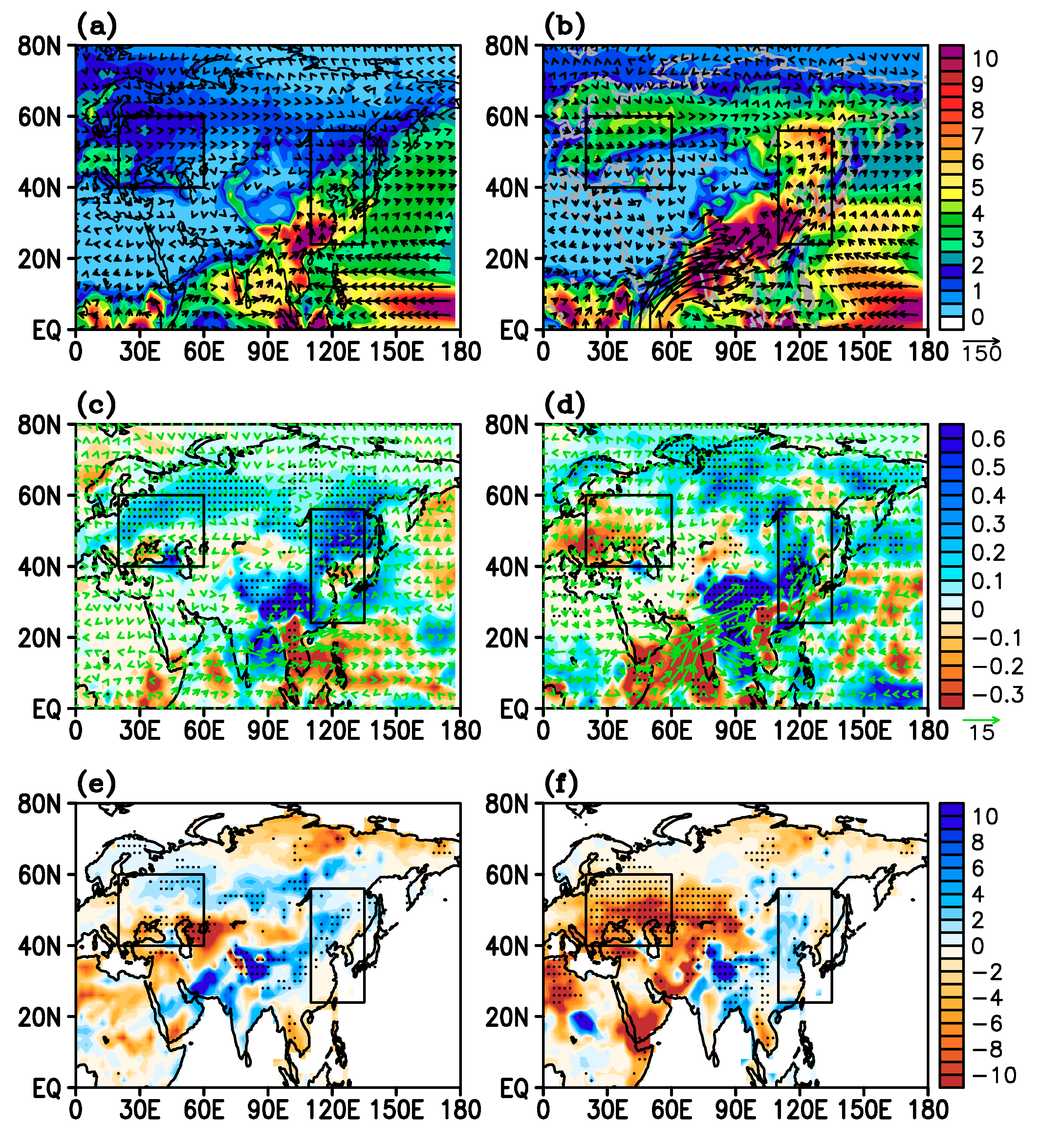
3.4. Changes in Atmospheric Circulations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lau, K.M.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, K.M. Asian summer monsoon anomalies induced by aerosol direct forcing: The role of the Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Dyn. 2006, 26, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Lau, W.K.M.; Kim, K.M.; Sang, J.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, W.S. Amplification of ENSO effects on Indian summer monsoon by absorbing aerosols. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 2657–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanner, M.G.; Zender, C.S.; Hess, P.G.; Mahowald, N.M.; Painter, T.H.; Ramanathan, V.; Rasch, P.J. Springtime warming and reduced snow cover from carbonaceous particles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2009, 8, 19819–19859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinoj, V.; Rasch, P.J.; Wang, H.; Yoon, J.; Ma, P.; Landu, K.; Singh, B. Short-term modulation of Indian summer monsoon rainfall by West Asian dust. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanap, S.D.; Pandithurai, G. The effect of absorbing aerosols on Indian monsoon circulation and rainfall: A review. Atmos. Res. 2015, 164–165, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegen, I.; Heinold, B. Large-scale modeling of absorbing aerosols and their semi-direct effects. Atmosphere (Basel) 2018, 9, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Lau, W.K.M.; Chin, M.; Kim, K.M.; Sud, Y.C.; Walker, G.K. Atmospheric teleconnection over Eurasia induced by aerosol radiative forcing during boreal spring. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 4700–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Kim, M.K. Effects of radiative forcing by black carbon aerosol on spring rainfall decrease over Southeast Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 3739–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanner, M.G.; Zender, C.S.; Randerson, J.T.; Rasch, P.J. Present-day climate forcing and response from black carbon in snow. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D11202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiscombe, W.J.; Warren, S.G. A model for the spectral albedo of snow. I: Pure snow. J. Atmos. Sci. 1980, 37, 2712–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Penner, J.E.; Flanner, M.G.; Sillman, S.; Xu, L.; Zhou, C. Radiative forcing of organic aerosol in the atmosphere and on snow: Effects of SOA and brown carbon. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 7453–7476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasunari, T.J.; Lau, K.-M.; Mahanama, S.P.P.; Colarco, P.R.; Da Silva, A.M.; Aoki, T.; Aoki, K.; Murao, N.; Yamagata, S.; Kodama, Y. The GOddard SnoW Impurity Module (GOSWIM) for the NASA GEOS-5 Earth System Model: Preliminary Comparisons with Observations in Sapporo, Japan. Sola 2014, 10, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasunari, T.J.; Koster, R.D.; Lau, W.K.M.; Kim, K.-M. Impact of snow darkening via dust, black carbon, and organic carbon on boreal spring climate in the Earth system. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 5485–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Bhawar, R.L.; Kim, M.K.; Sang, J. Study of aerosol effect on accelerated snow melting over the Tibetan Plateau during boreal spring. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 75, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.K.M.; Sang, J.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, K.M.; Koster, R.D.; Yasunari, T.J. Impacts of Snow Darkening by Deposition of Light-Absorbing Aerosols on Hydroclimate of Eurasia During Boreal Spring and Summer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 8441–8461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.K.M.; Kim, K.-M. Impact of Snow Darkening by Deposition of Light-Absorbing Aerosols on Snow Cover in the Himalayas – Tibetan Plateau and Influence on the Asian Summer Monsoon: A Possible Mechanism for the Blanford Hypothesis. Atmosphere (Basel) 2018, 9, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, T.; Kuchiki, K.; Niwano, M.; Kodama, Y.; Hosaka, M.; Tanaka, T. Physically based snow albedo model for calculating broadband albedos and the solar heating profile in snowpack for general circulation models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painter, T.H.; Deems, J.S.; Belnap, J.; Hamlet, A.F.; Landry, C.C.; Udall, B. Response of Colorado River runoff to dust radiative forcing in snow. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2010, 107, 17125–17130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasunari, T.J.; Koster, R.D.; Lau, K.-M.; Aoki, T.; Sud, Y.C.; Yamazaki, T.; Motoyoshi, H.; Kodama, Y. Influence of dust and black carbon on the snow albedo in the NASA Goddard Earth Observing System version 5 land surface model. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D02210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; David, R. The Effect of Snow Cover on the Climate. J. Clim. 1991, 4, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, K.; Wu, R.; Liu, Y. Interdecadal change of Eurasian snow, surface temperature, and atmospheric circulation in the late 1980s. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 2738–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanford, H.F. On the Connexion of the Himalaya Snowfall with Dry Winds and Seasons of Drought in India. Proc. R. Soc. London 1884, 37, 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, D.G.; Shukla, J. An apparent relationship between Eurasian snow cover and Indian monsoon rainfall. J. Atmos. Sci. 1976, 33, 2461–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, T.P.; Dümenil, L.; Schlese, U.; Roekner, E.; Latif, M. The Effect of Eurasian Snow Cover on Regional and Global Climate Variations. J. Atmos. Sci. 1989, 46, 661–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar-Rao, M.M.; Lau, K.M.; Yang, S. On the Relationship Between Eurasian Snow Cover and the Asian Summer Monsoon. Int. J. Climatol. 1996, 16, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, T.P.; Adam, J.C.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Potential impacts of a warming climate on water availability in snow-dominated regions. Nature 2005, 438, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, J.S.; Eltahir, E.A.B. Pathways relating soil moisture conditions to future summer rainfall within a model of the land-atmosphere system. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 1227–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenegger, C.; Brockhaus, P.; Bretherton, C.S.; Schär, C. The soil moisture-precipitation feedback in simulations with explicit and parameterized convection. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 5003–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, P.J.; Heiser, M.D.; Hall, F.G. Relations between surface conductance and spectral vegetation indexes at intermediate (100m2 to 15km2) length scales. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 19033–19059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, A.K.; Ball, J.H.; Viterbo, A.C.M.B.; Miller, M.J.; Pedro, A. Viterbo The land surface-atmosphere interaction: A review based on observational and global modeling perspectives. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 7209–7225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, R.D.; Dirmeyer, P.A.; Guo, Z.; Bonan, G.; Chan, E.; Cox, P.; Gordon, C.T.; Kanae, S.; Kowalczyk, E.; Lawrence, D.; et al. Regions of Strong Coupling Between Soil Moisture and Precipitation. Science 2004, 305, 1138–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Quiring, S.M. Examining the influence of spring soil moisture anomalies on summer precipitation in the U.S. Great Plains using the Community Atmosphere Model version 3. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, T.W.; Rapp, A.D.; Quiring, S.M.; Blake, J. Soil moisture-precipitation coupling: Observations from the Oklahoma Mesonet and underlying physical mechanisms. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 3617–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E.M.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Vidale, P.L.; Lüthi, D.; Schär, C. Soil moisture-atmosphere interactions during the 2003 European summer heat wave. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 5081–5099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stéfanon, M.; Drobinski, P.; D’Andrea, F.; Lebeaupin-Brossier, C.; Bastin, S. Soil moisture-temperature feedbacks at meso-scale during summer heat waves over Western Europe. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 42, 1309–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schär, C.; Lüthi, D.; Beyerle, U.; Heise, E. The soil-precipitation feedback: A process study with a regional climate model. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 722–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boé, J. Modulation of the summer hydrological cycle evolution over western Europe by anthropogenic aerosols and soil-atmosphere interactions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 7678–7685. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, L.; Dong, W. Land-atmosphere coupling and summer climate variability over East Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Yuan, X. Multiscale Land–Atmosphere Coupling and Its Application in Assessing Subseasonal Forecasts over East Asia. J. Hydrometeorol. 2018, 19, 745–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-E.; Hong, S.-Y. Impact of Soil Moisture Anomalies on Summer Rainfall over East Asia: A Regional Climate Model Study. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 5732–5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltahir, E.A.B.; Bras, R.L. Precipitation recycling in the Amazon basin. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1994, 120, 861–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltahir, E.A.B.; Bras, R.L. Precipitation recycling. Rev. Geophys. 1996, 34, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, F.; Kumar, P. Precipitation recycling variability and ecoclimatological stability—A study using NARR Data. Part I: Central U.S. plains ecoregion. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 5165–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, R.D.; Guo, Z.; Dirmeyer, P.a.; Bonan, G.B.; Chan, E.; Cox, P.M.; Gordon, C.T.; Kanae, S.; Kowalczyk, E.; Lawrence, D.M.; et al. GLACE: The Global Land – Atmosphere Coupling Experiment. Part I: Overview. J. Hydrometeorol. 2006, 7, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirmeyer, P.A.; Schlosser, C.A.; Brubaker, K.L. Precipitation, Recycling, and Land Memory: An Integrated Analysis. J. Hydrometeorol. 2009, 10, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, C.; Wu, D. Changes in precipitation recycling over arid regions in the Northern Hemisphere. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 131, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brubaker, K.L.; Entekhabi, D.; Eagleson, P.S. Estimation of continental precipitation recycling. J. Clim. 1993, 6, 1077–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Dai, A.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Parsons, D.B. The Changing Character of Precipitation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, C.-Y.; Yong, B.; Hu, J.; Sun, Z. Understanding the Changing Characteristics of Droughts in Sudan and the Corresponding Components of the Hydrologic Cycle. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 1520–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Wang, B. Circumglobal teleconnection in the Northern Hemisphere summer. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 3483–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linderholm, H.W.; Ou, T.; Jeong, J.H.; Folland, C.K.; Gong, D.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, D. Interannual teleconnections between the summer North Atlantic Oscillation and the East Asian summer monsoon. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rienecker, M.M.; Suarez, M.J.; Todling, R.; Bacmeister, J.; Takacs, L.; Liu, H.-C.; Gu, W.; Sienkiewicz, M.; Koster, R.D.; Gelaro, R.; et al. The GEOS-5 Data Assimilation System— Documentation of Versions 5.0.1, 5.1.0, and 5.2.0; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; Volume 27, pp. 1–81.
- Ducharne, A.; Koster, R.D.; Suarez, M.J.; Stieglitz, M.; Kumar, P. A catchment-based approach to modeling land surface processes in a general circulation model: 2. Parameter estimation and model demonstration. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 823–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, R.D.; Suarez, M.J.; Ducharne, A.; Stieglitz, M.; Kumar, P. A catchment-based approach to modeling land surface processes in a general circulation model 1. Model structure. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 24809–24822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, M.; Rood, R.B.; Lin, S.-J.; Müller, J.-F.; Thompson, A.M. Atmospheric sulfur cycle simulated in the global model GOCART: Model description and global properties. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 24671–24687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randles, C.A.; Colarco, P.R.; Silva, A. Da Direct and semi-direct aerosol effects in the NASA GEOS-5 AGCM: aerosol-climate interactions due to prognostic versus prescribed aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisselink, B.; Dolman, A.J. Precipitation Recycling: Moisture Sources over Europe using ERA-40 Data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishtawal, C.M.; Gautam, G.; Jaggi, S.; Pandey, P.C. Surface-level moisture transport over the Indian Ocean during southwest monsoon months using NOAA/HIRS data. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 1994, 69, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| AM | 0.089 | 0.007 | 0.096 ** | 92.7 | 7.3 |
| JJ | −0.034 | −0.038 | −0.072 * | 47.2 | 52.8 |
| AM | 0.056 | 0.218 | 0.274 *** | 20.4 | 79.6 |
| JJ | 0.006 | 0.208 | 0.214 * | 2.8 | 97.2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sang, J.; Kim, M.-K.; Lau, W.K.M.; Kim, K.-M. Possible Impacts of Snow Darkening Effects on the Hydrological Cycle over Western Eurasia and East Asia. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090500
Sang J, Kim M-K, Lau WKM, Kim K-M. Possible Impacts of Snow Darkening Effects on the Hydrological Cycle over Western Eurasia and East Asia. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(9):500. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090500
Chicago/Turabian StyleSang, Jeong, Maeng-Ki Kim, William K. M. Lau, and Kyu-Myong Kim. 2019. "Possible Impacts of Snow Darkening Effects on the Hydrological Cycle over Western Eurasia and East Asia" Atmosphere 10, no. 9: 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090500
APA StyleSang, J., Kim, M.-K., Lau, W. K. M., & Kim, K.-M. (2019). Possible Impacts of Snow Darkening Effects on the Hydrological Cycle over Western Eurasia and East Asia. Atmosphere, 10(9), 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090500






