Response of Urban Heat Stress to Heat Waves in Athens (1960–2017)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data and Area under Consideration
2.2. Heat Wave Identification Process
2.3. Heat Stress Assessment
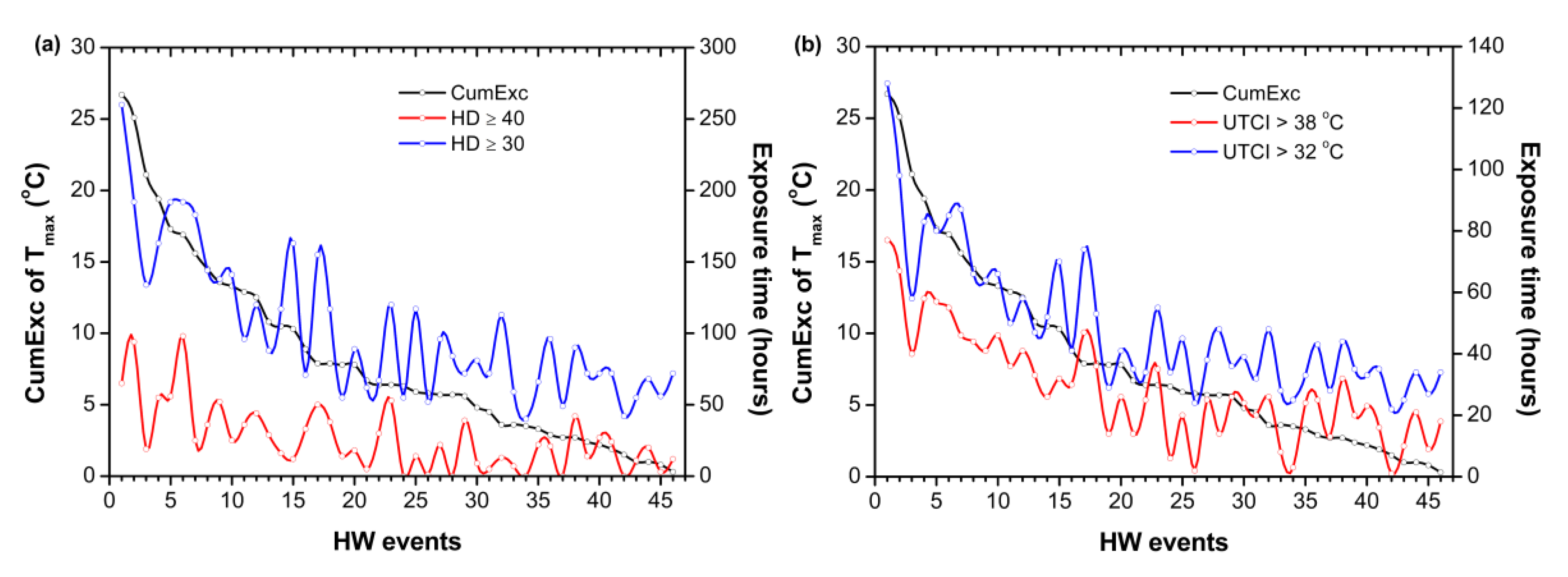
3. Results
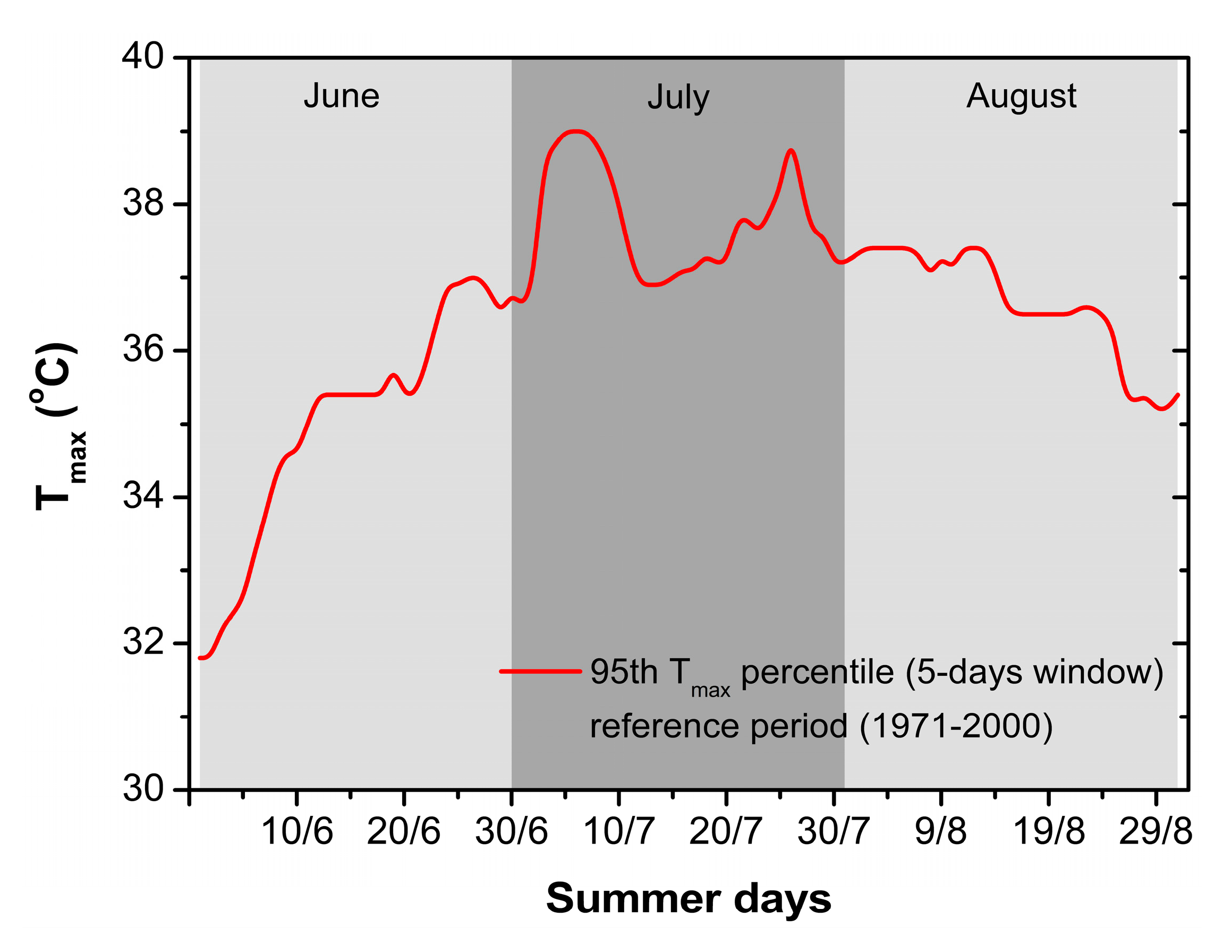
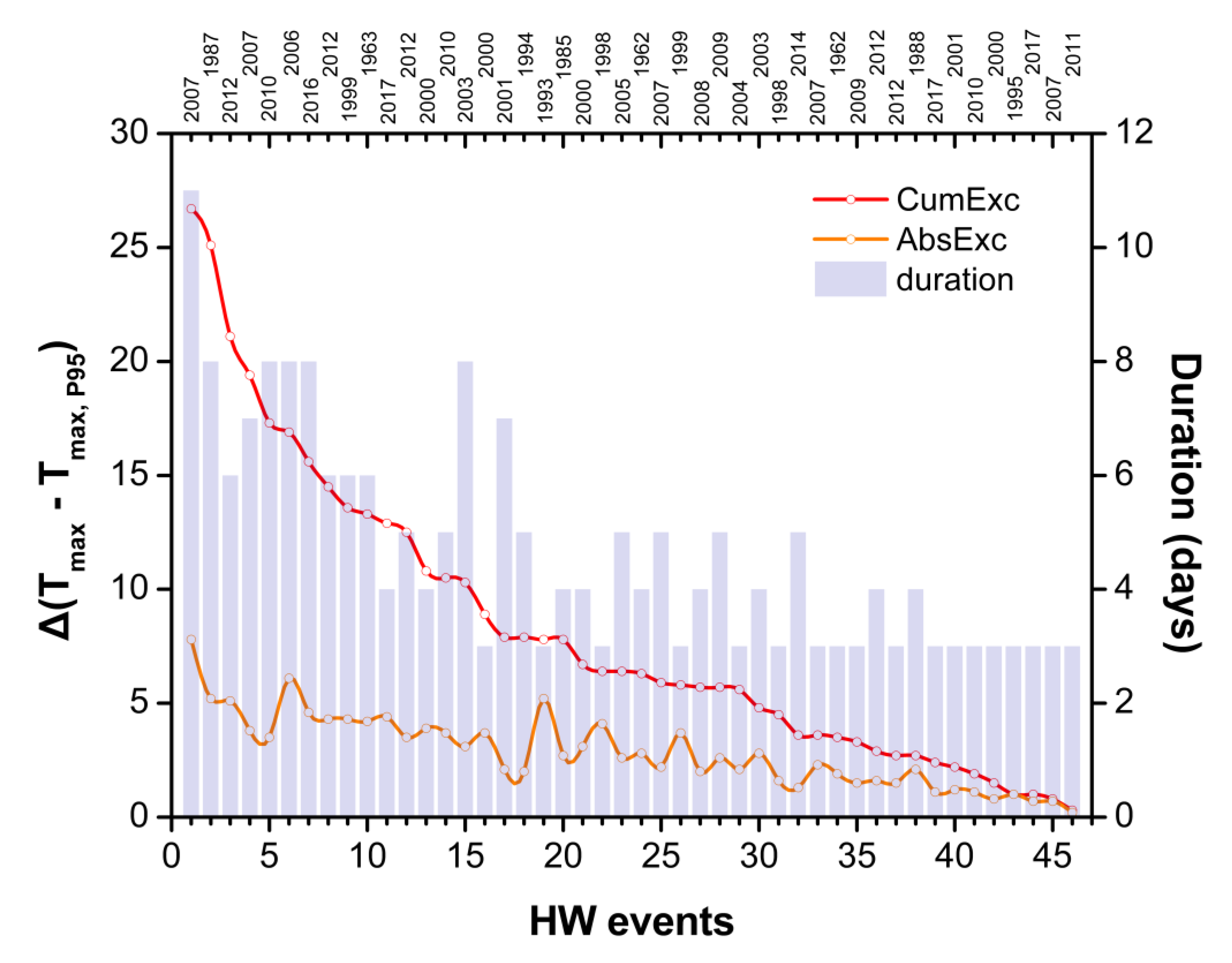
3.1. Heat Wave Identification
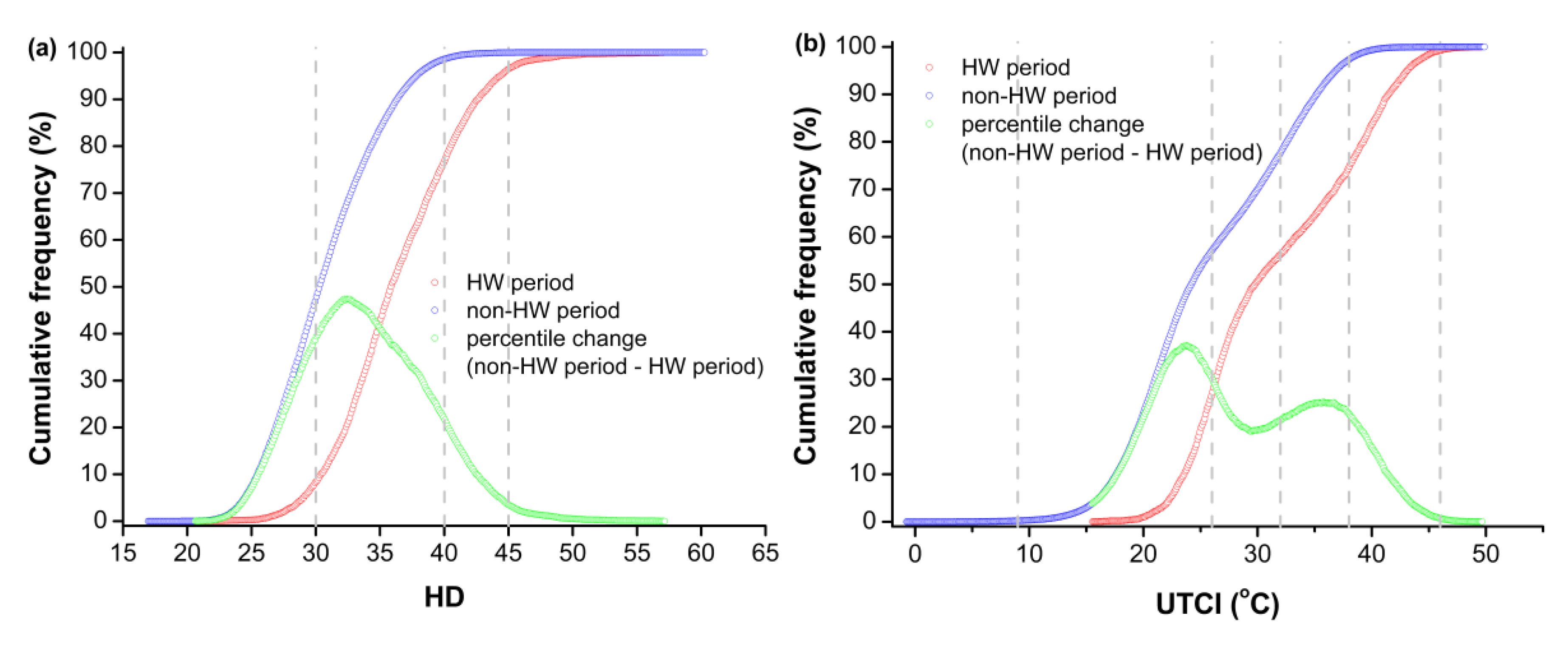
3.2. Changes in Heat Stress between HW and Non-HW Periods
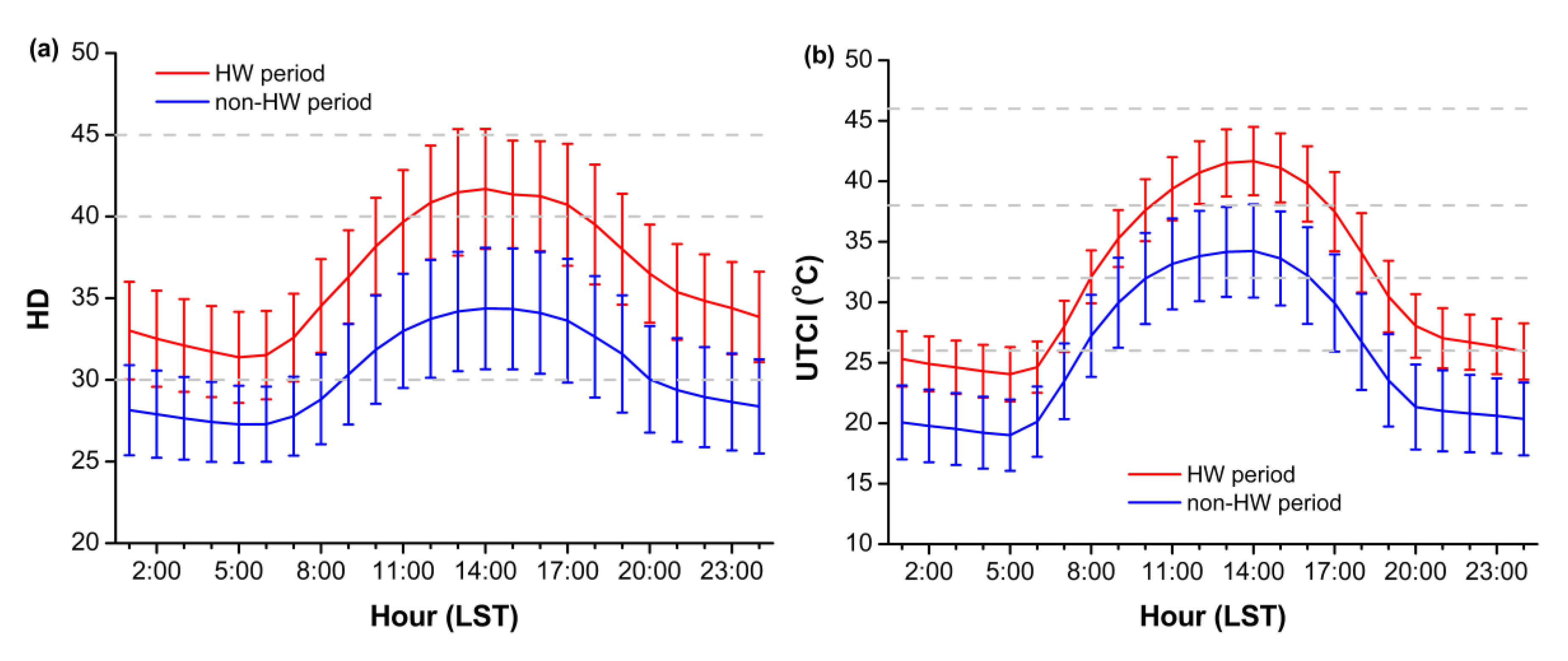
3.3. Urban Heat Stress Intensity between HW and Non-HW Conditions
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Meteorological Organization and World Health Organization. Heatwaves and Health: Guidance on Warning-System Development; McGregor, G.R., Bessemoulin, P., Ebi, K., Menne, B., Eds.; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015; p. 96. [Google Scholar]
- Kalkstein, L.S.; Greene, J.S.; Mills, D.; Perrin, A.; Samenow, J.; Cohen, J.C. Analog European heat waves for U.S. cities to analyze impacts on heat-related mortality. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 89, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuglitsch, F.G.; Toreti, A.; Xoplaki, E.; Della-Marta, P.M.; Zerefos, C.S.; Türkeş, M.; Luterbacher, J. Heat wave changes in the eastern Mediterranean since 1960. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L04802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampieri, M.; Russo, S.; di Sabatino, S.; Michetti, M.; Scoccimarro, E.; Gualdi, S. Global assessment of heat wave magnitudes from 1901 to 2010 and implications for the river discharge of the Alps. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjellstrom, T.; Briggs, D.; Freyberg, C.; Lemke, B.; Otto, M.; Hyatt, O. Heat, human performance, and occupational health: A key issue for the assessment of global climate change impacts. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2016, 37, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Nitschke, M.; Krackowizer, A.; Dear, K.; Pisaniello, D.; Weinstein, P.; Tucker, G.; Shakib, S.; Bi, P. Risk factors for deaths during the 2009 heat wave in Adelaide, Australia: A matched case-control study. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2017, 61, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.G.; Kim, K.R.; Kim, J.; Kim, B.J.; Cho, C.H.; Sheridan, S.C.; Kalkstein, L.S.; Kim, H.; Yi, S.M. Effects of heat waves on daily excess mortality in 14 Korean cities during the past 20 years (1991–2010): An application of the spatial synoptic classification approach. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2018, 62, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.; Venugopal, K.; Nitschke, M.; Nairn, J.; Fawcett, R.; Beattie, C.; Wynwood, G.; Bi, P. Regional morbidity and mortality during heatwaves in South Australia. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2018, 62, 1911–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, M.; Nitschke, M.; Williams, S.; McDonald, S.; Nairn, J.; Bi, P. Using the excess heat factor to indicate heatwave-related urinary disease: A case study in Adelaide, South Australia. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2019, 63, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboubakri, O.; Khanjani, N.; Jahani, Y.; Bakhtiari, B. The impact of heat waves on mortality and years of life lost in a dry region of Iran (Kerman) during 2005–2017. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, M.K.; Bang, J.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.K.; Oh, I. Estimation of thermal comfort felt by human exposed to extreme heat wave in a complex urban area using a WRF-MENEX model. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katavoutas, G.; Theoharatos, G.; Flocas, H.A.; Asimakopoulos, D.N. Measuring the effects of heat wave episodes on the human body’s thermal balance. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2009, 53, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, H.; Bailey, J.; Schwarz, L.; Vanos, J.; Ebi, K.; Benmarhnia, T. Impact of heat on mortality and morbidity in low and middle income countries: A review of the epidemiological evidence and considerations for future research. Environ. Res. 2019, 171, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Meteorological Organization. Guidelines on Analysis of Extremes in a Changing Climate in Support of Informed Decisions for Adaptation; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009; p. 52. [Google Scholar]
- Tolika, K. Assessing Heat Waves over Greece Using the Excess Heat Factor (EHF). Climate 2019, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, P.J. On the definition of a heat wave. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 762–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzarakis, A.; Nastos, P.T. Human-biometeorological assessment of heat waves in Athens. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2011, 105, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.T.; Zaitchik, B.F.; Gohlke, J.M. Heat waves in the United States: Definitions, patterns and trends. Clim. Chang. 2013, 118, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasilla, D.; Allende, F.; Martilli, A.; Fernández, F. Heat waves and human well-being in Madrid (Spain). Atmosphere 2019, 10, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, C.R.; Grigorieva, E.A. A comprehensive catalogue and classification of human thermal climate indices. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2015, 59, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, C.R.; Grigorieva, E.A. A comparison and appraisal of a comprehensive range of human thermal climate indices. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2017, 61, 487–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfano, F.R.D.A.; Palella, B.I.; Riccio, G. Thermal environment assessment reliability using temperature—Humidity indices. Ind. Health 2011, 49, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, T.R. The energetic basis of the urban heat island. Q. J. Royal Meteorol. Soc. 1982, 108, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Bou-Zeid, E. Synergistic interactions between urban heat islands and heat waves: The impact in cities is larger than the sum of its parts. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 2051–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Sun, T.; Liu, M.; Yang, L.; Wang, L.; Gao, Z. Contrasting responses of urban and rural surface energy budgets to heat waves explain synergies between urban heat islands and heat waves. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 054009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Founda, D.; Santamouris, M. Synergies between urban heat island and heat waves in Athens (Greece), during an extremely hot summer (2012). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Oppenheimer, M.; Zhu, Q.; Baldwin, J.W.; Ebi, K.L.; Bou-Zeid, E.; Guan, K.; Liu, X. Interactions between urban heat islands and heat waves. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 034003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Hou, Y.; Chen, W. Enhanced sensitivity of the urban heat island effect to summer temperatures induced by urban expansion. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamurthy, P.; Bou-Zeid, E. Heatwaves and urban heat islands: A comparative analysis of multiple cities. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Bueno, J.A.; Díaz, J.; Linares, C. Differences in the impact of heat waves according to urban and peri-urban factors in Madrid. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2019, 63, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diffenbaugh, N.S.; Pal, J.S.; Giorgi, F.; Gao, X. Heat stress intensification in the Mediterranean climate change hotspot. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L11706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzeau, G.; Soubeyroux, J.M.; Schneider, M.; Vautard, R.; Planton, S. Heat waves analysis over France in present and future climate: Application of a new method on the EURO-CORDEX ensemble. Clim. Serv. 2016, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Founda, D. Evolution of the air temperature in Athens and evidence of climatic change: A review. Adv. Build. Energy Res. 2011, 5, 7–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Founda, D.; Giannakopoulos, C. The exceptionally hot summer of 2007 in Athens, Greece—A typical summer in the future climate? Glob. Planet. Chang. 2009, 67, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastos, P.T.; Matzarakis, A. The effect of air temperature and human thermal indices on mortality in Athens, Greece. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2012, 108, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katavoutas, G.; Founda, D. Intensification of thermal risk in Mediterranean climates: Evidence from the comparison of rational and simple indices. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellenic Statistical Authority. Population and Housing Census of 2011. Available online: http://www.statistics.gr/en/2011-census-pop-hous (accessed on 9 April 2018).
- Peel, M.C.; Finlayson, B.L.; McMahon, T.A. Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Founda, D.; Kambezidis, H.D.; Petrakis, M.; Zanis, P.; Zerefos, C. A correction of the recent air-temperature record at the historical meteorological station of the National Observatory of Athens (NOA) due to instrument change. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2009, 97, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazadzis, S.; Founda, D.; Psiloglou, B.E.; Kambezidis, H.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Sanchez-Lorenzo, A.; Meleti, C.; Raptis, P.I.; Pierros, F.; Nabat, P. Long-term series and trends in surface solar radiation in Athens, Greece. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 2395–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, S.; Sillmann, J.; Fischer, E.M. Top ten European heat waves since 1950 and their occurrence in the coming decades. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 124003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Sinclair, V.A.; Räisänen, J.; Ruuhela, R. Heat waves in Finland: Present and projected summertime extreme temperatures and their associated circulation patterns. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 1393–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smid, M.; Russo, S.; Costa, A.C.; Granell, C.; Pebesma, E. Ranking European capitals by exposure to heat waves and cold waves. Urban Clim. 2019, 27, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feron, S.; Cordero, R.R.; Damiani, A.; Llanillo, P.J.; Jorquera, J.; Sepulveda, E.; Asencio, V.; Laroze, D.; Labbe, F.; Carrasco, J.; et al. Observations and projections of heat waves in south America. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masterson, J.; Richardson, F.A. Humidex, a Method of Quantifying Human Discomfort Due to Excessive Heat and Humidity; Environment Canada: Downsview, ON, Canada, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Environment Canada. Spring and Summer Weather Hazards! Available online: https://ec.gc.ca/meteo-weather/default.asp?lang=En&n=04A1BF3B-1&wbdisable=true (accessed on 17 April 2019).
- Fiala, D.; Havenith, G.; Bröde, P.; Kampmann, B.; Jendritzky, G. UTCI-Fiala multi-node model of human heat transfer and temperature regulation. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2012, 56, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havenith, G.; Fiala, D.; Błażejczyk, K.; Richards, M.; Bröde, P.; Holmér, I.; Rintamaki, H.; Benshabat, Y.; Jendritzky, G. The UTCI-clothing model. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2012, 56, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bröde, P.; Fiala, D.; Błażejczyk, K.; Holmér, I.; Jendritzky, G.; Kampmann, B.; Tinz, B.; Havenith, G. Deriving the operational procedure for the Universal Thermal Climate Index (UTCI). Int. J. Biometeorol. 2012, 56, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blazejczyk, K.; Epstein, Y.; Jendritzky, G.; Staiger, H.; Tinz, B. Comparison of UTCI to selected thermal indices. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2012, 56, 515–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matzarakis, A.; Rutz, F.; Mayer, H. Modelling radiation fluxes in simple and complex environments—Application of the RayMan model. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2007, 51, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matzarakis, A.; Rutz, F.; Mayer, H. Modelling radiation fluxes in simple and complex environments: Basics of the RayMan model. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2010, 54, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsouyanni, K.; Trichopoulos, D.; Zavitsanos, X.; Touloumi, G. The 1987 Athens heatwave. Lancet 1988, 32, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prezerakos, N.G. A contribution to the study of the extreme heatwave over the south Balkans in July 1987. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 1989, 41, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzarakis, A.; Mayer, H. The extreme heat wave in Athens in July 1987 from the point of view of human biometeorology. Atmos. Environ. 1991, 25, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolika, K.; Maheras, P.; Tegoulias, I. Extreme temperatures in Greece during 2007: Could this be a “return to the future”? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L10813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theoharatos, G.; Pantavou, K.; Mavrakis, A.; Spanou, A.; Katavoutas, G.; Efstathiou, P.; Mpekas, P.; Asimakopoulos, D. Heat waves observed in 2007 in Athens, Greece: Synoptic conditions, bioclimatological assessment, air quality levels and health effects. Environ. Res. 2010, 110, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantavou, K.; Theoharatos, G.; Mavrakis, A.; Santamouris, M. Evaluating thermal comfort conditions and health responses during an extremely hot summer in Athens. Build. Environ. 2011, 46, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Founda, D.; Pierros, F.; Petrakis, M.; Zerefos, C. Interdecadal variations and trends of the urban heat island in Athens (Greece) and its response to heat waves. Atmos. Res. 2015, 161, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, S.B.; Dawson, R.J.; Kilsby, C.; Lewis, E.; Ford, A. Future heat-waves, droughts and floods in 571 European cities. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 034009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morabito, M.; Crisci, A.; Messeri, A.; Messeri, G.; Betti, G.; Orlandini, S.; Raschi, A.; Maracchi, G. Increasing heatwave hazards in the southeastern European Union capitals. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Founda, D.; Pierros, F.; Katavoutas, G.; Keramitsoglou, I. Observed trends in thermal stress at European cities with different background climates. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, K.M.A.; Endlicher, W.R. Urban and rural mortality rates during heat waves in Berlin and Brandenburg, Germany. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2044–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Zheng, Y.; Tang, X.; Guo, C.; Li, L.; Song, G.; Zhen, X.; Yuan, D.; Kalkstein, A.J.; Li, F.; et al. The urban heat island and its impact on heat waves and human health in Shanghai. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2010, 54, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katavoutas, G.; Georgiou, G.K.; Asimakopoulos, D.N. Studying the urban thermal environment under a human-biometeorological point of view: The case of a large coastal metropolitan city, Athens. Atmos. Res. 2015, 152, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolopoulou, M.; Steemers, K. Thermal comfort and psychological adaptation as a guide for designing urban spaces. Energy Build. 2003, 35, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.K.C.; Gallant, A.J.; Tapper, N.J. Perceptions of thermal comfort in heatwave and non-heatwave conditions in Melbourne, Australia. Urban Clim. 2018, 23, 204–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D.; Guo, D.; Hou, Y.; Lin, C.; Chen, Q. Studies of outdoor thermal comfort in northern China. Build. Environ. 2014, 77, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Li, J.; Xie, Y.; Niu, J.; Mak, C.M. Simultaneous environmental parameter monitoring and human subject survey regarding outdoor thermal comfort and its modelling. Build. Environ. 2017, 125, 502–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bröde, P.; Krüger, E.L.; Rossi, F.A.; Fiala, D. Predicting urban outdoor thermal comfort by the Universal Thermal Climate Index UTCI—A case study in Southern Brazil. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2012, 56, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantavou, K.; Santamouris, M.; Asimakopoulos, D.; Theoharatos, G. Evaluating the performance of bioclimatic indices on quantifying thermal sensation for pedestrians. Adv. Build. Energy Res. 2013, 7, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantavou, K.; Theoharatos, G.; Santamouris, M.; Asimakopoulos, D. Outdoor thermal sensation of pedestrians in a Mediterranean climate and a comparison with UTCI. Build. Environ. 2013, 66, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keatinge, W.R.; Donaldson, G.C.; Cordioli, E.; Martinelli, M.; Kunst, A.E.; Mackenbach, J.P.; Nayha, S.; Vuori, I. Heat related mortality in warm and cold regions of Europe: Observational study. Br. Med. J. 2000, 321, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccini, M.; Biggeri, A.; Accetta, G.; Kosatsky, T.; Katsouyanni, K.; Analitis, A.; Anderson, H.R.; Bisanti, L.; D’Ippoliti, D.; Danova, J.; et al. Heat effects on mortality in 15 European cities. Epidemiology 2008, 19, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Armstrong, B.; Jaakkola, J.J.; Tong, S.; Pan, X. Extremely cold and hot temperatures increase the risk of ischaemic heart disease mortality: Epidemiological evidence from China. Heart 2013, 99, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| HD | Degree of Comfort |
|---|---|
| >45 | Dangerous—heat stroke possible |
| 40–45 | Great discomfort—avoid exertion |
| 30–39 | Some discomfort |
| ≤29 | No discomfort |
| UTCI (°C) | Stress Category |
|---|---|
| >46 | Extreme heat stress |
| 38–46 | Very strong heat stress |
| 32–38 | Strong heat stress |
| 26–32 | Moderate heat stress |
| 9–26 | No thermal stress |
| 0–9 | Slight cold stress |
| −13–0 | Moderate cold stress |
| −27–−13 | Strong cold stress |
| −40–−27 | Very strong cold stress |
| <−40 | Extreme cold stress |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Katavoutas, G.; Founda, D. Response of Urban Heat Stress to Heat Waves in Athens (1960–2017). Atmosphere 2019, 10, 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090483
Katavoutas G, Founda D. Response of Urban Heat Stress to Heat Waves in Athens (1960–2017). Atmosphere. 2019; 10(9):483. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090483
Chicago/Turabian StyleKatavoutas, George, and Dimitra Founda. 2019. "Response of Urban Heat Stress to Heat Waves in Athens (1960–2017)" Atmosphere 10, no. 9: 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090483
APA StyleKatavoutas, G., & Founda, D. (2019). Response of Urban Heat Stress to Heat Waves in Athens (1960–2017). Atmosphere, 10(9), 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090483




