Spatial Characteristics of Deep-Developed Boundary Layers and Numerical Simulation Applicability over Arid and Semi-Arid Regions in Northwest China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Method for Determining Boundary Layer Height
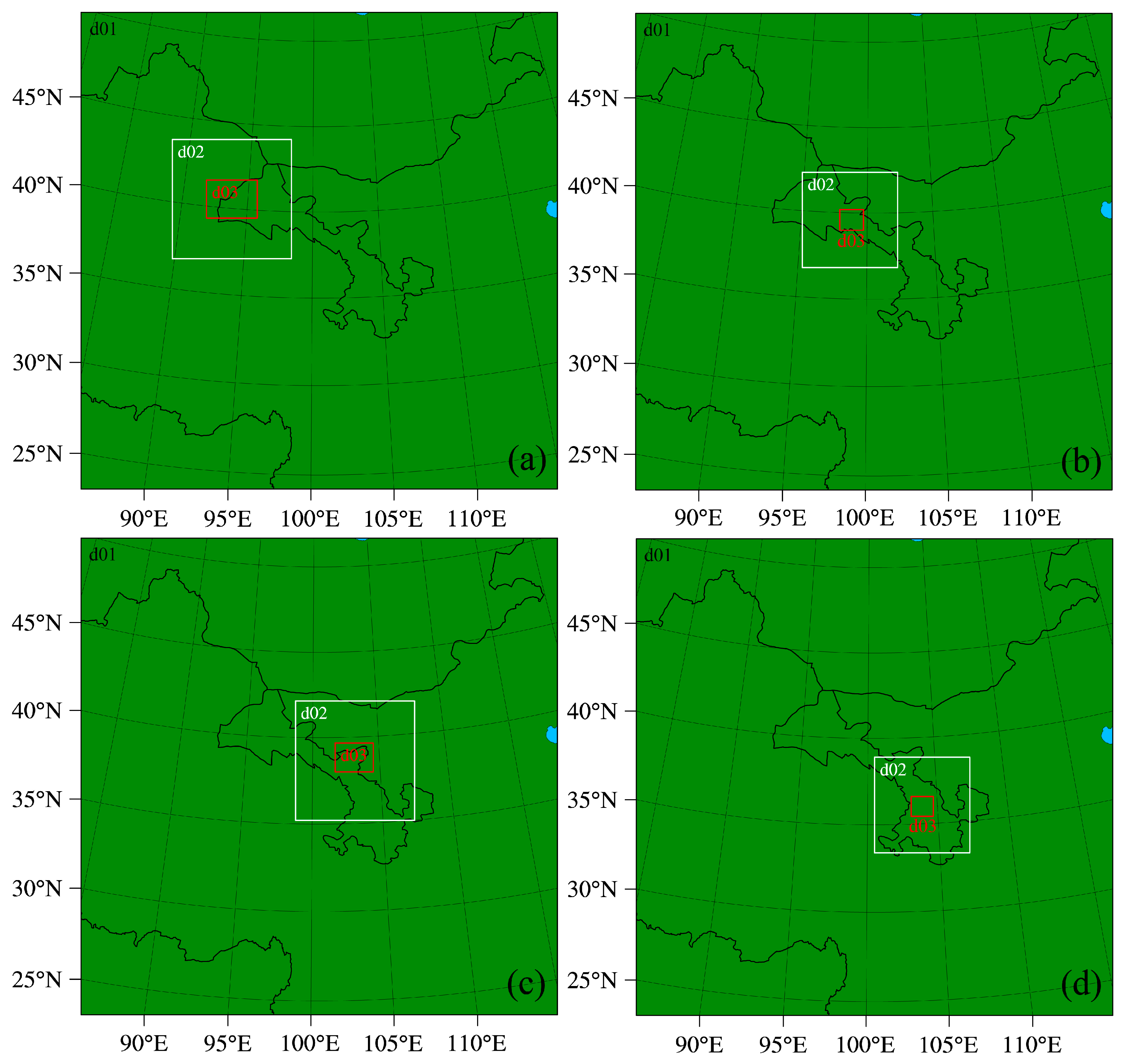
2.3. Scope of Research and Representative Regions
2.4. Numerical Model
3. Characteristics of Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions
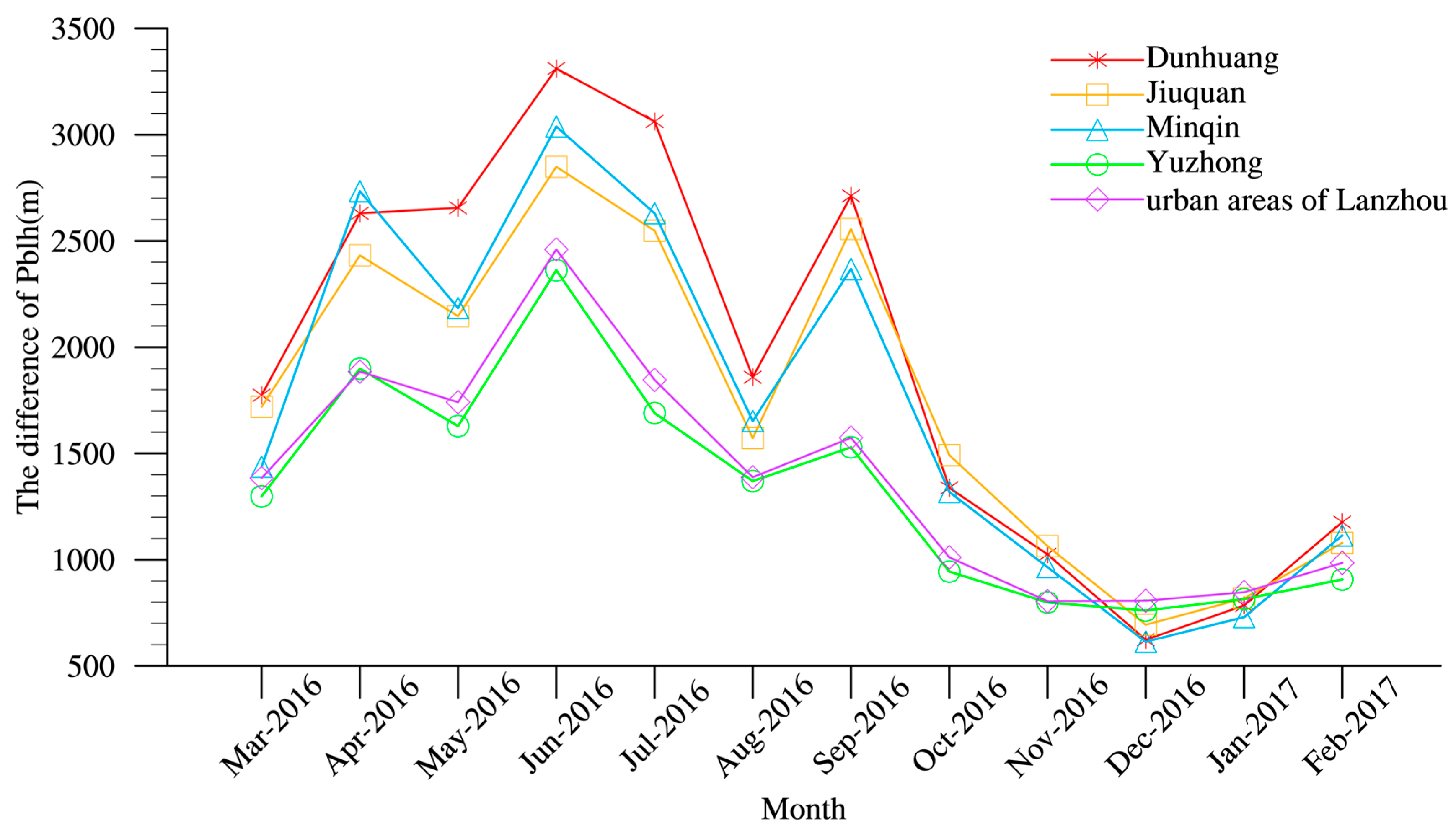
3.1. Monthly Variation of Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height
3.2. Deep-Developed Boundary Layer Height in Daytime
4. Spatial Distribution and Weather Influence
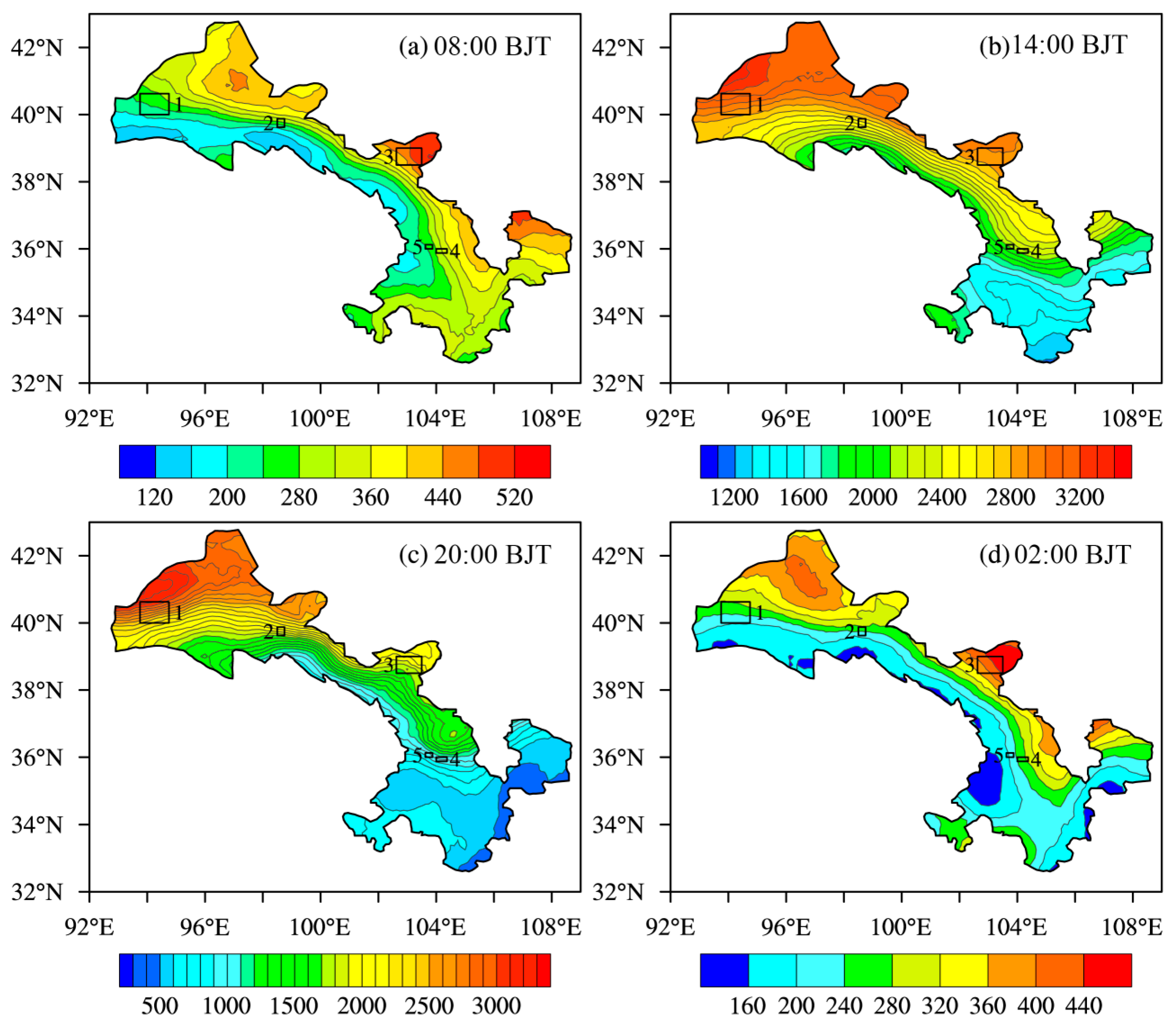
4.1. Spatial Distribution of Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height
4.2. Weather Influence on Atmospheric Boundary Layer Development
5. Numerical Simulation on Deep-Developed Boundary Layer Height
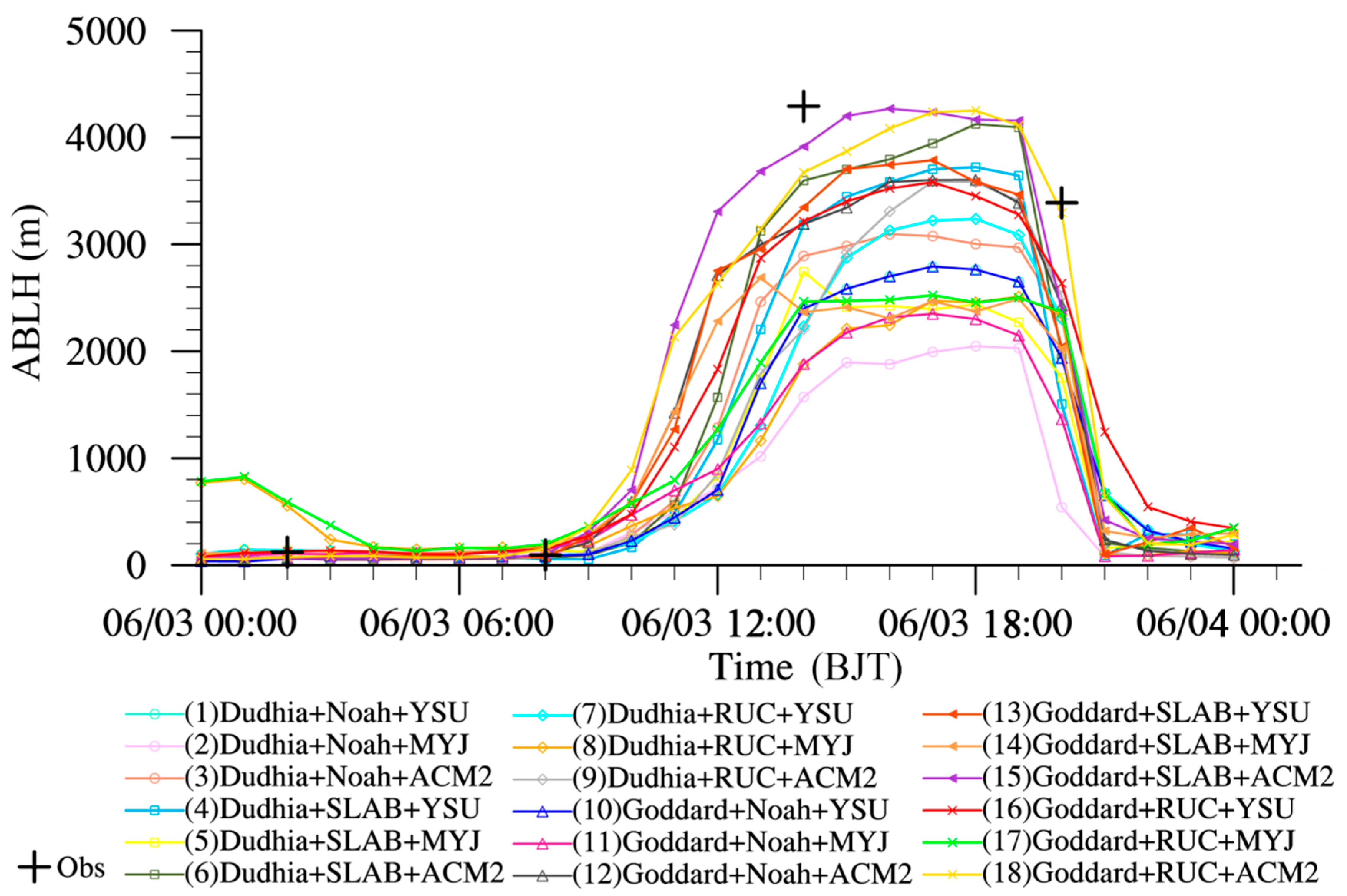
5.1. Experimental Design
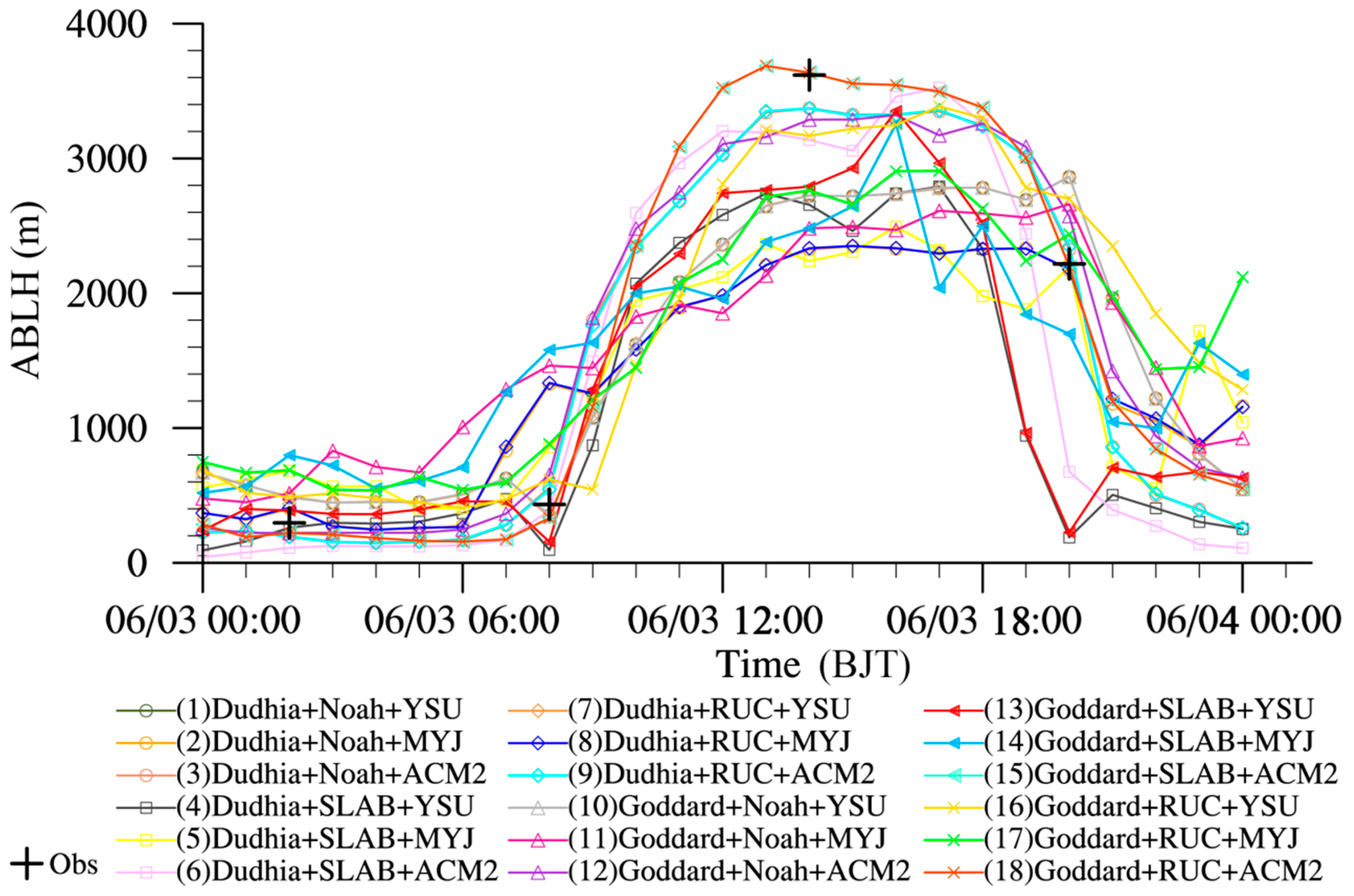
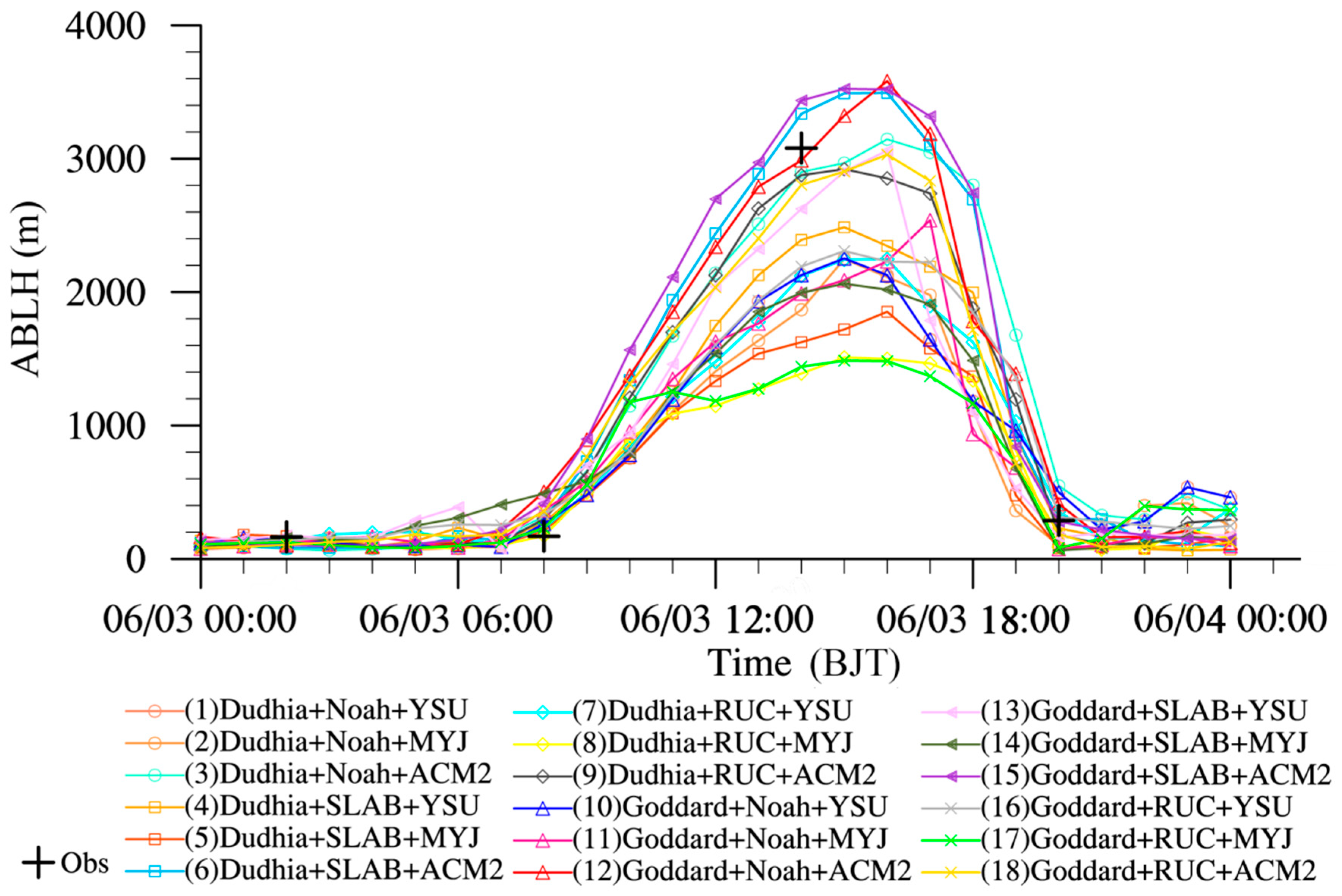
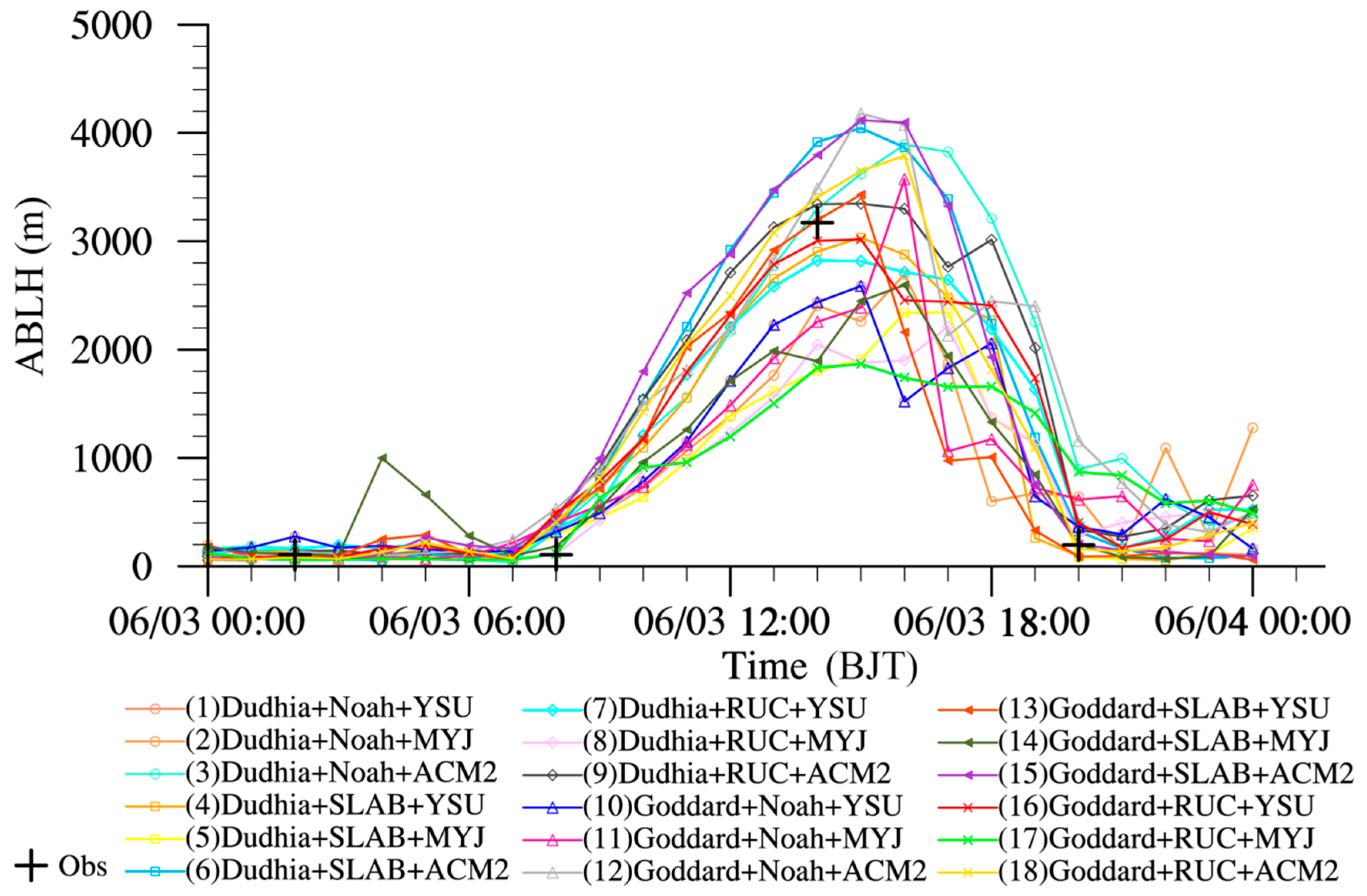
5.2. Simulation Results
6. Results and Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, M. Dynamics of Atmoshperic Boundary Layer; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Garratt, J.R. Review: The Atmospheric Boundary Layer; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992; pp. 89–134. [Google Scholar]
- Takemi, T. Structure and Evolution of a Severe Squall Line over the Arid Region in Northwest China. Mon. Weather Rev. 1999, 127, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q. Study on Depth of Atmospheric Thermal Boundary Layer in Extreme Arid Desert Regions. J. Desert Res. 2007, 27, 614–620. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.; Pu, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q. Characteristics and Numerical Simulations of Extremely Large Atmospheric Boundary-layer Heights over an Arid Region in North-west China. Bound. Lay. Meteorol. 2011, 140, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S. Comparison of Atmospheric Boundary Layer in Winter and Summer over Arid Region of Northwest China. J. Desert Res. 2010, 30, 422–431. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, S. On Physical Characteristics of Heavy Dust Storm and Its Climatic Effect. J. Desert Res. 2005, 25, 675–681. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xi, X.; Ye, Y. Monthly Temporal-Spatial Distribution of Sandstorms in China as Well as the Origin of Kosa in Japan and Kore. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 28, 820–827. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Huang, R. Interdecadal Variability of Sensible Heat in Arid and Semi-arid Regions of Northwest China and its Relation to Summer Precipitation in China. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 32, 1276–1288. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.Y.; Liang, X.Z. Observed diurnal cycle climatology of planetary boundary layer height. J. Clim. 2009, 23, 5790–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wei, W.; He, Q.; Zheng, W.; Hu, W. Radar Wind Profiler Observations of Convective Boundary Layer During Clear-Air Days over Taklimakan Desert. Meteorol. Mon. 2012, 38, 577–584. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhong, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhou, J. LIDAR exploration of atmospheric boundary layer over downtown of Beijing in summer. J. Appl. Op. 2008, 29, 96–100. [Google Scholar]
- Seidel, D.J.; Zhang, Y.; Beljaars, A.; Golaz, J.C.; Jacobson, A.R.; Medeiros, B. Climatology of the planetary boundary layer over the continental United States and Europe. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; He, J.; Lou, M.; Yan, Y.; Bian, L. The climatology of planetary boundary layer height in China derived from radiosonde and reanalysis data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 13309–13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Han, Z.; Zhang, R.; Fu, C. Evaluation and analysis of WRF-simulated meteorological variables in the urban and semi-arid areas of China. J. Meteorol. Sci. 2011, 31, 484–492. [Google Scholar]
- García-Díez, M.; Fernández, J.; Fita, L.; Yagüe, C. Seasonal dependence of WRF model biases and sensitivity to PBL schemes over Europe. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 139, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.M.; Nielsengammon, J.W.; Zhang, F. Evaluation of Three Planetary Boundary Layer Schemes in the WRF Model. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2010, 49, 1831–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Fung, J.C.H.; Chan, A.; Lau, A. Evaluation of nonlocal and local planetary boundary layer schemes in the WRF model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Q. Mesoscale Atmospheric Numerical Simulation and Its Progress. Arid Zone Res. 2012, 29, 273–283. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Miller, N.L.; Schlegel, N. Sensitivity Study of Four Land Surface Schemes in the WRF Model. Adv. Meteorol. 2010, 2010, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, L. Meteorological Characteristics in Lanzhou New District Simulated by WRF with Different Land Surface Model Parameterizations. J. Lanzhou Univ. 2017, 53, 329–340. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.; Zhao, C.; Ding, S.; Qin, Y. A Study on Impacts of Different Radiative Transfer Schemes on Mesoscale Precipitations. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2005, 16, 148–158. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Huang, H. Influence of Different Radiation Parameterization Schemes of WRF Model on Predicting Extreme Low Temperature Events. Arid Zone Res. 2016, 33, 718–723. [Google Scholar]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Zhai, P.; Yuan, C. Comparative Analysis of NCEP/NCAR, ECMWF and JMA Reanalysis. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2010, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Hao, L. Verification of ERA-Interim reanalysis data over China. J. Subtrop. Res. Environ. 2014, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Berrisford, P.; Dee, D.P.; Fielding, K.; Fuentes, M.; Kållberg, P.W.; Kobayashi, S.; Uppala, S.M. The ERA-Interim Archive. 2009. Available online: https://www.ecmwf.int/node/8173 (accessed on 1 August 2009).
- Vogelezang, D.H.P.; Holtslag, A.A.M. Evaluation and model impacts of alternative boundary-layer height formulations. Bound. Lay. Meteorol. 1996, 81, 245–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Hu, Z.; Lv, S.; Yao, J. Weather elements’ characteristics of atmosphere boundary layer over Northwest Arid Area of China in typical day of summer. Arid Land Geogr. 2007, 30, 871–878. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Cui, C.; Xu, H.; Wang, X. Observational Analysis on Atmospheric Boundary Layer over Yichang During Two Precipitation Processes in Winter. Torrential Rain Disasters 2008, 27, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Tang, J.; Fang, J.; Sun, X. Simulation of urban heat island effect and its impact on atmospheric boundary layer structure over Yangtze River Delta region in summer. J. Meteorol. Sci. 2011, 31, 431–440. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Wei, H. Numerical Simulation of the Impact of LUC on Characteristics of Atmospheric Boundary Layer in Lanzhou City. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2014, 4334–4337. [Google Scholar]
- National Center for Atmospheric Research. NCAR (2016) ARW Version 3.8 Modeling System’s User’s Guide. Available online: http://www2.mmm.ucar.edu/wrf/users/docs/user_guide_V3.8/ARWUsersGuideV3.8.pdf (accessed on 4 March 2019).
- Hong, S.Y.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A New Vertical Diffusion Package with an Explicit Treatment of Entrainment Processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleim, J.E. A Combined Local and Nonlocal Closure Model for the Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Part I: Model Description and Testing. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2007, 46, 1383–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjić, Z.I. Nonsingular Implementation of the Mellor–Yamada Level 2.5 Scheme in the NCEP Meso Model. Available online: https://repository.library.noaa.gov/view/noaa/11409 (accessed on 10 December 2001).
- Georg, G.; Dudhia, J.; Stauffer, D. A Description of the Fifth-Generation Penn State/NCAR Mesoscale Model (MM5), NCAR/TN-398+STR. Ncar Tech. Note 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ek, M.B.; Mitchell, K.E.; Lin, Y.; Rogers, E.; Grunmann, P.; Koren, V.; Gayno, G.; Tarpley, J.D. Implementation of Noah land surface model advances in the National Centers for Environmental Prediction operational mesoscale Eta model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, T.G.; Brown, J.M.; Benjamin, S.G. Performance of Different Soil Model Configurations in Simulating Ground Surface Temperature and Surface Fluxes. Mon. Weather Rev. 1997, 125, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, T.G.; Brown, J.M.; Benjamin, S.G.; Kim, D. Parameterization of cold-season processes in the MAPS land-surface scheme. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 4077–4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, J.; Wang, S. Relationship of Atmospheric Boundary Layer Depth with Thermodynamic Processes at the Land Surface in Arid Regions of China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E.M.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Vidale, P.L.; Lüthi, D.; Schär, C. Soil Moisture Atmosphere Interactions during the 2003 European Summer Heat Wave. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudhia, J. Numerical Study of Convection Observed during the Winter Monsoon Experiment Using a Mesoscale Two-Dimensional Model. J. Atmos. Sci. 1989, 46, 3077–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacis, A.A.; Hansen, J. A Parameterization for the Absorption of Solar Radiation in the Earth’s Atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 1974, 31, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, M.D.; Suarez, M.J. An Efficient Thermal Infrared Radiation Parameterization for Use in General Circulation Models. 1994. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.26.4850&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 8 November 1994).
- Lean, J.; Rind, D. Climate Forcing by Changing Solar Radiation. J. Clim. 1996, 11, 3069–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.M.; Mauersberger, K. Laser measurements of ozone absorption cross sections in the Chappuis Band. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 19, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
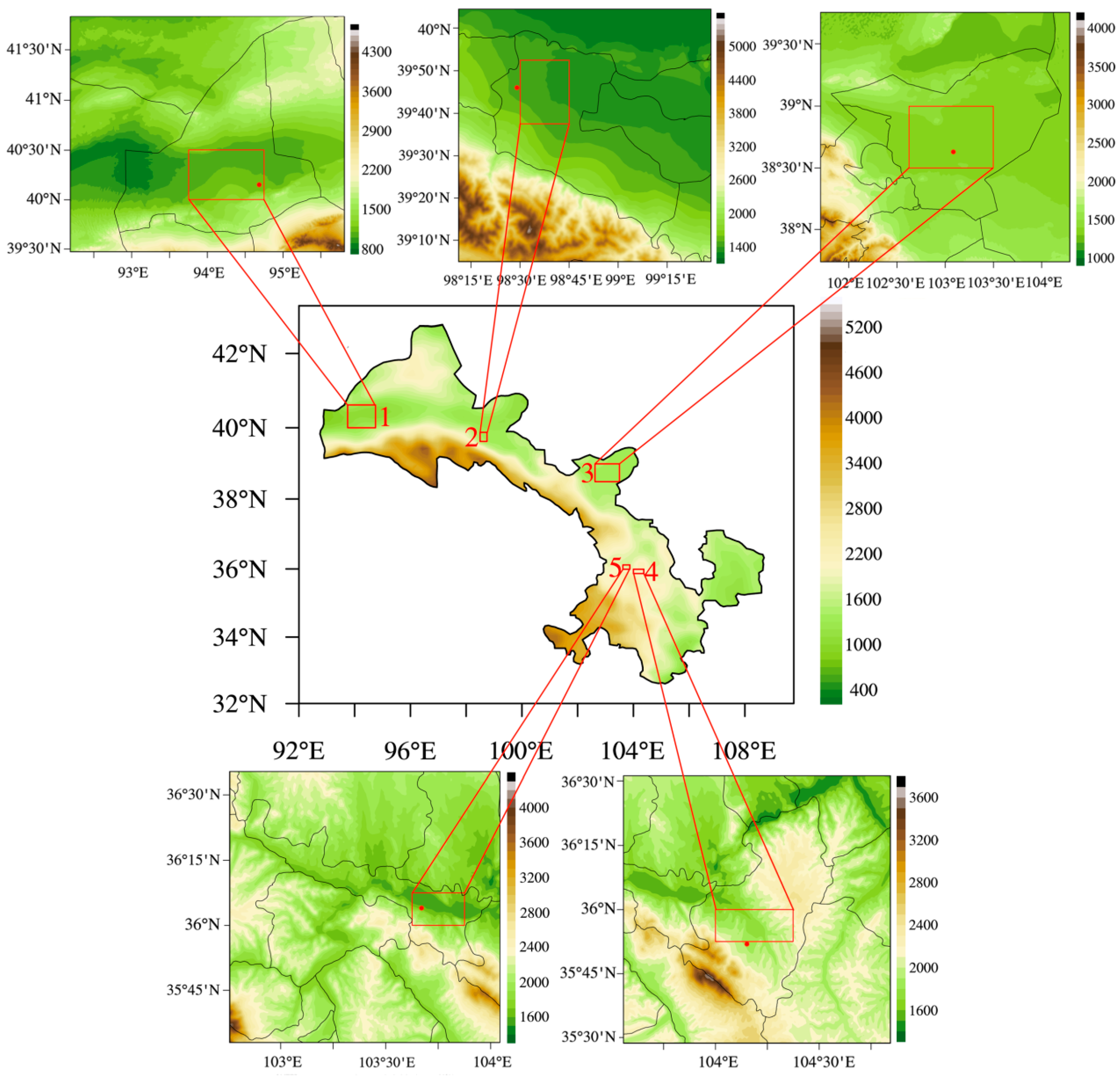
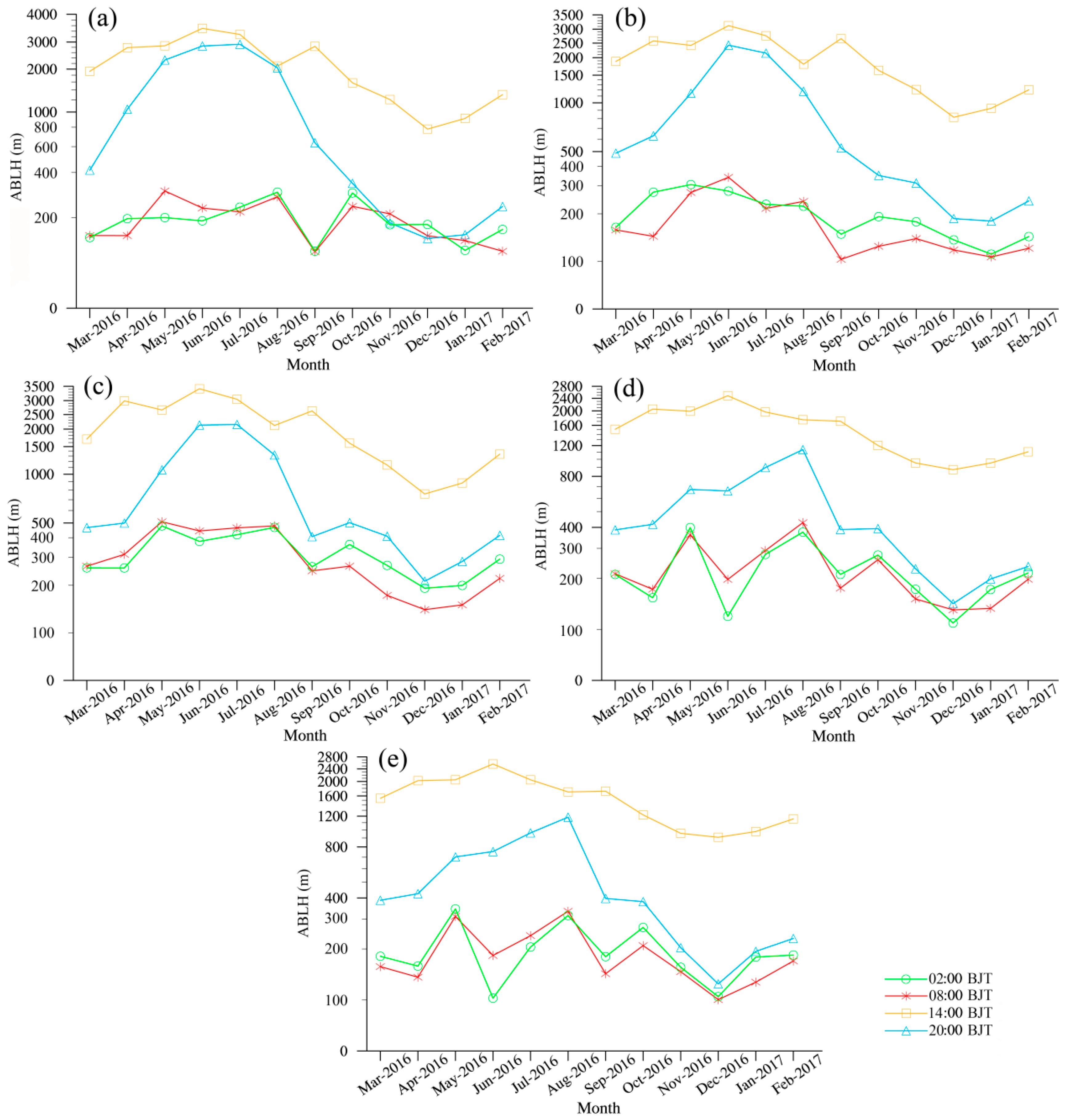
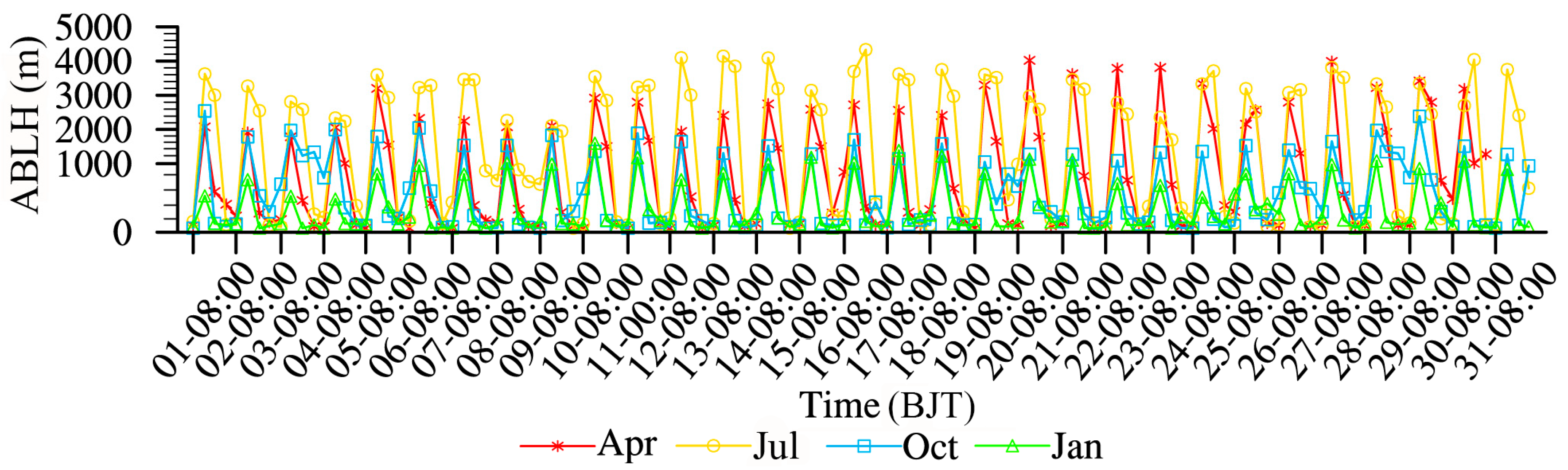
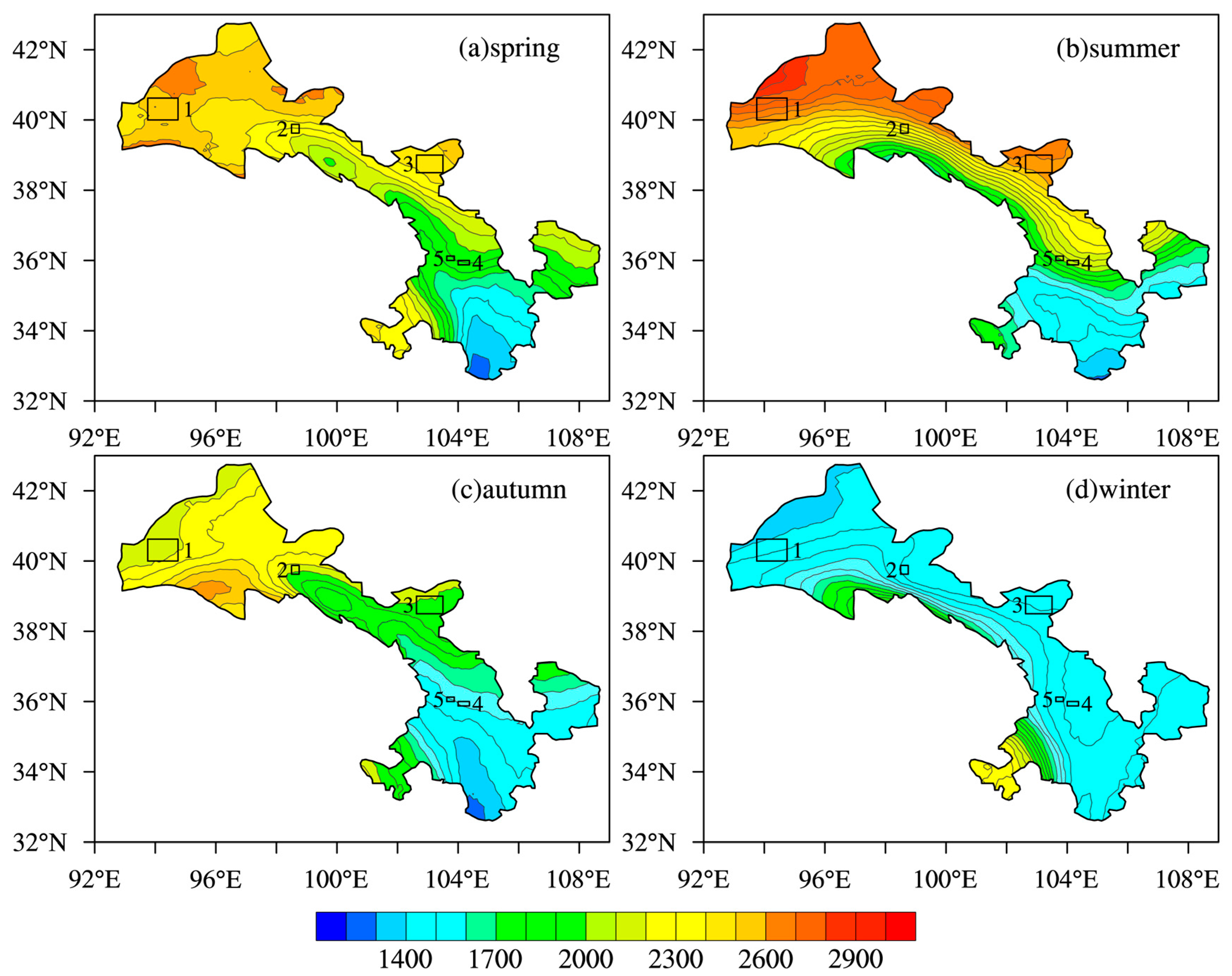

| Temperature | Dunhuang | Jiuquan | Minqin | Yuzhong | Lanzhou |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 08:00 BJT | 0.193 ** | 0.24 ** | 0.325 ** | 0.247 ** | 0.213 ** |
| 14:00 BJT | 0.802 ** | 0.749 ** | 0.757 ** | 0.629 ** | 0.654 ** |
| 20:00 BJT | 0.762 ** | 0.658 ** | 0.535 ** | 0.5 ** | 0.531 ** |
| 02:00 BJT | 0.158 ** | −0.024 | 0.209 ** | 0.159 ** | 0.093 * |
| ≥4000 m | 3000–4000 m | 2000–3000 m | 1000–2000 m | <1000 m | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dunhuang | Spring | 6 | 22 | 35 | 29 | 0 |
| Summer | 13 | 35 | 32 | 10 | 2 | |
| Autumn | 2 | 10 | 18 | 51 | 10 | |
| Winter | 0 | 0 | 3 | 33 | 54 | |
| Jiuquan | Spring | 2 | 19 | 32 | 39 | 1 |
| Summer | 6 | 30 | 30 | 20 | 6 | |
| Autumn | 1 | 9 | 23 | 43 | 15 | |
| Winter | 0 | 0 | 3 | 27 | 60 | |
| Minqin | Spring | 7 | 21 | 32 | 29 | 3 |
| Summer | 13 | 26 | 35 | 17 | 1 | |
| Autumn | 2 | 10 | 16 | 48 | 15 | |
| Winter | 0 | 1 | 2 | 33 | 54 | |
| Yuzhong | Spring | 2 | 6 | 23 | 53 | 8 |
| Summer | 2 | 9 | 34 | 37 | 10 | |
| Autumn | 0 | 1 | 10 | 46 | 34 | |
| Winter | 0 | 0 | 0 | 30 | 60 | |
| Lanzhou | Spring | 2 | 5 | 22 | 56 | 7 |
| Summer | 2 | 10 | 36 | 32 | 12 | |
| Autumn | 0 | 0 | 11 | 47 | 33 | |
| Winter | 0 | 0 | 0 | 31 | 59 |
| June | July | August | September | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dunhuang | sunny days | 12 | 14 | 4 | 14 |
| precipitation, cloudy and overcast days | 18 | 17 | 27 | 16 | |
| monthly average of the total cloud amount | 4.81 | 4.76 | 6.36 | 3.89 | |
| Jiuquan | sunny days | 10 | 16 | 4 | 15 |
| precipitation, cloudy and overcast days | 20 | 15 | 27 | 15 | |
| monthly average of the total cloud amount | 5.53 | 5.26 | 7.21 | 4.48 | |
| Minqin | sunny days | 24 | 19 | 14 | 20 |
| precipitation, cloudy and overcast days | 6 | 12 | 17 | 10 | |
| monthly average of the total cloud amount | 6.28 | 5.38 | 7.12 | 5.51 |
| Serial Number | Shortwave Radiation Scheme | Land Surface Scheme | Atmospheric Boundary Layer Scheme/Surface Layer Scheme |
|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | Dudhia | Noah | YSU/Monin–Obukhov |
| 02 | MYJ/MYJ Monin–Obukhov | ||
| 03 | ACM2/Monin–Obukhov | ||
| 04 | SLAB | YSU/Monin–Obukhov | |
| 05 | MYJ/MYJ Monin–Obukhov | ||
| 06 | ACM2/Monin–Obukhov | ||
| 07 | RUC | YSU/Monin–Obukhov | |
| 08 | MYJ/MYJ Monin–Obukhov | ||
| 09 | ACM2/Monin–Obukhov | ||
| 10 | Goddard | Noah | YSU/Monin–Obukhov |
| 11 | MYJ/MYJ Monin–Obukhov | ||
| 12 | ACM2/Monin–Obukhov | ||
| 13 | SLAB | YSU/Monin–Obukhov | |
| 14 | MYJ/MYJ Monin–Obukhov | ||
| 15 | ACM2/Monin–Obukhov | ||
| 16 | RUC | YSU/Monin–Obukhov | |
| 17 | MYJ/MYJ Monin–Obukhov | ||
| 18 | ACM2/Monin–Obukhov |
| Dunhuang | Jiuquan | Minqin | Yuzhong | Lanzhou | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| shortwave radiation scheme | 543 | 564 | 205 | 213 | 377 |
| atmospheric boundary layer scheme | 1255 | 972 | 1228 | 1202 | 1351 |
| land surface scheme | 678 | 272 | 568 | 516 | 532 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, M.; Tan, Z.; Ding, F.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y. Spatial Characteristics of Deep-Developed Boundary Layers and Numerical Simulation Applicability over Arid and Semi-Arid Regions in Northwest China. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10040195
Ma M, Tan Z, Ding F, Chen Y, Yang Y. Spatial Characteristics of Deep-Developed Boundary Layers and Numerical Simulation Applicability over Arid and Semi-Arid Regions in Northwest China. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(4):195. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10040195
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Minjin, Ziyuan Tan, Fan Ding, Yue Chen, and Yi Yang. 2019. "Spatial Characteristics of Deep-Developed Boundary Layers and Numerical Simulation Applicability over Arid and Semi-Arid Regions in Northwest China" Atmosphere 10, no. 4: 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10040195
APA StyleMa, M., Tan, Z., Ding, F., Chen, Y., & Yang, Y. (2019). Spatial Characteristics of Deep-Developed Boundary Layers and Numerical Simulation Applicability over Arid and Semi-Arid Regions in Northwest China. Atmosphere, 10(4), 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10040195




