Impact of Different Types of ENSO Years on Intensity Changes of Landfalling Tropical Cyclones over China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
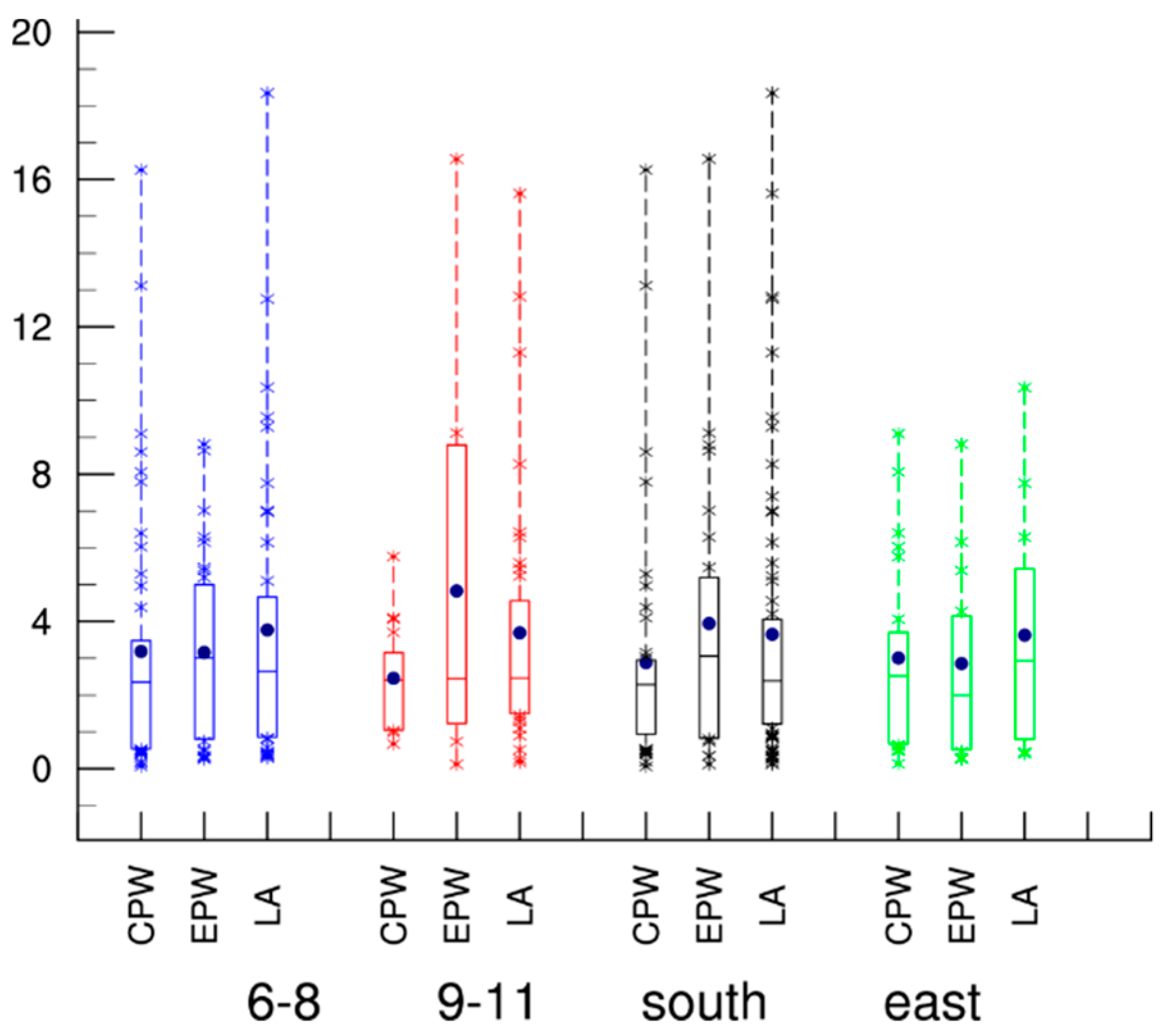
3. Characteristics of Landfalling Intensity
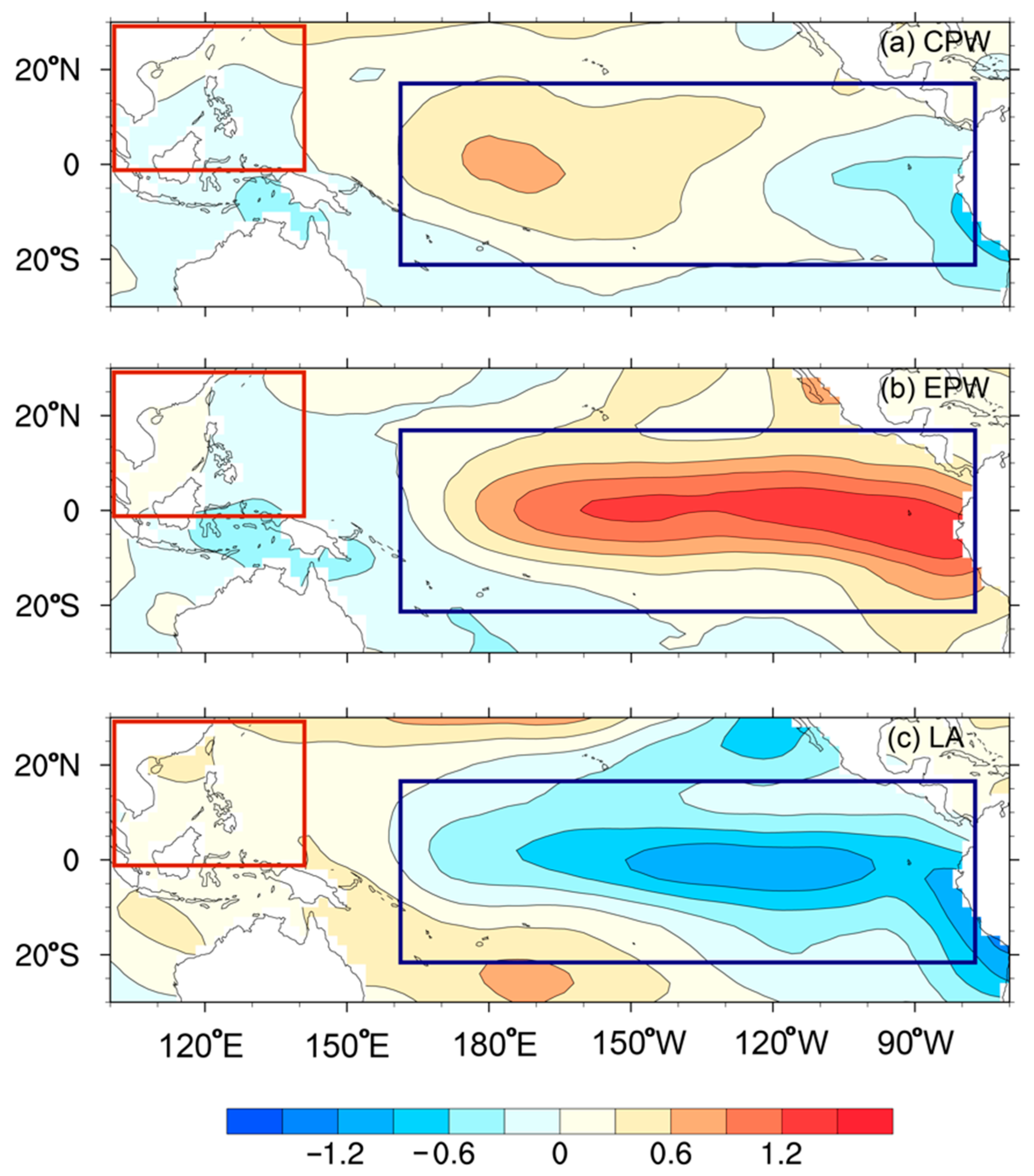
4. Large-Scale Circulation Analysis
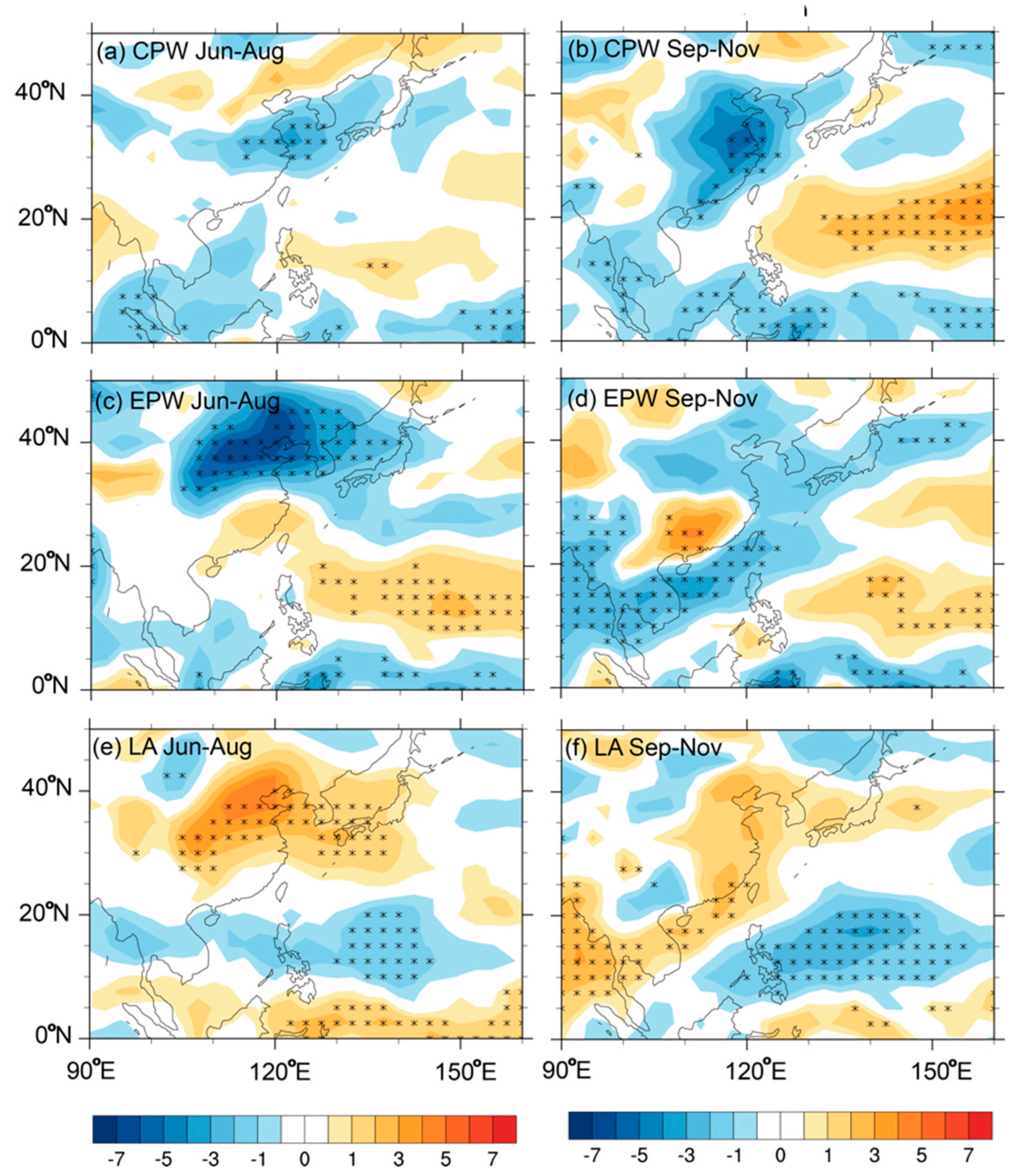
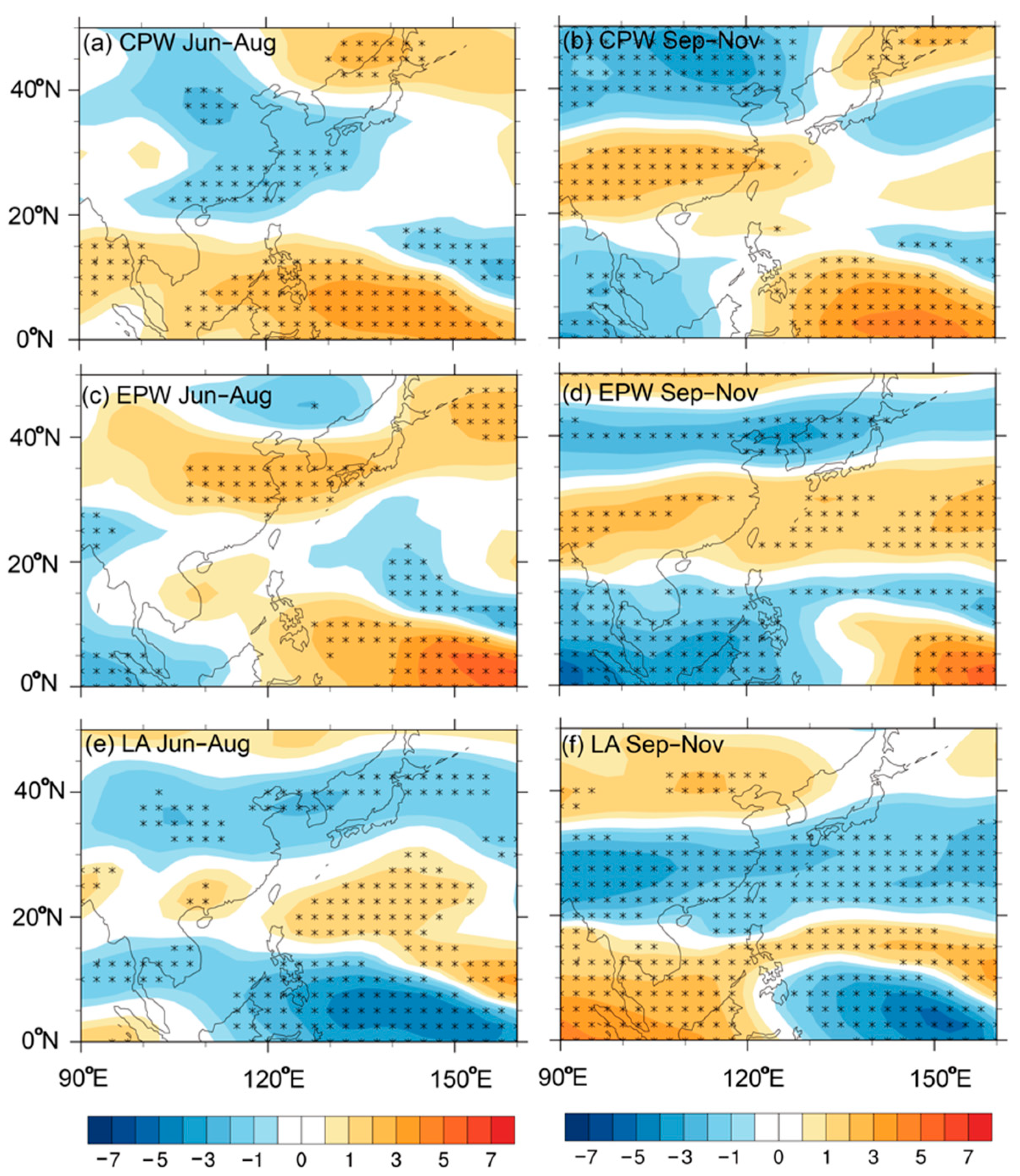
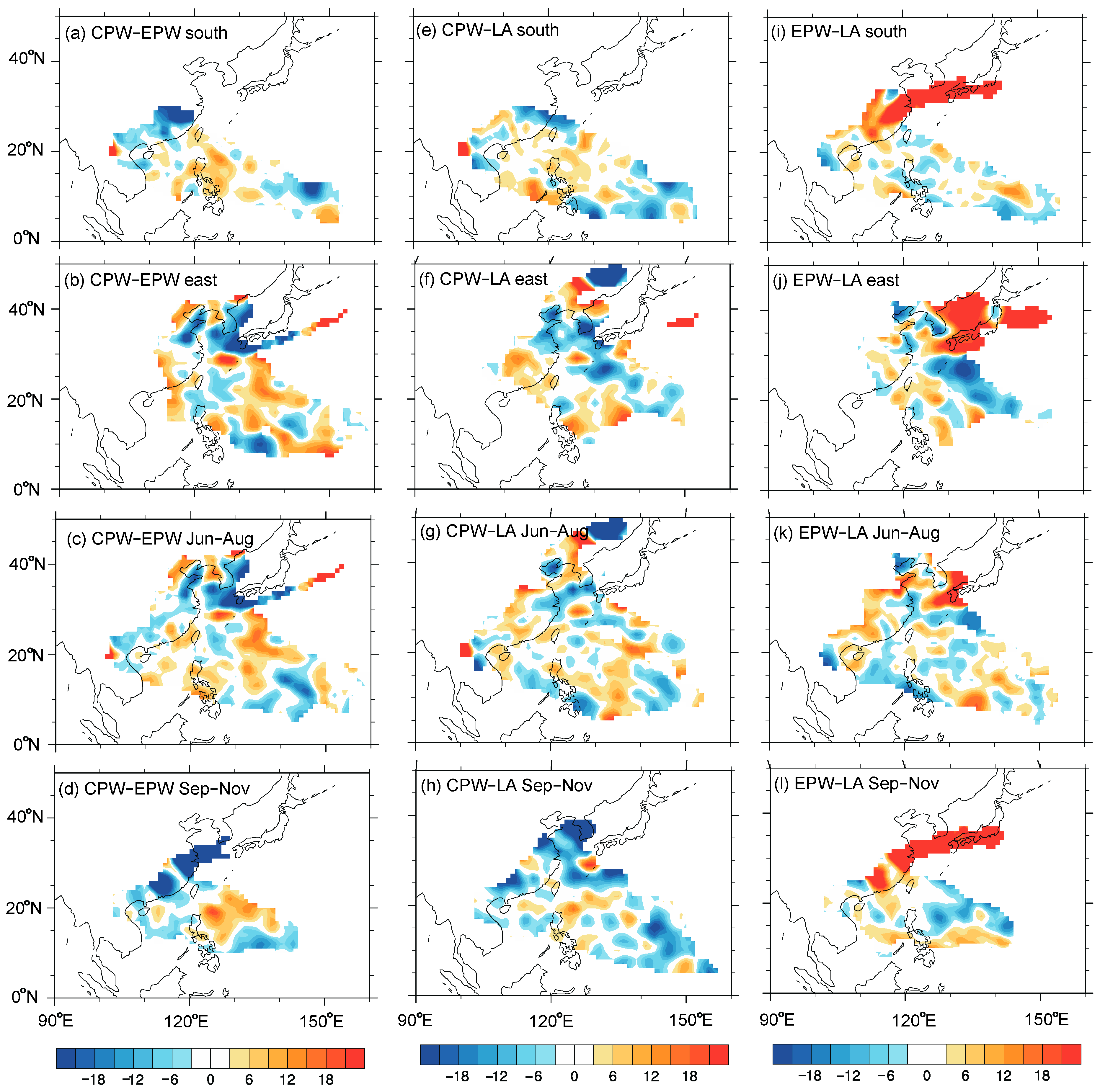
4.1. Thermodynamic Factors
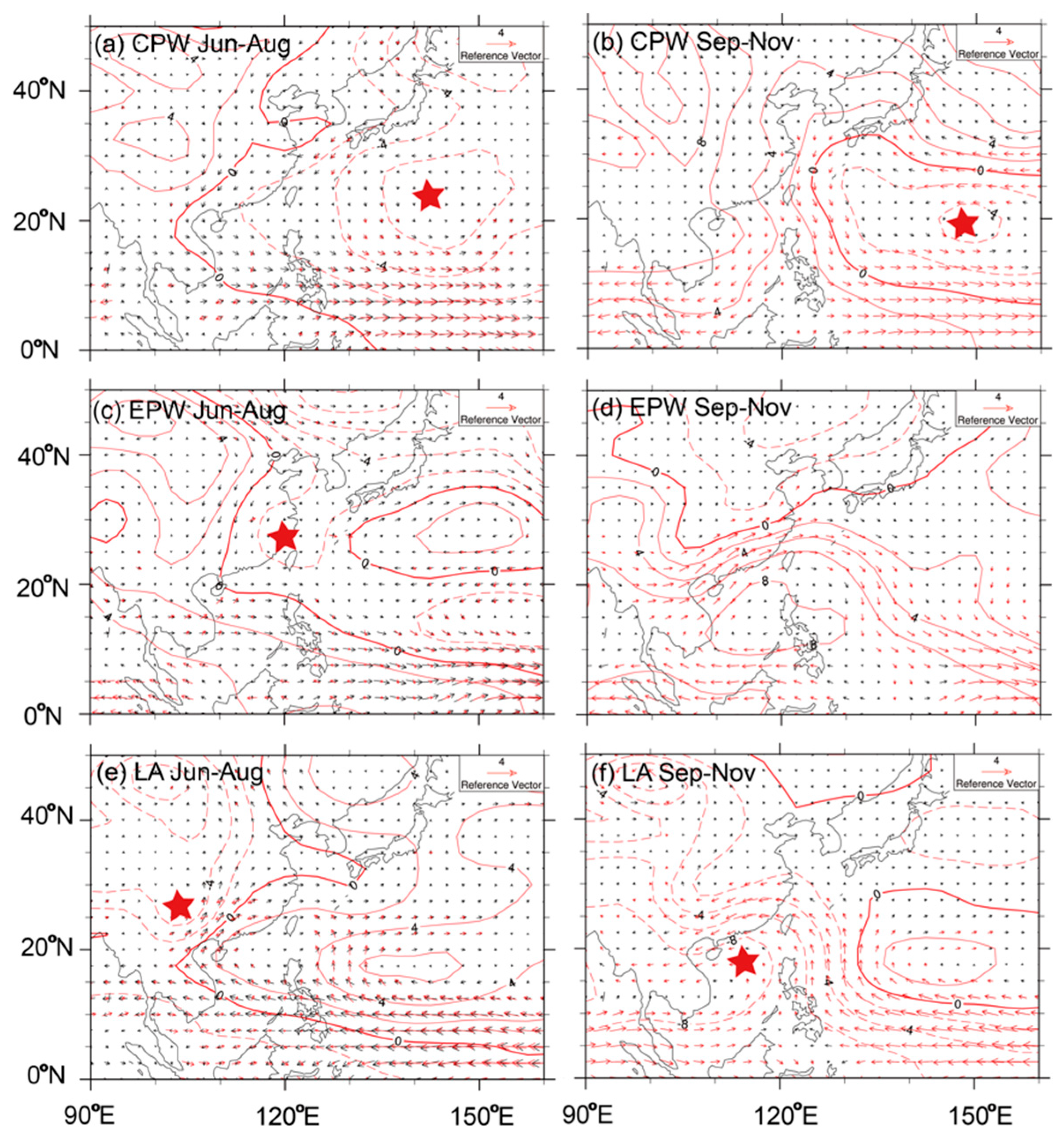
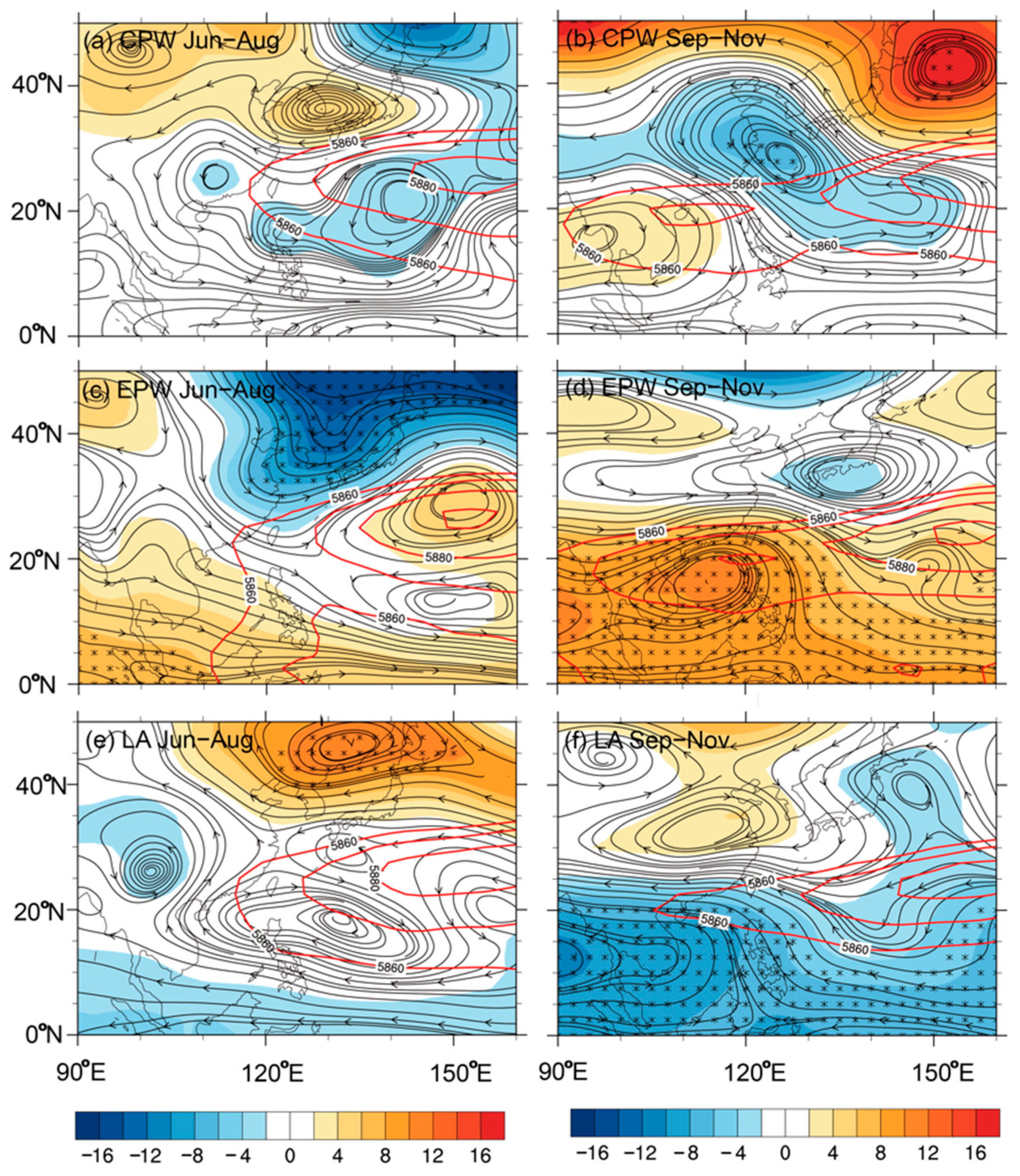
4.2. Atmospheric Circulation
5. Summary and Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, L.; Liu, Q. Tropical cyclone damages in China 1983–2006. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 90, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhao, B. Analysis of the climatic characteristics of landing tropical cyclones in East China. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2013, 19, 145. [Google Scholar]
- Kubota, H.; Chan, J.C. Interdecadal variability of tropical cyclone landfall in the Philippines from 1902 to 2005. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, 38108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinkle, J.; Maue, R.; Pielke, R., Jr. Historical global tropical cyclone landfalls. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 4729–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, S.W. US tropical cyclone landfall variability: 1950–2002. Wea. Forecast. 2004, 19, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.S.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, D.W.; Byun, H.R. Interdecadal variation of tropical cyclone making landfall over the Korean Peninsula. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 1472–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.S.R.; Ho, C.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.S. Spatially inhomogeneous trends of tropical cyclone intensity over the western North Pacific for 1977–2010. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 5088–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.C.; Liu, K.S.; Ching, S.E.; Lai, E.S. Asymmetric distribution of convection associated with tropical cyclones making landfall along the South China coast. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 2410–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, X. Classifying El Niño Modoki I and II by different impacts on rainfall in southern China and typhoon tracks. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 1322–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H. Observed rainfall asymmetry in tropical cyclones making landfall over China. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2015, 54, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W. Impacts of Tropical North Atlantic SST on Western North Pacific Landfalling Tropical Cyclones. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.S.R.; Ho, C.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.S. Strong landfall typhoons in Korea and Japan in a recent decade. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, 14801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lee, S.K. Global warming and United States landfalling hurricanes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 32396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Davidson, N.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, H. On the Relationship between Intensity and Rainfall Distribution in Tropical Cyclones Making Landfall over China. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2017, 56, 2883–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaukey, P. Wind speed changes of North Atlantic tropical cyclones preceding landfall. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2011, 50, 1913–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.C.Y.; Zhou, W.; Shun, C.M.; Lee, T.C. Change in destructiveness of landfalling tropical cyclones over China in recent decades. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 3367–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, S.J.; Sobel, A.H. Western North Pacific tropical cyclone intensity and ENSO. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 2996–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.C.L.; Xu, M. Inter-annual and inter-decadal variations of landfalling tropical cyclones in East Asia. Part I: Time series analysis. Int. J. Climatol. 2009, 29, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.S. ENSO and tropical cyclone activity. In Hurricanes and Typhoons: Past, Present, and Potential; Murnane, R.J., Liu, K.B., Eds.; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 297–332. [Google Scholar]
- Goh, A.Z.C.; Chan, J.C.L. Interannual and interdecadal variations of tropical cyclone activity in the South China Sea. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 827–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, J.; Zhou, Y.; Higgins, R.W. Characteristics of landfalling tropical cyclones in the United States and Mexico: Climatology and interannual variability. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 1247–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.C.; Chang, W.L.; Leung, W.M. Impacts of El Niño–Southern Oscillation events on tropical cyclone landfalling activity in the western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Lau, N.-C. A GCM simulation of the relationship between tropical-storm formation and ENSO. Mon. Weather Rev. 1992, 120, 958–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Vecchi, G.A.; Murakami, H.; Delworth, T.; Wittenberg, A.T.; Rosati, A.; Underwood, S.; Anderson, W.; Harris, L.; Gudgel, R.; et al. Improved Simulation of Tropical Cyclone Responses to ENSO in the Western North Pacific in the High-Resolution GFDL HiFLOR Coupled Climate Model. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 1391–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, B.; Camargo, S.J. The seasonally-varying influence of ENSO on rainfall and tropical cyclone activity in the Philippines. Clim. Dyn. 2009, 32, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.S.; Chan, J.C.L. Climatological characteristics and seasonal forecasting of tropical cyclones making landfall along the South China coast. Mon. Weather Rev. 2003, 131, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fudeyasu, H.; Iizuka, S.; Matsuura, T. Impact of ENSO on landfall characteristics of tropical cyclones over the western North Pacific during the summer monsoon season. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 27449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, K.; Behera, S.K.; Rao, S.A.; Weng, H.; Yamagata, T. El Niño Modoki and its possible teleconnection. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2007, 112, 3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, H.; Ashok, K.; Behera, S.K.; Rao, S.A.; Yamagata, T. Impacts of recent El Niño Modoki on dry/wet conditions in the Pacific rim during boreal summer. Clim. Dyn. 2007, 29, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.M.; Webster, P.J.; Curry, J.A. Modulation of North Pacific tropical cyclone activity by three phases of ENSO. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 1839–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Wang, C.; Enfield, D.B. On the impact of central Pacific warming events on Atlantic tropical storm activity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, 44459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, R.; Wu, R. Interdecadal variability in tropical cyclone frequency over the South China Sea and its association with the Indian Ocean sea surface temperature. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.M.; Webster, P.J.; Curry, J.A. Impact of shifting patterns of Pacific Ocean warming on North Atlantic tropical cyclones. Science 2009, 325, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Tam, C.Y. Different impacts of two kinds of Pacific Ocean warming on tropical cyclone frequency over the western North Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, 41708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, C. Simulated impacts of two types of ENSO events on tropical cyclone activity in the western North Pacific: Large-scale atmospheric response. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 42, 2727–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Graf, H.F.; Leung, Y.; Herzog, M. Different El Niño types and tropical cyclone landfall in East Asia. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 6510–6523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woollen, J.; et al. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, G.D.; Chelliah, M. Leading tropical modes associated with interannual and multidecadal fluctuations in North Atlantic hurricane activity. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 590–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, S.J.; Sobel, A.H. Formation of tropical storms in an atmospheric general circulation model. Tellus 2004, 56A, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K. Uncertainty in hurricanes and global warming. Science 2005, 308, 1753–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, M.D.; Reinhold, T.A. Tropical cyclone destructive potential by integrated kinetic energy. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, K. Increasing destructiveness of tropical cyclones over the past 30 years. Nature 2005, 436, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emanuel, K. Environmental factors affecting tropical cyclone power dissipation. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 5497–5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kossin, J.P.; Knapp, K.R.; Vimont, D.J.; Murnane, R.J.; Harper, B.A. A globally consistent reanalysis of hurricane variability and trends. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 28836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corporal-Lodangco, I.L.; Leslie, L.M.; Lamb, P.J. Impacts of ENSO on Philippine tropical cyclone activity. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 1877–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, S.; Sobel, A.H.; Barnston, A.G.; Emanuel, K.A. Tropical cyclone genesis potential index in climate models. Tellus 2007, 59A, 428–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, W.M. Hurricanes: Their formation, structure and likely role in the tropical circulation. In Meteorology over the Tropical Oceans; Shaw, D.B., Ed.; Royal Meteorological Society: Bracknell, UK, 1979; pp. 155–218. [Google Scholar]
- Chia, H.H.; Ropelewski, C.F. The interannual variability in the genesis location of tropical cyclones in the northwest Pacific. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 2934–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, W.M. Tropical cyclone formation. In A Global View of Tropical Cyclones; Elsberry, R., Ed.; Office of Naval Research: Arlington, VA, USA, 1987; pp. 53–90. [Google Scholar]
- Nitta, T.; Hu, Z.Z. Summer climate variability in China and its association with 500 hPa height and tropical convection. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 1996, 74, 425–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.Y.; Chou, C.; Chu, P.S. The abrupt shift of typhoon activity in the vicinity of Taiwan and its association with western North Pacific–East Asian climate change. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 3617–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chan, J.C.L. How strong ENSO events affect tropical storm activity over the western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 1643–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.D.; Chu, P.S. Interannual variation of tropical cyclone activity over the central North Pacific. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 2002, 80, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Leung, Y.; Chan, J.C. The Analysis of Tropical Cyclone Tracks in the Western North Pacific through Data Mining. Part I: Tropical Cyclone Recurvature. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 1394–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


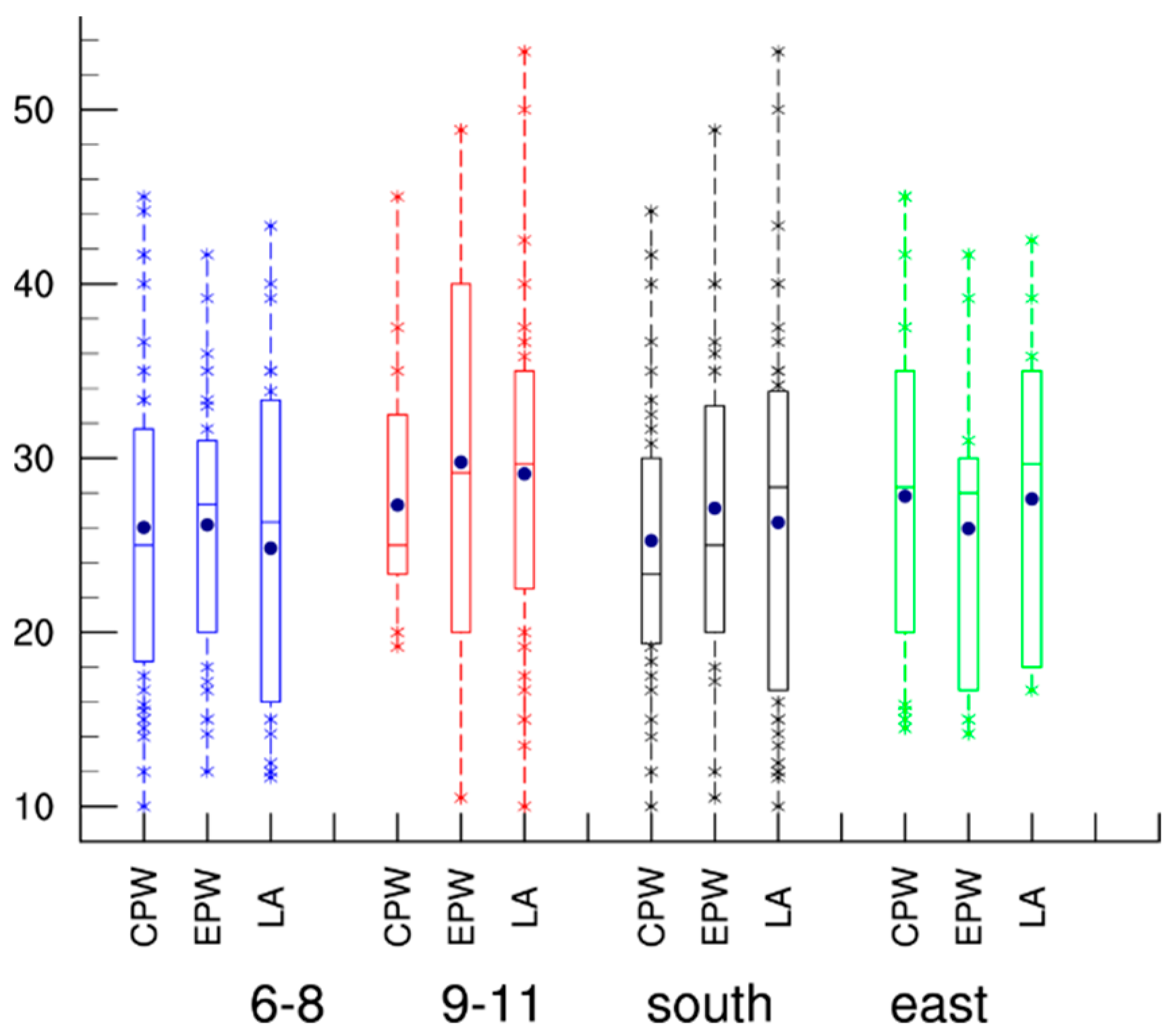
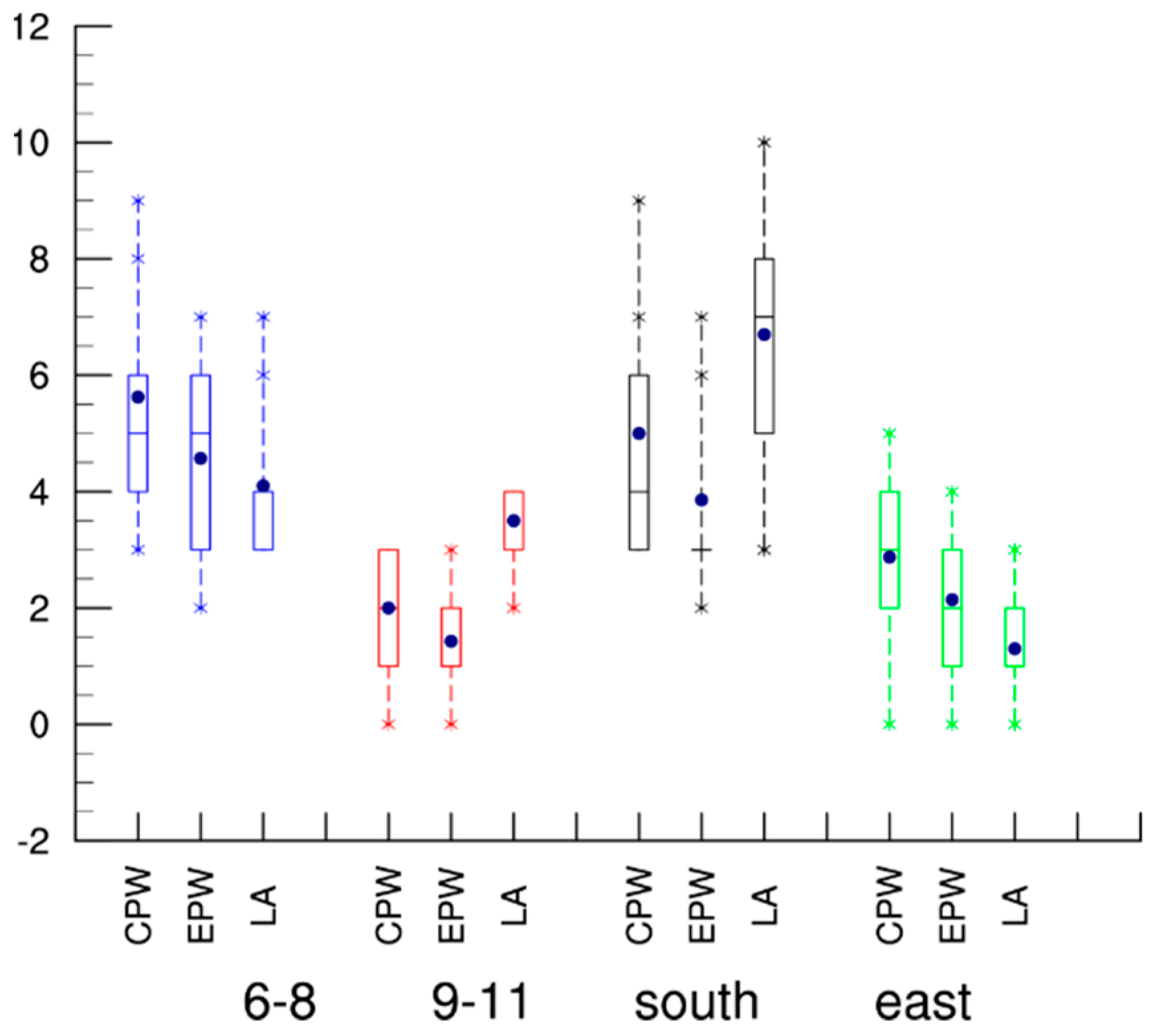
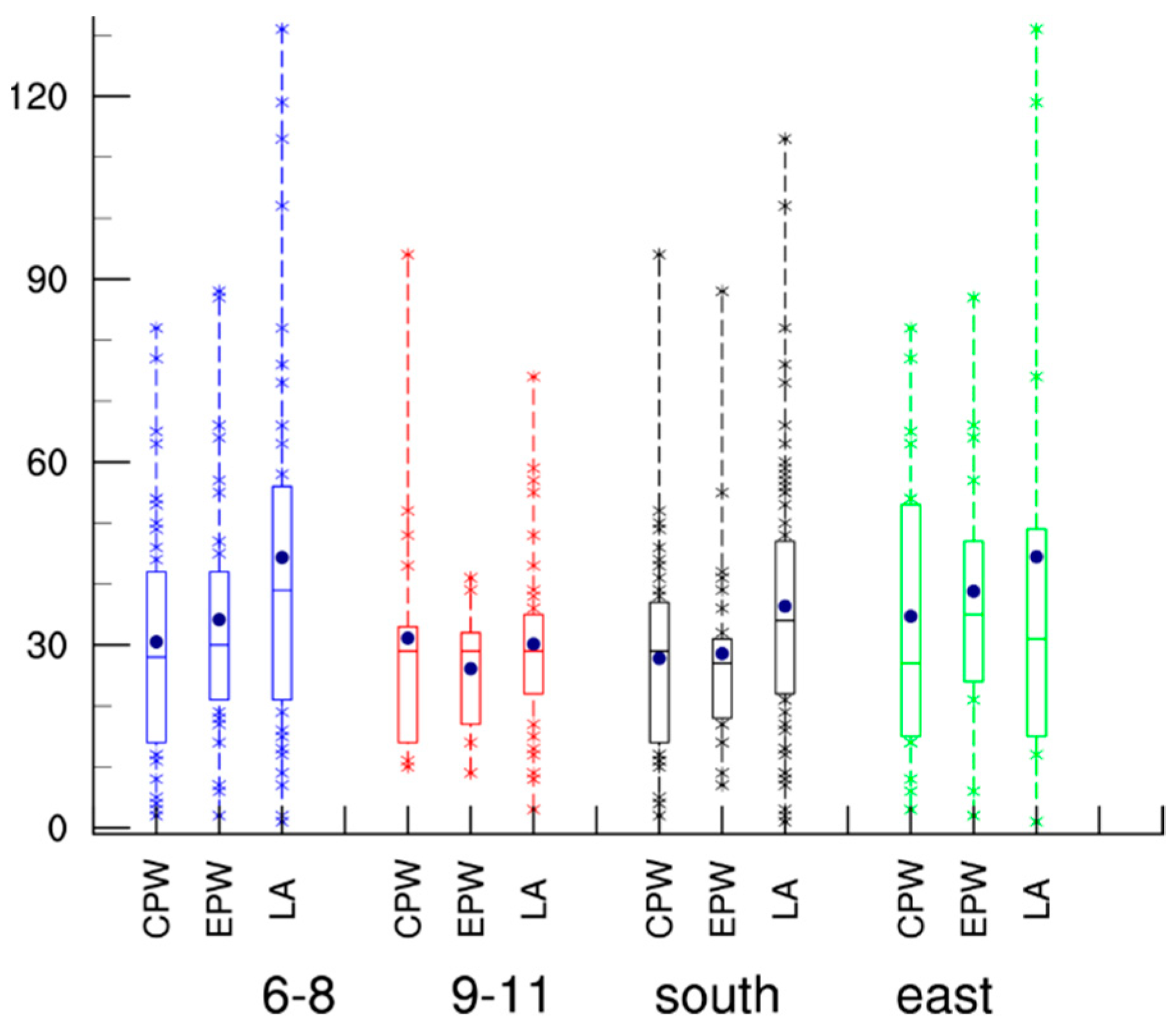

| Years | Total | LF | LT (h) | LFLT (h) | LF/T (%) | LFLT/LT (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPW | 36.9 | 7.8 | 143.9 | 30.3 | 21.4 | 21 |
| EPW | 31.3 | 6 | 192.84 | 32.2 | 19 | 16.7 |
| LA | 32.5 | 7.9 | 143.15 | 37.68 | 24.3 | 26.3 |
| avg | 32.6 | 7.5 | 171.65 | 33.8 | 23 | 19.7 |
| CPW; EPW; LA (Avg) | PDI | Intensity | Frequency | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TOTAL | 2.92; 3.56; 3.65 (3.5) | 26.2; 27.02; 26.5 (26.6) | 7.8; 6; 7.9 (7.5) | 30.3; 32.2; 37.68 (33.8) |
| JJA | 3.18; 3.15; 3.76 | 26.0; 26.2; 24.8 | 5.6; 4.6; 4.1 | 30.5; 34.1; 44.3 |
| SON | 2.45; 4.82; 3.69 | 27.3; 29.8; 29.0 | 2; 1.4; 3.5 | 31.1; 26.2; 30.1 |
| South | 2.88; 3.94; 3.64 | 25.26; 27.0; 26.3 | 5; 3.86; 6.7 | 27.8; 28.6; 36.36 |
| East | 3.0; 2.85; 3.62 | 27.8; 25.96; 27.65 | 2.87; 2.15; 1.3 | 34.69; 38.8; 44.46 |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L. Impact of Different Types of ENSO Years on Intensity Changes of Landfalling Tropical Cyclones over China. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10030161
Liu L. Impact of Different Types of ENSO Years on Intensity Changes of Landfalling Tropical Cyclones over China. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(3):161. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10030161
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Lu. 2019. "Impact of Different Types of ENSO Years on Intensity Changes of Landfalling Tropical Cyclones over China" Atmosphere 10, no. 3: 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10030161
APA StyleLiu, L. (2019). Impact of Different Types of ENSO Years on Intensity Changes of Landfalling Tropical Cyclones over China. Atmosphere, 10(3), 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10030161





