Time-Scaling Properties of Sunshine Duration Based on Detrended Fluctuation Analysis over China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Records and Method
2.1. Data Records
2.2. The DFA Method
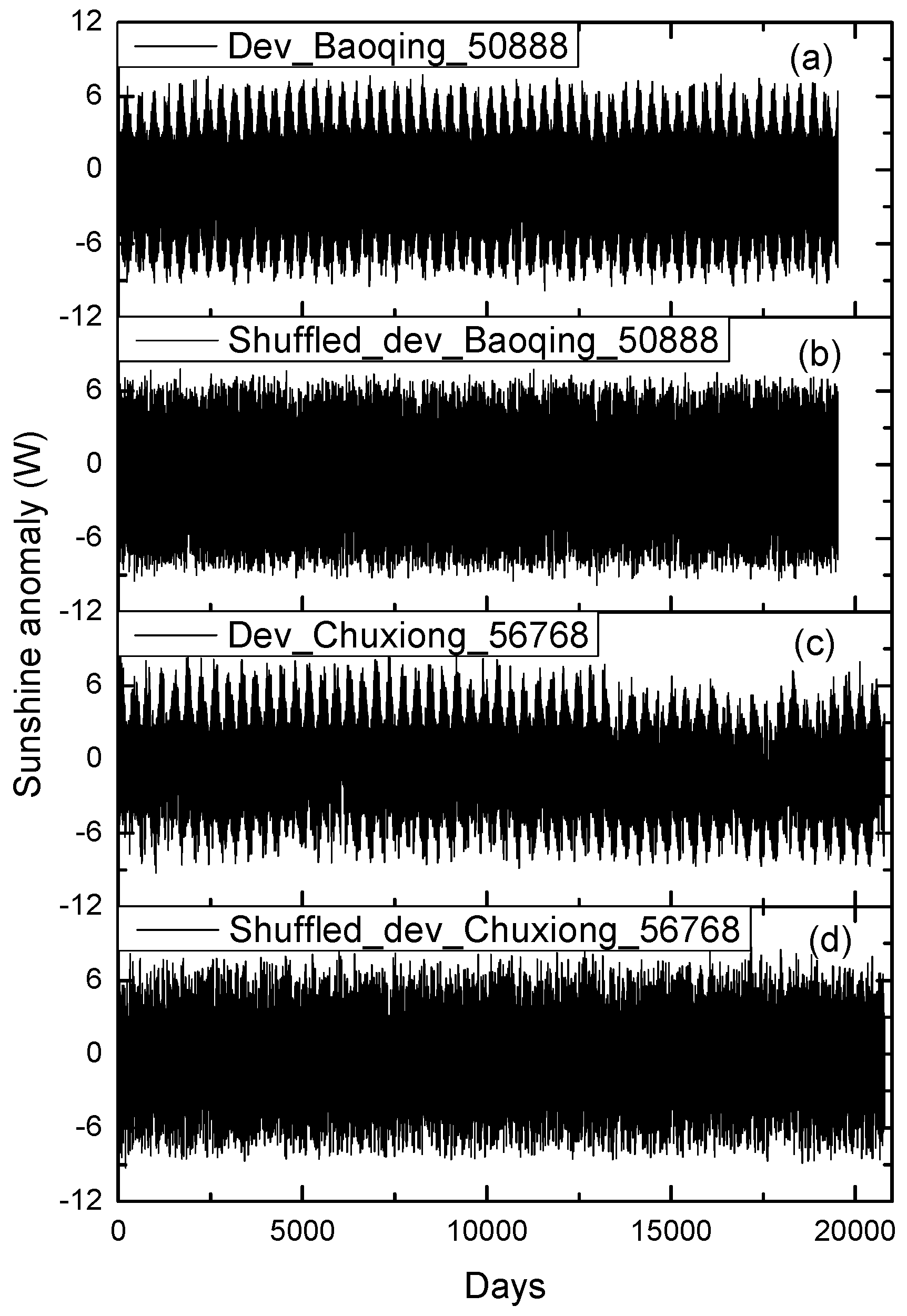
- In order to investigate the correlation characteristics in the SSD time series, xi, i = 1…N, N is the length of the time series. The SSD anomaly time series is integrated to obtain profile Y(i), and I = 1, …, N, is then obtained as follows.∆xk is the SSD anomaly time series from which the annual cycle is removed. The profile Y(i) is cut into Ns ≡ [N/s] non-overlapping segments with equal length s in order to carry out the fluctuation analysis. The part of a segment of length s will be left if N is not equal to an integer multiple of length s. The same procedure is recalculated starting from the end of the data records. Accordingly, the profile is performed twice in order to use all data records. We obtain 2Ns segments altogether [14,29].
- The local trend Pn(i) in each box of length s is calculated by a least-squares fit of the data records. Then, the integrated time series Yn(i) is detrended by subtracting the local trend.In the data sets of each segment, a least-square fit is used to calculate the local trend of each segment. K = 1,…, . In the nth order DFA (DFA1, DFA2,…, DFAn), the order n of the polynomials is used in the fitting procedure. Trends of nth order in the profile and (n − 1)th order in the original record are eliminated. By doing so, the trends of the profile are eliminated by subtracting the local polynomial fit. A comparison of the results for different orders of DFA allows us to estimate the strength of the trends in the time series.Yn(i) = Y(i) − Pn(i)
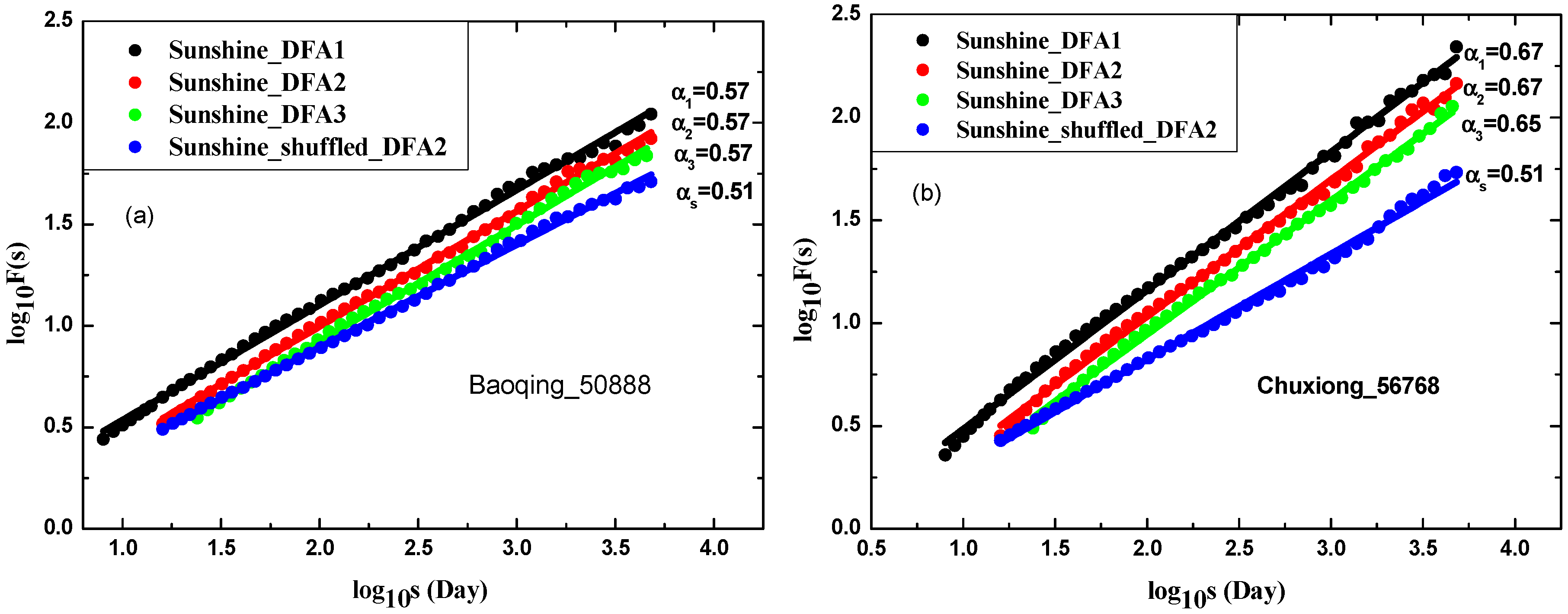
- The root-mean-square deviation of the profile from these local polynomial fits determines the deviation F(s) for a given n-size box.We obtain the fluctuation functions F(n)(s) by diverse detrending orders n.Finally, for long-range correlated data records, follows a power-law relationship and increases with time window s. The power-law relationship can be exhibited by a linear log-log plot, where α is the scaling exponent. In this method, the scaling exponent α taking values from 0 to 1 (0 < α < 1) allows the measure of LRCs for the time series as follows.
- If α = 0.5, Gaussian random walks.
- If 0.5 < α < 1, positive LRCs are indicated and the time series is persistent.
- If 0 < α < 0.5, the time series is anti-persistent.
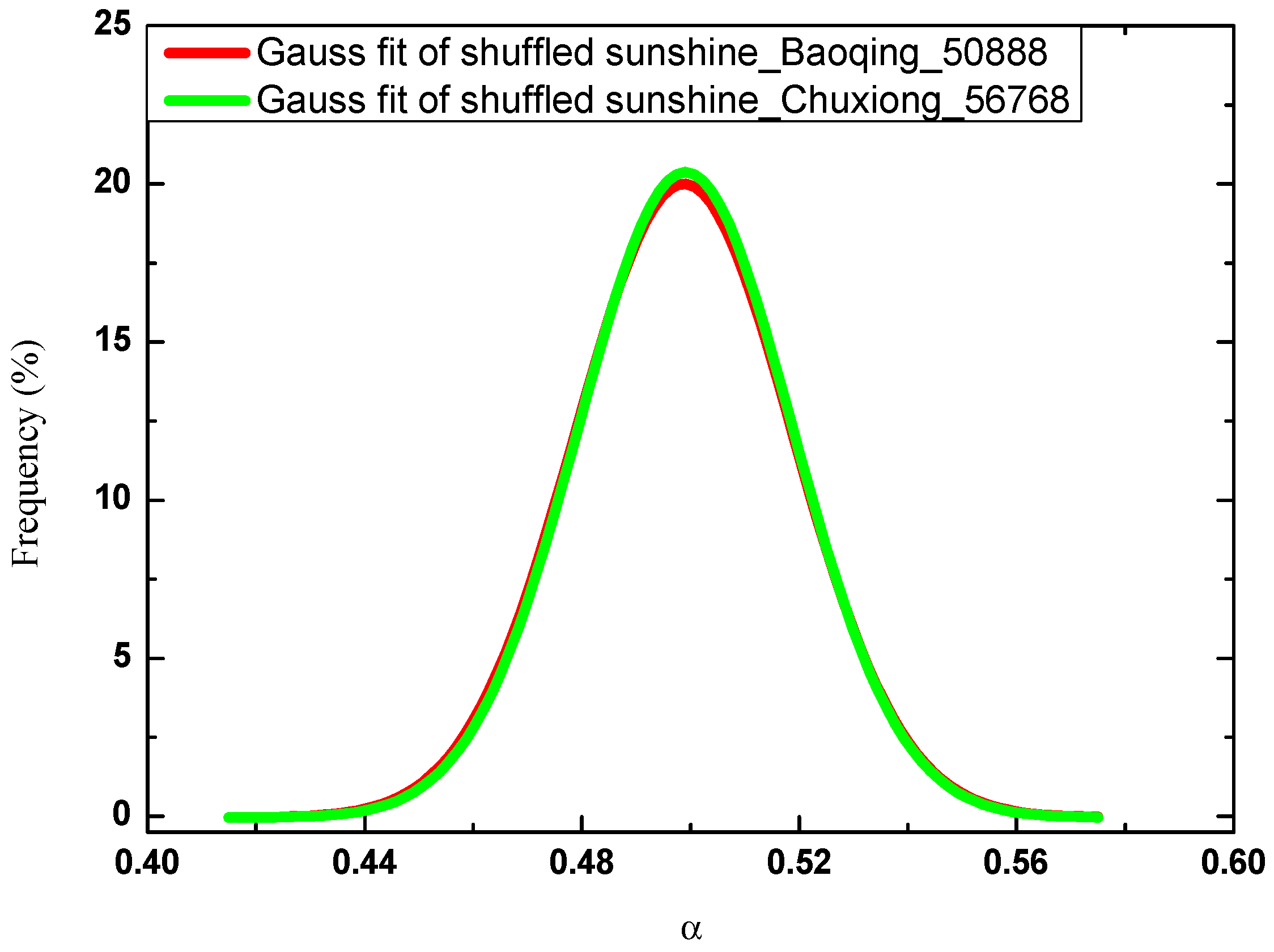
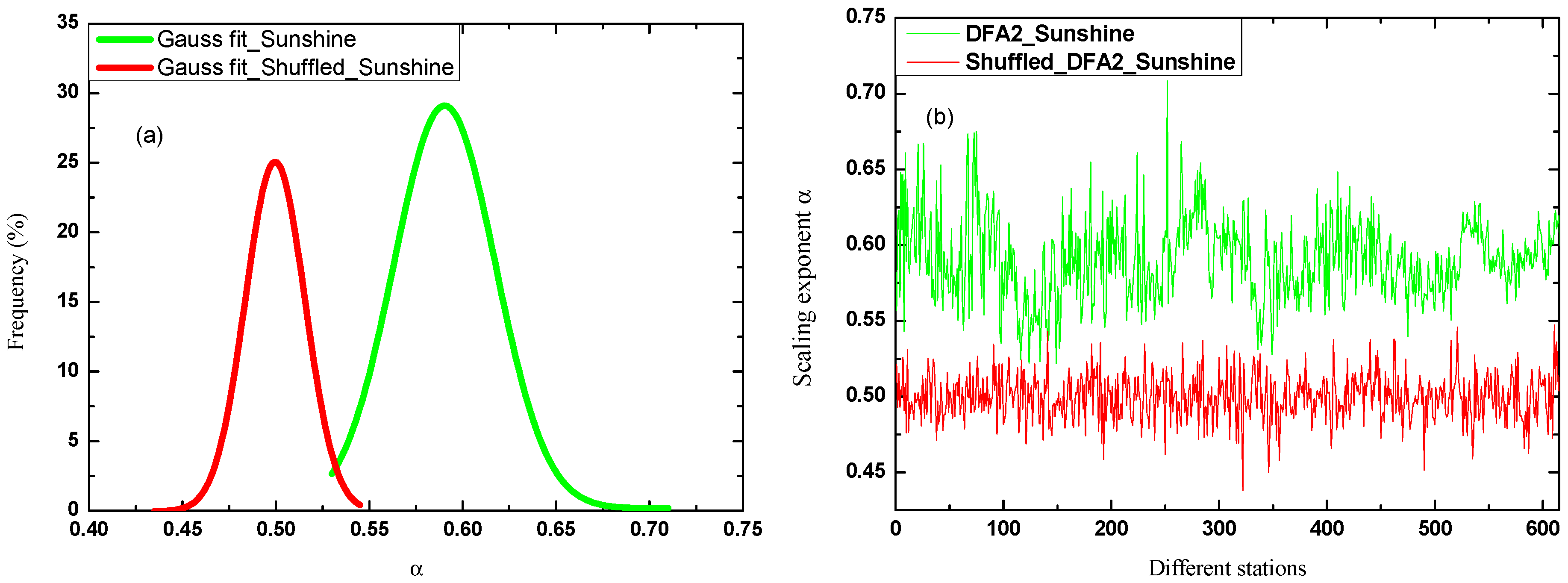
3. Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benson, R.B.; Paris, M.V.; Sherry, J.E.; Justus, C.G. Estimation of daily and monthly direct, diffuse and global solar radiation from sunshine duration measurements. Sol. Energy 1984, 32, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpabio, L.E.; Etuk, S.E. Relationship between global solar radiation and sunshine duration for Onne, Nigeria. Turk. J. Phys. 2003, 27, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Gopinathan, K.K. A general formula for computing the coefficients of the correlation connecting global solar radiation to sunshine duration. Sol. Energy 1988, 41, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almorox, J.Y.; Hontoria, C. Global solar radiation estimation using sunshine duration in Spain. Energy Convers. Manag. 2004, 45, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.Z.; Shi, G.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Arimoto, R.; Zhao, J.Q.; Xu, L.; Wang, B.; Chen, Z.H. Analysis of 40 years of solar radiation data from China, 1961–2000. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L. Relationship between global solar radiation and sunshine duration for Northwest China. Int. J Phys. Sci. 2010, 5, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Aksoy, B. Analysis of changes in sunshine duration data for Ankara, Turkey. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 1999, 64, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, D.P.; Qian, Y. Decreasing trends in sunshine duration over China for 1954–1998: Indication of increased haze pollution? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 38-1–38-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.C.; Wang, C.H.; Shiu, C.J.; Chang, H.W.; Hsiao, C.K.; Liaw, S.H. Reduction in sunshine duration over Taiwan: Causes and implications. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2002, 13, 523–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Kang, W.; Zhao, T.; Luo, Y.; Duan, C.; Chen, J. Long-term trends in sunshine duration over Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau in Southwest China for 1961–2005. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Zhao, N.; Hao, X.H.; Li, C.Q. Decreasing trend of sunshine hours and related driving forces in North China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2009, 97, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.K.; Buldyrev, S.V.; Havlin, S.; Simons, M.; Stanley, H.E.; Goldberger, A.L. Mosaic organization of DNA nucleotides. Phys. Rev. E 1994, 49, 1685–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunde, A.; Havlin, S.; Kantelhardt, J.W.; Penzel, T.; Peter, J.H.; Voigt, K. Correlated and uncorrelated regions in heart-rate fluctuations during sleep. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 3736–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantelhardt, J.W.; Koscielny-Bunde, E.; Rego, H.H.; Havlin, S.; Bunde, A. Detecting long-range correlations with detrended fluctuation analysis. Physica A 2001, 295, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.O.; Talkner, P. Spectra and correlations of climate data from days to decades. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 20131–20144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichner, J.F.; Koscielny-Bunde, E.; Bunde, A.; Havlin, S.; Schellnhuber, H.J. Power-law persistence and trends in the atmosphere: A detailed study of long temperature records. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 68, 046133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blender, R.; Fraedrich, K. Long time memory in global warming simulations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Fu, Z. A universal model to characterize different multi-fractal behaviors of daily temperature records over China. Physica A 2008, 387, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, N.; Fu, Z.; Mao, J. Different scaling behaviors in daily temperature records over China. Physica A 2010, 389, 4087–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varotsos, C.A.; Efstathiou, M.N.; Cracknell, A.P. On the scaling effect in global surface air temperature anomalies. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 5243–5253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Yuan, N.; Fu, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, X. Subarea characteristics of the long-range correlations, the index χ for daily temperature records over China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2012, 109, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Li, N.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, J. Long-range correlation behaviors for the 0-cm average ground surface temperature and average air temperature over China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 119, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Li, N.; Zhao, X. Scaling behaviors of precipitation over China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 128, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lin, G.; Fu, Z. Long-range correlations in daily relative humidity fluctuations: A new index to characterize the climate regions over China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monetti, R.A.; Havlin, S.; Bunde, A. Long-term persistence in the sea surface temperature fluctuations. Physica A 2003, 320, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Leung, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, W. Scaling behaviors of global sea surface temperature. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 3122–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, F. Multi-fractal scaling comparison of the Air Temperature and the Surface Temperature over China. Physica A 2016, 462, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ivanov, P.C.; Hu, K.; Stanley, H.E. Effect of nonstationarities on detrended fluctuation analysis. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 65, 041107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koscielny-Bunde, E.; Bunde, A.; Havlin, S.; Goldreich, Y. Analysis of daily temperature fluctuations. Physica A 1986, 231, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, L.; Zhang, J.; Fang, Y. Time-Scaling Properties of Sunshine Duration Based on Detrended Fluctuation Analysis over China. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10020083
Jiang L, Zhang J, Fang Y. Time-Scaling Properties of Sunshine Duration Based on Detrended Fluctuation Analysis over China. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(2):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10020083
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Lei, Jiping Zhang, and Yan Fang. 2019. "Time-Scaling Properties of Sunshine Duration Based on Detrended Fluctuation Analysis over China" Atmosphere 10, no. 2: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10020083
APA StyleJiang, L., Zhang, J., & Fang, Y. (2019). Time-Scaling Properties of Sunshine Duration Based on Detrended Fluctuation Analysis over China. Atmosphere, 10(2), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10020083




