Simulating the Effects of Urban Parameterizations on the Passage of a Cold Front During a Pollution Episode in Megacity Shanghai
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model Simulation and Scheme Settings
2.1. Urban Schemes
2.2. Model Settings
3. Observational Data and Synoptic Situations in Shanghai
3.1. Statistical Synoptic Situations During Air-Pollution Days in 2011–2013
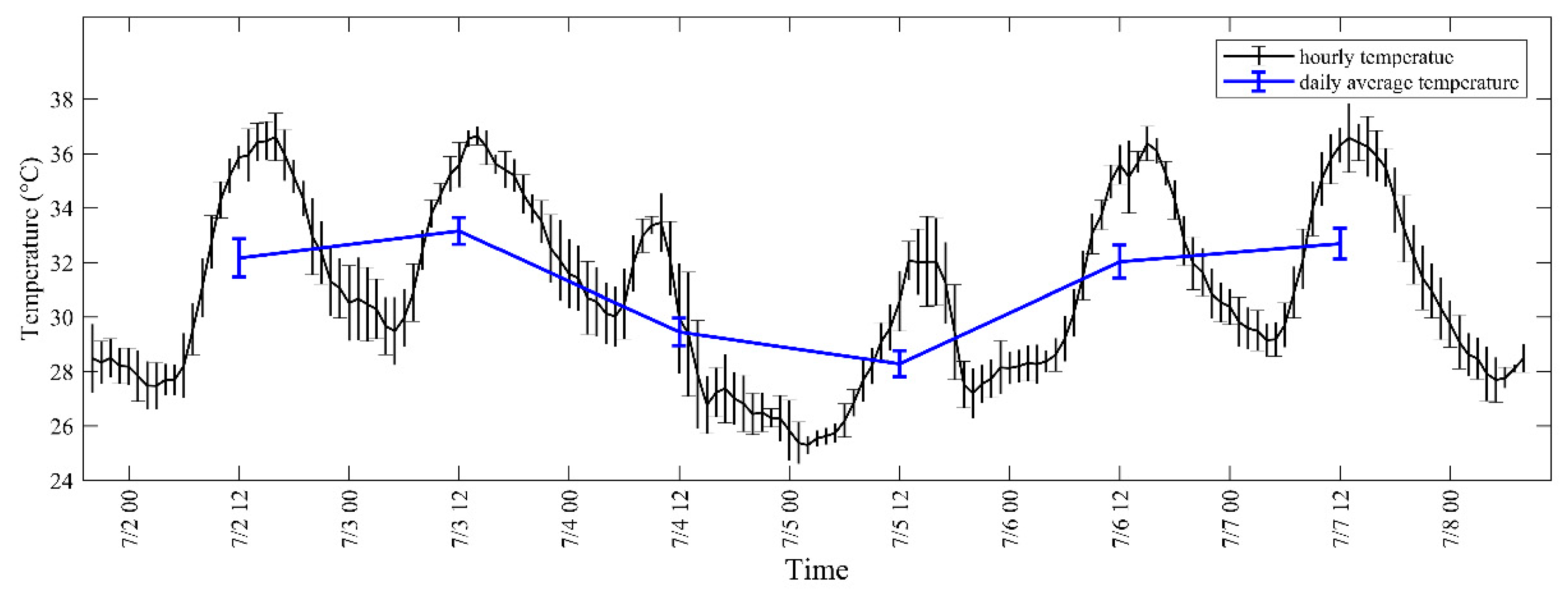
3.2. Observational Data for the Simulated Case
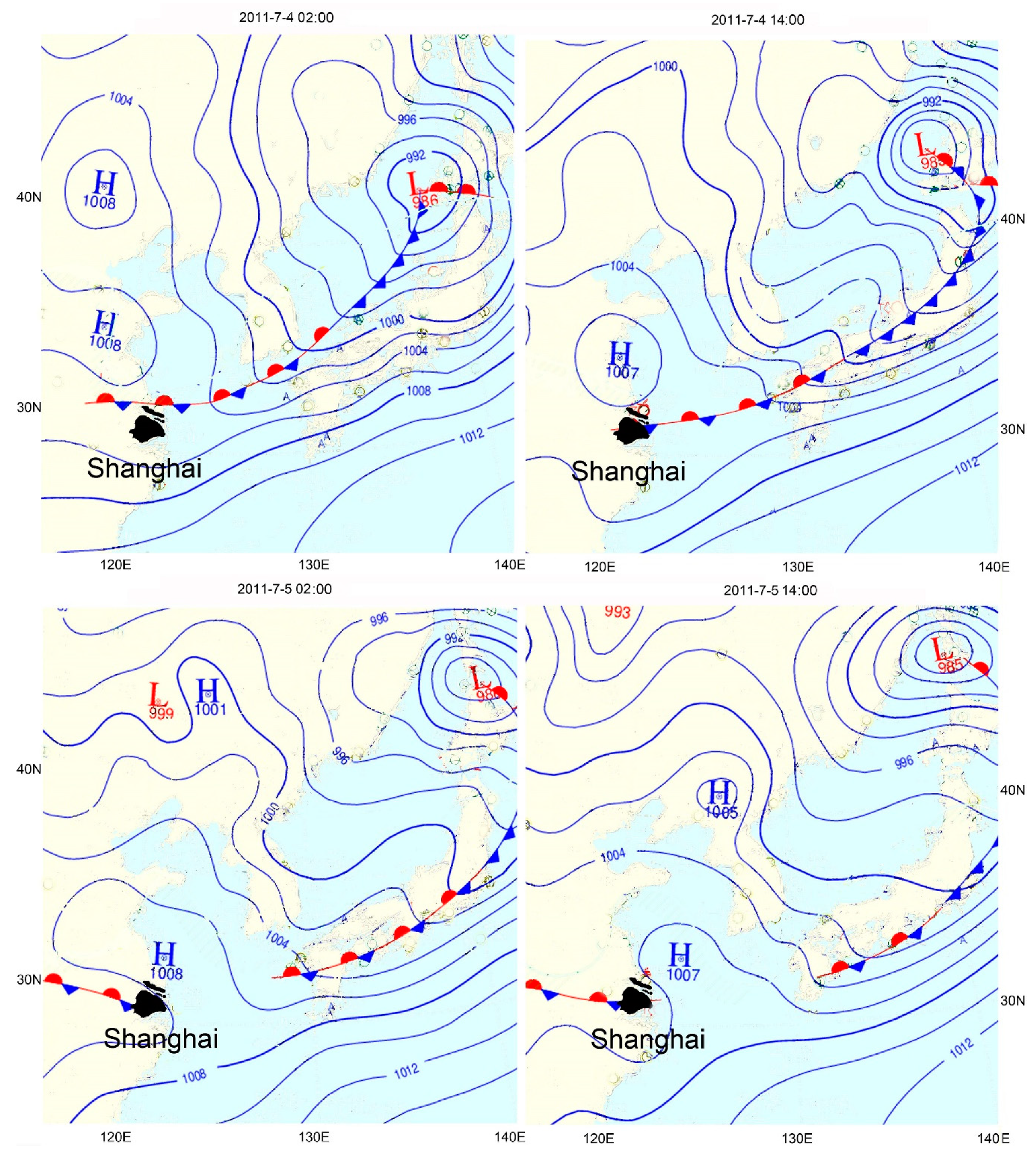
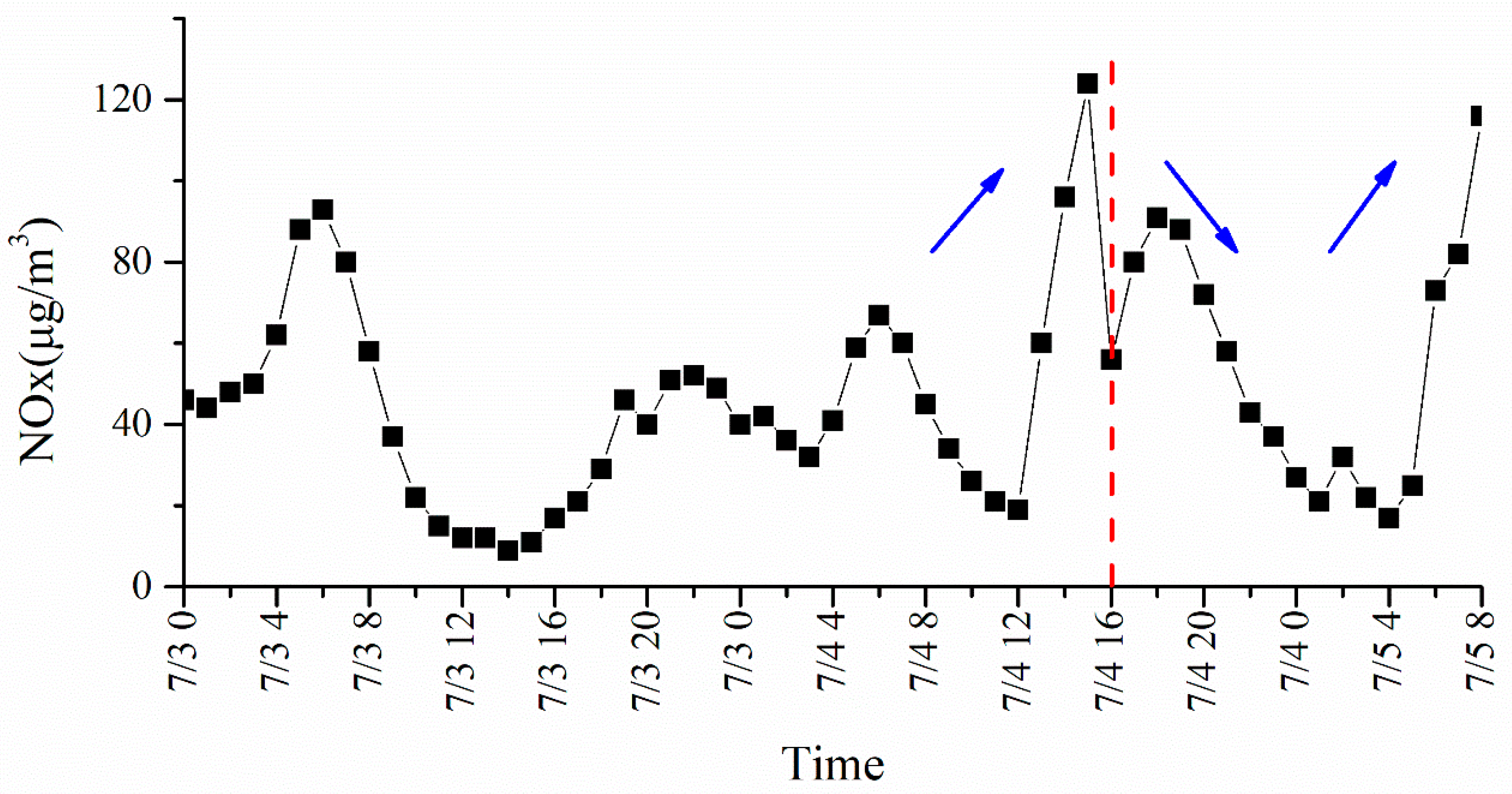
3.3. Weather and Pollution Situations for the Simulated Case
4. Comparison of the Measured Data and Simulated Results
4.1. Comparison of Statistical Parameters
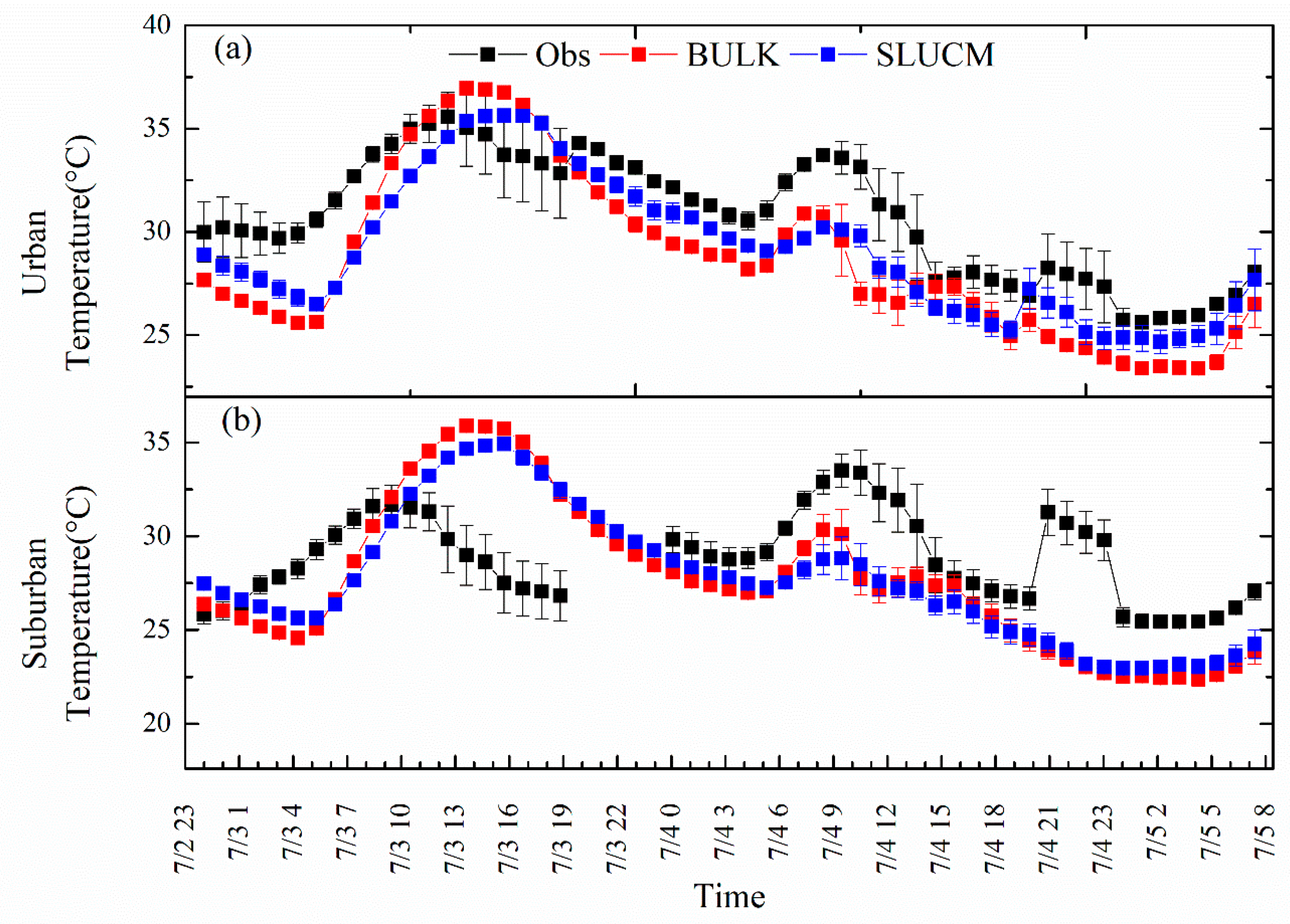
4.2. Comparison of Measurements and Simulations for Different Urban Classes
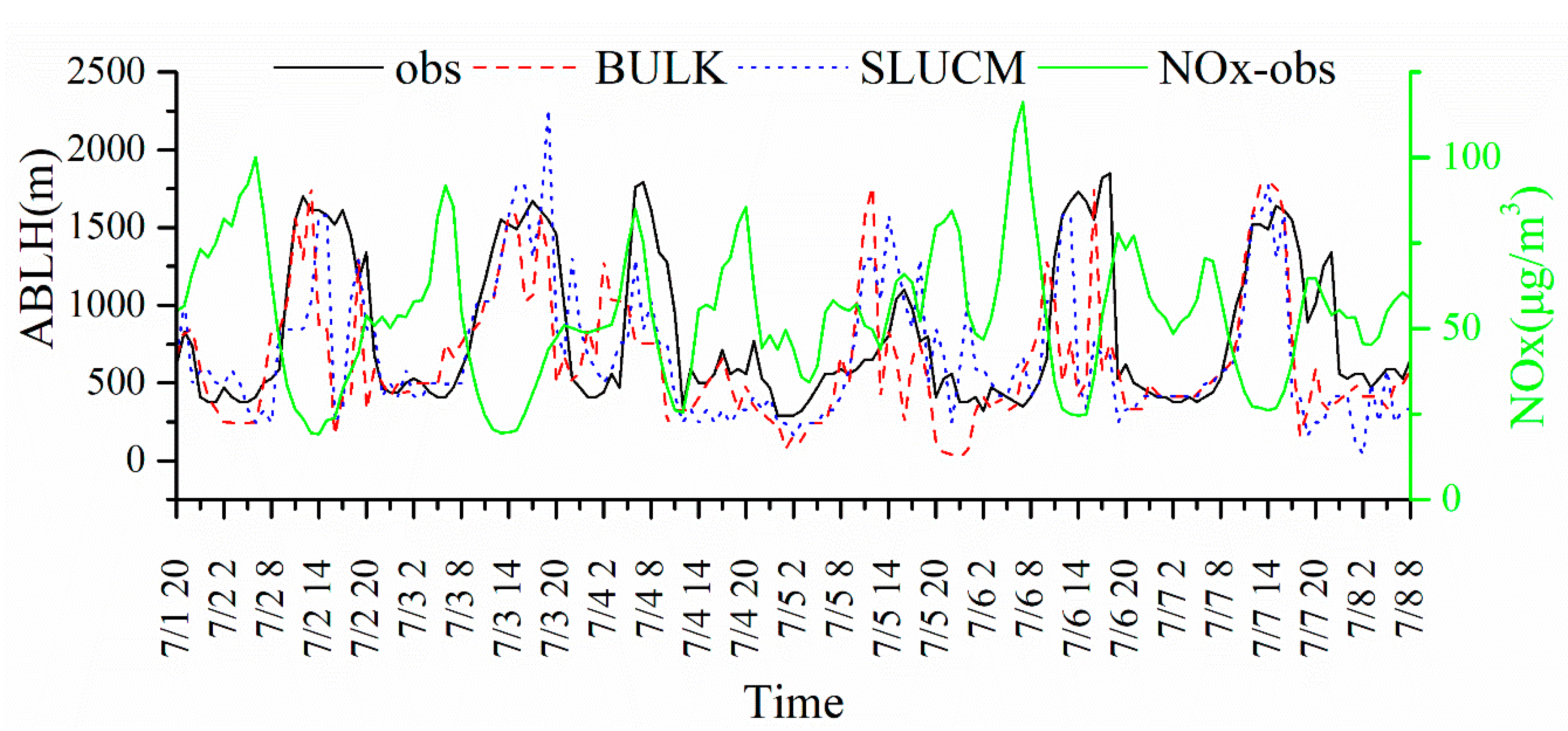
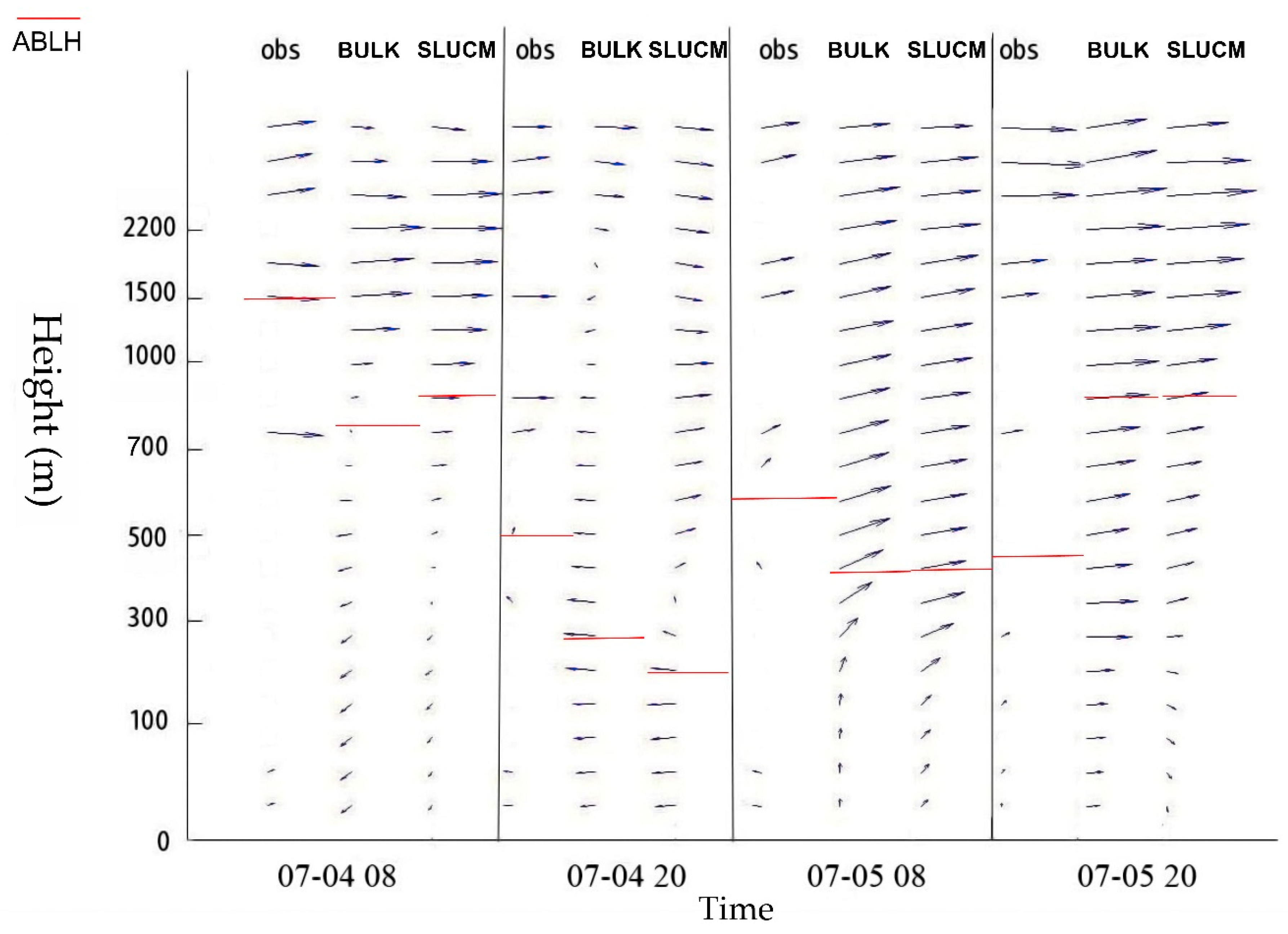
4.3. Comparison of Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height and Vertical Profile of Wind
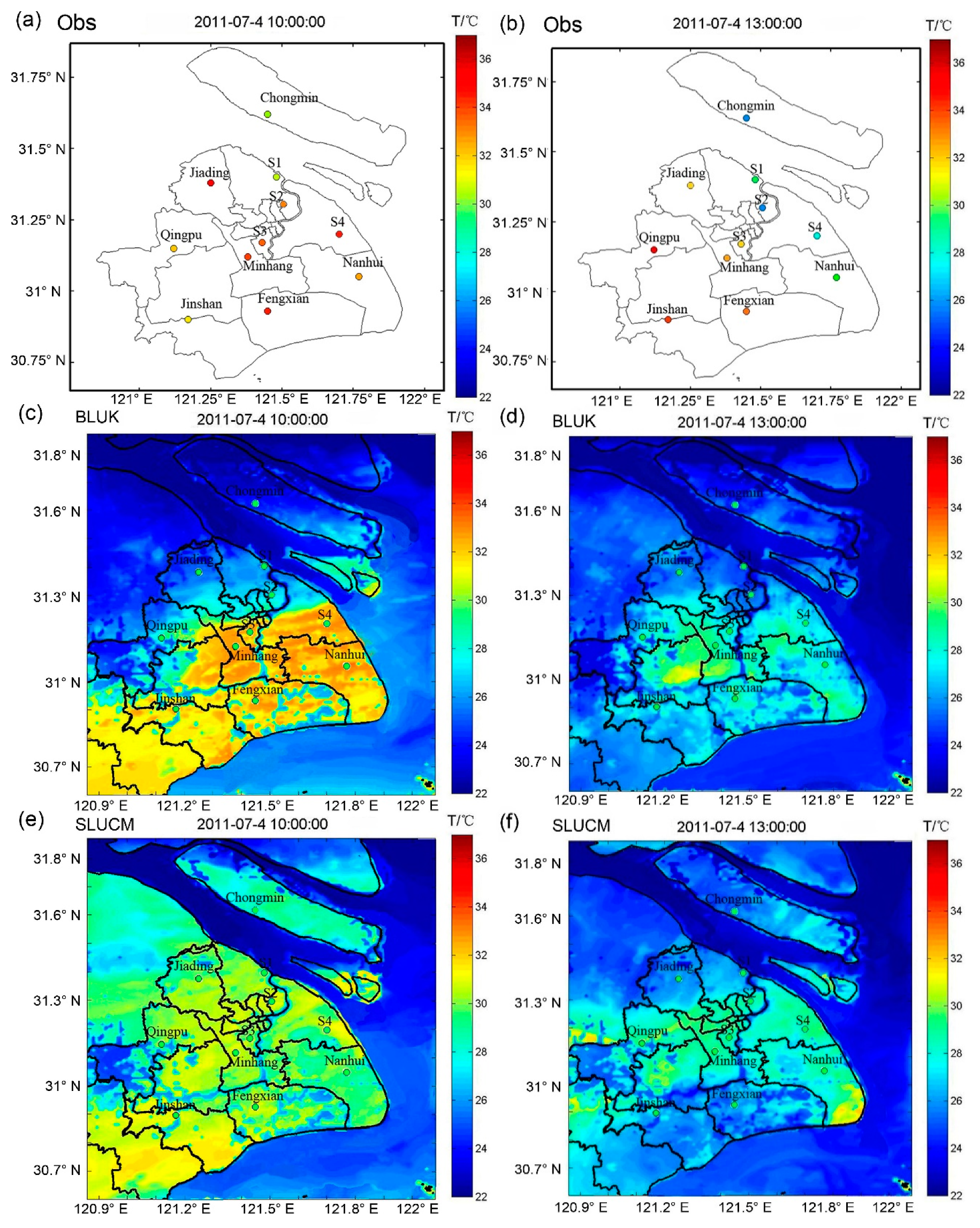
4.4. Comparison of the Surface Temperature Fields
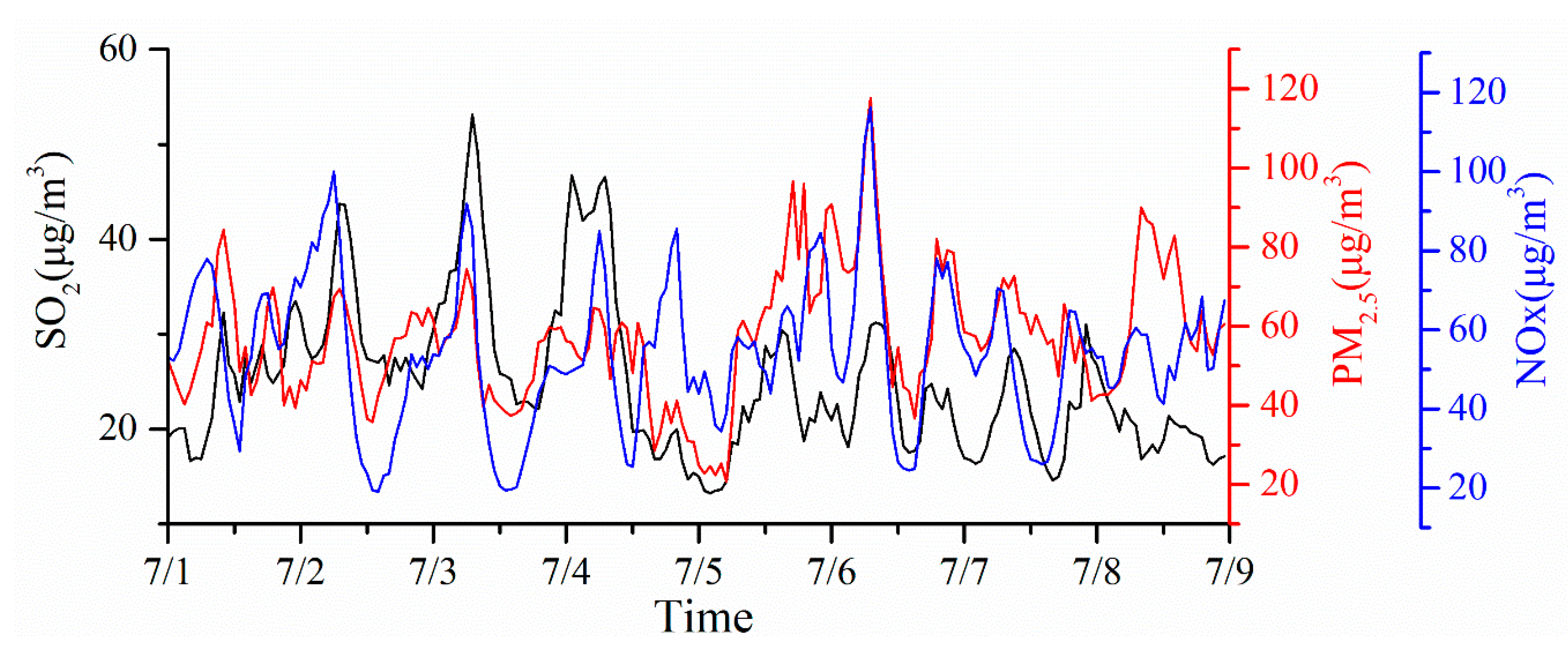
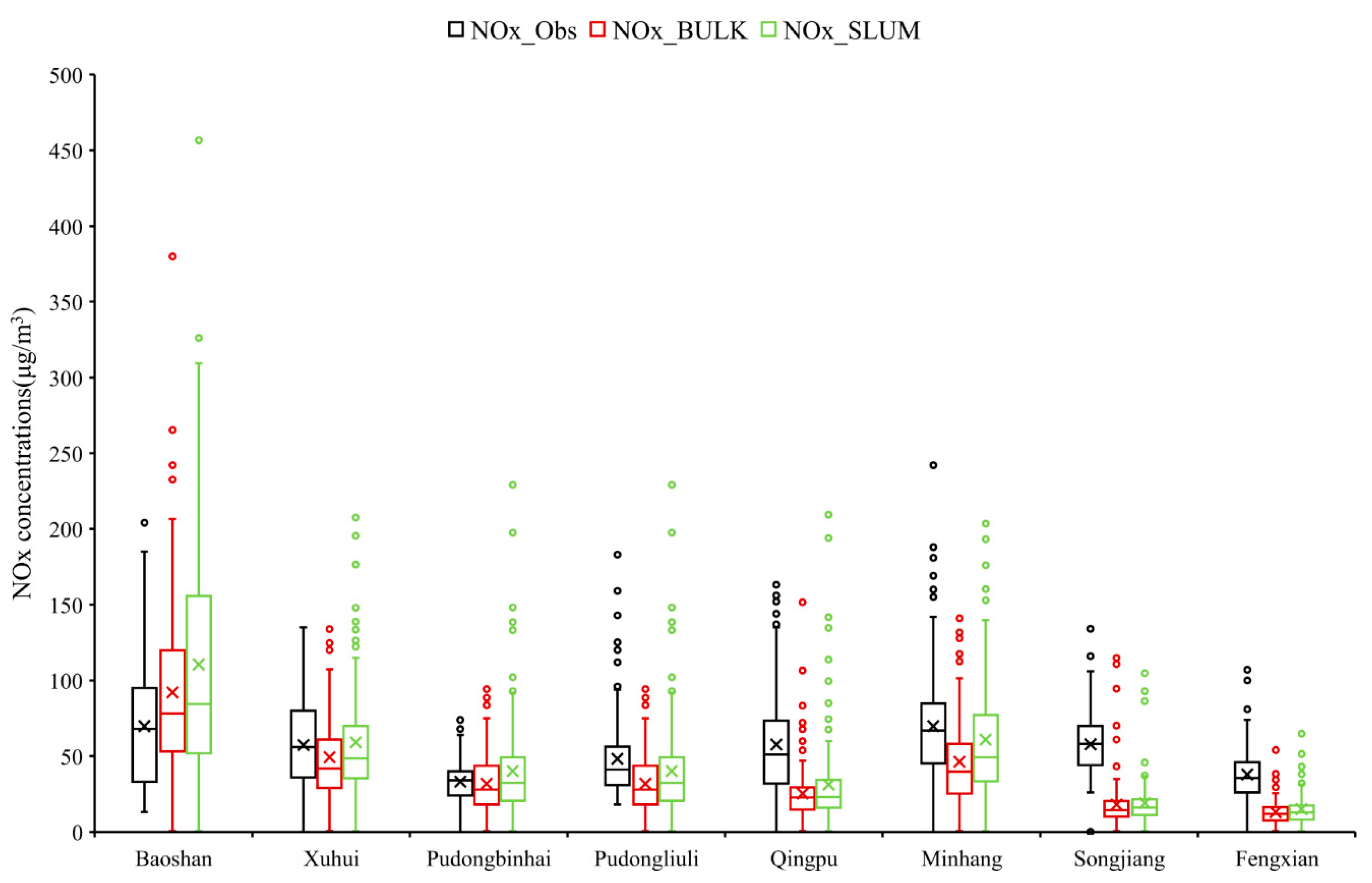
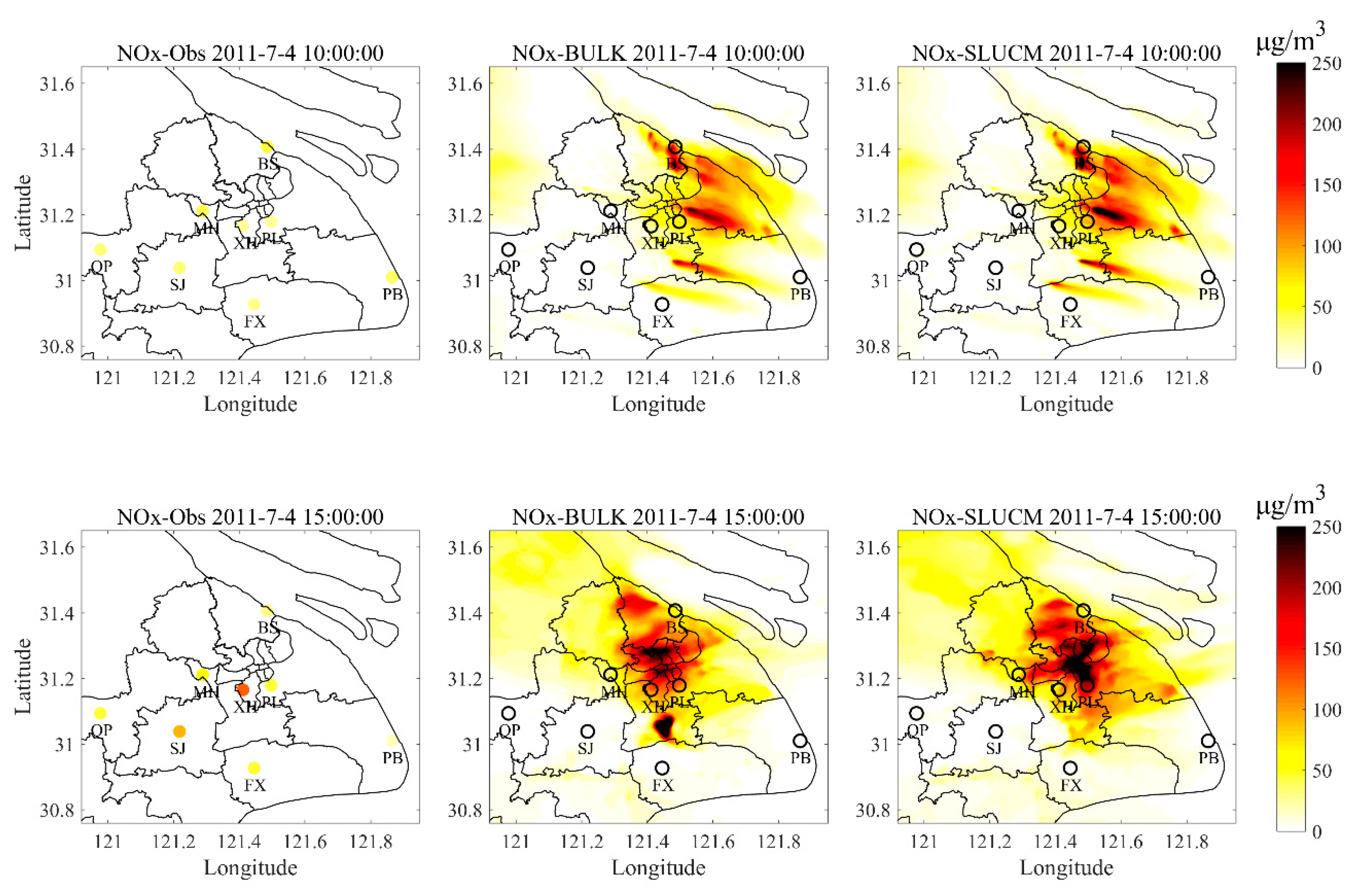
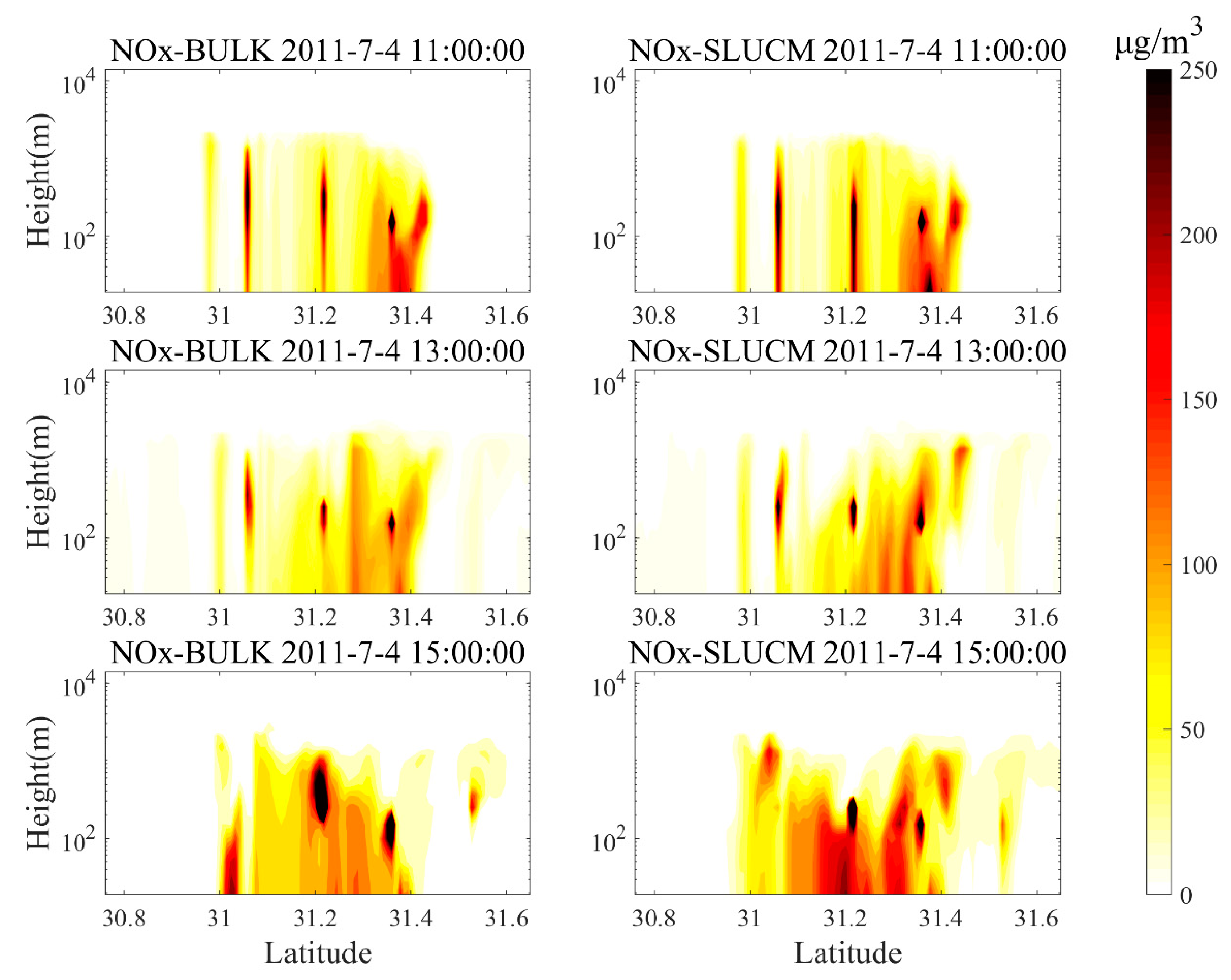
4.5. Comparison of the Concentrations of Air Pollutants
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, L.G.; Chen, M.N.; Ma, W.C. Land Use Dynamics of the Fast-Growing Shanghai Metropolis, China (1979–2008) and its Implications for Land Use and Urban Planning Policy. Sensors 2011, 11, 1794–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.J.; Xuan, C. The National Development and Reform Commission of China. The National New Urbanization Report 2015; China Planning Press: Beijing, China, 2016; Chapter 3. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L.; Shi, J. Urbanization and its environmental effects in Shanghai, China. Urban Clim. 2012, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Chen, F.; Miao, S.G.; Li, Q.C.; Xia, X.A.; Xuan, C.Y. Impacts of urban expansion and future green planting on summer precipitation in the Beijing metropolitan area. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D02116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Lin, W.S.; Yang, L.M.; Deng, R.R.; Lin, H. A numerical study of influences of urban land-use change on ozone distribution over the Pearl River Delta region, China. Tellus Series B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2007, 59, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Bian, L. Estimation of aerodynamic roughness length and displacement of an urban surface from single-level sonic anemometer data. Australian Meteorol. Mag. 2004, 54, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, S.; Hu, F.; Ma, N.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Jia, H. Influence of Beijing urbanization on the characteristics of atmospheric boundary layer. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 33, 859–867. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, W.J.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, W.C.; Yu, Q.; Chen, L.M. Estimating influences of urbanizations on meteorology and air quality of a Central Business District in Shanghai, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2013, 27, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Gao, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y. Modeling the impact of urbanization on the local and regional climate in Yangtze River Delta, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 102, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.Y.; Chin, S.C.; Liu, T.H. The role of boundary layer schemes in meteorological and air quality simulations of the Taiwan area. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 54, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.W.; Angevine, W.M.; Bianco, L.; McKeen, S.A.; Senff, C.J.; Trainer, M.; Tucker, S.C.; Zamora, R.J. Evaluation of urban surface parameterizations in the WRF model using measurements during the Texas Air Quality Study 2006 field campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 2127–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Mathur, R.; Pleim, J.; Pouliot, G.; Wong, D.; Eder, B.; Schere, K.; Gilliam, R.; Rao, S.T. Comparative evaluation of the impact of WRF/NMM and WRF/ARW meteorology on CMAQ simulations for PM2.5 and its related precursors during the 2006 TexAQS/GoMACCS study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 4091–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusaka, H.; Kondo, H.; Kikegawa, Y.; Kimura, F. A simple single-layer urban canopy model for atmospheric models: Comparison with multi-layer and slab models. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2001, 101, 329–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, T.; Pullen, J. Urban Canopy Modeling of the New York City Metropolitan Area: A Comparison and Validation of Single- and Multilayer Parameterizations. Mon. Weather Rev. 2007, 135, 1906–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, Y. Urban heat island and boundary layer structures under hot weather synoptic conditions: A case study of Suzhou City, China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 28, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Chen, F.; Lemone, M.A.; Tewari, M.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y. An Observational and Modeling Study of Characteristics of Urban Heat Island and Boundary Layer Structures in Beijing. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 484–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, Y.J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, J.; Fan, S. Aerosol chemistry and the effect of aerosol water content on visibility impairment and radiative forcing in Guangzhou during the 2006 Pearl River Delta campaign. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 3231–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, R.; Takegawa, N.; Kondo, Y.; Miyazaki, Y.; Miyakawa, T.; Hu, M.; Shao, M.; Zeng, L.M.; Hofzumahaus, A.; Holland, F.; et al. Formation of submicron sulfate and organic aerosols in the outflow from the urban region of the Pearl River Delta in China. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 3754–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Su, H.; Shao, M.; Zeng, L.; Zhong, L.; Xiang, Y.; Chang, C.; Chou, C.K.C.; Wahner, A. Regional ozone pollution and key controlling factors of photochemical ozone production in Pearl River Delta during summer time. Sci. China Chem. 2010, 53, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Hu, M.; Zhong, L.J.; Wiedensohler, A.; Liu, S.C.; Andreae, M.O.; Wang, W.; Fan, S.J. Regional Integrated Experiments on Air Quality over Pearl River Delta 2004 (PRIDE-PRD2004): Overview. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6157–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Su, H.; Zhong, L.J.; Cheng, Y.F.; Zeng, L.M.; Wang, X.S.; Xiang, Y.R.; Wang, J.L.; Gao, D.F.; Shao, M. Regional ozone pollution and observation-based approach for analyzing ozone–Precursor relationship during the PRIDE-PRD2004 campaign. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6203–6218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.; Nowak, A.; Achtert, P.; Wiedensohler, A.; Hu, M.; Shao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Andreae, M.O.; Poschl, U. Cloud condensation nuclei in polluted air and biomass burning smoke near the mega-city Guangzhou, China—Part 1: Size-resolved measurements and implications for the modelling of aerosol particle hygroscopicity and CCN activity. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 3365–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.F.; Wiedensohler, A.; Eichler, H.; Heintzenberg, J.; Tesche, M.; Ansmann, A.; Wendisch, M.; Su, H.; Althausen, D.; Herrmann, H.; et al. Relative humidity dependence of aerosol optical properties and direct radiative forcing in the surface boundary layer at Xinken in Pearl River Delta of China: An observation based numerical study. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6373–6397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.J.; Fan, Q.; Yu, W.; Luo, X.Y.; Wang, B.M.; Song, L.L.; Leong, K.L. Atmospheric boundary layer characteristics over the Pearl River Delta, China, during the summer of 2006: Measurement and model results. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 6297–6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.L.; Meng, F.; Xu, J.; He, Y.J. Process analysis about the impact of a strong cold front on air pollution transportation in Eastern China in spring. Res. Environ. Sci. 2013, 26, 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- Shahgedanova, M.; Burt, T.P.; Davies, T.D. Synoptic Climatology of Air Pollution in Moscow. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 1998, 61, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, G.R.; Peters, L.K.; Saylor, R.D. The STEM-II regional scale acid deposition and photochemical oxidant model—I. An overview of model development and applications. Atmos. Environ. Part B Urban Atmos. 1991, 25, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yang, D.; Li, L.; Huang, J.; Qi, B. Cold-front activities and its influence on air pollution at urban districts of Lanzhou in cold half year. Plateau Meteorol. 1998, 17, 142–149. [Google Scholar]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.O.; Barker, D.M.; Duda, M.G.; Huang, X.-Y.; Wang, W.; Powers, J.G. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF Version 3; National Centre of Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Byun, D.; Ching, J. Science Algorithms of the EPA Models-3 Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) Modeling System; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; EPA-600/R-99/030.
- Byun, D.; Schere, K.L. Review of the governing equations, computational algorithms, and other components of the models-3 community multiscale air quality (CMAQ) modeling system. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2006, 59, 51–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.N.; Yu, Q.; Ma, W.C.; Ma, J.L.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J. Development of refined emission inventory of air pollutants: A case study of shanghai baoshan district. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2014, 34, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.N.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, W.C.; Yu, Q.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.M. Impact of spatial resolution on air quality simulation: A case study in a highly industrialized area in Shanghai, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Kusaka, H.; Bornstein, R.; Ching, J.; Grimmond, C.S.B.; Grossman-Clarke, S.; Loridan, T.; Manning, K.W.; Martilli, A.; Miao, S.G.; et al. The integrated WRF/urban modelling system: development, evaluation, and applications to urban environmental problems. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jung, J.; Sugimoto, N.; Chang, S.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Fan, S.; Zeng, L. Influences of relative humidity and particle chemical composition on aerosol scattering properties during the 2006 PRD campaign. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1525–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusaka, H.; Kimura, F. Coupling a single-layer urban canopy model with a simple atmospheric model: Impact on urban heat island simulation for an idealized case. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2004, 82, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusaka, H.; Kimura, F. Thermal effects of urban canyon structure on the nocturnal heat island: Numerical experiment using a mesoscale model coupled with an urban canopy model. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 1899–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamanca, F.; Martilli, A.; Tewari, M.; Chen, F. A Study of the Urban Boundary Layer Using Different Urban Parameterizations and High-Resolution Urban Canopy Parameters with WRF. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2011, 50, 1107–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouermi, T.A.J.; Knoll, A.; Kirby, R.M.; Berzins, M. Optimization Strategies for WRF Single-Moment 6-Class Microphysics Scheme (WSM6) on Intel Microarchitectures. In Proceedings of the 2017 Fifth International Symposium on Computing and Networking (CANDAR), Aomori, Japan, 19–22 November 2017; IEEE Computer Society: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2018; pp. 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhan, W.J.; Ma, W.C.; Yu, Q.; Chen, L.M. Sensitivity analysis of meteorological conditions and air pollution concentration on land-use data in the YRD region. J. Nanjing Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2015, 51, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Eder, B.; Dennis, R.; Chu, S.H.; Schwariz, S. On the development of new metrics for the evaluation of air quality models. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2005, 7, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | LIR | HIR | COI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban fraction (%) | 0.75 | 0.85 | 0.95 |
| Building height (m) | 5 | 12.5 | 20 |
| Road width (m) | 10 | 15 | 20 |
| Buildings 5 m tall (%) | 55.3 | 1.0 | 0 |
| Buildings 10 m tall (%) | 24.7 | 14.0 | 2.0 |
| Buildings 15 m tall (%) | 12.4 | 42.3 | 4.6 |
| Buildings 20 m tall (%) | 7.6 | 27.7 | 5.4 |
| Buildings 25 m tall (%) | 0 | 10.2 | 18.8 |
| Buildings 30 m tall (%) | 0 | 4.8 | 8.0 |
| Buildings 40 m tall (%) | 0 | 0 | 18.7 |
| Buildings 50 m tall (%) | 0 | 0 | 15.5 |
| Buildings 60 m tall (%) | 0 | 0 | 27.0 |
| Surface | λ (W m−1 K−1) | C (× 106 J m−3 K−1) | T (°C) | ε | α | z0 (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roof | 3.24 | 3 | 20 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 0.01 |
| Wall | 3.24 | 3 | 20 | 0.9 | 0.2 | - |
| Road | 2.5 | 2.3 | 20 | 0.95 | 0.15 | 0.01 |
| Weather Pattern | Pollution Days | Heavy Pollution Days | Proportion (%) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equalizing pressure | 47 | 17 | 36.17 |
| Saddle shaped field pattern | 6 | 1 | 16.67 |
| Westerly in rear of high-pressure pattern | 18 | 5 | 27.78 |
| Cold front | 12 | 7 | 58.33 |
| MB = |
| MAGE = |
| RMSE = |
| FAE = |
| r = |
| T (°C) | WS (m s−1) | WD (°) | RH (%) | ABLH (m) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BULK | SLUCM | BULK | SLUCM | BULK | SLUCM | BULK | SLUCM | BULK | SLUCM | |
| Mean Obs. | 31.07 | 31.07 | 3.47 | 3.47 | 184.13 | 184.13 | 67.64 | 67.64 | 820.89 | 820.89 |
| Mean Sim. | 29.12 | 29.94 | 5.22 | 4.54 | 194.3 | 199.54 | 73.01 | 69.41 | 645.17 | 682.57 |
| MB | −1.95 | −1.13 | 1.75 | 1.08 | 10.17 | 15.41 | 5.37 | 1.77 | 175.72 | 138.32 |
| RMSE | 3.1 | 2.5 | 2.51 | 2 | 53.44 | 58.49 | 12.12 | 10.3 | 319.71 | 301.85 |
| MAGE | 2.56 | 1.97 | 2.08 | 1.6 | 38.76 | 41.17 | 9.81 | 7.87 | 472.73 | 431.95 |
| FAE (Unitless) | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.5 | 0.42 | 0.26 | 0.27 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.45 | 0.41 |
| r (Unitless) | 0.77 | 0.76 | 0.49 | 0.33 | 0.47 | 0.41 | 0.73 | 0.74 | 0.52 | 0.59 |
| 2-m Air Temperature (T) | HIR 1 | LIR 2 | Rural | |||
| BULK | SLUCM | BULK | SLUCM | BULK | SLUCM | |
| Mean Obs. | 31.64 | 31.64 | 31.49 | 31.49 | 29.65 | 29.65 |
| Mean Sim. | 29.35 | 30.33 | 29.28 | 30.10 | 28.58 | 29.24 |
| MB | −2.29 | −1.31 | −2.21 | −1.39 | −1.07 | 1.43 |
| RMSE | 4.08 | 2.96 | 2.96 | 2.41 | 2.13 | 1.84 |
| MAGE | 3.40 | 2.39 | 2.50 | 1.93 | 1.85 | 1.60 |
| FAE (Unitless) | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.05 |
| r (Unitless) | 0.56 | 0.66 | 0.85 | 0.81 | 0.82 | 0.75 |
| Relative Humidity (RH) | HIR 1 | LIR 2 | Rural | |||
| BULK | SLUCM | BULK | SLUCM | BULK | SLUCM | |
| Mean Obs. | 62.83 | 62.83 | 66.10 | 66.10 | 75.52 | 75.52 |
| Mean Sim. | 71.69 | 67.46 | 72.12 | 68.60 | 76.10 | 72.96 |
| MB | 8.86 | 4.63 | 6.02 | 2.50 | 9.92 | −2.57 |
| RMSE | 17.82 | 12.88 | 10.74 | 9.25 | 50.65 | 9.48 |
| MAGE | 15.25 | 10.54 | 8.58 | 7.22 | 6.85 | 6.51 |
| FAE (Unitless) | 0.24 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.09 |
| r (Unitless) | 0.50 | 0.66 | 0.83 | 0.80 | 0.78 | 0.70 |
| Wind Speed (WS) | HIR 1 | LIR 2 | Rural | |||
| BULK | SLUCM | BULK | SLUCM | BULK | SLUCM | |
| Mean Obs. | 4.03 | 4.03 | 3.02 | 3.02 | 3.80 | 3.80 |
| Mean Sim. | 5.16 | 4.57 | 5.24 | 4.62 | 5.22 | 4.37 |
| MB | 1.13 | 0.54 | 2.23 | 1.60 | 13.49 | 0.58 |
| RMSE | 2.07 | 1.74 | 2.81 | 2.28 | 40.89 | 9.18 |
| MAGE | 1.65 | 1.34 | 2.40 | 1.86 | 1.86 | 1.34 |
| FAE (Unitless) | 0.38 | 0.34 | 0.60 | 0.50 | 0.43 | 0.35 |
| r (Unitless) | 0.49 | 0.40 | 0.53 | 0.31 | 0.39 | 0.31 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Mao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, T.; Yu, Q.; Tan, J.; Ma, W. Simulating the Effects of Urban Parameterizations on the Passage of a Cold Front During a Pollution Episode in Megacity Shanghai. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10020079
Wang J, Mao J, Zhang Y, Cheng T, Yu Q, Tan J, Ma W. Simulating the Effects of Urban Parameterizations on the Passage of a Cold Front During a Pollution Episode in Megacity Shanghai. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(2):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10020079
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jian, Jingbo Mao, Yan Zhang, Tiantao Cheng, Qi Yu, Jiani Tan, and Weichun Ma. 2019. "Simulating the Effects of Urban Parameterizations on the Passage of a Cold Front During a Pollution Episode in Megacity Shanghai" Atmosphere 10, no. 2: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10020079
APA StyleWang, J., Mao, J., Zhang, Y., Cheng, T., Yu, Q., Tan, J., & Ma, W. (2019). Simulating the Effects of Urban Parameterizations on the Passage of a Cold Front During a Pollution Episode in Megacity Shanghai. Atmosphere, 10(2), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10020079






