Abstract
Through analyzing the concentrations of selected heavy metals (Ba, Mn, Pb, Sr, Zn) in the bones and teeth of wild living and ecologically equivalent ruminants from the Tian-Shan (Capra sibirica and Ovis ammon polii) and the West Carpathians (Rupicapra rupicapra tatrica) we compared the environmental pollution levels of these two mountain ranges. The samples were analyzed by X-ray fluorescence. Significantly higher contents of Zn and Mn as well as a higher frequency of measurable occurrences of Mn, Ba, and Pb in samples from the West Carpathians confirmed the results of our previous study, that the West Carpathians are relatively more polluted by heavy metals than the Tian-Shan Mountains. The most probably contamination sources are mining and smelting as well as traffic emissions, which can reach remote mountain ranges through long distance atmospheric transport.
1. Introduction
Anthropogenic emissions from the extended territory of the Soviet Union and China considerably influenced the concentration of heavy metals in the Northern Hemisphere [1,2,3,4]. Quantitative planetary boundaries for aerosol loading and chemical pollution have not yet been established and there is insufficient knowledge to suggest them [5].
The Tian-Shan is one of the most polluted mountain ranges in central Asia by anthropogenic sources of heavy metals [2,3,6,7,8]. According to a study on ice core records from the Inilchek glacier in central Tian-Shan, pollutant sources originated primarily from Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan and Kyrgyzstan [2]. When considering the data presented in the State Statistic Committee of the Kyrgyzstan Republic’s report in 2015, the volume of pollution released into the atmosphere from stationary pollution sources increased by 44 percent compared to 2011. Such a sharp increase in pollution is related to the increased use of coal by large scale heating plants due to low water periods. The emission of sulphur dioxide as one of the main air pollutants increased by 3.8 percent between 2014 and 2015 [9].
The environment as a whole is being polluted, including wild animals living within it. Because animals living in the wild depend exclusively on the natural resources and the condition of soils present in their habitats, the effects of such pollution can be analyzed without provable influence from direct anthropogenic factors. Environmental pollution caused by harmful substances can affect the animals inhabiting a given territory via the food or water they ingest and the air they breathe [10]. Toxic metals can accumulate in soil and plants and may subsequently enter the animal food chain and threaten their health. Heavy metals have a strong influence on nutritional values in plants (effects on protein, amino acids, carbohydrates, fats, and vitamins); therefore, plants grown in metal-contaminated soil are nutrient deficient and consumption of such vegetation may lead to nutritional deficiency in the consuming population [11]. Knowing that alpine ecosystems are often the main accumulation sites of trace metals from the atmosphere and that the concentrations of these pollutants increase with altitude, the main sources of trace metals for the plants that ruminants eat are atmospheric pollutants [8,12].
In Tian-Shan alpine ecosystems, there live two protected wild species of ruminants; the Asiatic ibex (Capra sibirica, Pallas 1776) and the Marco Polo sheep (Ovis ammon polii, Blyth 1840).
C. sibirica is typically found in the mountains of central Asia. In the central Tian-Shan (China), the iron mining industry developed rapidly in recent years and caused damage to the original habitat of ibex in the affected areas. Mine production operations, especially large transport vehicles, made ibex more sensitive to human disturbance [13]. Ibex numbers in the Tian-Shan of Kazakhstan may have declined in some areas [14].
Marco Polo sheep numbers have decreased greatly in the past because of uncontrolled hunting. Due to over-hunting and subsistence poaching, as well as competition with livestock and habitat loss, O. ammon has been categorized as an endangered species on several lists [15]. Uncontrolled killing of the Marco Polo sheep by firearms appears to be common; local militia and customs officials have killed dozens with gun-machines. In the Kara-Tau Mountains, the population could have been as low as 100 animals [16]. With regard to that information, the populations of both ruminants are relatively seriously endangered. Their populations may also be affected by atmospheric pollution, mainly by toxic heavy metals that accumulate in their bodies.
We have previously confirmed that the Carpathians are still one of the most polluted mountain ranges, and indicated that the Tatra mountains (West Carpathians) are more polluted by Pb than Tian-Shan [17,18]. In our previous study, we compared atmospheric pollution between Tian-Shan and European high mountain ranges (the Tatra, Vitosha and Rila mountains) via short living rodent species [17]. In terms of long-term monitoring, it is better to use tissues from longer-living herbivorous animals, which indicate primarily their accumulation of heavy metals from plants. We therefore investigated the heavy metal content in bones of the Tatra chamois (Rupicapra rupicapra tatrica, Blahout 1972), which is an equivalent ruminant species with similar habitat and food requirements to C. sibirica and O. ammon from the Tian-Shan mountains. Chamois (Rupicapra genera) are indigenous to several mountain ranges in Europe and also in Asia, and have been successfully introduced into new countries with mountain habitats such as New Zealand. The Tatra chamois is an endemic and protected species, inhabiting alpine and subalpine areas of the Tatra mountains.
Among heavy metals, essential elements, such as Mn and Zn in this study, ensure the normal development and function of the organism, whereas Ba, Pb and Sr are toxic elements which often cause acute and chronic environmental contamination. All of these metals can be transported through atmospheric flows. The target organs for Mn accumulation are bones, and Mn toxicity has been associated with dopaminergic dysfunction [19]. Mn exposure impacts neurotransmitter levels in the brain. Chronically high Mn levels in the brain are neurotoxic and can result in a progressive, irreversible neurological disorder known as manganism [20]. There are three common methods of absorption into the body (inhalation, through the skin, and by ingestion) [21]. The most probable route of entry for Zn into the animal body in alpine environments is by ingestion. Effects associated with long-term, excessive Zn intake include nausea, epigastric pain, diarrhea, elevated risk of prostate cancer, copper deficiency and sequelae, altered lymphocyte function, lethargy and focal neuronal deficits [22]. Environmental exposure to Ba causes cardiovascular and kidney diseases, as well as metabolic, neurological, and mental disorders [23]. Pb is a general accumulative metabolic poison affecting the hematopoietic, cardiovascular, nervous, renal, and reproductive systems [24]. Sr affects food intake, body weight gain [25] and bone biochemistry [26]. Ba, Pb, and Sr are mainly deposited in the skeleton, which is the major deposition site for many metals, where they are incorporated into bone minerals [27].
The main objective of our research was to compare contents of selected heavy metals (Ba, Mn, Pb, Sr, Zn) between two different mountain ranges. Because calcified tissues are good bioindicators of long-term metal accumulation [27,28], we analyzed concentrations of selected heavy metals in the bone and tooth tissues of wild living and ecologically equivalent ruminants from Tian-Shan (C. sibirica and O. ammon) and the Tatra mountains (R. r. tatrica).
2. Experiments
2.1. Sample Collection and Analyses
Knowing that heavy metal concentrations increase with altitude much more than with soil conditions or other ecological factors [8,29], to determine element concentrations we used bone and tooth tissues from wild ruminants of the Bovidae family living in alpine environments. Different bone and tooth tissues (axillar and appendicular skeleton, teeth) were used based on the possibility of finding samples in the field. According to some studies, types of bone and tooth tissues have less effect on the trace element content than the environmental distribution of samples with distinctive levels of elements [30,31]. Our samples were collected from two geographically isolated mountain ranges with distinctive possible pollution sources. In the Tian-Shan (N41.81961667°, E77.58944444°; Republic of Kyrgyzstan), we used samples from the Asiatic ibex (Capra sibirica) (Figure 1a) and the Marco Polo sheep (Ovis ammon polii) (Figure 1b). The samples were collected during spring and autumn in 2013. The altitude of the study sites in the Tian-Shan (Figure 2a) ranged from 2616 to 3545 m a.s.l. In the West Carpathians (Slovakia), samples from Rupicapra rupicapra tatrica were collected in alpine areas of the Tatra mountains (N49.16472222°, E20.13416667°) (Figure 2b) over a sixteen-year period (1993–2009 m a.s.l.).

Figure 1.
Bones contain useful information on some metal contamination in the mountains. Hundreds of (a) Asiatic ibex and (b) Marco Polo sheep skulls may be found in the valleys of Kyrgyzstan. The animals are hunted by local people for meat and heavy heads are usually left in the field. Photo: M. Janiga, 2013.
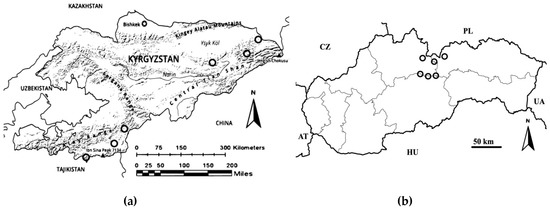
Figure 2.
Maps of sample sites in (a) the Tian-Shan mountains (Kyrgyzstan) and (b) the Tatra mountains (Slovakia). The sample sites are displayed as circles.
2.2. X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry
The samples were analyzed by X-ray fluorescence, using the hand-held XRF Spectrometer DELTA CLASSIC (Innov-X Systems, Inc., Woburn, MA, USA.) [32]. The handheld X-ray fluorescence was already used for scanning the hard tissues including horns, antlers, teeth and bones and it was demonstrated that a handheld XRF is an effective and accurate tool for analytical investigation [33]. We used the CONOSTAN calibration standard [34]. Samples of bones and teeth were mechanically cleaned and rinsed with distilled water, to prevent contamination of the sample with surface extrinsic elements. Subsequently, the upper layers of bones were carefully ground because of accumulated impurities from the environment, in order to obtain pure bone element contents. A direct method of analysis, without the usage of cuvettes nor homogenization of samples was used. We used multiple-beam measurement, in which every measurement consisted of 3 beams for 30 s, repeated three times, and then averaged. The results were given in ppm (part per million) units. We used 38 samples (tooth and bone tissues) from the Tian-Shan and 30 from the West Carpathians.
Our instrument was certified and verified by multiple measurements. We measured two soil matrix standards (No. 2710a and 2711a) [35,36] and one beef liver standard (NCS ZC 71001) [37]. There were minimal standard deviations between certified values and our measured values. We also repeated measurements on soil matrix standards, to demonstrate repeatability. The standard deviation (SD) was stable and minimal for all repeated measurements.
Using the multiple testing of our bone and tooth samples we found minimum values of the concentrations of distinct elements that our instrument was able to measure, in constant conditions. Limits of detection for each measured metal were determined from samples, in which the content of this metal was at the limit of detection. The minimum content of a particular element represented the current detection limit of the spectrometer for the measured material [38]. The minimum values are presented in Table 1 for the Tian-Shan and in the Table 2 for the West Carpathians.

Table 1.
Concentrations of the examined elements in the hard tissues (bones and teeth together) of ruminants from the Tian-Shan mountains.

Table 2.
Concentrations of the examined elements in the hard tissues (bones and teeth together) of ruminant species from the West Carpathians.
Certified limits of detection of selected elements measured in our samples for the handheld XRF Spectrometer DELTA CLASSIC using the soil matrix are: Mn: 10–30 ppm, Zn: 10–15 ppm, Ba: 40–60 ppm, Pb: 5–10 ppm, and Sr: 3–5 ppm [39].
2.3. Statistics
For statistical analysis, we chose elements measured in our samples with the highest accuracy that were found in both mountain ranges: Ba, Mn, Pb, Sr, and Zn. Data were standardized considering the possible eccentricity of some measurements. The average values of the elements were calculated. The Chi-squared test was applied to data with an abundance of positive and negative measurements of elements in the samples from different mountain ranges (p < 0.05). In cases where sample size was recorded as 20 to < 40, but an expected value was < 5, we used the Fisher’s Exact test (case of Zn). In the case of two zero values in the cells with total observation values, frequencies of element occurrence in different mountain ranges could not be evaluated (case of Sr). Because the distribution of observed levels of trace elements was normal according to the Shapiro-Wilk test, the parametric Student’s t-test was used to compare element concentrations between different mountain ranges. Statistical analyses were performed with Statistica 12 software for Windows (Stat Soft CR, Prague, Czech Republic).
3. Results
We determined the presence of the following elements in our samples from both mountain ranges: P, S, Cl, K, Ca, Ti, Cr, Mn, Fe, Ni, Cu, Zn, Rb, Sr, Zr, Mo, Ag, Sn, I, Ba, Hg, and Pb. Other elements, which were measured but were less than detection limit in all our samples, included Co, As, Se, Cd and Sb. Sr was found in all of our samples from the Tian-Shan as well as from the West Carpathians. Zn was measured in all samples from the West Carpathians. Selected heavy metals (Ba, Mn, Pb, Sr, Zn) were subsequently used for comparison of these two regions.
We found significant differences in the frequency of occurrences of Mn, Ba, Pb and Zn between the two mountain ranges, whereas Sr was measured in all samples from both mountain ranges (Table 3).

Table 3.
Contingency table with the frequencies of selected five elements and associations of its occurrences between positive and negative bone samples from the Tian-Shan mountains (TS) and the Tatra mountains (WC).
For each element, the means were calculated only from samples in which the amount of an element was above the detection limit of the spectrometer DELTA CLASSIC (Table 1 and Table 2).
Significant differences in element concentrations between mountain ranges were found only for Zn and Mn (Table 4).

Table 4.
Comparison of the concentrations of selected five element measurements between bone samples from the Tian-Shan mountains and the Tatra mountains by the Student’s t-test.
4. Discussion
It was found that Mn is poorly absorbed by ruminants [40]. Thus, the higher content of this element in animal bones is most likely the result of a long-lasting increase in exposure. The ‘‘normal’’ range of mammalian tissue Mn concentrations is 0.3–2.9 ppm [41]. However, bone, brain, liver, pancreas, and kidney tissue have high Mn concentrations [41]. This element was found in more samples and with higher content in the West Carpathians than in the Tian-Shan mountains. The major pool of Mn in soils originates from crustal rock, with other sources including direct atmospheric deposition, wash-off from plants and other surfaces, leaching from plant tissues, and the shedding or excretion from plant and animal matter [42]. The major anthropogenic source of environmental Mn include emission from Mn is mining. Another emerging source of Mn pollution is the gasoline additive methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl (MMT), an organic derivative of Mn that was introduced to automobile fuel formulas as an octane-boosting and antiknock agent [42]. According to a study on sediments in Smreczynski Staw Lake in the Tatra mountains, Mn concentrations have increased since the beginning of the 20th century, but most significantly since the end of the 20th century. This could be the result of transportation from remote sources and acid rain [43]. Contrary to the West Carpathians, the Inilchek glacier, located in central Tian-Shan, was recognized to contain a conservative natural crustal element, from metal dust containing Mn [2]. The majority of our samples originated from the Ysyk-Köl region (oblast), where the Inilchek glacier is located.
Ba and Pb were elements found in higher concentrations in the West Carpathians than in the Tian-Shan mountains (Table 1 and Table 2). Pb was found in only one of the samples from the Tian-Shan mountains, but in many samples (n = 17) from the West Carpathians (Table 3). This may be caused by traffic emissions. The highest emission levels in Central Asian countries are associated with big cities, which are further away from mountain ranges than they are in Europe [44]. Pb levels in Tatra lake sediments, increased in the samples from the 20th century, and are likely deposited from air pollution resulting from the development of road transport [43]. Ba is present in diesel and unleaded gasoline, so the element was recognized as a valuable tracer for vehicle emissions, in the place of Pb. Ba and Pb are both connected with vehicle emissions, so the presence of these elements is most likely a result of the differences in emission transport between the two mountain ranges [45]. In the Tian-Shan Inilchek glacier, Pb levels showed a decline during the 1980s in conjunction with the Soviet economic decline. Due to the rapid industrial and agricultural growth of western China, Pb increased during the 1990s, reflecting a transition from primarily central Asian sources to emission sources from western China (e.g., Xinjiang Province) [2]. It was found that coal burning emissions and Pb in vehicle gasoline were major sources of heavy Pb pollution in the Tian-Shan mountains region [3].
We found that R. r. tatrica, as the only West Carpathian ruminant species living in alpine habitats, had significantly higher levels of Zn than ruminants from the Tian-Shan mountains. Although anthropogenic emissions from the extended territory of the Soviet Union and China considerably influenced concentrations of heavy metals in the Northern Hemisphere, according to the results of several studies, Zn emissions have declining trends. These can be attributed to the economic downturn in industry, changes in technology to an increasing metal recovery from ores, the replacement of coal and oil by gas, and air pollution control [1,46,47]. Potential sources of heavy metals in the Tatra mountains may be northern Moravia in the Czech Republic and the Małopolska district in southern Poland with Zn-Pb mines and smelters [48,49,50,51]. In addition, our previous studies show high levels of Zn were found in the bones and teeth of Tatra marmots, with this element being detected in all samples [38,52]. In a study of snow voles from the Tatra mountains, Zn was also found in all samples, and the mean amount of Zn in bone tissues was 72.49 ppm ± 24.76 [53].
One-time uptake of Zn in higher concentrations from food sources is almost immediately excreted from the organism by feces. It is only after a long period of higher uptake that the ruminant will adapt to higher Zn levels [54]. It follows then, that there is a higher concentration of Zn in ruminant food sources in the West Carpathians than in the Tian-Shan mountains. This is, of course, applicable only for non-toxic dosages [54]. Furthermore, it was found that Zn was the most responsive to excessive supply and is deposited more commonly in bones compared to other body tissues [55]. Therefore, bones of ruminants can be a very good indicator of Zn availability in the area.
Main sources of environmental contamination of Zn and Pb, along with other heavy metals, include the coal and mining industries [56,57,58,59,60]. We expect that the Zn and Pb pollutants in our samples from the West Carpathians were transported by atmospheric flows from Zn-Pb smelters due to prevailing north-western winds in the Tatra mountains. However, Pb and Zn have not been mined in the neighboring Czech Republic recently, and mining and smelting of these heavy metals was also reduced in Poland [51]. Pb and Zn ore is still mined in southeastern Poland in the Silesia-Cracow region at two underground mines (the Olkuz-Pomorzany Mine and the Trzebionka Mine) [51], which are close to the Tatra mountains. In soils sampled at historical metal mining sites in western Małopolska, Pb content ranged from 72.8 to 16931 and Zn content ranged from 322 to 41860 ppm. These levels are indicative of heavy contamination of the surrounding environment by these metals [50].
Zn levels in the bones of Tatra chamois were similarly high compared to those found in bones of small rodents from Zn polluted areas in Slovakia [56,61]. Zn and Pb pollution in Slovakia may also be attributed to prevailing north-western winds from the highly polluted Upper Nitra region, which is home to various anthropogenic sources of pollution (chemical plant, coal power station, coal mines, stone and limestone pits, aluminum production, factories, and intensive agricultural production), as confirmed by several studies [28,56,61].
Zn accumulation due to traffic emissions should not be ignored. However, studies on heavy metals emitted by vehicles in Florence show that Ba, Mn, Pb, and Zn, along with Cu and Fe are all pollutants resulting from emissions [60]. Zn contaminants from mining and smelting, along with pollutants emitted by diesel-engine vehicles, could be deposited on mountain ridges through wet and dry atmospheric deposition.
Although Sr concentration results were non-significant, slightly higher mean values were measured in samples from the Tian-Shan mountains. Sr occurs frequently as an isotope in rocks. Due to weathering and hydrologic cycles, Sr from these rocks penetrates into soils, plants, and subsequently into animal skeletons [61]. In bones, Sr is highly related to P content [38]. It was found that Sr in bones decreases as dietary phosphorus increases [62]. When we consider that differing Sr values mainly occurred between the two species from the Tian-Shan mountains, not between species from different mountain ranges, we can potentially attribute them to the distinctive dietary preferences of each species [63], as different plants, mosses or lichens and different plant tissues contain specific concentrations of elements [8].
The concentration of (Ba, Mn, Pb, Sr, and Zn) in the West Carpathians may, in addition to mentioned sources, be associated to some extent with emissions from the paper and pulp factory located in Ružomberok (a town situated in north-western Slovakia). Several studies were conducted dealing with these heavy metal pollutants from the Ružomberok industrial zone [64,65,66]. This industrial zone is located near the Tatra mountain range and through prevailing north-western winds the emissions could easily be transported to alpine areas of the West Carpathians, as was also partially confirmed by a study on elements in the needles of Abies alba from the West Carpathians [67].
The content of elements in bone tissues may also be impacted by the exposure of the bones to the elements in the terrain. Bones from the terrain were already used for element analysis [68], but some studies show that element concentrations in older bones can be influenced by the presence of microorganisms, which, while helping to decompose the bone, impact element concentrations [69]. The element ratios in different, old bone samples may also be affected by biological degradation and environmental leaching [70]. In our study we used bone samples without evidence of visible marks of weathering or decomposition to mitigate this effect, and the samples were carefully cleaned and ground.
Tissue type (bone or tooth) may also potentially impact results. We used two different tissues: Bones and teeth. The analysis of ruminant permanent teeth is a useful indicator for assessing life-long intoxication by environmental pollution [71]. However, the concentrations of Ba, Mn and Zn in teeth of roe deer showed positive linear relationships with individual age. No such trends were recorded for trace element content in bones [71].
5. Conclusions
We found significant differences in the accumulation of Mn and Zn between bone samples from the Tian-Shan mountains and from the West Carpathians. The higher content of Zn and Mn pollutants in samples from the West Carpathians is likely attributable to mining and smelting, as well as road transport emissions in adjacent regions to the Tatra mountains. When analyzing the frequency of occurrence of selected heavy metals (Mn, Ba, Pb, Sr, Zn), we found significantly higher frequencies of measurable Mn, Ba, and Pb in samples from the West Carpathians than from the Tian-Shan mountains. Significant amounts of heavy metals (Mn, Ba, Pb, Sr, Zn) are discharged in the atmosphere from anthropogenic sources in the north-west parts of Europe and through the prevailing north-western winds transported to alpine areas of the West Carpathians, where atmospheric contaminants accumulate. Metal pollutants deposited to the surface of the Earth from the air gradually penetrate into soils, plants, and subsequently into animal skeletons. We found that the Tian-Shan mountains are less polluted by some heavy metals than the West Carpathians. This could be a result of the longer history of industrialization in Western Europe as well as relatively shorter distances between pollutant sources in Slovak, Poland and the Czech Republic to sample sites in the Tatra mountains. Trace metals in bones and teeth of wild ruminants have been shown to be qualitative indicators of heavy metal contamination from atmospheric deposition in high mountain ecosystems.
Author Contributions
Z.B. gave comments and ideas on the research and was responsible for statistical and ecological analyses, interpretation of the results, and writing the manuscript. M.J. gave basic ideas on the research and was responsible for field data collection, statistical and ecological analyses, interpretation of the results, and editing the manuscript. R.H. gave comments and ideas on the research and was responsible for field data collection, laboratory and ecological analyses, interpretation of the results, and writing parts of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by European Structural Funds (ITMS, Project number: 26210120006).
Acknowledgments
For English proofreading and improving, we are indebted to native English-speaking editor Amanda Clarahan.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Eichler, A.; Tobler, L.; Eyrikh, S.; Malygina, N.; Papina, T.; Schwikowski, M. Ice-core based assessment of historical anthropogenic heavy metal (Cd, Cu, Sb, Zn) emissions in the Soviet Union. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2635–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigholm, B.; Mayewski, P.A.; Aizen, V.; Kreutz, K.; Wake, C.P.; Aizen, E.; Kang, S.; Maasch, K.A.; Handley, M.J.; Sneed, S.B. Mid-twentieth century increases in anthropogenic Pb, Cd and Cu in central Asia set in hemispheric perspective using Tien Shan ice core. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 131, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Wu, J.; Liu, W. Two-century sedimentary record of heavy metal pollution from lake Sayram: A deep mountain lake in central Tianshan, China. Quat. Int. 2014, 321, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, D.; Song, L.; Yang, J.; Jin, Z.; Zhan, C.; Mao, X.; Liu, D.; Shao, Y. Increasing heavy metals in the background atmosphere of central north China since the 1980s: Evidence from a 200-year lake sediment record. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 138, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, W.; Persson, Å.; Deutsch, L.; Zalasiewicz, J.; Williams, M.; Richardson, K.; Crumley, C.; Crutzen, P.; Folke, C.; Gordon, L.; et al. The anthropocene: From global change to planetary stewardship. Ambio 2011, 40, 739–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhaoyong, Z.; Abuduwaili, J.; Fengqing, J. Heavy metal contamination, sources, and pollution assessment of surface water in the Tianshan mountains of China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Hong, S.; Hur, S.D.; Lee, K.; Pang, H.; Hou, S. High-resolution atmospheric cadmium record for ad 1776–2004 in a high-altitude ice core from the eastern Tien Shan, central Asia. Ann. Glaciol. 2016, 57, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciriaková, A.; Mursaliev, N.; Šoltés, R.; Lukáň, M.; Janiga, M. Lead concentrations in soils and plants of two altitudinal transects in the eastern Kyrgyz Tian Shan mountains—A preliminary study. Oecol. Mont. 2011, 20, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Orozbaeva, K.D.; Kerimalieva, N.K.; Mombekov, S.T. Environment in the Kyrgyz Republic; National Statistical Committee of the Kyrgyz Republic: Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan, 2016; p. 118. [Google Scholar]
- Tataruch, F. Red deer antlers as biomonitors for lead contamination. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1995, 55, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Khan, S.; Khan, M.A.; Qamar, Z.; Waqas, M. The uptake and bioaccumulation of heavy metals by food plants, their effects on plants nutrients, and associated health risk: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 13772–13799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Bing, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xiang, Z. Altitudinal patterns and controls of trace metal distribution in soils of a remote high mountain, southwest china. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yu, Y.-Q.; Shi, L. Foraging and bedding site selection by Asiatic ibex (Capra sibirica) during summer in central Tianshan mountains. Pak. J. Zool. 2015, 47, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Reading, R.; Shank, C. Capra sibirica. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2008. e.T42398A10695735. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/42398/10695735 (accessed on 11 April 2018).
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, R.; Chen, L.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, Y.; Qiu, Q.; Wang, W. Draft genome of the Marco Polo sheep (Ovis ammon polii). GigaScience 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, R.B.; Reading, R. Ovis ammon. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2008. e.T15733A5074694. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/15733/5074694 (accessed on 11 April 2018).
- Ballová, Z.; Janiga, M. Lead levels in the bones of small rodents from alpine and subalpine habitats in the Tian-shan mountains, Kyrgyzstan. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiga, M.; Hrehová, Z.; Dimitrov, K.; Gerasimova, C.; Lovari, S. Lead levels in the bones of snow voles Chionomys nivalis (Martins, 1842) (Rodentia) from European mountains: A comparative study of populations from the Tatra (Slovakia), Vitosha and Rila (Bulgaria). Acta Zool. Bulg. 2016, 68, 291–295. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neal, S.L.; Zheng, W. Manganese toxicity upon overexposure: A decade in review. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2015, 2, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neal, S.L.; Lee, J.W.; Zheng, W.; Cannon, J.R. Subacute manganese exposure in rats is a neurochemical model of early manganese toxicity. Neurotoxicology 2014, 44, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roney, N.; Smith, V.C.; Willims, M.; Osier, M.; Paikoff, S.J. Toxicological Profile for Zinc; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2005; p. 352. [Google Scholar]
- Plum, L.M.; Rink, L.; Haase, H. The essential toxin: Impact of zinc on human health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 1342–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravchenko, J.; Darrah, T.H.; Miller, R.K.; Lyerly, H.K.; Vengosh, A. A review of the health impacts of barium from natural and anthropogenic exposure. Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 36, 797–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demayo, A.; Taylor, M.C.; Taylor, K.W.; Hodson, P.V.; Hammond, P.B. Toxic effects of lead and lead compounds on human health, aquatic life, wildlife plants, and livestock. Crit. Rev. Environ. Control 1982, 12, 257–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandare, A.; Validandi, V.; Rao, S.; Dheeravath, S.; Nagalla, B. Synergistic effects of strontium and fluoride on nutritional status in guinea pigs (Cavia porcellus). Fluoride 2015, 48, 283. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, L.; Xia, L.; Chang, J.; Liu, J.; Jiang, L.; Wu, C.; Fang, B. The synergistic effects of Sr and Si bioactive ions on osteogenesis, osteoclastogenesis and angiogenesis for osteoporotic bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2017, 61, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priest, N.D.; Van de Vyver, F. Trace Metals and Fluoride in Bones and Teeth; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Ann Arbor, MI, USA; Boston, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Martiniaková, M.; Omelka, R.; Jančová, A.; Stawarz, R.; Formicki, G. Concentrations of selected heavy metals in bones and femoral bone structure of bank (Myodes glareolus) and common (Microtus arvalis) voles from different polluted biotopes in Slovakia. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 60, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šoltés, R. Correlation between altitude and heavy metal deposition in the Tatra Mts (Slovakia). Biologia 1998, 53, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, R.B.; Toots, H. Trace elements in bones as paleobiological indicators. In Fossils in the Making: Vertebrate Taphonomy and Paleoecology; Behrensmeyer, A.K., Hill, A.P., Eds.; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA; London, UK, 1988; p. 197. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, R. Phosphorus metabolic disorder of Guizhou semi-fine wool sheep. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, O.T.; Cairns, W.R.L.; Cook, J.M.; Davidson, C.M. Atomic spectrometry update—A review of advances in environmental analysis. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2017, 32, 11–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buddhachat, K.; Klinhom, S.; Siengdee, P.; Brown, J.L.; Nomsiri, R.; Kaewmong, P.; Thitaram, C.H.; Mahakkanukrauh, P.; Nganvongpanit, K. Elemental analysis of bone, teeth, horn and antler in different animal species using non-invasive handheld X-ray fluorescence. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conostan Calibration Standard. 316 Stainless Steel Alloy. Innov-X Systems: Waltham, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wise, S.A.; Watters, R.L., Jr. Certificate of Analysis Standard Reference Material 2710a. Montana I Soil, National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2009. Available online: https://www-s.nist.gov/srmors/view_detail.cfm?srm=2710A (accessed on 22 May 2009).
- Wise, S.A.; Watters, R.L., Jr. Certificate of Analysis Standard Reference Material 2711a. Montana II Soil, National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2009. Available online: https://www-s.nist.gov/srmors/view_detail.cfm?srm=2711A (accessed on 22 May 2009).
- Haizhou, W. Certificate of Certified Reference Material NCS ZC 71001. China National Analysis Center for Iron and Steel: Beijing, China, 2015. Available online: http://gsometal.ru/Catalogues%202011/NCS.pdf (accessed on 22 October 2018).
- Janiga, M.; Ballová, Z.; Angelovičová, M.; Korňan, J. The snow vole and Tatra marmot as different rodent bioindicators of lead pollution in an alpine environment: A hibernation effect. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Innov-X-Systems. Delta HHXRF Analyzers. Limits of Detection (LODs); Innov-X Systems, Inc.: Woburn, MA, USA; Available online: http://www.xrfrentals.com/images/documents/delta_detectable_elememts.pdf (accessed on 28 June 2018).
- Spears, J.W. Trace mineral bioavailability in ruminants. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 1506S–1509S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschner, J.L.; Aschner, M. Nutritional aspects of manganese homeostasis. Mol. Asp. Med. 2005, 26, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röllin, H.; Nogueira, C.M.C.A. Manganese: Environmental pollution and health effects. In Encyclopedia of Environmental Health; Elsevier: Burligton, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 617–629. [Google Scholar]
- Szarlowicz, K.; Reczynski, W.; Misiak, R.; Kubica, B. Radionuclides and heavy metal concentrations as complementary tools for studying the impact of industrialization on the environment. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2013, 298, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusev, A.; Ilyin, I.; Travnikov, O.; Sokovych, V. Model Assessment of Transboundary Pollution by Lead and Pcb-153 of the Central Asian Countries: Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan. EMEP/MSC-E Contribution to the UN ECE CAPACT Project; Meteorological Synthesizing Centre-East: Moscow, Russia, 2007; Available online: http://www.en.msceast.org/reports/6_2007.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2018).
- Monaci, F.; Bargagli, R. Barium and other trace metals as indicators of vehicle emissions. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1997, 100, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Li, G.; Qiu, G. A preliminary study on mercury contamination to the environment from artisanal zinc smelting using indigenous methods in Hezhang county, Guizhou, China—Part 1: Mercury emission from zinc smelting and its influences on the surface waters. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 6223–6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Feng, X.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, G.; Li, G.; Li, F.; Liu, T.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Z. Environmental contamination of heavy metals from zinc smelting areas in Hezhang county, western Guizhou, China. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janiga, M.; Hrehová, Z.; Kostková-Zelinová, V. Seasonal effects of lead uptake by snow vole Chionomys nivalis (Martins, 1842) in West Tatra Mts.: Bone metal concentrations and hematological indices. Pol. J. Ecol. 2012, 60, 611–619. [Google Scholar]
- Rybicka, E.H. Environmental impact of mining and smelting industries in Poland. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1996, 113, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanowicz, A.; Woch, M.; Kapusta, P. Soils from sites of historical metal mining in western Małopolska (S Poland) are strongly contaminated with Zn, Pb and Cd. E3S Web Conf. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steblez, W.G. The Mineral industries of Central Europe. The Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, and Slovakia. USGS Miner. Yearb. 2005, 3, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Angelovičová, M.; Janiga, M. Heavy metals and some other elements in the teeth of the Tatra marmot (Marmota marmota latirostris). Oecol. Mont. 2017, 26, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ftáčniková, V.; Némethy, M. Bio-indication of environmental pollution in alpine environments using X-ray analysis in snow vole (Chionomys nivalis) population. Oecol. Mont. 2017, 26, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Stake, P.; Miller, W.; Gentry, R.; Neathery, M. Zinc metabolic adaptations in calves fed a high but nontoxic zinc level for varying time periods 1. J. Anim. Sci. 1975, 40, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttle, N.F. Mineral Nutrition of Livestock, 4th ed.; MPG Books Group: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Martiniaková, M.; Omelka, R.; Jančová, A.; Formicki, G.; Stawarz, R.; Bauerová, M. Accumulation of risk elements in kidney, liver, testis, uterus and bone of free-living wild rodents from a polluted area in Slovakia. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2012, 47, 1202–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabłońska-Czapla, M.; Nocoń, K.; Szopa, S.; Łyko, A. Impact of the Pb and Zn ore mining industry on the pollution of the Biała Przemsza River, Poland. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Ye, B. Impacts of lead/zinc mining and smelting on the environment and human health in China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 2261–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martiniaková, M.; Omelka, R.; Jančová, A.; Stawarz, R.; Formicki, G. Heavy metal content in the femora of yellow-necked mouse (Apodemus flavicollis) and wood mouse (Apodemus sylvaticus) from different types of polluted environment in Slovakia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 171, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaci, F.; Moni, F.; Lanciotti, E.; Grechi, D.; Bargagli, R. Biomonitoring of airborne metals in urban environments: New tracers of vehicle emission, in place of lead. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 107, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, R.A. Strontium isotopes from the earth to the archaeological skeleton: A review. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2006, 13, 135–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostial, K.; Lutkić, A.; Gruden, N.; Vojvodić, S.; Harrison, G.E. The effect of dietary phosphorus on the metabolism of calcium and strontium in the rat. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. Relat. Stud. Phys. Chem. Med. 1963, 6, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivertsen, T.; Daae, H.L.; Godal, A.; Sand, G. Ruminant uptake of nickel and other elements from industrial air pollution in the norwegigan-russian border area. Environ. Pollut. 1995, 90, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klamárová, S.; Solár, J. Spatial distribution of elements in soils of experimental area, Ružomberok—X-ray analysis. Oecol. Mont. 2017, 26, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Sendecká, M.; Šoltés, R. Seasonal changes in the dust nuisance and contamination of mosses in the experimental study area Ružomberok. Oecol. Mont. 2017, 26, 24–34. [Google Scholar]
- Böhmová, P.; Šoltés, R. Accumulation of selected element deposition in the organs of Fallopia japonica during ontogeny. Oecol. Mont. 2017, 26, 35–46. [Google Scholar]
- Grešíková, S.; Janiga, M. Analysis of S, Cl, K, Ca, Cr, Mn, Fe, Zn, Rb, Sr, Mo, Ba and Pb concentrations in the needles of Abies alba and potential impact of paper mill industry. Oecol. Mont. 2017, 26, 47–55. [Google Scholar]
- Sobota, S.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I.; Gutowska, I.; Kupiec, M.; Dusza, K.; Machoy, Z.; Chlubek, D. Biomonitoring of lead and fluoride contamination in forests using chemical analysis of hard tissues of roe deer (Capreolus capreolus L.). Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2011, 20, 435–443. [Google Scholar]
- Turner-Walker, G. The chemical and microbial degradation of bones and teeth. Adv. Hum. Palaeopathol. 2008, 3–29. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/9780470724187.ch1 (accessed on 5 November 2018).
- Kasem, M.A.; Russo, R.E.; Harith, M.A. Influence of biological degradation and environmental effects on the interpretation of archeological bone samples with laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2011, 26, 1733–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demesko, J.; Markowski, J.; Słaba, M.; Hejduk, J.; Minias, P. Age-related patterns in trace element content vary between bone and teeth of the European roe deer (Capreolus capreolus). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 74, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).