Characterization of Multitermination CG Flashes Using a 3D Lightning Mapping System (FALMA)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Observations and Data Processing
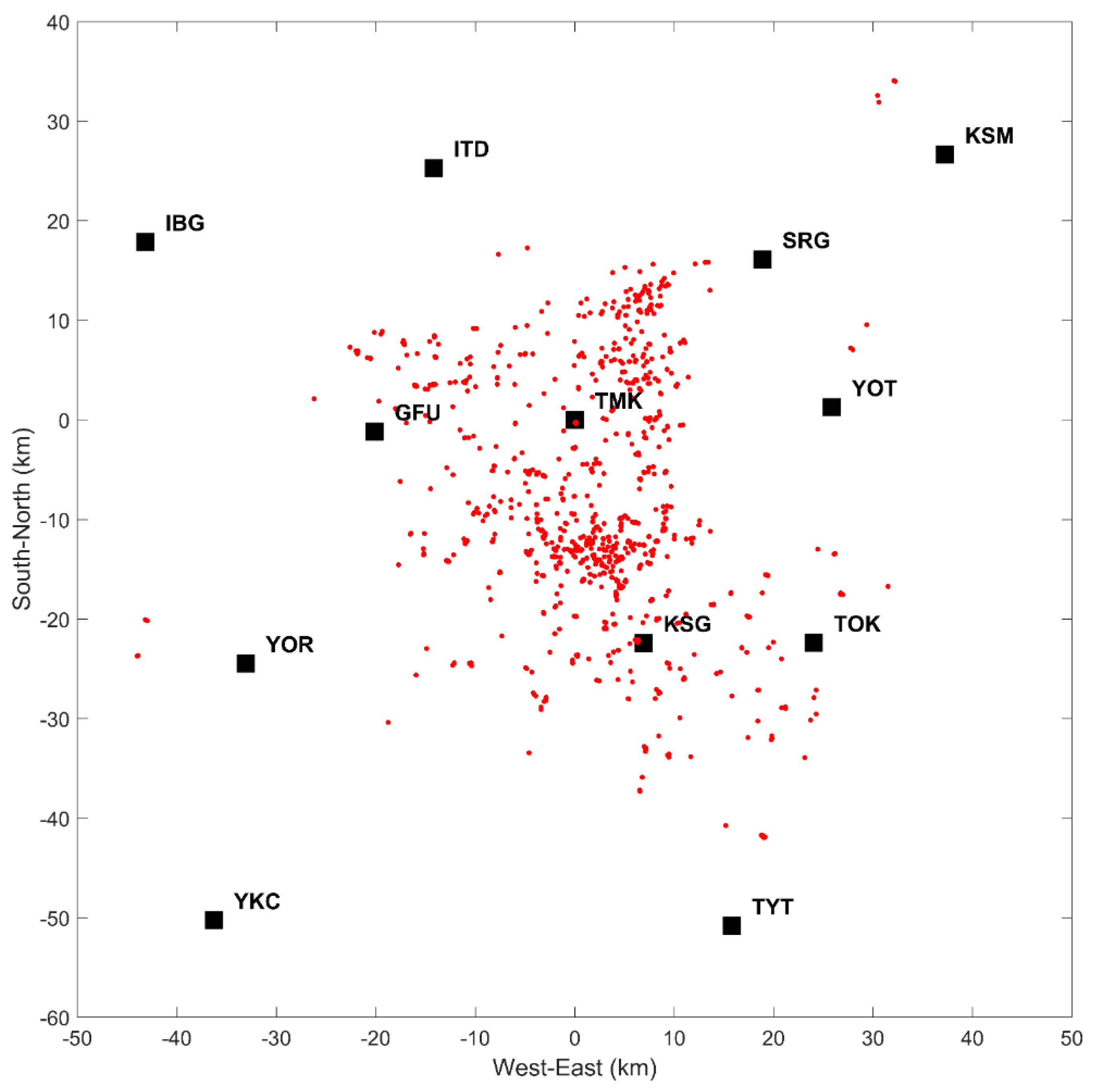
2.1. Observations
2.2. Data Processing
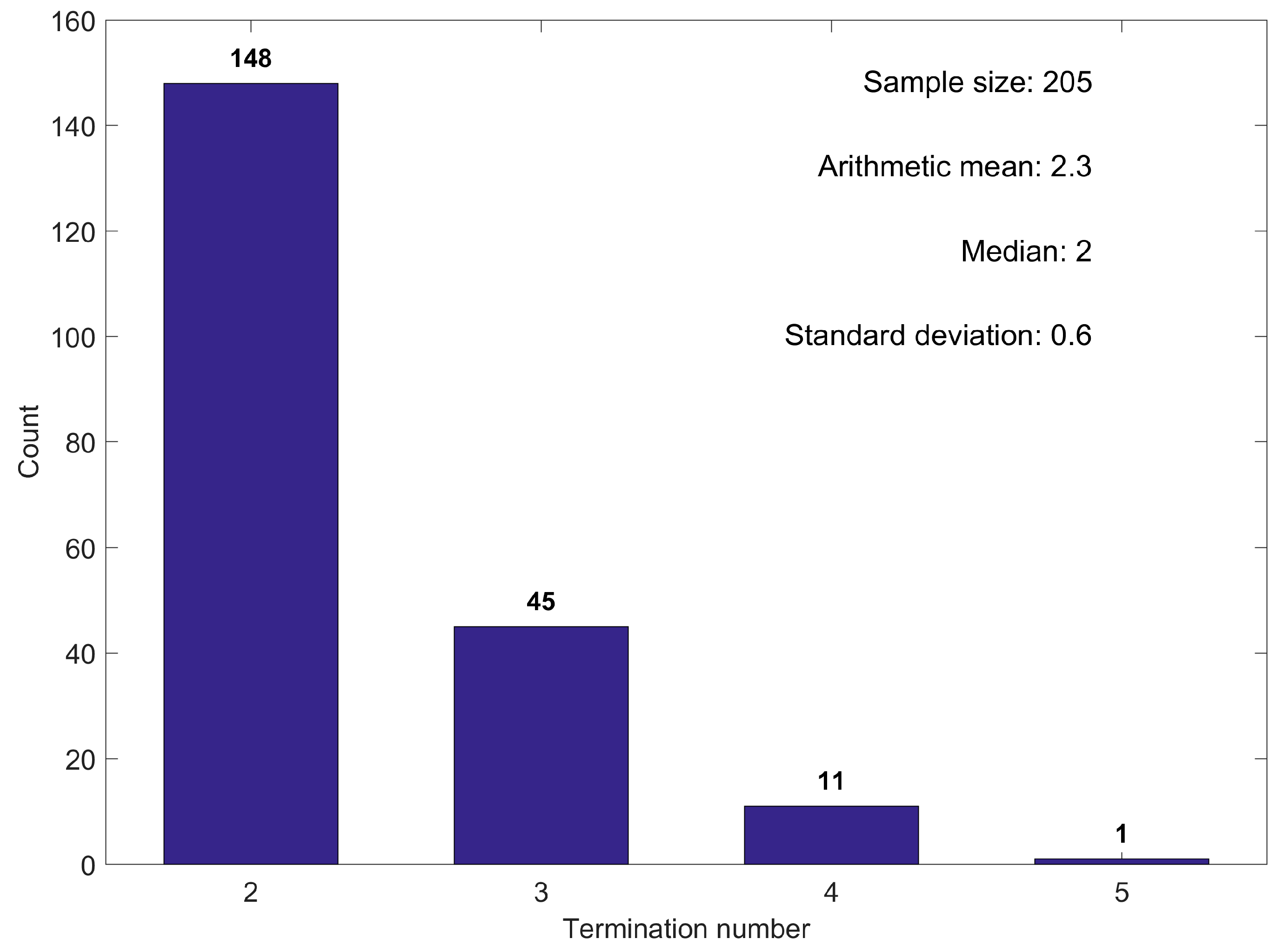
- Termination number: the number of terminations produced by each MTF;
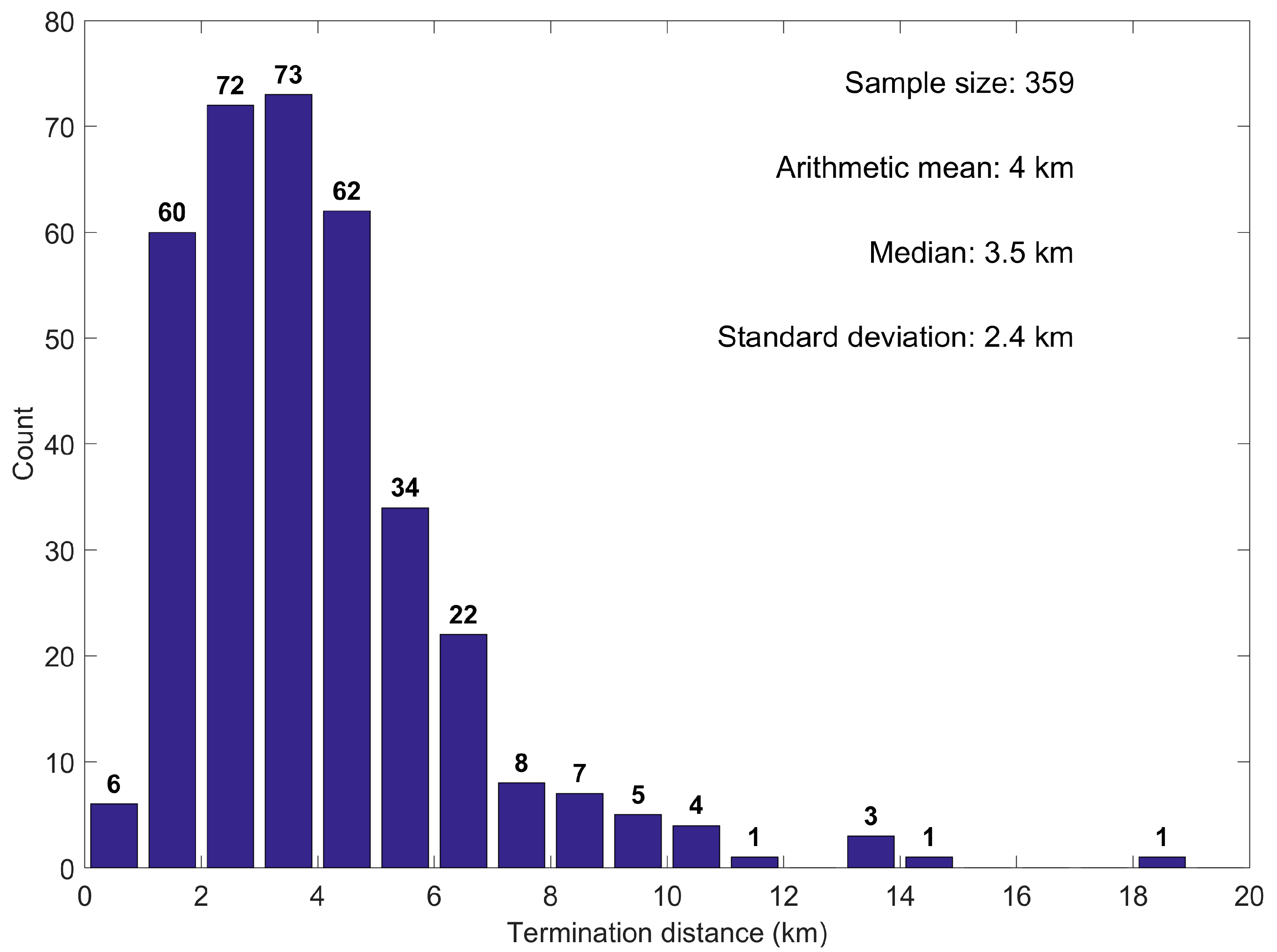
- Termination distance: the horizontal distance between any two terminations in each MTF;
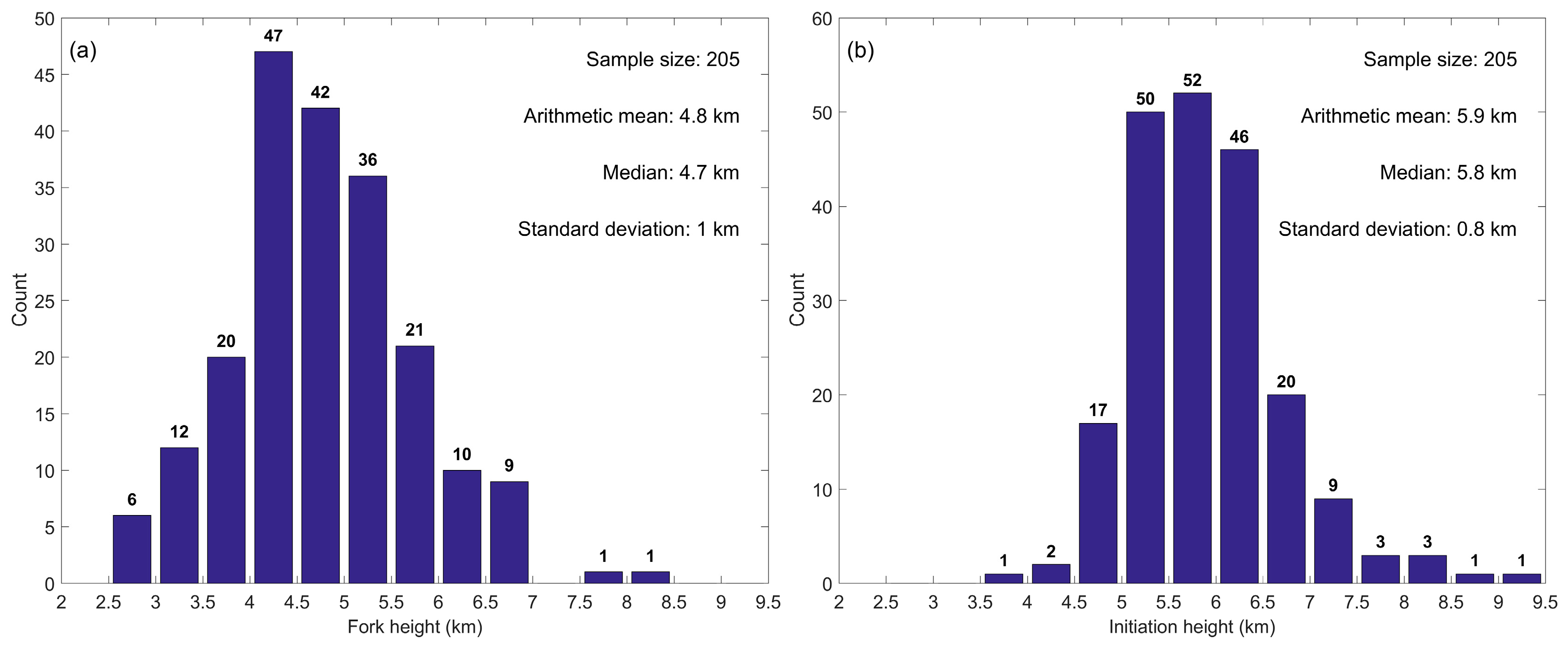
- Fork height: the altitude where the leader forked into different channels and eventually formed the different terminations;
- RS number: the number of RSs produced by each MTF;
- Time interval between the first strokes of each termination: the time difference between the first strokes of each termination;
- The shortest time difference between the strokes at different terminations: the shortest time interval between the strokes at different terminations;
- The first stroke intensity at each termination of an MTF: the range-normalized peak amplitude of the first stroke at each termination.
3. Results
3.1. Termination Number
3.2. Termination Distance
3.3. Fork Height
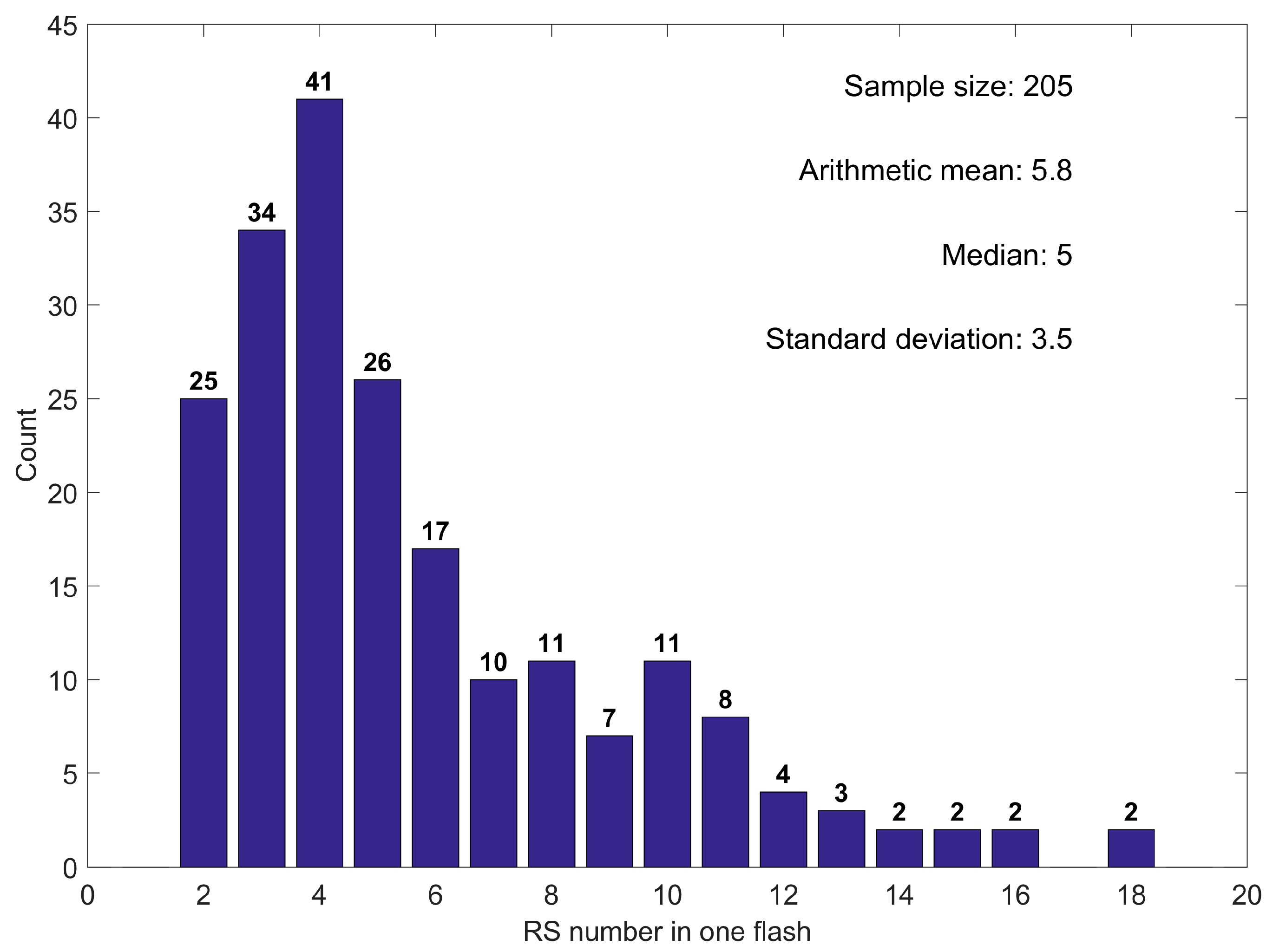
3.4. Return Stroke Number
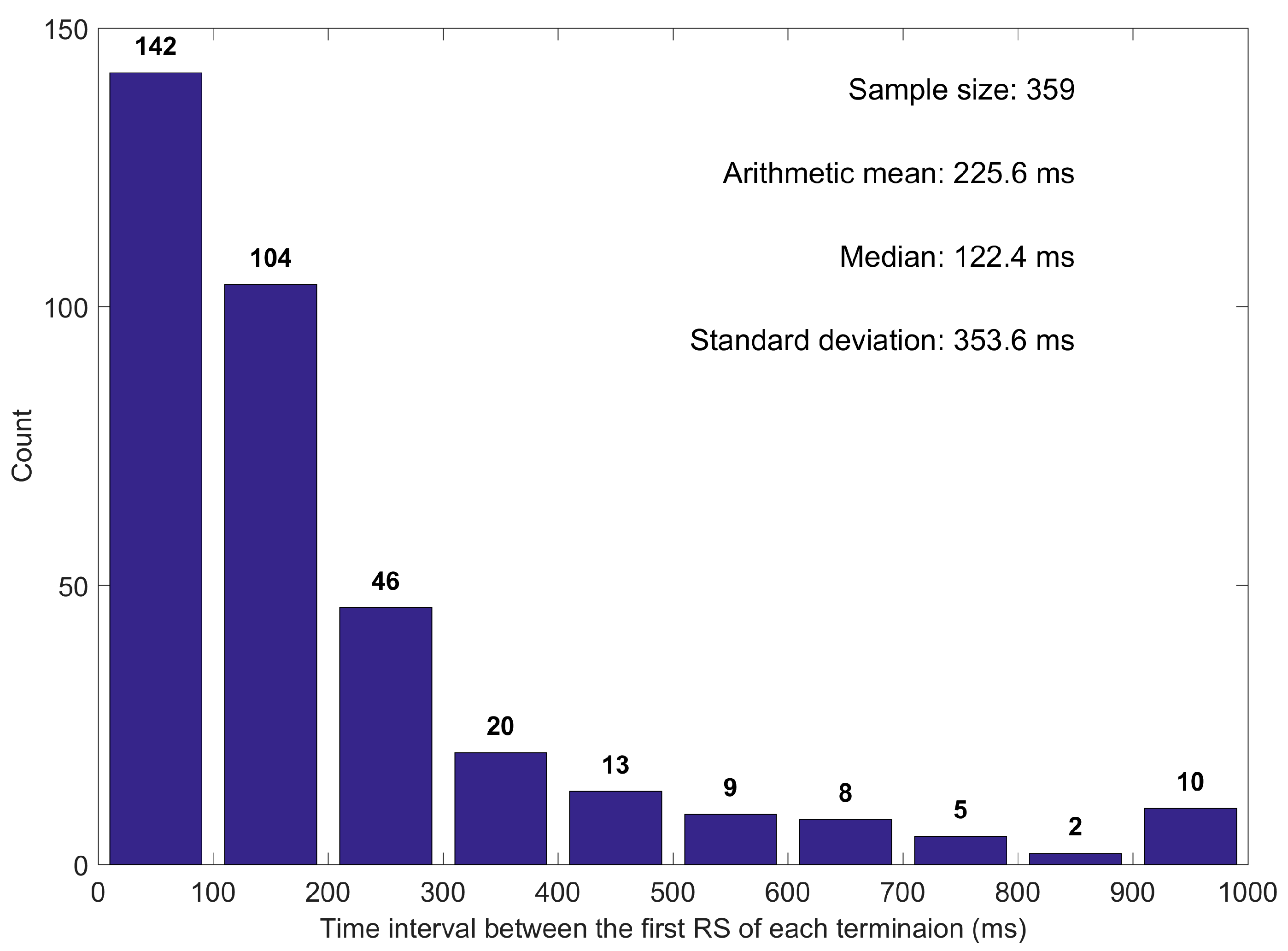
3.5. Time Interval between the First Strokes of Each Termination
3.6. Shortest Time Difference between the Strokes at Different Terminations
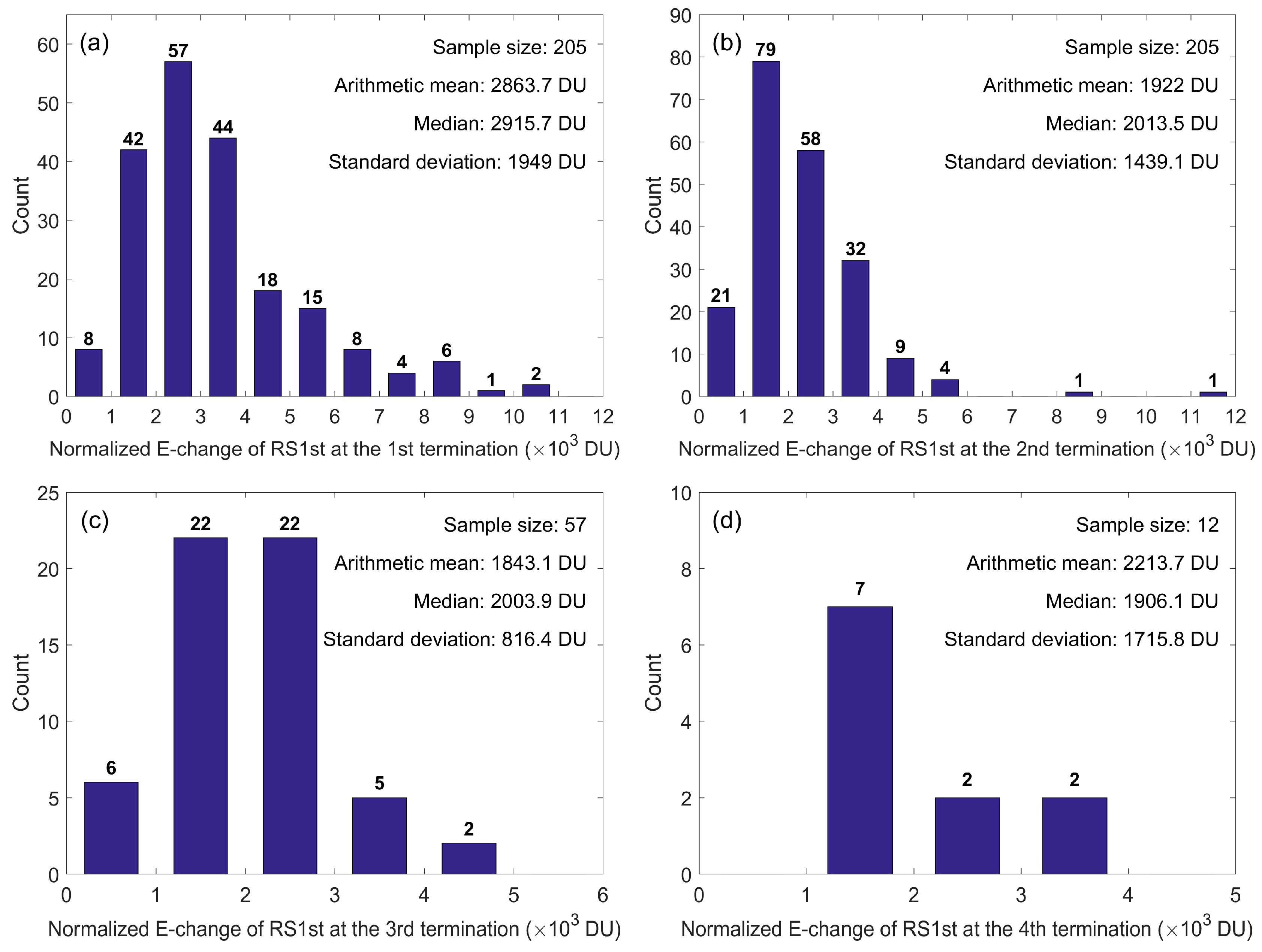
3.7. RS1st Intensity at Each MTF Termination
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schonland, B.F.J. Progressive lightning, 4, The discharge mechanism. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1938, 164, 132–150. [Google Scholar]
- Barasch, G.E. Spectral intensities emitted by lightning discharges. J. Geophys. Res. 1970, 75, 1041–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantley, R.D.; Tiller, J.A.; Uman, M.A. Lightning properties in Florida thunderstorms from video tape records. J. Geophys. Res. 1975, 80, 3402–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, N.; Brook, M.; Workman, E.J. Continuing currents in cloud-to-ground lightning discharges. J. Geophys. Res. 1962, 67, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krider, E.P. Some photographic observations of lightning. J. Geophys. Res. 1966, 71, 3095–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winn, W.P.; Aldridge, T.V.; Morse, C.B. Video tape recordings of lightning flashes. J. Geophys. Res. 1973, 78, 4515–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakov, V.A.; Uman, M.A.; Thottappillil, R. Review of Lightning Properties from Electric Field and TV Observations. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 10745–10750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakov, V.A.; Huffines, G.R. Return-Stroke Multiplicity of Negative Cloud-to-Ground Lightning Flashes. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2003, 42, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stall, C.A.; Cummins, K.L.; Krider, E.P.; Cramer, J.A. Detecting Multiple Ground Contacts in Cloud-to-Ground Lightning Flashes. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, D.; Takagi, N. Lightning mapping with an array of fast antennas. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 3698–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, D.; Takagi, N. Locating preliminary breakdown pulses in positive cloud-to-ground lightning. J. Geophys. Res. 2018, 123, 7989–7998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, D.; Takagi, N. Intracloud lightning flashes initiated at high altitudes and dominated by downward positive leaders. J. Geophys. Res. 2019, 124, 6982–6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Wang, D.; Wu, T.; Takagi, N. Correlation between the first return stroke of negative CG lightning and its preceding discharge processes. J. Geophys. Res. 2019, 124, 8501–8510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thottappillil, R.; Rakov, V.A.; Uman, M.A.; Beasley, W.H.; Master, M.J.; Shelukhin, D.V. Lightning subsequent stroke electric field peak greater than the first strike peak and multiple ground terminations. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 7503–7509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Takagi, N.; Watanabe, T.; Rakov, V.A.; Uman, M.A. Luminosity waves in branched channels of two negative lightning flashes. J. Atmos. Electr. 2000, 20, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Matsui, M.; Michishita, K.; Yokoyama, S. Characteristics of Negative Flashes with Multiple Ground Strike Points Located by the Japanese Lightning Detection Network. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2019, 61, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valine, W.C.; Krider, E.P. Statistics and characteristics of cloud-to-ground lightning with multiple ground contacts. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 4441–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, M.M.F.; Ballarotti, M.G.; Pinto, O., Jr. Negative cloud-to-ground lightning properties from high-speed video observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, 0148–0227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooray, V.; Perez, H. Some features of lightning flashes observed in Sweden. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 10683–10688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Qie, X.; Liu, M.; Jiang, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H. Characteristics of a negative lightning with multiple-ground terminations observed by a VHF lightning location system. J. Geophys. Res. 2016, 121, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, P.; Wang, D.; Shi, D.; Wu, T.; Takagi, N. Characterization of Multitermination CG Flashes Using a 3D Lightning Mapping System (FALMA). Atmosphere 2019, 10, 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10100625
Gao P, Wang D, Shi D, Wu T, Takagi N. Characterization of Multitermination CG Flashes Using a 3D Lightning Mapping System (FALMA). Atmosphere. 2019; 10(10):625. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10100625
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Panliang, Daohong Wang, Dongdong Shi, Ting Wu, and Nobuyuki Takagi. 2019. "Characterization of Multitermination CG Flashes Using a 3D Lightning Mapping System (FALMA)" Atmosphere 10, no. 10: 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10100625
APA StyleGao, P., Wang, D., Shi, D., Wu, T., & Takagi, N. (2019). Characterization of Multitermination CG Flashes Using a 3D Lightning Mapping System (FALMA). Atmosphere, 10(10), 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10100625



