The Influence of Stratospheric Sulphate Aerosol Deployment on the Surface Air Temperature and the Risk of an Abrupt Global Warming
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Models
2.1. Scenario Description
2.2. The OGI Climate Model
2.3. Adapting the OGI Climate Model to the Experiment
2.3.1. Parameter adjustments
2.3.2. GHG abundances
2.3.3. Sulphate aerosol layer due to geoengineering
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Testing the Performance of the OGI Climate Model
3.1.1. The eruption of Mount Pinatubo
3.1.2. The A1B SRES scenario
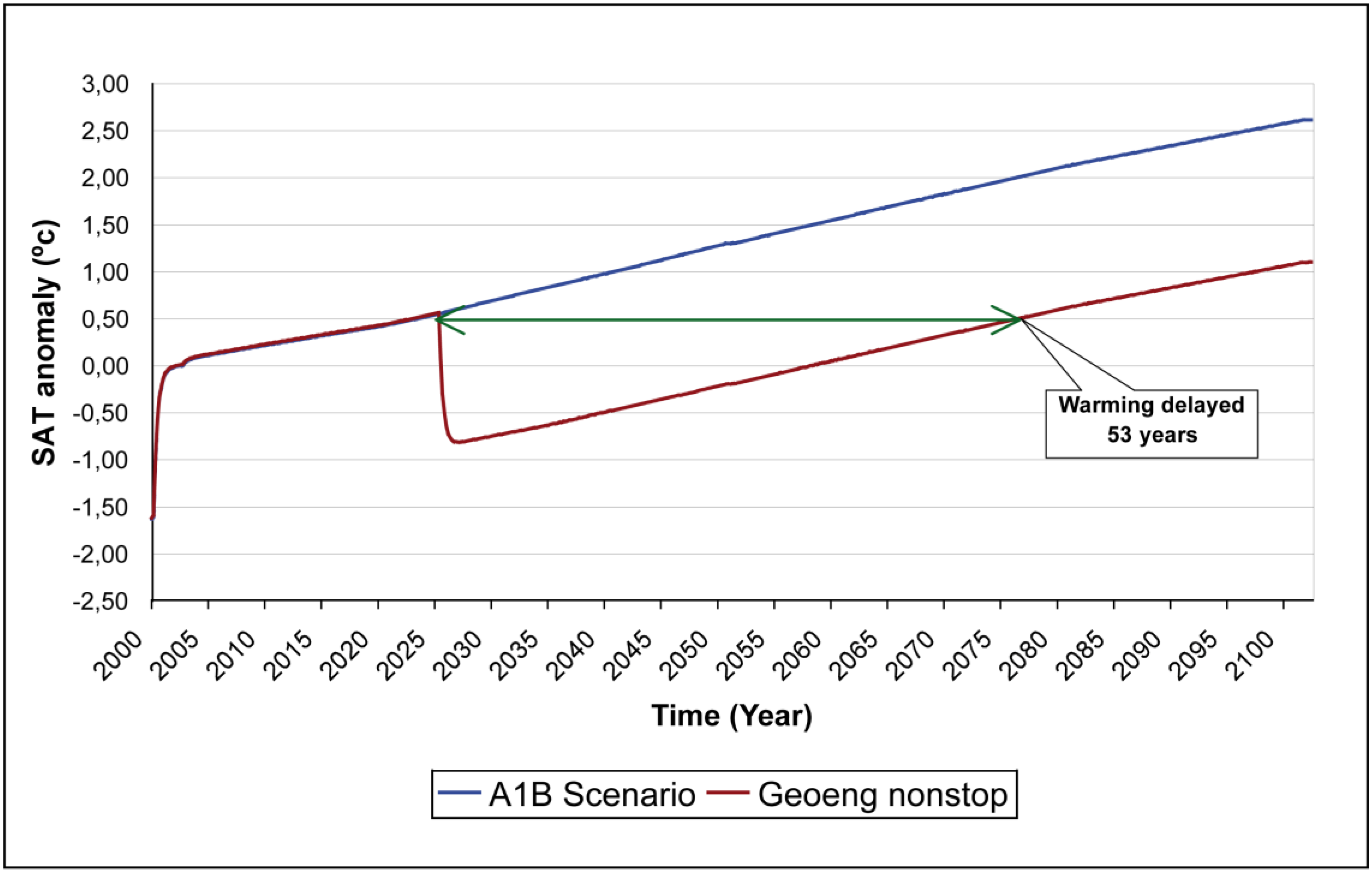
3.2. Geoengineering Deployment
3.2.1. Loading equivalent to Pinatubo’s eruption kept constant through injections
3.2.2. Loading equivalent to Pinatubo’s eruption increasing every year
- a)
- The loading injected increases by 1.9 % every year:
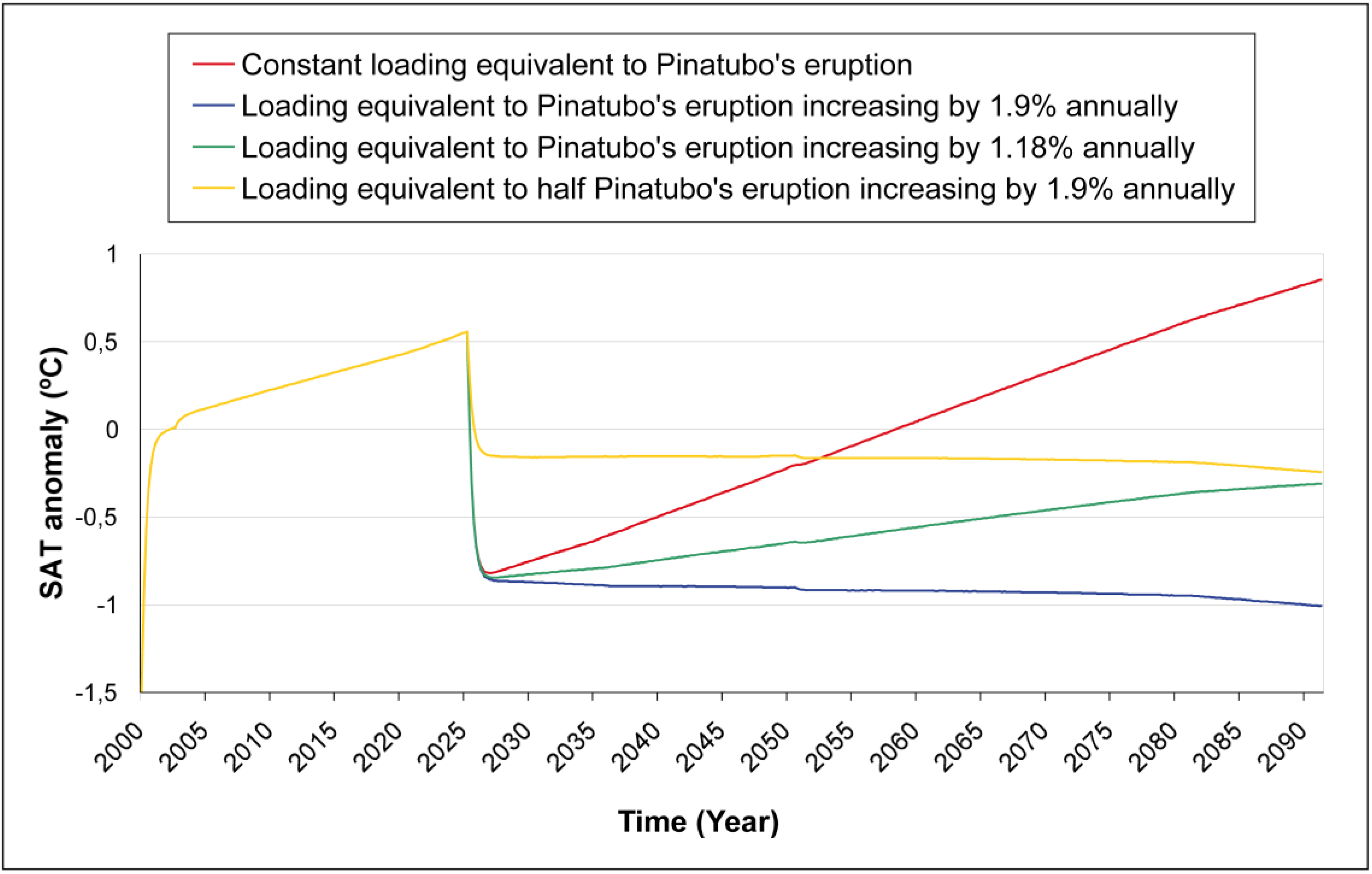
- b)
- The loading injected increases by 1.18 % every year:
3.2.3. Loading equivalent to half of the amount injected by Pinatubo’s eruption increasing by 1.9% every year
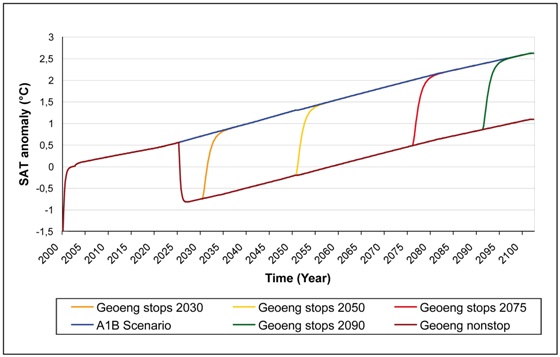
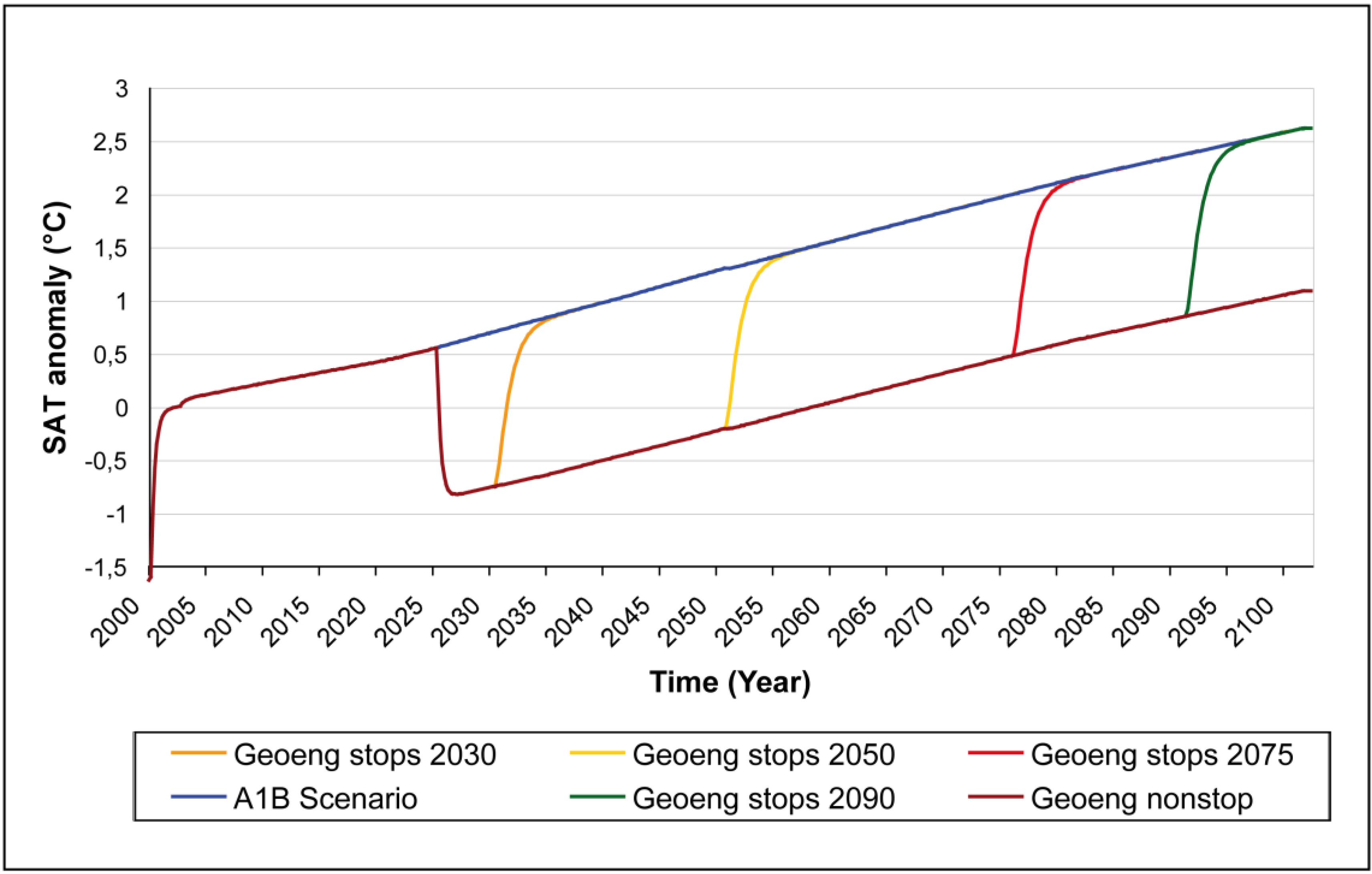
3.3. Geoengineering Failure Scenarios
3.3.1. Injections interrupted at 2030, 2050, 2075 and 2090 with a constant aerosol loading
3.3.2. Injections interrupted at 2050 and 2090 with a loading equivalent to half of the Pinatubo’s eruption increasing by 1.9% every year
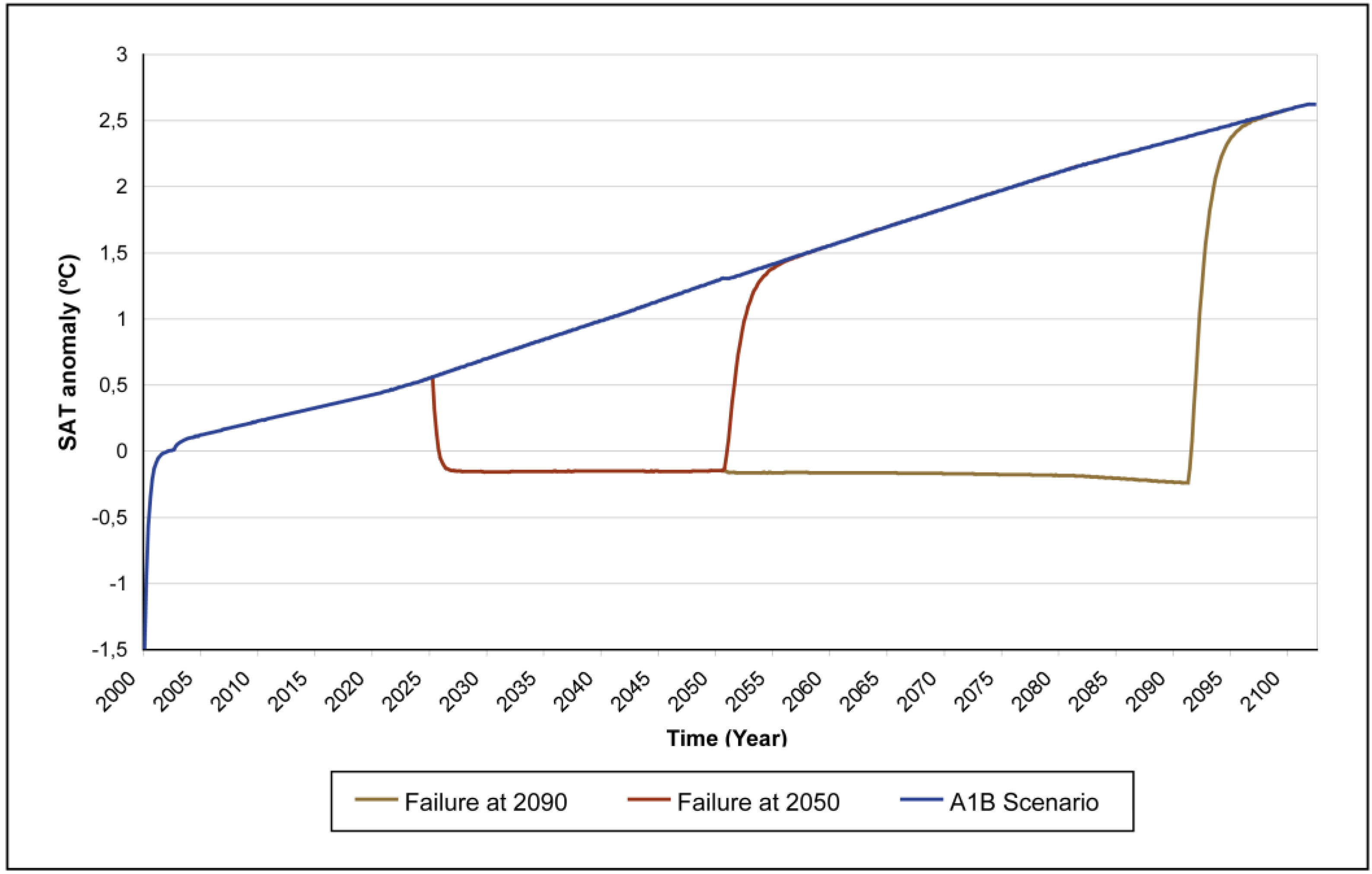
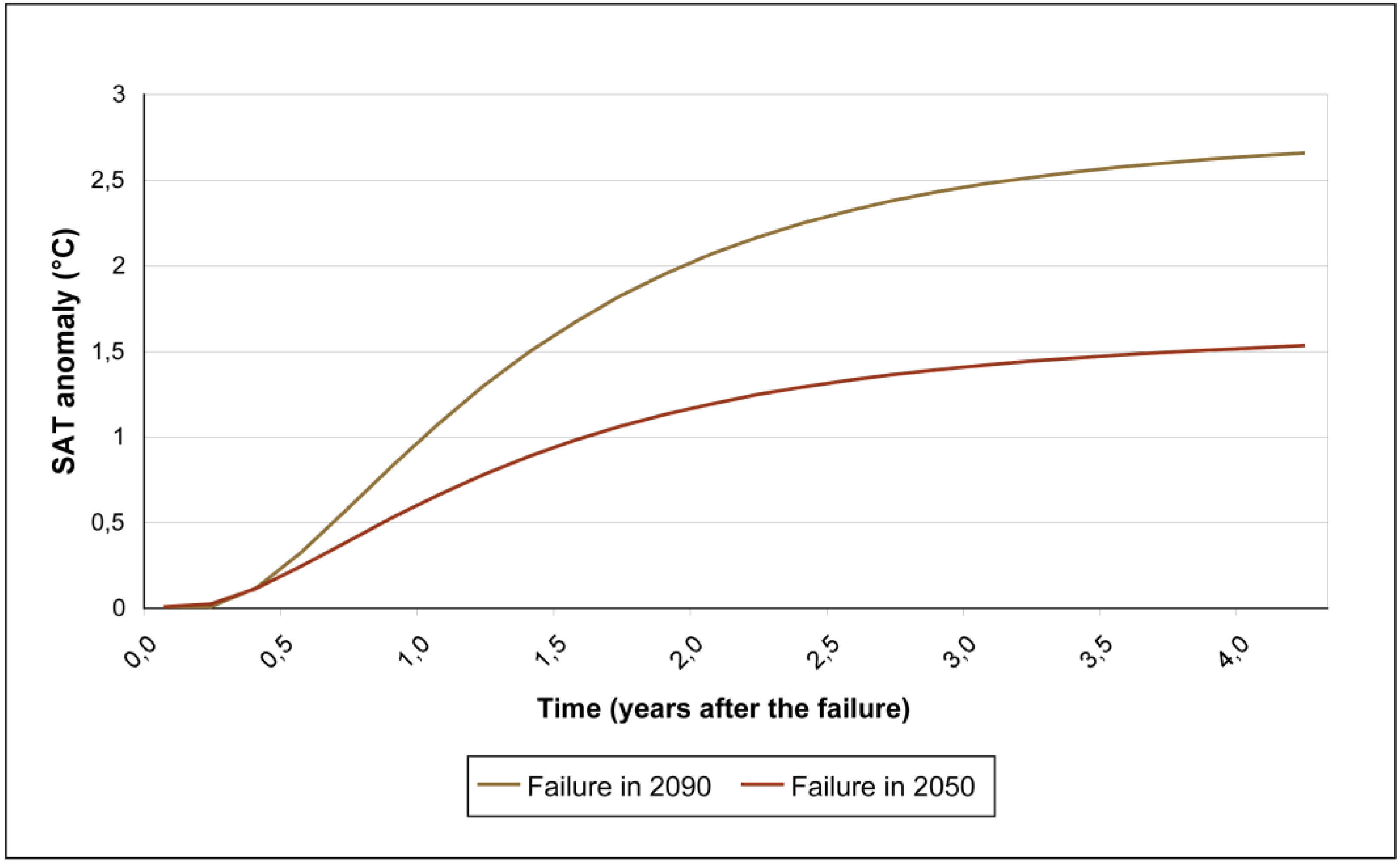
3.3.3. Injections interrupted at 2050 with different aerosol loadings
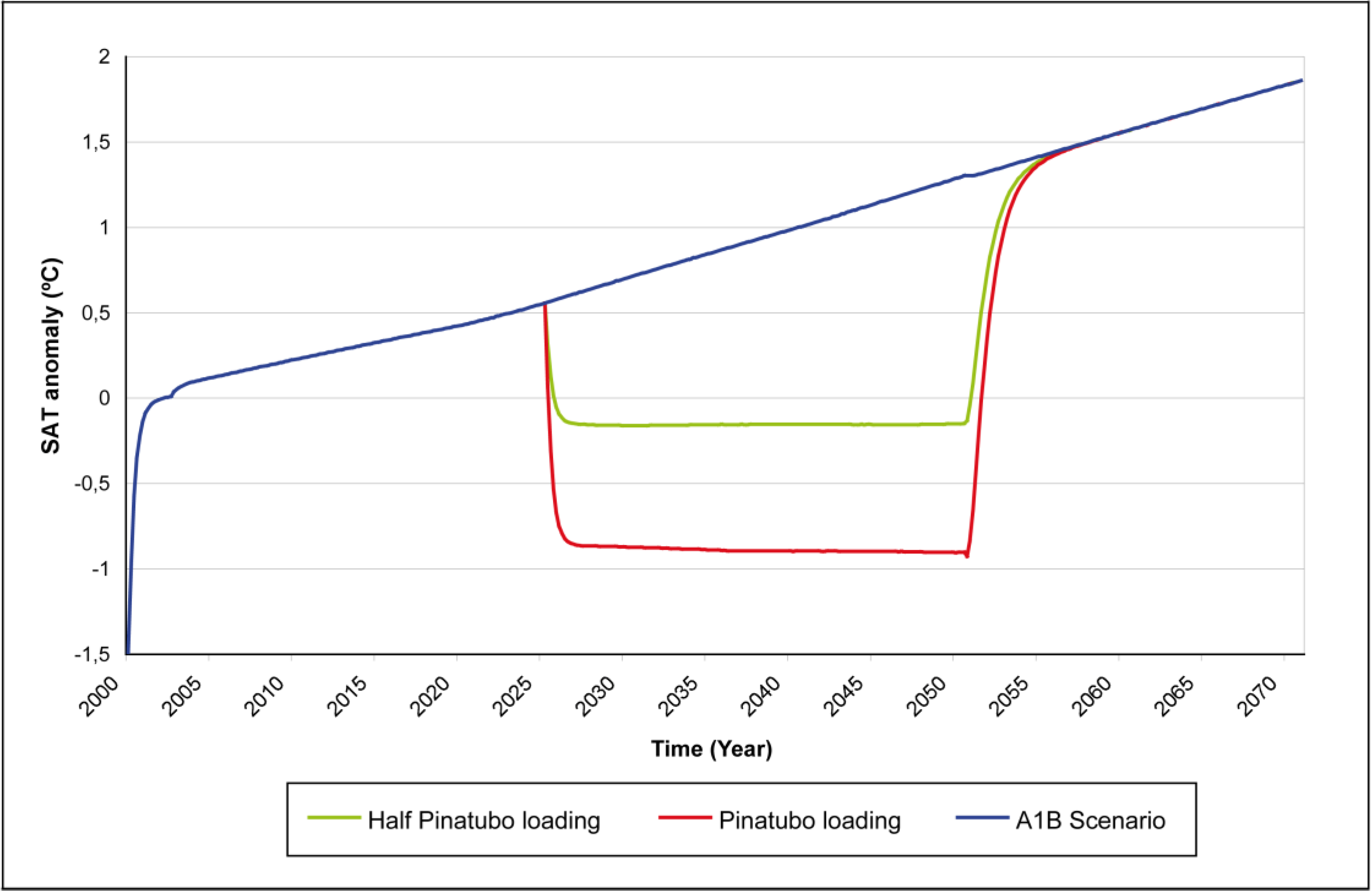
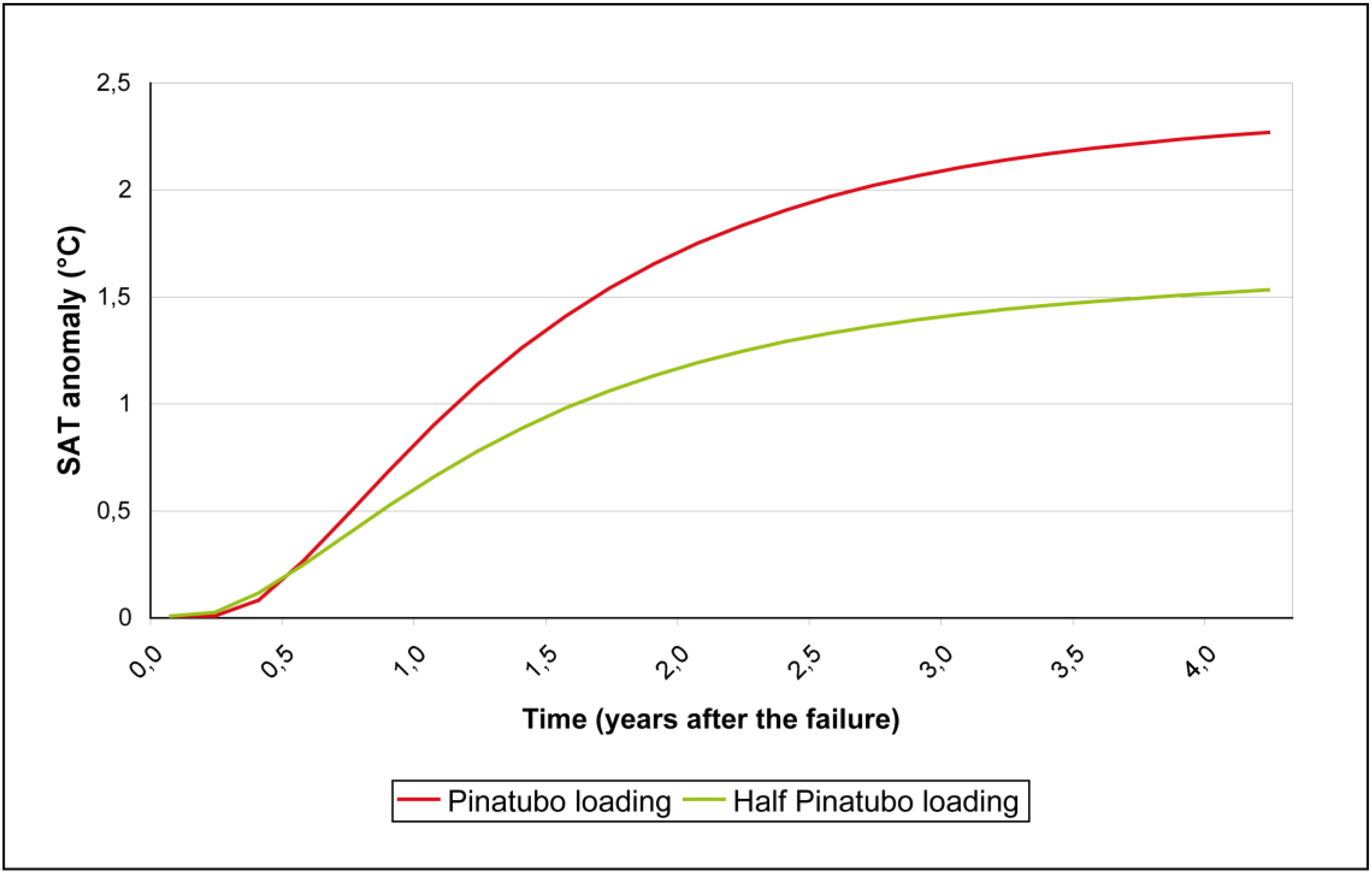
3.4. Shortcomings of This Geoengineering Scheme
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Lenton, T.M.; Vaughan, N.E. The radiative forcing potential of different climate geoengineering options. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5539–5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, D.W. Geoengineering. In Encyclopedia of Global Change; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 495–502. [Google Scholar]
- Cotton, W.R.; Pielke, R.A. Human Impacts on Weather and Climate; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Budyko, M.I. Climatic Changes. In American Geophysical Society; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1977; p. 244. [Google Scholar]
- Meixner, F.X.; Georgii, H.W.; Ockelmann, G.; Jäger, H.; Reiter, R. The arrival of the Mount St. Helens eruption cloud over Europe. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1981, 8, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.D.; Kelly, P.M. The effect of tropical explosive volcanic eruptions in surface air temperature. In Reprint from the Climatic Research Unit; University of East Anglia: Norwich, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Robock, A. Volcanic eruptions and climate. Rev. Geophys. 2000, 38, 191–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panel on Policy Implications of Greenhouse Warming; National Academy of Sciences; National Academy of Engineering; Institute of Medicine. Policy Implications of Greenhouse Warming: Mitigation, Adaptation, and the Science Base; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Keith, D.W. Geoengineering the climate: History and prospect. Annu. Rev. Energ. Environ. 2000, 25, 245–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, T.; Bashmakov, I.; Alharthi, A.; Amann, M.; Cifuentes, L.; Drexhage, J.; Duan, M.; Edenhofer, O.; Flannery, B.; Grubb, M.; Hoogwijk, M.; Ibitoye, F.I.; Jepma, C.J.; Pizer, W.A.; Yamaji, K. Mitigation from a cross-sectoral perspective. In Climate Change 2007: Mitigation of Climate Change; Contribution of Working Group III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Metz, B., Davidson, O.R., Bosch, P.R., Dave, R., Meyer, L.A., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Govindasamy, B.; Caldeira, K. Geoengineering earth’s radiation balance to mitigate CO2 induced climate change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 2141–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindasamy, B.; Caldeira, K.; Duffy, P.B. Geoengineering Earth's radiation balance to mitigate climate change from a quadrupling of CO2. Global Planet. Change 2003, 37, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutzen, P. Albedo enhancement by stratospheric sulfur injections: A contribution to resolve a policy dilemma? Climatic Change 2006, 77, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigley, T.M. A combined mitigation/geoengineering approach to climate stabilization. Science 2006, 314, 452–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, H.D.; Caldeira, K. Transient climate-carbon simulations of planetary geoengineering. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 2007, 104, 9949–9954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakicenovic, N.; Alcamo, J.; Davis, G.; de Vries, B.; Fenhann, J.; Gaffin, S.; Gregory, K.; Grubler, A.; Yong Jung, T.; Kram, T.; Lebre, La Rovere, E.; Michaelis, L.; Mori, S.; Morita, T.; Pepper, W.; Pitcher, H.; Price, L.; Riahi, K.; Roehrl, A.; Rogner, H.H.; Sankovski, A.; Schlesinger, M.; Shukla, P.; Smith, S.; Swart, R.; van Rooijen, S.; Victor, N.; Dadi, Z. Special Report on Emissions Scenarios (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change); Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, L.; Caldeira, K.; Chatfield, R.; Langhoff, S. Workshop Report on Managing Solar Radiation; National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA); Ames Research Center: Moffett Field, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rasch, P.J.; Crutzen, P.J.; Coleman, D.B. Exploring the geoengineering of climate using stratospheric sulfate aerosols: The role of particle size. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L02809. [Google Scholar]
- Robock, A.; Oman, L.; Stenchikov, G.L. Regional climate responses to geoengineering with tropical and Arctic SO2 injections. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D16101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brovkin, V.; Petoukhov, V.; Claussen, M.; Bauer, E.; Archer, D.; Jaeger, C. Geoengineering climate by stratospheric sulfur injections: Earth system vulnerability to technological failure. Climatic Change 2009, 92, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.; Matthews, H.D. Climate engineering and the risk of rapid climate change. Environ. Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 045103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliseev, A.; Mokhov, I.; Karpenko, A. Global warming mitigation by means of controlled aerosol emissions into the stratosphere: Global and regional peculiarities of temperature response as estimated in IAP RAS CM simulations. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2009, 22, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliseev, A.; Chernokulsky, A.; Karpenko, A.; Mokhov, I. Global warming mitigation by sulphur loading in the stratosphere: dependence of required emissions on allowable residual warming rate. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 101, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llanillo, P.J. The Influence of Planetary Geoengineering on the Surface Air Temperature. MSc Dissertation, University of East Anglia, Norwich, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ehhalt, D.; Prather, M.; Dentener, F.; Derwent, R.; Dlugokencky, E.; Holland, E.; Isaksen, I.; Katima, J.; Kirchhoff, V.; Matson, P.; Midgley, P.; Wang, M. SRES Tables. Appendix II. Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. In Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Joos, F.; Prentice, I.C.; Sitch, S.; Meyer, R.; Hooss, G.; Plattner, G.-K.; Gerber, S.; Hasselmann, K. Global warming feedbacks on terrestrial carbon uptake under the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Emission Scenarios. Global Biogeochem. Cycle. 2001, 15, 891–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentice, I.C.; Farquhar, G.D.; Fasham, M.J.R.; Goulden, M.L.; Heimann, M.; Jaramillo, V.J.; Kheshgi, H.S.; Le Quéré, C.; Scholes, R.J.; Wallace, D.W.R. The Carbon Cycle and Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide. Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. In Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ehhalt, D.; Prather, M.; Dentener, F.; Derwent, R.; Dlugokencky, E.; Holland, E.; Isaksen, I.; Katima, J.; Kirchhoff, V.; Matson, P.; Midgley, P.; Wang, M. Atmospheric Chemistry and Greenhouse Gases. Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. In Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, P.M.; Jones, P.D.; Pengqun, J. The spatial response of the climate system to explosive volcanic eruptions. Int. J. Climatol. 1996, 16, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluth, G.J.S.; Doiron, S.D.; Schnetzler, C.C.; Krueger, A.J.; Walter, L.S. Global tracking of the SO2 clouds from the June, 1991 Mount Pinatubo eruptions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1992, 19, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.; Lacis, A.; Ruedy, R.; Sato, M. Potential climate impact of Mount Pinatubo eruption. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1992, 19, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, D.E.; Wilson, H.; Jones, P.D.; Christy, J.R.; Folland, C.K. The impact of Mount Pinatubo on world-wide temperatures. Int. J. Climatol. 1996, 16, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.D.; Moberg, A.; Osborn, T.J.; Briffa, K.R. Surface climate responses to explosive volcanic eruptions seen in long European temperature records and mid-to-high latitude tree-ring density around the Northern Hemisphere. In Volcanism and the Earth’s Atmosphere; Robock, A., Oppenheimer, C., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 239–254. [Google Scholar]
- MacKay, R.M.; Khalil, M.A.K. Theory and development of a one dimensional time dependent radiative convective climate model. Chemosphere 1991, 22, 383–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forest, C.E.; Stone, P.H.; Sokolov, A.P. Estimated PDFs of climate system properties including natural and anthropogenic forcings. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L01705. [Google Scholar]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Dai, A. Effects of mount pinatubo volcanic eruption on the hydrological cycle as an analog of geoengineering. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L15702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robock, A. Twenty reasons why geoengineering might be a bad idea. Bull. Atom. Sci. 2008, 64, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Standard Atmosphere; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA): Washington, DC, USA, 1976.
- Meehl, G.A.; Stocker, T.F.; Collins, W.D.; Friedlingstein, P.; Gaye, A.T.; Gregory, J.M.; Kitoh, A.; Knutti, R.; Murphy, J.M.; Noda, A.; Raper, S.C.B; Watterson, I.J.; Weaver, A.J.; Zhao, Z.C. Global Climate Projections. In Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis; Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Decker, R.; Decker, B. Volcanoes; Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Martí, J.; Ernst, G. Volcanoes and the Environment; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, P.D.; New, M.; Parker, D.E.; Martin, S.; Rigor, I.G. Surface air temperature and its changes over the past 150 years. Rev. Geophys. 1999, 37, 173–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Jones, P.D.; Ambenje, P.; Bojariu, R.; Easterling, D.; Klein Tank, A.; Parker, D.; Rahimzadeh, F.; Renwick, J.A.; Rusticucci, M.; Soden, B.; Zhai, P. Observations: Surface and Atmospheric Climate Change. In Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis; Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, P.D.; Moberg, A. Hemispheric and large-scale surface air temperature variations: An extensive revision and an update to 2001. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 206–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goes, M.; Tuana, N.; Keller, K. The Economics (or lack thereof) of Aerosol Geoengineering. Climatic Change 2010. in review. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, S.H. Geoengineering: Could— or should— we do it? Climatic Change 1996, 33, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, G.; Duffy, P.B.; Taylor, K.E. Impact of geoengineering schemes on the global hydrological cycle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 2008, 105, 7664–7669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, H.D.; Cao, L.; Caldeira, K. Sensitivity of ocean acidification to geoengineered climate stabilization. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L10706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.C.; Jevrejeva, S.; Grinsted, A. Efficacy of geoengineering to limit 21st century sea-level rise. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 2010, 107, 15699–15703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rasch, P.J.; Tilmes, S.; Turco, R.P.; Robock, A.; Oman, L.; Chen, C.C.; Stenchikov, G.L.; Garcia, R.R. An overview of geoengineering of climate using stratospheric sulphate aerosols. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. A—Math. Phy. 2008, 366, 4007–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.H. Detecting Climatic Change Signals: Are There Any “Fingerprints”? Science 1994, 263, 341–347. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, S.H. Earth systems engineering and management. Nature 2001, 409, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.H. Geoengineering: could we or should we make it work? Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. A—Math. Phy. 2008, 366, 3843–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenzelmann, P.; Peter, T.; Fueglistaler, S.; Weisenstein, D.; Luo, D.; Schraner, M.; Rozanov, E. Geo-engineering side effects: Heating the tropical tropopause by sedimenting sulphur aerosol? In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science, ETH Zurich: Zürich, Switzerland, 2009; Volume 6, p. 452017. [Google Scholar]
- Tilmes, S.; Muller, R.; Salawitch, R. The sensitivity of polar ozone depletion to proposed geoengineering schemes. Science 2008, 320, 1201–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenchikov, G.; Hamilton, K.; Stouffer, R.J.; Robock, A.; Ramaswamy, V.; Santer, B.; Graf, H.-F. Arctic Oscillation response to volcanic eruptions in the IPCC AR4 climate models. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D07107. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, L.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Wofsy, S.C.; Munger, J.W.; Michalsky, J.J.; Urbanski, S.P.; Boden, T.A. Response of a deciduous forest to the mount Pinatubo eruption: Enhanced photosynthesis. Science 2003, 299, 2035–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robock, A. Atmospheric science. Whither geoengineering? Science 2008, 320, 1166–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izrael, Y.; Zakharov, V.; Petrov, N.; Ryaboshapko, A.; Ivanov, V.; Savchenko, A.; Andreev, Y.; Eran’kov, V.; Puzov, Y.; Danilyan, B.; Kulyapin, V.; Gulevskii, V. Field studies of a geo-engineering method of maintaining a modern climate with aerosol particles. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2009, 34, 635–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, P.G. Evaluating a technological fix for climate. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 9915–9916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, L. Geo-Engineering to Confine Climate Change: Is it at all feasible? Climatic Change 2006, 77, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Llanillo, P.; Jones, P.D.; Von Glasow, R. The Influence of Stratospheric Sulphate Aerosol Deployment on the Surface Air Temperature and the Risk of an Abrupt Global Warming. Atmosphere 2010, 1, 62-84. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos1010062
Llanillo P, Jones PD, Von Glasow R. The Influence of Stratospheric Sulphate Aerosol Deployment on the Surface Air Temperature and the Risk of an Abrupt Global Warming. Atmosphere. 2010; 1(1):62-84. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos1010062
Chicago/Turabian StyleLlanillo, Pedro, Phil D. Jones, and Roland Von Glasow. 2010. "The Influence of Stratospheric Sulphate Aerosol Deployment on the Surface Air Temperature and the Risk of an Abrupt Global Warming" Atmosphere 1, no. 1: 62-84. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos1010062
APA StyleLlanillo, P., Jones, P. D., & Von Glasow, R. (2010). The Influence of Stratospheric Sulphate Aerosol Deployment on the Surface Air Temperature and the Risk of an Abrupt Global Warming. Atmosphere, 1(1), 62-84. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos1010062