Oceanic Dimethyl Sulfide Emission and New Particle Formation around the Coast of Antarctica: A Modeling Study of Seasonal Variations and Comparison with Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Global Size-resolved Aerosol Model
3. Simulations and Results
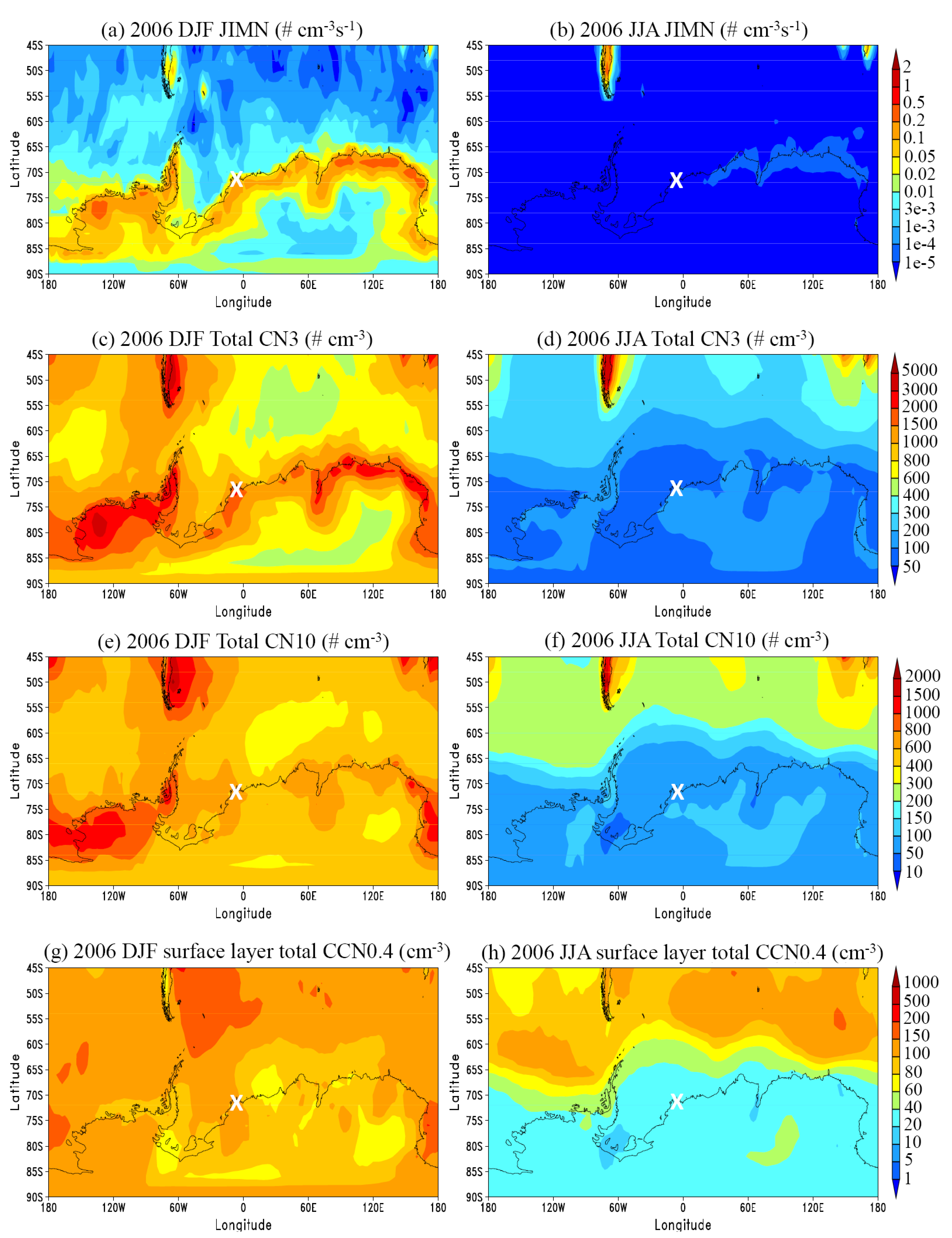
3.1. General Features

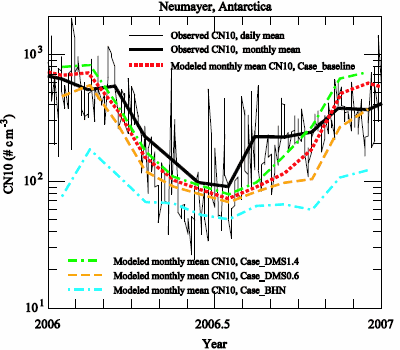
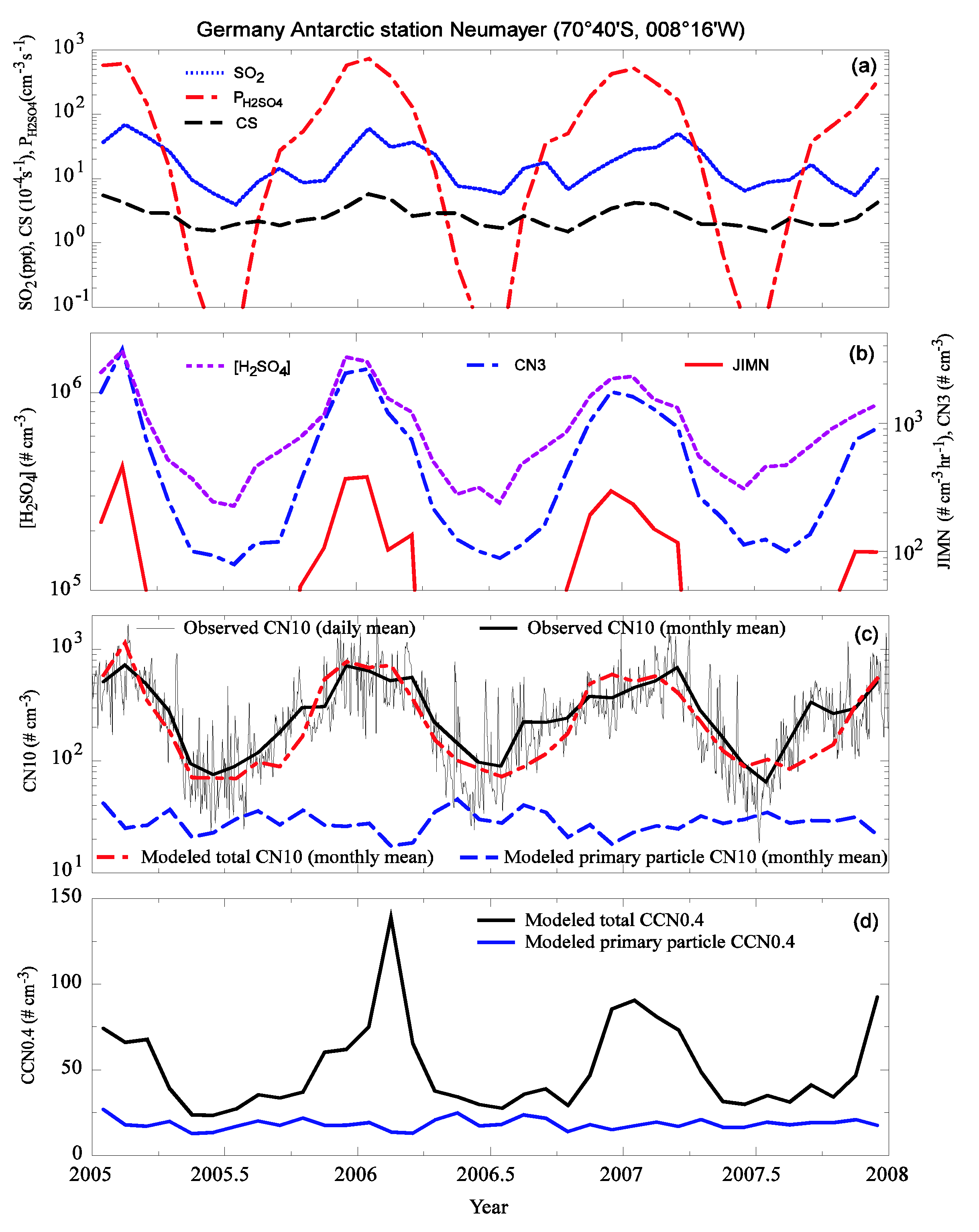
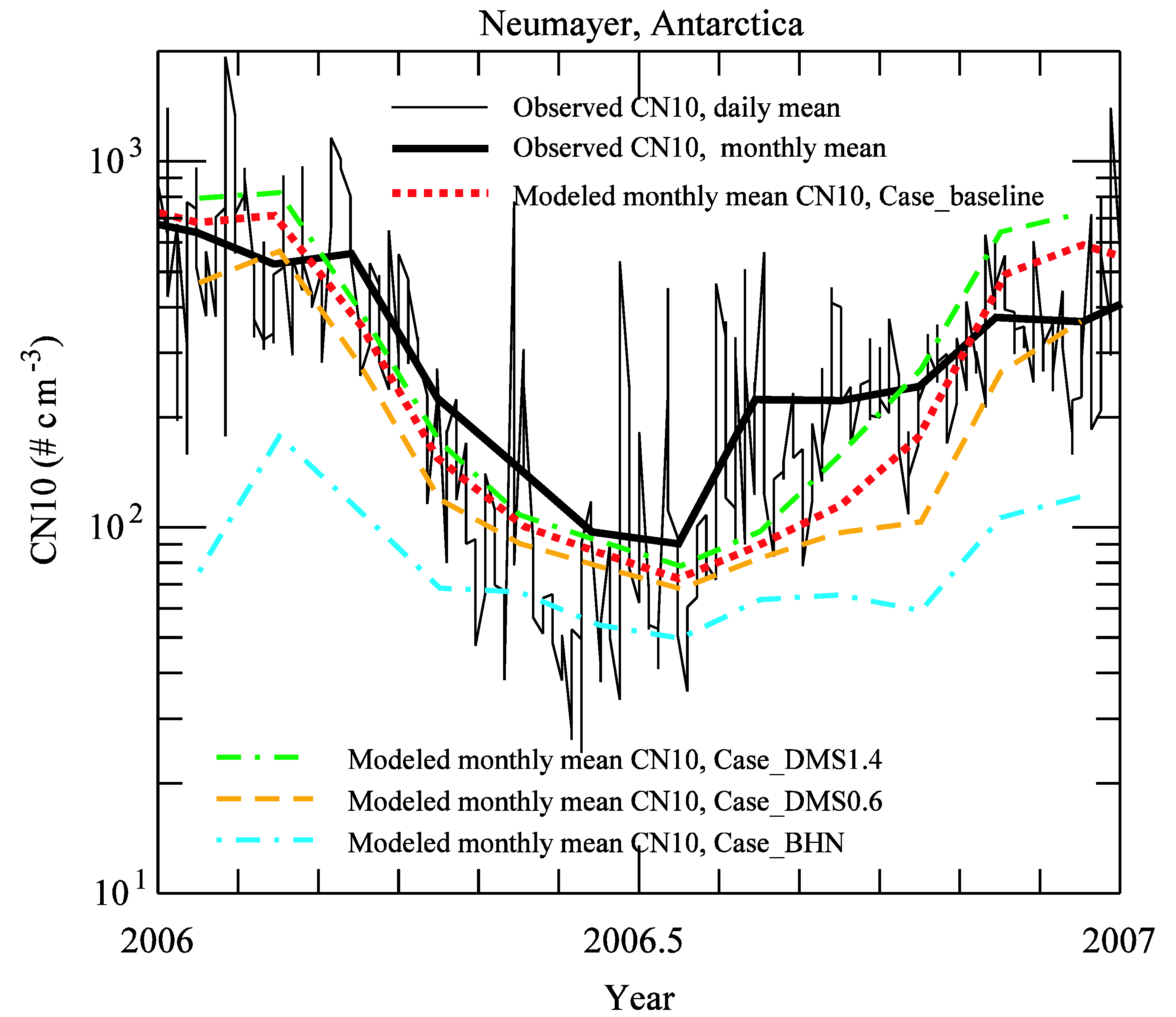
3.2. Comparison to Long-term Measurements
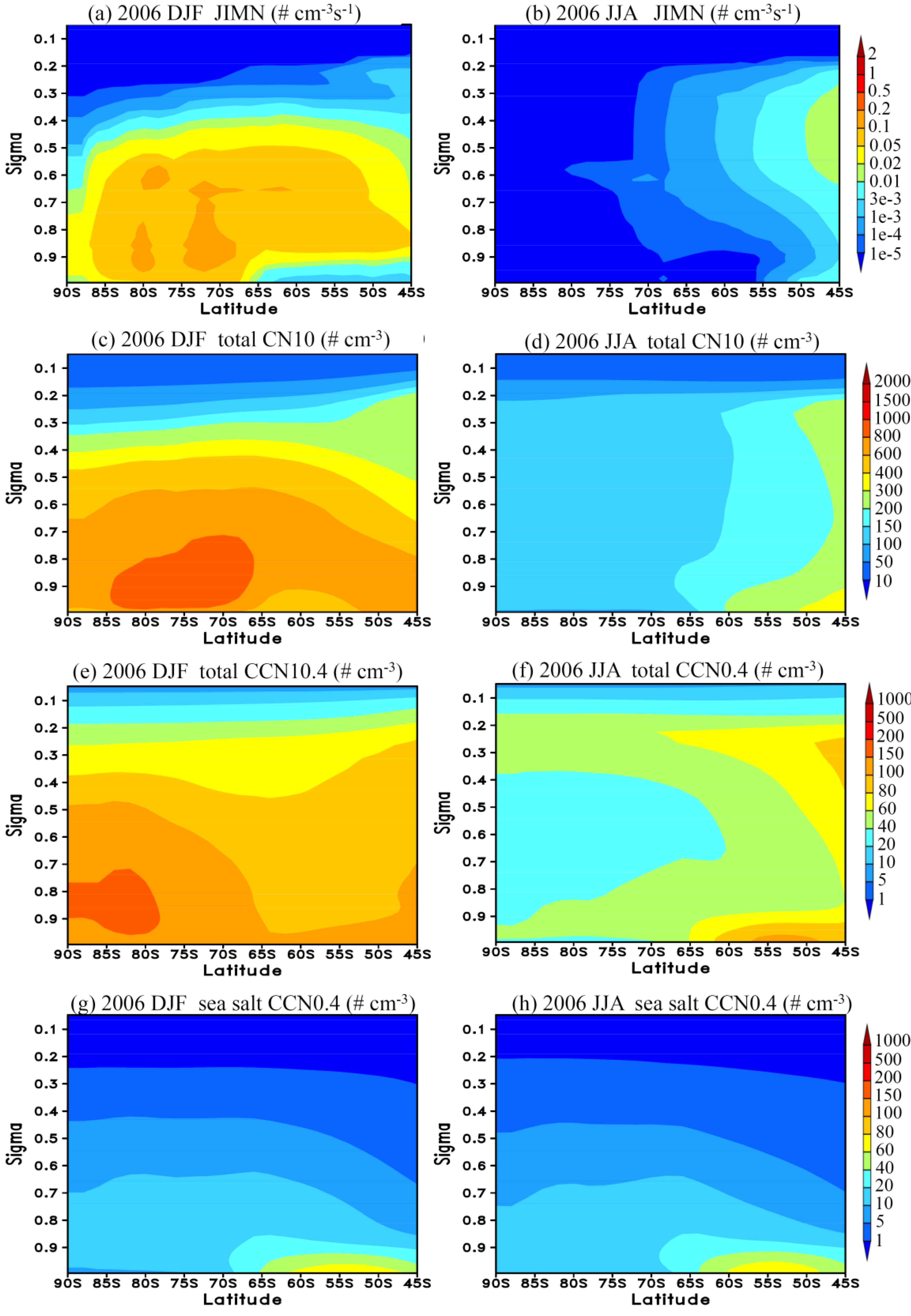
3.3. Vertical Profiles
3.4. Sensitivity Study: Impact of DMS Emission Variation and Contribution of BHN
| month | observation | Case_ | Case_ | Case_ | Case_ |
| 1 | 643 | 685 | 798 | 468 | 76 |
| Average | 311 | 304 | 364 | 217 | 85 |
| r | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.88 | 0.67 | |
| NMB | −0.02 | 0.17 | −0.30 | −0.73 |
4. Summary
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Faloona, I. Sulfur processing in the marine atmospheric boundary layer: A review and critical assessment of modeling uncertainties. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2841–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, R.J.; Lovelock, J.E.; Andreae, M.O.; Warren, S.G. Oceanic phytoplankton, atmospheric sulfur, cloud albedo and climate. Nature 1987, 326, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bopp, L.; Boucher, O.; Aumont, O.; Belviso, S.; Dufresne, J.L.; Pham, M.; Monfray, P. Will marine dimethylsulfide emissions amplify or alleviate global warming? A model study. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2004, 61, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunson, J.R.; Spall, S.A.; Anderson, T.R.; Jones, A.; Totterdell, I.J.; Woodage, M.J. Climate sensitivity to ocean dimethylsulphide emissions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L07701. [Google Scholar]
- Kloster, S.; Six, K.D.; Feichter, J.; Maier-Reimer, E.; Roeckner, E.; Wetzel, P.; Stier, P.; Esch, M. Response of dimethylsulfide (DMS) in the ocean and atmosphere to global warming. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, G03005. [Google Scholar]
- Ayers, G.P.; Cainey, J.M. The CLAW hypothesis: a review of the major developments. Environ. Chem. 2007, 4, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, A.W. Antarctic aerosols. J. App. Met. 1975, 14, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigg, E.K.; Gras, J.L.; Evans, C. Origins of Aitken particles in remote regions of the southern hemisphere. J. Atmos. Chem. 1984, 1, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, G.E. Antarctic aerosols: A review. Rev. Geophys. 1988, 26, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaenicke, R.; Dreiling, V.; Lehmann, E.; Koutsenoguii, P.K.; Stingl, J. Condensation nuclei at the German Antarctic station “Georg von Neumayer”. Tellus. Ser. B 1992, 44, 311–317. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, T. Size distribution of Antarctic submicron aerosols. Tellus. Ser. B 1993, 45, 145–159. [Google Scholar]
- Gras, J.L. Condensation nucleus size distribution at Mawson, Antarctica: Microphysics and chemistry. Atmos. Environ., Part A 1993, 27, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koponen, I.K.; Virkkula, A.; Hillamo, R.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Kulmala, M. Number size distributions and concentrations of marine aerosols: Observations during a cruise between the English Channel and the coast of Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koponen, I.K.; Virkkula, A.; Hillamo, R.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Kulmala, M. Number size distributions and concentrations of the continental summer aerosols in Queen Maud Land, Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, C.G.; Kamra, A.K. Physical properties of aerosols at Maitri, Antarctica. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet Sci.) 2004, 113, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Sakurai, H.; Vollmers, K.; McMurry, P.H. Aerosol size distributions measured at the South Pole during previous termISCATnext term 2000. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 5493–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, H.; Carslaw, K.S.; Spracklen, D.V.; Mann, G.W.; Woodhouse, M.T. Influence of oceanic dimethyl sulfide emissions on cloud condensation nuclei concentrations and seasonality over the remote Southern Hemisphere oceans: A global model study. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D15204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dowd, C.D.; Lowe, J.A.; Smith, M.H.; Davison, B.; Hewitt, C.N.; Harrison, R.M. Biogenic sulphur emissions and inferred non-sea-salt-sulphate cloud condensation nuclei in and around Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 12839–12854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virkkula, A.; Teinilä, K.; Hillamo, R.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Saarikoski, S.; Aurela, M.; Koponen, I. K.; Kulmala, M. Chemical size distributions of boundary layer aerosol over the Atlantic Ocean and at an Antarctic site. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D05306. [Google Scholar]
- Asmi, E.; Frey, A.; Virkkula, A.; Ehn, M.; Manninen, H.E.; Timonen, H.; Tolonen-Kivimäki, O.; Aurela, M.; Hillamo, R.; Kulmala, M. Hygroscopicity and chemical composition of Antarctic sub-micrometre aerosol particles and observations of new particle formation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 4253–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spracklen, D.V.; Carslaw, K. S.; Kulmala, M.; Kerminen, V. M.; Sihto, S. L.; Riipinen, I.; Merikanto, J.; Mann, G. W.; Chipperfield, M. P.; Wiedensohler, A.; Birmili, W.; Lihavainen, H. Contribution of particle formation to global cloud condensation nuclei concentrations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L06808. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Wang, Z.; Luo, G.; Turco, R.P. Ion-mediated nucleation as an important source of tropospheric aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 2537–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkonen, R.; Asmi, A.; Korhonen, H.; Kokkola, H.; Järvenoja, S.; Räisänen, P.; Lehtinen, K. E. J.; Laaksonen, A.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Järvinen, H.; Lohmann, U.; Bennartz, R.; Feichter, J.; Kulmala, M. Sensitivity of aerosol concentrations and cloud properties to nucleation and secondary organic distribution in ECHAM5-HAM global circulation model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 1747–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Penner, J.E. Aerosol indirect forcing in a global model with particle nucleation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 239–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, J.R.; Adams, P.J. Uncertainty in global CCN concentrations from uncertain aerosol nucleation and primary emission rates. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 1339–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merikanto, J.; Spracklen, D.V.; Mann, G.W.; Pickering, S.J.; Carslaw, K.S. Impact of nucleation on global CCN. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 8601–8616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Luo, G. Simulation of particle size distribution with a global aerosol model: Contribution of nucleation to aerosol and CCN number concentrations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 7691–7710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Luo, G.; Bates, T.; Anderson, B.; Clarke, A.; Kapustin, V.; Yantosca, R.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S. Spatial distributions of particle number concentrations in the global troposphere: Simulations, observations, and implications for nucleation mechanisms. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D17205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallina, S.M.; Simó, R.; Gassó, S. What controls CCN seasonality in the Southern Ocean? A statistical analysis based on satellite-derived chlorophyll and CCN and model-estimated OH radical and rainfall. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 2006, 20, GB1014. [Google Scholar]
- Meskhidze, N.; Nenes, A. Phytoplankton and cloudiness in the Southern Ocean. Science 2006, 314, 1419–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Yuter, S.E. Lack of correlation between chlorophyll a and cloud droplet effective radius in shallow marine clouds. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L13807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bey, I.; D. Jacob, J.; Yantosca, R.M; Logan, J. A.; Field, B.; Fiore, A. M.; Li, Q.; Liu, H.; Mickley, L. J.; Schultz, M. Global modeling of tropospheric chemistry with assimilated meteorology: Model description and evaluation. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 23073–23096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.V.; Jacob, D.J.; Yantosca, R.M.; Chin, M.; Ginoux, P. Global and regional decreases in tropospheric oxidants from photochemical effects of aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, R. J.; Jacob, D. J.; Field, B. D.; Yantosca, R. M.; Chin, M. Natural and transboundary pollution influences on sulfate-nitrate-ammonium aerosols in the United States: Implications for policy. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D15204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.J.; Jacob, D.J. Impact of new laboratory studies of N2O5 hydrolysis on global model budgets of tropospheric nitrogen oxides, ozone, and OH. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L09813. [Google Scholar]
- Nenes, A.; Seinfeld, J.H. Parameterization of cloud droplet formation in global climate models. J. Geoph. Res. 2003, 108, 4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Henze, D.K.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Wu, S.; Mickley, L.J. Biogenic secondary organic aerosol over the United States: Comparison of climatological simulations with observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D06201. [Google Scholar]
- Bond, T.C.; Bhardwaj, E.; Dong, R.; Jogani, R.; Jung, S.; Roden, C.; Streets, D. G.; Trautmann, N. M. Historical emissions of black and organic carbon aerosol from energyrelated combustion, 1850–2000. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 2007, 21, GB2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G.; Carmichael, G.R.; He, K.B.; Huo, H.; Kannari, A.; Klimont, Z.; Park, I. S.; Reddy, S.; Fu, J. S.; Chen, D.; Duan, L.; Lei, Y.; Wang, L. T.; Yao, Z. L. Asian emissions in 2006 for the NASA INTEX-B mission. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5131–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettle, A.J.; Andreae, M. O.; Amouroux, D.; Andreae, T. W.; Bates, T. S.; Berresheim, H.; Bingemer, H.; Boniforti, R.; Curran, M. A. J.; DiTullio, G. R.; Helas, G.; Jones, G. B.; Keller, M. D.; Kiene, R. P.; Leck, C.; Levasseur, M.; Malin, G.; Maspero, M.; Matrai, P.; McTaggart, A. R.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Nguyen, B. C.; Novo, A.; Putaud, J. P.; Rapsomanikis, S.; Roberts, G.; Schebeske, G.; Sharma, S.; Simo, R.; Staubes, R.; Turner, S.; Uher, G. A global database of sea surface dimethylsulfide (DMS) measurements and a procedure to predict sea surface DMS as a function of latitude, longitude, and month. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1999, 13, 399–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nightingale, P.D.; Malin, G.; Law, C.S.; Watson, A.J.; Liss, P.S.; Liddicoat, M.I.; Boutin, J.; Upstill-Goddard, R.C. In situ evaluation of air-sea exchange parameterizations using novel conservative and volatile tracers. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 2000, 14, 373–387. [Google Scholar]
- Woodhouse, M.T.; Carslaw, K.S.; Mann, G.W.; Vallina, S.M.; Vogt, M.; Halloran, P.R.; Boucher, O. Low sensitivity of cloud condensation nuclei to changes in the sea-air flux of dimethyl-sulphide. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 7545–7559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- GEOS-Chem model webpage. Available online: http://acmg.seas.harvard.edu/geos (accessed on 2 July 2010).
- Yu, F. Ion-mediated nucleation in the atmosphere: Key controlling parameters, implications, and look-up table. J. Geophy. Res. 2010, 115, D03206. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, G.; Yu, F. A numerical evaluation of global oceanic emissions of alpha-pinene and isoprene. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 20721–20738. [Google Scholar]
- German Antarctic station Neumayer webpage. Available online: http://www.awi.de/en/infrastructure/stations/neumayer_stations/ (accessed on 12 October 2010).
- König-Langlo, G.; King, J.C.; Pettré, P. Climatology of the three coastal Antarctic stations Dumont d’Urville, Neumayer, and Halley. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 10935–10946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, R.; Lampert, A. Optical properties and sulfate scattering efficiency of boundary layer aerosol at coastal Neumayer Station, Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D16208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Turco, R.P. Case studies of particle formation events observed in boreal forests: Implications for nucleation mechanisms. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 6085–6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F. Updated H2SO4-H2O binary homogeneous nucleation rate look-up tables. J. Geophy. Res. 2008, 113, D24201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, F.; Luo, G. Oceanic Dimethyl Sulfide Emission and New Particle Formation around the Coast of Antarctica: A Modeling Study of Seasonal Variations and Comparison with Measurements. Atmosphere 2010, 1, 34-50. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos1010034
Yu F, Luo G. Oceanic Dimethyl Sulfide Emission and New Particle Formation around the Coast of Antarctica: A Modeling Study of Seasonal Variations and Comparison with Measurements. Atmosphere. 2010; 1(1):34-50. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos1010034
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Fangqun, and Gan Luo. 2010. "Oceanic Dimethyl Sulfide Emission and New Particle Formation around the Coast of Antarctica: A Modeling Study of Seasonal Variations and Comparison with Measurements" Atmosphere 1, no. 1: 34-50. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos1010034
APA StyleYu, F., & Luo, G. (2010). Oceanic Dimethyl Sulfide Emission and New Particle Formation around the Coast of Antarctica: A Modeling Study of Seasonal Variations and Comparison with Measurements. Atmosphere, 1(1), 34-50. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos1010034